-
水合肼作为一种重要的精细化工产品,在化工、农药、染料、医药、航空航天等领域应用广泛。水合肼的生产方法主要包括拉西法、尿素法、酮连氮法、过氧化氢法和空气氧化法等[1]。其中,酮连氮法具有能耗低、收率高等优点[2],已在国内大规模使用。酮连氮法制水合肼会产生大量废盐,据统计,每生产1 t水合肼成品,会产生4~5 t的废盐[3]。这些废盐与标准工业盐存在较大差距,无法直接回用。将酮连氮法制水合肼产生的废盐回用于离子膜电解制造烧碱是废盐资源化利用的一个出路。但废盐中的有机物等杂质会造成槽电压迅速升高[4],减少离子膜的使用寿命,从而增加企业的生产成本。为了提高生产效率,降低生产成本,就必须对废盐进行除杂提纯。
目前,针对废盐中有机物的处理方法主要有高温煅烧法[5-6]、热解法[7-8]、水洗法[9-10]等。高温煅烧法处理废盐中有机物较为彻底且此过程释放的热能还可用于发电等用途。但是,此法能耗较高,且易产生有毒有害的烟气和飞灰,对人体健康会产生危害。热解法相较于高温煅烧法所采取的处理温度较低,因此具有能耗较低的优点。但热解工艺的处理效果受多种因素影响,诸如热解炉构造、供热方式、热解温度等,需要针对不同的废盐体系采取有针对性的热解处理办法。水洗法是采用水或有机溶剂对废盐进行洗涤处理,使得废盐中的杂质能被淋洗剂带走,从而实现盐与有机物的分离。宁文琳等[11]采用二甲苯作为洗涤剂来处理呋喃酚醚化废盐,处理后单醚的回收率可达86.4%。分离的废盐可达工业盐标准,二甲苯在经过真空干燥后也可重新返回淋洗工序。CHEN等[12]采用水洗法处理垃圾焚烧循环流化床残渣,残渣中的水溶性氯盐提取量达83%,且残渣中的二恶英和二苯并呋喃等有机物不会随盐一起溶解到水中。通过水洗法不仅可处理焚烧残渣,提高其回收利用率,还可获得较为纯净的可进一步回收利用的混盐。陆振荣[13]采用水洗法处理尿素法制水合肼副产废盐,分离出的盐可回用于烧碱电解,洗涤母液吸收二氧化硫后经过一系列反应生产硫代硫酸钠,每年可为企业带来200×104元的利润。水洗法对于有机杂质种类较少的废盐较为适用,其操作简单、成本低、能耗少;该方法利用杂质与盐溶解性的差异即可去除废盐中大部分有机物。酮连氮法制水合肼副产废盐为三效蒸发后的结晶盐。其中,有机物种类基本上以未反应完的生产原料和生产过程中的副产物为主,可基本满足水洗法处理的要求。
响应曲面法是一种分析多变量间对响应值交互作用影响的手段,在食品、医药、废水处理及工程实验方面有广泛应用[14-22]。通过Box-Behnken实验设计能大大减少实验工作量,并利用响应曲面模型得出最优解[23]。针对酮连氮法制水合肼副产废盐中有机物含量高[24-25]、回收利用效益差等问题,本研究提出采用水洗法处理废盐的方式,通过研究水洗过程中的液固质量比、水洗次数和盐温度对废盐中有机物水洗处理效果的影响,并结合BBD(Box-Behnken)响应面优化法,探究水洗法处理废盐的最优工艺参数。
HTML
-
废盐取自山西省某酮连氮法生产水合肼车间,将废盐配制成300 g·L−1的溶液后,测得其UV254值为0.919、TOC值为152.4 mg·L−1。废盐中的主要元素Na、Cl、C、O、S、Mg的质量分数分别为32.14%、51.55%、12.98%、3.25%、0.04%和0.04%。NaCl,分析纯。
-
滤纸称重并折叠放入玻璃漏斗中,使用超纯水将滤纸润湿;称取40 g废盐倒入漏斗中,然后将超纯水倒入;通过改变液固质量比、水洗次数及盐温度,对废盐进行水洗处理。其中,淋洗水温度为25 ℃,盐温度通过鼓风干燥箱调节,在废盐达到对应温度后保持10 min,之后取出进行水洗实验。水洗后沥干时间为5 min,处理后的盐放入鼓风干燥箱干燥24 h,称重至示数恒定,然后将处理后的盐配制成300 g·L−1的盐溶液,并将溶液透过0.45 μm孔径的过滤膜进行抽滤处理,以除去水中不溶性杂质。所有实验均设3组平行样,结果取平均值。
根据预实验确定考察因素液固质量比(A)、水洗次数(B)、盐温(C)的中心点,以废盐的失重率和UV254去除率为响应值,采用Box-Behnken (BBD)模型设计3因素3水平实验,各独立变量及其范围水平结果见表1。
-
采用配备2个光程为10 mm方形石英池的紫外分光光度计(UV-2600,UV-VIS SPECTROPHOTOMETER,SHIMADZU,日本)测定废盐溶液在波长254 nm的吸光度;并在185~400 nm的波长范围内以0.5 nm的采样间隔扫描样品,测定废盐溶液的吸收光谱;用超纯水作空白参考。三维荧光光谱采用荧光分光光度计(F-7000, HITAHCHI,日本)进行扫描。总有机碳(TOC)由非色散红外吸收总有机碳分析仪(TOC-L/CPH,SHIMADZU,日本)测定。
废盐的失重率按式(1)计算。废盐的UV254去除率按式(2)计算。
式中:m1表示称取的废盐质量,g;m2表示坩埚质量,g;m3表示滤纸质量,g;m4表示废盐经处理烘干后的质量,g。
式中:A0表示处理前废盐溶液在波长为254 nm处的吸光度;A1表示处理后废盐溶液在波长为254 nm处的吸光度。
因TOC检测较为复杂,为快速检测实验效果,本研究确定采用溶液的UV254值代替TOC值来表征有机物的去除效果,该方法在水质检测中也有较多应用[26-30]。通过测定不同浓度下废盐溶液的UV254值和TOC值,并以溶液的UV254值为自变量x,溶液的TOC值为因变量y对2者进行分析;得到二者的线性方程为y=1 267.121x+3.979,拟合度R2为0.998。因此,本研究采用废盐溶液的UV254值来进行实验效果的表征是快速且可行的,能够很好地表征废盐中有机物的含量。
1.1. 供试原料
1.2. 实验方法
1.3. 分析方法
-
根据表2的实验结果,采用Design expert 12软件分析数据,建立失重率和UV254去除率的3阶回归数学模型(式(3)和式(4))。
式中:A、B、C分别代表液固质量比、水洗次数和盐温度的编码值。
对上述数学模型进行方差分析,结果见表3和表4。通过采用Design Expert 12软件进行上述模型的方差分析和回归分析发现,废盐失重率模型的R2为0.9935、R2Adj−R2Pred=0.06<0.2;废盐UV254去除率模型的R2为0.9932、R2Adj−R2Pred=0.09<0.2。以上结果表明,这2个模型的拟合程度高,实验的误差较小[31]。因此,可用这2个模型对废盐水洗的结果进行预测,模型可信度高。
在响应面模型中,P值的大小与模型的显著程度有关联[32]。由表3可知,在考察3个影响因素A、B、C对废盐失重率的影响中,液固质量比和水洗次数对废盐失重率的作用效果较为显著(P<0.05);废盐温度对废盐失重率的作用效果不明显(P>0.05)。废盐失重率模型一次项系数A(液固质量比)、B(水洗次数)远大于C(盐温度),且失重率随C(盐温度)呈负相关。3个独立变量对废盐失重率的影响关系为,水洗次数>液固质量比>盐温度。但是在表4中,3个影响因素A、B、C对废盐UV254去除率的效果均显著;尤其以水洗次数和盐温度对去UV254去除率的影响最为明显。3个独立变量对废盐UV254去除率的影响关系为,水洗次数>盐温度>液固质量比。
-
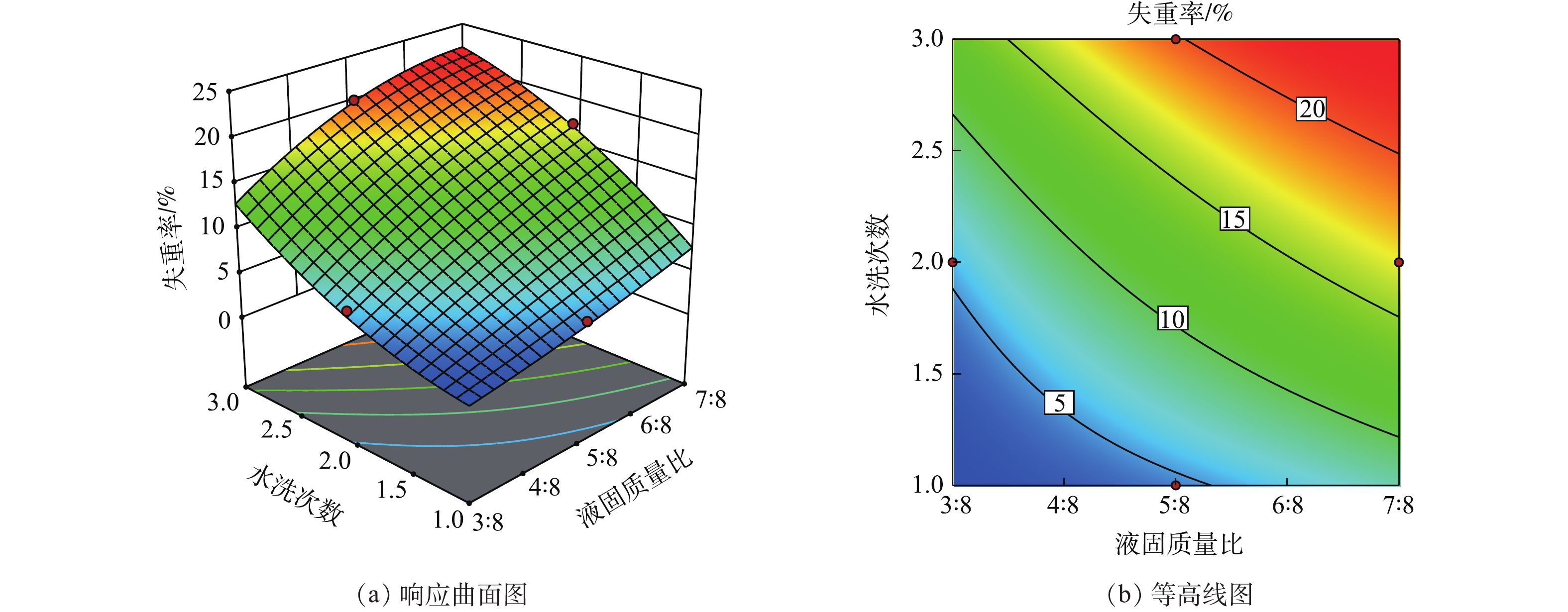
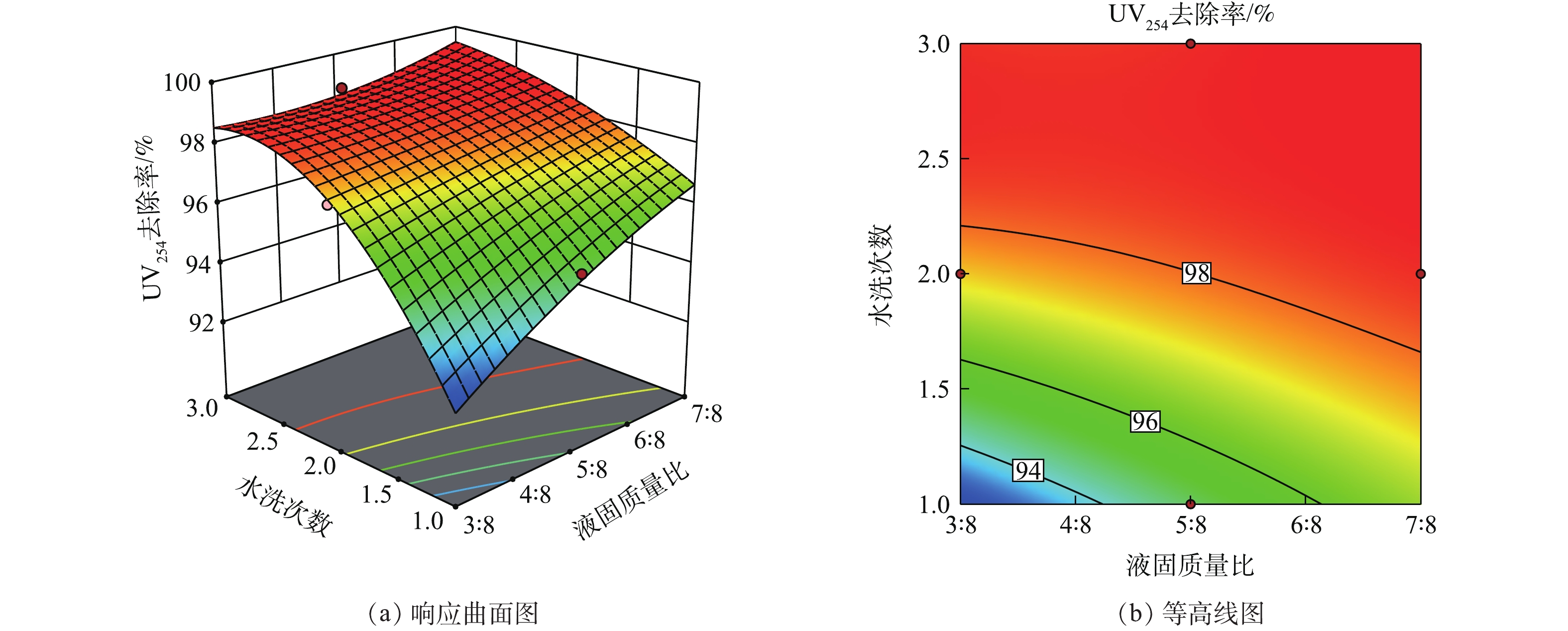
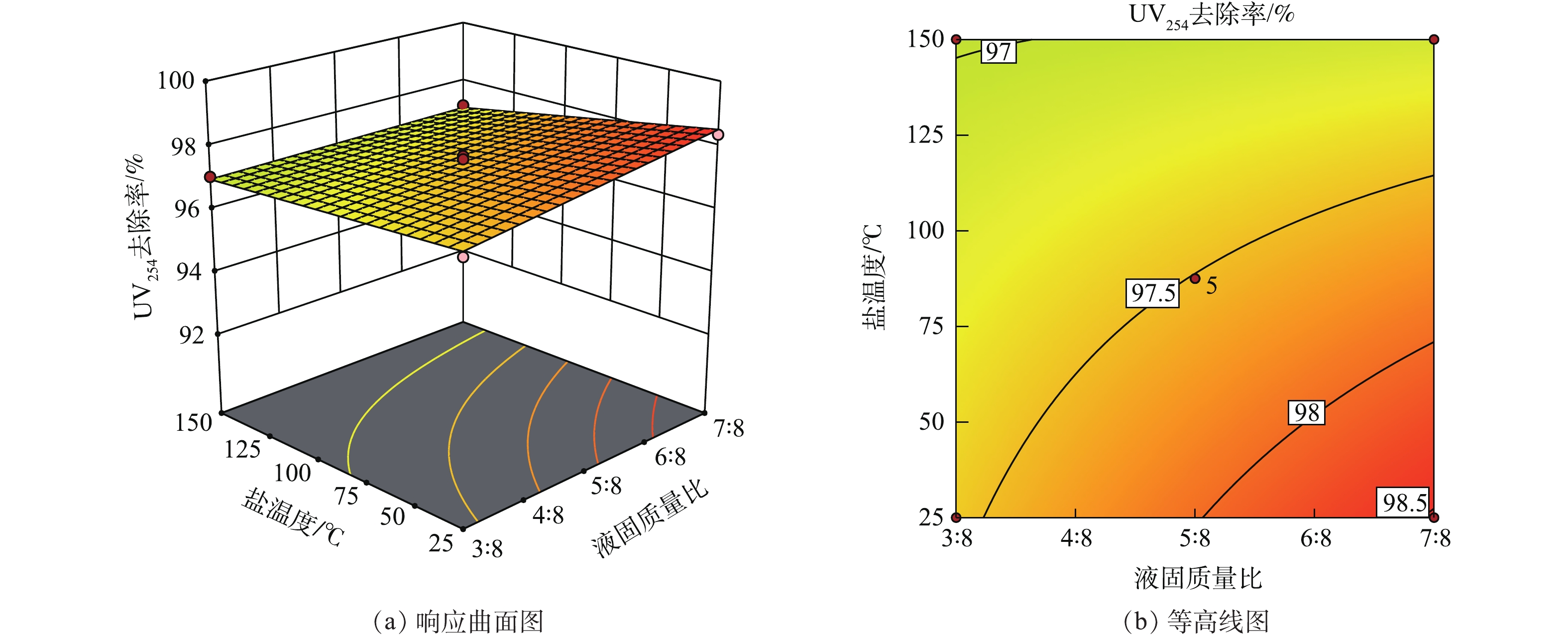
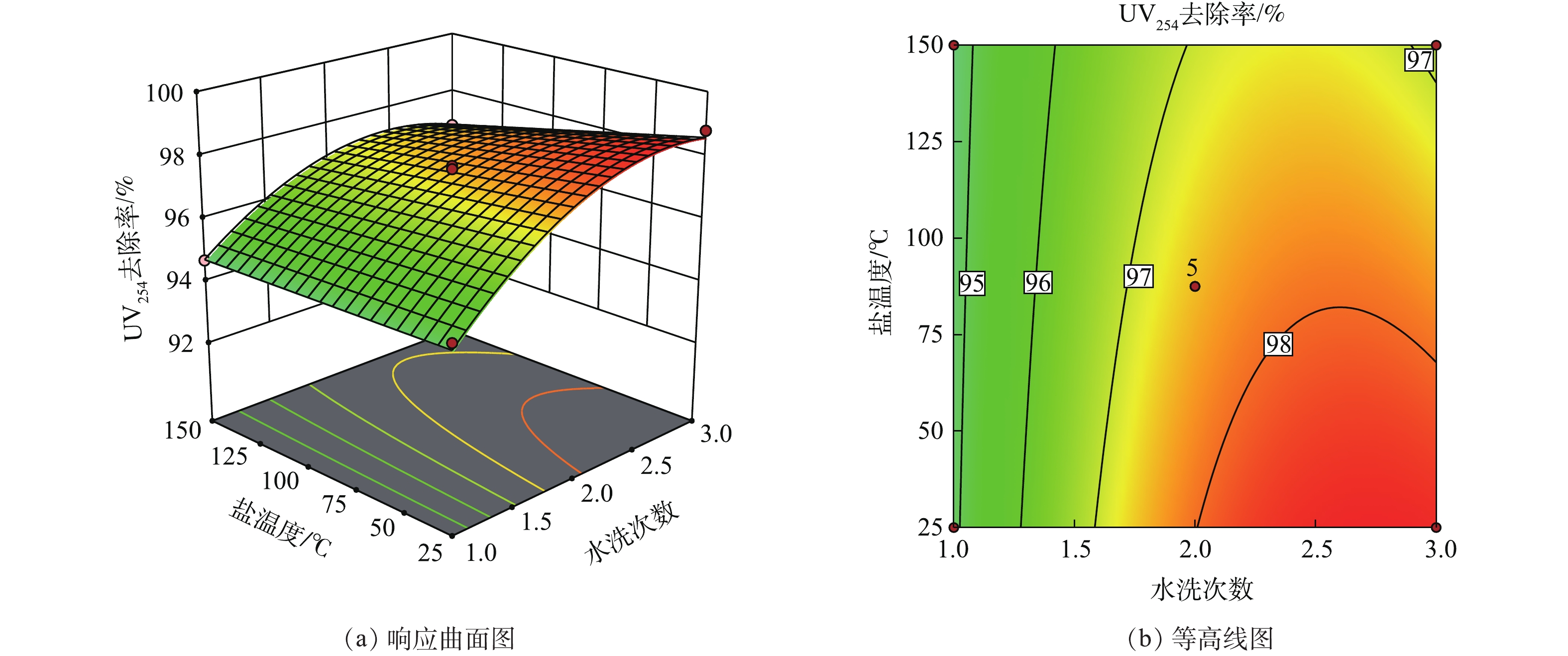
在响应曲面法中,响应曲面图及等高线图可以直观地反映各因素对响应值的影响。响应曲面陡峭,则说明变量对响应值的作用显著;曲面平缓,则说明作用不显著。等高线的弯曲程度表示变量的交互作用,弯曲程度越大其影响作用越显著。当等高线没有闭合时,曲线由密到疏表明独立变量对响应值的影响变化较为均匀[33-35]。
如图1(a)所示,废盐失重率随液固质量比和水洗次数的增加而变大,但液固质量比和水洗次数对失重率的影响没有明显的极值产生。这是因为,废盐的失重受水量影响较大。当淋洗水量较小时,水溶解NaCl及盐中杂质的量比较少;随着水量的增加,水中可溶解的有机物以及NaCl的量也不断增加。当淋洗水超过一定量时,废盐中可溶解脱出的有机物已经全部溶于淋洗水中,此时若一味增加水量将不会提高废盐的有机物去除率,反而会使NaCl在水中的溶解量增加。因此,不论是液固质量比的增加还是水洗次数的增加,本质上均是增加了淋洗水量及淋洗水与废盐的接触,使得部分NaCl溶解到水中,从而造成废盐失重率的增加。因此,在选择合适的液固质量比和水洗次数时,还应考虑两者对废盐的UV254去除率的影响。从图1(b)可以看出,在液固质量比小于5∶8、水洗次数小于等于2次时,两者的交互作用对失重率的影响较为显著,随着液固质量比和水洗次数的增加,两者的交互作用对失重率的影响越来越小。
液固质量比和淋洗次数的增加会提高废盐UV254去除率,该去除率最高可达98%以上。如图2所示,液固质量比和淋洗次数的交互作用对UV254去除率的变化均匀且影响显著。观察图2(a)可发现,曲面在液固质量比和水洗次数比较低时较为陡峭,但随着淋洗次数和液固质量比的增加,曲面变得较为平缓。这表明,水洗去除盐中有机污染物的效果受到了限制,这与LI等[36]的响应曲面分析结果一致。通过水洗的方式去除废盐中的有机物是有一定限度的,淋洗只能带走废盐中部分易溶的、与NaCl结合不紧密的有机物;而对一些难溶水的、被废盐晶体颗粒包裹的有机物则难以通过淋洗的方式去除。
由图3(a)可以看出,响应曲面较为平缓。这说明,液固质量比和盐温度对UV254去除率的影响较弱;且在25~150 ℃内,废盐的UV254去除率均保持在96%~99%,温度的影响在废盐水洗实验中对有机物的去除较弱。如图3(b)所示,等高线弯曲程度较小,且疏密均匀。这表明,因素间的相互影响不太显著,即液固质量比和盐温度对UV254去除率的影响是不显著的,这与狄军贞等[37]的响应曲面分析结果一致。废盐UV254去除率的极值在等高线图的右下角范围内出现;此区域表明,废盐水洗过程中盐的温度越低,废盐水洗处理效果越好。在同一液固质量比的条件下,由于盐温度的升高,废盐颗粒之间存在粘连、结块现象,从而造成水洗处理过程中水与废盐颗粒的接触面积减小。因此,废盐中有机物的去除效果有所降低。
图4显示了水洗次数和盐温度对UV254去除率的交互作用。响应曲面在水洗次数坐标轴方向上的变化较大,当水洗次数小于2次时较为陡峭,而在盐温度方向上的变化则较为平缓。这说明废盐中有机物的去除效果受水洗次数的影响大,受盐温度的影响小。盐温度越低、水洗次数越多,废盐的UV254去除率越高。两者的等高线弯曲程度较大,这说明两者交互程度显著。在实际生产过程中,要重点考虑废盐的温度和水洗次数对废盐有机物去除率的影响。
-
以废盐失重率最小值、废盐UV254去除率最大值为指标,利用Design Expert 12软件预测的最佳实验条件为:液固质量比为5:8、水洗次数为2次、盐温度25 ℃。在此条件下,废盐的失重率预测值为12.2%、废盐的UV254去除率为98%。在此条件下进行了3次平行实验,以验证模型的准确性。结果表明,废盐的失重率为(12.6±0.2)%、UV254去除率为(97.8±0.1)%,此实验结果与模型预测的结果较为吻合。这说明,响应面法对于预测废盐水洗结果可靠性较高。
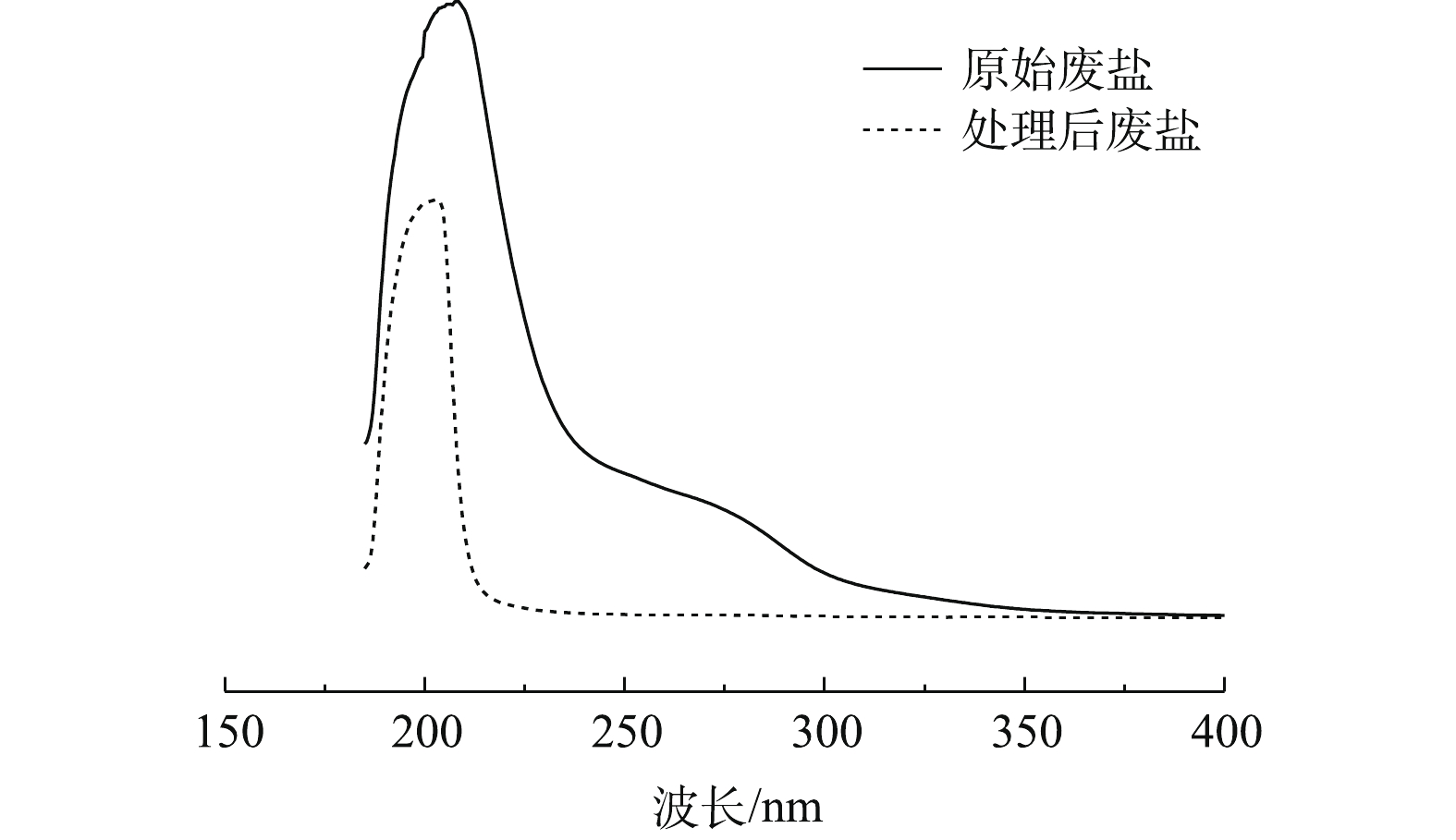
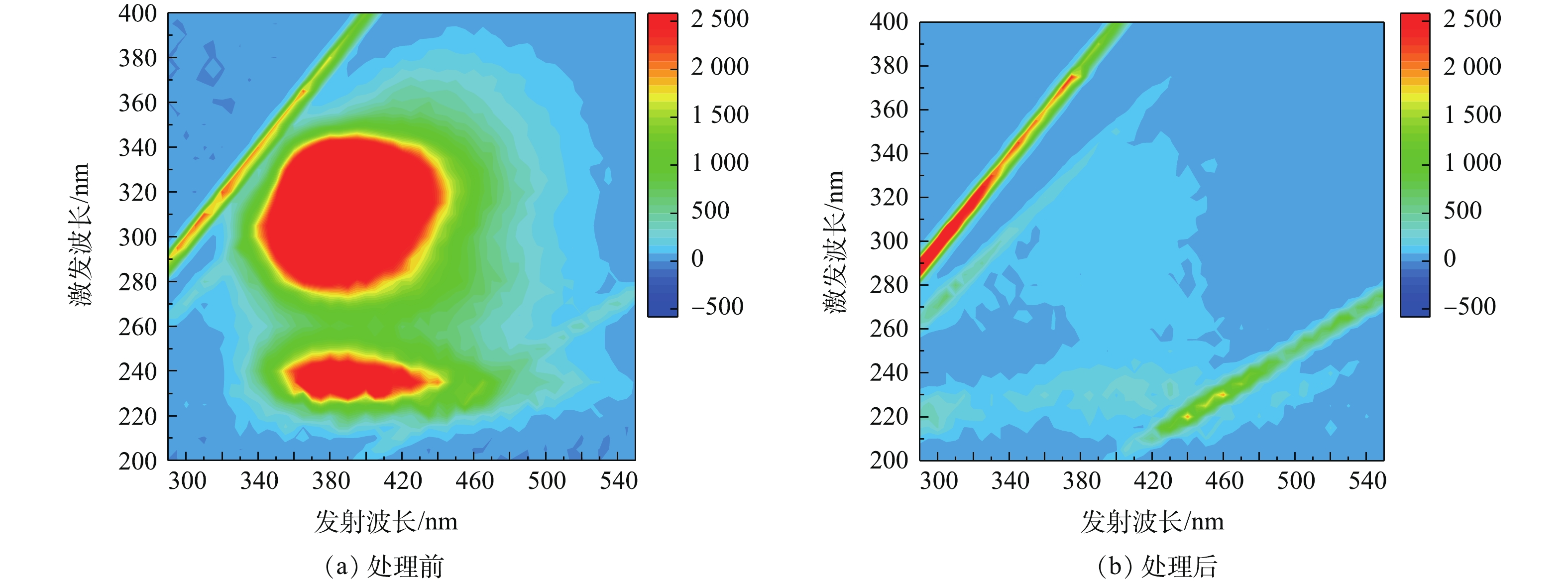
如图5所示,对比处理前后废盐溶液的紫外吸收光谱可以看出,经过水洗处理后,废盐中的有机物已被去掉,且水洗处理没有改变废盐的紫外吸收光谱。三维荧光光谱技术可以用来检测溶液中溶解性有机物,反映有机物结构和性质的变化[38]。如图6所示,通过对比处理前后废盐的三维荧光光谱可发现,废盐在发射波长为380~550 nm、激发波长为200~250 nm的区域内和发射波长为380~550 nm、激发波长为250~400 nm的区域内有明显的荧光峰;经水洗处理后,上述区域的荧光强度均有所降低。这说明,废盐中有机物可通过水洗的方式得到去除。在最佳实验条件下,饱和盐溶液的TOC降至19.81 mg·L−1,TOC去除率达80%以上,均可满足隔膜电解制碱所用NaCl指标TOC<200 mg·L−1的要求[39-41]。后续再经光催化氧化处理后,废盐溶液的TOC可降至10 mg·L−1以下,可满足离子膜电解所用NaCl的要求。
2.1. BBD实验结果和方差分析
2.2. 响应曲面分析
2.3. 废盐水洗去除有机污染物模型预测
-
1)采用响应曲面法所建立的水洗法处理酮连氮法生产水合肼副产废盐的废盐失重率和UV254去除率预测模型,拟合程度高、预测结果可靠。
2)就对废盐失重率的影响而言,水洗次数>液固质量比>盐温度;就对废盐UV254去除率的影响而言,水洗次数>盐温度>液固质量比。综合考虑,在实际应用中应以水洗次数和液固质量比为主要考虑因素。
3)废盐的最佳处理条件为,液固质量比为5∶8、水洗次数为2次、盐温度为25 ℃。在此条件下,得到废盐的失重率为12.6%、UV254去除率为97.8%。





 DownLoad:
DownLoad:
