-
相对于铁氧化物而言,土壤中锰氧化物含量相对较低,但由于其比表面积大、表面电荷低、对金属的亲合力强等独特的表面性质,一定程度上深刻影响着土壤中痕量金属的移动性和生物可利用性[1],此外,由于锰氧化物具有较高的氧化还原电位,也控制着环境中变价(类)金属如As(Ⅲ/Ⅴ)、Cr(Ⅲ/Ⅵ)、Sb(Ⅲ/Ⅴ)等的迁移转化行为和毒性效应。多年以来,土壤铁氧化物受到较多关注且发展了较为成熟的化学提取方法[2-4],但对锰氧化物的研究和提取方法一直以来关注较少,一定程度上限制了锰氧化物在土壤中的进一步研究[5]。本文从土壤中锰的来源、锰氧化物的类型和表面特性、主要提取方法等几个方面进行综述。
-
地壳中锰元素的丰度为0.085%[6],是含量仅次于铁(4.65%)的过渡金属元素[7-8],一般土壤中锰的含量约为铁的十分之一左右[9-10]。土壤中的锰主要来自于成土母质[11],少量来自于植物残体和大气中的锰。岩石风化后产生的Mn2+迁移性较强,一定条件下可被氧化成高价锰氧化物,但此过程的化学氧化较慢,而细菌、真菌等微生物介导的Mn2+的生物氧化成为环境条件下控制锰矿物形成的主导因素[12],因此自然形成的锰氧化物大多是来自于微生物氧化的直接产物或间接产物[13],而土壤中锰氧化物为锰的主要矿物形式[14]。土壤中锰含量具有较大的地域差异性,我国土壤中的大致趋势为锰氧化物南多北少,而其他形式的锰南少北多。南方的红壤和砖红壤中活性锰含量较高,而北方石灰性土壤中活性锰含量较低,因此缺锰土壤主要分布在我国北方。
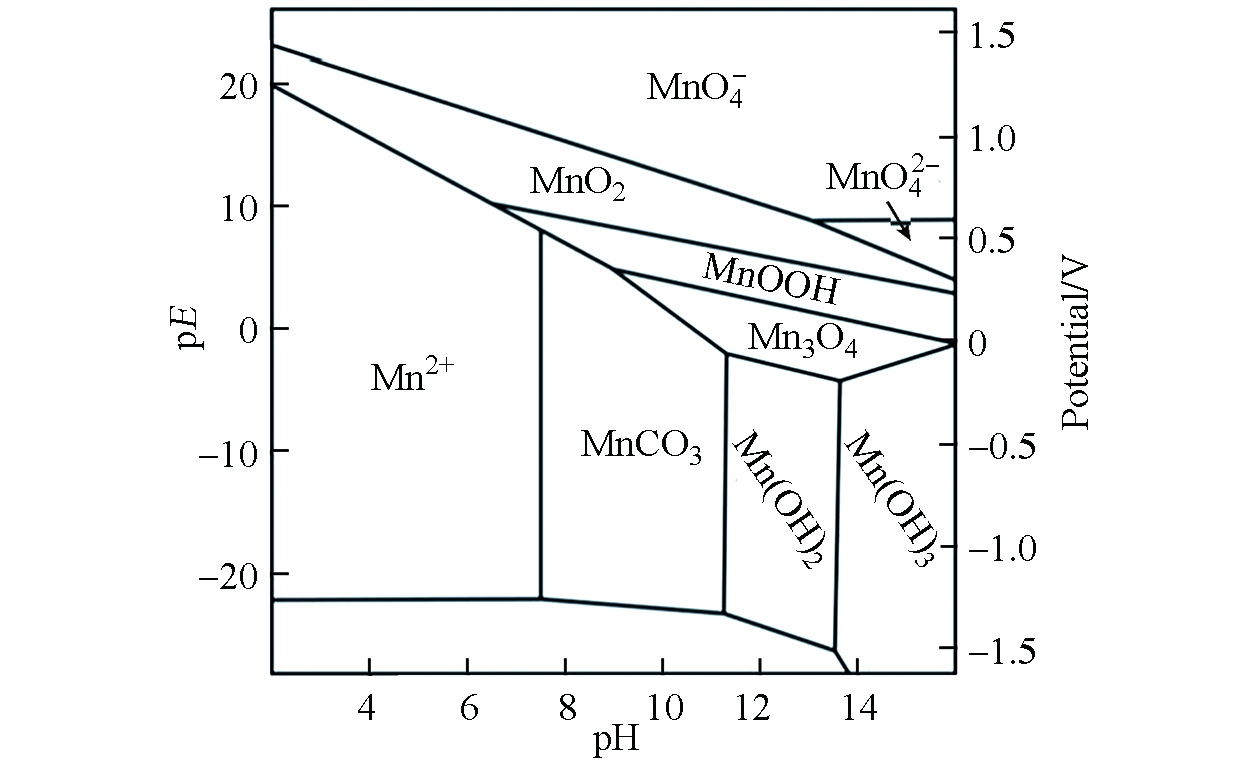
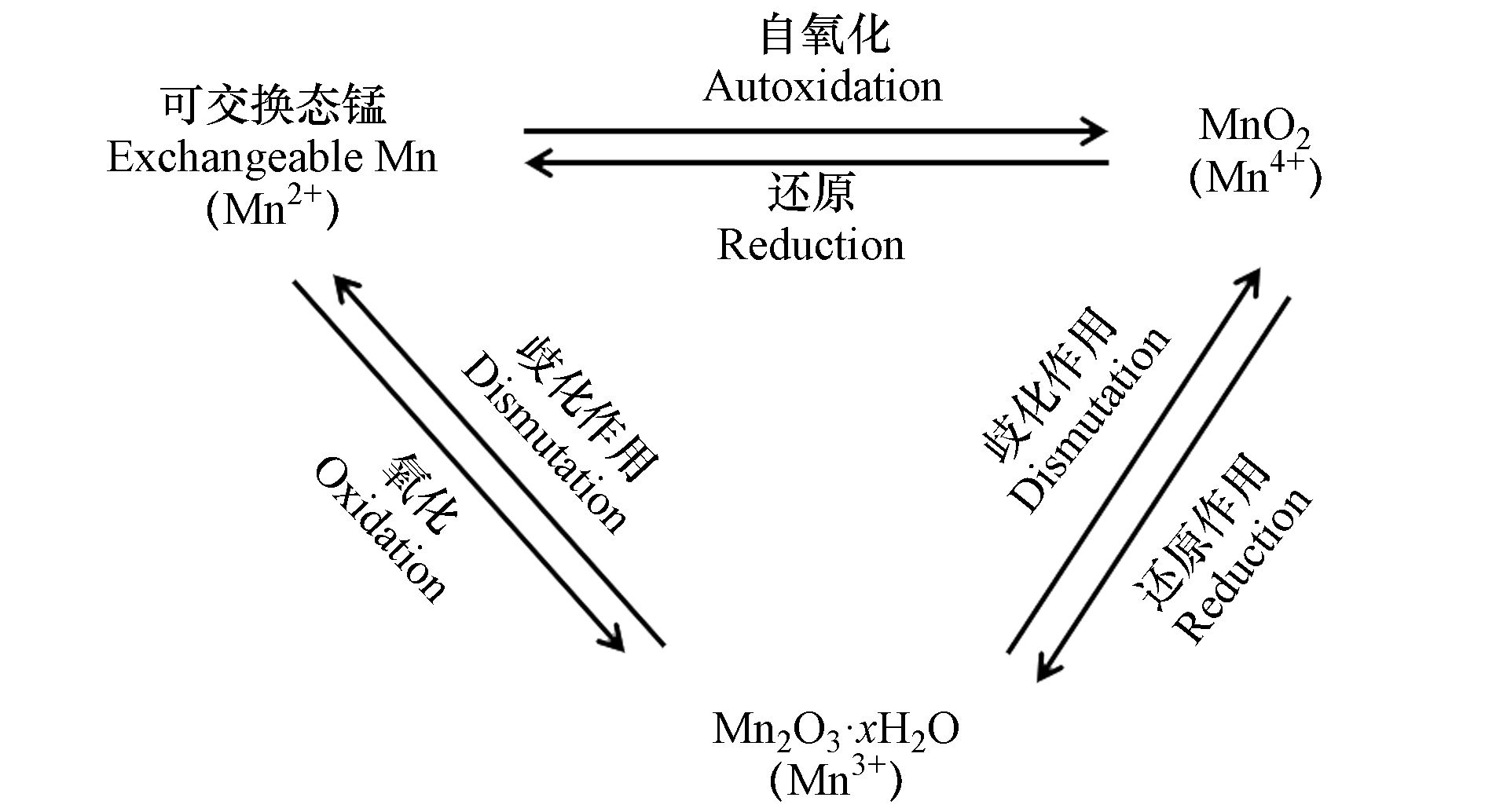
土壤中的锰元素主要以+2、+3、+4价存在[15]。+2价锰溶解性较强,主要以可溶态或可交换态的Mn2+形态存在于土壤中,在低pH(pH<5.5)且厌氧的土壤环境中较稳定;+3价锰极不稳定,容易发生歧化反应转变为+2价锰或者+4价锰;+4价锰溶解性低,主要是以锰氧化物形式存在于土壤中,在好氧及偏碱性的土壤环境中较稳定[16]。不同价态锰随环境条件的改变而维持动态平衡(图1)。土壤中的锰可以作为颗粒迁移到空气或水中,也能够以可溶态从土壤中浸出,其移动性取决于土壤参数,如酸度、湿度、有机质含量、微生物的生物活性等,其中,土壤pH、氧化还原电位和有机质是最主要的影响因素[16-17]。
锰的pH-Eh关系图如图2所示。锰的移动性随pH降低或氧化还原电位降低而增加。土壤好氧条件下,氧化还原电位高,土壤和沉积物中的锰主要以各种氧化物和水合氧化物的沉淀形式存在,移动性较低[19];厌氧条件下,还原生成的Mn2+溶解度和移动性均相应增加[10]。例如,Weeraratna等[20]研究了旱地和淹水土壤条件下水稻对锰的吸收,结果发现与未淹水条件相比,在淹水条件下生长的水稻吸收了更多的锰,这表明厌氧土壤环境,即氧化还原电位低的土壤中,锰主要是以溶解度较高Mn2+形式存在。但随着pH增加和土壤有机质含量升高,Mn2+的溶解度和对植物的生物有效性也随之降低。如pH值>6.0的土壤中Mn2+主要与有机质、氧化物和硅酸盐结合,某些情况下可能会出现缺锰现象[16, 21]。
-
土壤中锰主要以锰氧化物或水合锰氧化物形式存在[24],不同成土过程和环境条件导致土壤中锰氧化物类型多样、种类繁多[25],常见锰氧化物有软锰矿(pyrolusite,β-MnO2)、水钠锰矿(birnessite,δ-MnO2)、水锰矿(manganite,γ-MnOOH)等(表1)。按照晶体结构类型可分为隧道结构、层状结构和低价锰氧化物的3种类型[26](图3)。Mn4+的隧道结构(图3 a)由单链、双链或多链组成,沿Z轴延伸,MnO6八面体通过共棱或共角使链与链连接成方形或三角形隧道,隧道中间一般填充阳离子(Ba2+、Ca2+、K+、Na+等)或水分子[11]。隧道结构中最典型的是软锰矿,由MnO6八面体单链以共棱方式形成,其所含锰的价态均为+4价[27]。Mn4+的层状结构(图3 b)由MnO6八面体连接成层,层与层之间含有水分子或者阳离子,其中最典型的是水钠锰矿,由一层MnO6八面体与一层水分子交互堆叠而成[28-29],层间距在0.7—1 nm。水钠锰矿层中的Mn主要为+4价,也有部分+3价Mn,同时晶层中存在少量的空穴。与层状的蒙脱石相比,水钠锰矿层间负电荷更高,且吸附的阳离子能与水钠锰矿的结构氧直接配位,在层间形成内层吸附(inner-sphere adsorption),从而对金属离子有很强的吸附能力。有研究认为层状结构的锰氧化物较隧道结构的锰氧化物更稳定[30]。低价锰氧化物为低于+4价的锰氧化物或者氢氧化物,主要有MnOOH、Mn2O3、Mn(OH)2、MnO等多种类型,其中水锰矿最常见且最稳定,晶体结构与软锰矿类似(图3c)。
-
锰氧化物是土壤环境中最常见的金属吸附剂和氧化剂之一,由于其具有比表面积大、零点电荷(pHpzc)低、表面负电荷量多、表面活性强等特点[47],对土壤中的重金属及有机物等均具有很强的吸附和氧化作用[48]。
-
天然锰氧化物在土壤中通常以细小颗粒或表面包覆物的团聚体形式存在,比表面积大,尤其是隧道结构和层状结构的锰氧化物。据报道,锰氧化物的比表面积一般在74—746 m2·g−1范围内[49]。不同结构的锰氧化物比表面积不同。人工合成的锰氧化物,其比表面积也相差甚远。一方面是因为矿物本身的结晶程度等不同;另一方面可能因为目前常用于测定比表面积的BET-N2法难以测定矿物的内比表面积,而对于隧道或层状锰氧化物而言,其内比表面积远远大于外比表面积。因此,采用BET-N2法测定的锰氧化物的比表面积大小一般远小于其实际比表面积。
不同结构的锰氧化物零电荷点(pHpzc)不同,土壤中锰氧化物的pHpzc一般在1.3(水钠锰矿)—4.6(锰钡矿族)之间[49-51],因此其表面常带有大量负电荷而十分有利于金属阳离子吸附。相同锰氧化物的pHpzc因测定方法、组成以及结晶程度等不同而有所差异,因此pHpzc值的确定一直是锰氧化物表面化学特性研究中的难点。
-
锰氧化物由于表面负电荷多,对金属阳离子有着极强的吸附能力。表2中汇总了一些锰氧化物对不同金属的吸附顺序的报道,可以看出不同锰氧化物对Pb2+的吸附较强,而对Zn2+和Ni2+的吸附较弱。与铁氧化物相比,两者对金属的吸附能力略有差别。如McKenzie [52]提出不同金属在针铁矿和赤铁矿上吸附的顺序分别为:Pb2+ > Cu2+ > Zn2+ > Co2+ > Ni2+ > Mn2+和Cu2+ > Pb2+ > Zn2+ > Co2+ > Ni2+ > Mn2+;Mathur和Dzombak等[53]发现针铁矿上金属的吸附顺序为Cu2+ > Pb2+ > Co2+ > Zn2+ > Cd2+。对比可见,锰氧化物和铁氧化物对Pb2+和Cu2+的吸附均较强,但锰氧化物对Mn2+和Cd2+的吸附能力较强,而对Zn2+和Ni2+的吸附较弱,而铁氧化物对Zn2+和Ni2+的吸附能力要强于Cd2+和Mn2+。这可能是因为锰氧化物本身含有Mn3+和Mn4+,因此对Mn2+具有较强的特异性吸附。
不同类型锰氧化物对金属的吸附能力也存在较大差异。Feng等[55]研究了pH 4.5条件下水钠锰矿、钡镁锰矿、锰钾矿和黑锰矿对Pb2+、Co2+、Cu2+、Cd2+、Zn2+的吸附等温线,结果表明,水钠锰矿对5种金属的最大吸附量分别为1832、1084、1268、1042、1207 mmol·kg−1,钡镁锰矿对5种金属的最大吸附量分别为284.3、117.3、191.4、85.1、67.3 mmol·kg−1,锰钾矿对5种金属的最大吸附量分别为292.8、75.5、132.5、88.8、87.1 mmol·kg−1,黑锰矿对5种金属的最大吸附量分别为105.3、44.4、189.0、3.3、43.1 mmol·kg−1。在上述几种锰氧化物中,水钠锰矿对5种金属的吸附能力均最强。
对于同一金属,锰氧化物的吸附容量一般远大于铁氧化物。van Genuchten等[58]研究了pH 5.5条件下的吸附等温线,结果表明,水铁矿对Cd2+和Pb2+的最大吸附量为40 mol·kg−1和160 mol·kg−1,δ-MnO2对Cd2+和Pb2+的最大吸附量为230 mol·kg−1和460 mol·kg−1。Della Puppa等[47]研究了pH 4.0和pH5.5条件下水钠锰矿对Pb2+、Cu2+、Cd2+、Zn2+的吸附等温线,pH 4.0时水钠锰矿对4种金属的最大吸附量分别为554、499、501、475 mmol·kg−1,pH 5.5时水钠锰矿对4种金属的最大吸附量分别为553、500、496、481 mmol·kg−1。Peacock等[59]的研究发现pH 3.6和pH7.0条件下Ni2+在水钠锰矿表面的最大吸附量分别为234.3 mmol·kg−1和421.7 mmol·kg−1。对于铁氧化物中最典型的针铁矿,Zhu等[60]研究发现pH 4.5条件下Cu2+的最大吸附量为23.98 mmol·kg−1。Du等[61]研究发现pH 5.5条件下针铁矿对Cu2+、Cd2+、Ni2+的最大吸附量分别为77.79、53.82、49.11 mmol·kg−1。Guo等[62]研究表明pH 6.8时针铁矿对Co2+的最大吸附量为140 mmol·kg−1。Juang等[63]发现,pH 5.0时针铁矿对Cu2+和Zn2+的最大吸附量分别为82.32 mmol·kg−1和25.20 mmol·kg−1。可以看出,锰氧化物对二价金属阳离子的吸附容量要远高于铁氧化物,尤其是水钠锰矿,其对金属的吸附容量常比针铁矿大一个数量级。
-
锰氧化物是已知的土壤中氧化还原电位最高的天然矿物(E0 (MnO2/Mn2+) = 1.22 V),能够氧化As(Ⅲ/Ⅴ)、Cr(Ⅲ/Ⅵ)和Sb(Ⅲ/Ⅴ)等多种金属/类金属以及有机物[64],进而控制这些金属/类金属及有机物在土壤中的迁移、转化、生物有效性和毒性[30, 65-69]。以水钠锰矿为例:
As(Ⅲ/Ⅴ):Nesbitt等[70]利用X射线光电子能谱(XPS)发现水钠锰矿对As(Ⅲ)的氧化分两步进行,第一步是MnO2中的Mn4+被As(Ⅲ)还原成中间产物MnOOH*,第二步是MnOOH*被As(Ⅲ)进一步还原生成Mn2+,两步反应方程式如(1)(2)所示,总的反应为方程式(3)。Manning等[71]采用常规搅拌反应装置研究了As(Ⅲ)和As(Ⅴ)与水钠锰矿的反应,结果表明,As(Ⅲ)被水钠锰矿氧化成As(Ⅴ),As(Ⅴ)进一步吸附在水钠锰矿固相上,通过延伸X射线吸收精细结构谱(EXAFS)分析,证明了在水钠锰矿表面形成了As(Ⅴ)吸附络合物,As(Ⅴ)在水钠锰矿表面吸附的反应方程式如(4)所示。Lafferty等[72]通过搅拌流动实验进一步研究发现As(Ⅲ)被δ-MnO2氧化过程中,矿物表面会出现钝化现象,即随反应进行,氧化速率降低,钝化的机制一方面可能是由于反应产生Mn2+吸附在δ-MnO2表面,从而降低其氧化能力,另一方面也可能是由于中间产物MnOOH*中的Mn3+氧化活性低于Mn4+,且研究表明反应前期Mn2+的吸附可能是钝化的主要机制,后期由于Mn3+的生成和吸附以及As(Ⅴ)的吸附也开始影响Mn的氧化活性。
Cr(Ⅲ/Ⅵ):Banerjee等[73]采用XPS研究水钠锰矿对Cr(Ⅲ)的氧化表明,Mn4+先被还原生成Mn3+(以MnOOH*中间体形式存在),之后生成Mn2+;Cr(Ⅲ)先后被氧化生成Cr(Ⅳ)和Cr(Ⅴ),最后生成毒性比Cr(Ⅲ)更强的Cr(Ⅵ)进入溶液中,该过程的总反应方程式为(5)。Nico等[74]根据焦磷酸盐可以与Mn3+形成强配合物,将焦磷酸盐添加到Cr(Ⅲ)-水钠锰矿的反应体系中,以隔离有效的Mn3+,发现Mn3+可能是促进Cr(Ⅲ)氧化为Cr(Ⅵ)的一个重要因素。Fendorf等前期研究[75]也发现氧化过程中的钝化现象,认为可能是由于Cr(Ⅲ)形成的Cr(OH)3沉淀覆盖在MnO2表面,从而阻碍溶液中Cr(Ⅲ)的进一步吸附和氧化。而Landrot等[76]通过EXAFS发现pH 2.5、3和3.5下,Cr(Ⅵ)主要通过外层(outer-sphere)松散的吸附在MnO2表面,而Cr(Ⅲ)通过内层(inner-sphere)紧密吸附在MnO2表面,但并未在MnO2表面观察到Cr(OH)3表面沉淀,推测Cr(Ⅲ)氧化反应的终止可能有其他原因。Pan等[77]研究了pH值5—9下δ-MnO2氧化Cr(OH)3的速率,结果发现氧化速率高度依赖于pH。当pH5—7时,氧化速率起初很快,但很快变慢并停止,推测可能是由于当pH>4时Cr(Ⅲ)在MnO2表面形成沉淀从而阻止反应进一步进行;但当pH>7时,尽管Cr(Ⅵ)的生成速率较低,但Cr(Ⅵ)的总生成量却高于低pH值时,这可能是因为在较高的pH值下,溶解氧对水中Mn2+进行了再氧化,产生更多的MnO2,进一步将Cr(Ⅲ)氧化为Cr(Ⅵ)。最近的一项关于铬渣返黄机制的研究表明[78],缺氧和碱性pH(9—11)条件下,主要是δ-MnO2氧化机制,但有氧条件下存在3种氧化途径:1)经O2氧化,2)经δ-MnO2氧化,3)经Mn2+催化氧化。其中后两种为主要机制,且第3种机制可持续进行且贡献随pH增加而增加。说明铬渣中少量的锰氧化物在碱性条件下会持续催化铬渣重新返黄。
Sb(Ⅲ/Ⅴ):Sun等[79]提出δ-MnO2对Sb(Ⅲ)的氧化过程为方程式(6)(7),反应中产生的Mn2+和Mn3+会干扰氧化和吸附过程,钝化原因同水钠锰矿对As(Ⅲ/Ⅴ)氧化还原行为中的类似。此外,XPS、EXAFS和ATR-FTIR技术证实Sb(Ⅴ)吸附在δ-MnO2的边缘位置形成MnO(H)-Sb(Ⅴ)的单齿单核配合物。Sun等[80]研究了两种不同性质的水钠锰矿(δ-MnO2和三斜水钠锰矿)对Sb氧化和吸附方面的异同,结果表明,Sb与两种水钠锰矿的反应机理相似,水钠锰矿的边缘位置是Sb(Ⅲ)氧化的主要部位,Sb(Ⅴ)通过取代水钠锰矿的OH基团而被吸附在水钠锰矿的边缘位置,与水钠锰矿形成共角络合物。但两种水钠锰矿对Sb的吸附和氧化能力有显著差异,结晶不良的δ-MnO2比结晶良好的三斜水钠锰矿具有更高的氧化和吸附能力,这可能是由于前者比后者有更多的边缘位点。
上述研究可见,水钠锰矿可将As(Ⅲ)氧化成As(Ⅴ)、Cr(Ⅲ)氧化成Cr(Ⅵ)、Sb(Ⅲ)氧化成Sb (Ⅴ),从而降低As和Sb的毒性,但是会增加Cr的毒性。同时,水钠锰矿氧化变价金属/类金属的过程涉及水钠锰矿表面的钝化,随反应进行,氧化速率降低,可能主要由于反应过程中产生Mn2+或其离子吸附在水钠锰矿表面,从而降低其氧化能力。
-
土壤中锰的提取可分为Mn2+、Mn3+、锰氧化物的提取以及不同形态锰的连续提取,针对Mn2+、Mn3+、锰氧化物的单一提取见表3,而不同形态的连续提取见表4。
-
土壤中的Mn2+通过静电作用吸附在土壤各固相表面,具有较大的活动性,可与土壤溶液中其他阳离子进行相互交换,因此属于可交换态锰。一般常用中性盐,如Ca(NO3)2、Mg(NO3)2、Zn(NO3)2、NH4Cl、CH3COONH4等溶液提取交换态Mn2+[15, 81-83],其原理是Ca2+、Mg2+、Zn2+、NH4+等可与土壤各固相表面的Mn2+发生阳离子交换,从而将Mn2+置换出来进行测定。由于在碱性条件下,Mn2+很容易被氧化成Mn3+,而Mn3+易与焦磷酸盐络合形成稳定的络合物,因此Heintze等[84]提出用碱性焦磷酸盐提取的锰也能反映土壤总Mn2+含量,然而,有机质络合Mn2+会使得提取的量较实际含量偏低,因此,土壤有机质含量会影响土壤中Mn2+的提取。除此之外,CH3COOH、EDTA和DTPA也被用于提取土壤中Mn2+[15, 85-86],且它们的效果相近,这是由于它们能和Mn2+形成有机鳌合物,从而将Mn2+提取出来。
在上述Mn2+提取方法的基础上,部分研究者根据需要提出了一些改进的方法。Nadirshaw 等[87]比较了单独中性CH3COONH4溶液和含0.2%对苯二酚的中性CH3COONH4溶液的提取效果,由于对苯二酚可以还原活性态Mn3+,因此含0.2%对苯二酚的中性CH3COONH4溶液提取的锰是交换态Mn2+和活性态Mn3+,比单纯的中性CH3COONH4溶液更能反映土壤对植物的供锰能力。在中性和碱性有机质土壤中含0.2%对苯二酚的中性CH3COONH4溶液提取的锰随有机质含量的升高而降低,其原因是有机质会结合对苯二酚还原形成的Mn2+,而采用含亚硫酸盐的中性CH3COONH4溶液提取能克服有机质的这种影响,且亚硫酸氢盐比对苯二酚更容易还原黑锰矿等锰氧化物中的高价态锰,此外,Heintze等[88]对比了含0.2%对苯二酚的中性CH3COONH4溶液和含0.4%亚硫酸盐的中性CH3COONH4溶液对有机质土壤中Mn2+的提取效果,结果也表明后者的提取量大于前者。
-
除极少数强酸性土壤外,Mn2+在大多数土壤中只占总锰的一小部分,因此常被忽略不计,而易还原性的Mn3+在矿质土中可占到总锰的20%,在某些沼泽土中可达90%[82]。为了与用中性Ca(NO3)2提取的Mn2+对比[81],Heintze提出用含0.2%对苯二酚的Ca(NO3)2提取Mn3+的方法,这是基于对苯二酚可以还原Mn3+,且Ca(NO3)2可以提取Mn2+,但该方法不适用于强酸性土壤,因为强酸性土壤Mn2+含量高,会对Mn3+含量产生影响。由于焦磷酸盐能与Mn3+形成稳定的络合阴离子[89-90],因此也常采用中性焦磷酸盐溶液提取土壤中的Mn3+[18, 84, 91]。
-
提取土壤铁氧化物时,常使用过氧化氢(H2O2)将土壤中的有机质消解掉再用盐酸羟胺(NH2OH·HCl)提取,但是对于锰氧化物而言呈酸性的H2O2会导致锰氧化物的溶解[92]。有研究指出,含25% CH3COOH的0.1 mol·L−1 NH2OH·HCl不仅能提取锰氧化物,还能提取一定量的铁氧化物[93]。由于酸性NH2OH·HCl能选择性地溶解活性较强的锰氧化物,Chao等[19]于1972年提出根据单独NH2OH·HCl溶液对锰氧化物特异性溶解作用,可采用0.1 mol·L−1 NH2OH·HCl(用0.01 mol·L−1 HNO3调节pH至2.0)在土液比1∶50下振荡30 min,能有效地溶解锰氧化物同时,限制铁氧化物的溶解,此方法被广泛应用于土壤锰氧化物的提取或溶解[5, 94-98]。该方法可提取沉积物中85%的锰氧化物,对高度风化的土壤锰氧化物的提取量也能达到50%左右,而铁氧化物的提取量分别仅为5%和小于1%[94]。虽然上述方法被广泛使用,但由于它没有得到充分的评估,是否能应用于各种类型土壤需要进一步探究。Suda等在此方面做了较多的研究[5]。Suda等[99]研究了该方法在几种不同类型土壤上提取锰氧化物的应用,表明该方法可用于非火山土,而火山土中的锰氧化物的溶解度明显偏低。在其进一步的研究中,采用0.5 mol·L−1 NH2OH·HCl(pH 1.5,25℃下振荡16 h,土液比1∶40)[100]可以从非火山土中提取了几乎全部的锰氧化物,但部分锰氧化物仍未能从火山土中提取且锰氧化物的提取量与NH2OH·HCl的pH值(在pH 1.0—3.5之间)无关。Chao的方法不适用于火山土,可能是因为该种土壤中有机质含量较高,Suda等[101]对该方法进行了进一步改进,改进的方法分三步进行:(1)用0.01 mol·L−1 NH2OH·HCl (pH 5.0)还原锰氧化物16 h(土液比1∶40);(2)加入0.02 mol·L−1 HCl配制的0.5 mol·L−1 NH4Cl再振荡10 min(土液比1∶40);(3)用超纯水洗涤残渣(土液比1∶20),将三步的上清液收集混匀测量锰浓度。即先采用NH2OH·HCl将锰氧化物还原为Mn2+,再加入NH4Cl提取Mn2+,最后采用超纯水洗涤来提取剩余的Mn2+。新的方法虽然相较于Chao的方法提取锰氧化物的效果更好、对不同土壤适用范围更广,但是具有提取时间长、过程复杂等缺点。Suda等[102]通过改进Tessier方法(0.04 mol·L−1 NH2OH·HCl—25% CH3COOH)发现锰提取量随着NH2OH·HCl浓度的升高而增加,提出采用0.6 mol·L−1 NH2OH·HCl—25% CH3COOH(土液比1∶20,6 h,沸水)来提取土壤中的锰氧化物。
草酸盐也常被用于锰氧化物的提取,由于草酸铵提取的锰是锰氧化物和有机结合态锰的总和,而有机结合态锰没有合适的方法量化以及当pH<6.0时锰与有机质结合较弱,因此,有时可以采用草酸铵提取的锰量近似作为土壤中总的锰氧化物含量[21]。
总体而言,目前土壤中锰氧化物提取方法大多是在Chao法基础上进行的改进,因此NH2OH·HCl成为提取土壤锰氧化物最主要的提取剂。此外,不同土壤类型因土壤性质不同,相同提取方法的效果也有所差异,对于有机质含量较低的土壤,可采用传统的Chao法[19],而对于有机质含量较高的土壤,可采用Suda改进的方法[101-102]。
-
土壤中的锰可以根据提取剂提取能力差异进行形态分级提取,但对于土壤中锰不同形态的提取尚没有建立标准化方法。土壤中的锰有时被当作微量金属而按照Tessier连续提取法[105]进行分级和测定不同形态的浓度。Shuman等[106-107]则将土壤中锰形态分为可交换态、有机结合态、锰氧化物、无定型铁氧化物结合态、晶型铁氧化物结合态和残渣态六种。在其方法中,可交换态采用中性盐Mg(NO3)2提取,与单一提取方法中Mn2+提取方法吻合。有机结合态的锰则采用NaOCl提取,原因是H2O2提取有机结合态时会溶解无机态的锰,从而使得有机结合态的锰提取量相较于实际含量偏高,而NaOCl不会溶解无机态的锰[108]。该方法认为Chao的方法提取的是总锰氧化物[19],剩下的分为无定形铁氧化物结合态、晶型铁氧化物结合态和残渣态,分别采用草酸盐提取、连二亚硫酸钠-柠檬酸钠-碳酸氢钠(DCB)提取法提取、HF消解获得。无定形铁氧化物结合态锰的提取方法与土壤中无定形铁氧化物提取的方法一致[109],该方法认为DCB提取的是晶型铁氧化物结合态锰,而在铁氧化物的提取中认为DCB提取的是总的铁氧化物含量[110]。Warden等[111]则提出将土壤中锰分为易溶态、弱吸附态、碳酸盐结合态(石灰质土)/特异性吸附态(非石灰质土)、锰氧化物的4种。其中,易溶态和总锰氧化物的提取与上述Shuman等的方法类似,均是分别通过中性盐(Ca(NO3)2)和NH2OH·HCl提取获得,不同之处在于该方法认为剩下的锰形态分为弱吸附态和碳酸盐结合态(石灰质土)/特异性吸附态(非石灰质土),而不是有机结合态、无定型铁氧化物结合态、晶型铁氧化物结合态和残渣态。
-
土壤中锰氧化物的含量较低,因此一直以来对锰氧化物研究较少,但是锰氧化物对金属的吸附量很大,因此其在土壤中的作用也不可忽略。自从Chao[19]报道了利用酸化的NH2OH·HCl选择性溶解土壤和沉积物中的锰氧化物,这种方法对于单独溶解锰以及确定其释放的金属离子十分有效,之后该方法被应用到各种土壤及沉积物锰氧化物的溶解和提取中。例如,Chao和Anderson等[112]采用NH2OH·HCl可提取61.9%—75.6%的水系沉积物中的锰氧化物,沉积物中的Ag与锰氧化物密切相关,表明含Ag矿物风化释放出的Ag主要被锰氧化物保留。Chao和Theobald等[113]通过分析数千个活跃水系沉积物样品,发现锰氧化物是水系沉积物中Ag清除的主要控制因素,铁氧化物起次要作用;土壤中的Co也被锰氧化物优先吸附。Tokashiki等[114]以日本冲绳岛的3个土壤锰结核样品、合成水钠锰矿和锂硬锰矿为试验材料,采用的NH2OH·HCl未用HNO3酸化到pH 2,而是pH 3.6,发现未酸化的NH2OH·HCl可以选择性溶解水钠锰矿而不会溶解锂硬锰矿。Bibak等[115]采用Chao法去除土壤中的锰氧化物,比较去除前后土壤对Cu的吸附,发现吸附边结果相差不大,由此认为锰氧化物可忽略不计。Dong等[116]采集水系沉积物,通过改变NH2OH·HCl浓度、提取时间和HNO3浓度,研究发现完全提取锰氧化物的最佳NH2OH·HCl浓度、提取时间和HNO3浓度分别为0.02 mol·L−1、20 min和0.01 mol·L−1。Chon等[117]选取了韩国原位风化形成的7个土壤剖面中的25个土壤样品,研究土壤氧化能力与可提取土壤锰、铁氧化物和其他土壤性质之间的关系,其中锰氧化物提取方法选择DCB法(Mnd)、Chao法(Mnh)以及对苯二酚(Mnr)进行提取,结果表明3种方法提取的锰氧化物含量相近,Mnd和Mnh浓度与Cr氧化试验的相关性优于Mnr浓度,从而表明Mnd和Mnh比Mnr更能解释土壤样品的氧化能力。
-
土壤中锰氧化物种类较多,且不同类型锰氧化物的表面特性、吸附特性和氧化特性等均不相同,但目前常用的提取方法主要针对不同价态锰氧化物总量,尚缺乏针对不同类型或晶形锰氧化物的提取方法研究,也缺乏土壤中不同类型锰氧化物吸附、催化、氧化污染物的比较研究。尽管土壤铁氧化物含量比锰氧化物含量约高一个数量级左右,但锰氧化物的PZC值更低,氧化还原电位更高,两者在污染物的迁移转化过程的实际贡献及主要影响因素还缺乏精细定量化比较。此外,锰氧化物在土壤污染修复中得到广泛应用,如Hettiarachchi等[118]采用锰钾矿(Cryptomelane)作为锰氧化物的代表来原位稳定Pb污染土壤。但由于锰氧化物形态可能随土壤环境条件变化而变化,因此,也有必要进一步研究不同形态锰氧化物的修复机制与效果,以便于筛选最佳修复方案。
土壤中锰氧化物的形态及其化学提取方法综述
Soil manganese oxides and its extraction methods:A review
-
摘要: 土壤中锰元素主要来自于成土母质,风化后的锰主要以锰氧化物形式存在于土壤中。锰氧化物因具有比表面积大、表面电荷低、对金属的亲合力强、氧化还原电位高等特性,对土壤中痕量金属的环境行为存在重要影响。化学提取方法是研究土壤中不同固相组分的重要手段。本文首先从土壤中锰的来源及主要存在形态出发,介绍了不同价态锰(+2、+3、+4)在土壤中转化的影响因素;其次对土壤中不同锰氧化物的类型进行梳理,并就其表面特性、对金属阳离子的吸附特性、对金属/类金属的氧化还原特性进行了介绍;最后重点总结了土壤中不同价态锰单一提取方法和不同形态的连续提取方法,以及锰氧化物提取方法的应用,为土壤中锰氧化物的进一步研究提供参考。Abstract: Manganese (Mn) in soil mainly comes from parent minerals and weathered Mn mainly exists in soil in forms of Mn oxides. Manganese oxides have large specific surface area, low surface charge, strong affinity for metals, and high redox potential, hence they have important effects on environmental behavior of trace metals in soil. Chemical extraction is an important method to study the solid-phase components in soil. At first, this review introduced the source and existence of Mn oxides with different valences (+2, +3, +4) in soil, and the factors affecting the transformation of Mn; secondly, we summarized different types of Mn oxides in soil and their surface characteristics, adsorption abilities, redox properties; finally, the single extraction and the sequential extraction method of different forms of Mn in soil are summarized, as well as the application of the extraction method. This review provides a reference for the further study of Mn oxides in the soil.
-
Key words:
- soil /
- manganese oxide /
- properties /
- single extraction /
- sequential extraction
-

-
结构类型
Structure Type矿物名称
Mineral Name分子式
Molecular Formula参考文献
ReferencesMn4+隧道结构 软锰矿(Pyrolusite) MnO2 [27] 斜方锰矿(Ramsdellite) MnO2 [31] 六方锰矿(Nsutite) Mn(O,OH)2 [32] 锰钡矿(Hollandite) Bax(Mn4+,Mn3+)8O16 [33] 锰钾矿(Cryptomelane) Kx(Mn4+,Mn3+)8O16 [33] 锰钠矿(Manjiroite) Nax(Mn4+,Mn3+)8O16 [34] 铅硬锰矿(Coronadite) Pbx(Mn4+,Mn3+)8O16 [46] 钡硬锰矿(Romanechite) Ba0.66(Mn4+,Mn3+)5O10·1.34H2O [35] 钙锰矿(Todorokite) (Ca,Na,K)x(Mn4+,Mn3+)6O12·3.5H2O [36-37] Mn4+层状结构 锂硬锰矿(Lithiophorite) LiAl2(Mn24+,Mn3+)O6(OH)6 [29, 38] 黑锌锰矿(Chalcophanite) ZnMn3O7·3H2O [39] 水钠锰矿(Birnessite) (Na,Ca)Mn7O14·2.8H2O [28-29] 水羟锰矿(Vernadite) MnO2·nH2O [40] 低价锰氧化物 水锰矿(Manganite) MnOOH [36] 锰榍石(Groutite) MnOOH [41] 六方水锰矿(Feitknechtite) MnOOH [42] 黑锰矿(Hausmannite) Mn2+Mn23+O4 [43] 方铁锰矿(Bixbyite) Mn2O3 [44] 片水锰矿(Pyrochroite) Mn(OH)2 [42] 方锰矿(Manganosite) MnO [45] 注:加粗的为土壤中常见锰氧化物类型.
Note: The bold font is the most common types of manganese oxides in soil.表 2 典型锰氧化物对金属的吸附顺序
Table 2. Adsorption order of several typical manganese oxides to metals
矿物名称 Mineral Name 顺序 Sequence 参考文献 References 水合锰氧化物(HMO) Pb2+>Cu2+>Zn2+ [54] 水合锰氧化物(HMO) Mn2+>Co2+>Cu2+>Zn2+>Ni2+>Cd2+ [49] 水钠锰矿(Birnessite) Pb2+>Cu2+≧Co2+>Mn2+>Zn2+>Ni2+ [52] 水钠锰矿(Birnessite) Pb2+>Cu2+>Zn2+>Co2+>Cd2+ [55] 水钠锰矿(Birnessite) Pb2+>Cu2+>Zn2+>Cd2+ [56] 水钠锰矿(Birnessite) Pb2+ > Cu2+ ≈ Co2+ > Cd2+ > Mn2+ > Zn2+ > Ni2+ [57] 锰钾矿(Cryptomelane) Pb2+>Cu2+ ≈ Cd2+>Zn2+>Co2+ [55] 黑锰矿(Hausmannite) Cu2+>Pb2+>Co2+ ≈ Zn2+>Cd2+ [55] 钡镁锰矿(Todorokite) Pb2+>Cu2+>Co2+>Cd2+>Zn2+ [55] 表 3 土壤锰单一提取方法
Table 3. Single extraction method of soil manganese
提取对象
Target提取剂
Extractant参考文献
ReferencesMn2+ 焦磷酸盐(pH 9.4) [84] 含0.2%对苯二酚CH3COONH4(pH 7.0)、含有0.4%亚硫酸盐的CH3COONH4(pH 7.0) [88] 中性盐,如:Ca(NO3)2、Mg(NO3)2、Zn(NO3)2、CH3COONH4 [15,81-84] CH3COONH4(pH 7.0)、含0.2%对苯二酚的CH3COONH4 (pH 7.0) [87] 0.05 mol·L−1 EDTA (pH 7.0) [103] 1 mol·L−1 NH4Cl、1 mol·L−1 CH3COONH4、2.5% CH3COOH、0.05 mol·L−1 EDTA (pH 7.0) [85] DTPA [86] Mn3+ 焦磷酸盐(pH 7.0) [18, 84, 91] 含0.2%对苯二酚的Ca(NO3)2 [82] 锰氧化物(Mn4+) 0.1 mol·L−1 NH2OH·HCl—0.01 mol·L−1 HNO3 (pH 2.0,土液比1∶50,振荡30 min) [19, 99, 104] 0.1 mol·L−1 NH2OH·HCl—0.01 mol·L−1 HNO3(pH 1.5) [100] (1)用0.01 mol·L−1 NH2OH·HCl(pH 5.0)还原锰氧化物16 h(土液比1∶40);
(2)加入0.02 mol·L−1 HCl配制的0.5 mol·L−1 NH4Cl再振荡10 min(土液比1∶40);
(3)用超纯水洗涤残渣(土液比1∶20)。[101] 0.6 mol·L−1 NH2OH·HCl—25%CH3COOH(土液比1∶20,6 h,沸水) [102] (NH4)2C2O4—H2C2O4 [21] 表 4 土壤锰连续提取方法
Table 4. Sequential extraction methods of soil manganese
形态
Speciation提取剂
Extractant参考文献
References1 可交换态 1 mol·L−1 Mg(NO3)2(pH 7.0) [106-107] 2 有机结合态 0.7 mol·L−1 NaOCl(pH 8.5) 3 锰氧化物 0.1 mol·L−1 NH2OH·HCl(pH 2.0) 4 无定型铁氧化物结合态 0.2 mol·L−1 (NH4)2C2O4·H2O—0.2 mol·L−1 H2C2O4(pH 3.0) 5 晶型铁氧化物结合态 DCB:0.3 mol·L−1 Na3C6H5O7·2H2O—0.1 mol·L−1 NaHCO3—1 g Na2S2O4 6 残渣态 HF 1 易溶态 0.05 mol·L−1 Ca(NO3)2 [111] 2 弱吸附态 0.025 mol·L−1 CaDTPA—0.025 mol·L−1 Na2B4O7 (pH 8.5) 3a 碳酸盐结合态(石灰质土) 1.6 mol·L−1 HNO3 3b 特异性吸附态(非石灰质土) 0.05 mol·L−1 Cu(NO3)2—0.05 mol·L−1 Ca(NO3)2 4 锰氧化物 0.1 mol·L−1 NH2OH·HCl—0.01 mol·L−1 HNO3 -
[1] 刘凡, 谭文峰, 刘桂秋, 等. 几种土壤中铁锰结核的重金属离子吸附与锰矿物类型 [J]. 土壤学报, 2002, 39(5): 699-706. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2002.05.012 LIU F, TAN W F, LIU G Q, et al. Adsorption of heavy metal ions on Fe-Mn nodules in several soils and types of Mn oxide minerals [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2002, 39(5): 699-706(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2002.05.012
[2] HALL G E M, VAIVE J E, BEER R, et al. Selective leaches revisited, with emphasis on the amorphous Fe oxyhydroxide phase extraction [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1996, 56(1): 59-78. doi: 10.1016/0375-6742(95)00050-X [3] HERON G, CROUZET C, BOURG A C M, et al. Speciation of Fe(Ⅱ) and Fe(Ⅲ) in contaminated aquifer sediments using chemical extraction techniques [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1994, 28(9): 1698-1705. [4] VOELZ J, JOHNSON N W, CHUN C L, et al. Quantitative dissolution of environmentally accessible iron residing in iron-rich minerals: A review [J]. ACS Earth and Space Chemistry, 2019, 3(8): 1371-1392. doi: 10.1021/acsearthspacechem.9b00012 [5] SUDA A M, MAKINO T. Functional effects of manganese and iron oxides on the dynamics of trace elements in soils with a special focus on arsenic and cadmium: A review [J]. Geoderma, 2016, 270: 68-75. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2015.12.017 [6] PEARSON G F, GREENWAY G M. Recent developments in manganese speciation [J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2005, 24(9): 803-809. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2005.02.008 [7] 顾明华, 李志明, 陈宏, 等. 施锰对土壤锰氧化物形成及镉固定的影响 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2020, 29(2): 360-368. GU M H, LI Z M, CHEN H, et al. Effects of manganese application on the formation of manganese oxides and cadmium fixation in soil [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2020, 29(2): 360-368(in Chinese).
[8] 徐水萍, 梁美娜, 张庆, 等. 铁锰氧化物及其复合材料的研究进展 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2019, 42(10): 197-206. XU S P, LIANG M N, ZHANG Q, et al. Review of research progress on iron-manganese oxides and its composites [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 42(10): 197-206(in Chinese).
[9] MICHALKE B, HALBACH S, NISCHWITZ V. Speciation and toxicological relevance of manganese in humans [J]. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 2007, 9(7): 650-656. doi: 10.1039/b704173j [10] GRYGO-SZYMANKO E, TOBIASZ A, WALAS S. Speciation analysis and fractionation of manganese: A review [J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2016, 80: 112-124. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2015.09.010 [11] POST J E. Manganese oxide minerals: Crystal structures and economic and environmental significance [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1999, 96(7): 3447-3454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.7.3447 [12] 刘凡, 冯雄汉, 陈秀华, 等. 氧化锰矿物的生物成因及其性质的研究进展 [J]. 地学前缘, 2008, 15(6): 66-73. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2008.06.009 LIU F, FENG X H, CHEN X H, et al. Advances in the study of biological genesis of manganese oxide minerals and their characteristics [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2008, 15(6): 66-73(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2008.06.009
[13] 孟佑婷, 郑袁明, 张丽梅, 等. 环境中生物氧化锰的形成机制及其与重金属离子的相互作用 [J]. 环境科学, 2009, 30(2): 574-582. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2009.02.044 MENG Y T, ZHENG Y M, ZHANG L M, et al. Formation and reactions of biogenic manganese oxides with heavy metals in environment [J]. Environmental Science, 2009, 30(2): 574-582(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2009.02.044
[14] TEBO B M, BARGAR J R, CLEMENT B G, et al. Biogenic Manganese Oxides: Properties and mechanisms of formation [J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2004, 32(1): 287-328. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.32.101802.120213 [15] LEEPER G W. The forms and reactions of manganese in the soil [J]. Soil Science, 1947, 63(2): 79-94. doi: 10.1097/00010694-194702000-00001 [16] MULDER E G, GERRETSEN F C. Soil manganese in relation to plant growth [J]. Advances in Agronomy, 1952, 4: 221-277. [17] CHRISTENSEN P D, TOTH S J, BEAR F E. The status of soil manganese as influenced by moisture, organic matter, and pH [J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1951, 15(C): 279-282. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1951.036159950015000C0064x [18] DION H G, MANN P J G. Three-valent manganese in soils [J]. The Journal of Agricultural Science, 1946, 36(4): 239-245. doi: 10.1017/S0021859600023960 [19] CHAO T T. Selective dissolution of manganese oxides from soils and sediments with acidified hydroxylamine hydrochloride [J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1972, 36(5): 764-768. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1972.03615995003600050024x [20] WEERARATNA C S. Absorption of manganese by rice under flooded and unflooded conditions [J]. Plant and Soil, 1969, 30(1): 121-125. doi: 10.1007/BF01885270 [21] JARVIS S C. The forms of occurrence of manganese in some acidic soils [J]. Journal of Soil Science, 1984, 35(3): 421-429. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2389.1984.tb00298.x [22] BRUINS J H, PETRUSEVSKI B, SLOKAR Y M, et al. Manganese removal from groundwater: Characterization of filter media coating [J]. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2015, 55(7): 1851-1863. doi: 10.1080/19443994.2014.927802 [23] STUMM W. Aquatic chemistry: Chemical equilibria and rates in natural waters[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1996. [24] MCKENZIE R M. The reaction of cobalt with manganese dioxide minerals [J]. Soil Research, 1970, 8(1): 97. doi: 10.1071/SR9700097 [25] 谭文峰, 刘凡, 李永华, 等. 我国几种土壤铁锰结核中的锰矿物类型 [J]. 土壤学报, 2000, 37(2): 192-201. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2000.02.006 TAN W F, LIU F, LI Y H, et al. Mineralogy of manganese in iron-manganese nodules of several soils in China [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2000, 37(2): 192-201(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2000.02.006
[26] 刘凡, 谭文峰, 王贻俊. 土壤中氧化锰矿物的类型及其与土壤环境条件的关系 [J]. 土壤通报, 2002, 33(3): 175-180. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.2002.03.005 LIU F, TAN W F, WANG Y J. Types of Mn oxide minerals in SSoils relationship between their types and soil environment conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2002, 33(3): 175-180(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.2002.03.005
[27] BAUR W H. Rutile-type compounds. Ⅴ. Refinement of MnO2 and MgF2 [J]. Acta Crystallographica Section B Structural Crystallography and Crystal Chemistry, 1976, 32(7): 2200-2204. doi: 10.1107/S0567740876007371 [28] POSR J E, VEBLEN D R. Crystal structure determinations of synthetic sodium, magnesium, and potassium birnessite using TEM and the Rietveld method [J]. American Mineralogist, 1990, 75(5-6): 477-489. [29] MANCEAU A, TOMMASEO C, RIHS S, et al. Natural speciation of Mn, Ni, and Zn at the micrometer scale in a clayey paddy soil using X-ray fluorescence, absorption, and diffraction [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2005, 69(16): 4007-4034. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2005.03.018 [30] VODYANITSKII Y N. Mineralogy and geochemistry of manganese: A review of publications [J]. Eurasian Soil Science, 2009, 42(10): 1170-1178. doi: 10.1134/S1064229309100123 [31] BYSTRÖM A M, LUND E W, LUND L K, et al. The crystal structure of ramsdellite, an orthorhombic modification of MnO2 [J]. Acta Chemica Scandinavica, 1949, 3: 163-173. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.03-0163 [32] ZWICKER W K, JAFFE H W, MEIJER W O J. Nsutite-A widespread manganese oxide mineral [J]. American Mineralogist, 1962, 47(3-4): 246-266. [33] POST J E, von DREELE R B, BUSECK P R. Symmetry and cation displacements in hollandites: Structure refinements of hollandite, cryptomelane and priderite [J]. Acta Crystallographica Section B Structural Crystallography and Crystal Chemistry, 1982, 38(4): 1056-1065. doi: 10.1107/S0567740882004968 [34] GUTZMER J. Asbestiform manjiroite and todorokite from the Kalahari manganese field, South Africa [J]. South African Journal of Geology, 2000, 103(3/4): 163-174. [35] TURNER S, POST J E. Refinement of the substructure and superstructure of romanechite [J]. American Mineralogist, 1988, 73(9-10): 1155-1161. [36] SZYMAŃSKI W, SKIBA M, BŁACHOWSKI A. Mineralogy of Fe-Mn nodules in albeluvisols in the Carpathian foothills, Poland [J]. Geoderma, 2014, 217/218: 102-110. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2013.11.008 [37] POST J E, BISH D L. Rietveld refinement of the todorokite structure [J]. American Mineralogist, 1988, 73(7-8): 861-869. [38] POST J E, APPLEMAN D E. Crystal-structure refinement of lithiophorite [J]. American Mineralogist, 1994, 79(3-4): 370-374. [39] POST J E, APPLEMAN D E. Chalcophanite, ZnMn3O7·3H2O-New crystal-structure determinations [J]. American Mineralogist, 1988, 73(11-12): 1401-1404. [40] LEE S, XU H F, XU W Q, et al. The structure and crystal chemistry of vernadite in ferromanganese crusts[J]. Acta Crystallographica Section B, Structural Science, Crystal Engineering and Materials, 2019, 75(Pt 4): 591-598. [41] GLASSER L S D, INGRAM L. Refinement of the crystal structure of groutite – MnOOH [J]. Acta Crystallographica Section B Structural Crystallography and Crystal Chemistry, 1968, 24(9): 1233-1236. doi: 10.1107/S0567740868004036 [42] BRICKER O. Some stability relations in system MnO2-H2O at 25 degrees and 1 atmosphere total pressure [J]. American Mineralogist, 1965, 50(9): 1296. [43] SATOMI K. Oxygen positional parameters of tetragonal Mn3O4 [J]. Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 1961, 16(2): 258-266. doi: 10.1143/JPSJ.16.258 [44] GELLER S. Structure of α-Mn2O3, (Mn0.983Fe0.017)2O3 and (Mn0.37Fe0.63)2O3 and relation to magnetic ordering [J]. Acta Crystallographica Section B Structural Crystallography and Crystal Chemistry, 1971, 27(4): 821-828. doi: 10.1107/S0567740871002966 [45] SASAKI S, FUJINO K, TAKÉUCHI Y, et al. On the estimation of atomic charges by the X-ray method for some oxides and silicates [J]. Acta Crystallographica Section A, 1980, 36(6): 904-915. doi: 10.1107/S0567739480001908 [46] POST J E, BISH D L. Rietveld refinement of the coronadite structure [J]. American Mineralogist, 1989, 74(7-8): 913-917. [47] DELLA PUPPA L, KOMÁREK M, BORDAS F, et al. Adsorption of copper, cadmium, lead and zinc onto a synthetic manganese oxide [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2013, 399: 99-106. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2013.02.029 [48] MAYANNA S, PEACOCK C L, SCHÄFFNER F, et al. Biogenic precipitation of manganese oxides and enrichment of heavy metals at acidic soil pH [J]. Chemical Geology, 2015, 402: 6-17. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2015.02.029 [49] TONKIN J W, BALISTRIERI L S, MURRAY J W. Modeling sorption of divalent metal cations on hydrous manganese oxide using the diffuse double layer model [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2004, 19(1): 29-53. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(03)00115-X [50] ZHAO W, FENG X H, TAN W F, et al. Relation of lead adsorption on birnessites with different average oxidation states of manganese and release of Mn2+/H+/K+ [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2009, 21(4): 520-526. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62302-5 [51] HEM J D. Redox processes at surfaces of manganese oxide and their effects on aqueous metal ions [J]. Chemical Geology, 1978, 21(3/4): 199-218. [52] MCKENZIE R M. The adsorption of lead and other heavy metals on oxides of manganese and iron [J]. Soil Research, 1980, 18(1): 61. doi: 10.1071/SR9800061 [53] MATHUR S S, DZOMBAK D A. Surface complexation modeling: Goethite [J]. Interface Science and Technology, 2006, 11: 443-468. [54] GADDE R R, LAITINEN H A. Studies of heavy-metal sorption by Hydrous oxides [J]. Abstracts of Papers of the American Chemical Society, 1974: 142. [55] FENG X H, ZHAI L M, TAN W F, et al. Adsorption and redox reactions of heavy metals on synthesized Mn oxide minerals [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2007, 147(2): 366-373. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2006.05.028 [56] 王砚, 谭文峰, 冯雄汉, 等. 水钠锰矿对几种重金属离子的吸附及其与锰氧化度和吸附位点的关系 [J]. 环境科学, 2011, 32(10): 3128-3136. WANG Y, TAN W F, FENG X H, et al. Adsorption of heavy metals on the surface of birnessite relationship with its Mn average oxidation state and adsorption sites [J]. Environmental Science, 2011, 32(10): 3128-3136(in Chinese).
[57] LI Y, ZHAO X P, WU J T, et al. Surface complexation modeling of divalent metal cation adsorption on birnessite [J]. Chemical Geology, 2020, 551: 119774. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2020.119774 [58] van GENUCHTEN C M, PEÑA J. Sorption selectivity of birnessite particle edges: A d-PDF analysis of Cd(Ⅱ) and Pb(Ⅱ) sorption by δ-MnO2 and ferrihydrite [J]. Environmental Science:Processes & Impacts, 2016, 18(8): 1030-1041. [59] PEACOCK C L, SHERMAN D M. Sorption of Ni by birnessite: Equilibrium controls on Ni in seawater [J]. Chemical Geology, 2007, 238(1/2): 94-106. [60] ZHU J, HUANG Q Y, PIGNA M, et al. Competitive sorption of Cu and Cr on goethite and goethite-bacteria complex [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2012, 179: 26-32. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2011.07.011 [61] DU H H, HUANG Q Y, PEACOCK C L, et al. Competitive binding of Cd, Ni and Cu on goethite organo-mineral composites made with soil bacteria [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 243: 444-452. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.08.087 [62] GUO Z Q, XU D P, ZHAO D L, et al. Influence of pH, ionic strength, foreign ions and FA on adsorption of radiocobalt on goethite [J]. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 2011, 287(2): 505-512. doi: 10.1007/s10967-010-0706-2 [63] JUANG R S, CHUNG J Y. Equilibrium sorption of heavy metals and phosphate from single- and binary-sorbate solutions on goethite [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2004, 275(1): 53-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2004.01.035 [64] 李媛, 魏东斌, 杜宇国. 锰氧化物对有机污染物的转化机制研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2013, 32(7): 1288-1299. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2013.07.024 LI Y, WEI D B, DU Y G. A review on the transformation mechanisms of typical organic pollutants by manganese oxide [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2013, 32(7): 1288-1299(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2013.07.024
[65] LUO Y, DING J Y, SHEN Y G, et al. Interaction mechanism and kinetics of ferrous sulfide and manganese oxides in aqueous system [J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2018, 18(2): 564-575. doi: 10.1007/s11368-017-1774-5 [66] LIU Y, ZHANG F, HOU J T, et al. Peroxymonosulfate improves the activity and stability of manganese oxide for oxidation of arsenite to arsenate [J]. CLEAN – Soil, Air, Water, 2020, 48(2): 1900195. doi: 10.1002/clen.201900195 [67] FU L, SHOZUGAWA K, MATSUO M. Oxidation of antimony (Ⅲ) in soil by manganese (Ⅳ) oxide using X-ray absorption fine structure [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2018, 73: 31-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2018.01.003 [68] WANG Y H, BENKADDOUR S, MARAFATTO F F, et al. Diffusion- and pH-dependent reactivity of layer-type MnO2: Reactions at particle edges versus vacancy sites [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(6): 3476-3485. [69] NEGRA C, ROSS D S, LANZIROTTI A. Oxidizing behavior of soil manganese: Interactions among abundance, oxidation state, and pH [J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2005, 69(1): 87-95. doi: 10.2136/sssaj2005.0087a [70] NESBITT H W, CANNING G W, BANCROFT G M. XPS study of reductive dissolution of 7Å-birnessite by H3AsO3, with constraints on reaction mechanism [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1998, 62(12): 2097-2110. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(98)00146-X [71] MANNING B A, FENDORF S E, BOSTICK B, et al. Arsenic(Ⅲ) oxidation and arsenic(Ⅴ) adsorption reactions on synthetic birnessite [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2002, 36(5): 976-981. [72] LAFFERTY B J, GINDER-VOGEL M, ZHU M Q, et al. Arsenite oxidation by a poorly crystalline manganese-oxide. 2. results from X-ray absorption spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(22): 8467-8472. [73] BANERJEE D, NESBITT H W. Oxidation of aqueous Cr(Ⅲ) at birnessite surfaces: Constraints on reaction mechanism [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1999, 63(11/12): 1671-1687. [74] NICO P S, ZASOSKI R J. Importance of Mn(Ⅲ) availability on the rate of Cr(Ⅲ) oxidation on δ-MnO2 [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2000, 34(16): 3363-3367. [75] FENDORF S E, FENDORF M, SPARKS D L, et al. Inhibitory mechanisms of Cr(Ⅲ) oxidation by δ-MnO2 [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1992, 153(1): 37-54. doi: 10.1016/0021-9797(92)90296-X [76] LANDROT G, GINDER-VOGEL M, LIVI K, et al. Chromium(Ⅲ) oxidation by three poorly crystalline manganese(Ⅳ) oxides. 2. Solid phase analyses [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(21): 11601-11609. [77] PAN C, LIU H, CATALANO J G, et al. Understanding the roles of dissolution and diffusion in Cr(OH)3 oxidation by δ-MnO2 [J]. ACS Earth and Space Chemistry, 2019, 3(3): 357-365. doi: 10.1021/acsearthspacechem.8b00129 [78] LIU W Z, LI J, ZHENG J Y, et al. Different pathways for Cr(Ⅲ) oxidation: Implications for Cr(Ⅵ) reoccurrence in reduced chromite ore processing residue [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(19): 11971-11979. [79] SUN Q, LIU C, ALVES M E, et al. The oxidation and sorption mechanism of Sb on δ-MnO2 [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 342: 429-437. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.02.091 [80] SUN Q, CUI P X, LIU C, et al. Antimony oxidation and sorption behavior on birnessites with different properties (δ-MnO2 and triclinic birnessite) [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 246: 990-998. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.12.027 [81] HEINTZE S G. Readily soluble manganese of soils and Marsh Spot of peas [J]. The Journal of Agricultural Science, 1938, 28(2): 175-186. doi: 10.1017/S0021859600050590 [82] HEINTZE S G. Manganese deficiency in peas and other crops in relation to the availability of soil manganese [J]. The Journal of Agricultural Science, 1946, 36(4): 227-238. doi: 10.1017/S0021859600023959 [83] JONES L H P, LEEPER G W. Available manganese oxides in neutral and alkaline soils [J]. Plant and Soil, 1951, 3(2): 154-159. doi: 10.1007/BF01676371 [84] HEINTZE S G, MANN P J G. Divalent manganese in soil extracts [J]. Nature, 1946, 158(4022): 791-792. doi: 10.1038/158791a0 [85] DAGNALL R M, KIRKBRIGHT G F, WEST T S, et al. Multichannel atomic fluorescence and flame photometric determination of calcium, copper, magnesium, manganese, potassium, and zinc in soil extracts [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1971, 43(13): 1765-1769. doi: 10.1021/ac60307a036 [86] NAGESWARA RAO D V K. Evaluation of soil extractants in terms of growth [J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 2005, 36(11/12): 1513-1523. [87] NADIRSHAW M, CORNFIELD A H. Direct determination of manganese in soil extracts by atomic-absorption spectroscopy [J]. Analyst, 1968, 93(1108): 475. doi: 10.1039/an9689300475 [88] HEINTZE S G, MANN P J G. A study of various fractions of the manganese of neutral and alkaline organic soils [J]. Journal of Soil Science, 1951, 2(2): 234-242. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2389.1951.tb00604.x [89] COWLEY J M, WALKLEY A. Reaction between manganous ion and manganese dioxide [J]. Nature, 1948, 161(4083): 173. doi: 10.1038/161173a0 [90] KOSTKA J E, LUTHER G W Ⅲ, NEALSON K H. Chemical and biological reduction of Mn (Ⅲ)-pyrophosphate complexes: Potential importance of dissolved Mn (Ⅲ) as an environmental oxidant [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(5): 885-894. [91] HEINTZE S G, MANN P J G. Soluble complexes of manganic manganese [J]. The Journal of Agricultural Science, 1947, 37(1): 23-26. doi: 10.1017/S0021859600013009 [92] TU Q, SHAN X Q, NI Z M. Evaluation of a sequential extraction procedure for the fractionation of amorphous iron and manganese oxides and organic matter in soils [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 1994, 151(2): 159-165. doi: 10.1016/0048-9697(94)90172-4 [93] CHESTER R, HUGHES M J. A chemical technique for the separation of Ferro-manganese minerals, carbonate minerals and adsorbed trace elements from pelagic sediments [J]. Chemical Geology, 1967, 2: 249-262. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(67)90025-3 [94] SHUMAN L M. Separating soil iron- and manganese-oxide fractions for microelement analysis [J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1982, 46(5): 1099-1102. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1982.03615995004600050044x [95] DENYS A, JANOTS E, AUZENDE A L, et al. Evaluation of selectivity of sequential extraction procedure applied to REE speciation in laterite [J]. Chemical Geology, 2021, 559: 119954. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2020.119954 [96] YAN N, ZHONG H, BRUSSEAU M L. The natural activation ability of subsurface media to promote in situ chemical oxidation of 1, 4-dioxane [J]. Water Research, 2019, 149: 386-393. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.11.028 [97] SPINKS S C, UVAROVA Y, THORNE R, et al. Detection of zinc deposits using terrestrial ferromanganese crusts [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 80: 484-503. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.07.015 [98] YU M, TEEL A L, WATTS R J. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by subsurface minerals [J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2016, 191: 33-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2016.05.001 [99] SUDA A M, MAKINO T, HIGASHI T. Applicability of selective dissolution of manganese oxide by acidified 0.1 M NH2OH-HCl in Japanese soils [J]. Geoderma, 2011, 163(3/4): 291-295. [100] SUDA A M, MAKINO T, HIGASHI T. Extractability of manganese and iron oxides in typical Japanese soils by 0.5 mol L−1 hydroxylamine hydrochloride (pH 1.5) [J]. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2012, 58(6): 684-695. doi: 10.1080/00380768.2012.742002 [101] SUDA A M, MAKINO T, HIGASHI T. An improved selective extraction method for Mn oxides and occluded metals with emphasis on applicability to Andisols [J]. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2013, 59(6): 840-851. doi: 10.1080/00380768.2013.857580 [102] SUDA A M, MAKINO T, HIGASHI T. Improvement of the NH2OH-HCl-HOAc method for extracting manganese and iron oxides in Japanese Andisols and other soil types in Japan [J]. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2013, 59(5): 700-714. doi: 10.1080/00380768.2013.834242 [103] URE A M, BERROW M L. Analysis of edta extracts of soils for copper, zinc and manganese by atomic absorption spectrophotometry with a mechanically separated flame [J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 1970, 52(2): 247-257. doi: 10.1016/S0003-2670(01)80955-7 [104] KIM Y J, MOON J W, ROH Y, et al. Mineralogical characterization of saprolite at the FRC background site in Oak Ridge, Tennessee [J]. Environmental Geology, 2009, 58(6): 1301-1307. doi: 10.1007/s00254-008-1633-1 [105] TESSIER A, CAMPBELL P G C, BISSON M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1979, 51(7): 844-851. doi: 10.1021/ac50043a017 [106] SHUMAN L M. Fractionation method for soil microelements [J]. Soil Science, 1985, 140(1): 11-22. doi: 10.1097/00010694-198507000-00003 [107] MCDANIEL P A, BUOL S W. Manganese distributions in acid soils of the north Carolina piedmont [J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1991, 55(1): 152-158. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1991.03615995005500010027x [108] SHUMAN L M. Sodium hypochlorite methods for extracting microelements associated with soil organic matter [J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1983, 47(4): 656-660. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1983.03615995004700040010x [109] GU X Y, EVANS L J. Modelling the adsorption of Cd(Ⅱ), Cu(Ⅱ), Ni(Ⅱ), Pb(Ⅱ), and Zn(Ⅱ) onto fithian illite [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2007, 307(2): 317-325. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2006.11.022 [110] DIJKSTRA J J, MEEUSSEN J C L, COMANS R N J. Evaluation of a generic multisurface sorption model for inorganic soil contaminants [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009, 43(16): 6196-6201. [111] WARDEN B T, REISENAUER H M. Fractionation of soil manganese forms important to plant availability [J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1991, 55(2): 345. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1991.03615995005500020007x [112] CHAO T T, ANDERSON B J. The scavenging of silver by manganese and iron oxides in stream sediments collected from two drainage areas of Colorado [J]. Chemical Geology, 1974, 14(3): 159-166. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(74)90125-9 [113] CHAO T T, THEOBALD P K. The significance of secondary iron and manganese oxides in geochemical exploration [J]. Economic Geology, 1976, 71(8): 1560-1569. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.71.8.1560 [114] TOKASHIKI Y, DIXON J B, GOLDEN D C. Manganese oxide analysis in soils by combined X-ray diffraction and selective dissolution methods [J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1986, 50(4): 1079-1084. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1986.03615995005000040049x [115] BIBAK A. Copper retention by Danish Spodosols in relation to contents of organic matter and aluminum, iron, and manganese oxides [J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 1997, 28(11/12): 939-948. [116] DONG D M, LI Y, ZHANG B Y, et al. Selective chemical extraction and separation of Mn, Fe oxides and organic material in natural surface coatings: Application to the study of trace metal adsorption mechanism in aquatic environments [J]. Microchemical Journal, 2001, 69(1): 89-94. doi: 10.1016/S0026-265X(01)00068-6 [117] CHON C M, KIM J G, LEE G H, et al. Influence of extractable soil manganese on oxidation capacity of different soils in Korea [J]. Environmental Geology, 2008, 55(4): 763-773. doi: 10.1007/s00254-007-1029-7 [118] HETTIARACHCHI G M, PIERZYNSKI G M, RANSOM M D. In situ stabilization of soil lead using phosphorus and manganese oxide [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2000, 34(21): 4614-4619. -



 下载:
下载: