-
水体富营养化会带来水华、嗅味、水生生态系统恶化等问题,是目前水库面临的最主要的挑战之一[1-3],随着政府部门的重视,造成水体富营养化的外源因素得到了有效的控制,但水库的内部营养负荷对水体的富营养化仍有着重要的影响[4-5]. 底泥作为内部营养元素的主要蓄积地,其营养元素的浓度水平和空间分布直接影响着水库的水质及整个水生生态系统[6]. 单宝庆等[7]采用沉积物质量准则、有机污染指数和有机氮指数对我国东部淡水流域的沉积物质量进行评价,发现沉积物受氮、磷污染严重,其质量问题亟待解决. 孙庆业等[8]采集了董铺水库沉积物样本,通过计算氮磷综合污染指数和有机污染指数发现评价库区有88.9%的河流断面沉积物属于清洁-中度污染. 黄廷林等[9]通过TOC、TN、TP之间的相互关系,推测出纤维束植物碎屑是周村水库沉积物有机质的主要来源. 水库沉积物作为水体营养元素污染重要的汇与源[10],通过分析其中营养元素含量及生态风险评价,对保障水库供水安全和生态系统修复有重要的指导意义[11].
湖漫水库是温岭市最大的集中式饮用水源水库,是温岭市区和周边石桥镇、城南镇、箬横镇、松门镇等区域的饮用水水源,供应20余万市民生活用水[12],同时担负防洪、灌溉、养殖等作用[13]. 鉴于湖漫水库在浙江省温岭市重要地位,本文率先研究营养盐垂向分布特征与生态风险评价,一方面填补水库建成后沉淀淤积引起营养盐空间变化规律空白;另一方面为考察蓝雪春等[14-15]指出湖漫水库自2011—2019年水质富营养化状态逐年升高是否与内源污染关联性;同时为政府管理部门对水库清淤底泥处置[16]与清淤经费估算等决策提供基础性依据.
本研究采集湖漫水库表、中、底层沉积物,测定其中TP、TN、TOC含量,分析营养元素分布特征;并采用沉积物质量准则、综合污染指数、有机污染指数和有机氮指数评价水库沉积物的生态风险等级;最后通过营养元素之间的相关性分析,探究主要污染来源.
-
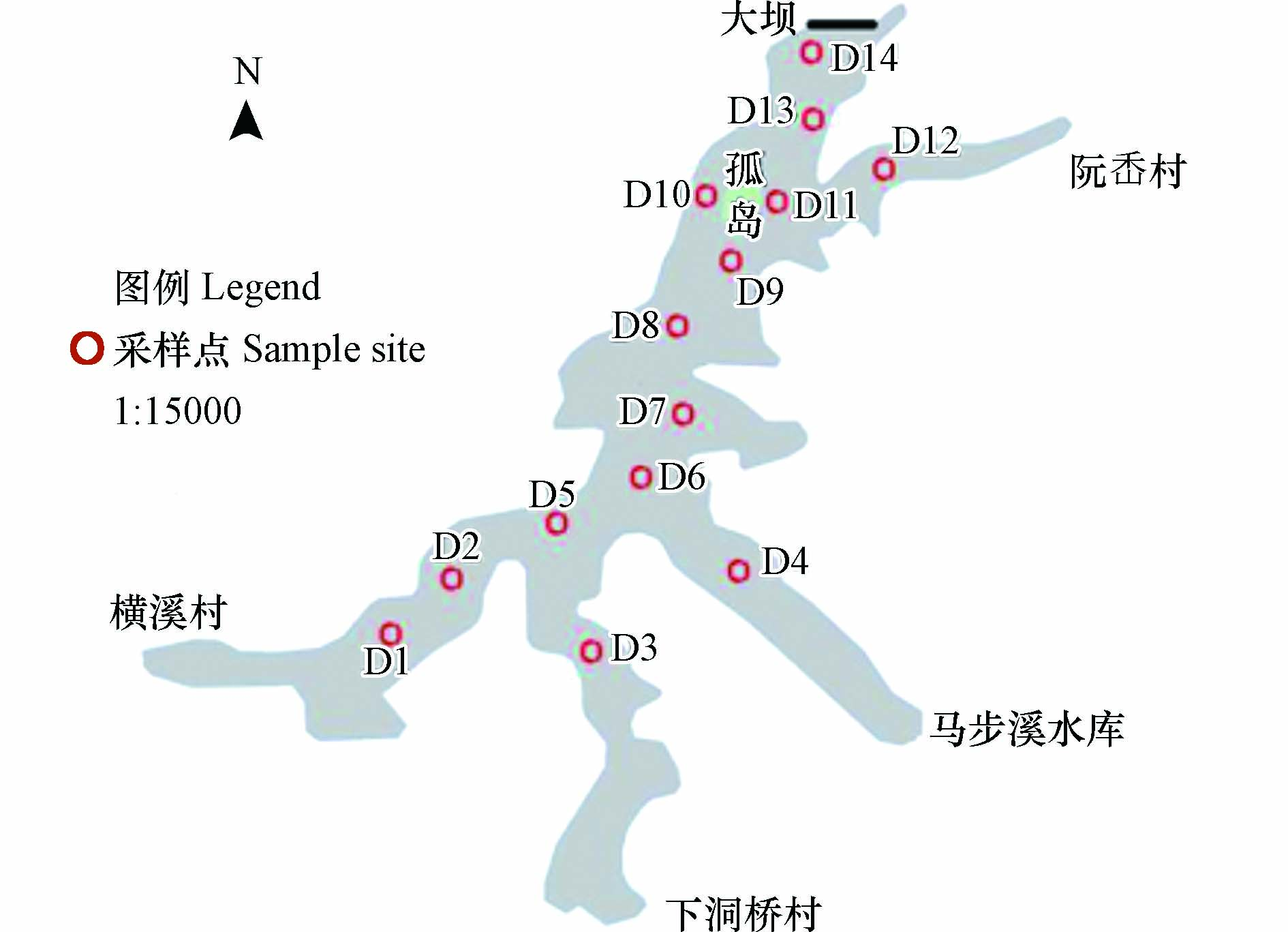
湖漫水库(28°30´,121°40´)位于浙江省温岭市,总库容达3503万m3,集水面积为32.48 km2[15]. 库区两岸土地以林业用地为主,支流两岸土地以居民用地和农业用地为主. 结合湖漫水库库区形态、支流、水动力等综合因素,在库区、大坝附近和4条支流(横溪村、下洞桥村、马步溪水库、阮岙村)共设置14个采样点,采样点具体分布、经纬度、所属区域如图1和表1所示.
-
于2018年3月采用奥地利产UWITEC柱状采泥器采集沉积物样品,将采集后的样品迅速运往实验室. 依据文献[17]采用拐点法确定底泥环保疏浚最适合深度多为20—40 cm,综合考虑《土壤环境监测技术规范》所规定取样质量要求,本研究以20 cm间隔将沉积物分为表层(0—20 cm)、中层(20—40 cm)和底层(40—60 cm). 将采集的沉积物样品置于风干盘中,摊成2—3 cm的薄层. 风干后,用球磨仪进行研磨,采用四分法将样品通过60、100目土壤筛,备用. TP采用碱熔-钼锑抗分光光度法(HJ 632—2011)测定;TN采用凯氏法(HJ 717—2014)测定;TOC的测定方法为燃烧氧化-非分散红外法(HJ 695—2014).
-
本文对沉积物的生态风险评价主要有环境质量评价指南分析和综合污染指数[9]、有机指数、有机氮指数[7]分析. 其中环境质量评价指南分析参考加拿大安大略省环境和能源部1992 年制定的沉积物环境质量评价指南(表2),根据沉积物中的污染物对底栖生物的生态毒性效将沉积物分为安全级、最低级和严重级3个级别[18]. 综合污染指数、有机指数和有机氮指数计算公式如下:
单因子污染指数:
$ S_{i}=C_{i} / C_{s} $ 综合污染指数:
$ F F=\sqrt{\dfrac{S^{2}+S_{\max }^{2}}{2}} $ 有机指数:OPI=TOC(%)×TN(%)×0.95
有机氮指数:ONI=TN(%)×0.95
式中,Ci为评价因子实测值,Cs为评价因子的评价标准含量;S为评价因子的评价指数平均值,Smax为最大单项评价指数.
沉积物综合污染程度分级标准详见表3;有机指数和有机氮指数评价分级标准详见表4. 本文采用Sufer软件对营养元素的空间分布进行绘图,营养元素的相关性采用SPSS进行计算.
-
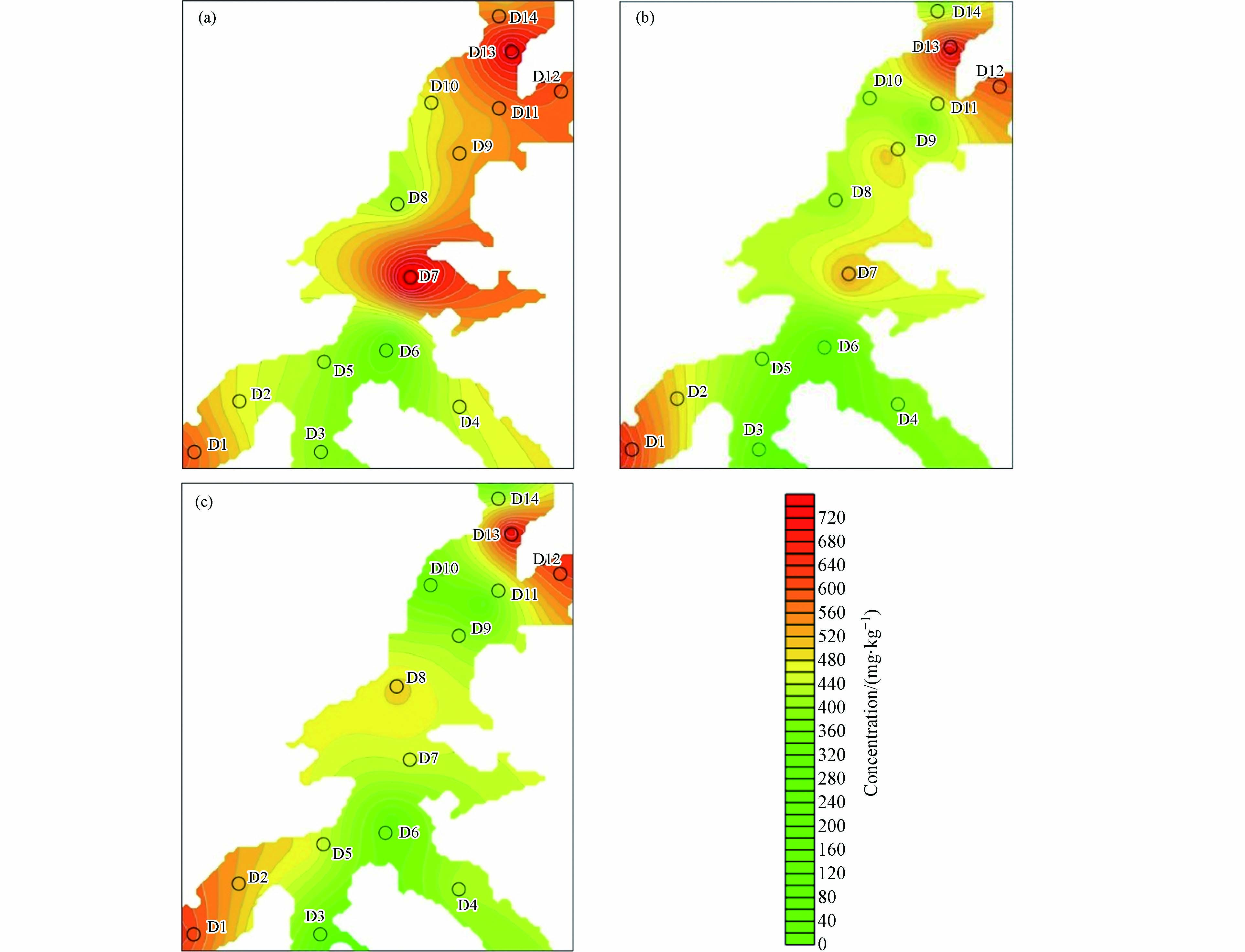
湖漫水库库区表、中、底层沉积物中的TP含量空间分布分别如图2所示,库区表层沉积物中TP含量范围为272—785 mg·kg−1,平均值为516.43 mg·kg−1. 由图2(a)可以看出,表层沉积物中TP含量较高的区域集中在大坝附近、库区中心及阮岙村、横溪村两个支流处,分别对应的采样点为D14、D7、D12、D1,TP含量分别为523、785、590、616 mg·kg−1. 如表5所示,与我国其他水库沉积物TP含量相比,湖漫水库沉积物中的TP浓度处于中低水平,远低于太湖(1150 mg·kg−1)、三峡水库(1014 mg·kg−1)[19],略高于浙江省长潭水库(430 mg·kg−1)[20]. 中层和底层沉积物中TP含量范围分别为233—710 mg·kg−1、201—623 mg·kg−1,平均含量为450.71 mg·kg−1、359.29 mg·kg−1. 在大坝附近、阮岙村支流和横溪村支流处中层和底层沉积物的TP含量均较高,其中大坝附近D14的中层和底层沉积物中TP含量分别为363、266 mg·kg−1,阮岙村支流的中层和底层淤泥中TP含量分别603、577 mg·kg−1,横溪村支流的中层和底层淤泥中TP含量分别663、572 mg·kg−1. 对比图2,不难发现湖漫水库沉积物的TP含量大小顺序为:表层>中层>底层,这与前人的研究结果一致[21-22]. 表层与中、底层沉积物的TP浓度空间分布规律略有不同,库心区域仅表层沉积物的TP含量较高,中、底层沉积物的TP含量明显减小.
-
图3分别表示湖漫水库表、中、底层沉积物中TN含量的空间分布图. 由图3(a)可得,表层沉积物中TN含量的空间分布差异较为明显,TN浓度范围在623—2510 mg·kg−1,平均浓度为1690 mg·kg−1. 与我国其他水库相比(表5),TN浓度处于中等水平,略高于长潭水库(1460 mg·kg−1)[20]. 高TN含量集中在大坝附近、库心及阮岙村、横溪村支流处,分别为2030、2070、2460、2510 mg·kg−1. 大坝附近和库心的高浓度TN分布与前人的研究结果一致[23]. 参照美国环境保护部标准[24],可以判定湖漫水库表层沉积物为氮元素为中度污染. 由图3(b)可以看出,仅大坝附近的中层沉积物TN含量较高,为2770 mg·kg−1. 而大坝附近和阮岙村、横溪村两支流处的底层沉积物TN含量均很较低. 对比图3发现,随着深度的增加,沉积物中的TN含量明显下降.
-
湖漫水库表、中、底层沉积物中TOC的空间分布如图4所示. 与TP、TN浓度空间分布规律相似,大坝附近、库区中间及阮岙村、横溪村支流处的沉积物TOC含量较高,百分含量分别为:1.61%、1.81%、1.53%、1.64%. 库区表层沉积物的平均TOC含量为1.28%,与我国其他水库相比,处于中低水平[25]. 对比图4可以明显看出,随着深度的增加,沉积物中的TOC含量呈逐渐下降的趋势,可能的原因是水生生物的排泄物及残骸逐渐在表层沉积物中积累. 大坝附近和库区中间处沉积物的TOC含量随深度变化较为显著,底层TOC仅为表层TOC的43.5%.
综上所述,湖漫水库表层沉积物中的TP、TN、TOC均存在明显的空间差异性,高营养元素含量主要集中于大坝、库心及阮岙村、横溪村支流区域. 随着深度的增加,沉积物中的营养元素呈下降趋势,底层沉积物中TP含量为表层的77%,TN和TOC余约为表层的62%. 此外,相比大坝附近和阮岙村、横溪村支流区域,库心的营养元素随沉积物深度的增加下降趋势更明显.
-
参考2.1节的分析结果,本节仅对湖漫水库的表层沉积物进行生态风险评价. 首先,参考加拿大安大略省环境和能源部(1992年) 制定的沉积物环境质量评价指南,分析沉积物中污染物对底栖生物造成的生态毒性效应. 湖漫水库79%的表层沉积物TP浓度小于600 mg·kg−1,仅D1、D7、D13处的TP大于600 mg·kg−1,表明湖漫水库大部分区域TP的生态毒性处于安全级别,极少部分为最低级. 库区表层沉积物的TN浓度较高,最低值为623 mg·kg−1,最高值为2510 mg·kg−1,TN浓度范围介于生态安全毒性最低级别浓度范围内(550—4800 mg·kg−1). 库区大部分区域表层沉积物TOC的含量介于10—100 mg·g−1,即生态毒性处于最低级别;仅D3、D4、D5、D6处沉积物的TOC含量小于10 mg·g−1,生态毒性处于安全级别. 由此可见,湖漫水库的营养元素污染对底栖生物存在最低级的生态毒性效应,主要来源于氮和有机质.
计算14处采样点表层沉积物的综合污染指数,结果如表6所示. 根据沉积物综合污染评价标准[9,34],将14处采样点表层沉积物的氮、磷污染和综合污染分为4级,级数越大表明污染越严重. 由沉积物中氮的单价评价指数可以看出,14个采样点中有4级9处、3级3处、2级1处、1级1处;14个采样点的磷评价指数中有4级2处、3级9处、2级3处. 综合氮、磷污染指数,得出的综合污染指数中有4级9处、3级1处、2级3处、1级1处. 这说明湖漫水库表层沉积物中有64.3%的区域处于重度营养盐污染,有28.6%的区域处于中度及轻度污染,7.1%的区域未受污染. 此外,对比氮、磷单项污染指数和综合污染指数,由图5可以发现综合污染指数的级数受TN评价指数影响较大,表明湖漫水库的营养盐污染主要来源于氮污染.
针对库区沉积物中污染较为严重的有机质和氮,进行有机指数和有机氮指数分析[19],结果如表7所示. 参照有机氮指数的评价标准[35],发现湖漫水库表层沉积物中的有机氮指数范围为0.06—0.24,均处于中度至重度污染水平. 库区表层沉积物的有机指数范围为0.02—0.45,其中14%为几乎未被污染,64%为轻度污染,21%的部分受到中度污染.
结合沉积物质量准则、污染指数、有机指数和有机氮指数的分析,发现湖漫水库表层沉积物对底栖生物存在生态毒性,毒性级别为最低级别. 生物毒性主要来源于沉积物中氮污染,尤其是有机氮污染较为严重. 有研究表明在偏酸性和厌氧条件下,沉积物中的氮更易释放到上覆水中,从而可能会引起藻华[7]. 湖漫水库沉积物的pH范围为5.05—6.08,由此可推断氮污染严重,且存在释放风险,可能造成水库内源污染.
-
沉积物中营养元素的相关性与其附近的土地利用类型、人口密度、工农业发达程度等因素密切相关[11],水库内部的地球生物过程也对氮磷的存在形态具有重要的影响[36]. 故本节通过分析沉积物中C、N、P的相互关系以探究湖漫水库营养元素污染的主要来源.
-
表8表示的是TOC与TP、TN的相关性,可以看出,TOC与TP、TN均显著正相关(系数>0.01). 这说明沉积物中C、N、P具有同源性,且N、P以有机态存在较多[37]. TOC与TP、TN的相关系数分别为0.863、0.955,表明TOC与TN有更强的相关性. 结合表9中TOC、TP、TN的载荷系数,可以得出主成分和沉积物中营养元素的关系为:Y=0.585 TOC+0.563 TP+0.584 TN.
-
经2.1节分析,可以看出大坝附近、库区中间及阮岙村、横溪村支流的营养元素含量较高,本节主要分析D14、D7、D12、D1采样点处营养元素的比值,探究其主要污染元素及污染来源. 由N/P比可以看出,N/P比均小于7,即库区水体富营养化过程中氮质量浓度相对较低[38]. 因此,要控制库区富营养化过程,须主要控制氮的营养负荷. 有研究表明,C/N比可反应有机质来源的差异[39]. 由表10可以看出,沉积物C/N值均小于10,表明湖漫水库中外源和内源有机质基本达到平衡,属于混源有机质[7,40]. D1处的C/N比小于7,可推断此处沉积物中的有机质主要来源于浮游动物;D7、D12、D14处的C/N比分布范围为7—10,表明其有机质主要来源于浮游植物和藻类[9]. 对比表、中、底层沉积物的C/N比,发现除D1外,其他采样点处表层沉积物的C/N比均小于底层,这与前人的研究结果一致[9].
此外,C/P比可反应沉积物中有机碳和磷化合物的分解速度[35]. D1、D7、D12、D14处沉积物的C/P比值范围为20—27,表明沉积物中TOC含量较高,TP含量相对较低. 对比表、中、底、层沉积物的C/P比,发现除D7外,其他营养元素污染较严重的区域,表层沉积物的C/P比均比底层大,这可能是受大量外源有机质影响,其夹带的磷元素随有机质的沉积富集在底层沉积物中[37].
-
(1)湖漫水库沉积物中的营养元素TP、TN、TOC分布规律基本一致,均在大坝附近、库区中心及阮岙村、横溪村两个支流处浓度较高. 表层沉积物中的营养元素浓度最高,随着深度的增加,TP、TN、TOC浓度均呈下降趋势,其中库心位置的营养元素浓度下降趋势最明显.
(2)通过综合污染指数、有机指数和有机氮指数的分析,发现表层沉积物中有64.3%的区域处于重度营养盐污染,28.6%的区域处于中度及轻度污染,其余区域未受污染.
(3)沉积物中的营养盐污染主要来源于氮,尤其是有机氮的污染,并且存在释放风险.
(4)湖漫水库沉积物的营养元素污染主要来源于浮游动物、浮游植物和藻类等水生生物的排泄物及残骸在表层沉积物积累.
浙江省温岭湖漫水库沉积物中营养盐分布及风险评价
Distribution and risk assessment of nutrients in sediments of Human Reservoir in Wenling City, Zhejiang Province
-
摘要: 湖漫水库是温岭市最大的集中式饮用水源水库,水质富营养化状态逐年升高的趋势亟需系统调查该水库内源污染现状. 以湖漫水库为研究对象,采集表、中、底层沉积物,根据TP、TN、TOC等影响水库富营养化因素,进行营养元素空间分布特征分析和生态风险评价,通过营养元素间的相互关系初步探究水库主要污染源. 结果表明,湖漫水库表层沉积物中TP、TN、TOC均值分别为516.43 mg·kg−1、1690 mg·kg−1、1.28%. 营养元素主要在大坝附近、库区中心、阮岙村和横溪村两个支流处富集;随着深度的增加,浓度逐渐降低,底层沉积物中TP含量为表层的77%,TN和TOC含量为表层的62%;水库中有64.3%的表层沉积物处于重度营养盐污染,主要为氮,尤其是有机氮污染,且存在可能释放的风险;该水库沉积物营养盐污染经解析主要由浮游动物、浮游植物和藻类等水生生物的排泄物及残骸逐渐在表层沉积物积累引起.Abstract: Human reservoir is the largest drinking water reservoirs in Wenling City. It was urgent to investigate systematically the internal pollution of the reservoir in view of the increasing trend of water eutrophication. The spatial distribution characteristics of nutrient elements and ecological risk evaluation were carried out by sampling the surface, middle and bottom sediments of the reservoir and exploring the influencing factors of eutrophication, such as the contents of TP, TN, TOC. The main eutrophication sources of the reservoir were primarily investigated through the correlation between nutrient elements. The results showed that the mean concentrations of TP, TN and TOC in surface sediment were 516.43 mg·kg−1, 1690 mg·kg−1 and 1.28%, respectively. The nutrients were mainly enriched near the dam, in the center of the reservoir, and in the two tributaries of Ruanao village and Hengxi village. The nutrient concentration decreased gradually with the increase of depth. The TP content in bottom sediments was 77% of that in the surface layer, and TN and TOC contents were 62% of those in the surface sediments. Additionally, 64.3% of the surface sediments in the reservoir were seriously polluted by nutrients (especially organic nitrogen), and there was a risk of possible release. According to the correlation and ratio between nutrients, it was speculated that the nutrient pollution of sediments in this reservoir was mainly caused by the gradual accumulation of excreta and debris from aquatic organisms such as zooplankton, phytoplankton and algae on the surface sediment.
-
Key words:
- sediment /
- eutrophication /
- distribution characteristics /
- risk assessment.
-

-
表 1 湖漫水库采样点位置
Table 1. The sampling location in Human reservoir
点位
Sampling site经度(°)
Longitude纬度(°)
Latitude所属区域
Sampling areaD1 28.354350 121.408059 横溪村 D2 28.356668 121.409816 横溪村 D3 28.352161 121.414641 下洞桥村 D4 28.356176 121.420027 马步溪水库 D5 28.357241 121.412904 库区 D6 28.358084 121.414936 库区 D7 28.360416 121.418762 库心 D8 28.363027 121.420298 库心 D9 28.366514 121.419453 库心 D10 28.367967 121.418594 库区 D11 28.367172 121.421153 库区 D12 28.368954 121.425226 阮岙村 D13 28.371008 121.422957 库区 D14 28.372602 121.422118 大坝附近 表 2 沉积物质量评价指南
Table 2. Manual for the sediment assessment
生态毒性效应
Ecotoxicological toxicityTN/(mg·kg−1) TP/(mg·kg−1) TO(mg·kg−1) 安全级别 <550 <600 <10 最低级别 550—4800 600—2000 10—100 严重级别 ≥4800 ≥2000 ≥100 表 3 沉积物综合污染程度分级标准
Table 3. Standard of comprehensive pollution level in sediments
污染程度
Pollution levelSTN STP FF 等级
Grade未受污染 <1.0 <0.5 ≤1.0 1 轻度污染 1.0—1.5 0.5—1.0 1.0—1.5 2 中度污染 1.5—2.0 1.0—1.5 1.5—2.0 3 重度污染 ≥2.0 ≥1.5 ≥2.0 4 表 4 沉积物有机指数及有机氮评价标准
Table 4. Sediment evaluation standards by organic index and organic nitrogen index
有机指数评价标准
Assessment standards of OPI<0.05 0.05—0.20 0.20—0.50 ≥0.50 清洁 轻度污染 中度污染 重度污染 有机氮评价标准
Assessment standards of ONI<0.0033 0.0033—0.066 0.066—0.133 >0.133 清洁 轻度污染 中度污染 重度污染 表 5 国内其他水库沉积物营养元素含量对比
Table 5. Concentrations of nutrients in sediments of other reservoir in China
所属省份
Province湖库名称
Reservoir沉积物类型
SedimentTN/(mg·kg−1) TP/(mg·kg−1) TOC/% 文献来源
Reference浙江省 分水江水库 表中底层 1710 820 1.56 张明等[26] 湖北省 黄柏河水库 表层 1500.4 8578 2.69 王雨春等[27] 江西省 柘林水库 表层 1832.6 657.5 3.2 李学梅等[28] 广东省 白盆珠水库 表层 2550 140 0.88 陈建耀等[23] 湖北省 玄庙观水库 表层 1209.5 8133 3.03 王雨春等[29] 河北省 潘家口水库 表层 4765.1 946.5 / 王洪伟等[30] 广东省 清林径水库 表层 1611 218 1.12 兰建洪等[31] 广东省 茜坑水库 表层 3442 1648 1.477 黄廷林等[32] 陕西省 西北某小型水库 表层 460 170 1.168 黄廷林等[33] 浙江省 长潭水库 表层 1460 430 1.367 陈光才等[20] 表 6 湖漫水库表层沉积物综合污染程度评价
Table 6. Pollution assessment of surface sediments in Human reservoir
采样点
Sampling siteTN评价指数 TP评价指数 综合污染指数 STN 等级
GradeSTP 等级
GradeFF 等级
GradeD1 3.75 4 1.40 3 3.21 4 D2 2.60 4 1.10 3 2.25 4 D3 1.54 3 0.82 2 1.37 2 D4 1.61 3 1.03 3 1.47 2 D5 1.24 2 0.96 2 1.17 2 D6 0.93 1 0.62 2 0.86 1 D7 3.67 4 1.78 4 3.23 4 D8 2.33 4 1.07 3 2.04 4 D9 1.81 3 1.20 3 1.66 3 D10 2.81 4 1.08 3 2.41 4 D11 3.30 4 1.20 3 2.82 4 D12 3.09 4 1.34 3 2.69 4 D13 3.61 4 1.65 4 3.16 4 D14 3.03 4 1.19 3 2.61 4 平均值 2.52 4 1.17 3 2.21 4 表 7 湖漫水库表层沉积物有机指数和有机氮指数
Table 7. Organic index and organic nitrogen index of surface sediments in Human reservoir
D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 有机氮指数ONI 0.24 0.17 0.10 0.10 0.08 0.06 0.23 有机指数OPI 0.39 0.24 0.07 0.08 0.04 0.02 0.42 D8 D9 D10 D11 D12 D13 D14 有机氮指数ONI 0.15 0.11 0.18 0.21 0.20 0.23 0.19 有机指数OPI 0.19 0.14 0.28 0.31 0.30 0.45 0.31 表 8 沉积物中TOC与TP、TN的相关性矩阵
Table 8. Correlation matrix between TP,TN and TOC
TOC TP TN TOC 1.000 TP 0.863 1.000 TN 0.955 0.857 1.000 表 9 主成分载荷矩阵表
Table 9. Principle component load matrix
分析指标
Parameters主成分系数
CoefficientTOC 0.976 TP 0.940 TN 0.974 表 10 沉积物中TN/TP、TOC/TN、TOC/TP比值
Table 10. The ratio of TN/TP,TOC/TN,TOC/TP
点位
Sampling siteTN/TP TOC/TN TOC/TP 表层 中层 底层 表层 中层 底层 表层 中层 底层 D1 4.07 3.08 3.83 6.53 6.97 5.80 26.59 21.45 22.20 D7 3.13 3.13 2.75 7.37 7.12 8.57 23.08 22.28 23.56 D12 3.51 2.89 2.53 7.38 7.90 7.91 25.88 22.80 20.00 D14 3.88 3.20 2.58 7.92 7.24 7.22 30.75 23.15 26.32 -
[1] ZHANG W Q, JIN X, MENG X, et al. Phosphorus transformations at the sediment–water interface in shallow freshwater ecosystems caused by decomposition of plant debris [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 201: 328-334. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.006 [2] von SPERLING E, Da SILVA FERREIRA A C, NUNES LUDOLF GOMES L. Comparative eutrophication development in two Brazilian water supply reservoirs with respect to nutrient concentrations and bacteria growth [J]. Desalination, 2008, 226(1/2/3): 169-174. [3] 丁润楠, 姚晓龙, 傅大放, 等. 中国东部湖泊有机氮浓度时空特征及影响因素 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2021, 44(6): 35-42. DING R N, YAO X L, FU D F, et al. Spatial and seasonal characteristics of organic nitrogen concentrations in lakes of Eastern China and its influencing factors [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 44(6): 35-42(in Chinese).
[4] WEN S L, WANG H W, WU T, et al. Vertical profiles of phosphorus fractions in the sediment in a chain of reservoirs in North China: Implications for pollution source, bioavailability, and eutrophication [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 704: 135318. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135318 [5] 马腾飞, 罗汉金, 李志敏, 等. 水源水库富营养化趋势分析及预警模型构建 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2020, 43(5): 145-153. MA T F, LUO H J, LI Z M, et al. Eutrophication trend analysis and forewarning model construction of water source reservoirs [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 43(5): 145-153(in Chinese).
[6] BREUNING-MADSEN H, LYNGSIE G, AWADZI T W. Sediment and nutrient deposition in Lake Volta in Ghana due to Harmattan dust [J]. CATENA, 2012, 92: 99-105. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2011.11.018 [7] ZHANG W Q, JIN X, LIU D, et al. Assessment of the sediment quality of freshwater ecosystems in Eastern China based on spatial and temporal variation of nutrients [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017, 24(23): 19412-19421. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-9532-1 [8] 于坤, 张坤, 孙庆业, 等. 董铺水库及入库河流表层沉积物污染状况评价 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(10): 2045-2052. YU K, ZHANG K, SUN Q Y, et al. Assessment of surface sediment pollution in Dongpu Reservoir and its inflow rivers [J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 2019, 28(10): 2045-2052(in Chinese).
[9] 黄廷林, 刘飞, 史建超. 水源水库沉积物中营养元素分布特征与污染评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(1): 166-172. HUANG T L, LIU F, SHI J C. Distribution characteristics and pollution status evaluation of sediments nutrients in a drinking water reservoir [J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 37(1): 166-172(in Chinese).
[10] 张明, 唐访良, 张伟, 等. 杭州青山水库沉积物中多环芳烃的垂直分布、来源及潜在生态风险 [J]. 地球与环境, 2020, 48(4): 405-412. doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2020.48.065 ZHANG M, TANG F L, ZHANG W, et al. Vertical profile, source and potential ecological risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediment cores from the Qingshan Reservoir of Hangzhou [J]. Earth and Environment, 2020, 48(4): 405-412(in Chinese). doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2020.48.065
[11] 叶宏萌, 袁旭音, 李国平, 等. 闽北建溪流域表层沉积物营养元素分布特征及生态风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(11): 2481-2488. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017121801 YE H M, YUAN X Y, LI G P, et al. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of nutrient elements in surface sediments of Jianxi Watershed in northern Fujian [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(11): 2481-2488(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017121801
[12] 蓝雪春, 张玲. 湖漫水库面源污染特征解析 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2022, 44(8): 1042-1045,1053. LAN X C, ZHANG L. Characteristics analysis of nonpoint source pollution in Human Reservoir [J]. Environmental Pollution and Control, 2022, 44(8): 1042-1045,1053(in Chinese).
[13] 李其峰. 基于典型入库径流的水库供水预警研究: 以温岭市湖漫水库为例 [J]. 浙江水利科技, 2017, 45(1): 64-68,72. LI Q F. Study on the warning of water supply for the reservoir based on the typical reservoir runoff [J]. Zhejiang Hydrotechnics, 2017, 45(1): 64-68,72(in Chinese).
[14] 蓝雪春, 张玲. 湖漫水库面源污染源强分析 [J]. 水电能源科学, 2022, 40(9): 79-81,133. LAN X C, ZHANG L. Analysis of nonpoint source pollution intensity of human reservoir [J]. Water Resources and Power, 2022, 40(9): 79-81,133(in Chinese).
[15] 郑珍芝, 王文初, 吴星星. 温岭市湖漫水库水质状况与污染防治对策分析 [J]. 能源环境保护, 2019, 33(3): 60-64. ZHENG Z Z, WANG W C, WU X X. Water quality status and pollution prevention measures of Human Reservoir in Wenling [J]. Energy Environmental Protection, 2019, 33(3): 60-64(in Chinese).
[16] 范成新, 钟继承, 张路, 等. 湖泊底泥环保疏浚决策研究进展与展望 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2020, 32(5): 1254-1277. doi: 10.18307/2020.0506 FAN C X, ZHONG J C, ZHANG L, et al. Research progress and prospect of environmental dredging decision-making of lake sediment [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2020, 32(5): 1254-1277(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2020.0506
[17] 梁佳文, 阳涛, 韩雪, 等. 城市河道底泥疏浚适宜深度初步研究: 以伊通河为例 [J]. 环境生态学, 2020(11): 81-90. LIANG J W, YANG T, HAN X, et al. Preliminary research on the appropriate depth of sediment dredging in urban river: Case study on Yitong River [J]. Environmental Ecology, 2020(11): 81-90(in Chinese).
[18] 王亚平, 黄廷林, 周子振, 等. 金盆水库表层沉积物中营养盐分布特征与污染评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(3): 659-665. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.03.2016071305 WANG Y P, HUANG T L, ZHOU Z Z, et al. Distribution and pollution evaluation of nutrients in surface sediments of Jinpen Reservoir [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(3): 659-665(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.03.2016071305
[19] ZHANG Z B, LV Y F, ZHANG W, et al. Phosphorus, organic matter and nitrogen distribution characteristics of the surface sediments in Nansi Lake, China [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2015, 73(9): 5669-5675. doi: 10.1007/s12665-014-3821-5 [20] 张涵丹, 党宁, 林雪锋, 等. 长潭水库水体沉积物营养盐分布特征及其污染评价 [J]. 水土保持研究, 2023, 30(2): 438-443,450. doi: 10.13869/j.cnki.rswc.2023.02.041 ZHANG H D, DANG N, LIN X F, et al. Distribution characteristics of nutrients and pollution status evaluation of sediments in changtan reservoir [J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2023, 30(2): 438-443,450(in Chinese). doi: 10.13869/j.cnki.rswc.2023.02.041
[21] 王慎, 张思思, 许尤, 等. 不同水温分层水库沉积物间隙水营养盐垂向分布与细菌群落结构的关系 [J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(6): 2753-2763. WANG S, ZHANG S S, XU Y, et al. Relationship between the vertical distribution of nutrients and bacterial community structures in sediment interstitial waters of stratified reservoirs with different water temperatures [J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(6): 2753-2763(in Chinese).
[22] 夏建东, 庞燕, 高亚萍, 等. 城市化对甘肃省牛谷河沉积物氮磷分布的影响 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2020, 43(1): 45-54. XIA J D, PANG Y, GAO Y P, et al. Effect of urbanization on distribution of nitrogen and phosphorus in sediments of Niugu River in Gansu Province [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 43(1): 45-54(in Chinese).
[23] 何宜颖, 陈建耀, 高磊, 等. 惠州白盆珠水库沉积物营养元素时空变化特征及源解析 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2020, 29(7): 1419-1426. HE Y Y, CHEN J Y, GAO L, et al. Spatial and temporal variations of sediment nutrients and relevant sources identification in baipenzhu reservoir, Guangdong Province [J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 2020, 29(7): 1419-1426(in Chinese).
[24] ZHU Y Y, JIN X, TANG W Z, et al. Comprehensive analysis of nitrogen distributions and ammonia nitrogen release fluxes in the sediments of Baiyangdian Lake, China [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2019, 76: 319-328. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2018.05.024 [25] 陈小华, 钱晓雍, 李小平, 等. 洱海湖心区沉积柱芯营养盐垂向分布及时间演化特征 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2016, 25(10): 1693-1698. CHEN X H, QIAN X Y, Li X P, et al. The vertical distributions and temporal evolution characteristics and of nutrient concenctration in the sediment core at the center of Lake Erhai [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2016, 25(10): 1693-1698(in Chinese).
[26] 张明, 唐访良, 姚建良, 等. 杭州分水江水库沉积物中碳、氮、磷的分布及污染评价[C]//中国环境科学学会2022年科学技术年会论文集(三), 2022: 436-442. ZHANG M, TANG F L, YAO J L, et al. Distribution and pollution assessment of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in sediments of Fenshuijiang Reservoir, Hangzhou[C]//Proceedings of the 2022 Science and Technology Annual Meeting of the Chinese Society of Environmental Sciences, 2022: 436-442(in Chinese).
[27] 包宇飞, 胡明明, 王殿常, 等. 黄柏河梯级水库沉积物营养盐与重金属分布特征及污染评价 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(5): 1005-1016. BAO Y F, HU M M, WANG D C, et al. Distribution and pollution assessment of nutrients and heavy metals in sediments of the cascade reservoirs in huangbai river [J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 2021, 30(5): 1005-1016(in Chinese).
[28] 孟子豪, 杨德国, 陈康, 等. 柘林水库表层沉积物氮、磷、有机质的时空分布及污染评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2023, 42(1): 138-149. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2022080103 MENG Z H, YANG D G, CHEN K, et al. Temporal-spatial distribution and pollution assessment of nitrogen, phosphorus and organic matter in surface sediments of Zhelin Reservoir [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2023, 42(1): 138-149(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2022080103
[29] 包宇飞, 李姗泽, 王雨春, 等. 磷矿背景区水库沉积物碳氮磷空间分布及污染评价分析[C]//水库大坝和水电站建设与运行管理新进展. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2022: 781-788. BAO Y F, LI S Z, WANG Y C, et al. Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in reservoir sediments in phosphate rock background areas[C]//New progress in the construction and operation management of reservoir DAMS and hydropower stations. Beijing: China Waterpower Press, 2022: 781-788(in Chinese).
[30] 王洪伟, 王少明, 张敏, 等. 春季潘家口水库沉积物-水界面氮磷赋存特征及迁移通量 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(9): 4284-4293. WANG H W, WANG S M, ZHANG M, et al. Occurrence characteristics and transport fluxes of nitrogen and phosphorus at sediment-water interface of Panjiakou Reservoir in spring [J]. China Environmental Science, 2021, 41(9): 4284-4293(in Chinese).
[31] 兰建洪, 刘丰, 郭晓玮, 等. 清林径水库表层沉积物营养盐分布特征及污染评价 [J]. 中国水利水电科学研究院学报, 2021, 19(2): 269-275. LAN J H, LIU F, GUO X W, et al. Pollution characteristics and evaluation of nutrients in surface sediments of Qinglinjing Reservoir [J]. Journal of China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research, 2021, 19(2): 269-275(in Chinese).
[32] 王斌, 黄廷林, 翟振起, 等. 水源水库沉积物碳氮磷分布特征及污染评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2023, 42(4): 1304-1312. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021112205 WANG B, HUANG T L, ZHAI Z Q, et al. Distribution characteristics of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in sediments of water sourcereservoir and pollution assessment [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2023, 42(4): 1304-1312(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021112205
[33] 黄道军, 薛睿康, 李凯, 等. 西北某水库沉积物污染特征与评价 [J]. 西安建筑科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 53(1): 103-108. HUANG D J, XUE R K, LI K, et al. Characteristics and evaluation of pollution in sediments of a reservoir in Northwest China [J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Architecture & Technology, 2021, 53(1): 103-108(in Chinese).
[34] 唐永杰, 夏婧业, 陈雅娟, 等. 独流减河水体及沉积物质量评价 [J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2019, 36(4): 537-544. TANG Y J, XIA J Y, CHEN Y J, et al. Quality assessment of water and sediment in Duliujianhe River [J]. Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019, 36(4): 537-544(in Chinese).
[35] 余辉, 张文斌, 卢少勇, 等. 洪泽湖表层底质营养盐的形态分布特征与评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2010, 31(4): 961-968. YU H, ZHANG W B, LU S Y, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics of surface sediments nutrients in Lake Hongze and their pollution status evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Science, 2010, 31(4): 961-968(in Chinese).
[36] 刘坤, 王仕禄, 檀迪, 等. 乌江流域三个梯级水库氮磷形态的比较研究 [J]. 地球与环境, 2022, 50(6): 821-830. doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2022.50.037 LIU K, WANG S L, TAN D, et al. Comparative study on nitrogen and phosphorus species of three cascade reservoirs in Wujiang River Basin [J]. Earth and Environment, 2022, 50(6): 821-830(in Chinese). doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2022.50.037
[37] 冀峰, 王国祥, 韩睿明, 等. 无锡市农村黑臭河流沉积物营养盐垂向分布与污染特征分析 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(7): 3462-3470. JI F, WANG G X, HAN R M, et al. Vertical distribution and pollution characteristics of nutrient in sediment of rural malodorous black river in Wuxi City, China [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2016, 10(7): 3462-3470(in Chinese).
[38] 单保庆, 菅宇翔, 唐文忠, 等. 北运河下游典型河网区水体中氮磷分布与富营养化评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(2): 352-358. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2012.02.017 SHAN B Q, JIAN Y X, TANG W Z, et al. Temporal and spatial variation of nitrogen and phosphorus and eutrophication assessment in downstream river network areas of north canal river watershed [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Science, 2012, 33(2): 352-358(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2012.02.017
[39] YUAN H Z, TAI Z Q, LI Q, et al. Characterization and source identification of organic phosphorus in sediments of a hypereutrophic lake [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 257: 113500. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113500 [40] MEYERS P A. Preservation of elemental and isotopic source identification of sedimentary organic matter [J]. Chemical Geology, 1994, 114(3/4): 289-302. -



 下载:
下载: