-
环境中重金属问题日趋严重,2020年《中国生态环境状况公报》中土壤污染状况详查结果显示,影响农用地土壤环境的主要污染物是重金属,其中镉为首要污染物[1]. 重金属具有不可降解性和高毒性等特点,不能被生物降解且具有生物累积性,被认为是重度污染物,可以直接威胁人类健康和生态安全[2]. 国内外学者对土壤、沉积物、水体(含地表和地下水体)和植物等不同介质中重金属的来源方式、迁移转化、环境风险、修复治理等展开研究[3-9]. 重金属来源方式主要有自然因素的岩石风化[10]、大气沉降[11]、沉积物释放[12]、河床岩石的化学浸出[13]等,也有来自人类活动的“三废”排放[14]、采矿冶炼[15]、农药化肥的使用[16]等. 但不同介质中重金属的来源方式不同,如土壤中的重金属受交通影响较大但沉积物受此影响较小. 重金属受大气沉降、降水入渗、地下水流动和植被等多种因素的影响,通过物理、化学或生物作用在不同介质体系中发生迁移转化[17-18],如土壤中的重金属通过降水入渗会解吸或溶解到水体中,水体中重金属在地下水流动的过程中也会吸附或沉积到土壤和沉积物中. 目前国内外学者对重金属研究较多集中在单一介质体系中[19-23],不能全面系统地了解土-水系统中重金属的来源方式和迁移转化,想要系统查清重金属的污染及来源需要从土-水介质系统角度进行综合研究. 系统研究重金属的分布特征和来源方式可为相关管理部门制定污染预测预警和防治管控措施提供理论依据和科学决策支撑.
抚河作为江西省第二大河流,是鄱阳湖的主要支流之一,整体流向由南向北,途径南昌县,汇入鄱阳湖[24]. 学者们对鄱阳湖流域多条支流、入湖口及鄱阳湖本身的重金属时空分布、来源分析、风险评价等内容进行了研究[25-32],但是抚河流域的相关研究较少. 周文斌等[33]对抚河南昌段底泥重金属进行研究,结果表明,研究区内底泥中重金属含量严重超标,并会对食物链构成重大威胁. 本课题组[34]对抚河南昌段水体中的7种重金属进行研究,结果表明,地表水中 V、Fe、Mn 的平均浓度均超过《地表水环境质量标准》(GB3838-2002)的标准限值; 地下水中 As 平均浓度超过《地下水质量标准》(GBT14848-2017)Ⅲ类水质标准,表明抚河流域地表水体中存在重金属污染问题,但来源方式和迁移转化机制不明. 因此,本文选择抚河南昌段水体中重金属污染较严重的抚河周边典型地区,对土壤、沉积物、地表水和地下水进行采样测试分析,系统分析土-水系统中7种重(类)金属(As、Cd、Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb、Zn)的空间分布,采用相关性和主成分分析法分析土-水系统中重金属来源,为鄱阳湖流域的水资源管理和重金属污染防治提供理论参考意义.
-
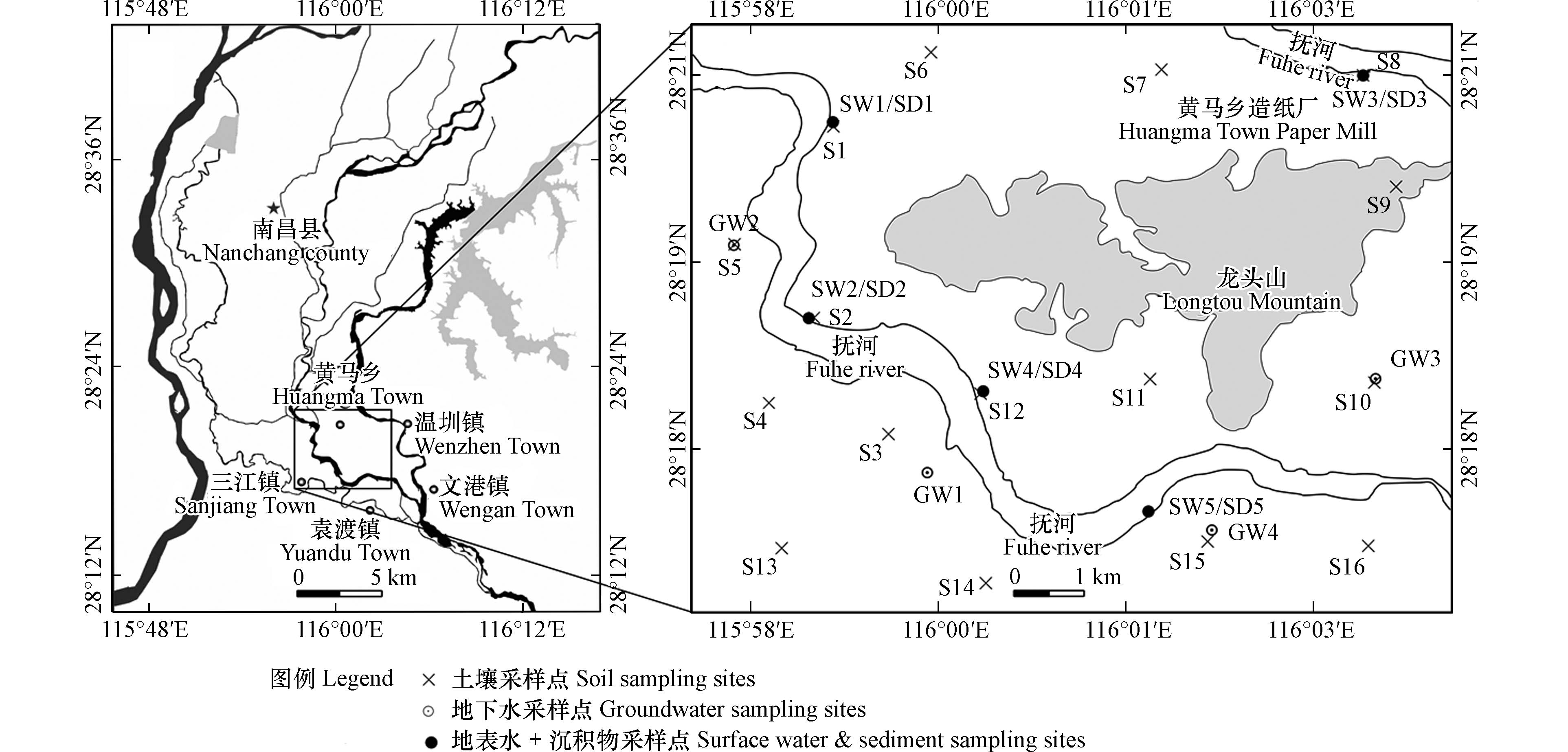
抚河周边龙头山地区具体包含三江镇、黄马乡等地,内部发育有抚河故支的两个支流(见图1),前期调研结果表明该地区抚河地表水中重金属超标现象明显[34],且该地区人口密度较高,以农田土壤为主,种植农作物多为水稻. 土壤表层样品整体采用矩形布点法(网格大小2.5 km×2.5 km)并结合地表水采样点进行适当调整,尽量保证土壤采样点接近矩形中心点,于2021年6月共采集16个土壤样品(S1—S16); 地表水和沉积物采样点布设在同一水平位置上,沿河道采样间隔为2.5—3 km,分别采集地表水样品5个(SW1-SW5)和沉积物样品5个(SD1-SD5); 此外采集地下水样品4个(GW1—GW4),各采样点位位置具体见图1.
土壤样品为0—20 cm的表层土壤,取样时使用五点取样法,沉积物样品使用抓斗式底泥采样器进行表层沉积物取样,土壤和沉积物样品采样完成后装入密封袋中带回实验室常温风干待测. 地表水样品使用聚氯乙烯采样器进行表层水(深约0.5 m)采集,地下水样品则在沿岸村庄民用水井中采集. 将采集的水样置于洁净的150 mL聚乙烯塑料瓶中,滴入少量浓硝酸调节pH至2以下,密封处理后放入便携式冰箱中,带回实验室进行4 ℃保存待测.
-
水样上机测试前通过0.45 μm的微孔过滤膜过滤处理. 土壤和沉积物则经过室内自然风干后,四分法取样,过100目尼龙筛后准确称取土壤0.2 g进行三酸(浓硝酸、氢氟酸、高氯酸)消解[35]. 消解完成后用0.45 μm的滤膜进行过滤处理待上机测试,使用电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(Agilent 5100ICP-OES)测试As、Cd、Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb、Zn7种重(类)金属含量[34]. 实验过程中使用的玻璃器皿进行24 h的稀硝酸浸泡,并使用超纯水洗涤之后烘干待用. 使用GNM-M261071-2013标准物质进行标准曲线配制,测试结果表明所有待测元素的相对标准偏差(RSD)都小于15%,相对误差(RE)都小于±20%,相关系数高达0.9999,测试数据符合要求.
-
土壤中重金属来源分析采用的方法为相关性分析法和主成分分析法. 相关性分析法[36]可以识别出土壤中重金属的元素是否具有同源性,通过该方法可以确定不同重金属的环境相似性和人类影响程度的强弱[37]. 主成分分析法[38]是一种经典的多元统计方法,核心是利用降维分析的手段将多项关联数据转为几类综合指标.
采用Excel软件对数据进行整体分析统计;统计软件(IBM SPSS Statistics 24)进行描述性统计、相关性及主成分分析;绘图软件(Coreldraw 2019)绘制采样点分布图;采用反距离插值法利用Arc map10.8绘制重金属空间分布图;不同介质中重金属含量箱线图则使用软件Origin 2018绘制.
-
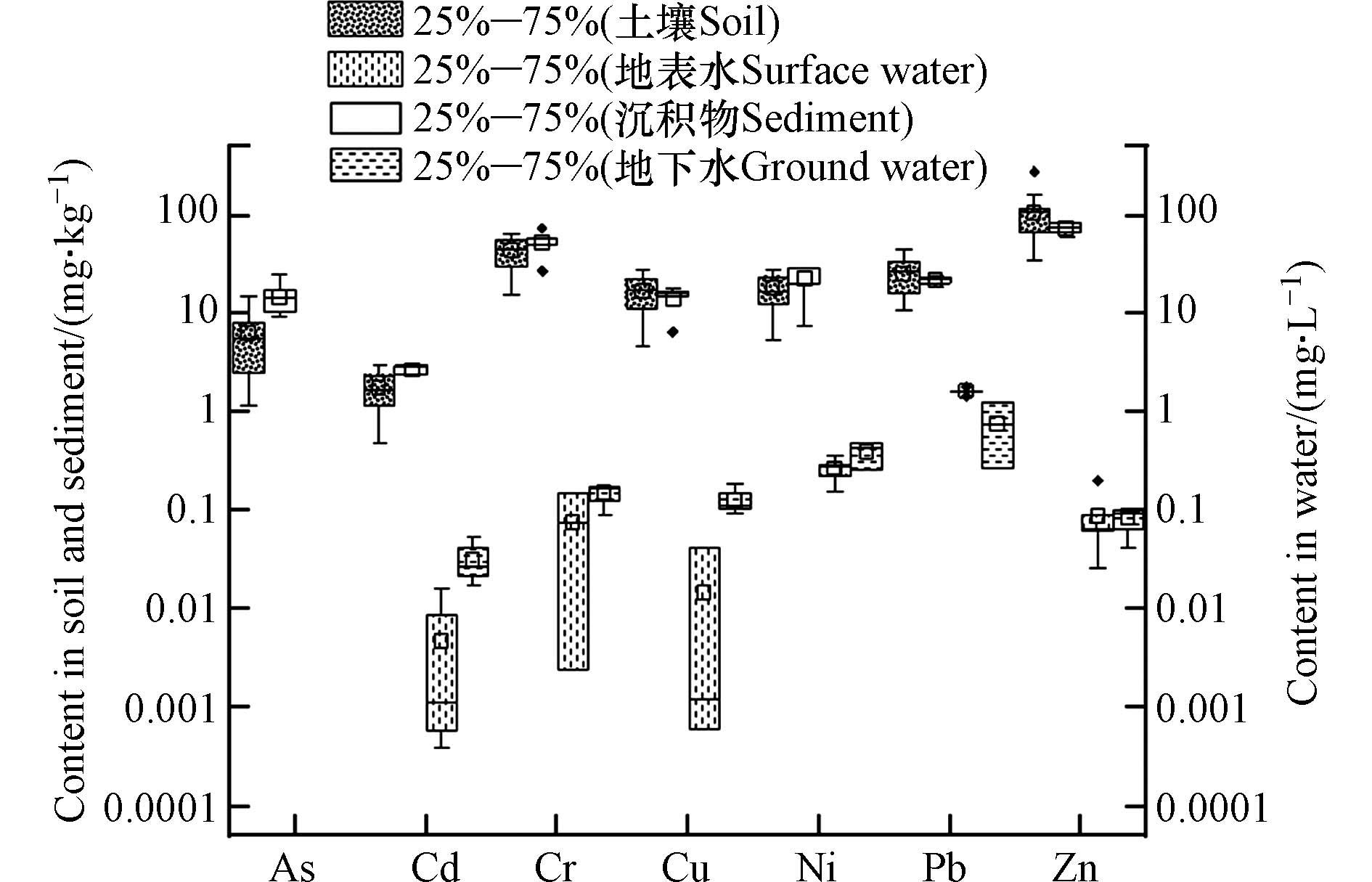
土-水系统中重金属含量箱线图如图2所示,土壤中As的含量为1.20—15.03 mg·kg−1,Cd的含量为0.49—3.13 mg·kg−1,Cr的含量为15.53—66.42 mg·kg−1,Cu的含量为4.74—28.33 mg·kg−1,Ni的含量为5.54—28.68 mg·kg−1,Pb的含量为10.75—45.25 mg·kg−1,Zn的含量为35.32—283.50 mg·kg−1. 土壤中重金属的平均浓度大小排列为: Zn(107.38 mg·kg−1)>Cr(44.32 mg·kg−1)>Pb(25.41 mg·kg−1)>Ni(18.62 mg·kg−1)> Cu(16.94 mg·kg−1)>As (6.29 mg·kg−1) >Cd(1.79 mg·kg−1).
沉积物As的含量为9.22—24.91 mg·kg−1,Cd的含量为2.36—3.09 mg·kg−1,Cr的含量为27.48—74.87 mg·kg−1,Cu的含量为6.61—18.47 mg·kg−1,Ni的含量为7.51—29.07 mg·kg−1, Pb的含量为18.85—24.36 mg·kg−1,Zn的含量为60.45—86.75 mg·kg−1. 沉积物中重金属的平均浓度大小排列为: Zn(74.69 mg·kg−1)>Cr(52.70 mg·kg−1)>Ni(22.82 mg·kg−1)>Pb(22.04 mg·kg−1)> As(15.28 mg·kg−1)>Cu(14.60 mg·kg−1)> Cd(2.76 mg·kg−1).
地表水和地下水中均未检出As,地表水中重金属的平均浓度大小排列为: Pb(1.66 mg·L−1)> Ni(0.27 mg·L−1)>Zn(0.09 mg·L−1)>Cr(0.08 mg·L−1)>Cu(0.01 mg·L−1)>Cd(0.005 mg·L−1);地下水中各个重金属的平均浓度大小排列为Pb(0.78 mg·L−1)>Ni(0.39 mg·L−1)>Cr(0.15 mg·L−1)>Cu(0.13 mg·L−1)>Zn (0.08 mg·L−1)> Cd(0.03 mg·L−1). 综上可知,同一重金属在土壤和沉积物中的含量比水体中含量高出约1—3个数量级,本研究区重金属主要集中在土壤和沉积物中,不同介质间重金属的含量差使得土壤和沉积物成为水体中的重金属污染来源之一,在研究水体重金属污染时应从土-水系统进行综合考虑.
表1 为鄱阳湖及其支流土壤和沉积物中重金属含量分布情况统计. 由表1可知,抚河流域龙头山与其他流域相比,重金属含量水平整体处于同一数量级,数值大小介于其他流域的最大值和最小值之间. 具体表现为: 与鄱阳湖相比,龙头山地区土壤中Cd、Cr含量较高,Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb、Zn含量较低;沉积物中Cr含量高,其他重金属含量低,土壤和沉积物呈现相似的规律;与信江流域和饶河流域相比,沉积物中所有元素含量均较低;与赣江流域相比,沉积物中As、Cu含量较高,其余元素含量较低;与修水入鄱阳湖湖口处相比,沉积物中重金属含量均为较高水平.
-
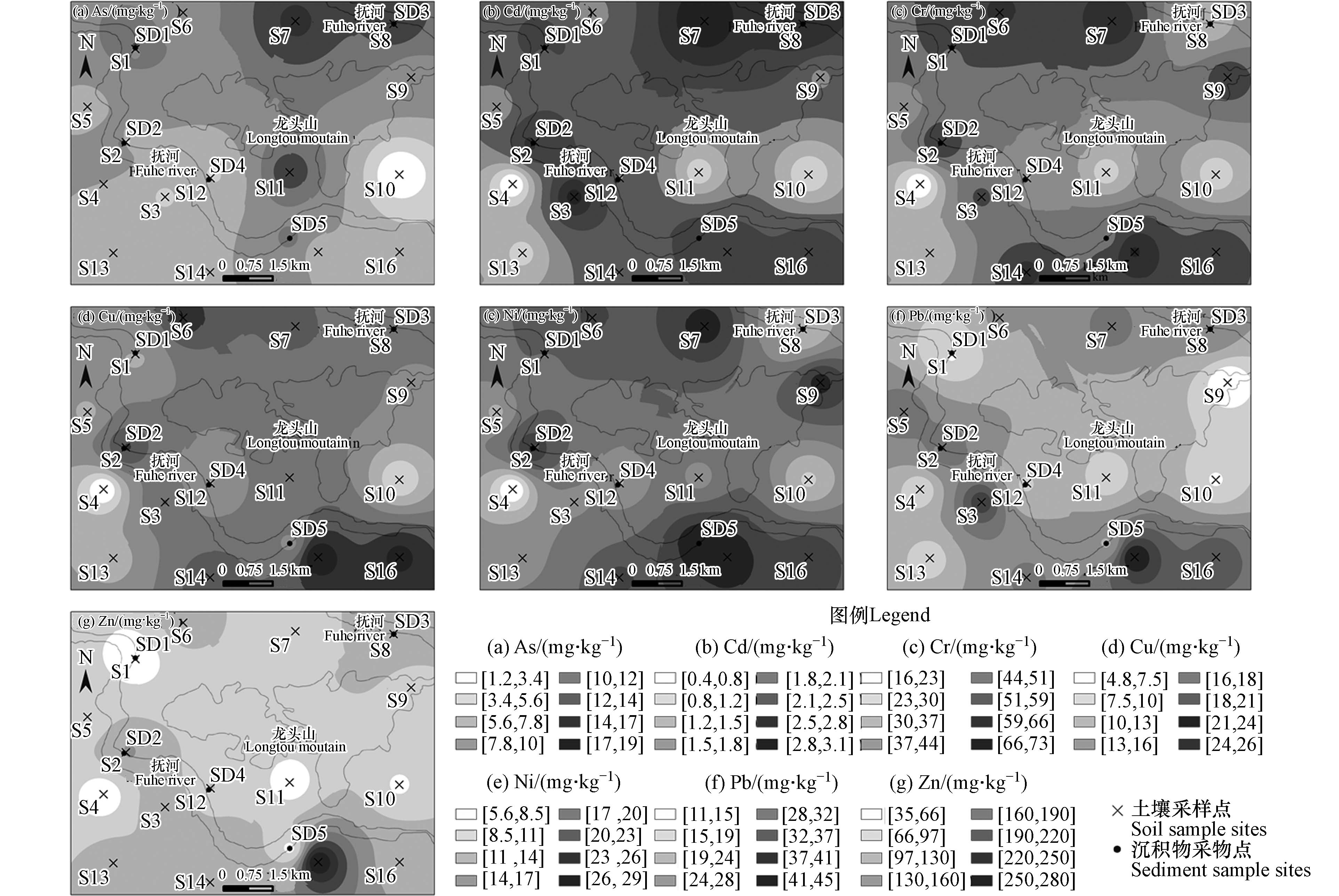
本研究区重金属主要集中在土壤和沉积物中,采用变异系数初步分析重金属空间分布特征. 变异系数[39](CV)代表不同采样点间数据的离散程度,变异系数(CV,%)=(标准偏差/平均数)×100,一般认为CV≤10%为弱变异性,10%<CV<100%为中等变异性,CV≥100%为强变异性. 7种重金属变异系数的计算结果按顺序从大到小排序为: As(72.10%)> Zn(54.46%)> Cu(40.45%)> Cd(38.85%)>Pb(38.30%)>Ni (38.23%)>Cr(35.08%),表明7种重金属的空间离散程度均属于中等变异程度,7种重金属含量在空间分布上存在一定的离散程度,分布不均匀,其中As的空间离散程度最高,空间分布最为不均匀, Zn、Cu次之,而Cd、Pb、Ni、Cr分布相对较为均匀.
采用反距离插值法对土壤-沉积物系统中重金属含量空间分布特征进行空间插值分析,土壤-沉积物中不同重金属浓度空间分布见图3.
结果表明,7种重金属空间分布整体呈现出一定规律,具体为抚河沿岸重金属含量较明显地高于其他地方,其中低值区位于龙头山(S10和S11附近)和西南角(S4和S13附近),表明重金属含量与采样点距抚河的距离有关,距抚河越近,重金属含量可能越高,污染的可能性越大. 这是因为水资源作为一种重要资源,影响了社会发展和人类活动,使得流域沿岸地区的人类活动更加频繁,可能与农田灌溉、工业生产和养殖等工农业人类活动有关. 不同重金属的空间分布特征表现为: As中间高而东西两侧低,Cd、Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb南北两侧较高,西南角和中部偏低,Zn则表现为南侧高于北侧. As元素含量高值区位于S7和S11附近,最高点为S7(图3a);Cd元素高值点出现在S3和S7,最高点为S7(图3b); Cr元素高值点出现在S7、S15,最高点为S15(图3c); Cu元素高值点出现在S8和S15,最高点为S8(图3d); Ni元素高值点出现在S7、S9、SD5和S15,最高点为S15(图3e); Pb元素高值点出现在S7和S11,最高点为S15(图3f); Zn元素高值点出现在S7和S11,最高点为S15(图3g). 总体而言,7种重金属在采样点S7、S8、S13和S15处含量偏高,在采样点S1、S4处含量较低;采样点 S7、S8、S15、S16处的重金属含量普遍高于S10、S11(除As外). 7种重金属的最高值分别位于S7(As和Cd)、S8(Cu)、S15(Cr、Ni、Pb和Zn),表明这些采样点附近土壤中重金属污染较为严重,其中采样点S7为稻田土,附近曾建有黄马乡造纸厂,目前已退役拆除,造纸厂[46]污水灌溉会导致土壤中各种重金属的升高,可能是造成此处重金属含量浓度较高的原因;点S8则邻近抚河,为岸边自然砂土样,该点Cu含量为最高值,但远远小于农用地污染风险筛选值,各采样点间Cu含量变化不明显,据现场调查附近无铜锌矿的开采和冶炼等相关的人类活动,仅存在少量生活垃圾,推测Cu可能来源于自然条件下的岩石风化造成; 采样点S15同样位于抚河沿岸的农田里,可能是由于化肥或者农药[39]的不当使用导致重金属含量过高; 采样点S7与S8距离较近,但重金属含量整体差别较的原因主要在与土地利用类型的不同,S7为农用地,受人类活动特别是农业活动的影响明显,而S8则为绿地,受人类活动影响较小.
-
(1)不同系统中重金属含量的相关性
对距离较近的(<1 km)不同系统(土壤、沉积物、地表水和地下水)中的重金属进含量行相关性分析,具体计算结果见表2和表3. 结果表明,土壤和沉积物间的相关系数为0.918—0.958(表2),邻近采样点间具有显著的相关性,表明土壤和沉积物中的重金属可能具有同源性;而邻近土壤/沉积物与地表水/地下水间的相关系数为-0.493— -0.093(表2和表3),邻近采样点间二者无显著或极显著的相关性,表明邻近土壤/沉积物与地表水/地下水中重金属的来源方式可能不同. 因此,根据不同系统中重金属含量的相关性分析结果,因此将土壤-沉积物系统可以作为一个联合体系进行重金属的来源解析.
(2)土壤-沉积物不同重金属间的相关性
土壤-沉积物不同重金属间的相关性分析结果见表4,土壤-沉积物中As只与Cd具有相关性,相关系数为0.523,呈显著相关性. Cd除了As相关外,还与除了Zn之外的其他重金属间都相关. 其他5种重金属,除了Ni与Pb、Ni与Zn之外,都呈现出了显著或者极显著的相关性,相关程度最高的为Cr与Ni,达到了0.852的极显著相关,这5种重金属元素间相关程度高,可能具有同源性. 分析结果表明As可能具有一个独立的来源方式,5种重金属(除As和Cd外)共同具有一个来源方式,Cd可能有两个或两个以上的来源方式.
(3)土壤-沉积物中重金属含量和上地壳金属浓度(UCC)相关性
上地壳中的金属浓度能够反映区域地球化学背景,通过上地壳金属浓度分析可以区分污染物是自然来源还是人为来源[47],将土壤-沉积物中的重金属含量与上地壳金属浓度(UCC)进行相关性分析,分析结果见图4. 据图4土壤-沉积物中重金属含量与上地壳金属浓度(UCC)两者间呈现正相关关系,相关系数(R2)等于0.9383. 重金属Pb、Ni、Cu、Cr、Zn落在虚线 (1:1直线) 附近,表明这5种重金属主要是自然来源,As、Cd则明显位于1:1直线以上,推测有一定程度的人为源输入.
-
土壤-沉积物中重金属主成分分析前需要进行KMO和巴特利特检验,KMO取样适切性量数为0.674,巴特利特值为0.000(P<0.005),说明可以采用主成分分析进行土壤-沉积物中的重金属来源分析. 主成分分析具体结果见表5,结果表明土壤-沉积物中的7种重金属共提取特征值大于1的两个主成分,累计贡献率达到了76.098%,其中主成分1和2的贡献率分别为50.903%、25.195%. 主成分1包括Cd、Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb、Zn,它们的权重系数分别为: 0.665、0.862、0.842、0.756、0.769、0.711,主成分2包括As和Cd,权重系数分别为0.875和0.536的权重. Cu、Cr、Pb、Ni、Zn的变异系数(Cv)较小,即空间分布较为均匀,重金属见相关性分析结果(表4)表明这5种重金属之间具有很强的同源性,同时联合UCC相关性分析结果,这5种重金属主要表现为自然源输入. 此外相关研究表明土壤中的Cr和Ni主要受地球化学成因影响[48], Zhao等[49]在黄河河口的研究也认为Cu、Cr、Pb、Ni、Zn来源于自然,与本文结论一致. 因此,主成分1 可解释为自然因素中的岩石风化.As的变异系数最大,表现出了点源污染的特征. As是煤炭燃烧,纸张生产等工业活动的产物之一[39],根据现场调查发现As含量高值区曾建有黄马乡造纸厂,现已拆除; 此外As、Cd等也是矿山开采的特征污染物[50],结合现场调查和南昌政法网监察报道内容,研究区存在河沙和零散矿山开采等活动[51],所以主成分2可解释为人为因素中的工业活动. Cd同时也是施用化肥和农药等的标识元素[52],农业污染一般呈现面源污染的特点,而研究区内采样点处为农田土壤,因此Cd也可能来源于农业活动,该结论与重金属间相关性分析的结论“Cd可能有两个或两个以上的来源方式”一致.
-
(1)抚河周边龙头山地区重金属主要集中在土壤与沉积物中,同一重金属在土壤和沉积物中的含量比水体中高出约1—3个数量级; 土壤或沉积物种重金属含量普遍高于上地壳金属浓度(UCC),与其他流域相比重金属含量处于同一数量级水平.
(2)7种重金属的空间离散程度均属于中等变异程度,其中As的空间离散程度最高; 7种重金属的含量空间分布整体呈现出一定的分布规律,具体为抚河沿岸重金属含量较明显地高于其他地方,其中低值区位于龙头山(S10 和S11附近)和西南角(S4和S13附近), 其中As中间高而东西两侧低,Cd、Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb南北两侧较高,西南角和中部偏低,Zn则表现为南侧高于北侧.
(3)邻近土壤和沉积物中采样点间重金属具有显著的相关性,邻近土壤/沉积物和地表水/地下水间无显著相关性; 重金属间相关性分析表明As具有较独立的来源方式,Cd可能有两个或两个以上的来源方式,其他5种重金属元素间相关程度高,可能具有同源性;土壤-沉积物中重金属含量和上地壳金属浓度(UCC)相关性及主成分分析分析结果表明, Pb、Ni、Cu、Cr、Zn 等5种元素主要是自然来源,As主要来源于工业污染,Cd来源于工农业复合污染.
抚河周边龙头山地区土-水系统中重(类)金属空间分布特征及来源分析
Spatial distribution characteristics and sources analysis of heavy metal(loid)s in a water-soil system of Longtoushan area around the Fuhe River
-
摘要: 选择抚河南昌段水体中重金属污染较严重的抚河周边龙头山地区为研究区,于2021年6月共采集土壤样品16个,地表水及沉积物样品各5个,地下水样品4个,利用ICP-OES测试分析As、Cd、Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb、Zn等7种重(类)金属含量,采用反距离插值法研究土-水系统中重金属空间分布特征,进一步采用相关性分析和主成分分析进行重金属来源分析. 结果表明,重金属主要集中在土壤和沉积物中,其含量普遍高于上地壳金属浓度(UCC),与其他流域相比处于同一数量级水平;空间离散程度均属于中等变异程度,整体空间分布特征表现为抚河沿岸的重金属含量明显高于其他地方;邻近土壤和沉积物中采样点间重金属具有显著的相关性,邻近土壤/沉积物和地表水/地下水间无显著相关性;重金属Cu、Cr、Pb、Ni、Zn主要来源于自然因素中的岩石风化,As主要来源于工业污染,Cd则来源于工农业复合污染. 研究结果可为抚河流域土-水体系统中重金属来源分析和污染防治提供科学依据和理论支撑.Abstract: This study selected Longtoushan area around the Fuhe river where water body of Nanchang section was seriously polluted by heavy metals as the study area. A total of 16 soil samples, 5 surface water samples, 5 sediment samples and 4 groundwater samples were collected in June 2021. Contents of 7 heavy metal(loid)s (i.e., As、Cd、Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb、Zn) were quantified by ICP-OES, and spatial distributions of these metal(loid)s in soil-water system were delineated with an inverse distance interpolation method. Possible sources of heavy metal(loid)s were investigated by correlation analysis and principal component analysis. Results showed that heavy metal(loid)s were accumulated in soil and sediments, and their contents were generally higher than the values of the upper crust metal concentration (UCC), although they were in the same order of magnitude compared with other basins. Spatially, heavy metal(loid)s showed significantly higher contents along the Fuhe River as compared to other locations with a moderate spatial dispersion degree. There was a significant indigenous correlation between different heavy metal(loid)s concentrations in adjacent soil and sediment samples, while no significant indigenous correlation between adjacent soil/sediment and surface water/groundwater samples were observed. Heavy metals including Cu, Cr, Pb, Ni, and Zn were mainly derived from weathering of natural rocks. As came from industrial practices, and Cd was sourced from industrial and agricultural compound activities. The results will provide scientific basis and theoretical support for source analysis, and prevention and management of heavy metal(loid)s pollution in natural soil-water systems of the Fuhe river.
-
Key words:
- heavy metal /
- soil and water system /
- spatial distribution /
- source analysis /
- Fuhe River
-

-
表 1 鄱阳湖及其支流重金属含量统计(mg·kg−1)
Table 1. Statistics of heavy metal contents in Poyang Lake and its tributaries
位置
Location介质
MediumAs Cd Cr Cu Ni Pb Zn 参考文献
References鄱阳湖
Poyang Lake土壤 0.75 41.56 31.06 23.52 35.85 115.72 [40] 沉积物 18.00 0.108 42.10 39.20 24.90 46.01 119.30 [40] 抚河
Fuhe River土壤 6.29 1.79 44.32 16.94 18.62 25.41 107.38 本文 沉积物 15.28 0.73 52.70 14.60 22.82 22.04 74.69 本文 信江
Xinjiang沉积物 22.5 1.67 104.0 77.8 57.5 176.1 [41] 赣江
Ganjiang沉积物 12.5 0.36 69.3 24.6 31.3 86.1 [42] 饶河
Rao River沉积物 18.39 1.86 35.19 51.92 35.83 179.67 [43] 修水
Xiu River沉积物 10.98 <0.45 40.94 7.00 <3.00 13.00 [18] 上地壳金属浓度
Upper Crust Concentrations1.50 0.10 35.00 25.00 20.00 17.00 71.00 [44-45] 表 2 邻近区域3种介质中重金属相关性分析
Table 2. Correlation analysis of heavy metals among three media in neighboring zone
采样点
Sample sitesSW1 SD1 S1 采样点
Sample sitesSW2 SD2 S2 SW1 1 SW2 1 SD1 −0.493 1 SD2 −0.129 1 S1 −0.421 0.958** 1 S2 −0.132 0.924** 1 采样点
Sample sitesSW3 SD3 S8 采样点
Sample sitesSW4 SD4 S12 SW3 1 SW4 1 SD3 −0.068 1 SD4 −0.138 1 S8 −0.177 0.933** 1 S12 −0.167 0.918** 1 注:** 在 0.01 级别(双尾),相关性极显著. * 在 0.05 级别(双尾),相关性显著.
Note:** Extremely Significant correlation at 0.01 level (two-tailed). * Significant correlation at 0.05 level (two-tailed)表 3 邻近区域2种介质中重金属相关性分析
Table 3. Correlation analysis of heavy metals between two media in neighboring zone
采样点
Sample sitesSW5 SD5 采样点
Sample sitesGW2 S5 采样点
Sample sitesGW3 S10 采样点
Sample sitesGW4 S15 SW5 1 GW2 1 GW3 1 GW4 1 SD5 −0.187 1 S5 −0.093 1 S10 −0.167 1 S15 −0.185 1 表 4 土壤-沉积物不同重金属间的相关性
Table 4. Correlation between different heavy metals in soil-sediment
元素
ElementsAs Cd Cr Cu Ni Pb Zn As 1 Cd 0.523* 1 Cr 0.377 0.658** 1 Cu -0.077 0.484* 0.692** 1 Ni 0.418 0.555** 0.852** 0.618** 1 Pb -0.121 0.565** 0.510* 0.735** 0.390 1 Zn -0.296 0.351 0.478* 0.708** 0.301 0.706** 1 注: ** 在 0.01 级别(双尾),相关性极显著. * 在 0.05 级别(双尾),相关性显著.
Note: ** Extremely Significant correlation at 0.01 level (two-tailed). * Significant correlation at 0.05 level (two-tailed)表 5 土壤-沉积物重金属主成分分析结果统计
Table 5. Statistics for Principle component analysis results of heavy metals in soil-sediment
重金属
Heavy metal成分
Component1 2 As 0.029 0.875 Cd 0.665 0.536 Cr 0.862 0.316 Cu 0.842 -0.316 Ni 0.756 0.334 Pb 0.769 -0.343 Zn 0.711 -0.530 特征值 3.563 1.764 贡献率/% 50.903 25.195 累计贡献率/% 50.903 76.098 -
[1] 中华人民共和国生态环境部. 中华人民共和国环境状况公报[R], 2021. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China. Bulletin on the Ecological and Environmental Monitoring Results of the Three Gorges Project in 2021[R], 2021 (in Chinese).
[2] 王宏镔, 束文圣, 蓝崇钰. 重金属污染生态学研究现状与展望 [J]. 生态学报, 2005, 25(3): 596-605. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2005.03.029 WANG H B, SHU W S, LAN C Y. Ecology for heavy metal pollution: Recent advances and future prospects [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2005, 25(3): 596-605(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2005.03.029
[3] 杨静, 刘敏, 陈玲, 等. 上海市湖泊沉积物重金属的空间分布 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2018, 38(10): 3941-3948. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.10.042 YANG J, LIU M, CHEN L, et al. Spatial distribution of heavy metals in lake surface sediments in Shanghai [J]. China Environmental Science, 2018, 38(10): 3941-3948(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.10.042
[4] 郭杰, 王珂, 于琪, 等. 长江中游近岸表层沉积物重金属污染特征分析及风险评估 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(11): 4625-4636. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2021.0317 GUO J, WANG K, YU Q, et al. Pollution characteristics of the heavy metals and their potential ecological risk assessment in nearshore sediments of the middle reaches of the Yangtze River [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2021, 41(11): 4625-4636(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2021.0317
[5] CHAKRABORTY R, ASTHANA A, SINGH A K, et al. Adsorption of heavy metal ions by various low-cost adsorbents: A review [J]. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 2022, 102(2): 342-379. doi: 10.1080/03067319.2020.1722811 [6] KARAOUZAS I, KAPETANAKI N, MENTZAFOU A, et al. Heavy metal contamination status in Greek surface waters: A review with application and evaluation of pollution indices [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 263: 128192. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128192 [7] SELVI A, RAJASEKAR A, THEERTHAGIRI J, et al. Integrated remediation processes toward heavy metal removal/recovery from various environments-a review [J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2019, 7: 66. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2019.00066 [8] ASAD S A, FAROOQ M, AFZAL A, et al. Integrated phytobial heavy metal remediation strategies for a sustainable clean environment - A review [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 217: 925-941. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.11.021 [9] QIN G W, NIU Z D, YU J D, et al. Soil heavy metal pollution and food safety in China: Effects, sources and removing technology [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 267: 129205. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129205 [10] 张银英. 大亚湾沉积物中重金属元素背景值研究 [J]. 热带海洋, 1991, 10(3): 76-80. ZHANG Y Y. A background value study on heavy metal elements in the sediments of Daya Bay [J]. Tropic Oceanology, 1991, 10(3): 76-80(in Chinese).
[11] EREL Y, VERON A, HALICZ L. Tracing the transport of anthropogenic lead in the atmosphere and in soils using isotopic ratios [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1997, 61(21): 4495-4505. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00353-0 [12] 赵凤霞, 程瑶, 高朋阳, 等. 漳河上游流域沉积物中重金属生态风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(9): 2860-2871. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021052802 ZHAO F X, CHEN Y, GAO P Y, et al. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of the upper reaches of Zhanghe River [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(9): 2860-2871(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021052802
[13] SOARES H M V M, BOAVENTURA R A R, MACHADO A A S C, et al. Sediments as monitors of heavy metal contamination in the Ave River Basin (Portugal): Multivariate analysis of data [J]. Environmental Pollution, 1999, 105(3): 311-323. doi: 10.1016/S0269-7491(99)00048-2 [14] MANNO E, VARRICA D, DONGARRÀ G. Metal distribution in road dust samples collected in an urban area close to a petrochemical plant at Gela, Sicily [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2006, 40(30): 5929-5941. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.05.020 [15] TENG Y G, NI S J, WANG J S, et al. A geochemical survey of trace elements in agricultural and non-agricultural topsoil in Dexing area, China [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2010, 104(3): 118-127. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2010.01.006 [16] 丛艳国, 魏立华. 土壤环境重金属污染物来源的现状分析 [J]. 现代化农业, 2002(1): 18-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0254.2002.01.025 CONG Y G, WEI L H. Analysis on the current situation of sources of heavy metal pollutants in soil [J]. Modernizing Agriculture, 2002(1): 18-20(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0254.2002.01.025
[17] 朱水, 申泽良, 王媛, 等. 垃圾处理园区周边土壤-地下水重金属分布特征 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(9): 4320-4332. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.09.039 ZHU S, SHEN Z L, WANG Y, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics of heavy metals in the soil-groundwater system around an integrated waste management facility [J]. China Environmental Science, 2021, 41(9): 4320-4332(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.09.039
[18] 曾欢, 张华, 丁明军, 等. 鄱阳湖典型湿地土壤-植物系统重金属沿湖向富集及迁移转换特征分析[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(2): 781-795. ZENG H, ZHANG H, DING M J, et al. Enrichments, migrations, and conversions of heavy metal in the soil/sediment-plant system towards to the lake in typical Poyang lake wetland[J]. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(2): 781-795(in Chinese).
[19] 李宏薇, 尚二萍, 张红旗, 等. 耕地土壤重金属污染时空变异对比: 以黄淮海平原和长江中游及江淮地区为例 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2018, 38(9): 3464-3473. LI H W, SHANG E P, ZHANG H Q, et al. Comparative research on spatio-temporal variability of heavy metal pollution in cultivated soils—a case study of Huang-Huai-Hai Plain and middle reaches of the Yangtze River and Jianghuai Region [J]. China Environmental Science, 2018, 38(9): 3464-3473(in Chinese).
[20] 杨冰雪, 方晨, 马勤, 等. 浙江省某地区农田土壤重金属污染的健康风险评价 [J]. 安徽农业科学, 2021, 49(7): 66-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2021.07.018 YANG B X, FANG C, MA Q, et al. Health risk assessment of heavy metals pollution in farmland soils in a region of Zhejiang Province [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 49(7): 66-69(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2021.07.018
[21] 王贞岩, 王姝, 付腾飞, 等. 秦皇岛海岸带地下水重金属特征及健康风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(4): 1157-1166. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020091405 WANG Z Y, WANG S, FU T F, et al. Characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in groundwater of Qinhuangdao coastal zone [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(4): 1157-1166(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020091405
[22] 刘芳慧, 黄丹, 钟聪, 等. 桂西北典型矿区周边水稻田土壤剖面汞分布特征及其影响因素 [J]. 土壤通报, 2020, 51(6): 1342-1350. doi: 10.19336/j.cnki.trtb.2020.06.11 LIU F H, HUANG D, ZHONG C, et al. Distribution characteristics of mercuryand its influencing factors of paddy fields around the typical mining areas in northwest Guangxi [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2020, 51(6): 1342-1350(in Chinese). doi: 10.19336/j.cnki.trtb.2020.06.11
[23] 黄楚珊, 张倩, 唐夫凯, 等. 江西陡水水库水环境重金属时空分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 环境化学,2022, 41(9): 2919-2930 HUANG C S, ZHANG Q, TANG F K, et al. Profiles of heavy metals pollution and potential influence to aquatic environment of Doushui Reservoir from Jiangxi Province[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(9): 2919-2930(in Chinese).
[24] YANG J, YAN D, YANG Q J, et al. Fish species composition, distribution and community structure in the Fuhe River Basin, Jiangxi Province, China [J]. Global Ecology and Conservation, 2021, 27: e01559. doi: 10.1016/j.gecco.2021.e01559 [25] 曹维鹏, 罗明标, 丁建桦, 等. 鄱阳湖主要支流底泥中重金属形态研究 [J]. 东华理工学院学报, 2006, 29(1): 66-73. CAO W P, LUO M B, DING J H, et al. Study of heavy metal speciation in branch rivers sediments of Poyang Lake [J]. Journal of East China Institute of Technology, 2006, 29(1): 66-73(in Chinese).
[26] 李鸣. 鄱阳湖重金属污染特征研究及环境容量估算[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2010. LI M. Heavy metal pollution characteristics and environmental capacity estimate of Poyang Lake[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2010(in Chinese).
[27] 刘小真. 鄱阳湖流域底质重金属及杀虫剂类POPs垂直污染分布特征[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2008. LIU X Z. Perpendicularity pollution and distributing character of both heavy metal and OCPs of sediment in Poyang Lake drainage basin[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2008(in Chinese).
[28] 胡春华. 鄱阳湖水环境特征及演化趋势研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2010. HU C H. The water environmental characteristic and its evolutionary trends of Poyang Lake[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2010(in Chinese).
[29] 李鸣, 吴结春, 张小林, 等. 鄱阳湖五河入湖口重金属污染和分析评价 [J]. 南昌大学学报(理科版), 2008, 32(5): 483-485,497. LI M, WU J C, ZHANG X L, et al. Assessment on heavy metal pollution at five estuaries of Poyang Lake [J]. Journal of Nanchang University (Natural Science), 2008, 32(5): 483-485,497(in Chinese).
[30] 胡春华, 周鹏, 黄萍, 等. 鄱阳湖流域溶解态重金属行为特征及健康风险评价 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2012, 31(5): 1009-1014. HU C H, ZHOU P, HUANG P, et al. Behavior characteristics of dissolved heavy metals and health risks assessment from Poyang Lake Basin, China [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2012, 31(5): 1009-1014(in Chinese).
[31] 匡荟芬, 胡春华, 吴根林, 等. 结合主成分分析法(PCA)和正定矩阵因子分解法(PMF)的鄱阳湖丰水期表层沉积物重金属源解析 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2020, 32(4): 964-976. doi: 10.18307/2020.0406 KUANG H F, HU C H, WU G L, et al. Combination of PCA and PMF to apportion the sources of heavy metals in surface sediments from Lake Poyang during the wet season [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2020, 32(4): 964-976(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2020.0406
[32] 何亚卓, 徐哲婷, 于涛, 等. 鄱阳湖重要支流重金属污染特征及环境风险 [J]. 能源与环境, 2021(2): 91-95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9064.2021.02.035 HE Y Z, XU Z T, YU T, et al. Pollution characteristics and environmental risk of heavy metals in important tributary of Poyang Lake [J]. Energy and Environment, 2021(2): 91-95(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9064.2021.02.035
[33] 刘小真, 周文斌, 胡利娜, 等. 抚河南昌段底泥重金属污染特征研究 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2008, 31(5): 30-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2008.05.009 LIU X Z, ZHOU W B, HU L N, et al. Contamination characteristics of heavy metals of fu river sediments at Nanchang segment [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 31(5): 30-34(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2008.05.009
[34] 陈俊华, 章艳红, 沈威, 等. 抚河南昌段重金属空间分布特征及来源分析 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(11): 4936-4944. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.11.035 CHEN J H, ZHANG Y H, SHEN W, et al. Distribution characteristics and source analysis of heavy metals in Nanchang section of the Fuhe River [J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(11): 4936-4944(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.11.035
[35] GAO P, HUANG J, WANG Y, et al. Effects of nearly four decades of long-term fertilization on the availability, fraction and environmental risk of cadmium and arsenic in red soils [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 295: 113097. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113097 [36] 王乔林, 宋云涛, 王成文, 等. 滇西地区土壤重金属来源解析及空间分布 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(8): 3693-3703. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.08.026 WANG Q L, SONG Y T, WANG C W, et al. Source identification and spatial distribution of soil heavy metals in Western Yunnan [J]. China Environmental Science, 2021, 41(8): 3693-3703(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.08.026
[37] 陆志华, 蔡梅, 王元元, 等. 太湖沿岸区浅层底泥重金属污染分析及生态风险评价 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2022, 34(2): 455-467. doi: 10.18307/2022.0208 LU Z H, CAI M, WANG Y Y, et al. Heavy metal pollution analysis and ecological risk assessment of shallow sediments in the coastal area of Lake Taihu [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2022, 34(2): 455-467(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2022.0208
[38] RODRÍGUEZ MARTÍN J A, RAMOS-MIRAS J J, BOLUDA R, et al. Spatial relations of heavy metals in arable and greenhouse soils of a Mediterranean environment region (Spain) [J]. Geoderma, 2013, 200/201: 180-188. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2013.02.014 [39] 易啸, 郑若欣, 舒帮云, 等. 土壤化肥重金属污染问题分析与研究 [J]. 化工设计通讯, 2020, 46(7): 243-244. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6490.2020.07.158 YI X, ZHENG R X, SHU B Y, et al. Analysis and research on heavy metal pollution of soil chemical fertilizer [J]. Chemical Engineering Design Communications, 2020, 46(7): 243-244(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6490.2020.07.158
[40] 匡荟芬. 鄱阳湖区沉积物和土壤重金属污染特征、风险评价及源解析[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2020. KUANG H F. Pollution characteristics, risk assessment and source apportionment of heavy metals in sediments and soils of Poyang Lake area[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2020(in Chinese).
[41] 刘佳伟, 杨明生. 鄱阳湖流域重金属污染评价与分析 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2022, 44(1): 99-103. LIU J W, YANG M S. Assessment and analysis of heavy metal pollution in Poyang Lake Basin [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2022, 44(1): 99-103(in Chinese).
[42] 刘佳伟. 鄱阳湖边缘地带沉积物-土壤重金属污染评价[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2021. LIU J W. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in sediments and soils of Poyang Lake marginal zone[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2021(in Chinese).
[43] 吕雅宁, 余杨, 黄爱平, 等. 饶河河口沉积物重金属累积特征及风险评价 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2019, 42(11): 178-186. doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2019.11.026 LYU Y N, YU Y, HUANG A P, et al. Accumulation characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediment from Raohe River Estuary [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 42(11): 178-186(in Chinese). doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2019.11.026
[44] 马建华, 董运武, 陈彦芳. 开封市周边地区地表灰尘重金属背景值研究 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(5): 1798-1806. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2019.0477 MA J H, DONG Y W, CHEN Y F. Background values of heavy metals in surface dusts in the vicinity of Kaifeng, Henan Province [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(5): 1798-1806(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2019.0477
[45] TAYLOR S R, MCLENNAN S M. The geochemical evolution of the continental crust [J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1995, 33(2): 241. doi: 10.1029/95RG00262 [46] 李丽锋, 苏芳莉, 关驰, 等. 造纸废水灌溉对湿地土壤重金属累积影响及趋势评价 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2015, 35(9): 2964-2970. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2014.0956 LI L F, SU F L, GUAN C, et al. The effect of irrigation with paper-making wastewater on the accumulation of heavy metals and their fate assessment in wetland soil [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2015, 35(9): 2964-2970(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2014.0956
[47] 张倩, 刘湘伟, 税勇, 等. 黄河上游重金属元素分布特征及生态风险评价 [J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 57(2): 333-340. doi: 10.13209/j.0479-8023.2020.124 ZHANG Q, LIU X W, SHUI Y, et al. Distribution of heavy metals in the upstream of Yellow River and ecological risk assessment [J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2021, 57(2): 333-340(in Chinese). doi: 10.13209/j.0479-8023.2020.124
[48] 蔡立梅, 马瑾, 周永章, 等. 东莞市农业土壤重金属的空间分布特征及来源解析 [J]. 环境科学, 2008, 29(12): 3496-3502. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2008.12.034 CAI L M, MA J, ZHOU Y Z, et al. Multivariate geostatistics and GIS-based approach to study the spatial distribution and sources of heavy metals in agricultural soil in the Pearl River Delta, China [J]. Environmental Science, 2008, 29(12): 3496-3502(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2008.12.034
[49] ZHAO Q Q, BAI J H, GAO Y C, et al. Heavy metal contamination in soils from freshwater wetlands to salt marshes in the Yellow River Estuary, China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 774: 145072. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145072 [50] 杨安, 邢文聪, 王小霞, 等. 西藏中部河流、湖泊表层沉积物及其周边土壤重金属来源解析及风险评价 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(10): 4557-4567. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.10.043 YANG A, XING W C, WANG X X, et al. Source and risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of rivers, lakes and their surrounding soils in central Tibet [J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(10): 4557-4567(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.10.043
[51] 李闽莉, 黄自安. 抚河堤坝非法采沙获利50余万五人涉嫌非法采矿被批捕[DB/OL]. [2019-1-22]. http://jxzfw.gov.cn/2019/0122/201901223766.html. [52] FILZEK P D B, SPURGEON D J, BROLL G, et al. Pedological characterisation of sites along a transect from a primary cadmium/lead/zinc smelting works [J]. Ecotoxicology, 2004, 13(8): 725-737. doi: 10.1007/s10646-003-4472-6 -



 下载:
下载: