-
我国土壤镉(Cd)污染严重. 据研究报道,我国无机污染超标点位占全部超标点位的82.8%,其中Cd污染点位超标率为7.0%,居无机污染物之首 [1]. Cd是一种剧毒金属,为I类致癌物,可通过食物链进入人体,影响酶活性,干扰细胞正常功能,威胁人体健康[2-3]. 水稻是中国乃至亚洲的主要粮食作物之一,易于积累Cd,在Cd污染土壤中种植水稻可能导致稻米Cd含量超过食品中污染物限量标准[4],食用富含Cd的稻米将增加人体Cd暴露风险[5-6],因此急需发展科学可行的实用修复技术治理土壤Cd污染.
土壤重金属污染修复技术通常通过去除重金属或改变重金属形态来实现修复目标,一般可分为物理修复技术、生物修复技术和化学修复技术三类[7]. 其中化学修复技术中的化学钝化法,因其成效快、成本低和操作简单等优点成为目前农田土壤重金属污染修复最为经济有效的方法[8]. 化学钝化法的核心是钝化材料的选择,目前广泛使用的钝化材料包括生物炭材料、含磷材料、矿物材料和微生物材料等[9]. 已有研究发现,生物炭材料具有比表面积大、含氧官能团丰富和阳离子交换能力强等特点,施入土壤后能改变土壤理化性质,通过吸附、离子交换等途径降低土壤中Cd有效态含量[10-12] . 含磷材料中含有大量活性磷组分,施入土壤后能解离出磷酸根与重金属反应生成难溶磷酸盐沉淀,从而降低土壤重金属的有效性[13-14]. 这两类材料在田间应用都有一定的局限性. 生物炭在土壤中的修复效果容易受土壤pH值、含水量等环境因素的影响,导致其对重金属钝化效果减弱;而含磷材料在土壤中释放的活性磷酸根基团容易随灌溉水或地表径流流失,造成钝化效果降低和水体富营养化等问题. 钝化材料配施可弥补单一材料的缺点,整合不同材料的优势,协同提升对重金属的固持效能,是目前土壤重金属污染修复材料的研究热点之一[15]. 段然等[16]研究发现,生物炭和草酸活化磷矿粉配施处理土壤弱酸提取态镉含量降低了58.0%左右,显著优于单施生物炭(43.1%)和草酸活化磷矿粉(36.3%)处理,对镉的钝化修复效果比单施更好. 王云丽等[17]的研究表明,羟基磷灰石和生物炭的联合应用对土壤Cd污染修复具有协同作用,与对照相比,土壤Cd有效态含量和油菜Cd积累量分别降低53.3%和51.2%,降低幅度显著高于材料单独应用. 然而目前利用生物炭和含磷材料配施修复Cd污染土壤的研究较少,在田间条件下的应用探讨更是鲜见.
猪粪是典型的农业有机固废,采用资源化技术将其制成猪粪炭应用于钝化修复土壤Cd污染已有一些研究成果[18]. 黄磷渣是磷矿生产过程中的一类废弃物,属于典型的含磷材料,将其发展为土壤钝化材料用于重金属污染修复的前景广阔. 本研究基于水稻田间试验,分析猪粪炭和黄磷渣两种钝化材料单施和配施处理下土壤理化性质、Cd有效态和不同化学形态分布,以及水稻生长发育和不同部位Cd含量的变化,探讨不同处理对土壤-水稻间Cd转运和积累的影响,研究猪粪炭和黄磷渣不同施用方式对土壤Cd污染的钝化修复效果,以期为钝化材料配施技术的发展与应用提供科技支撑.
-
本试验于2017年8月至11月在福建省某水稻田中开展,该地年平均降水量1147 mm,是典型亚热带海洋季风气候,土壤类型为红壤. 供试土壤基本理化性质如表1所示,土壤Cd含量超过《土壤环境质量 农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行)(GB 15618-2018)》规定的风险筛选值(0.4 mg∙kg−1).
-
供试水稻品种为Ⅱ优28.
-
猪粪炭为实验室自制,原材料猪粪由嘉兴华腾牧业提供,猪粪干燥破碎后在500 ℃高温缺氧热解2 h,研磨过2 mm筛备用,供试猪粪炭的基本理化性质见表2. 黄磷渣由云南磷化集团提供,是磷矿原矿石、焦炭和硅石在1000 ℃电炉反应制备黄磷工艺中产出的尾矿渣,研磨过0.15 mm筛备用,供试黄磷渣的基本理化性质见表3.
-
实验设计4个处理组如表4所示,分别为对照处理组(CK),单施猪粪炭处理组(BC),单施黄磷渣处理组(YP)和猪粪炭与黄磷渣配施处理组(CP,质量比为1:1,W/W),每个处理组面积为2亩. 每个处理组土壤中镉总量及钝化材料施入量见表4.
底肥为复合肥(18-12-16型,新洋丰农业科技股份有限公司)和尿素(沧州正元化肥有限公司),施用量分别为0.30 t·ha−1和0.15 t·ha−1. 水稻种植前施入供试钝化材料,充分混匀隔天翻地施肥. 施肥后土壤稳定1 d插秧,种植按常规农艺操作,淹水3—5 cm,分蘖后期晒田,复淹至灌浆期,排干收割. 在每个处理地块随机选取8个点位采集水稻植株及其根际土壤样品,每个点位采集2株水稻样品及其根部区域0—20 cm的土壤样品. 土壤样品自然风干后,研磨过 2.00 mm尼龙筛测定 pH值、阳离子交换容量(CEC)、有效磷含量(A-P)及土壤Cd有效态含量(A-Cd),取一部分研磨过 0.15 mm尼龙筛用于测定有机质含量(OM)及Cd化学形态;水稻样品根、茎(含叶)及稻谷分离,去离子水洗净后于烘箱中90 ℃杀青4 h,然后在60 ℃烘干至恒重,将稻谷脱壳,即每个水稻样品分成4个部分(根、茎、稻壳、籽粒),称量测定水稻各部分生物量(干重),将不同部分样品研磨过 0.18 mm尼龙筛用于测定Cd含量.
-
实验中所用试剂均为分析纯,实验用水为超纯水,所用器皿均在 10%硝酸中浸泡12 h,用去离子水冲洗,超纯水润洗后烘干备用.
-
猪粪炭pH值、CNS的测定及BET比表面积的测定方法参考范家俊[18]对生物炭的研究,黄磷渣pH值、阳离子交换量、有效磷含量和BET比表面积的测定方法参考刘昭[19] 对磷尾矿的研究.
土壤和钝化材料重金属总量采用改进HClO4-HNO3混酸消解法[20] 处理,电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS)(7500cx,美国Agilent公司)测定.
土壤理化性质测定方法参考《土壤农业化学分析方法》[21]. 土壤pH值采用水提法(固液比为1:2.5,W/V),pH计(ST3100,OHAUS,China)测定;阳离子交换容量(CEC)用乙酸钠-火焰光度计(M6,Thermo Fisher Scientific,USA)法测定;土壤有机质(OM)用高温外热重铬酸钾氧化容量法测定;土壤有效磷(A-P)采用碳酸氢钠浸提(固液比1:20,W/V),比色法测定.
土壤Cd有效态(A-Cd)含量采用0.01 mol·L−1 CaCl2溶液浸提(固液比1:10,W/V)[22],电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS)(7500cx,美国Agilent公司)测定.
-
采用Tessier[23-24]五步连续提取法对土壤样品中Cd的不同化学形态分级提取,各级提取液离心后用 0.22 μm水系滤膜过滤,Cd含量用电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS)测定,仪器检测限为0.0005 mg·kg−1,采用土壤成分分析标准物质GSS-6(GBW07406)(购自中国地质科学院地球物理地球化学勘察研究所)进行质量控制,回收率为80.50%—118.83%.
-
水稻不同部位样品Cd含量采用改良硝酸消解法[25]浸提. 浸提液用0.22 μm水系滤膜过滤,Cd含量用电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS)测定,检测限为0.0005 mg·kg−1,采用生物成分分析标准物质圆白菜GSB-5(GBW10014)(购自中国地质科学院地球物理地球化学勘查研究所)进行质量控制,标样回收率为81.06%—110.78%.
-
采用富集系数(Concentration Factor,简称CF)和转运系数(Transfer Factor,简称TF)评估水稻从土壤中富集和水稻体内转运Cd的含量变化,计算公式[26]如下:
其中,水稻中营养物质从B传输到A.
-
采用Microsoft Office Excel 2007软件计算数据,SPSS 16.0分析数据间差异显著性(P<0.05为差异显著,P<0.01为差异极显著),Origin8.5作图,本文数据均采用均值±标准偏差的格式表述.
-
猪粪炭和黄磷渣单施和配施对土壤理化性质的影响如表5所示. 相比对照,施加钝化材料后土壤pH值均呈升高趋势,其中配施处理下土壤pH值显著高于对照及单施处理(P<0.05),最大可增加0.97个单位. 有研究表明碱性钝化材料能与酸性土壤黏粒或有机质中带负电的官能团相互作用,降低土壤溶液中质子浓度,进而提高土壤pH值[27-28]. 本研究中两种钝化材料均为碱性,施加到酸性供试土壤中可提高土壤pH值. 配施处理下两种碱性钝化材料对pH值的影响可能存在一定协同作用,从而使土壤pH值升高幅度大于单施处理.
施加钝化材料后土壤有机质含量均呈增加趋势,其中单施猪粪炭和配施处理下土壤有机质含量分别增加了38.59%和20.90%,显著高于对照及单施黄磷渣处理(P<0.05). 已有研究表明生物炭本身含有丰富的有机碳,在高温热解条件下可转变为含碳官能团为主的稳定碳形态,有效固定碳元素,同时生物炭进入土壤后还能促进土壤团聚体的形成和稳定,进而提高土壤有机质含量[29-32]. 配施处理下土壤有机质含量增幅小于单施猪粪炭处理,这可能与黄磷渣自身有机质含量低,配施后发生“稀释”作用有一定的关联,聂新星等[33]研究也发现生物炭与氮肥配施对土壤有机质影响小于单施处理.
两种钝化材料单施及配施处理下土壤阳离子交换容量变化均不显著(P>0.05),这可能与土壤及钝化材料的性质有关,当土壤本身阳离子交换容量较大时,施加钝化材料对阳离子交换容量的影响较弱[34-35],具体作用机制还有待深入探讨.
配施处理下土壤有效磷含量显著高于对照及单施处理(P<0.05),最高可增加63.88%,但两种钝化材料单施处理下土壤有效磷含量没有显著差异(P>0.05). 黄磷渣中有效磷含量较高,施加到土壤应能提高土壤有效磷含量,但由于水稻田的淹水环境导致土壤中活性磷素易流失,因此单施黄磷渣处理下土壤有效磷含量变化不明显(P>0.05). 配施处理下土壤有效磷含量显著提高,可能是由于生物炭能通过表面吸附及阳离子交换作用等固持部分磷酸根基团,从而减少了磷素流失[36-37].
-
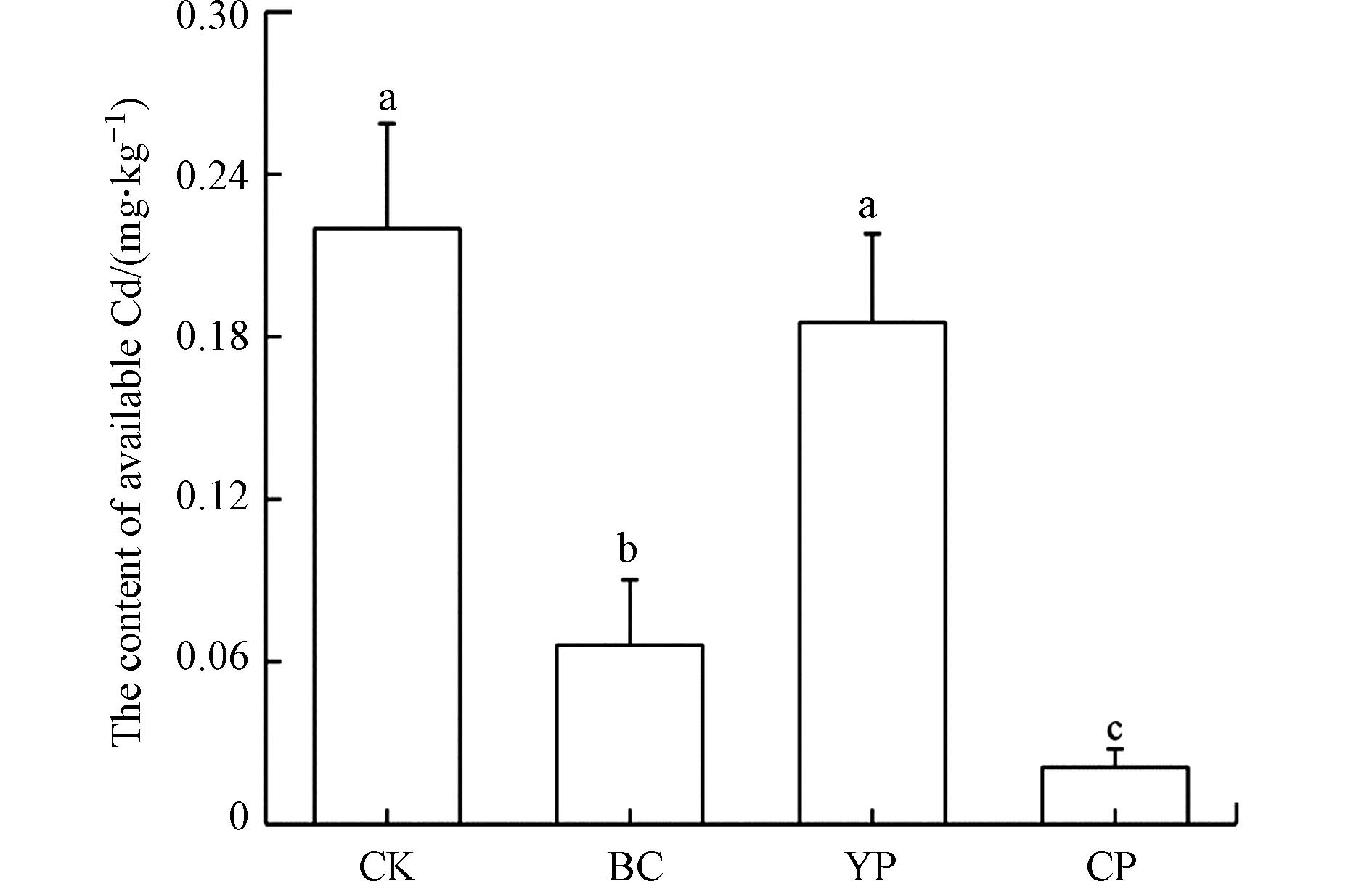
不同处理下土壤Cd有效态含量变化如图1所示.
与对照相比,单施猪粪炭、黄磷渣及配施处理下土壤Cd有效态含量分别降低了69.95%、15.77%和90.49%. 其中单施猪粪炭和配施处理下土壤Cd有效态含量显著低于对照及单施黄磷渣处理(P<0.05),配施处理下土壤Cd有效态含量最低,为0.02 mg·kg−1,显著低于单施猪粪炭处理(P<0.05).
钝化材料主要通过两种方式降低土壤中Cd有效态含量,一是材料自身对Cd的吸附作用,二是材料施加改变土壤理化性质,进而影响Cd的有效性和迁移能力. 猪粪炭具有较大的比表面积、丰富的表面官能团和多种无机矿物组分,在反应过程中猪粪炭上的含碳官能团和无机组分溶解的碳酸根和磷酸根等可通过吸附、沉淀等多种方式固持土壤中的Cd[38-40]. 而黄磷渣中含有大量交换性阳离子和有效磷,可通过离子交换、表面络合及溶解/沉淀等方式钝化土壤中的Cd[41]. 这两种材料均可通过自身的特性以不同作用机制有效降低土壤Cd有效态含量. 土壤理化性质对Cd有效性影响较大,土壤pH值是最重要因素. 土壤pH值升高能增加土壤表面可变负电荷,降低土壤溶液中氢离子浓度,增强Cd在土壤表面的沉淀作用,降低Cd的生物有效性[42-43]. REN等[44]研究发现Cd在pH值为2—6的土壤中活性大,迁移转化能力强,而在pH值为6.5—8.5时,土壤中的Cd易被土壤胶体、离子等吸附或反应生成沉淀,从而被固持在土壤中. 配施处理下土壤pH值为7.01,显著高于单施处理的6.14和6.04,有利于对Cd的钝化. 土壤有效磷含量也会影响土壤Cd的活性,磷酸根能与Cd反应生成沉淀,降低土壤中Cd的活性和迁移性,进而减轻Cd对植物的毒害作用[45]. 配施处理下土壤有效磷含量显著高于对照及单施处理,这可能是配施处理对Cd的钝化效果优于单施处理的原因之一. 此外土壤有机质含量的提高也有利于降低Cd在土壤中的活性[46],单施猪粪炭比单施黄磷渣处理土壤有机质含量高10.6 g·kg−1,可能是单施猪粪炭可更显著降低土壤Cd有效态含量的主要原因. 总体而言,猪粪炭和黄磷渣配施处理有效发挥了两种钝化材料对Cd的固持作用,同时改善了土壤理化性质促使Cd更容易被钝化.
-
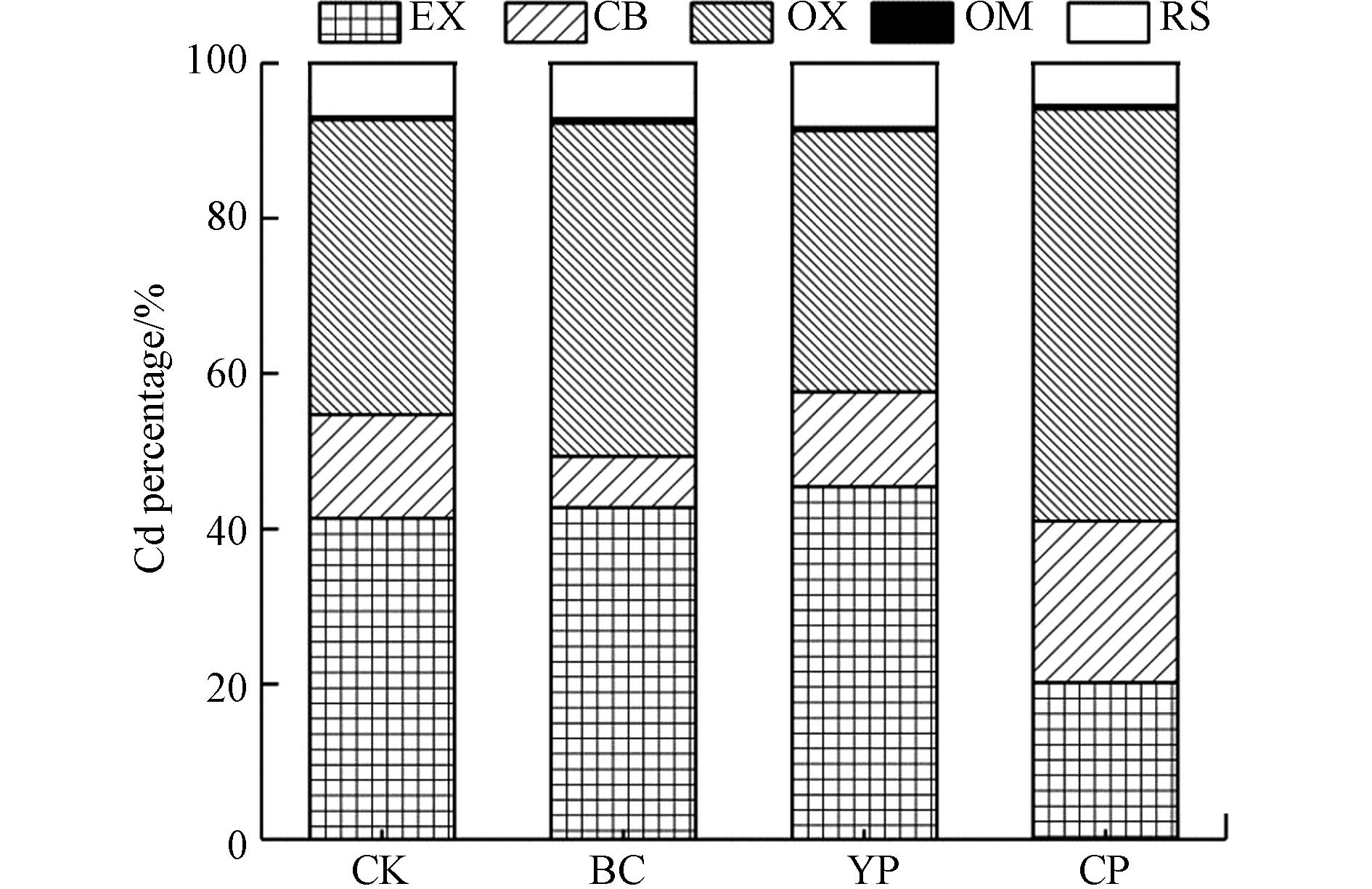
通常认为,Tessier连续提取法中5种Cd化学形态的迁移能力排序为:可交换态>碳酸盐结合态>铁/锰氧化物结合态>有机结合态>残渣态,其中可交换态和碳酸盐结合态是易迁移的形态[47],也是土壤污染修复研究中需要重点关注的化学形态. 不同处理下土壤Cd化学形态分布如图2所示. 结果显示,对照土壤中Cd以可交换态和铁锰氧化物结合态为主,其中可交换态Cd占总量的41.31%,是主要的化学形态,也表明受试土壤中Cd的迁移性较强. 与对照相比,配施处理下土壤可交换态Cd比例降低了51.21%. 各处理下易迁移的可交换态和碳酸盐结合态的数据显示,两态之和占比的排序为:CP<BC<YP≈CK,这与土壤Cd有效态含量分析结果基本一致. 与对照相比,配施处理下土壤中铁锰氧化物结合态Cd和有机结合态Cd的比例分别增加了39.73%和38.15%;单施猪粪炭处理下土壤有机结合态Cd和残渣态Cd的比例分别增加了67.92%和2.85%;单施黄磷渣土壤中残渣态Cd的比例增加了19.26%. 表明两种钝化材料施加后,土壤中易迁移形态Cd的比例降低,难迁移形态Cd的比例增加,有利于土壤Cd污染的修复治理. 总体而言,配施处理对易迁移Cd形态降低幅度高于单施处理,对Cd的钝化效果最佳.
单施猪粪炭处理下土壤Cd碳酸盐结合态的比例降低,有机结合态的比例增加,可能与猪粪炭中富含多种有机官能团及其施加后显著提高了土壤有机质含量有关. 研究表明生物炭含有羧基、酯基等多种有机官能团,能与Cd结合形成更稳定的配位键[12];同时土壤有机质含量的增加可以提高土壤对Cd的吸附能力,促进Cd向更稳定的形态转化[48-49]. 单施黄磷渣处理下土壤中残渣态Cd含量增加,可能是由于黄磷渣中的钙镁离子与重金属离子发生离子交换共沉淀反应或黄磷渣中的PO43-与重金属离子发生沉淀反应,从而导致碳酸盐结合态Cd比例降低,残渣态Cd比例增加. 赵庆圆等[27]和BOLAN等[50] 研究磷酸盐和矿物材料与Cd作用机理发现,磷酸根和钙镁离子沉淀作用是材料钝化修复土壤重金属污染的主要方式. 土壤pH值升高,铁锰氧化物的还原溶解作用减弱,沉淀作用增强[51],同时土壤中碳酸盐、有机质和铁锰氧化物等与Cd结合的稳定性提高,Cd可交换态含量减少导致迁移能力降低 [42-43]. 土壤有效磷含量提高,磷酸根可与Cd结合形成磷酸盐沉淀,使Cd更多转化为难迁移形态,降低易被植物吸收的Cd含量,进而使土壤Cd污染对水稻的毒害风险降低[52-54]. 配施处理对土壤Cd的固持效果优于单施处理不仅因其有效整合了两种钝化材料的吸附特性,还与其对土壤理化性质的影响更有利于降低Cd的迁移能力有关. 配施处理下两种钝化材料吸附Cd的同时,通过提高土壤pH值、有效磷及有机质含量,促进Cd向更稳定的铁锰氧化物结合态、有机结合态转化,降低其迁移性. 段然等[16]也发现生物炭和磷矿粉配施影响了土壤理化性质,进而促进土壤中Cd向稳定形态转化.
-
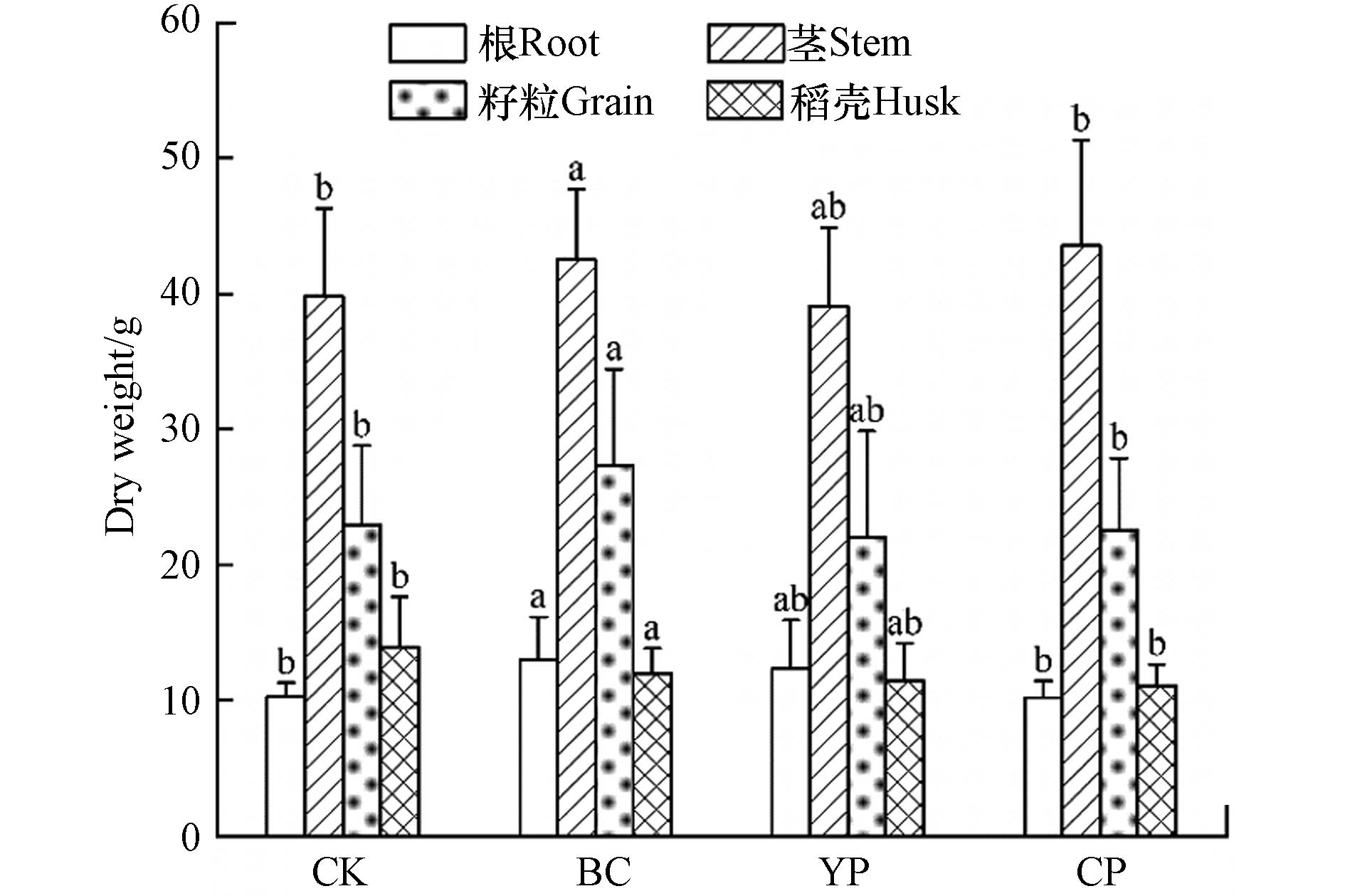
不同处理下单株水稻不同部位生物量的变化如图3所示. 与对照相比,只有单施猪粪炭处理下水稻根部生物量显著提高(P< 0.05). 总体而言,各处理对水稻正常生长都没有负面影响.
-
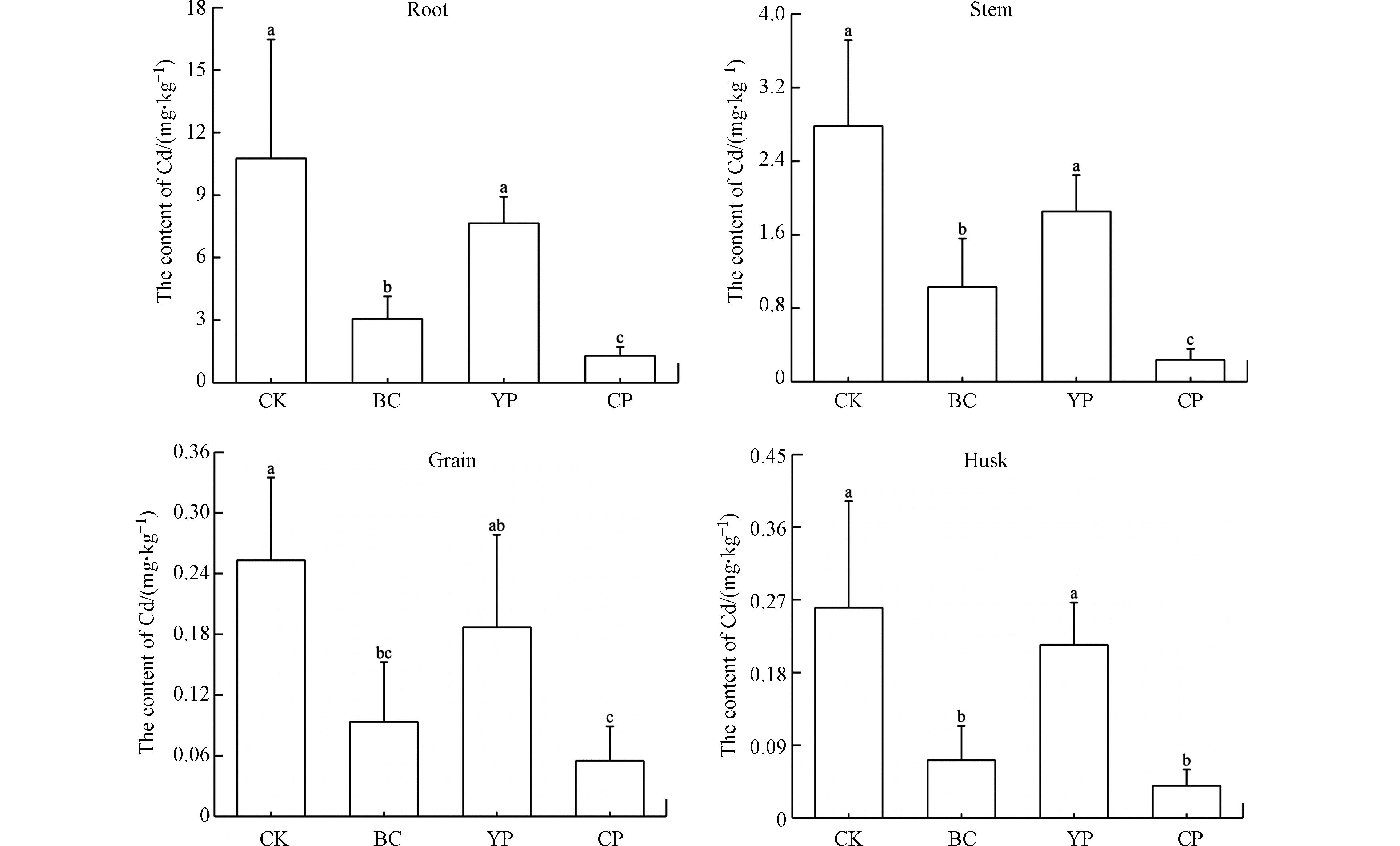
不同处理下水稻根、茎、稻壳和籽粒中Cd含量如图4所示. 与对照相比,两种钝化材料单施和配施均不同程度降低了水稻各部位中Cd含量,其中单施猪粪炭和配施处理下水稻不同部位Cd含量显著低于对照及单施黄磷渣处理(P <0.01). 配施处理下水稻根、茎、稻壳和籽粒中的Cd含量分别降低了88.03%、91.48%、84.67%和78.31%,均低于单施猪粪炭处理. 配施处理下籽粒中Cd含量从0.25 mg·kg−1降低到0.05 mg·kg−1,远低于《食品安全国家标准 食品中污染物限量标准(GB 2762-2017)》规定的稻米Cd安全限量(0.2 mg·kg−1). 配施处理下水稻籽粒中Cd含量降低幅度显著高于单施处理,有效控制了土壤Cd污染对水稻籽粒的毒害风险,保证了食品安全.
水稻对Cd的吸收量与土壤中Cd有效态或易迁移态(可交换态和碳酸盐结合态)含量存在正相关关系[55]. 配施处理下水稻各部位中Cd含量均显著低于对照及单施处理,可能是由于两种钝化材料配施处理比单施处理更高效的降低土壤Cd有效态含量,同时促使易迁移的可交换态Cd转化为难迁移的铁锰结合态和有机结合态,有效抑制了土壤Cd的活性. 郭彬等[56]通过施加有机-无机复合型钝化材料降低了土壤中交换态Cd含量,固持土壤中Cd后有效降低了稻米中Cd含量,与本研究结果一致.
-
不同处理下Cd在土壤-水稻间的富集系数和水稻不同部位间的转移系数如表6所示. 施加两种钝化材料后水稻对土壤中Cd的富集系数均降低,其中配施处理下富集系数降低了9.93个单位,降幅明显高于单施处理,表明配施处理更有效抑制了水稻从土壤中富集Cd. BIN等[57]发现水稻从土壤中吸收Cd后,约49.0%—79.0%的Cd富集根部,其中具有潜在移动能力的Cd约占根部总量的24.0%. 配施处理下水稻中Cd从地下部分(根)向上转移系数相比对照降低了0.05个单位,降幅高于单施处理,表明配施处理更有效抑制了Cd从水稻根部向上转移. 配施处理下水稻由根到茎的转移系数降低了0.08个单位,降幅也高于单施处理,表明其主要通过抑制Cd由根向茎的转移来降低籽粒中Cd的积累量.
-
(1)相比对照,猪粪炭和黄磷渣单施和配施均会影响土壤理化性质,其中配施对土壤pH值、有机质及有效磷含量的提升幅度显著高于单施处理.
(2)猪粪炭和黄磷渣单施和配施处理下土壤Cd有效态含量均明显降低,配施对土壤Cd的固持效果好于单施处理. 配施处理下,土壤中易迁移的可交换态Cd比例明显降低,难迁移的铁锰氧化物结合态和有机结合态Cd比例显著增加.
(3)猪粪炭和黄磷渣在田间的单施和配施处理均显著降低水稻不同部位Cd含量,其中配施处理降低效果优于单施处理. 配施处理下富集系数最低,籽粒Cd含量最低,满足国家食品安全标准要求,表明猪粪炭和黄磷渣配施对农田Cd污染土壤有较好的修复效果,具有一定的应用潜力.
田间条件下猪粪炭与黄磷渣配施对土壤镉污染的修复效果
Remediation effect of combined application of pig manure biochar and yellow phosphorus slag on cadmium contaminated paddy soil
-
摘要: 为探究猪粪炭和黄磷渣配施对田间土壤镉(Cd)污染的修复效果,本研究以镉污染水稻田为研究对象,探讨两种钝化材料单施和配施对土壤理化性质、Cd有效态含量、Cd化学形态及水稻不同部位Cd含量的影响. 结果表明猪粪炭与黄磷渣配施处理下土壤Cd有效态含量降低幅度最大,达90.49%,单施猪粪炭和单施黄磷渣处理下土壤Cd有效态含量分别降低了69.95%和15.77%. 化学形态分析结果表明,相比对照,配施处理下土壤中易迁移的可交换态Cd比例降低了51.21%,而土壤中难迁移的铁锰氧化物结合态和有机结合态Cd比例分别增加了39.73%和38.15%. 各处理对水稻生物量都没有负面影响,但水稻各部位Cd含量相比对照均显著降低.配施处理下水稻各部位中Cd含量均低于对照及单施处理,其中水稻籽粒中Cd含量降幅为78.31%,降低至0.05 mg·kg−1,远低于国家标准食品污染物限量标准值(<0.2 mg·kg−1). 生物炭与黄磷渣配施显著降低水稻土中Cd有效态含量和水稻籽粒中Cd的积累量,对Cd污染水稻田钝化修复效果优于单施处理,本研究结果可为土壤Cd污染的修复提供科学依据.Abstract: Field experiment was conducted to investigate the effects of single and combined application of pig manure biochar and yellow phosphorus slag on remediation of cadmium(Cd) polluted paddy soil, and the reduction of accumulation in rice. The available Cd and Tessier speciation of Cd in the soil, and the concentration of Cd in different parts of rice were determined. The reduction of available Cd in soil with combined application was 90.49%, which was lower than that with single application of pig manure biochar (69.95%) and yellow phosphorus slag (15.77%). Compared with the control, the ratio of exchangeable fraction of Cd in soil decreased by 51.21%, while the ratio of Fe-Mn oxides-bound and organic-bound fraction increased by 39.73% and 38.15%, respectively. All treatments significantly reduced the concentration of Cd in different parts of rice. The content of Cd in all parts of rice followed by the combined application was lower than that by single application, especially in grains, the Cd concentration decreased to 0.05 mg·kg−1, which was 78.31% lower than that of the control group, also far below the National standard for food safety - Limits of contaminants in foods (<0.2 mg·kg−1). The combined application of pig manure biochar and yellow phosphorus slag could effectively reduce the content of available Cd in soil and the accumulation of Cd in rice, the immobilization effect was better than that of single application. The results of this study could provide scientific basis for the remediation of cadmium polluted soils.
-
Key words:
- pig manure biochar /
- yellow phosphorus slag /
- combined application /
- immobilization /
- cadmium /
- paddy field
-

-
表 1 供试土壤基本理化性质
Table 1. The properties of soil
土壤类型
Soil type土壤pH
Soil pH有机质/%
OM阳离子交换
容量/(cmol∙kg−1)
CEC有效磷/
(mg∙kg−1)
Available P镉总量/
(mg∙kg−1)
Total Cd铜总量/
(mg∙kg−1)
Total Cu铅总量/
(mg∙kg−1)
Total Pb红壤 6.04±0.09 3.11±0.05 8.17±2.18 34.58±1.06 1.32±0.09 12.54±0.36 92.62±4.60 注:表中数据格式为均值±标准偏差,下同.
Note: The data in the table are in the format of mean ± standard deviation. The same below.表 2 供试猪粪炭的基本理化性质
Table 2. Physicochemical properties of pig manure biochar
测试指标
IndexespH CNS分析/%
Element(CNS) content镉总量/(mg∙kg−1)
Total CdBET比表面积/(m2∙g−1)
BET surface aeraC N S 猪粪炭 8.16±0.09 46.13±0.62 4.76±0.94 0.61±0.09 0.50±0. 09 50.90 表 3 供试黄磷渣的基本理化性质
Table 3. Physicochemical properties of yellow phosphorus slag
测试指标
IndexespH 阳离子交换量/(cmol∙kg−1)
CEC有效磷/(mg∙kg−1)
Available P镉总量/(mg∙kg−1)
Total CdBET比表面积/(m2∙g−1)
BET surface aera黄磷渣 11.34±0.02 14.80±0.15 0.85±0.01 0.24±0.03 5.59 表 4 实验处理
Table 4. Treatments in the experiment
处理编号
Treatment猪粪炭/(t·ha−1)
Pig manure biochar黄磷渣/(t·ha−1)
Yellow phosphorus slag镉总量/(mg·kg−1)
Total CdCK — — 1.41±0.13a BC 2.25 — 1.31±0.18a YP — 2.25 1.31±0.22a CP 2.25 2.25 1.23±0.16a 注:表中不同小写字母表示处理组间存在显著差异(P < 0.05),下同.
Note: Different lower-case letters in the table indicate significant differences between treatment groups (P < 0.05). The same below.表 5 不同处理下土壤的理化性质
Table 5. The physical and chemical properties of soil under different treatments
处理
Treatment土壤pH
Soil pH有机质/%
OM阳离子交换容量/(cmol∙kg−1)
CEC有效磷/(mg∙kg−1)
Available PCK 6.04±0.09b 3.11±0.05c 8.17±2.18a 34.58±1.06b BC 6.14±0.21b 4.31±0.15a 8.33±0.88a 31.78±3.49b YP 6.04±0.20b 3.25±0.22c 7.78±0.61a 31.56±2.46b CP 7.01±0.06a 3.76±0.24b 8.72±1.95a 56.67±3.40a 表 6 不同处理下Cd的富集和转移系数
Table 6. The CF and TF of Cd in soils and rice under different treatments.
处理
Treatments富集系数
(CF)转移系数(TF) 地上部分/地下部分
Aboveground/Underground茎/根
Stem/Root籽粒/茎
Grain/StemCK 11.51 0.31 0.26 0.09 BC 6.27 0.39 0.34 0.09 YP 9.26 0.30 0.24 0.10 CP 1.58 0.26 0.18 0.23 -
[1] 陈能场, 郑煜基, 何晓峰, 等. 《全国土壤污染状况调查公报》探析 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2017, 36(9): 1689-1692. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2017-1220 CHEN N C, ZHENG Y J, HE X F, et al. Analysis of the Report on the national general survey of soil contamination [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2017, 36(9): 1689-1692(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2017-1220
[2] JAISHANKAR M, TSETEN T, ANBALAGAN N, et al. Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals [J]. Interdisciplinary Toxicology, 2014, 7(2): 60-72. doi: 10.2478/intox-2014-0009 [3] DUAN G L, SHAO G S, TANG Z, et al. Genotypic and environmental variations in grain cadmium and arsenic concentrations among a panel of high yielding rice cultivars [J]. Rice, 2017, 10(1): 9. [4] ZHAO F J, MA Y B, ZHU Y G, et al. Soil contamination in China: Current status and mitigation strategies [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(2): 750-759. [5] SIMMONS R W, PONGSAKUL P, SAIYASITPANICH D, et al. Elevated levels of cadmium and zinc in paddy soils and elevated levels of cadmium in rice grain downstream of a zinc mineralized area in Thailand: Implications for public health [J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2005, 27(5/6): 501-511. [6] MEHARG A A, NORTON G, DEACON C, et al. Variation in rice cadmium related to human exposure [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(11): 5613-5618. [7] 王宏鹏. 石灰性土壤镉污染原位钝化修复材料研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2020. WANG H P. Study on in situ passivation materials for remediation of calcareous cadmium contaminated soil[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2020(in Chinese).
[8] 卢维宏, 张乃明, 苏友波, 等. 联合施肥对复合污染农田水稻As、Cd吸收的影响 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(10): 2217-2226. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-0573 LU W H, ZHANG N M, SU Y B, et al. Effects of combined fertilization on the absorption of As and Cd in rice from polluted farmland [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(10): 2217-2226(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-0573
[9] 温小情, 林亲铁, 肖荣波, 等. 镁基膨润土和水泥对砷铅复合污染土壤的钝化效能与机理研究 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(9): 3397-3404. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2020.0168 WEN X Q, LIN Q T, XIAO R B, et al. Study on passivation efficiency and mechanism of Mg-bentonite and cement on As/Pb contaminated soil [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(9): 3397-3404(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2020.0168
[10] HOUBEN D, EVRARD L, SONNET P. Beneficial effects of biochar application to contaminated soils on the bioavailability of Cd, Pb and Zn and the biomass production of rapeseed (Brassica napus L. ) [J]. Biomass and Bioenergy, 2013, 57: 196-204. doi: 10.1016/j.biombioe.2013.07.019 [11] ABBAS T, RIZWAN M, ALI S, et al. Effect of biochar on alleviation of cadmium toxicity in wheat (Triticum aestivum L. ) grown on Cd-contaminated saline soil [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2018, 25(26): 25668-25680. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-8987-4 [12] LU H L, ZHANG W H, YANG Y X, et al. Relative distribution of Pb2+ sorption mechanisms by sludge-derived biochar [J]. Water Research, 2012, 46(3): 854-862. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2011.11.058 [13] GARRIDO F, ILLERA V, CAMPBELL C G, et al. Regulating the mobility of Cd, Cu and Pb in an acid soil with amendments of phosphogypsum, sugar foam, and phosphoric rock [J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 2006, 57(2): 95-105. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2389.2005.00719.x [14] 冯磊, 刘永红, 胡红青, 等. 几种矿物材料对污染土壤中铜形态的影响 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2011, 31(11): 2467-2473. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2011.11.025 FENG L, LIU Y H, HU H Q, et al. Effect of several mineral materials on copper form in contaminated soil [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2011, 31(11): 2467-2473(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2011.11.025
[15] 殷飞, 王海娟, 李燕燕, 等. 不同钝化剂对重金属复合污染土壤的修复效应研究 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2015, 34(3): 438-448. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2015.03.005 YIN F, WANG H J, LI Y Y, et al. Remediation of multiple heavy metal polluted soil using different immobilizing agents [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2015, 34(3): 438-448(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2015.03.005
[16] 段然, 胡红青, 付庆灵, 等. 生物炭和草酸活化磷矿粉对镉镍复合污染土壤的应用效果 [J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(11): 4836-4843. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201704028 DUAN R, HU H Q, FU Q L, et al. Remediation of Cd/Ni contaminated soil by biochar and oxalic acid activated phosphate rock [J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(11): 4836-4843(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201704028
[17] 王云丽, 石耀鹏, 赵文浩, 等. 设施菜地土壤镉钝化剂筛选及应用效果研究 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(7): 1503-1510. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-0303 WANG Y L, SHI Y P, ZHAO W H, et al. Screening of amendments for the remediation of cadmium-polluted protected agriculture soil [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(7): 1503-1510(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-0303
[18] 范家俊. 巯基改性生物炭的制备及其修复重金属污染土壤的研究[D]. 泉州: 华侨大学, 2019. FAN J J. Preparation of thiol modified biochar and its remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil[D]. Quanzhou: Huaqiao University, 2019(in Chinese).
[19] 刘昭. 改性磷矿浮选尾矿对重金属吸附特性及土壤修复效应研究[D]. 泉州: 华侨大学, 2020. LIU Z. Adsorption characteristics of modified phosphate flotation tailing for heavy metals and its remediation effect on contaminated soils[D]. Quanzhou: Huaqiao University, 2020(in Chinese).
[20] LEE C S L, LI X D, SHI W Z, et al. Metal contamination in urban, suburban, and country park soils of Hong Kong: A study based on GIS and multivariate statistics [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2006, 356(1/2/3): 45-61. [21] 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 1999. LU R K. Methods for agricultural chemical analysis of soils[M]. Beijing: China agricultural science and technology press, 1999 (in Chinese).
[22] 郭朝晖, 朱永官. 典型矿冶周边地区土壤重金属污染及有效性含量 [J]. 生态环境, 2004, 13(4): 553-555. GUO Z H, ZHU Y G. Contamination and availabile contents of heavy metals in soils in the typical mining and smelting circumjacent districts [J]. Ecology and Environmnet, 2004, 13(4): 553-555(in Chinese).
[23] TESSIER A, CAMPBELL P G C, BISSON M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1979, 51(7): 844-851. doi: 10.1021/ac50043a017 [24] 李东, 贺丽洁, 盛培培. Tessier连续提取法用于土壤铬分析的Cr(Ⅵ)-Cr(Ⅲ)转化及适用性 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(7): 2368-2378. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202012141 LI D, HE L J, SHENG P P. Transformation of Cr(Ⅵ)-Cr(Ⅲ) and application suitability in Tessier sequential extraction of soil chromium [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2021, 15(7): 2368-2378(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202012141
[25] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. 食品安全国家标准 食品中多元素的测定: GB 5009.268—2016[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017. National health commission of China, National medical products administration. National standard for food safety-determination of multiple elements in food: GB 5009.268—2016[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2017(in Chinese).
[26] YANG Z M, FANG Z Q, ZHENG L C, et al. Remediation of lead contaminated soil by biochar-supported nano-hydroxyapatite [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2016, 132: 224-230. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.06.008 [27] 赵庆圆, 李小明, 杨麒, 等. 磷酸盐、腐殖酸与粉煤灰联合钝化处理模拟铅镉污染土壤 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(1): 389-398. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201705273 ZHAO Q Y, LI X M, YANG Q, et al. Passivation of simulated Pb-and Cd-contaminated soil by applying combined treatment of phosphate, humic acid, and fly ash [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(1): 389-398(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201705273
[28] LOMBI E, HAMON R E, MCGRATH S P, et al. Lability of Cd, Cu, and Zn in polluted soils treated with lime, beringite, and red mud and identification of a non-labile colloidal fraction of metals using istopic techniques [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2003, 37(5): 979-984. [29] LI H B, DONG X L, da SILVA E B, et al. Mechanisms of metal sorption by biochars: Biochar characteristics and modifications [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 178: 466-478. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.03.072 [30] 许云翔, 何莉莉, 刘玉学, 等. 施用生物炭6年后对稻田土壤酶活性及肥力的影响 [J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(4): 1110-1118. XU Y X, HE L L, LIU Y X, et al. Effects of biochar addition on enzyme activity and fertility in paddy soil after six years [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(4): 1110-1118(in Chinese).
[31] 周俊杰, 孙硕, 赵远, 等. 混合改良剂对镉污染土壤川芎镉积累及生长的影响 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(11): 3608-3616. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020070501 ZHOU J J, SUN S, ZHAO Y, et al. Effects of mixed amendments on the cadmium accumulation and growth of Ligusticum Chuanxiong hort in cadmium-contaminated soil [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(11): 3608-3616(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020070501
[32] 徐美丽, 陈永光, 肖荣波, 等. 生物炭对土壤有效态重金属的作用机制进展 [J]. 环境工程, 2021, 39(8): 165-172,226. XU M L, CHEN Y G, XIAO R B, et al. Progress in influential mechanisms of biochar on available heavy metals in soil [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2021, 39(8): 165-172,226(in Chinese).
[33] 聂新星, 张自咏, 黄玉红, 等. 生物炭与氮肥配施对高粱生长及镉吸收的影响 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(12): 2749-2756. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2019-1071 NIE X X, ZHANG Z Y, HUANG Y H, et al. Effects of simultaneous biochar and nitrogen fertilizer application on the photosynthesis and Cd uptake of Sorghum [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38(12): 2749-2756(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2019-1071
[34] 闫家普, 丁效东, 崔良, 等. 不同改良剂及其组合对土壤镉形态和理化性质的影响 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(9): 1842-1849. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-0187 YAN J P, DING X D, CUI L, et al. Effects of several modifiers and their combined application on cadmium forms and physicochemical properties of soil [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(9): 1842-1849(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-0187
[35] SINGH B P, HATTON B J, BALWANT S, et al. Influence of biochars on nitrous oxide emission and nitrogen leaching from two contrasting soils [J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2010, 39(4): 1224-1235. doi: 10.2134/jeq2009.0138 [36] LEHMANN J, JOSEPH S. Biochar for Environmental Management[M]. London: Routledge, 2015. [37] MUKHERJEE A, ZIMMERMAN A R, HARRIS W. Surface chemistry variations among a series of laboratory-produced biochars [J]. Geoderma, 2011, 163(3/4): 247-255. [38] 黄菲, 闫梦, 常建宁, 等. 不同菌糠生物炭对水体中Cu2+、Cd2+的吸附性能 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(4): 1116-1128. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019091604 HUANG F, YAN M, CHANG J N, et al. Adsorption performance of Cu2+ and Cd2+ in water by different biochars derived from spent mushroom substrate [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(4): 1116-1128(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019091604
[39] 王震宇, 刘国成, Monica Xing, 等. 不同热解温度生物炭对Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附特性 [J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(12): 4735-4744. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2014.12.042 WANG Z Y, LIU G C, XING M, et al. Adsorption of Cd(Ⅱ) varies with biochars derived at different pyrolysis temperatures [J]. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(12): 4735-4744(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2014.12.042
[40] 陈昱, 梁媛, 郑章琪, 等. 老化作用对水稻秸秆生物炭吸附Cd(Ⅱ)能力的影响 [J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(11): 2337-2343. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.11.2016031601 CHEN Y, LIANG Y, ZHENG Z Q, et al. Effect of ageing on Cd adsorption ability by rice-straw derived biochar [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(11): 2337-2343(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.11.2016031601
[41] CHRYSOCHOOU M, DERMATAS D, GRUBB D G. Phosphate application to firing range soils for Pb immobilization: The unclear role of phosphate [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2007, 144(1/2): 1-14. [42] ZHU X M, CHEN B L, ZHU L Z, et al. Effects and mechanisms of biochar-microbe interactions in soil improvement and pollution remediation: A review [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 227: 98-115. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.04.032 [43] 刘艺芸, 陈志国, 王秀梅, 等. 蓄电池拆解区铅、镉复合污染农田土壤钝化修复 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(4): 1138-1146. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020081807 LIU Y Y, CHEN Z G, WANG X M, et al. Remediation of lead and cadmium contaminated farmland soil in battery dismantling area [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(4): 1138-1146(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020081807
[44] REN J, ZHANG Z, WANG M, et al. Phosphate-induced differences in stabilization efficiency for soils contaminated with lead, zinc, and cadmium [J]. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 2017, 12(2): 1-9. [45] 王秀丽, 梁成华, 马子惠, 等. 施用磷酸盐和沸石对土壤镉形态转化的影响 [J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(4): 1437-1444. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2015.04.042 WANG X L, LIANG C H, MA Z H, et al. Effects of phosphate and zeolite on the transformation of Cd speciation in soil [J]. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(4): 1437-1444(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2015.04.042
[46] 潘丽萍. 生物质炭对镉—阿特拉津复合污染土壤的修复研究[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2014. PAN L P. Study on remediation of cadmium and atrazine combined pollution soil by biochars[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2014(in Chinese).
[47] LIANG X F, QIN X, HUANG Q Q, et al. Mercapto functionalized sepiolite: A novel and efficient immobilization agent for cadmium polluted soil [J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(63): 39955-39961. doi: 10.1039/C7RA07893E [48] 邢金峰, 仓龙, 葛礼强, 等. 纳米羟基磷灰石钝化修复重金属污染土壤的稳定性研究 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2016, 35(7): 1271-1277. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2016.07.007 XING J F, CANG L, GE L Q, et al. Long-term stability of immobilizing remediation of a heavy metal contaminated soil with nano-hydroxyapatite [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2016, 35(7): 1271-1277(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2016.07.007
[49] 辜娇峰, 周航, 吴玉俊, 等. 复合改良剂对稻田Cd、As活性与累积的协同调控 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2016, 36(1): 206-214. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.01.035 GU J F, ZHOU H, WU Y J, et al. Synergistic control of combined amendment on bioavailability and accumulation of Cd and As in rice paddy soil [J]. China Environmental Science, 2016, 36(1): 206-214(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.01.035
[50] BOLAN N, KUNHIKRISHNAN A, THANGARAJAN R, et al. Remediation of heavy metal(loid)s contaminated soils - To mobilize or to immobilize? [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 266: 141-166. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.12.018 [51] 陈思慧, 张亚平, 李飞, 等. 钝化剂联合农艺措施修复镉污染水稻土 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(3): 563-572. CHEN S H, ZHANG Y P, LI F, et al. Remediation of Cd-polluted paddy soils using amendments combined with agronomic measures [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38(3): 563-572(in Chinese).
[52] 刘芳, 刘世亮, 介晓磊, 等. 石灰性土壤中磷镉交互作用对菠菜生长及其吸收磷镉的影响 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2005, 21(4): 310-314. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2005.04.087 LIU F, LIU S L, JIE X L, et al. Influence of P and Cd interaction on spinach growth and uptake P and Cd in calcareous soil [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2005, 21(4): 310-314(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2005.04.087
[53] MA Q Y, LOGAN T J, TRAINA S J. Lead immobilization from aqueous solutions and contaminated soils using phosphate rocks [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1995, 29(4): 1118-1126. [54] SCHECKEL K G, IMPELLITTERI C A, RYAN J A, et al. Assessment of a sequential extraction procedure for perturbed lead-contaminated samples with and without phosphorus amendments [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2003, 37(9): 1892-1898. [55] 罗惠方. 基于人体肾功能的尿镉、大米镉和土壤镉基准剂量研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2017. LUO H F. Study on bmd of cadmium in urine, rice and soil based on human renal function[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2017(in Chinese).
[56] 郭彬, 刘琛, 傅庆林, 等. 有机-无机型钝化剂对水稻土镉钝化效果研究 [J]. 核农学报, 2017, 31(6): 1173-1178. doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2017.06.1173 GUO B, LIU C, FU Q L, et al. Study on the effect of organic-inorganic passivant on cadmium passivation in paddy soils [J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 31(6): 1173-1178(in Chinese). doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2017.06.1173
[57] LIU B, CHEN L, CHEN S B, et al. Subcellular Cd accumulation characteristic in root cell wall of rice cultivars with different sensitivities to Cd stress in soil [J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2016, 15(9): 2114-2122. doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(15)61227-8 -



 下载:
下载: