-
我国能源长期依赖以低阶煤为主的煤炭资源,其中褐煤储量达1 300×108 t,占总煤炭资源的13%[1]。由于高水分、高灰分、低热值的特点,褐煤直接利用难度较高,而中低温(400~800 ℃)煤热解能快速将其转化为煤气、焦油等煤基产品,是当代煤炭能源产业发展的重要途径[2]。然而,由于较低的反应温度和煤质,低阶煤热解过程产生的废水比以往的煤气化废水更复杂,芳香化合物残余量更高,其中以酚类和含氮杂环化合物为主,大多是高毒性、高致癌性化合物,因此,煤热解废水会加剧煤工业的环境危机和治理难度[3]。近年来,我国加紧推进煤工业废水零排放,酚类和杂环类物质的降解成为煤热解废水零排放的关键。
煤热解废水有机质含量极高,化学需氧量(COD)约为10 000~40 000 mg·L−1,其中酚类含量最高,总酚(Tph)约为4 000~8 000 mg·L−1,氮杂环物质含量随煤质及工艺参数波动较大,通常在100 mg·L−1以上[4]。由于共轭环结构的稳定性,传统活性污泥法难以实现高浓度酚类等物质降解。经过长期探索和工程实验,以蒸氨脱酚为预处理、厌氧-缺氧-好氧等多级生物工艺为主体、高级氧化为深度处理的典型工艺流程已普遍应用于煤化工废水处理[5-6]。但随着零排放政策的推进,在水质波动或工况改变的情况下,现行绝大多数煤化工废水处理工程难以保证长期稳定的出水达标。河南某低阶煤制气废水在SBR主生化工段进水水质波动时无法满负荷运行,且曝气池产生大量的泡沫,后续工艺相继崩溃,出水COD和氨氮难以达标[7]。云南某褐煤制化肥企业的酚氨回收、A2O生化和芬顿氧化全流程长期运行不达标,产生大量废气、含酚废水和废渣,该厂多次被勒令停产整顿[8]。同时,国内的煤化工废水处理大多只关注COD、氨氮等常规综合指标,芳香化合物的降解性能极少涉及,造成严重的环境安全隐患,并凸显煤热解废水处理过程中芳香污染物降解研究的重要性。
基于上述分析,本研究选取河南某煤热解废水典型工艺流程为研究对象,深入探讨了该废水处理流程中污染物的降解性能和废水特性转变,并通过统计分析评估了各单元在芳香化合物降解过程的贡献,解析了存在的主要技术问题,并针对性地提出了改进方案,为类似的废水处理提供参考。
全文HTML
-
图1为国内煤热解废水处理的典型工艺流程,经酚氨预处理后,废水的处理单元主要有空气气浮、厌氧水解、两级厌氧、SBR、缺氧酸化、好氧、空气气浮和次氯酸钠强氧化。其中厌氧前端的气浮1主要用于去除废水浮油,而好氧后端气浮2主要去除出水漂浮的泡沫等,酸化-好氧单元相当于分置式的缺氧-好氧(AO)工艺。
-
项目废水为河南省某低阶煤制气产生的高酚氨废水,经酚氨回收系统预处理后,COD为4 000 mg·L−1以上,总酚为1 000~2 000 mg·L−1。经气相色谱-质谱定性分析出34种有机化合物,废水中主要含有苯酚、邻苯二酚、对甲酚、2-甲基苯酚等酚类化合物、3-甲基-1,2-苯二醇、3-甲基苯甲酸等芳香酸和醇类物质,其中原水酚类物质占有机质的80%左右,并通过液相色谱识别了废水中的吡啶、喹啉、吲哚3种主要的氮杂环类物质。
-
废水常规综合指标如COD、Tph、溶解氧(DO)等根据标准方法[9]测定。酚氨回收预处理出水通过气相色谱-质谱联用仪(6890GC-5973/5975MSD,安捷伦,美国)定性鉴别。同时,通过高效液相色谱(1260 Infinity,安捷伦,美国)定量测定吡啶、喹啉和吲哚,流动相为乙腈/水=50%∶50%,检测波长分别为253、313和287 nm。经0.45 μm滤膜过滤后,紫外-可见光光谱(珀金埃尔默,美国)、三维荧光光谱(F-7000,日立,日本)和凝胶渗透色谱(沃特世,美国)用于表征废水溶解性有机物分子特性。
-
常规指标、紫外光谱及液相色谱重复3次测定,均利用OriginLab 2016(OriginLab Corporation, USA)绘图。根据各单元COD、Tph去除量及对应废水DO分布,利用Canoco 5.1(Microcomputer Power, USA)非限制性主成分分析识别各单元降解性能的差异。
1.1. 工艺流程
1.2. 实验水质
1.3. 测定项目及方法
1.4. 数据处理
-
表1反映了各单元出水COD及Tph浓度变化。可以看出,Tph沿流程逐渐下降,因此,本工艺能够有效去除酚类污染物。废水中有机质以酚类为主,COD变化与Tph基本一致;然而,水解段去除5.03%的酚类物质,但COD相对于气浮1单元却略有上升(6.77%)。根据肖剑[1]的研究结果,大分子芳香化合物由于存在共轭环结构,热稳定性较高,尤其是缺π电子结构的氮杂环类物质,因此,消解法检测COD难以有效降解芳香环,从而导致结果偏低。厌氧水解工艺出水COD升高表明其能够打开大分子的共轭环,从而提升废水整体降解性能。相比而言,两级厌氧单元出水COD和Tph分别下降了26.36%和20.33%,这说明两级厌氧生物降解不仅破坏了芳香环结构,更有效地实现了部分有机物的矿化。通常,有机物的矿化主要发生在有氧单元[9],其中DO为2.0~3.0 mg·L−1的SBR工艺实现了全流程最高幅度的COD(84.07%)和Tph(96.13%)降解,其次是次氯酸钠强氧化(51.95%和86.97%)。值得注意的是,中间的酸化工艺(DO=0.3 mg·L−1)和好氧工艺(DO=6 mg·L−1)对有机物的降解效率均在25%以下,这种分置式AO工艺对有机物降解效果偏低,并最终导致全流程出水COD长期在200 mg·L−1附近波动,COD和酚类物质常超出污水综合排放标准(GB 8978-1996)二级指标(表2)。根据当前我国对于煤工业废水零排放要求,出水必须厂区回用,而本流程出水有机物无法满足城市污水再生利用工业用水水质标准(GB 19923-2005)中锅炉补给水和冷却循环水要求(COD≤60 mg·L−1),因此,仍须进一步深度处理。
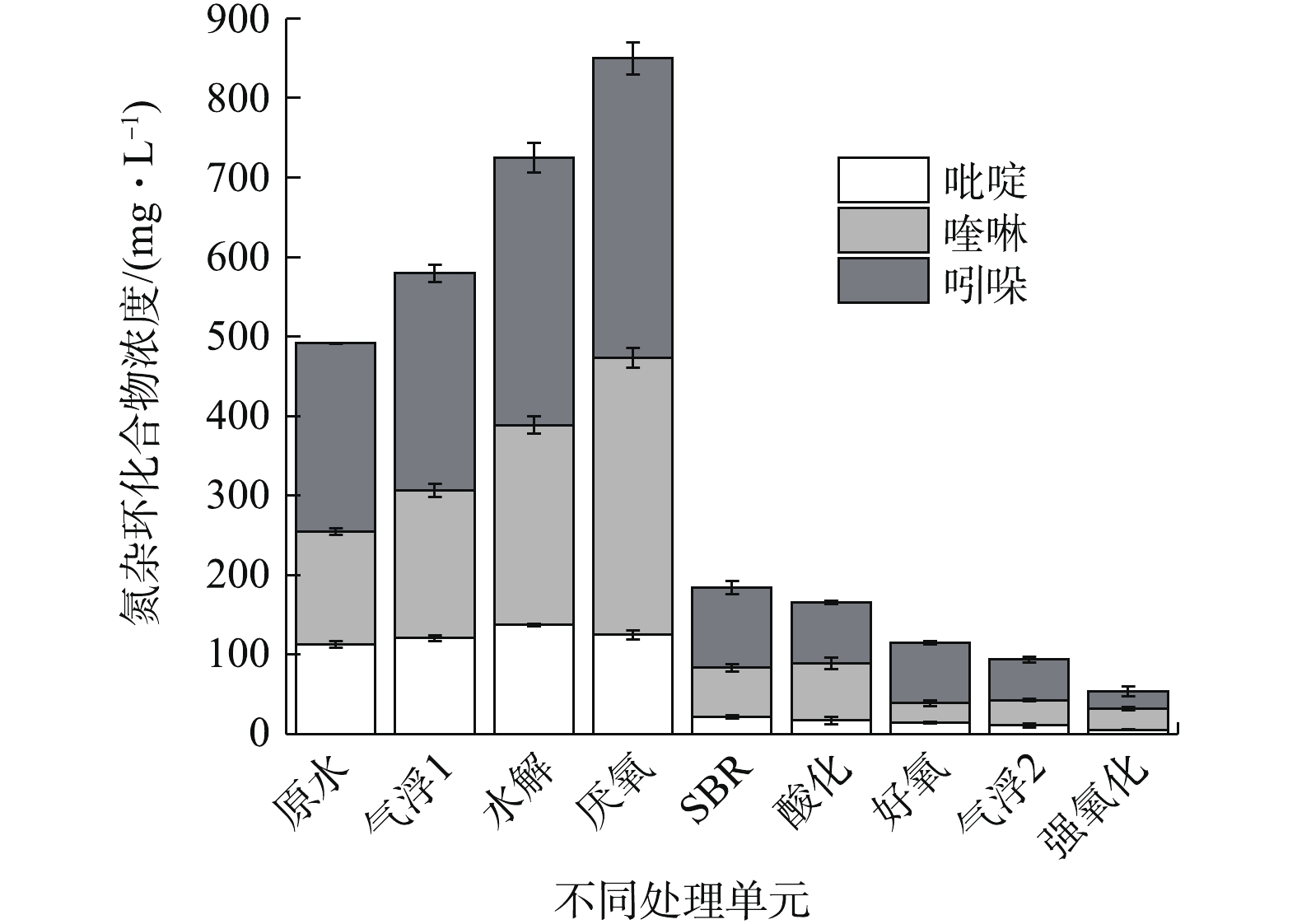
图2反映了废水中主要的吡啶、喹啉和吲哚等3种氮杂环类小分子化合物含量的变化。根据上述对厌氧工艺的分析,推测水解和厌氧工艺出水中3种物质总量的上升(25.02%和17.21%)可能是大分子向小分子化合物的转化所致。其中吡啶的含量基本不变,说明其结构最稳定,这与何苗等[10-12]的研究结果一致。此外,厌氧前端的空气气浮也导致出水杂环类物质上升,且出水颜色显著加深,这可能是由于高浓度芳香化合物复杂的氧化反应所造成的,李丹阳[8]的研究也证实了空气气浮导致煤气化废水出水副产物大幅增加。对于有氧单元,类似于酚类降解,SBR工艺也表现出对氮杂环类最高的降解性能(78.33%),其次是强氧化工艺(42.30%),酸化和好氧工艺分别去除10.00%和30.60%的氮杂环物质,而气浮2中的去除率为18.42%。同时,这3种杂环化合物之间的降解性能存在明显差异,吲哚类化合物在厌氧工艺之后各单元均有降解,而喹啉类化合物的浓度只在SBR(76.55%)、好氧(76.90%)和强氧化(16.66%)单元有所下降,吡啶类化合物的降解也主要发生在SBR(82.64%)和强氧化(49.31%)单元,由此推测,这3种杂环类化合物降解性能为吲哚>喹啉>吡啶,这再次验证了何苗等[10]对杂环化合物稳定性的研究结果。综上所述,SBR工艺对于酚类、氮杂环类物质的降解性能最优,其次为强氧化工艺,酸化-好氧“分置式AO”工艺对芳香化合物的降解性能较差。
-
图3反映了原水沿处理流程的分子质量及芳香性变化。由图3(a)可见,原水分子质量主要分布在10 kDa以上,而气浮1之后分子质量主要分布在4 kDa以下,这说明气浮1可去除部分大分子油类物质,但其出水波形不规则,推测空气气浮导致废水中大量氧化副产物的产生。另一方面,除强氧化外,各单元出水均在停留时间T=1 000 s有显著峰型,因此,对应的分子质量为3 kDa左右的物质可能是煤热解废水关键的难降解物质。而T>1 200 s之后的峰则对应分子质量小于1 kDa的小分子物质,水解、厌氧和SBR出水中T=1 350 s的峰强度依次升高,这说明由水解到SBR,大分子物质逐渐向小分子转化。酸化单元之后,峰的停留时间继续后移,但同时好氧和气浮2出水分子质量为3 kDa的物质比例再次上升,综上推测T=1 350 s的物质可生化性较高,而好氧代谢大量消耗该类物质,同时空气氧化反应导致废水中难降解物质比例再次升高。强氧化出水的峰主要分布于T=1 450 s和1 550 s附近,T=1 000 s的峰几乎消失,可见次氯酸钠与难生化污染物有显著的反应;而在T=1 100 s附近产生的新峰说明次氯酸钠氧化并不能将难降解物质彻底降解,反而可能产生更难降解的物质。
由于UV254与废水整体芳香性呈正相关性[13],由图3(b)可知,气浮1相对原水UV254下降可能因为空气气浮去除了浮油中的苯类等疏水芳香族物质。水解和厌氧工艺出水UV254升高与上述小分子氮杂环含量上升有关,并与T=1 350 s的物质比例升高相对应,这说明水解和厌氧工艺促进了大分子芳香化合物向小分子化合物的转化。SBR出水UV254相对厌氧工艺下降了8倍以上,结合水解、厌氧单元中相似的分子质量变化趋势(图3(a)),SBR不仅进一步实现了大分子向小分子的转化,并且更彻底地降解了芳香类化合物。同时,有研究[13-14]认为,UV300/UV400能够有效表征废水整体的分子质量水平,由此推断,气浮2之前各段出水整体分子质量并没有明显差异,这很大程度上归因于分子质量为3 kDa的难降解物质主导了废水的光谱特征。
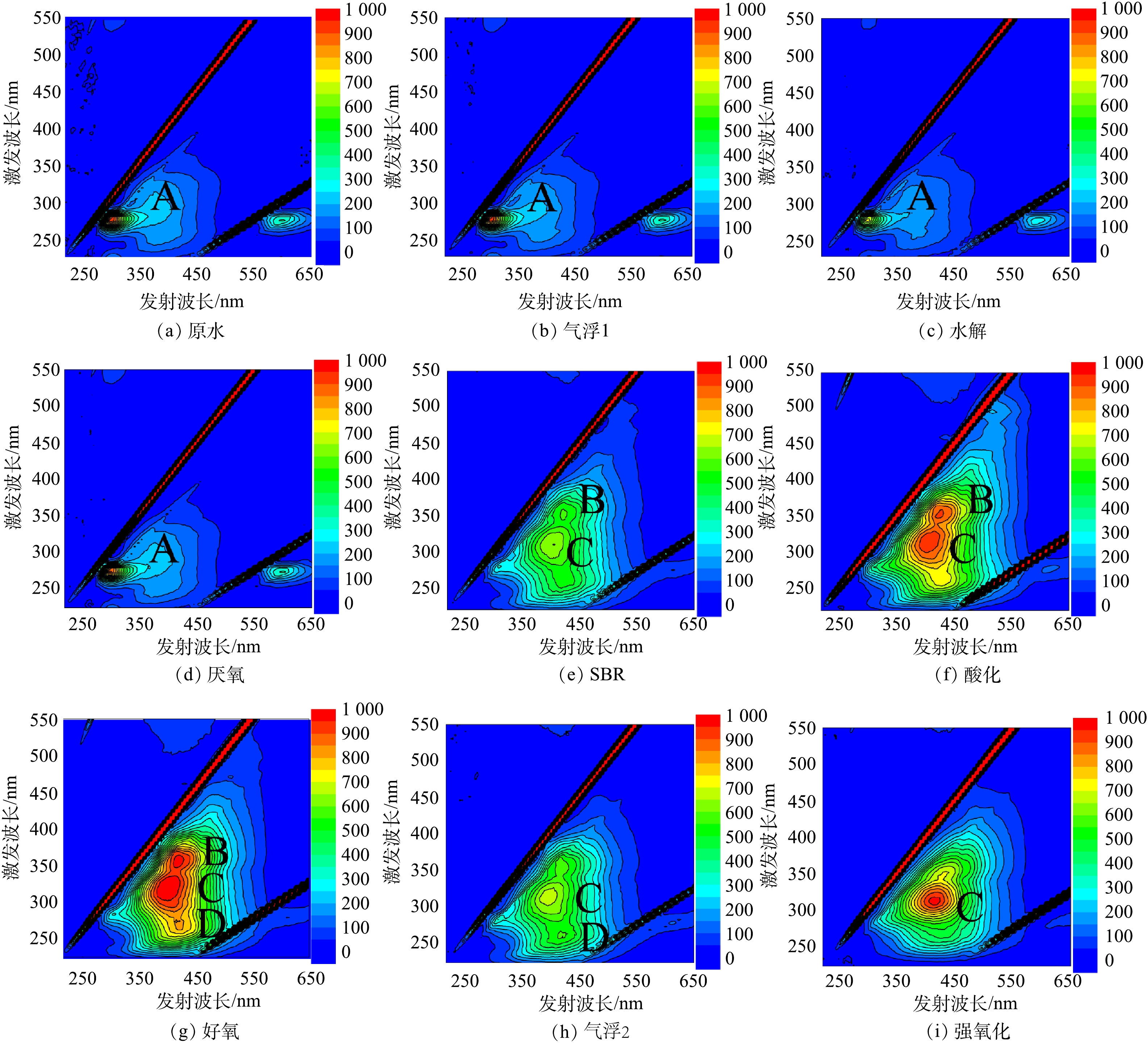
图4(a)~图4(i)分别表示由调节池出水至强氧化出水的荧光光谱。根据PENG等[14]的研究,全流程出水荧光光谱划分为A酚类(Ex/Em=275 nm/300 nm),B、C腐殖酸(Ex/Em=(300~370) nm/(400~450) nm)和D富里酸(Ex/Em=(200~250) nm/(400~450) nm) 4个荧光区域。由图4(a)~图4(d)中单独的A荧光区域可见, 酚类在SBR工艺之前的废水成分中占绝对主导地位,结合图4(e)~图4(i)中有氧单元A区域荧光的消失可知,厌氧反应相比好氧反应对酚类的降解效果较差。有氧生物单元出水以腐殖酸、富里酸为主,其中SBR出水B、C区荧光强度最低,因此,腐质化程度最低。B和C区域尤其是C区域荧光在有氧单元出水极其显著,其可能对应分子质量为3 kDa的关键难降解物质,酸化、好氧和气浮2出水C区域荧光强度升高也与3 kDa物质变化一致(图3(a))。酸化(DO=0.3 mg·L−1)、好氧(DO=6 mg·L−1)分别处于严格缺氧和好氧条件,C区域荧光变化结果进一步说明分置的缺氧-好氧工艺无法有效去除难降解芳香化合物。此外,好氧和气浮2工艺均产生D区域荧光对应着图3(a)中T>1 350 s产生的新峰,证明充分的空气氧化形成了更多的氧化副产物。强氧化出水仍保留显著的C荧光区域,同样对应着图3(a)中T=1 100 s左右的新型降解产物,这说明次氯酸钠无法充分降解该荧光区域的难生化物质。
-
实际工程设计的各单元在煤热解废水降解中起到不同的作用,因此,须各单元降解性能综合对比分析,进而评估各单元是否实现了其设计功能。图5(a)为主成分分析图。各单元与污染物指标夹角越小,与原点距离越大,其相应降解贡献越大,由此可见,SBR为有机物降解的最主要单元。图5(b)将各单元依据含氧量划分为不同工艺,其中厌氧水解、两级厌氧和缺氧酸化属于低氧工艺,其余均属于高氧工艺,而SBR的DO=2.0~3.0 mg·L−1,处于低水平好氧环境。在低氧工艺中,两级厌氧对芳香类化合物降解的贡献最大,水解及酸化属于同种工艺,其主要用于提升后续工段废水的可生化性。水解对污染物去除的贡献最小,但由2.1节推断,其可实现芳香环的裂解,提升了废水可生化性[9]。由图3推测,酸化并未有效分解大分子物质及杂环物质,没有达到改善好氧单元进水水质的目的。
就高氧工艺而言,无论气浮1、气浮2还是好氧生物单元均产生了复杂的氧化反应,形成更多的副产物。实际工程考察发现,气浮1、气浮2分别有效去除悬浮油类和泡沫,但出水色度均显著加深,可见气浮工艺虽然实现设计目标,但可以引发新的问题。本工艺流程中的好氧单元持续高强度曝气但无法适应波动的水质,且出水残余有机物过多导致气浮2和强氧化工艺功耗、药耗持续较高,这是造成出水不达标和成本较高的最主要原因之一。对于强氧化工艺,国内煤热解废水处理通常采用高级氧化如臭氧氧化、芬顿氧化等作为深度处理工艺。本研究采用的次氯酸钠氧化工艺虽然节省了成本,但由图3和图4可知,强氧化并没有将难降解物质消除,并可能产生更难降解的物质,因此,导致出水难以回用,进而无法实现零排放目标。由此可见,酸化、气浮、好氧、强氧化单元是本工艺流程降解芳香化合物的薄弱环节和导致出水不达标的主要症结。
李丹阳[8]提出并应用的氮气气浮工艺不仅能够利用煤热解工厂富裕氮气去除悬浮物,而且不会造成过度的氧化反应,是对当前空气气浮工艺改进的优先选择。在生化工艺方面,严格的厌氧和高氧工艺均不适合作为芳香化合物降解的核心工艺,因为芳香环降解路径需要厌氧和好氧反应的协同参与[15]。最新研究[9]表明,限氧条件(DO=1.0~2.0 mg·L−1)移动生物床(MBBR)工艺中兼性微生物通过连续的厌氧-好氧微环境高效水解芳香环并快速降解开环后的物质。因此,笔者建议将SBR调整为限氧环境的MBBR工艺,取消酸化单元或将其与好氧单元合建为一体式AO工艺,下调曝气强度并同样投加填料改造成MBBR工艺,这能够在不增加基础建设、缩减能耗的前提下实现工艺改良。最后,对于强氧化工艺,应当升级成为臭氧氧化工艺,依据物料平衡,能够大幅削减含盐水的产量,进而降低尾水处理费用及回用难度。
目前,韩洪军等[5]研发的EBA工艺就是整合氮气气浮、厌氧共代谢、微氧生物工艺和改良AO工艺的处理流程,EBA应用于内蒙古图克煤制气项目,经高级氧化后出水符合城市污水再生利用工业用水水质标准(GB 19923-2005)的要求,并在全厂实现再生水回用,是国内煤热解废水处理值得借鉴的典型案例,部分验证了本研究的理论分析。近期该工程将进一步应用填料改造生化工艺,而其对芳香化合物的降解性能则有待进一步研究。
2.1. 芳香化合物的降解效能
2.2. 各工艺出水光谱特性表征
2.3. 各工艺单元降解性能评估
-
1) 本研究中处于低水平好氧环境的SBR工艺是降解芳香污染物的核心工艺,能够高效降解废水中酚类(96.13%)和氮杂环(78.13%)物质,出水主要是分子质量低于1 kDa的小分子芳香化合物。
2) 通过光谱分析结果,推测煤热解废水中关键的难降解成分为分子质量在3 kDa左右,荧光峰为Ex/Em=(300~370) nm/(400~450) nm的腐殖酸物质。
3) 通过各单元降解性能评估,酸化、气浮、好氧、强氧化工艺单元是全流程中降解性能较差的环节,并推荐采用氮气气浮、限氧移动生物床和臭氧氧化对现有煤热解废水处理工艺升级改造。




 下载:
下载: