-
重金属污染由于其毒性、生物蓄积性和在自然环境中的持久性,已成为当今主要的环境问题之一。即使是微量的重金属也对人体有害,特别是镉(Cd)[1]。毒理学研究表明,Cd是毒性最强的重金属之一[2],并被全球癌症与科研组织列入第一致癌物[3]。其进入生物体后,会在生物体内富集,并通过食物链进入人体,最终会诱发人体的各种疾病。目前,去除污水中镉离子最常见的方式有化学沉淀法[4]、离子交换法[5]、膜分离法[6]、吸附法[7]等。吸附法因其高效、成本低、易操作、对环境无二次危害等优点,成为目前应用最广的方法。粉煤灰(fly ash,FA)是燃煤电厂中产生的固体废弃物。我国每年都会产生大量的FA,无法被有效利用,并且会导致环境污染。SiO2、Al2O3是FA的主要组成成分,此外,FA中富含SiO2-、Al2O3-等含有许多微小的活性通道的活性玻璃体颗粒,因而有利于吸附废水中的重金属离子[8]。但FA的比表面积和孔径较小,导致其吸附容量较小,可通过对其改性来增加吸附容量。相比于传统的改性方法如高温煅烧,水浴共沉淀法制备简便,能耗与成本较低。在碱性条件下通过水浴共沉淀法制备的层状双金属氢氧化物(layered double hydroxides,LDHs),因其具有高比表面积、粗糙多孔等优异性能而被广泛应用于吸附领域。其结构呈八面体[9],通常情况下是以带正电荷的二价金属氢氧化物和三价金属氢氧化物为层板,层间由带负电的阴离子构成[10]。张翔凌等[11]在碱性条件下采用水浴-共沉淀法制备了ZnAl-LDHs、ZnFe-LDHs并覆膜改性麦饭石,发现ZnFe-LDHs改性麦饭石的吸附性能远高于ZnAl-LDHs,且有较好的再生性能。故本研究拟用吸附和再生性能较好的ZnFe-LDHs作为改性前体,并将其负载于粉煤灰,制备ZnFe-LDHs改性粉煤灰(ZFLFA),且探究了其对Cd2+吸附的影响因素及可能的吸附机理,以期为改性粉煤灰应用于废水中Cd2+的吸附提供参考。
-
本研究所用主要仪器为:GBC-XplorAA原子吸收分光光度计,SHA-BA水浴恒温振荡器,DP-01无油真空泵,UPY-Ⅲ-103纯水/超纯水制造系统,GFL-70鼓风干燥箱。本研究所用的粉煤灰来自大唐河南电厂,主要试剂为购自凯马特化工科技有限公司的ZnCl2(AR)、FeCl3·6H2O(AR)、NaOH(AR)、CdCl2(AR)等。
-
在碱性条件下采用水浴共沉淀法制备ZFLFA。将质量为100 g的粉煤灰置于1 L烧杯中,后将2 mol·L−1的ZnCl2和1 mol·L−1的FeCl3水溶液各250 mL同时添加到烧杯中。将混合物加热至恒定80 ℃,同时搅拌4 h。在此过程中,将质量浓度为25%的NaOH溶液滴加到混合物中,以维持pH为11左右。搅拌4 h后,将混合物于80 ℃陈化16 h。将陈化后的混合物用去离子水洗涤,直到最终流出物为中性(pH=7)。将洗涤后的混合物继续在60 ℃下干燥,最终获得ZFLFA。
-
采用火焰原子吸收分光光度法测定Cd2+质量浓度。使用比表面与孔隙度分析仪(ASAP 2 460,美国麦克仪器公司)、扫描电子显微镜(TESCAN MIRA4,捷克泰思肯公司)、X射线荧光光谱仪(ARL QUANT X,赛默飞世尔科技(中国)有限公司)、X射线粉末衍射仪(Smartlae-SE,日本株式会社理学公司)、傅立叶红外光谱仪(V80,德国布鲁克公司)对改性前后粉煤灰进行表征分析。
-
1)对比实验。称取0.3 g的FA和ZFLFA置于锥形瓶中,加入体积为100 mL、初始质量浓度为100 mg·L−1的模拟含镉废水,pH调节为6,在25 ℃恒温、转速160 r·min−1条件下振荡 120 min后,测定剩余Cd2+的质量浓度。
2)投加量对吸附效果的影响。称取一定质量(0.05、0.1、0.2、0.3、0.4、0.5、1.0 g)的ZFLFA置于锥形瓶中,加入体积为100 mL、初始质量浓度为100 mg·L−1的模拟含镉废水,pH调节为6,在25 ℃恒温、转速160 r·min−1条件下振荡 120 min后,测定剩余Cd2+的质量浓度。
3) pH对吸附效果的影响。称取0.3 g ZFLFA置于锥形瓶中,加入体积为100 mL、初始质量浓度为100 mg·L−1的含镉废水,调节不同pH分别为3、4、5、6、7、8,在25 ℃恒温、转速160 r·min−1条件下振荡120 min后,测定剩余Cd2+的质量浓度。
4)吸附等温线实验。称取0.3 g ZFLFA置于锥形瓶中,加入体积为100 mL、不同初始质量浓度(10、50、100、150、200、300、400、500 mg·L−1)的模拟含镉废水,pH调节为6,在25 ℃恒温、转速160 r·min−1条件下振荡120 min后,测定剩余Cd2+的质量浓度。
对实验数据进行Langmuir模型(式(1))、Freundlich模型(式(2))、Temkin模型(式(3))拟合。
式中:qe为单分子层吸附量,mg·g−1;Ce为吸附平衡时Cd2+的质量浓度,mg·L−1;qm为理论最大饱和吸附量,mg·g−1;KL为Langmuir平衡常数,L·mg−1;KF为Freundlich平衡常数,mg1-n·g−1·Ln;n为与吸附强度或吸附程度有关的特征常数;R为理想气体常数,8.314 J·(mol·K)−1;T为绝对温度,K;KT,b为吸附常数。
5)吸附动力学实验。称取0.3 g ZFLFA置于锥形瓶中,加入体积为100 mL、初始质量浓度为100 mg·L−1的含镉废水,pH调节为6,在25 ℃恒温、转速160 r·min−1条件下分别振荡5、10、15、20、30、60、90、120、180 min后,测定剩余Cd2+的质量浓度。
对实验数据进行准一级动力学模型(式(4))、准二级动力学模型(式(5))、Elovich动力学模型(式(6))与颗粒内扩散模型拟合(式(7))。
式中:qt为t时刻吸附量,mg·g−1;qe为平衡吸附量,mg·g−1;t为吸附时间,min;K1为准一级动力学吸附速率常数,min−1; K2为准二级动力学吸附速率常数,g·(mg·min)−1;a、b为平衡速率常数,mg·g−1;Ks为颗粒内扩散系数,mg·(kg·min1/2)−1;C为常数,mg·g−1。
6)吸附热力学实验。设计不同温度(288.15、293.15、298.15、303.15、308.15、318.15 K),称取0.3 g ZFLFA置于锥形瓶中,加入体积为100 mL、初始质量浓度为100 mg·L−1的模拟含镉废水,pH调节为6,在25 ℃恒温、转速160 r·min−1条件下振荡120 min后,测定剩余Cd2+的质量浓度。
采用热力学参数吉布斯自由能(ΔGθ)、焓变(ΔHθ )和熵变(ΔSθ )来反应热力学效应.热力学方程如式(8)、式(9)、式(10)所示。
式中:Kc为平衡常数;CAe为吸附平衡时溶液中被吸附的镉离子质量浓度,mg·L−1;Ce为吸附平衡时溶液中剩余的镉离子质量浓度,mg·L−1;ΔGθ为吉布斯自由能,kJ·mol−1;ΔHθ为焓变,kJ·mol−1;ΔSθ为熵变,J·(mol·K)−1;R为理想气体常数,8.314 J·(mol·K)−1;T为绝对温度,K。
7)再生利用实验。称取0.3 g ZFLFA放入3个锥形瓶中,加入体积为100 mL、初始质量浓度为100 mg·L−1的模拟含镉废水,pH调节为6,在25 ℃恒温、转速160 r·min−1条件下振荡120 min,吸附完成后用不同浓度的NaCl溶液(1、2、4 mol·L−1)作为解吸剂,对达到吸附饱和的ZFLFA进行解吸,将解吸后的ZFLFA再次吸附Cd2+,吸附完成后测定剩余Cd2+的质量浓度,重复3次。
-
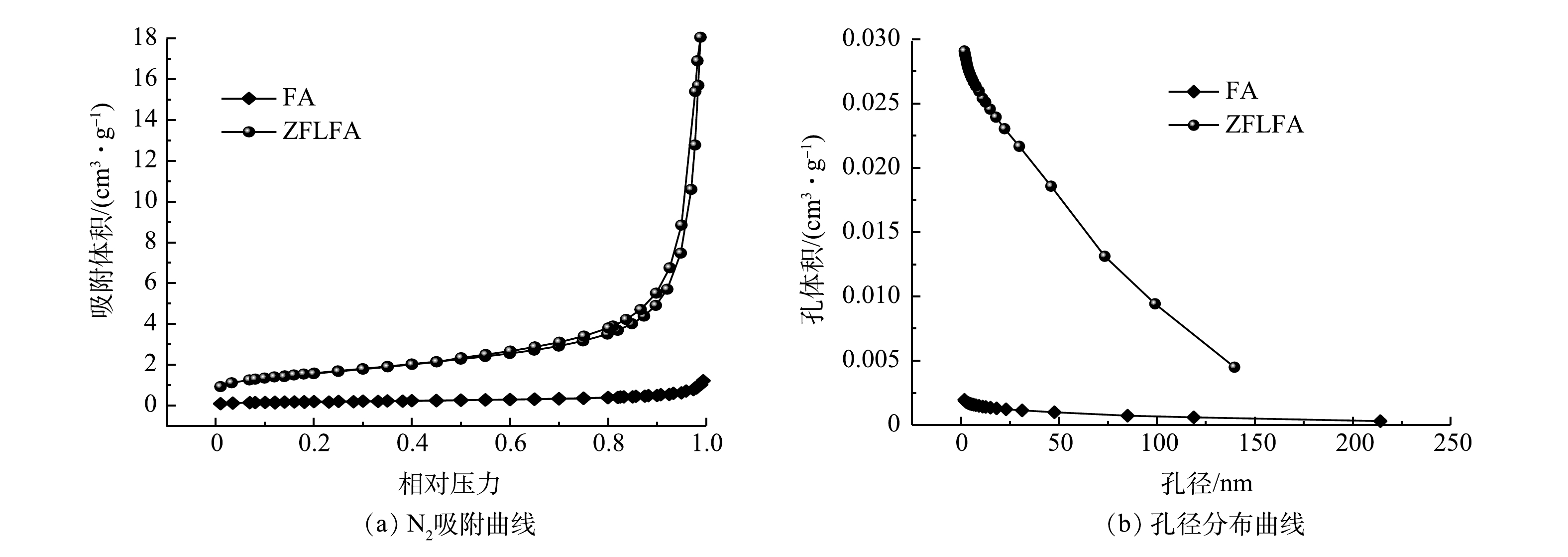
1) BET分析。如图1所示,FA与ZFLFA的N2吸脱附曲线均属于Ⅳ型吸附等温线,磁滞线的形状接近H3型。这表明ZFLFA具有介孔结构[12]。当相对压力较低时,改性前后FA的吸附量均较低,此时N2在FA表面发生单分子层吸附;在较高相对压力时(P/P0>0.8),吸附量迅速增加,这说明N2可能在FA表面发生了多分子层吸附[13]。
由表1可知,ZFLFA的BET比表面积为5.68 m2·g−1,比FA增加了近9倍。这可为吸附Cd2+提供更多的吸附位点[14]。平均孔径(19.0 nm)也比FA增大了近1倍,孔径属于介孔(2 nm<d<50 nm),这说明ZnFe-LDHs改性改善了FA孔隙结构,可极大地提升吸附性能。
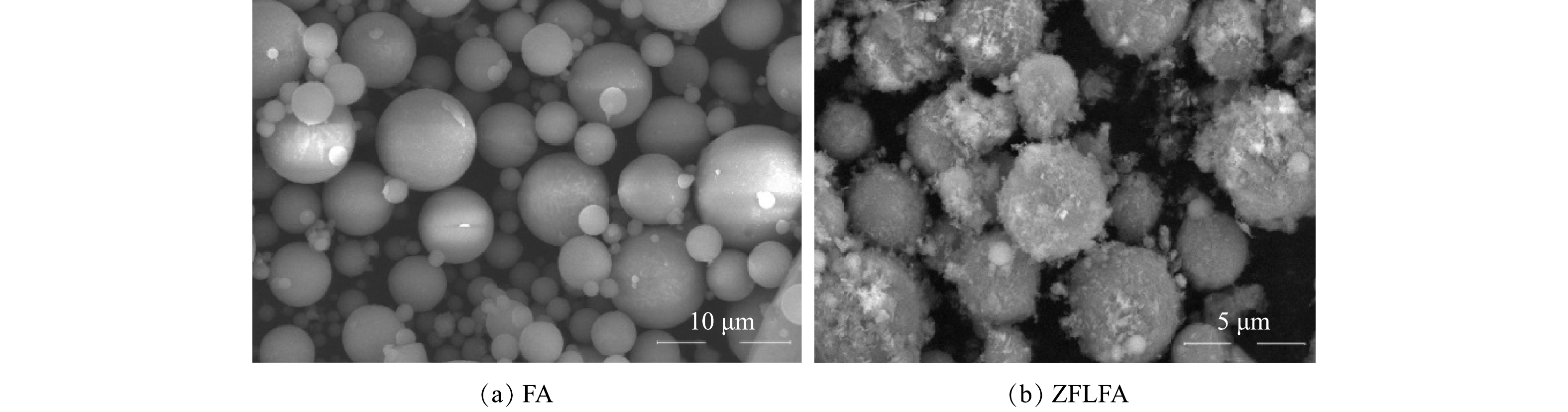
2) SEM分析。由图2(a)可见,FA为较为规则的圆球体,大小不同,表面较为光滑,未观察到孔隙结构。这与JOSRPH等[15]的研究结果一致。由图2(b)可见,改性后的FA表面有大量的附着物,使FA表面变得粗糙,这极大地提高了其比表面积。
3) XRF分析。由表2可见,FA的主要成分为SiO2、Al2O3、Fe2O3、CaO、K2O,此外,还含有微量的Na、Mg、Zn元素。经过ZnFe-LDHs改性后的FA组成成分含量发生了变化,SiO2和Al2O3物质占比分别下降了12.73%和7.61%,ZnO、Fe2O3占比分别升高了18.82%和9.94%,增加的Zn、Fe摩尔比为1.91。
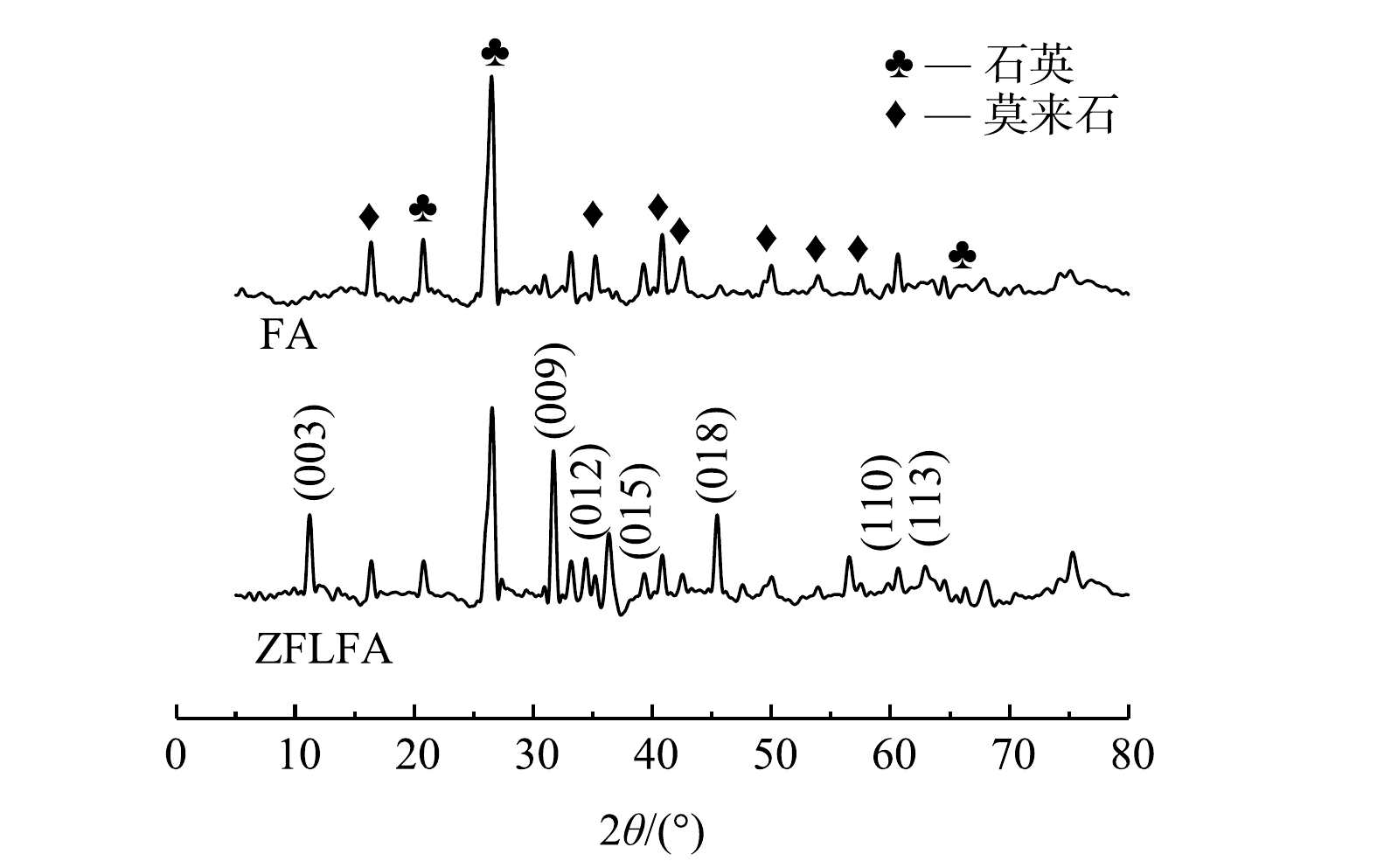
4) XRD分析。如图3所示,FA主要是由莫来石和石英组成。石英衍射峰主要在20.86°、26.64°附近;莫来石的衍射峰则主要在39.47°、40.29°、42.45°、45.79°附近。经ZnFe-LDHs改性后的FA,不仅保有FA的衍射峰,并在2θ为11.27°(003)处出现层间水分子[16],并且在31.70°、35.75°、39.14°、46.78°、60.3°、61.9°处出现7个衍射峰,分别对应(009)、(012)、(015)、(018)、(110)、(113)晶面。这与ZnFe-LDHs的典型衍射峰一致[17-19]。由XRF结果可知,增加的Zn、Fe摩尔比为1.91,结合XRD分析结果可断定ZnFe-LDHs成功负载FA上。
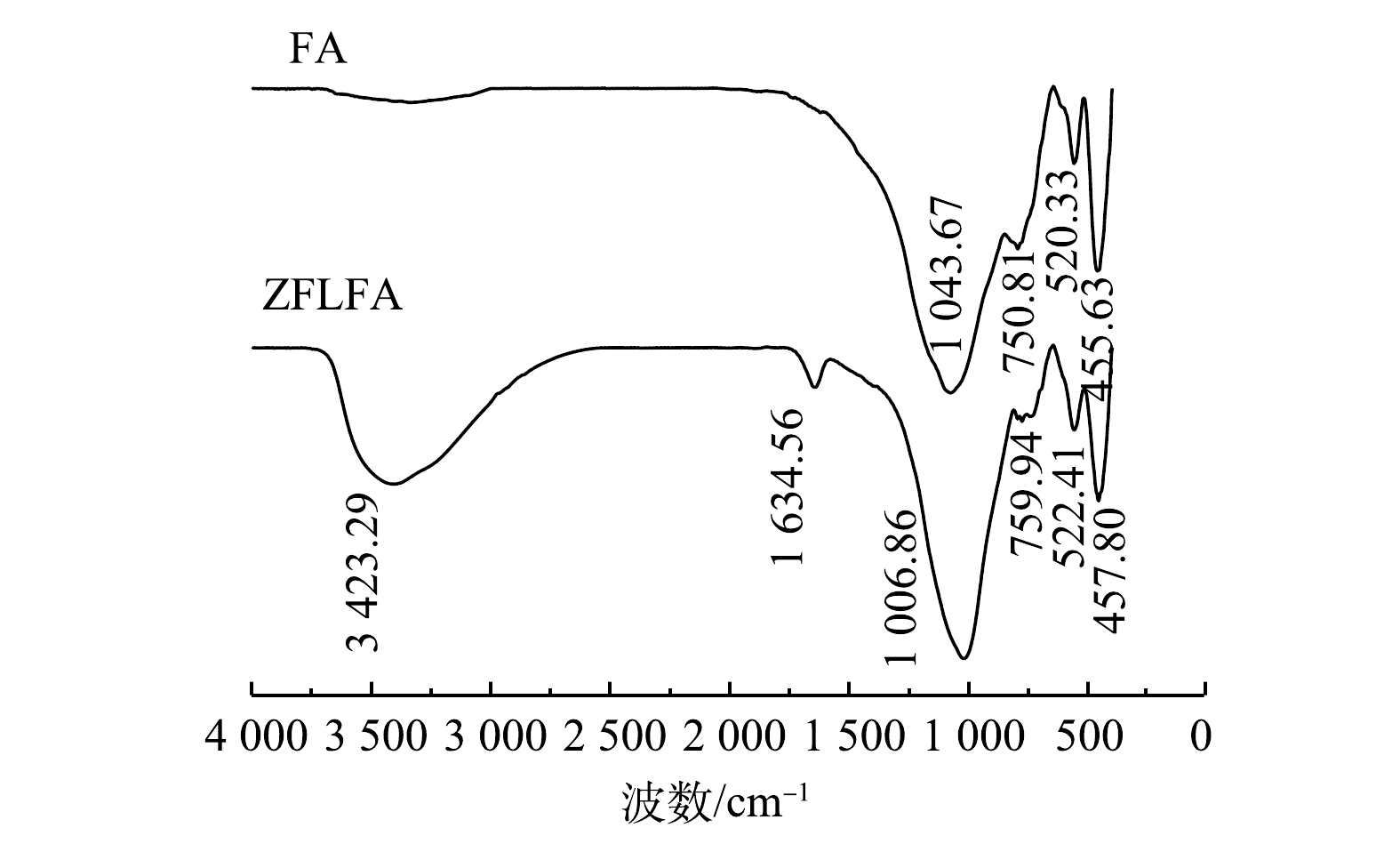
5) FTIR分析。如图4所示,FA表面含有丰富的官能团。455.63 cm−1处为Si—O的弯曲振动峰[20],520.33 cm−1处为Al—O—Al的对称伸缩振动峰,750.81 cm−1处为Si—O—Si的对称伸缩振动峰,1 043.67 cm−1处为硅氧四面体不对称的拉伸振动峰。这与具有吸附能力的分子筛结构相似[21]。在改性后的FA中,出现2个新的衍射峰:1 634.56 cm−1处为夹层水分子羟基官能团的H—O—H伸缩振动峰;3 423.29 cm−1处为LDHs层间水分子的O—H伸缩振动带[22],且峰强较大。这表明FA表面增加了大量的羟基基团,羟基基团能与Cd2+发生络合配位反应[23],可有效的去除废水中的Cd2+。
-
FA与ZFLFA除镉效果的对比结果如表3所示。由表3可见,ZFLFA较FA的吸附容量有了较大提高,与表征结果分析一致。
-
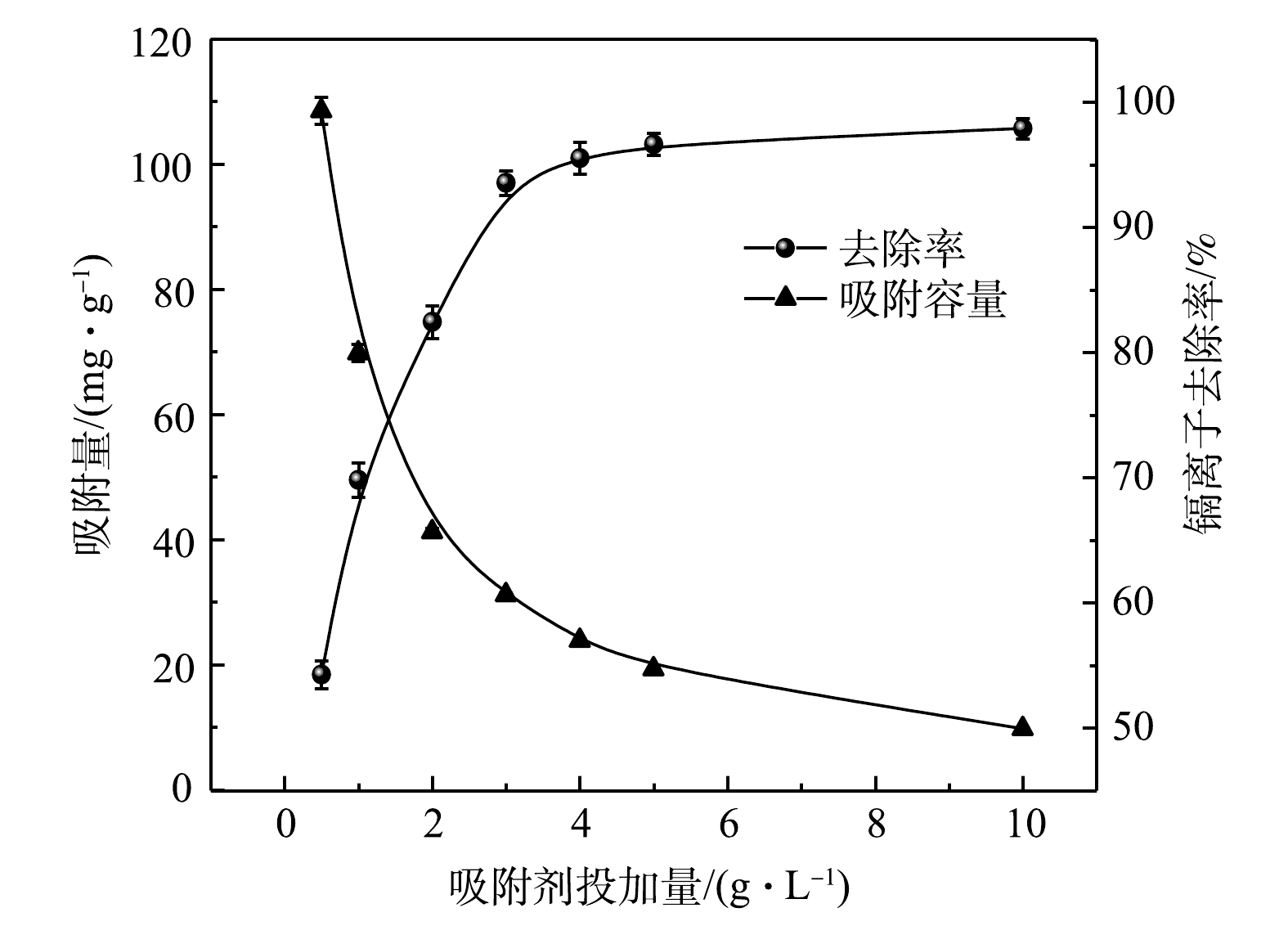
如图5所示,随着ZFLFA投加量的增加,吸附量持续降低,对Cd2+去除率先上升后趋于平缓;当ZFLFA投加量由0.5 g·L−1增加到3 g·L−1时,Cd2+去除率变化最为明显,由54.2%快速增加到93.5%,此时吸附量为31.2 mg·g−1,当从3 g·L−1增至10 g·L−1时,去除率增长变缓,而吸附量持续减小。溶液中ZFLFA的投加量增加,提供的吸附位点也随之增多,有利于对Cd2+的吸附;当投加量过大时,吸附反应已经达到饱和,吸附位点出现过剩现象,导致Cd2+去除率不再显著增加,ZFLFA利用率降低。因此,综合考虑对Cd2+去除效果与ZFLFA利用率等因素,选择3 g·L−1作为后续实验研究的最佳投加量。
-
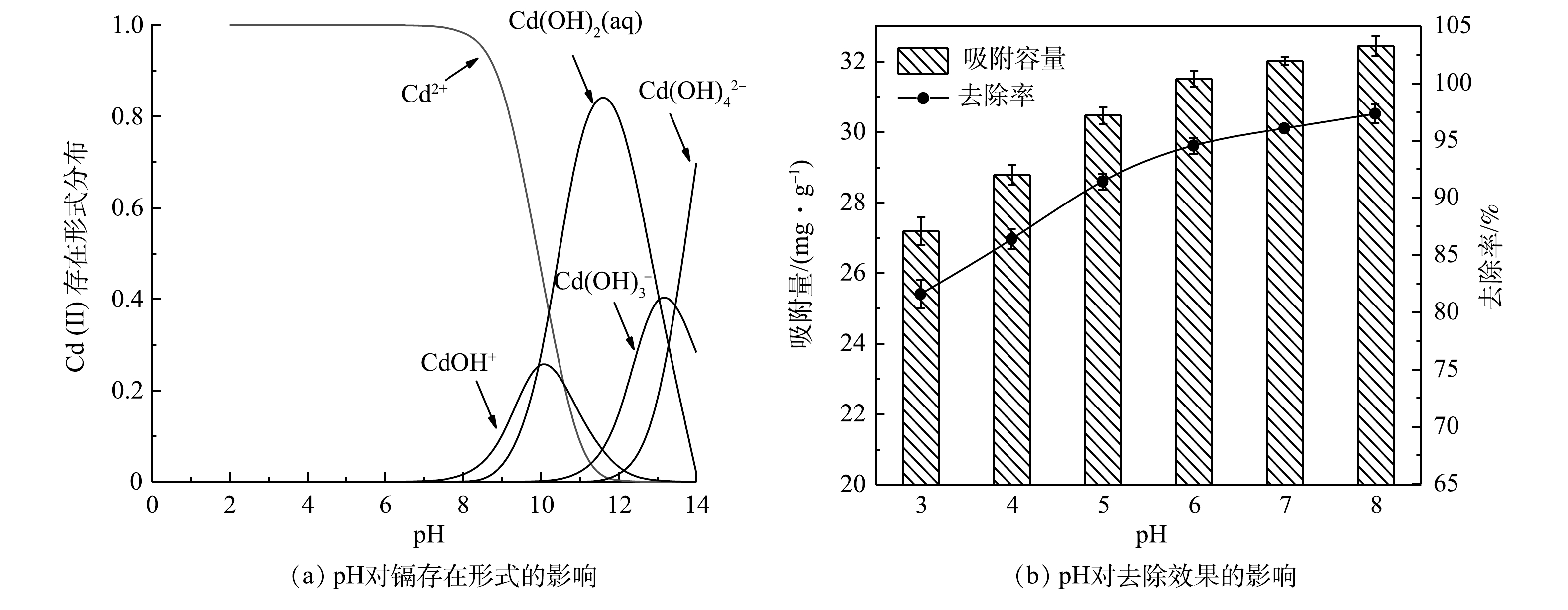
不同pH条件下Cd的存在形式不同,使用Visual MINTEQ 3.1模拟了不同pH下Cd2+的水解情况。如图6(a)所示,Cd的存在形式分别为Cd2+、Cd(OH)+、Cd(OH)2(aq)、Cd(OH)3−、Cd(OH)42-。当pH<7时,Cd主要以Cd2+形式存在;pH>7后,Cd(OH)+配合物浓度逐渐增加;pH>8后,Cd(OH)2(aq)逐渐增加;pH>12后,Cd2+水解情况较为复杂,主要以沉淀形式存在。故pH<8时,主要以ZFLFA的吸附作用去除水中Cd2+。这与杨雅芃等[24]的研究结果相同。
如图6(b)所示,ZFLFA对Cd2+的吸附量和去除率随着pH增加而升高。pH在3~6时,吸附量由27.1增加至31.5 mg·g−1,去除率由81.5%增长至94.5%。之后随着pH的增加,吸附量和去除率增长变缓,吸附量增长至32.4 mg·g−1,去除率增长至97.3%。当pH较低时,水中H+浓度高,H+会使ZFLFA表面质子化,不利于对阳离子Cd2+的吸附;此外,溶液中H+与Cd2+形成竞争关系,H+会抢占ZFLFA的吸附位点,导致Cd2+的去除率较低。
-
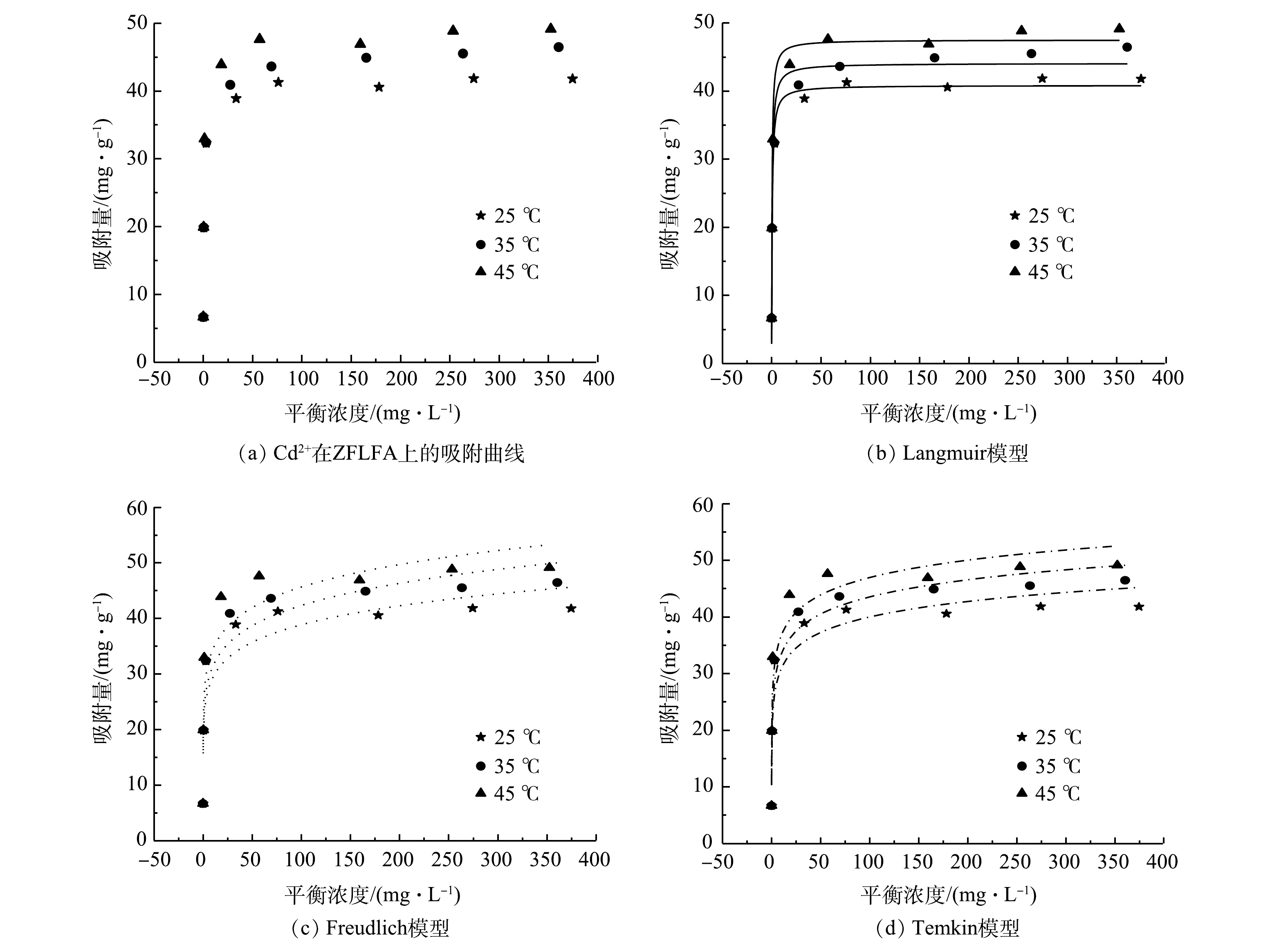
由图7(a)可见,在Cd2+浓度较低时,在25、35、45 ℃下ZFLFA的平衡吸附量均随着Cd2+质量浓度的增加快速升高;当Cd2+质量浓度超过150 mg·L−1后,平衡吸附量增长变缓,最终趋于稳定,进而达到吸附饱和。在Cd2+质量浓度较低时,ZFLFA未达到吸附饱和,吸附剩余位点较多,吸附容量随Cd2+质量浓度的增加而升高;但随Cd2+质量浓度进一步增加,吸附位点逐渐被占据,或者被新生成的沉积物掩盖,吸附达到饱和,吸附容量则不再增加。由表4以及Langmuir(图7(b))、Freundlich(图7(c))、Temkin(图7(d))模型的拟合结果可见,ZFLFA对Cd2+的吸附在3个温度条件下的Langmuir模型、Temkin模型R2均高于0.9,Freundlich模型均低于0.9。这说明ZFLFA对Cd2+的吸附更符合Langmuir和Temkin模型。符合Temkin模型说明ZFLFA对Cd2+的吸附过程主要为化学吸附;符合Langmuir吸附等温模型表明ZFLFA对Cd2+的吸附是单分子层主导的吸附过程。理论最大饱和吸附量qm在25、35、45 ℃时分别为40.83、44.07、47.51 mg·g−1,qm随着温度的升高而增加。这归因为以下2点:一是ZFLFA对Cd2+的吸附过程为吸热过程,升高温度有利于反应的正向进行;二是随着温度升高,溶液中混乱度增加,使ZFLFA表面的活性位点与Cd2+的接触概率提高,导致qm增加。Freundlich模型假设非均相表面上的多层吸附,n为与吸附强度或吸附程度有关的特征常数,当1/n<1时,表示吸附容易进行, 3个温度下ZFLFA对Cd2+的吸附特征常数1/n均<1,说明其吸附过程容易发生。
-
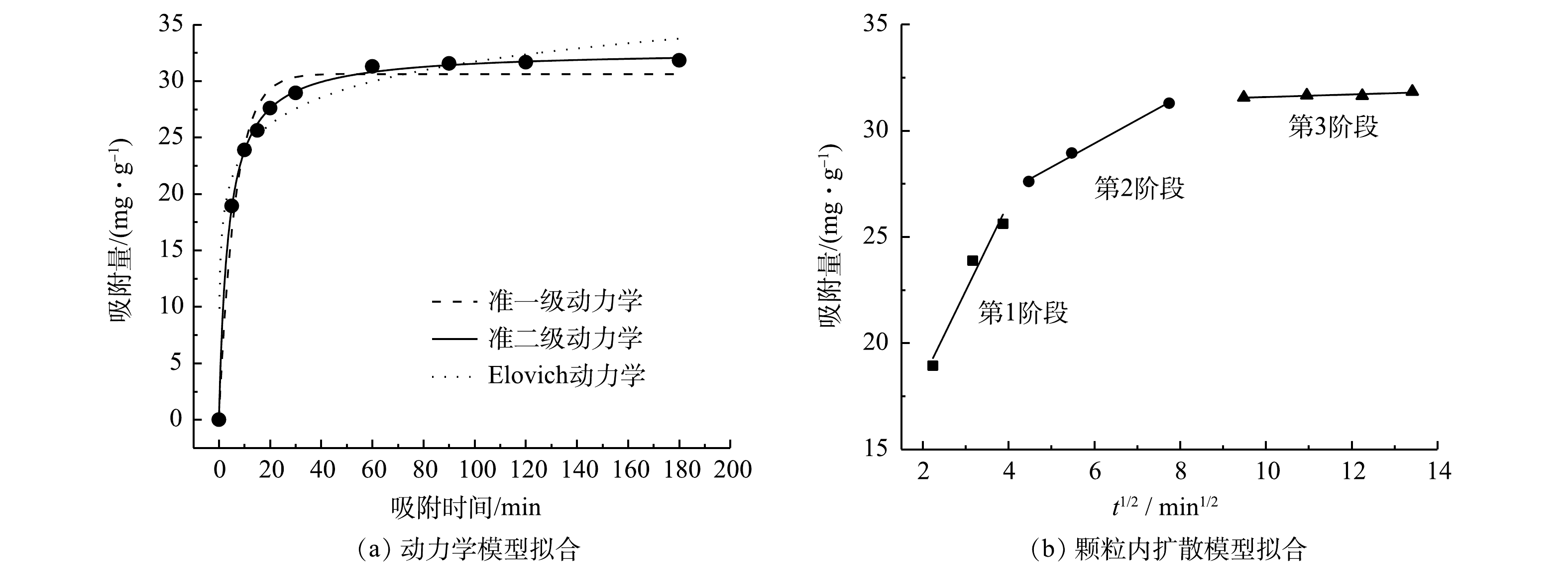
ZFLFA对Cd2+的准一级动力学、准二级动力学、Elovich动力学拟合结果如表5和图8(a)所示。从拟合结果可见,准二级动力学模型可决系数R2最高,说明准二级动力学模型能更好的描述ZFLFA对Cd2+的吸附过程。由准二级动力学拟合得到的理论吸附容量为32.71 mg·g−1,与实验得到的31.8 mg·g−1最为接近。可见ZFLFA对Cd2+的吸附为化学吸附。由Elovich动力学模型拟合结果可见,ZFLFA对Cd2+的吸附速率由表面吸附位点与内扩散共同控制。可通过内扩散动力学模型来揭示吸附过程中实际速率控制步骤。ZFLFA对Cd2+吸附的颗粒内扩散模型的KS1、KS2、KS3分别为4.14、1.11、0.06 mg·(kg·min1/2)−1。这表明:第1阶段的吸附反应速率最快,Cd2+在ZFLFA表面的扩散速率由静电力主导;第2阶段是Cd2+由外表面扩散至吸附剂内表面,速率缓慢,由颗粒内扩散控制;第3阶段为吸附平衡阶段,吸附位点达到饱和[23]。由图8(b)可知,颗粒内扩散模型拟合曲线为一次线性关系,但没有经过原点,说明内扩散不是吸附过程中唯一的速率控制步骤。这与准二级动力学模型、Elovich动力学模型描述一致。因此,ZFLFA对Cd2+的吸附速率是由表面吸附位点与内扩散共同控制,吸附过程以化学吸附为主。
-
由表6可知,在不同温度下,ΔGθ均为负值,说明ZFLFA对Cd2+的吸附过程为自发的反应过程。ΔHθ=49.85 KJ·mol−1,为正值,说明其对Cd2+吸附过程为吸热反应,反应过程中伴有化学反应或键合[25]。ΔSθ=189.39 J·(mol·K)−1,为正值,说明吸附过程中固-液系统中混乱度增加,这与吸附等温实验所得结果相符合。
-
如图9所示,解吸剂的浓度分别为1、2、4 mol·L−1,第1次解吸时的吸附量分别为27.59、28.85、29.15 mg·g−1,解吸效果较好。随着解吸次数的增加,3种浓度条件下解吸剂的吸附量均有所下降,1 mol·L−1解吸剂的吸附量下降速度最快,2、4 mol·L−1的解吸剂变化速度相差较小,故在实际应用中选用2 mol·L−1的解吸剂最为合适。经3次解吸后,吸附量仍可达到19.76 mg·g−1。以上结果表明,ZFLFA具有良好可重复利用性。
-
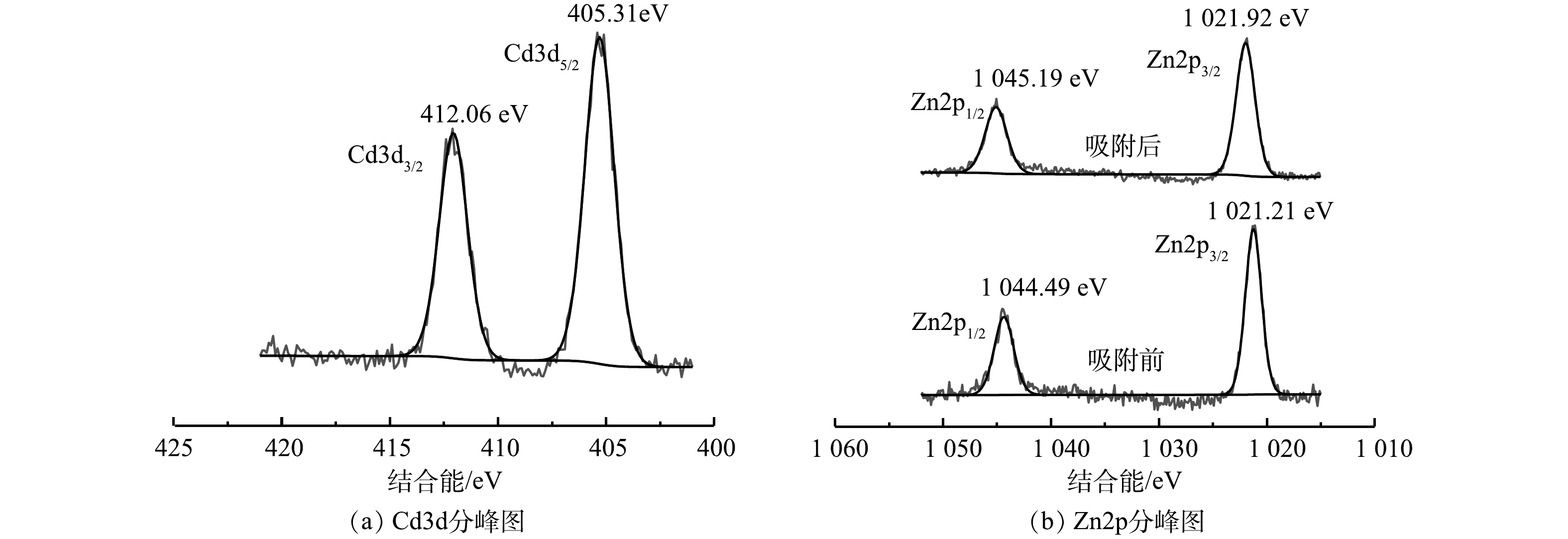
为探究ZFLFA对Cd2+的吸附机理,对吸附前后的ZFLFA进行了XPS分析,结果见图10。由Cd3d分峰图(图10(a))可知,在结合能为405.31 eV和412.06 eV处出现的双特征峰分别为Cd3d5/2和Cd3d3/2,这2个特征峰与Cd(OH)2的特征峰匹配度较高[23],即Cd2+在ZFLFA上有沉淀形式存在,表明ZFLFA去除溶液中的Cd2+的方式有表面络合和表面诱导沉淀。由Zn2p分峰图(图10(b))可见,在结合能为1 021.21 eV和1 044.49 eV处出现的双特征峰分别为Zn2p3/2和Zn2p1/2,并在吸附Cd(II)后结合能升高,这是由于Zn与Cd发生了离子交换[25]。
-
1)改性后的FA表面粗糙多孔,比表面积由0.67 m2·g−1增至5.68 m2·g−1,比改性前增加了近9倍,平均孔径由10.41 nm增至19.00 nm,可为吸附Cd2+提供更多的吸附位点;改性后的FA中增加了大量羟基官能团,可与Cd2+发生络合配位反应,从而提高其对Cd2+的吸附性能。
2) ZFLFA对Cd2+有较好的吸附效果,吸附过程更符合Langmuir吸附等温模型和准二级动力学模型,在25、35、45 ℃时的理论最大饱和吸附容量分别为40.83、44.07、47.51 mg·g−1,吸附过程为以化学吸附为主的单分子层吸附。ZFLFA对Cd2+的吸附速率主要由表面活性位点与内扩散吸附共同控制。
3) ZFLFA对Cd2+吸附为自发吸热反应,温度升高有利于吸附反应的进行。在解吸剂为2 mol·L−1时,经3次解吸后仍对Cd2+有较好的吸附能力,说明ZFLFA具有良好的再生性能。
4) ZFLFA对Cd2+的作用机制包括羟基基团与镉离子发生外表面络合反应、诱导生成氢氧化镉沉淀、离子交换作用。
ZnFe-LDHs改性粉煤灰对模拟废水中镉离子的吸附性能
Adsorption performance of ZnFe-LDHs modified fly ash to cadmium ions in simulated wastewater
-
摘要: 在碱性条件下利用共沉淀法制备了ZnFe层状双金属氢氧化物(ZnFe-LDHs)改性的粉煤灰,用以去除废水中镉离子。采用BET、SEM、XRF、XRD和FTIR等对改性粉煤灰进行了表征,并研究了其对Cd2+吸附特性。结果表明,经ZnFe-LDHs改性后,粉煤灰表面形态发生了较大改变,比表面积与平均孔径均有较大增加;改性粉煤灰对模拟废水中镉离子吸附过程符合Langmuir吸附等温模型和准二级动力学模型,3个温度(25、35、45 ℃)下的理论最大饱和吸附容量分别为40.83、44.07、47.51 mg·g−1,属于以化学吸附为主的单分子层吸附;吸附反应为自发的吸热反应;吸附机理为表面络合、表面诱导沉淀与离子交换。以上研究结果可为实际废水除镉提供参考。Abstract: Fly ash modified by ZnFe layered bimetallic hydroxides (ZnFe-LDHs) was prepared by coprecipitation under alkaline conditions to remove cadmium ions from wastewater. BET, SEM, XRF, XRD, and FTIR were used to characterize ZnFe-LDHs, and its adsorption properties to Cd2+ were studied. The results show that after ZnFe-LDHs modification, the surface morphology of fly ash changed greatly, and the specific surface area and average pore diameter increased significantly. The adsorption process of ZnFe-LDHs to Cd2+ conformed to Langmuir adsorption isothermal model and quasi second-order kinetic model. The theoretical maximum saturated adsorption capacities at three temperatures (25, 35 and 45℃) were 40.83, 44.07 and 47.51 mg·g−1, respectively, which belonged to monolayer adsorption dominated by chemical adsorption. The adsorption reaction was a spontaneous endothermic reaction. The adsorption mechanisms involved surface complexation, surface-induced precipitation and ion exchange. This study can provide a reference for cadmium removal from actual wastewater.
-
Key words:
- fly ash /
- ZnFe-LDHs /
- modification /
- cadmium /
- adsorption
-

-
表 1 改性前后粉煤灰的结构参数
Table 1. Structural parameters of fly ash before and after modification
样品 BET比表面积/(m2·g−1) 平均孔径/nm 总孔容积/(cm3·g−1) FA 0.67 10.4 0.001 9 ZFLFA 5.68 19.0 0.029 表 2 改性前后粉煤灰的XRF分析结果
Table 2. XRF analysis results of fly ash before and after modification %
样品 SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO K2O ZnO 其它 FA 54.04 23.64 9.82 4.27 3.98 0.05 4.25 ZFLFA 37.49 16.03 19.76 2.62 1.95 18.87 3.28 注:表中数据为检测项目占总质量的百分比。 表 3 FA与ZFLFA除镉效果的对比
Table 3. Comparison of cadmium removal effects between FA and ZFLFA
材料 初始质量浓度/(mg·L−1) 投加量/(g·L−1) pH 吸附温度/℃ 吸附时间/min 吸附量/(mg·g−1) FA 100 3 6 25 120 10.88 ZFLFA 100 3 6 25 120 32.12 表 4 ZFLFA对Cd2+的吸附等温线参数
Table 4. Adsorption isotherm parameters of Cd2+ on ZFLFA
温度/℃ Langmuir Freundlich Temkin qm/(mg·g−1) KL/(L·mg−1) R2 KF/(mg1-n·g−1·Ln) 1/n R2 KT b R2 25 40.83 1.770 0.988 1 22.16 0.121 7 0.804 2 250.7 3.951 0.902 5 35 44.07 1.724 0.963 9 23.25 0.130 0 0.865 8 216.7 4.364 0.955 4 45 47.51 2.343 0.981 4 25.95 0.122 5 0.837 3 397.9 4.437 0.932 5 表 5 ZFLFA对Cd2+的吸附动力学参数
Table 5. Adsorption kinetic parameters of Cd2+ on ZFLFA
准一级动力学 准二级动力学 Elovich动力学 qe /(mg·g−1) K1/min−1 R2 qe/(mg·g−1) K2/(g·(mg·min)−1) R2 a/(mg·g−1) b/(mg·g−1) R2 30.64 0.1557 0.9753 32.71 0.0081 0.9991 15.78 3.462 0.9790 表 6 ZFLFA对Cd2+的吸附热力学参数
Table 6. Adsorption thermodynamic parameters of Cd2+ on ZFLFA
温度/K ΔGθ/
(KJ·mol-1)ΔHθ/
(KJ·mol-1)ΔSθ/
(J·(mol·K)-1)R2 288.15 -4.99 49.85 189.39 0.988 3 293.15 -6.02 49.85 189.39 0.988 3 298.15 -6.97 49.85 189.39 0.988 3 303.15 -7.54 49.85 189.39 0.988 3 308.15 -8.62 49.85 189.39 0.988 3 318.15 -10.85 49.85 189.39 0.988 3 -
[1] 李显波, 叶军建, 刘志红, 等. 粉煤灰微波碱熔辅助水热合成沸石及其对水溶液中Cd(Ⅱ)的强化吸附作用[J]. 中南大学学报(英文版), 2018, 25(1): 9-20. [2] MEDELLIN-CASTILLO NA, PADILLA-ORTEGA E, REGULES-MARTINEZ MC, et al. Single and competitive adsorption of Cd(Ⅱ) and Pb(Ⅱ) ions from aqueous solutions onto industrial chili seeds (Capsicum annuum) waste[J]. Sustainable Environment Research, 2017, 27: 61-69. doi: 10.1016/j.serj.2017.01.004 [3] 张彤, 张长平, 陈亚博, 等. 纤维素/沸石复合材料的制备、表征及吸附性能研究[J]. 河北工业大学学报, 2018, 47(6): 80-86. [4] 谭浩强, 吴维, 刘志滨, 等. 化学沉淀法去除水中镉的特性研究[J]. 供水技术, 2010, 4(4): 9-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9353.2010.04.003 [5] 杨莉丽, 康海彦, 李娜, 等. 离子交换树脂吸附镉的动力学研究[J]. 离子交换与吸附, 2004, 4(2): 138-143. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-5493.2004.02.007 [6] 王岩, 王玉军, 骆广生, 等. 中空纤维膜萃取镉离子的研究[J]. 化学工程, 2002(5): 62-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9954.2002.05.013 [7] XU H, HU X J, CHEN Y H, et al. Cd(II) and Pb(II) absorbed on humic acid-iron-pillared bentonite: Kinetics, thermodynamics and mechanism of adsorption[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2021, 612: 126005. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.126005 [8] 黄训荣, 赵航航, 张贵宾, 等. 改性粉煤灰对废水中镉的吸附作用[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(9): 3215-3223. [9] SHI Y L, LI J Q, ZHANG B Y, et al. Tuning electronic structure of CoNi LDHs via surface Fe doping for achieving effective oxygen evolution reaction[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 565: 150506. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.150506 [10] CHEERA P, HUA T, QIN Q L, et al. An overview of semiconductors/layered double hydroxides composites: Properties, synthesis, photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical applications[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2019, 289: 111114. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111114 [11] 陈丽红, 张翔凌, 何春艳, 等. Zn-LDHs覆膜改性麦饭石对Cd(Ⅱ)吸附性能及其作用机理研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2019, 39(12): 4004-4014. [12] JOHNSTON A L, LESTER E, WILLIAMS O, et al. Understanding layered double hydroxide properties as sorbent materials for removing organic pollutants from environmental waters[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2021, 9(4): 105197. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.105197 [13] LI H, DAI M W, DAI S L, et al. Methylene blue adsorption properties of mechanochemistry modified coal fly ash[J]. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment:An International Journal, 2018, 24(8): 1-9. [14] YUAN Z Y, REN T Z, VANTOMME A, et al. Facile and generalized preparation of hierarchically mesoporous macroporous binary metal oxide materials[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2004, 16(24): 5096-5106. doi: 10.1021/cm0494812 [15] WANG J, HAO J, LIU D, et al. Flower stamen-like porous boron carbon nitride nanoscrolls for water cleaning[J]. Nanoscale, 2017, 9(28): 9787-9791. doi: 10.1039/C7NR03084C [16] JOSEPH IV, TOSHEVA L, DOYLE AM. Simultaneous removal of Cd(II), Co(II), Cu(II), Pb(II), and Zn(II) ions from aqueous solutions via adsorption on FAU-type zeolites prepared from coal fly ash[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2020, 8(4): 103895. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2020.103895 [17] WANG WW, ZHOU JB, ACHARI G, et al. Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solutions by hydrothermal synthetic layered double hydroxides: Adsorption performance, coexisting anions and regeneration studies[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2014, 457: 33-40. [18] 张倩. 层状双金属氢氧化物除磷材料及氨基酸插层改性性能研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2018. [19] RAJESHKHANNA G, KANDULA S, SHRESTHA KR, et al. A new class of Zn1-xFex -oxyselenide and Zn1-xFex-LDH nanostructured material with remarkable bifunctional oxygen and hydrogen evolution electrocatalytic activities for overall water splitting[J]. Small, 2018, 14(51): 1803638. doi: 10.1002/smll.201803638 [20] 边靖, 王艳芳, 赫俊国, 等. 微波-碱改性粉煤灰钝化贮存污泥中Cu、Zn的研究[J]. 中国给水排水, 2016, 32(13): 91-95. [21] SHEN YF, ZHOU PT, SHAO QF. Porous silica and carbon derived materials from rice husk pyrolysis char[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2014, 188: 46-76. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2014.01.005 [22] FRANUS W, WDOWIN M, FRANUS M. Synthesis and characterization of zeolites prepared from industrial fly ash[J]. Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, 2014, 186(9): 5721-5729. [23] ZHOU HG, JIANG ZM, WEI SQ, et al. Adsorption of Cd(II) from aqueous solutions by a novel layered double hydroxide FeMnMg-LDH[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2018, 229(3): 1-16. [24] 杨雅芃, 张超兰, 陈俊先, 等. KOH活化制备蚕沙基生物炭及其对镉的吸附特性[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(11): 3504-3514. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202107123 [25] SHAN RR, YAN LG, YANG K, et al. Adsorption of Cd(II) by Mg–Al–CO3- and magnetic Fe3O4/Mg–Al–CO3-layered double hydroxides: Kinetic, isothermal, thermodynamic and mechanistic studies[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 299: 42-49. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.06.003 -



 下载:
下载: