-
将传统生物转化方式向着节能途径转变,对现行工艺进行升级改造,是污水处理行业追求减污降碳协同增效的有效途径。在污水生物脱氮除磷方面,反硝化除磷与传统生物脱氮除磷相比,可节省有机碳源、氧气消耗并减少污泥产量。以亚硝酸盐为电子受体的反硝化除磷相比硝酸盐作为电子受体,可进一步减少碳源和能耗需求,是低碳的污水处理工艺[1-3]。然而,由于对碳源的竞争和污泥龄不同,难以为各类细菌提供最佳生长环境,因碳源不足导致的低效生物除磷,需要化学除磷的辅助[4-5]。研究表明,通过合理调节参数反硝化除磷功能得以强化,如提高好氧区水力停留时间、适宜流量比的旁路进水策略、调控好氧/缺氧时长联合分区排泥、优化曝气和回流方式等[6-10]。A2N工艺(厌氧、缺氧和硝化)是专门为反硝化除磷设计的一种工艺,其中硝化生物膜和反硝化除磷悬浮污泥在2个污泥系统中进行,从而避免了不同菌种间的竞争[11]。然而A2N-SBR系统的反应器结构复杂,致使其工程推广难度较大[12]。此外,Dephanox、A2/O-BAF、A2/O-BCO双污泥工艺较单污泥工艺在实现反硝化除磷方面更具优势[13-15]。
生物强化可通过侧流反应器中富集硝化细菌回流至主流以提高主流中硝化细菌的比例,从而提高污水处理系统的硝化效能[16]。为强化反硝化除磷效能,可扩大活性污泥中反硝化除磷优势菌属的比例[17]。基于反硝化除磷菌(denitrifying phosphate accumulating organisms, DPAOs)的生理特性,现有研究集中于采用序批式反应器(sequencing batch reactor,SBR)通过厌氧-缺氧或厌氧-缺氧-好氧条件来富集DPAOs[18-19],并发现亚硝酸盐或游离亚硝酸(free nitrous acid,FNA)不同阈值可能导致对DPAOs产生抑制[18,20-21]。然而,DPAOs亦可抵抗亚硝酸盐或FNA阈值在污泥培养过程中的逐渐提高[18,22-23]。DPAOs属于聚磷菌(phosphate accumulating organisms,PAOs)的分支之一,亦有研究证明某些类型的反硝化细菌具有除磷功能[24-28]。
本研究中通过底物反应速率调节底物的流加速率,以期在SBR反应器中富集培养以亚硝酸盐和硝酸盐作为电子受体的反硝化菌群,并将其添加至单污泥A2/O工艺中,以刺激反硝化细菌发挥生物除磷功能,进而加速反应器启动。本研究旨在为基于传统活性污泥工艺进行低碳工艺改造,以处理低COD/N生活污水提供参考。
-
本研究富集反硝化菌群及A2/O反应器内的接种污泥均取自北京高碑店污水处理厂A2/O工艺回流污泥。A2/O反应器进水由北京东坝污水处理厂提供,为实际生活污水,其主要指标为:COD 72.33~228.47 mg·L−1、NH4+-N 22.36~79.91 mg·L−1、总磷(TP) 1.09~5.15 mg·L−1、COD/N 1.2~4.2、pH 7.38~7.85。
-
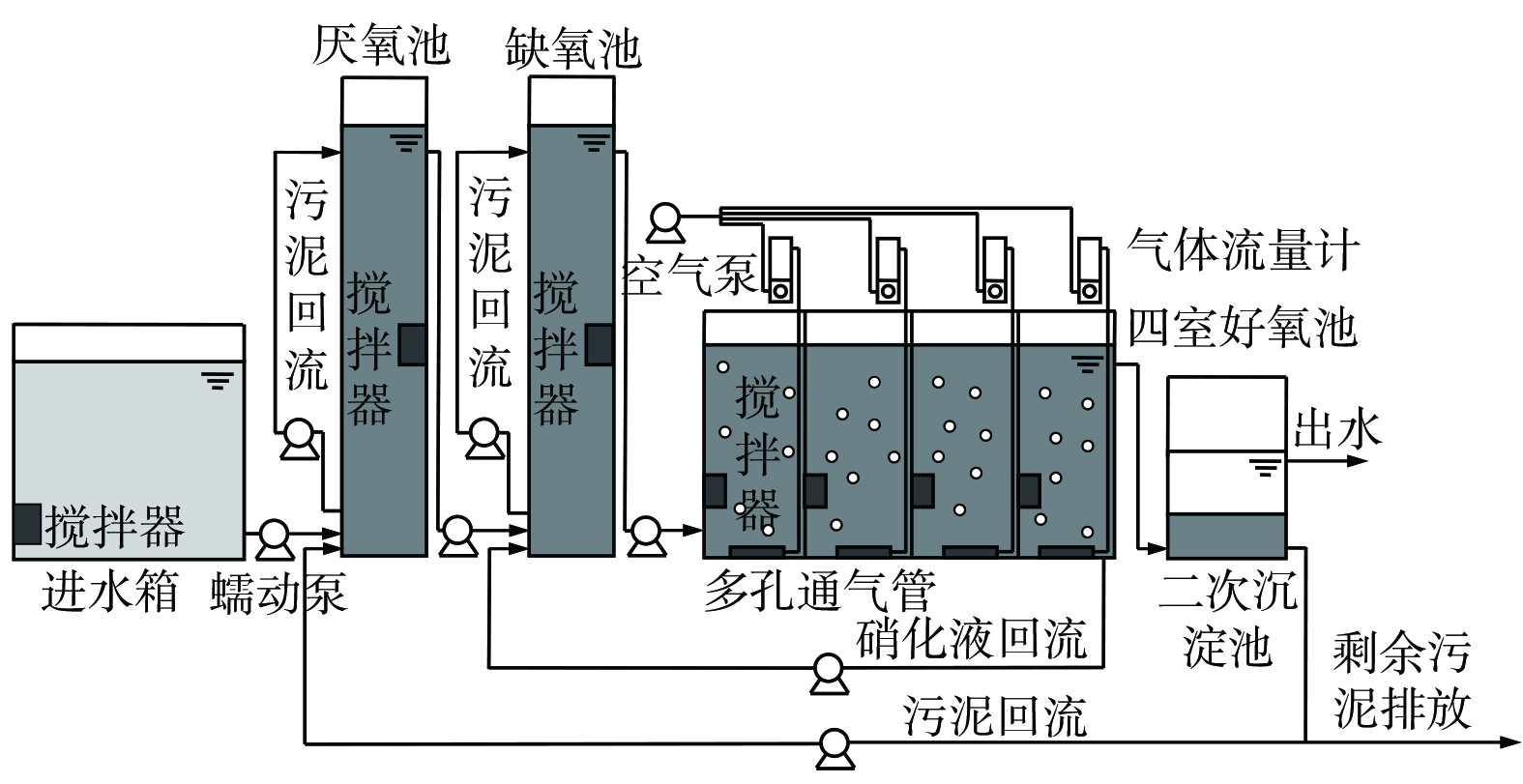
A2/O反应器的有效容积为102 L,结构如图1所示。反应器包含3个独立的反应池和1个二次沉淀池,二沉池有效容积为16 L。第1个和第2个圆柱体反应器分别是厌氧(有效容积16 L)和缺氧池(有效容积16 L)。第3个反应池(有效容积54 L)为好氧池,被分成了4个室,泥水混合液在其中经“S”型缺口流动。
-
系统总体运行近110 d。厌氧池、缺氧池、好氧池和二次沉淀池的水力停留时间(hydraulic retention time,HRT)分别控制在2 h、2 h、6.7 h和2 h。机械搅拌器(HJ-541/HJ-931,SUNSUN公司,中国)用于进水箱中污水搅拌、促进厌氧池和缺氧池污泥内循环,以及好氧池中的污泥流动。实际污水的pH为7.38~7.85,储存于1个水箱中,由泵引入反应器。内循环由最后一个好氧室到缺氧池进行污泥回流,外循环由二次沉淀池到厌氧池进行污泥回流。进水流量、内外循环流量均由蠕动泵控制(BT100-2J/BT300-2J,LONGER公司,中国),流量为193 L·d−1。对厌氧池和缺氧池进行污泥循环,以使得污水和活性污泥完全混合,流量为386 L·d−1。由气泵提供连续曝气(最大流速50 L·min−1,SQG Corp公司,中国),并连接穿孔管至每个好氧室,溶解氧(dissolved oxygen,DO)保持在0.3~2.0 mg·L−1,采用空气流量计控制曝气量。pH和DO由pH和DO测定仪监测(HQ30d,HACH公司,美国)。反应液温度控制在15~29 ℃。当温度低于15 ℃时,进水箱和好氧池第三室采用加热装置(JRB-230/JRB-210,SUNSUN公司,中国)进行加温。污泥停留时间(sludge retention time,SRT)为20~30 d,通过手动从二次沉淀池排放适量污泥以控制污泥龄。
-
1)启动阶段(第1天至第15天)。接种污泥至A2/O反应器,初始反应器内平均污泥质量浓度接近5 000 mg·L−1。随着反应器运行,接种污泥逐渐适应厌氧-缺氧-好氧的环境及本研究所采用的实验参数,期间对反应器的生物除磷能力进行分析,以明确生物除磷途径。
2)阶段1(第16天至第41天)。考察系统的生物除磷性能及生物除磷途径。
3)阶段2(第42天至第110天)。在第41天,向A2/O反应器中加入富含反硝化菌群的活性污泥,添加比例约为3.4%(由3.5 L添加至102 L)。该菌群来源于SBR在(20±2) °C、pH(7.5±0.2)和DO为0的条件下,以亚硝酸钠和乙酸钠为底物,根据前一周期的底物反应速率和COD/N适当调节本周期的底物流加速率即底物浓度,富集培养得到反硝化菌群。该菌群中含假单胞菌属Pseudomonas 56.13%,脱氯单胞菌属Dechloromonas 5.19%,黄杆菌属Flavobacterium 11.70%,陶厄氏菌属Thauera 7.76%和红杆菌属Rhodobacter 3.48%,总占比为84.26%。系统的最高亚硝酸盐反硝化速率超过270 mg·(L·h)−1,COD/N约为2.7。该菌群可同时利用亚硝酸盐和硝酸盐为电子受体进行反硝化[29],实验评价添加反硝化菌群后系统的生物除磷性能及生物除磷途径。
-
在进行化学分析前,样品首先采用中速定性滤纸进行过滤。分析指标有TP、COD、NO3−-N等,按照国家环保总局规定的标准方法测定[30]。
反硝化除磷率 (η) 定义为反硝化吸磷量占总吸磷量的比例[31]。计算式为式 (1) 。
式中:CTP-Ano-S和CTP-Ano-E分别指缺氧段磷吸收开始和结束时TP,mg·L−1;CTP-Aer-S和CTP-Aer-E分别指好氧段磷吸收开始和结束时的TP,mg·L−1。
-
取污泥样品进行DNA提取、PCR扩增(V3–V4)、琼脂糖凝胶电泳、DNA纯化,采用Illumina Miseq03测序平台进行16S rRNA高通量测序(生工生物工程股份有限公司,上海)。对结果进行过滤处理,得到优化序列。在97%相似度水平下进行操作分类单元(OTU)聚类分析,研究结果用于描述不同微生物群落之间的相似性和差异性,从而明确主要物种比例。
-
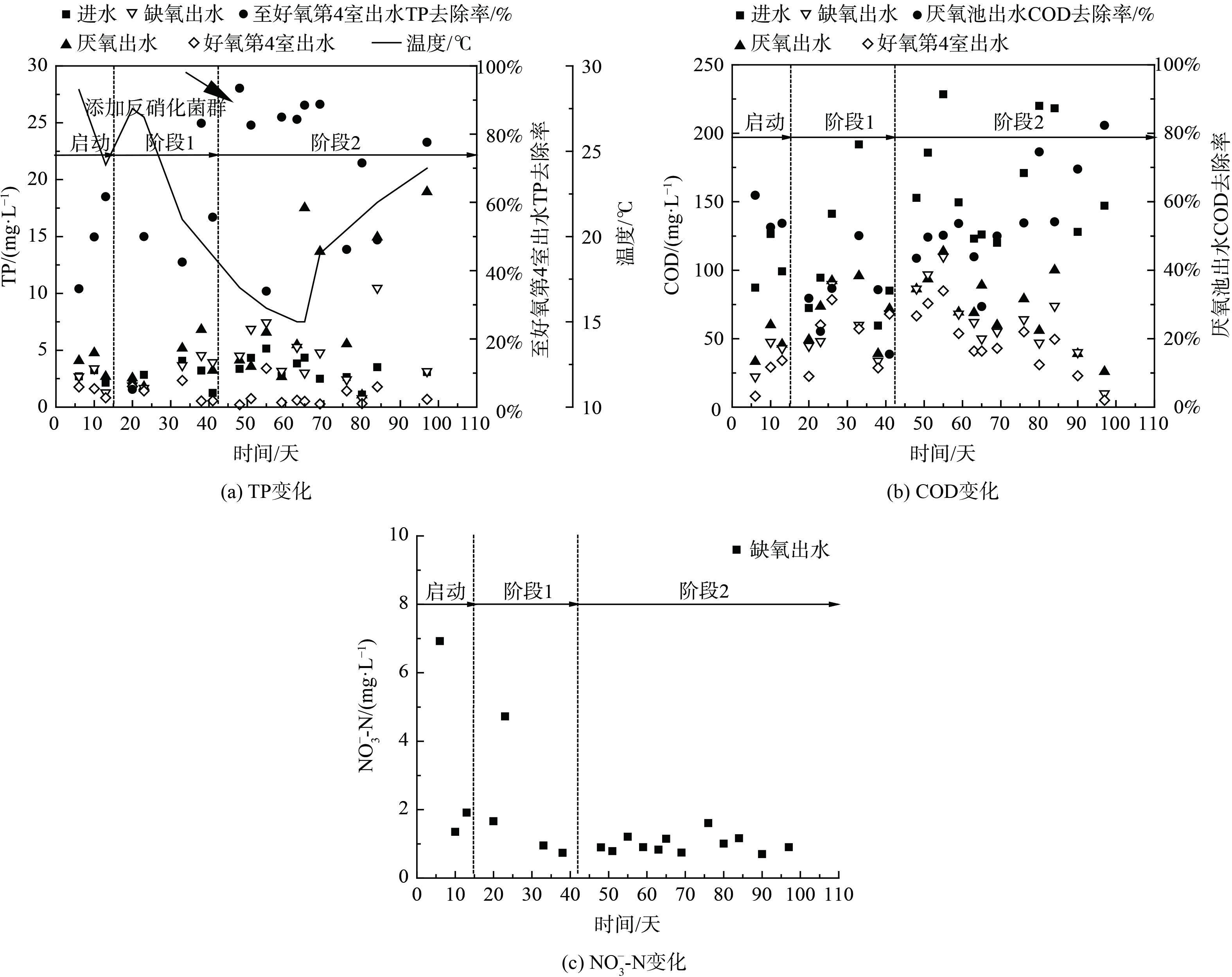
在近15 d的反应器启动期内,TP去除率呈逐渐上升趋势且跨度很大,由34.69%经49.85%至61.68%。COD去除率较为稳定,为52.53%~61.86%。这说明取自污水处理厂的接种污泥在本研究的设计参数下,已逐渐适应了A2/O工艺的运行,结果如图2所示。从除磷效果来分析,在阶段1,TP的去除途径以厌氧释磷和好氧吸磷为主,反硝化除磷现象并不显著。
待反应进行至第41天,A2/O系统加入富集的反硝化菌群,添加比例约为3.4%(3.5 L添加至102 L)。该菌群来源于SBR在(20±2) °C、pH(7.5±0.2)和DO为0的条件下,根据底物反应速率调节底物的流加速率,富集得到的富含反硝化菌群的活性污泥,其最高亚硝酸盐反硝化速率超过270 mg·(L·h)−1,系统中COD/N约为2.7,且该菌群可同时利用亚硝酸盐和硝酸盐为电子受体进行反硝化[29]。系统运行至第65天后,出现了显著的反硝化除磷现象,进水TP为4.34 mg·L−1,厌氧释磷后TP升至17.52 mg·L−1,缺氧出水TP大幅降至3.02 mg·L−1。即使温度低至约15 °C,反硝化除磷效果仍很显著,在TP去除率为88.48%的前提下,反硝化除磷率高达85.19%。当反应进行至第69天,好氧第4室的TP为最小值 (0.28 mg·L−1) 。在第65天后,反硝化除磷率持续保持在较高且稳定的水平,平均值约为64.62%,反硝化除磷途径TP去除负荷均值约为0.014 8 kg·(m3·d)−1。
图2(b)表明,在阶段2,反硝化菌群添加到A2/O系统内,厌氧区COD利用率逐渐增加至约80%,并且伴随着明显的厌氧释磷现象。这表明在厌氧区用于释磷的COD比例逐渐增加。然而,缺氧区COD的减少量较小,这说明细菌是利用储存的内碳源PHA进行的有效吸磷。已证实短链脂肪酸(short-chain fatty acid,SCFA),即挥发性脂肪酸(volatile fatty acid,VFA)在厌氧区可作为碳源用于PHA的释放和储存,然后将储存的PHA用于缺氧区磷吸收[32]。本研究富集培养反硝化菌群采用的碳源是乙酸钠,属于VFA,故该菌群可利用实际生活污水中所含的VFA。此外,缺氧出水的NO3−-N大体约为1 mg·L−1,这表明NO3−基本上已通过反硝化除磷和反硝化2种途径实现脱氮,而缺氧出水中TP仍较高,这表明因硝酸盐不足致使磷被吸收的目标并未在缺氧段全部实现。
结合研究结果对此现象进行解释:1) 在启动期、阶段1和阶段2前期,虽然A2/O反应器中存在土著反硝化菌群,但并未发挥出显著的反硝化除磷能力,可能是由于能发挥反硝化除磷功能的细菌比例小、活性低;2) 以往研究表明,A2/O反应器常规运行,未能将土著反硝化菌群驯化发挥出反硝化除磷功能,本研究通过外加功能菌且保留,并淘洗无用细菌 (“换泥”) 方能实现;3) 本研究为单因素实验,在未改变A2/O反应器运行参数的前提下,只投加了富集得到的富含反硝化菌群的活性污泥,故出现的显著反硝化除磷现象归因于添加的富集得到的反硝化菌群;4) 已有研究报道某些类型的反硝化细菌具有除磷功能[24-28],有些类型的PAOs也可进行反硝化除磷,通过在A2/O系统交替的厌氧-缺氧-好氧条件,刺激反硝化菌群逐渐发挥生物除磷功能,此过程需要一段时间;5) 富集得到的富含反硝化菌群的活性污泥,反硝化菌比例和活性均极高 (相比于土著反硝化菌) ,且投加比例适宜。
-
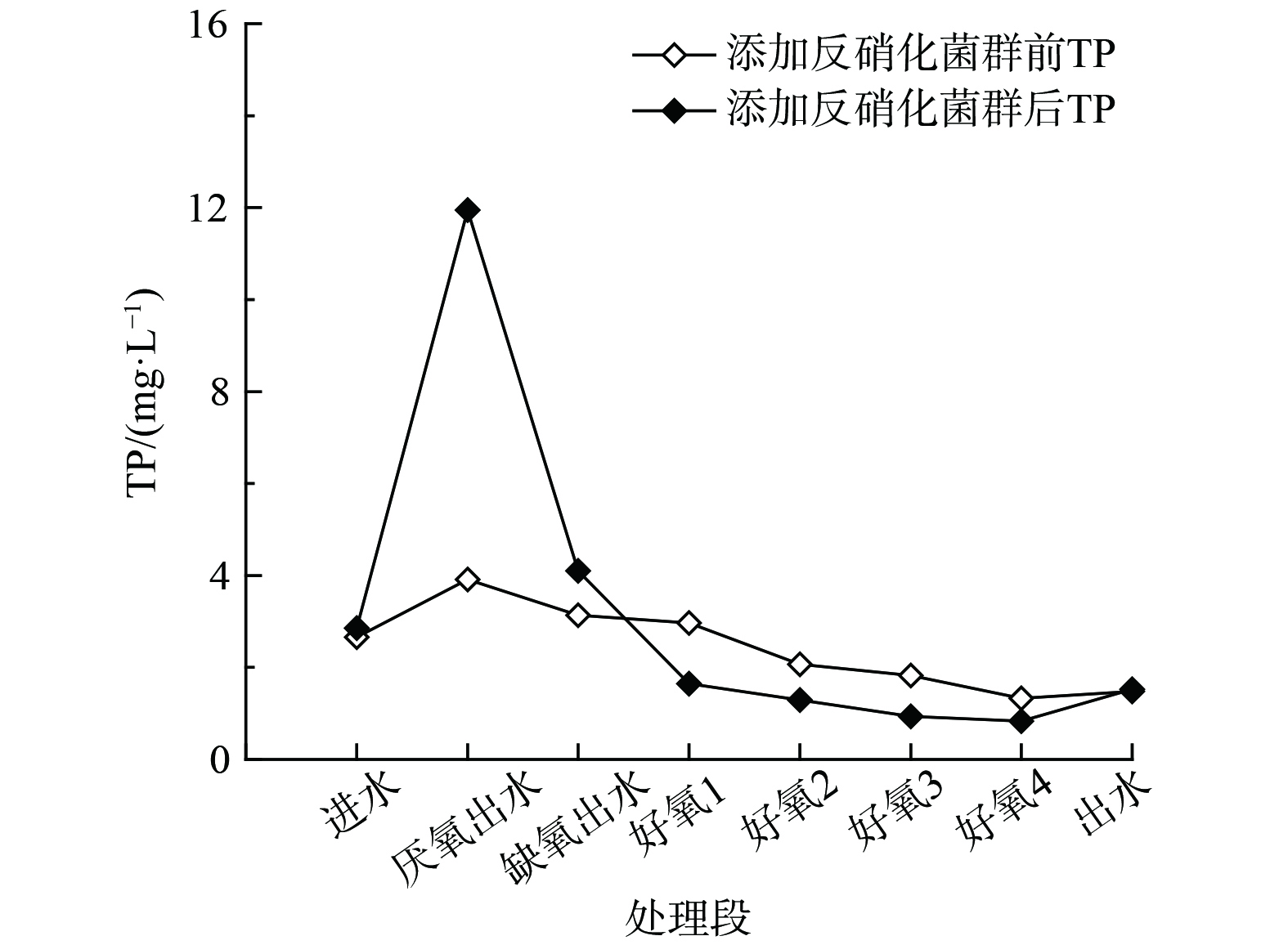
图3表明系统中生物除磷的途径在反硝化菌群添加前后发生了显著变化。由厌氧释磷-好氧吸磷逐渐过渡到厌氧释磷-缺氧吸磷的反硝化除磷途径,通过阶段1和阶段2不同反应池TP稳定期均值变化可证实。添加反硝化菌群之前(阶段1),进水、厌氧出水、缺氧出水和好氧第4室出水的TP平均值分别为2.66 mg·L−1、3.91 mg·L−1、3.14 mg·L−1和1.33 mg·L−1。因此,计算得到的缺氧吸磷量(0.77 mg·L−1)与好氧吸磷量(1.81 mg·L−1)的比率约为0.43,即平均反硝化除磷率约为29.84%。这表明好氧吸磷在生物除磷中发挥了重要作用。然而,在A2/O系统中添加富集的反硝化菌群后(阶段2自第65天起),进水、厌氧出水、缺氧出水和好氧第4室出水的TP分别为2.86 mg·L−1、11.95 mg·L−1、4.10 mg·L−1和0.83 mg·L−1,缺氧吸磷量(7.85 mg·L−1)与好氧吸磷量(3.27 mg·L−1)的比率显著增加到2.40,即平均反硝化除磷率提高至73.34%。这说明反硝化除磷在生物除磷中起主导作用。上述分析证明了该单污泥A2/O系统可达到反硝化除磷的预期效果。此外,由于二次沉淀池出现二次释磷现象,故将其有效体积缩小至11 L,以缩短水力停留时间,缓解二次释磷的程度。
-
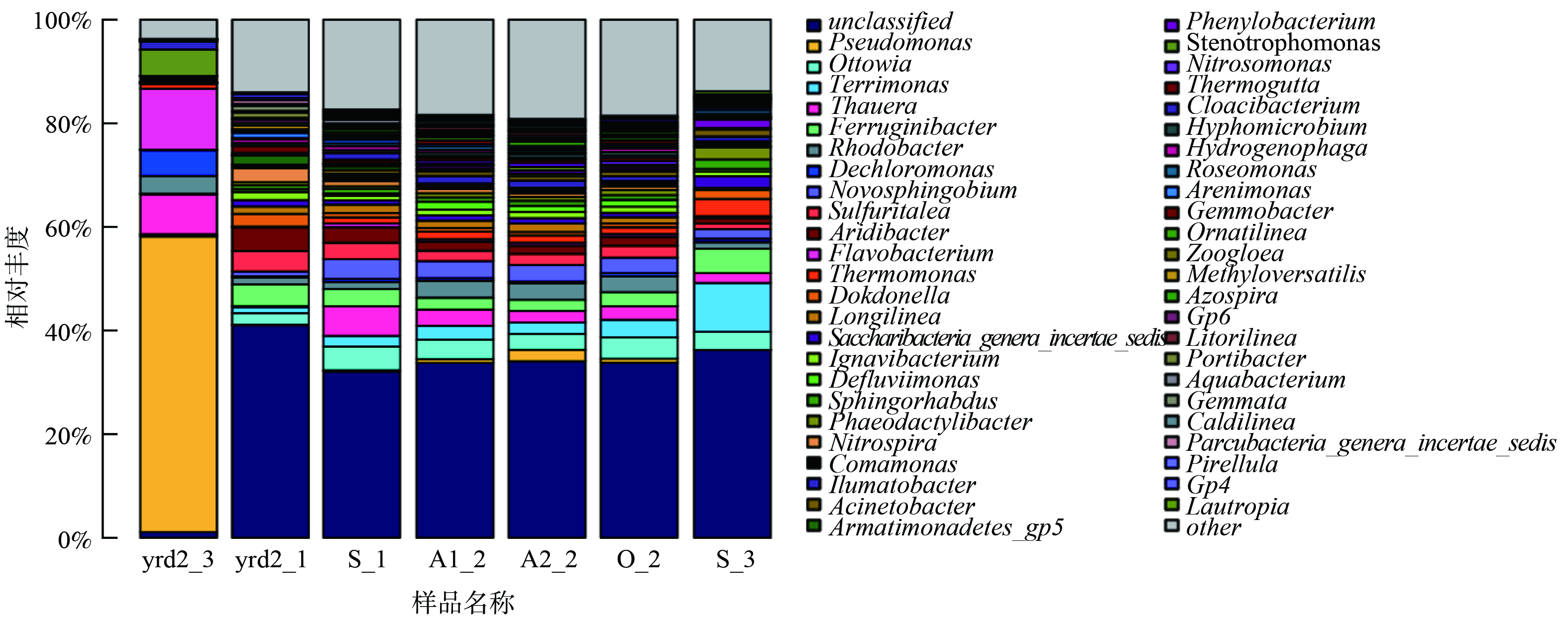
属水平细菌群落结构如图4所示。yrd2_1为接种污泥;yrd2_3为富集培养后的反硝化菌群;S_1为A2/O反应器添加菌群前(运行第41天)的混合污泥样品;A1_2为A2/O反应器添加菌群后(运行第42天)的厌氧池污泥样品;A2_2为A2/O反应器添加菌群后(运行第42天)的缺氧池污泥样品;O_2为A2/O反应器添加菌群后(运行第42天)的好氧池污泥样品;S_3为A2/O反应器添加菌群后(运行第101天)的混合污泥样品。反硝化菌群富集后,已报道的具有反硝化功能的假单胞菌属Pseudomonas、脱氯单胞菌属Dechloromonas、黄杆菌属Flavobacterium、陶厄氏菌属Thauera、红杆菌属Rhodobacter、热单胞菌属Thermomonas为主要优势菌属,相对丰度分别增加至56.13%、5.19%、11.70%、7.76%、3.48%和0.87%,较接种污泥显著提高[29]。A2/O反应器运行至第41天(未添加反硝化菌群),未出现显著的反硝化除磷现象。此时,混合污泥样品S_1中Thauera、Ottowia、Ferruginibacter、Novosphingobium、Sulfuritalea等几种菌属比例相对较高,约为3%~6%,主要发挥其反硝化功能[33-36]。
待在A2/O反应器缺氧区添加了富集的反硝化菌群后,由于活性污泥A2/O工艺为连续流运行,活性污泥流动和混合良好,故不同反应池的细菌群落结构相似(见图4中的A1_2、A2_2和O_2样品)。运行至第101天时,混合污泥样品S_3显示,Terrimonas、Ferruginibacter、Ottowia、Rhodobacter、Thermomonas、Dechloromonas等菌属占优势,其中已知Dechloromonas、Rhodobacter属DPAOs,Thermomonas属PAOs[24-28]。这几种具有反硝化除磷功能的菌属在反硝化菌群富集后比例升高,且在A2/O反应器运行至第101天反硝化除磷现象显著时为相对优势菌属。在接种污泥中Dechloromonas、Rhodobacter、Thermomonas占比分别为0.27%、1.33%、0.11%,反硝化菌群富集后分别占比4.95%、3.49%、0.87%,A2/O反应器运行至第101天分别占比0.66%、1.27%、3.38%。推测所富集的反硝化菌群添加至A2/O反应器内,在长期运行中,受反应参数等因素影响,如Dechloromonas、Rhodobacter、Thermomonas等几类具有反硝化除磷功能的菌属与反应器内活性污泥中的其他一部分菌属产生协同或竞争作用并逐渐发挥优势作用,因而出现较为显著的反硝化除磷现象。尽管比例较小,但生物活性较高。具体涉及的菌属间的作用机制较为复杂,尚需进一步探究。
-
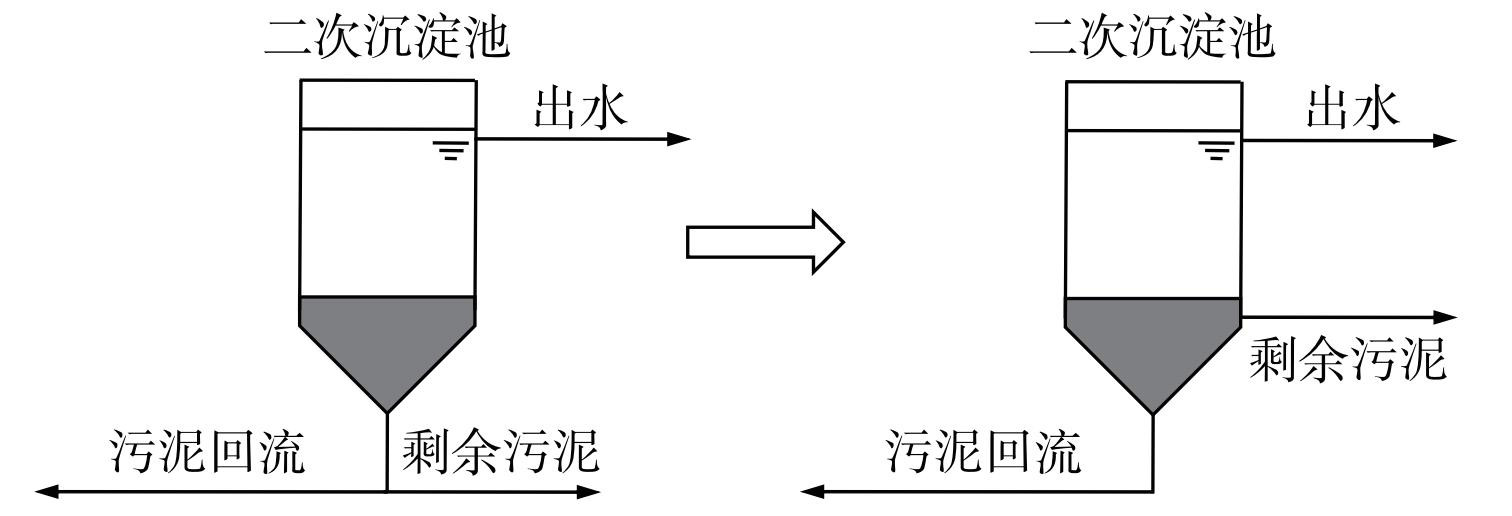
采用单一和易降解有机碳源会产生污泥膨胀现象[37],而本研究所添加的反硝化菌群由SBR富集培养得到,在富集期间以乙酸钠作为唯一有机碳源[29],未发生污泥膨胀且污泥沉降性能提高(SVI由高于110 mL·g−1下降至低于70 mL·g−1)。该结果与间歇运行每周期开始快速进料模式和晶核假说原理有关[38-39]。结果表明,沉降能力强的污泥易分布于沉淀池底部靠近中心管的位置[40]。由于A2/O反应器内的接种污泥与SBR内的接种污泥均取自同一污水处理厂回流污泥,且SBR富集培养后活性污泥沉降性提高,故添加的富含反硝化菌群的活性污泥易分布于A2/O反应器的二次沉淀池底部。传统活性污泥工艺二次沉淀池的剩余污泥与外回流污泥均由沉淀池底部输出,如图5所示。因此,为防止添加的反硝化菌群随剩余污泥排放而流失,可将二次沉淀池剩余污泥排泥位置由池底部提高[41],至沉淀泥面层下方接近泥面层位置,使得该菌群保留于A2/O反应器内,延长其污泥龄并提高其比例,实现生物强化作用。
-
1)将反硝化菌群添加到单污泥A2/O工艺中,通过活性污泥在厌氧-缺氧-好氧的环境下交替运行,刺激反硝化菌群发挥生物除磷功能,简化了DPAOs在厌氧-缺氧条件或厌氧-缺氧-好氧条件下的富集培养程序。研究结果可为探索基于传统活性污泥系统的低碳途径生物脱氮除磷工艺、并更好地利用反硝化除磷菌提供参考。
2)在该反硝化菌群添加于A2/O工艺后,体系的除磷途径由明显的厌氧释磷-好氧吸磷途径向厌氧释磷-缺氧吸磷的反硝化除磷途径过渡,表现出显著的反硝化除磷现象,且具有反硝化除磷功能的菌群为相对优势菌属。
3)添加的富含反硝化菌群的活性污泥的沉降能力高于A2/O系统内的活性污泥,将传统二次沉淀池剩余污泥排泥位置由池底部提高至沉淀泥面层下方接近泥面层位置,可防止添加的反硝化菌群随剩余污泥排放而流失。
添加反硝化菌群的A2/O反硝化除磷低碳工艺启动
Start-up of low-carbon denitrifying phosphorus removal in an A2/O process after augmentation of denitrifying bacterial community
-
摘要: 为探究反硝化除磷低碳工艺的实际效果,采用序批式反应器(SBR)根据底物反应速率来调节底物的流加速率,并以温度(20±2) °C、pH(7.5±0.2)和溶解氧(DO)为0的反应条件富集反硝化菌群。得到可同时利用亚硝酸盐和硝酸盐为电子受体的反硝化菌群,将其添加至厌氧-缺氧-好氧(A2/O)工艺中,以刺激反硝化细菌在反应器中发挥生物除磷功能,并开展工艺启动研究。结果表明:在加入反硝化菌群后,A2/O工艺发生了明显的反硝化除磷反应,且系统运行稳定;反硝化除磷途径的TP去除负荷均值约为0.014 8 kg·(m3·d)−1;厌氧出水TP平均值为11.95 mg·L−1,且缺氧吸磷量与好氧吸磷量的平均比率约为2.40,即平均反硝化除磷率高达73.34%。这表明在单污泥A2/O工艺中成功实现了反硝化除磷的启动,从而证明了反硝化菌群的生物强化作用,其中的反硝化除磷功能菌群的相对优势菌属包括Dechloromonas、Rhodobacter、Thermomonas等。本研究可为探索基于传统活性污泥系统的低碳生物脱氮除磷工艺,并更好地利用反硝化除磷菌(DPAOs)提供了案例参考。Abstract: In order to explore the practical effect of low-carbon denitrification phosphorus removal process, the start-up study of the process was carried out in sequencing batch reactor (SBR). The substrate flow acceleration rate was adjusted according to the substrate reaction rate under a condition of a temperature of (20±2) °C, a pH of (7.5±0.2), and a dissolved oxygen (DO) content of 0. Denitrifying bacterial community that could use both nitrite and nitrate as electron acceptors was enriched and added into an anaerobic-anoxic-oxic (A2/O) process to stimulate the denitrifying bacteria to play the biological phosphorus removal function in the reactor. The results revealed that after adding denitrifying bacterial this A2/O process had obvious denitrification and phosphorus removal reaction, and the system ran stably. The average load of TP removal by denitrifying phosphorus removal was around 0.0148 kg·(m3·d)−1. The average concentration in the anaerobic effluent reached 11.95 mg·L−1, and the average ratio of anoxic phosphorus uptake amount to aerobic phosphorus uptake amount reached 2.40, that is the average denitrifying phosphorus removal rate was as high as 73.34%. This indicated that the start-up of denitrifying phosphorus removal was achieved in this single-sludge A2/O process, thus demonstrating the biological strengthening effect of denitrifying bacterial, and the comparative advantages of denitrifying phosphorus removal bacteria including Dechloromonas , Rhodobacter , Thermomonas , etc. This work proposed an available choice to take better advantage of DPAOs in a traditional activated sludge system to accomplish low-carbon biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal.
-

-
-
[1] JI Z Y, CHEN Y G. Using sludge fermentation liquid to improve wastewater short-cut nitrification-denitrification and denitrifying phosphorus removal via nitrite[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(23): 8957-8963. [2] GUO J H, Ni B J, Han X Y, et al. Unraveling microbial structure and diversity of activated sludge in a full-scale simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal plant using metagenomic sequencing[J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2017, 102: 16-25. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2017.03.009 [3] 缪新年, 程诚, 朱琳, 等. 短程硝化和反硝化除磷耦合工艺研究进展[J]. 水处理技术, 2020, 46(12): 12-16. [4] VALVE M, RANTANEN P, KALLIO J. Enhancing biological phosphorus removal from municipal wastewater with partial simultaneous precipitation[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2002, 46(4-5): 249-255. doi: 10.2166/wst.2002.0598 [5] OEHMEN A, LEMOS P C, CARVALHO G, et al. Advances in enhanced biological phosphorus removal: from micro to macro scale[J]. Water Research, 2007, 41(11): 2271-2300. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2007.02.030 [6] ZENG W, LI L, YANG Y Y, et al. Denitrifying phosphorus removal and impact of nitrite accumulation on phosphorus removal in a continuous anaerobic-anoxic-aerobic (A2O) process treating domestic wastewater[J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2011, 48(2): 134-142. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2010.10.010 [7] MA Y, PENG Y Z, WANG X L. Improving nutrient removal of the AAO process by an influent bypass flow by denitrifying phosphorus removal[J]. Desalination, 2009, 246(1-3): 534-544. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2008.04.061 [8] 王文琪, 李冬, 高鑫, 等. 不同好氧/缺氧时长联合分区排泥优化生活污水短程硝化反硝化除磷颗粒系统运行[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(9): 4406-4413. [9] 王启镔, 李浩, 董旭, 等. 改良型A2/O污水处理厂的工艺优化调控方案及其对同步脱氮除磷效率的提升[J]. 环境工程学报, 2022, 16(2): 659-665. [10] 吕亮, 尤雯, 张敏, 等. 硝化液回流比对ABR-MBR工艺反硝化除磷效能的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(3): 1309-1315. [11] KUBA, T, VAN LOOSDRECHT, M. C. M, HEIJNEN, J. J. Phosphorus and nitrogen removal with minimal COD requirement by integration of denitrifying dephosphatation and nitrification in a two-sludge system[J]. Water Research, 1996, 30(7): 1702-1710. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(96)00050-4 [12] DAI H L, CHEN W L, DAI Z Q, et al. Efficient model calibration method based on phase experiments for anaerobic-anoxic/nitrifying (A2N) two-sludge process[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017, 24(23): 19211-19222. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-9437-z [13] 卞晓峥, 闫阁, 黄健平, 等. 双污泥系统反硝化除磷新工艺研究进展[J]. 水处理技术, 2021, 47(7): 19-24. [14] 张淼, 彭永臻, 张建华, 等. 进水C/N对A2/O-BCO工艺反硝化除磷特性的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 2016, 36(5): 1366-1375. [15] CHEN P, Wu JUNKANG, Lu X. Denitrifying phosphorus removal and microbial community characteristics of two-sludge DEPHANOX system: Effects of COD/TP ratio[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 172: 108059. doi: 10.1016/j.bej.2021.108059 [16] SALEM S, BERENDS D H J G, HEIJNEN J J, et al. Bio-augmentation by nitrification with return sludge[J]. Water Research, 2003, 37(8): 1794-1804. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00550-X [17] 王启镔, 苑泉, 宫徽, 等. SBR系统在低浓度污水条件下培养好氧颗粒污泥的特性及微生物分析[J]. 环境工程学报, 2018, 12(11): 3043-3052. [18] HU J Y, ONG S L, NG W J, et al. A new method for characterizing denitrifying phosphorus removal bacteria by using three different types of electron acceptors[J]. Water Research, 2003, 37(14): 3463-3471. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00205-7 [19] PODEDWORNA J, ŻUBROWSKA-SUDOŁ M. Nitrogen and phosphorus removal in a denitrifying phosphorus removal process in a sequencing batch reactor with a forced anoxic phase[J]. Environmental Technology, 2012, 33(2): 237-245. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2011.563428 [20] ZHOU Y, PIJUAN M, YUAN Z G. Free nitrous acid inhibition on anoxic phosphorus uptake and denitrification by poly-phosphate accumulating organisms[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2007, 98(4): 903-912. doi: 10.1002/bit.21458 [21] PENG Y Z, WU C Y, WANG R D, et al. Denitrifying phosphorus removal with nitrite by a real-time step feed sequencing batch reactor[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 2011, 86(4): 541-546. doi: 10.1002/jctb.2548 [22] 韦佳敏, 沈耀良, 黄慧敏, 等. 基质浓度对ABR-MBR短程反硝化除磷工艺效能的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(3): 939-945. [23] WANG Y Y, GUO Gang, WANG Hong. Long-term impact of anaerobic reaction time on the performance and granular characteristics of granular denitrifying biological phosphorus removal systems[J]. Water Research, 2013, 47: 5326-5337. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2013.06.013 [24] KIM J M, LEE H J, LEE D S, et al. Characterization of the denitrification-associated phosphorus uptake properties of "Candidatus Accumulibacter phosphatis" clades in sludge subjected to enhanced biological phosphorus[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2013, 79(6): 1969-1979. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03464-12 [25] HAN Y H, ZHAN W X, LU W X, et al. Co-immobilization of Pseudomonas stutzeri YHA-13 and Alcaligenes sp. ZGED-12 with polyvinyl alcohol–alginate for removal of nitrogen and phosphorus from synthetic wastewater[J]. Environmental Technology, 2014, 35(22): 2813-2820. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2014.923516 [26] ZHAO W H, BI X J, PENG Y Z, et al. Research advances of the phosphorus-accumulating organisms of Candidatus Accumulibacter, Dechloromonas and Tetrasphaera: Metabolic mechanisms, applications and influencing factors[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 307: 135675. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135675 [27] 连丽丽. 聚磷菌的筛选及其对污水的除磷特性研究[D]. 辽宁: 辽宁师范大学, 2009. [28] 温馨. 低氨氮废水SNAD-DPR协同处理技术与微生物作用机制研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2018. [29] YAO R D, YUAN Q, WANG K J. Enrichment of denitrifying bacterial community using nitrite as an electron acceptor for nitrogen removal from wastewater[J]. Water, 2020, 12(1): 48. [30] 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002. [31] RONG Y, LIU X C, WEN L J, et al. Advanced nutrient removal in a continuous A2/O process based on partial nitrifification-anammox and denitrifying phosphorus removal[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2020, 36: 101245. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101245 [32] CARVALHO G, LEMOS P C, OEHMEN A, et al. Denitrifying phosphorus removal: Linking the process performance with the microbial community structure[J]. Water Research, 2007, 41(19): 4383-4396. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2007.06.065 [33] 马小茜, 张哲, 刘超, 等. 生活垃圾焚烧厂渗沥液厌氧氨氧化脱氮效能及微生物机理分析[J]. 环境工程, 2021, 39(11): 110-118. [34] YU W J, LAWRENCE N C, SOOKSA-NGUAN T, et al. Microbial linkages to soil biogeochemical processes in a poorly drained agricultural ecosystem[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2021, 156: 108228. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2021.108228 [35] 周石磊, 黄廷林, 白士远, 等. 贫营养好氧反硝化菌的分离鉴定及其脱氮特性[J]. 中国环境科学. 2016, 36(1): 238-248. [36] YANG Z C, ZHOU Q, SUN H M, et al. Metagenomic analyses of microbial structure and metabolic pathway in solid-phase denitrification systems for advanced nitrogen removal of wastewater treatment plant effluent: A pilot-scale study[J]. Water Research, 2021, 196: 117067. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.117067 [37] LIU Y, TAY J H. State of the art of biogranulation technology for wastewater treatment[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2004, 22(7): 533-563. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2004.05.001 [38] QIN L, TAY J H, LIU Y. Selection pressure is a driving force of aerobic granulation in sequencing batch reactors[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2004, 39(5): 579-584. doi: 10.1016/S0032-9592(03)00125-0 [39] LETTINGA G, VELSEN A F M, HOBMA S W, et al. Use of the upflow sludge blanket (USB) reactor concept for biological wastewater treatment, especially for anaerobic treatment[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 1980, 22(4): 699-734. doi: 10.1002/bit.260220402 [40] 吴越, 赵传峰, 孙法文, 等. 双区沉淀池用于连续流好氧颗粒污泥工艺的可行性[J]. 中国给水排水, 2020, 36(19): 9-15. [41] 姚仁达. 氨氧化和硝化细菌菌群筛选与富集培养及其固定化研究[D]. 北京: 北京工业大学, 2017. -



 下载:
下载: