-
重金属具有富集性、高毒性和生物放大性的特点,能够通过吸附、络合等作用在水体底泥中蓄积,目前已经在鱼、贝类等水生生物中超量检出重金属物质[1-2],由此可推断重金属污染已经对水生生态系统及人类健康构成潜在威胁。淡水湖泊是人类生产生活的重要资源之一,沉积物是河床必不可少且充满生态活力的部分,重金属以各种化学形式存在其中[3],但并非永久的存储于底泥中。在浅水湖泊与河口环境中,水环境容易受到自然因素、生物扰动和人类活动的影响,使沉积物发生再悬浮并导致水环境条件改变,进而引起水-沉积物界面污染物再活化,被束缚的重金属可能会因此解吸释放回上覆水域[4],对于大型浅水湖泊,水动力是影响底泥污染物扩散释放的重要因素,水体受到扰动后会促使微量重金属从固相向水体迁移[5-6],使水体与颗粒物间发生物质交换改变。这期间水溶态重金属浓度可瞬间提高,造成次生污染,且转化为更具生物利用性或毒性更强的化学形式[7],并可能在上覆水持续很长时间对水体生物产生急性毒害[8],从而通过食物链严重危害人体健康[9]。
巢湖流域作为我国典型富营养化程度较高的淡水湖泊之一,重金属污染问题也不容忽视。已有学者对巢湖流域不同河流和入湖河口上覆水与沉积物中重金属的浓度与分布做了广泛研究[10-12],巢湖底泥重金属含量处于中等水平,与此同时,巢湖是一个较为开放的水域,上覆水体易受到人为活动的干扰,促使沉积物再悬浮发生,但目前针对巢湖沉积物再悬浮对重金属释放迁移特性的系统研究非常少。巢湖东半湖区与巢湖闸相连,每年汛期,因防洪巢湖闸需要开放,泄洪事件会极大增加东半湖区沉积物再悬浮的发生几率[13],因此本研究选取巢湖东半湖区湖心取水区作为再悬浮模拟实验的研究点,探究沉积物受到扰动后上层水体环境条件的变化,分析水体扰动期间重金属(Zn、Cr、Pb、Hg)的迁移释放去向与迁移转化机制,凸显沉积物再悬浮对水-沉积物界面环境条件与重金属含量变化的影响。旨对巢湖湖泊水环境评估管理与重金属污染修复有更深刻的意义。
-
巢湖流域属于长江下游左岸水系,流经安徽省社会和经济发展水平较高的地区,是长江经济带和长三角经济圈重要版块;巢湖是我国第五大淡水湖之一,为皖江城市带和合肥都市圈核心区域。自20 世纪60 年代开始,巢湖闸、裕溪闸建成,为保证流域防洪安全,闸口仅在汛期打开,所以巢湖为人工控制的半封闭型浅水湖泊. 巢湖流域拥有重要的渔业资源,有着丰富且优质的水产,巢湖在为当地和全国市场提供水产品的同时也对当地居民生计起着非常重要的作用,而船舶行驶、拖网捕鱼、泄洪等人为活动,都是导致底泥沉积物扰动重要原因。前期对巢湖流域重金属污染分布的研究发现巢湖湖区重金属元素总量整体表现出东西高,中间低的分布特征,且西湖区受到合肥市工业面源的影响导致重金属含量明显高于其它湖区[14],东半湖区水质相对较好。研究者有关沉积物再悬浮的实验表明,在静水条件下,上覆水水质可能呈现良好状态,但沉积物再悬浮会扩大重金属向上覆水释放的风险[15-16]。
-
本研究于2020年9月前去巢湖东湖心取水区(117°37'12.02",31°31'19.05")采集湖面0.5 m以下水样约20 L,暂存至聚乙烯塑料桶中(10%硝酸浸泡24 h,去离子水冲洗),使用彼得森抓斗式采泥器,在东湖心采样点采集0—5 cm表层沉积物2.5 kg左右,装入密实聚乙烯塑料袋,暂存于装有冰袋的保温箱内。水样运回实验室后立即分出250 mL经过0.45 μm微孔滤膜的过滤,测定水样重金属含量。沉积物样品使用Christ冷冻干燥机经超低温冷冻干燥后,研磨过100目筛,检测沉积物重金属含量。后续用未经滤膜的东湖心水样和湿样底泥进行再悬浮实验。样品的采集、运输、保存具体参照《水和废水监测分析方法(第四版)》[17]。
-
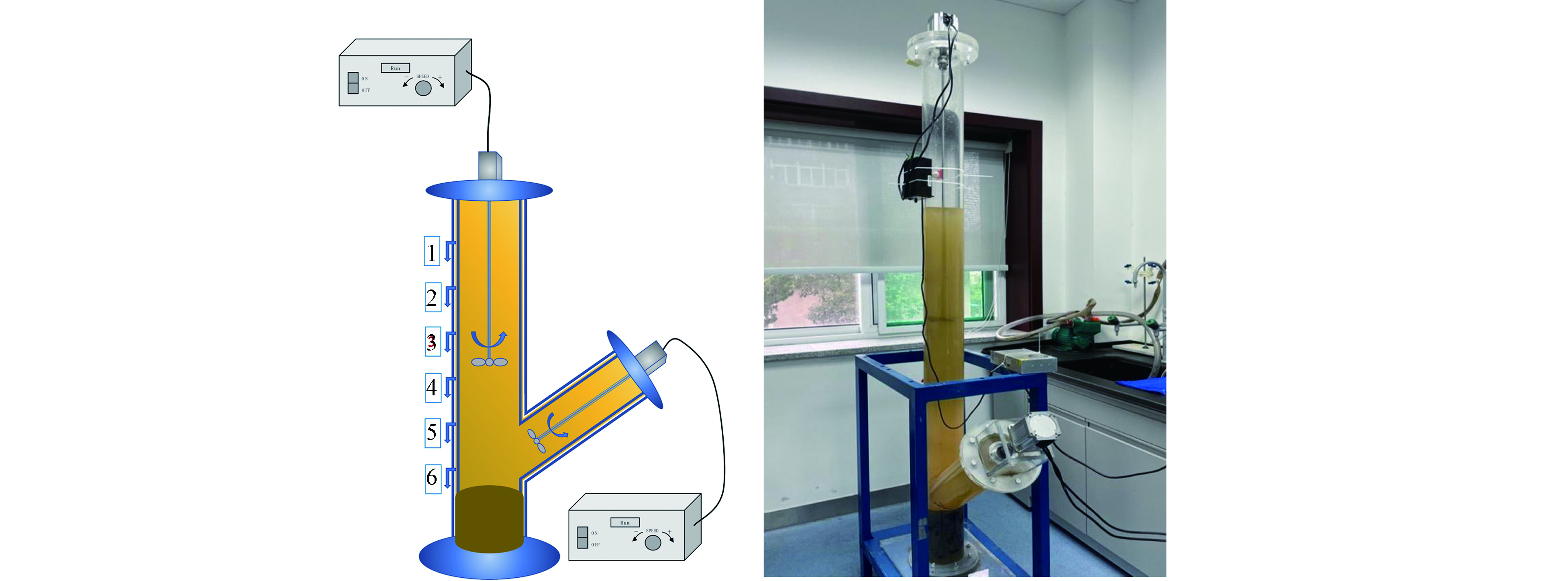
本研究参考范成新[18]发明专利的Y型再悬浮装置,模拟水下沉积物再悬浮状态。如下图1所示。装置主体是由亚克力材料制成的一直管与一斜管相连的组合体,直管和侧管均为内径110 mm的固形透明管,两管各配有聚四氟乙烯搅拌器由顶端的法兰封闭固定,并分别与两个搅拌电机相连。直管的侧边自上而下分别为1—6号取水口,自上而下分别距离沉积物表面高度为:105、85、65、45、25、5 cm。
将东湖心取水区的沉积物(高约20 cm)慢慢移入Y型再悬浮装置,注入上覆湖水,保持每次实验时水柱高度约140 cm,放置一周待泥样恢复自然分层后开始模拟实验。根据实验需要设定调控电机电动的转动速率(r·min−1),模拟不同的扰动强度和扰动持续时间下底泥沉积物再悬浮情况。实验期间的电机转速设定参考Y型再悬浮装置专利对太湖风速风量对沉积物再悬浮影响研究模拟的方法[19],具体的操作方法如下:(1)下部电机扰动转速固定为(270±2)r·min−1,上部电机分别进行Ⅰ级(280±2)r·min−1、Ⅱ级(310±2)r·min−1的扰动实验。每一扰动状态分别进行5、30 min后取样;(2)上部电机扰动转速固定为(310±2)r·min−1,下部电机扰动转速为Ⅲ级(330±2)r·min−1、Ⅳ级(360±2)r·min−1。由于扰动转速增大,考虑悬浮颗粒物的稳定时间相应增加,所以每一扰动状态分别进行15 min、45 min后取样。
每次扰动实验结束后,从1—6号取样口取约150 mL的水样至聚乙烯瓶内,实时检测不同扰动状态下上覆水体溶解氧与pH的变化情况。每次取样后需补充水样至原来的水柱高度。每级扰动的两个不同干扰时间为一组实验,每组扰动实验前和结束静置1 h后分别从1号和6号口取样进行对照。扰动实验结束后,所取水样均经孔径为0.45 μm的微孔滤膜过滤,加酸使其pH<2,置于4 ℃保存待测重金属含量。
-
水体样品使用电热板消解法[17],水样汞的消解方法参照《水质汞、砷、硒、铋和锑的测定原子荧光法(HJ 694—2014)》。沉积物中的重金属形态测定使用BCR连续提取法[20-21],实验过程中所使用的实验试剂均为优级纯。再悬浮实验后,对带有悬浮颗粒物的滤膜,使用烘干失重法测得上覆水体悬浮颗粒物的含量,并对带有悬浮颗粒物的滤膜进行刮取,与泥样进行相同的冷冻干燥,悬浮颗粒物与沉积物样品均使用HF-HNO3-HClO4三酸消解法[22],以备重金属总量的分析。每组实验均设置空白对照样品。消解液中Cr、Pb使用电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS)测定,Zn含量的测定使用火焰原子吸收分光光度仪,Hg使用原子荧光分析仪测定。为保证实验分析的可靠性,使用水系沉积物标准样品(GSD-6)作为质控样,各重金属元素的回收率均为90%以上。此外,每组实验均设置了平行样,各元素的相对标准偏差均控制在5%以内。
-
东湖心取水区上覆水体的重金属含量如下表1所示。夏季丰水期是重金属元素含量最高的季节,有较明显的季节差异性[11],本次研究所采集的样品处于9月,湖区范围内的水温仍然较高,Zn、Cr、Hg含量超出了《地表水环境质量标准》(GB3838—2002)Ⅰ级标准,而溶解态Pb浓度较低,低于Ⅰ类标准值。Hg元素含量较高,为0.144 μg·L−1,仅介于地表水环境质量Ⅲ与Ⅳ水质之间,上覆水环境中汞元素的污染较严重。Li[23]等对巢湖全湖区上覆水域重金属研究中报道的汞含量为0.24—0.74 μg·L−1,含量较高的主要集中在巢湖南部。
东湖心沉积物中的重金属含量见下表2所列,与安徽省土壤重金属环境背景值对比[24],这4种重金属元素含量均超出了背景值,Zn、Hg在沉积物中的含量比较高,分别为149.05、0.086 mg·kg−1,是背景值的2倍之多。巢湖周边的城市共拥有约34个工业行业,工业污水通过各支流进入巢湖流域,从而加重湖区的污染负荷,根据研究者们对湖区沉积物分布的调查发现,Hg在西部湖区浓度明显升高[12, 25],汞污染情况已经较为严重,所以对外源污染输入的有效控制依旧需格外重视。
-
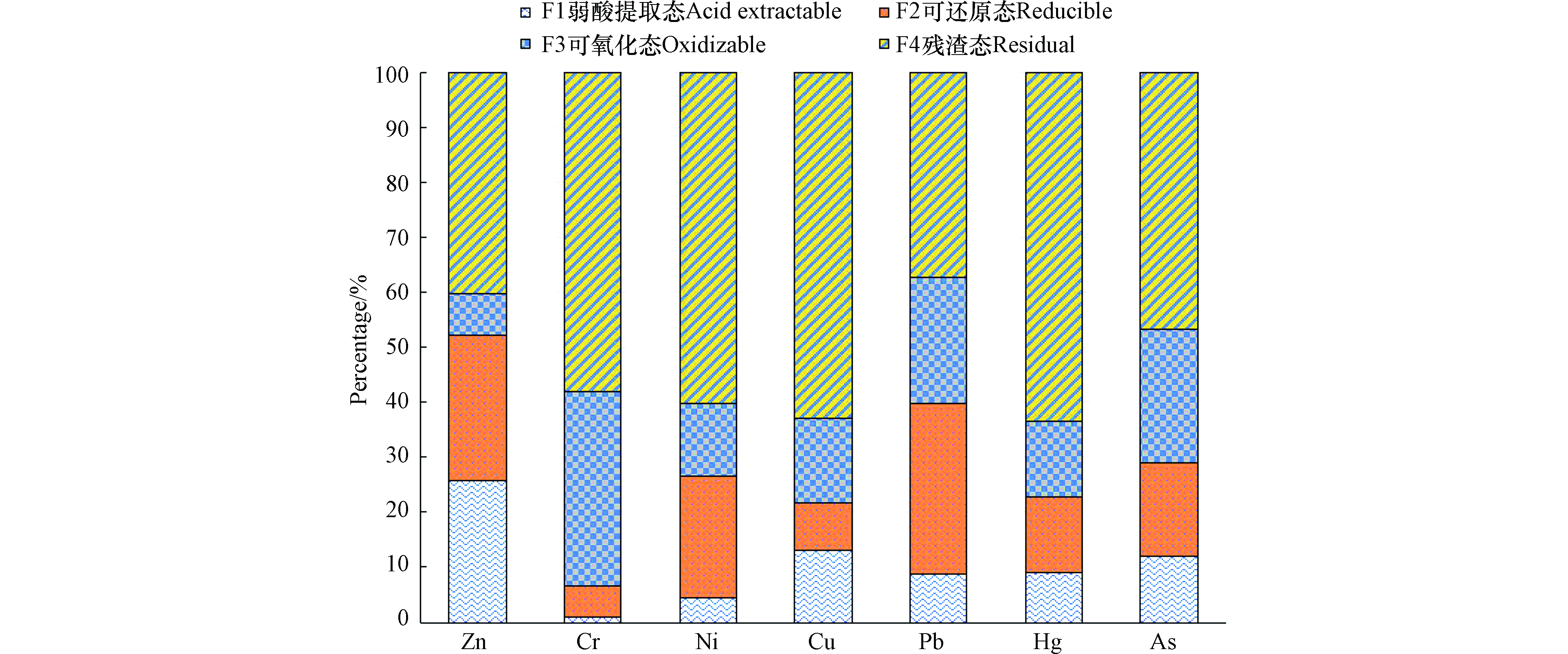
BCR续级提取法对沉积物中重金属元素的赋存形态分为4类:第一类是可交换及碳酸盐结合态(即弱酸提取态),第二类是Fe-Mn氧化物结合态(即可还原态),第三类是有机物及硫化物结合态(即可氧化态),第四类是属于残渣态。其中前3种形态较不稳定,容易被生物所利用,称为可提取态或有效态[26-28],若可提取态占比较大,元素则更容易释放析出,所以重金属形态会影响其对水体的污染程度与生物毒性[29]。巢湖东湖心沉积物4种重金属的各形态比例分布如下图2所示。Zn和Pb元素的有效态占据了很大比例,分别为59.86%、62.61%,比例越高说明重金在沉积物中的生物有效性与迁移性较越强。Zn元素弱酸以提取态与可还原态为主要赋存形态,在中性条件下易释放且能被植物吸收,水溶态和可交换态部分对环境条件变化较敏感,在酸性条件下容易释放,所以弱酸提取态的重金属元素最易迁移转化,生物有效性也最强[30]。Pb元素主要以Fe-Mn氧化物结合态与可氧化态为主,这两类形态的重金属也会受到环境条件的影响,当水体遇酸雨或水环境条件变化时,极易随环境的变化而迁移转化释出,从而转化至生物可利用的活性态,对环境具有潜在的危害性[30],再次释放会对水体造成二次污染[31]。Cr与Hg以残渣态为主要存在形式,因此在沉积物中的性质比较稳定,释放率与生物有效性均较低[26, 32],其中Cr元素有机结合态比例为35.15%,是4种元素中可氧化态占比最高的元素,虽然非有效态是Cr主导形态,但在碱性或氧化环境下,可氧化态重金属容易转化至活性态[33],所以其生态风险仍然不可忽视。
-
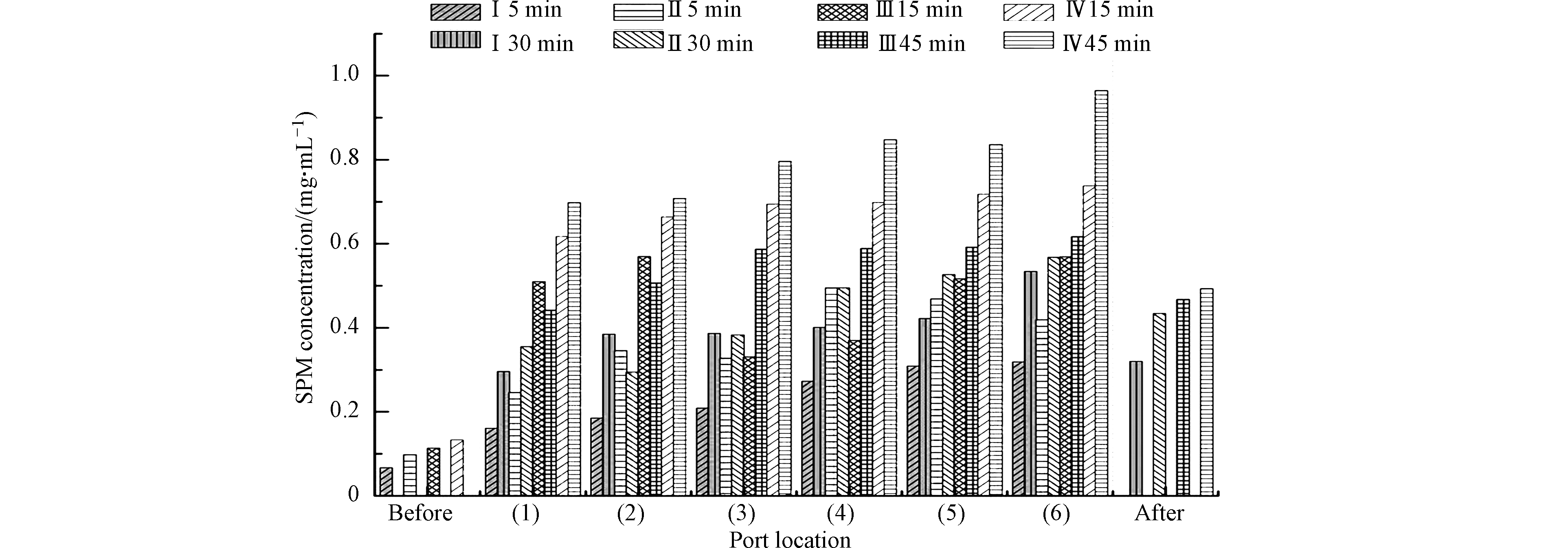
再悬浮期间上覆水悬浮颗粒物含量随扰动频率与持续时间的增加逐渐增长,扰动结束1 h后,悬浮颗粒物含量虽大幅下降,但仍然保持比实验前高的状态(图3)。扰动实验过程中,上覆水各深度的悬浮颗粒物含量呈现出明显的阶梯式增长趋势,且增长速率由急变缓。Ⅳ级扰动频率时,上覆水体中悬浮颗粒物含量增长至最高,与平静状态的颗粒物含量相比,因扰动造成颗粒物上浮量增长约20倍。悬浮颗粒物在垂向分布上由均匀分布逐渐转变为随液面深度增加而明显上升的趋势。
Ⅰ—Ⅲ级再悬浮过程中大量颗粒物从深层水体上浮水中,各深度颗粒物含量的区分度不大,而在Ⅳ级扰动后,体积更大的颗粒物被搅起,主要积累在靠近沉积物表面的深层水区,所以越靠近底层收集到的颗粒物质越多。外力干扰是沉积物再悬浮的主要动力来源,沉积物颗粒因受到外力干扰作用,在水-沉积物界面形成的切应力达到了临界值,当扰动的频率与时间足够时,就会引起更多颗粒再悬浮至上层水体中。悬浮颗粒物受到的水动力能量随时间持续的延长而增大,环境条件和悬浮颗粒物的数量会影响其在水体中的沉降速度,并最终改变吸附在颗粒物上的污染物在水柱中停留的时间[34]。
-
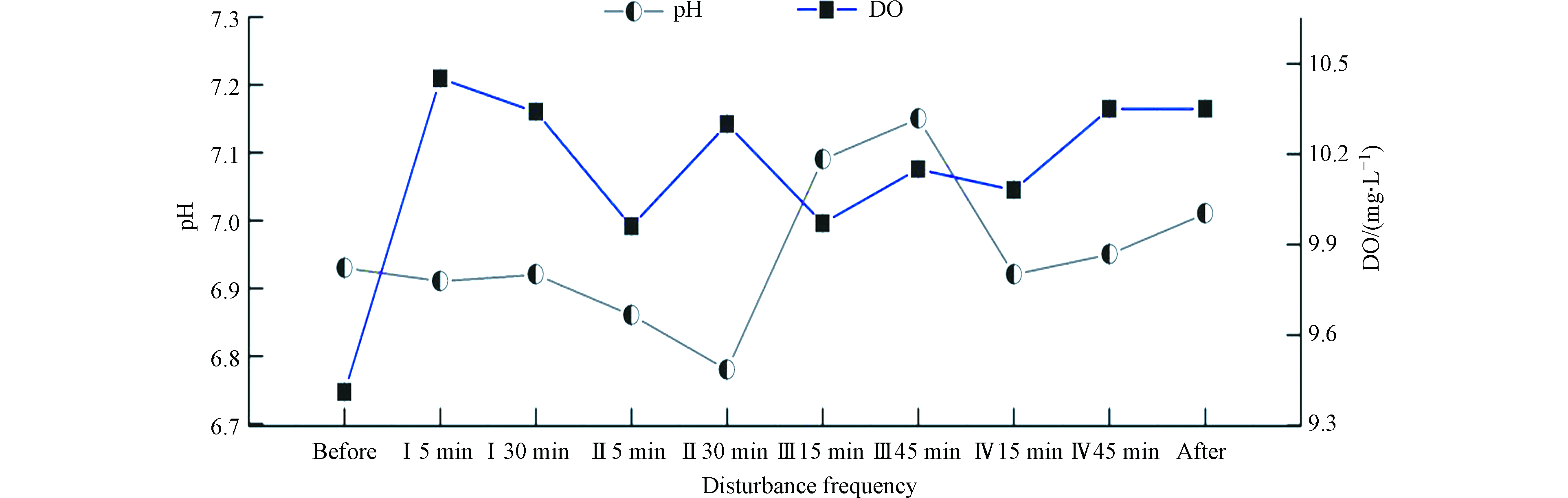
实验过程中上覆水pH值、DO浓度的变化情况如图4所示。水体在受到扰动后,上覆水pH与DO整体均呈现向上增长的趋势,这与柳肖竹[35]、Pourabadehei[36]等对沉积物再悬浮的研究情况相似。东湖心pH值的峰值出现在Ⅲ级扰动45 min,后续水流扰动使pH回落至实验前期的数值,水体静置1 h后,又出现了少量增长的趋势。DO浓度的峰值出现在扰动开始Ⅰ级5 min时,浓度为10.45 mg·L−1,后续的实验过程中DO浓度有较大的变化波动,水面恢复平静后DO浓度仍较高为10.35 mg·L−1。
水体的pH值与重金属的释放有很大的相关性,水环境为酸性条件时,易“引诱”沉积物中碳酸盐结合态及铁锰氧化物结合态的重金属再次释放溶解回水中,所以水体pH值越低,重金属的释放量则会逐渐增大[37]。东湖心沉积物Zn、Pb元素弱酸提取态与可还原态占据了大量赋存比例,在前期扰动浮动下,上覆水的pH值少量下降,较弱的外部动力条件极有可能影响沉积物中重金属的分布。随着大量沉积物颗粒上浮,水体pH值本应继续下降,但受到水体自身缓冲能力的作用,上层水缓冲了由硫化物或金属硫化物氧化所引起的pH值降低现象[38],因此在实验后期水体的pH值反而升高。
溶解氧是沉积物有机物分解与污染物质赋存形态的关键因素[39]。再悬浮实验过程中,DO浓度从前期大幅增长转变为稳定伴有少量减少的趋势,这是由于沉积物中的硫化物或金属硫化物不断氧化消耗水中的氧气,使溶解氧始终达不到饱和状态[40]。扰动实验后期水面恢复平静,由上覆水中DO浓度继续下降可以推测,沉积物的再悬浮使得水-沉积物界面的大量硫化物或金属硫化物再悬浮至上覆水中[41]。
-
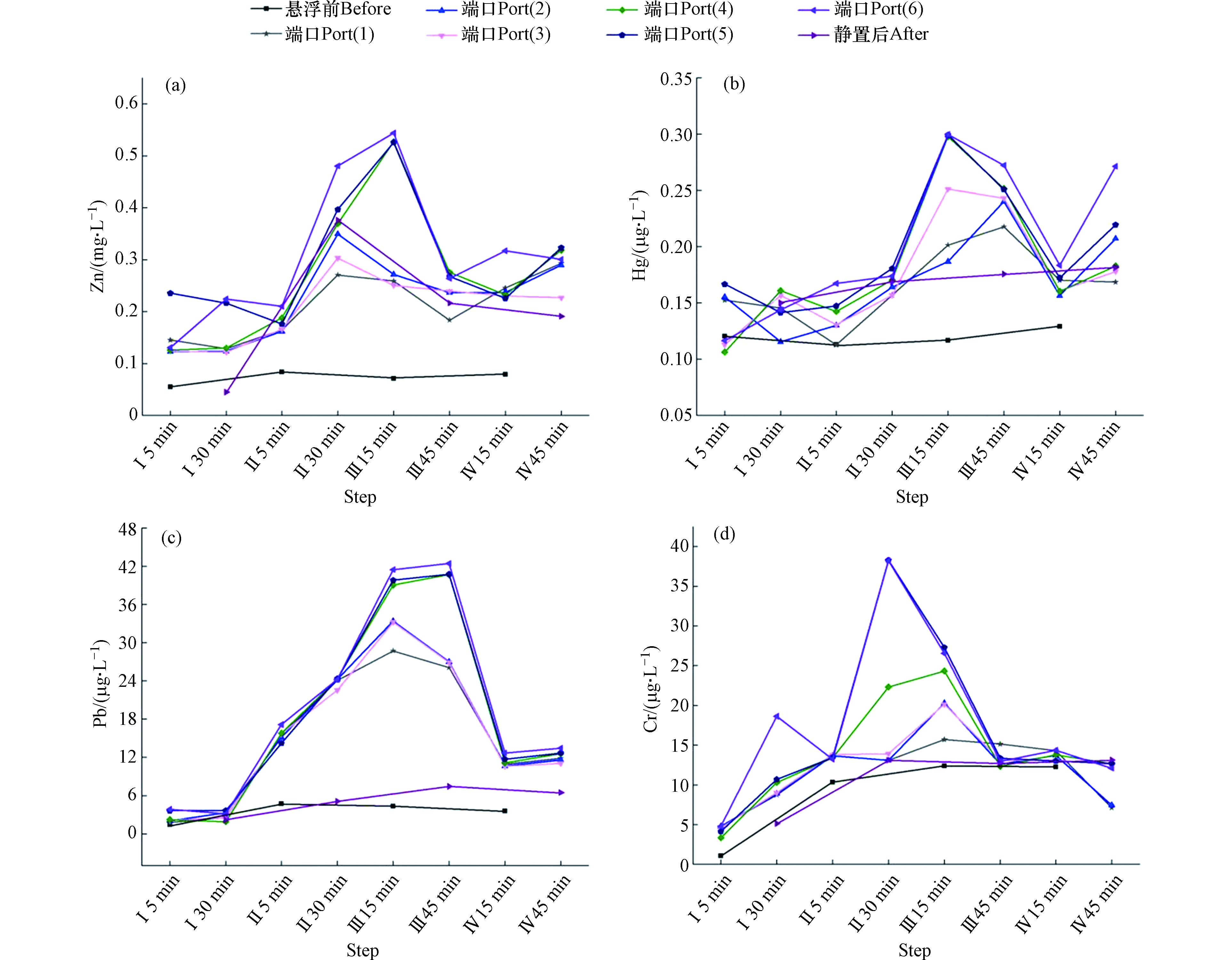
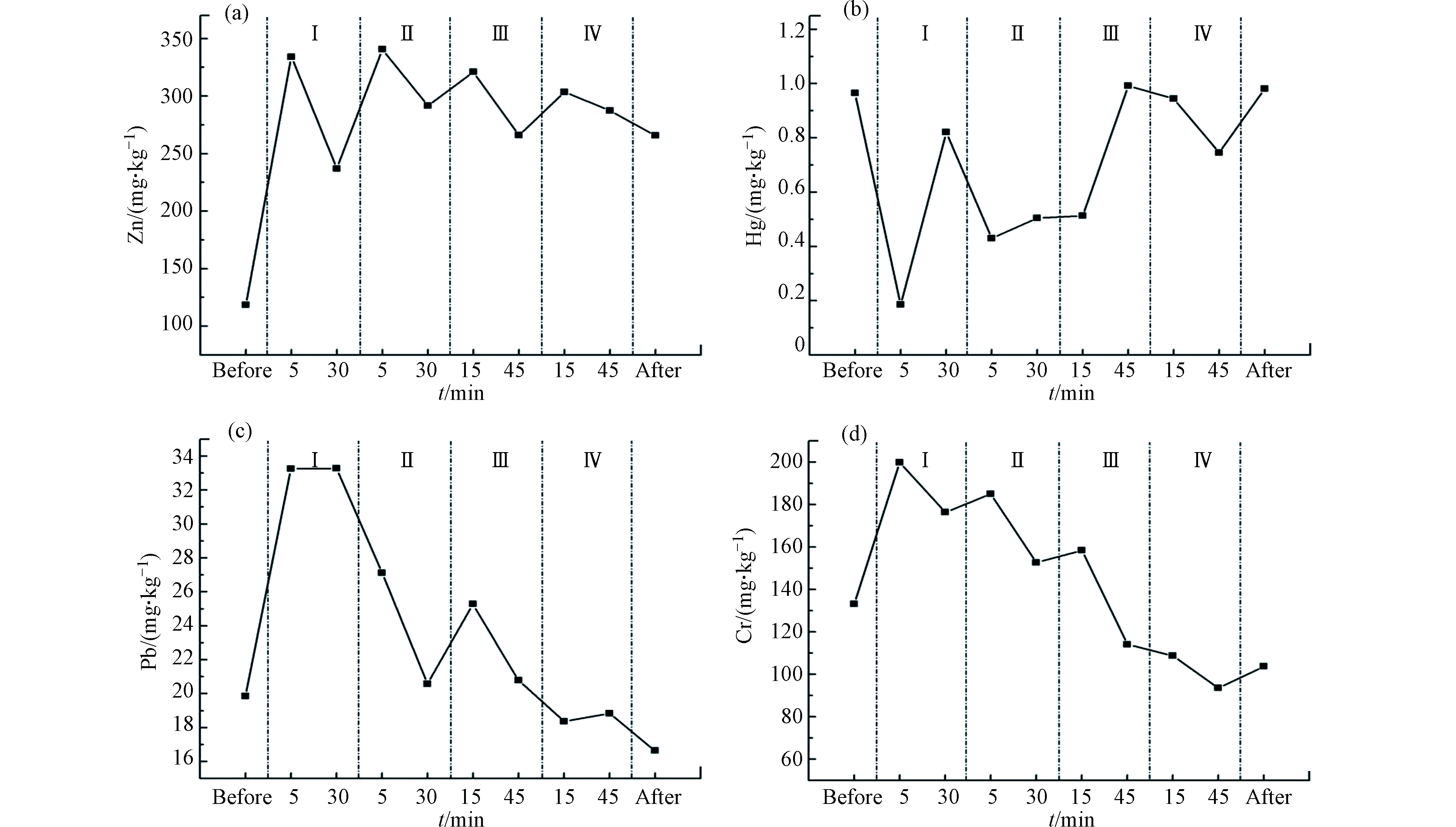
东湖心沉积物再悬浮期间,溶解态重金属含量如下图5所示,水面受到干扰后,溶解态重金属浓度增长峰值均在实验过程Ⅱ或Ⅲ级扰动条件下的出现,且主要分布于4—6号端口的深层水体中,而后并没有随扰动强度与扰动时间的增加出现猛烈增长,但仍超出水面平静时溶解态重金属含量。在实验初期Ⅰ级转速下,重金属元素的浓度几乎没有波动起伏,直至扰动强度扩大后,才有较小幅度的增长。其中水溶态Zn、Hg、Pb均在扰动转速Ⅱ级时浓度最高,Pb的增长幅度最大为9.8倍,其次为Zn元素,增长起伏超7倍;Cr在Ⅲ级扰动过程中浓度最大,为38.28 μg·L−1。
沉积物发生再悬浮后,水体扰动在沉积物表面产生了较大的剪切力,颗粒物由于剪切力生成细颗粒形成新的更密实的聚集体,新的聚集体具有更大表面积和吸附点位[42],所以扰动实验初期,重金属含量并没有明显起伏。东湖心处沉积物的黏土含量较高,平均粒径稍小约为8.33 μm,细颗粒物占比较大[43],细粒径颗粒比表面积更大,高浓度的黏土矿物和有机质含量也更多,所以对重金属有较强的吸附能力[44],缓冲了扰动初期造成的重金属大量释放,直至扰动强度继续增加溶解态重金属浓度才大幅上升。重金属形态的弱酸提取态与可还原态重金属对环境条件的变化都十分敏感,而东湖心沉积物中Zn和Pb在这两部分占据了极大的赋存比例,随沉积物再悬浮后水体环境的变化,Zn和Pb的浓度起伏量最明显,直至后期水体pH值升高,溶解至水中的浓度开始降低,所以pH控制缓冲了溶解态重金属含量的增长。
-
由于东湖心沉积物再悬浮过程中,各取水口所得悬浮颗粒物量较少未达到消解最低重量要求,因此将6个取水口所刮去的悬浮颗粒物合并测得再悬浮期间颗粒态重金属浓度的变化,结果如下图6所示。Pb和Cr元素的颗粒态浓度呈现“波浪”式上涨下降的变化趋势,而颗粒态Zn在沉积物再悬浮期间,有较大幅度的增长,上涨约5倍左右。初期受到较小的水流扰动后Pb和Cr颗粒态浓度均急剧升高1倍左右,继续增大电机扰动转速后,两个元素浓度开始下降,至扰动实验结束后,Pb由初始19.86 mg·kg −1降至18.84 mg·kg−1,而Cr由133 mg·kg−1降至94 mg·kg−1。颗粒态Hg含量在Ⅰ级扰动5 min时呈现下降趋势,后续开始逐渐增涨,待Ⅲ级扰动后期上涨回再悬浮前阶段的浓度。除Hg以外,颗粒态重金属元素在扰动实验初期急剧上涨至一个高峰,因为沉积物受到扰动后,大量颗粒物再次悬浮进入上层水体,造成水中颗粒态重金属含量也随之迅速增加,水体流速更高后,颗粒态重金属浓度开始稳定并向下回落,这是由于高流速下带有更多低重金属浓度的大粒径颗粒物进入上覆水[45],对水体中颗粒态重金属产生了稀释作用,即“颗粒浓度效应”[46],所以当水中颗粒物浓度继续增加后,部分颗粒相的重金属浓度反而降低,这与前期研究者们的结果相似[47-49]。
-
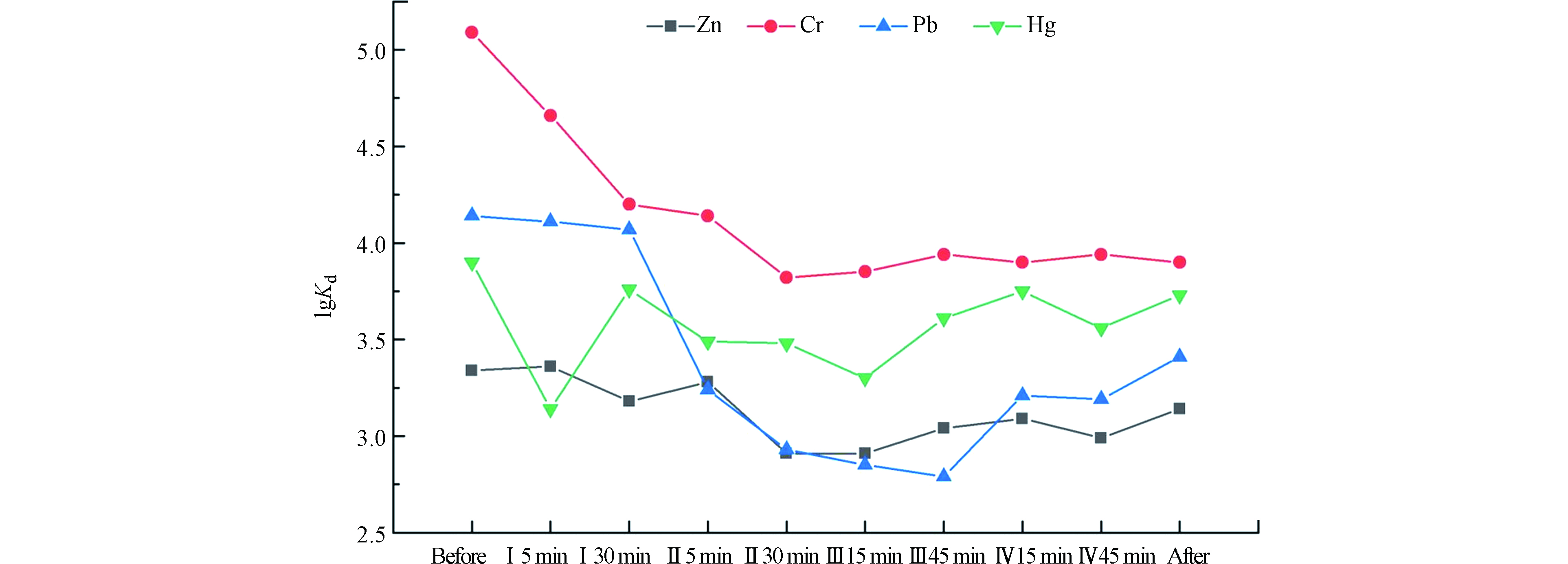
溶解相和颗粒相重金属浓度间的分配系数Kd反应了其相对亲和性,Kd=CP/CD,式中CP为颗粒态重金属含量(mg·kg−1),CD为溶解态重金属含量(mg·L−1)。若Kd值(L·kg−1)越高则说明重金属易被颗粒相吸附,反之Kd值越低说明水相对重金属的亲和力更高,重金属释放迁移力更强,生态危害潜力也随之增加。东湖心沉积物再悬浮后,上覆水中的Zn、Hg、Pb和Cr的分配系数(lg Kd)如下图7所示。
沉积物再悬浮期间,除Hg元素外,Zn、Pb和Cr的分配系数为随水流速增加而降低的变化规律,Cr与Pb元素lg Kd值下降最为明显。虽然Cr在水体受到干扰后lg Kd值的下降幅度最大,但仍然为4种重金属元素中最高的水平,说明相比于其他元素,上覆水中Cr元素更倾向于结合在悬浮颗粒物上,其扩散至溶解相的可能性也相对减小,这也与其赋存形态相关。当底部沉积物开始受到扰动后,上覆水中Hg元素的lg Kd迅速降低,但随水体流速继续增大后,lg Kd值却开始逐渐上升并与实验前持平,说明短时间较小强度的水流活动,更易造成颗粒相结合的Hg发生释放。水中流速增大后,重金属元素分配系数降低,随水体流速不断增加后,更多粗颗粒物质进入上层水中,这部分颗粒物对重金属的富集能力较弱,所以易造成颗粒相中重金属的转移[46-47],同时由于粗颗粒的上浮较小了悬浮在上覆水中胶体的比表面积,即影响其对重金属的亲和力[50],随着DO浓度的增加,表层沉积物中部分金属硫化物发生氧化,Fe、Mn等二价离子被释放出来,并迅速形成水合铁锰氧化物胶体物质,增大了水中溶解态部分的胶体比例[41],因此再悬浮实验后期,重金属元素的分配系数(lg Kd)整体下降。
-
水面由静置转变为动水条件后,原本堆积于水-沉积物界面处的重金属随颗粒物活动开始活化,逐渐通过孔隙水以溶解态的形式扩散到水中,在较小的扰动强度下,重金属的释放速度较慢,大多数重金属依旧被吸附于悬浮颗粒物上。随着扰动频率增加以及时间的延长,更多细颗粒及大粒径颗粒物重新进入上覆水,使盐离子与溶解性有机质在水中含量急剧上升,与重金属间对悬浮颗粒物的吸附点位产生了竞争效应,促进重金属从悬浮颗粒物上解吸[51],因此扰动实验中期,重金属进入快速释放阶段,溶解态重金属含量急剧上涨,分配系数也明显降低。各重金属元素的释放程度不仅与水动力条件有关,还受到了其在沉积物中赋存形态的影响,水动力条件下,4种重金属迁移释放程度为Pb>Zn>Cr>Hg。
重金属普遍与硫在静态水环境或低强度扰动状态时形成相对稳定的金属硫化物,而硫以及大多数重金属是多价态的氧化还原环境敏感性元素[52],所以易受到pH值、氧化还原电位、有机质含量等环境条件的影响[53]。沉积物再悬浮期间,靠近沉积物表面的深层水体中溶解态重金属浓度更高,这是由于受到酸可挥发性硫化物(AVS)的影响,其在表层沉积物的浓度较低,而在深层底泥相对稳定[54-55],因扰动给水-沉积物界面及深层底泥带来更多溶解氧,使沉积物中更多的金属硫化物发生了氧化,并迅速形成了胶体物质,进一步增加溶解态重金属含量[56]。此外在有氧环境下,底泥中好氧微生物的活性增强,从而加速沉积物中有机质结合态重金属的释放,这些影响因素造成再悬浮期间溶解态重金属浓度在垂直方向上随深度增加。
-
(1)沉积物再悬浮后,上覆水体理化性质出现明显变化:水体中悬浮颗粒物含量与水体受到的扰动转速、时间呈正相关性,且水流速度增大后,靠近沉积物表面的深层水收集到的颗粒物最多,颗粒物上浮量超过20倍;上覆水pH整体均呈现增长的趋势,底泥扰动给水体带来了更多溶解氧。
(2)溶解态重金属浓度主要在扰动实验的中期有较大幅度的上升趋势,后续阶段重金属浓度仅有少量波动,由于有效态是Zn和Pb元素在沉积物中的主要赋存形态,所以增长幅度最明显;当大量悬浮颗粒物进入上覆水后,颗粒态Pb、Cr浓度浓度开始波动并呈逐渐下降的趋势,而Zn浓度相比水面平静时整体为增长的,Hg元素的变化趋势为先下降后升高。
(3)水动力条件下,重金属元素整体分配系数随水流速增加后均出现降低的变化规律,说明与静水条件相比,再悬浮会使颗粒相中形态不稳定的重金属通过间隙水转移至上覆水中,尤其在深层水体中水溶态重金属浓度的增加较明显,4种重金属迁移释放程度为Pb>Zn>Cr>Hg。
(4)再悬浮颗粒能够较长时间漂浮在水中,并持续向水中释放重金属,颗粒相重金属可能成为生态系统的长期暴露源。后续对沉积物再悬浮期间重金属的释放研究,需要探寻底泥扰动对重金属赋存形态的影响,建立重金属释放的动力学预测模型,更深入地研究沉积物颗粒与水体之间重金属的交换,从时间和空间尺度上对沉积物再悬浮后重金属释放对水环境的影响进行评估,为大型浅水湖泊内源次生污染做更有效的科学防控。
巢湖东湖心沉积物重金属的分布及其在外力扰动下的释放特征
Distribution and release characteristics of heavy metals in sediments from the East Chaohu Lake under external disturbance
-
摘要: 本研究以巢湖东湖心的表层沉积物为研究对象,分析上覆水和沉积物中重金属的分布特征。借助Y型再悬浮装置,探究不同扰动条件下,上覆水体Zn、Hg、Pb、Cr含量与理化条件的变化及沉积物再悬浮释放规律。结果表明,沉积物中Zn、Hg、Pb、Cr含量均超出了背景值,分别为149.05、0.086、33.18、87.9 mg·kg-1,且Cr、Hg以残渣态为主,而Zn、Pb有效态占比很高,分别为59.86%、62.61%,赋存形态影响再悬浮期间重金属的迁移程度;水体流动使上覆水悬浮颗粒物含量逐层增加,pH发生较大波动,DO随物理扰动的强度、时间增加而上升;水溶态重金属在扰动过程的中段上升幅度明显,但并没有持续增长,而分布于颗粒相上的重金属扰动初期急剧上涨至一个高峰,后续逐渐下降;水体扰动促使颗粒相上的重金属解吸,不同重金属的释放速率不同,Pb的迁移程度最明显,由于再悬浮进入上层水体的沉积物颗粒给上层水体尤其是水-沉积物界面带来了更多重金属污染。Abstract: Surface sediments from the eastern center of the Chaohu Lake were studied for the distribution characteristics of heavy metals in the aqueous environment and sediments. Using a Y-type resuspension device, the changes of Zn, Hg, Pb, Cr contents and physicochemical parameters in the overlying water under different disturbance intensities and durations were explored, with an aim of illustrating the release characteristics of heavy metals during sediment resuspension. Our results show that (1) The contents of Zn, Hg, Pb and Cr in the sediments were 149.05, 0.086, 33.18, 87.9 mg·kg−1, respectively, which all exceeded their background value. Cr and Hg were mainly in the residual form, while 59.86% of Zn and 62.61% of Pb were in the available form. The forms of occurrence affected the migration degrees of heavy metals during sediment resuspension. (2) Under hydrodynamic conditions, the content of suspended particulate matter in overlying water increased layer by layer, pH fluctuated greatly, and DO increased with the increase of intensity and time duration of physical disturbance. (3) The contents of water-soluble heavy metals increased significantly in the middle of the disturbance process, but did not continue to grow, while the heavy metals in the particle phases increased sharply to a peak at the beginning of the disturbance, and then decreased gradually. (4) Water disturbance promotes the desorption of heavy metals in the particle phases, and each heavy metal has distinct release degrees and velocities. Notably, the migration degree of Pb is the most obvious. Due to the resuspension of sediment particles into the upper water body, more heavy metal pollutants were released to the upper water body, especially at the water sediment interface.
-
Key words:
- resuspension /
- sediment /
- heavy metal /
- physical disturbance /
- Chaohu lake
-

-
表 1 东湖心上覆水Zn、Cr、Pb、Hg含量
Table 1. Contents of Zn, Cr, Pb and Hg in overlying water of East Chaohu Lake
Zn/(mg·L−1) Cr/(μg·L−1) Pb/(μg·L−1) Hg/(μg·L−1) Ⅲ类标准值 1.0 50 50 0.1 东湖心 0.0193 11.532 3.393 0.144 表 2 东湖心沉积物Zn、Cr、Pb、Hg含量(mg·kg-1)
Table 2. Contents of Zn, Cr, Pb and Hg in sediments of the East Chaohu Lake(mg·kg-1)
Zn Cr Pb Hg 背景值[24] 53.2 69.4 25.9 0.041 东湖心 149.05 87.90 33.18 0.086 -
[1] TEKIN-ÖZAN S, KIR İ. Seasonal variations of heavy metals in some organs of carp (Cyprinus carpio L., 1758) from Beyşehir Lake (Turkey) [J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2008, 138(1/2/3): 201-206. [2] SAKAN S, DEVIĆ G, RELIĆ D, et al. Risk assessment of trace element contamination in river sediments in Serbia using pollution indices and statistical methods: A pilot study [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2015, 73(10): 6625-6638. doi: 10.1007/s12665-014-3886-1 [3] ALI M M, ALI M L, ISLAM M S, et al. Preliminary assessment of heavy metals in water and sediment of Karnaphuli River, Bangladesh [J]. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management, 2016, 5: 27-35. [4] LIU S F, WU B, SEDDIQUE A A, et al. Distribution, sources and chemical screening-level assessment of toxic metals in the northern Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2020, 150: 110676. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110676 [5] SUPERVILLE P J, PRYGIEL E, MAGNIER A, et al. Daily variations of Zn and Pb concentrations in the Deûle River in relation to the resuspension of heavily polluted sediments [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 470/471: 600-607. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.10.015 [6] KALNEJAIS L H, MARTIN W R, BOTHNER M H. The release of dissolved nutrients and metals from coastal sediments due to resuspension [J]. Marine Chemistry, 2010, 121(1/2/3/4): 224-235. [7] LÉCRIVAIN N, CLÉMENT B, DABRIN A, et al. Water-level fluctuation enhances sediment and trace metal mobility in lake littoral [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 264: 128451. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128451 [8] 俞慎, 历红波. 沉积物再悬浮-重金属释放机制研究进展 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2010, 19(7): 1724-1731. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2010.07.038 YU S, LI H B. Perspectives on the release of heavy metals via sediment resuspension [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2010, 19(7): 1724-1731(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2010.07.038
[9] HU B F, JIA X L, HU J, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and health risks in the soil-plant-human system in the Yangtze River Delta, China [J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2017, 14(9): 1042. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14091042 [10] 钱贞兵, 唐晓先, 徐升, 等. 巢湖湖区底泥重金属污染状况评估 [J]. 安徽农业大学学报, 2018, 45(4): 690-695. doi: 10.13610/j.cnki.1672-352x.20180825.034 QIAN Z B, TANG X X, XU S, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in sediment in Chaohu Lake [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 2018, 45(4): 690-695(in Chinese). doi: 10.13610/j.cnki.1672-352x.20180825.034
[11] 吴蕾, 刘桂建, 周春财, 等. 巢湖水体可溶态重金属时空分布及污染评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(2): 738-747. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201703099 WU L, LIU G J, ZHOU C C, et al. Temporal-spatial distribution and pollution assessment of dissolved heavy metals in Chaohu lake [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(2): 738-747(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201703099
[12] 刘刚, 蒋晨韵, 李小龙, 等. 巢湖沉积物重金属浓度分布及风险指数[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2018, 41(增刊1): 376-380. LIU G, JIANG C Y, LI X L, et al. The concentration distribution and risk index of sediment heavy metals in lake Chaohu[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 41(Sup 1): 376-380 (in Chinese).
[13] FRÉMION F, COURTIN-NOMADE A, BORDAS F, et al. Impact of sediments resuspension on metal solubilization and water quality during recurrent reservoir sluicing management [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 562: 201-215. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.03.178 [14] 余秀娟. 巢湖沉积物重金属质量基准的研究[D]. 芜湖: 安徽师范大学, 2012. YU X J. Studies on sediment quality criteria of heavy metals in lake Chaohu, China[D]. Wuhu: Anhui Normal University, 2012 (in Chinese).
[15] 王沛芳, 胡燕, 王超, 等. 动水条件下重金属在沉积物水之间的迁移规律 [J]. 土木建筑与环境工程, 2012, 34(3): 151-158. WANG P F, HU Y, WANG C, et al. Analysis on mobility of heavy metals between sediment-water under different hydrodynamic conditions [J]. Journal of Civil, Architectural & Environmental Engineering, 2012, 34(3): 151-158(in Chinese).
[16] CIFFROY P, MONNIN L, GARNIER J M, et al. Modelling geochemical and kinetic processes involved in lead (Pb) remobilization during resuspension events of contaminated sediments [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 679: 159-171. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.192 [17] 魏复盛. 水和废水监测分析方法(第4版)[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002. WEI F S. Methods for monitoring and analysis of water and wastewater (Version 4) [M]. Beijing: China Environmental Press, 2002 (in Chinese).
[18] 范成新. 一种室内模拟水下沉积物再悬浮状态的方法及装置: CN1277111C[P]. [2006-09-27]. FAN C X. Method and apparatus for indoors simulating refloating state of underwater deposition: CN1277111C[P]. [2006-09-27](in Chinese).
[19] 尤本胜, 王同成, 范成新, 等. 太湖沉积物再悬浮模拟方法 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2007, 19(5): 611-617. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2007.05.018 YOU B S, WANG T C, FAN C X, et al. Quantitative simulative method of sediment resuspension in Lake Taihu [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2007, 19(5): 611-617(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2007.05.018
[20] 徐圣友, 叶琳琳, 朱燕, 等. 巢湖沉积物中重金属的BCR形态分析 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2008, 31(9): 20-23,28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2008.09.006 XU S Y, YE L L, ZHU Y, et al. Chemical speciation of heavy metals from Chaohu lake sediments using BCR procedure [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 31(9): 20-23,28(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2008.09.006
[21] BAIG J A, KAZI T G, ARAIN M B, et al. Arsenic fractionation in sediments of different origins using BCR sequential and single extraction methods [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 167(1/2/3): 745-751. [22] 生态环境部. 中华人民共和国环保行业标准: 土壤和沉积物 铜、锌、铅、镍、铬的测定 火焰原子吸收分光光度法 HJ 491—2019[S]. 北京: 中国环境出版社, 2019. Environmental Protection Standard of the People's Republic of China: Soil and sediment—Determination of copper, zinc, lead, nickel and chromium—Flame atomic absorption spectrophotometry. HJ 491—2019[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Publishing Group, 2019 (in Chinese).
[23] LI G L, LIU G J, ZHOU C C, et al. Spatial distribution and multiple sources of heavy metals in the water of Chaohu Lake, Anhui, China [J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2012, 184(5): 2763-2773. doi: 10.1007/s10661-011-2149-9 [24] 陈兴仁, 陈富荣, 贾十军, 等. 安徽省江淮流域土壤地球化学基准值与背景值研究 [J]. 中国地质, 2012, 39(2): 302-310. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.02.004 CHEN X R, CHEN F R, JIA S J, et al. Soil geochemical baseline and background in Yangtze River–Huaihe River basin of Anhui Province [J]. Geology in China, 2012, 39(2): 302-310(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.02.004
[25] 刘新, 蒋豫, 高俊峰, 等. 巢湖湖区及主要出入湖河流表层沉积物重金属污染特征及风险评价 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2016, 28(3): 502-512. doi: 10.18307/2016.0305 LIU X, JIANG Y, GAO J F, et al. Pollution characteristics of heavy metals and the risk assessment for the surface sediments from Lake Chaohu and its main tributary rivers [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2016, 28(3): 502-512(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2016.0305
[26] 林承奇, 胡恭任, 于瑞莲, 等. 九龙江表层沉积物重金属赋存形态及生态风险 [J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(3): 1002-1009. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201607087 LIN C Q, HU G R, YU R L, et al. Speciation and ecological risk of heavy metals in surface sediments from Jiulong river [J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(3): 1002-1009(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201607087
[27] TAPIA J, DAVENPORT J, TOWNLEY B, et al. Sources, enrichment, and redistribution of As, Cd, Cu, Li, Mo, and Sb in the Northern Atacama Region, Chile: Implications for arid watersheds affected by mining [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 185: 33-51. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2017.10.021 [28] YUAN G L, LIU C, CHEN L, et al. Inputting history of heavy metals into the inland lake recorded in sediment profiles: Poyang Lake in China [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 185(1): 336-345. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.09.039 [29] CLOZEL B, RUBAN V, DURAND C, et al. Origin and mobility of heavy metals in contaminated sediments from retention and infiltration ponds [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2006, 21(10): 1781-1798. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2006.06.017 [30] 刘恩峰, 沈吉, 朱育新. 重金属元素BCR提取法及在太湖沉积物研究中的应用 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2005, 18(2): 57-60. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6929.2005.02.012 LIU E F, SHEN J, ZHU Y X. Determination of heavy metal chemical forms by BCR method for Taihu lake sediments [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2005, 18(2): 57-60(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6929.2005.02.012
[31] 李国莲. 巢湖污染物赋存、来源及风险评价研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2012. LI G L. Study on enrichment, source and risk assessment of pollutants in Chaohu lake[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2012(in Chinese).
[32] 郑志侠, 潘成荣, 丁凡. 巢湖表层沉积物中重金属的分布及污染评价 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2011, 30(1): 161-165. ZHENG Z X, PAN C R, DING F. Distribution and environmental pollution assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Chaohu lake, China [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2011, 30(1): 161-165(in Chinese).
[33] 方小红. 洞庭湖“四水”入湖沉积物重金属污染的地球化学研究 [D]. 长沙: 湖南师范大学, 2020. FANG X H. Geochemical study on heavy-metal contamination in sediments from the Four River inlets of Dongting Lake, China [D]. Changsha: Hunan Normal University, 2020(in Chinese).
[34] WHALLEY C, ALDRIDGE J. Storm disturbance of sediment contaminants around the UK: The possibility of increased storminess in Liverpool Bay and potential release of contaminants from sediment [R]. CEFAS Report for DEFRA contract AE1223, 2000. [35] 柳肖竹, 刘群群, 王文静, 等. 水力扰动对河口沉积物中重金属再释放的影响 [J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2020, 36(11): 1460-1467. doi: 10.19741/j.issn.1673-4831.2019.1009 LIU X Z, LIU Q Q, WANG W J, et al. Effect of hydraulic disturbance on Re-release of heavy metals in estuarine sediments [J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2020, 36(11): 1460-1467(in Chinese). doi: 10.19741/j.issn.1673-4831.2019.1009
[36] POURABADEHEI M, MULLIGAN C N. Effect of the resuspension technique on distribution of the heavy metals in sediment and suspended particulate matter [J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 153: 58-67. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.03.026 [37] KRÓL A, MIZERNA K, BOŻYM M. An assessment of pH-dependent release and mobility of heavy metals from metallurgical slag [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 384: 121502. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121502 [38] SIMPSON S L, APTE S C, BATLEY G E. Effect of short-term resuspension events on the oxidation of cadmium, lead, and zinc sulfide phases in anoxic estuarine sediments [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2000, 34(21): 4533-4537. [39] 刘伟, 周斌, 王丕波, 等. 沉积物再悬浮氮磷释放的机制与影响因素 [J]. 科学技术与工程, 2020, 20(4): 1311-1318. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.04.003 LIU W, ZHOU B, WANG P B, et al. Mechanism and influencing factors of nitrogen and phosphorus release via sediment Re-suspension [J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2020, 20(4): 1311-1318(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.04.003
[40] 毕春娟, 陈振楼, 李猛, 等. 再悬浮作用下长江口近岸沉积物中Cd、Pb和Cr的迁移与释放 [J]. 环境科学, 2011, 32(9): 2512-2521. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2011.09.012 BI C J, CHEN Z L, LI M, et al. Transport and release of cd, Pb and Cr from the Yangtze estuarine sediments during sediment resuspension event [J]. Environmental Science, 2011, 32(9): 2512-2521(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2011.09.012
[41] 毕春娟, 陈振楼, 沈军, 等. 再悬浮作用下长江河口沉积物中Hg的迁移与释放 [J]. 环境科学, 2009, 30(11): 3256-3261. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2009.11.021 BI C J, CHEN Z L, SHEN J, et al. Transfer and release of Hg from the Yangtze estuarine sediment during sediment resuspension event [J]. Environmental Science, 2009, 30(11): 3256-3261(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2009.11.021
[42] LI T, WANG D S, ZHANG B, et al. Characterization of the phosphate adsorption and morphology of sediment particles under simulative disturbing conditions [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006, 137(3): 1624-1630. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.04.051 [43] 肖洒. 巢湖沉积物孔隙结构研究与重金属污染评价[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2015. XIAO S. The research of the sediment pore structure and heavy metal pollution assessment in Chaohu Lake[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2015(in Chinese).
[44] 黄维, 方俊华. 河流中污染物迁移转化模型研究进展 [J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 2012, 10(6): 142-146,158. HUANG W, FANG J H. Research progress on transport and transformation model of river pollutants [J]. South-to-North Water Diversion and Water Science & Technology, 2012, 10(6): 142-146,158(in Chinese).
[45] BIBBY R L, WEBSTER-BROWN J G. Characterisation of urban catchment suspended particulate matter (Auckland region, New Zealand);a comparison with non-urban SPM [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2005, 343(1/2/3): 177-197. [46] ALKHATIB E, BERNA E. Simulation of arsenic partitioning in tributaries to drinking water resevoirs [J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2008, 137(1/2/3): 197-204. [47] 黄建枝, 葛小鹏, 杨晓芳, 等. 利用环流槽研究再悬浮条件下凉水河底泥沉积物中重金属的迁移与分布 [J]. 科学通报, 2012, 57(21): 2015-2021. doi: 10.1360/csb2012-57-21-2015 HUANG J Z, GE X P, YANG X F, et al. Remobilization of heavy metals during the resuspension of Liangshui River sediments using an annular flume [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(21): 2015-2021(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/csb2012-57-21-2015
[48] LU Y F, ALLEN H E. Partitioning of copper onto suspended particulate matter in river waters [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2001, 277(1/2/3): 119-132. [49] 郝廷, 许国辉, 王刚, 等. 底床液化下沉积物中重金属释放规律的水槽试验研究 [J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 43(8): 92-98. HAO T, XU G H, WANG G, et al. Laboratory flume study on heavy metal release from liquefied bed sediments [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2013, 43(8): 92-98(in Chinese).
[50] BAO T L, WANG P F, HU B, et al. Investigation on the effects of sediment resuspension on the binding of colloidal organic matter to copper using fluorescence techniques [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 236: 124312. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.07.043 [51] 华祖林, 王苑. 水动力作用下河湖沉积物污染物释放研究进展 [J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 46(2): 95-105. HUA Z L, WANG Y. Advance on the release of pollutants in river and lake sediments under hydrodynamic conditions [J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 2018, 46(2): 95-105(in Chinese).
[52] 范成新. 湖泊沉积物-水界面研究进展与展望 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2019, 31(5): 1191-1218. doi: 10.18307/2019.0514 FAN C X. Advances and prospect in sediment-water interface of lakes: A review [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2019, 31(5): 1191-1218(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2019.0514
[53] ZHOU Y Y, SONG C L, CAO X Y, et al. Phosphorus fractions and alkaline phosphatase activity in sediments of a large eutrophic Chinese lake (Lake Taihu) [J]. Hydrobiologia, 2008, 599(1): 119-125. doi: 10.1007/s10750-007-9185-z [54] XIE M W, JARRETT B A, da SILVA-CADOUX C, et al. Coupled effects of hydrodynamics and biogeochemistry on Zn mobility and speciation in highly contaminated sediments [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(9): 5346-5353. [55] CANTWELL M G, BURGESS R M, KING J W. Resuspension of contaminated field and formulated reference sediments Part Ⅰ: Evaluation of metal release under controlled laboratory conditions [J]. Chemosphere, 2008, 73(11): 1824-1831. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.08.007 [56] 夏义雄, 陈华林. 河水中悬浮颗粒物对重金属的吸附行为 [J]. 亚热带资源与环境学报, 2012, 7(4): 82-86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7105.2012.04.014 XIA Y X, CHEN H L. Sorption behaviors of heavy metals on suspended particulate matter in river water [J]. Journal of Subtropical Resources and Environment, 2012, 7(4): 82-86(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7105.2012.04.014
-



 下载:
下载: