-
生活垃圾无害化处理方式主要包括卫生填埋、焚烧和堆肥等[1]。截至2020年,焚烧处理占62%成为我国生活垃圾的主要处理方式[1]。在生活垃圾焚烧过程中易生成具有致癌、致畸、致突变和伤害免疫系统等危害的二恶英 (PCDD/Fs) ,它包括多氯代二苯并呋喃 (PCDFs) 和多氯代二苯并二恶英 (PCDDs) [2-4]。目前,生活垃圾焚烧厂采用“3T+E”的焚烧方式配合烟道活性炭喷射+布袋等措施加以控制[5]。然而,因为缺少二恶英的在线监测设施,二恶英的控制仍存在较大的不确定性[6],难以达到实时控制要求。
近年来,研究者在生活垃圾焚烧设施二恶英防控和软测量方面开展了诸多研究。结果表明,在生活垃圾焚烧过程中,二恶英主要在烟气降温区间 (400~200 ℃) 生成 [7],二恶英的生成机理包括“高温气相生成”、“从头合成 (de novo) ”和“前驱物生成”3种,其中,“从头合成”和“前驱物生成”占主导地位[5,8-9]。在二恶英的排放与预测方面,有研究者发现,其排放量主要与生活垃圾成分、燃烧状态和烟道活性炭喷射等因素密切相关,并采用随机森林法、人工神经网络和支持向量机回归算法等构建了二恶英排放的预测模型[6,10-11] ,但仍然很难为实时调控二恶英的排放提供科学支持[11]。
针对如何通过实时调节运行参数实现二恶英减排的问题,本研究以华南某生活垃圾焚烧发电厂为研究对象,通过分析焚烧系统的各种运行状态下的炉内特征、二恶英和常规大气污染物的排放特征,阐明二恶英的生成机理及其调控方案,以期为优化焚烧过程和降低二恶英排放提供参考依据。
-
某生活垃圾焚烧发电厂3台生活垃圾焚烧炉 (1#炉、2#炉、3#炉) 型号一致,均为机械炉排炉。烟气处理工艺均为SNCR+半干法 (干法) 脱酸+活性炭喷射+布袋除尘,烟气处理设施的厂家和型号均一致。它们同时建成同时投入运行,截至2022年均已正常运行5年。
数据收集时间范围。2019年1月至2021年12月,数据采集期间内该厂焚烧处置的对象仅为服务区内的生活垃圾。在线监测数据数量为72 268条,其中1#炉24 684条、2#炉24 047条、3#炉23 537条;在线监测数据包括常规污染物 (颗粒物、SO2、NOX、HCl、CO小时均值) 和烟气参数 (烟气流量、烟气含氧量、烟气温度、烟气压力、烟气湿度小时均值) ,共计10种。剔除在线监测设备维护、启炉和停炉等异常时段数据后,其余数据进行统计分析。二恶英的采样频率为每季度1次,每次每台炉采集烟气样品3个,共计108个样品。所有样品的采样位置均为烟囱取样口。
-
颗粒物监测设备 (LSS2004型,安荣信 (北京) 科技有限公司) ,监测原理为激光后向散射法。SO2、NOX、HCl、CO、烟气湿度监测设备 (MBGAS-3000型,ABB Inc. Measurement & Analytics) ,监测原理为傅里叶红外光谱法。烟气温度、烟气流速、烟气压力监测设备为 (PT-1D,重庆川仪分析仪器有限公司) ,监测原理为铂电阻法和皮托管原理。烟气含氧量监测设备 (GMS10,重庆川仪分析仪器有限公司) ,监测原理为氧化锆法。二恶英数据来源于经过计量认证的第三方检测机构。
-
k-Means算法是一种无须对数据进行标记而发现数据内在统计特征的无监督学习算法[12]。k-Means算法对于给定的数据集,采用欧式距离作为相似性指标,将数据及划分为k个簇 (类) 。聚类目标是使得各类的聚类平方和最小,即最小化式(1)。
式中:E为均方误差,i为聚类类别,k为聚类类别数量,Ai为第i类样本集合,x为属于Ai类别的样本,μi为Ai的均值向量。
在本研究中,采用Kolmogorov-Smirnov (KS) 检验和Krusal-Wallis非参检验完成正态分布和卡方分布拟合优度检验;采用单因素Levene检验完成方差齐性检验;采用Kruskal-Wallis H检验、Mann-Whitney U检验完成差异检验;采用k-Means算法挖焚烧炉和烟气处理设施运行状态;采用Spearman秩相关检验完成相关性分析;采用bootstrap自助法完成二恶英数据的均值估计。
k-Means算法和统计检验采用python语言和scipy 1.7.3统计包、sklearn 1.1.1机器学习库完成。
-
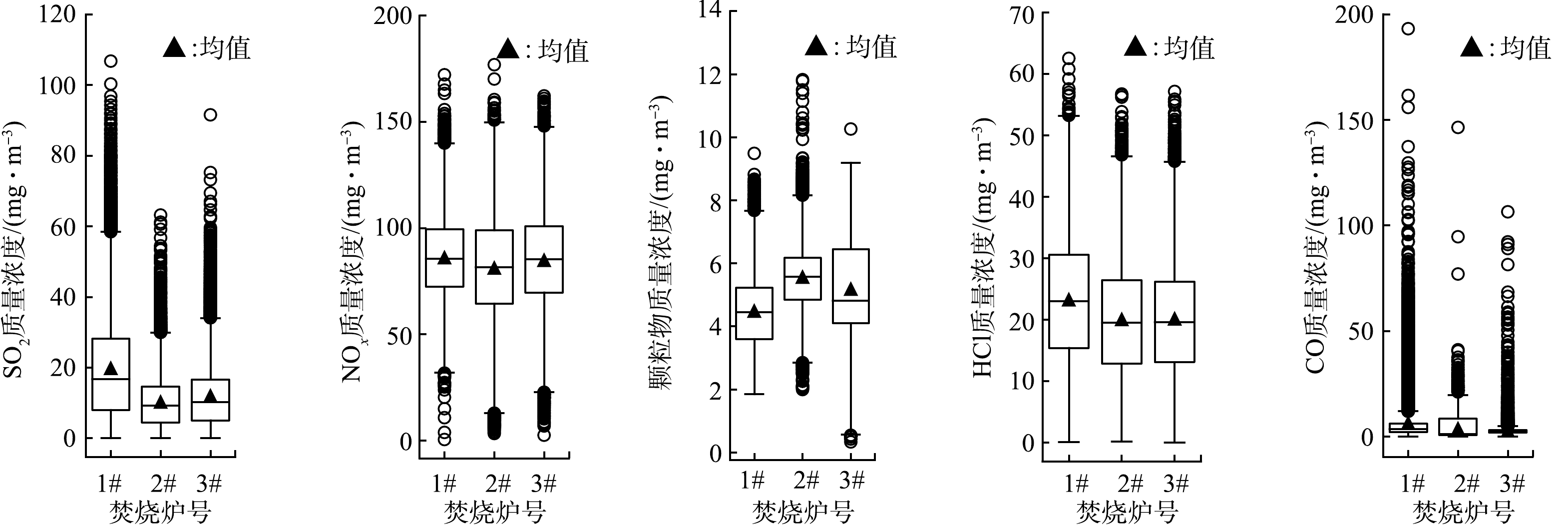
将各焚烧炉排放的污染物的质量浓度数据用统计检验进行处理。Kolmogorov-Smirnov (KS) 检验结果显示,各焚烧炉各常规污染物排放因子均不服从正态分布。Levene检验显示3台焚烧炉排放的各项大气污染物质量浓度的方差不齐 (p<0.05) 。Kruskal-Wallis H检验表明各焚烧炉排放的5种常规污染物的质量浓度均具有显著性差异 (p<0.05) 。由于样本数量大,常规污染物质量浓度仍采用算术均值讨论。该生活垃圾焚烧发电厂3台焚烧炉烟气中各常规污染物的排放特征如图1所示。由图1可以看出,1#炉排放的SO2质量浓度最高,其平均质量浓度是2#炉的2倍、3#炉的1.7倍;3台炉排放的NOx基本一致;2#、3#炉的颗粒物排放质量浓度基本一致,其平均质量浓度是1#炉的1.2倍;1#炉排放的HCl质量浓度最高,其平均质量浓度是2#、3#炉的1.2倍左右;1#炉排放的CO质量浓度最高,是2#炉、3#炉的1.7倍和2.4倍。这说明,在相同的生活垃圾来源、焚烧炉参数和烟气处理工艺下,各焚烧炉存在显著不同的污染物排放特征。其可能的原因与炉内状态及其和烟气处理设施所处的运行状态有关。比较特别的是,3台焚烧炉排放的NOx质量浓度较一致,这与文献报道的当炉内温度达到850 ℃时,NO的质量浓度基本不随温度的升高而变化一致[13]。
-
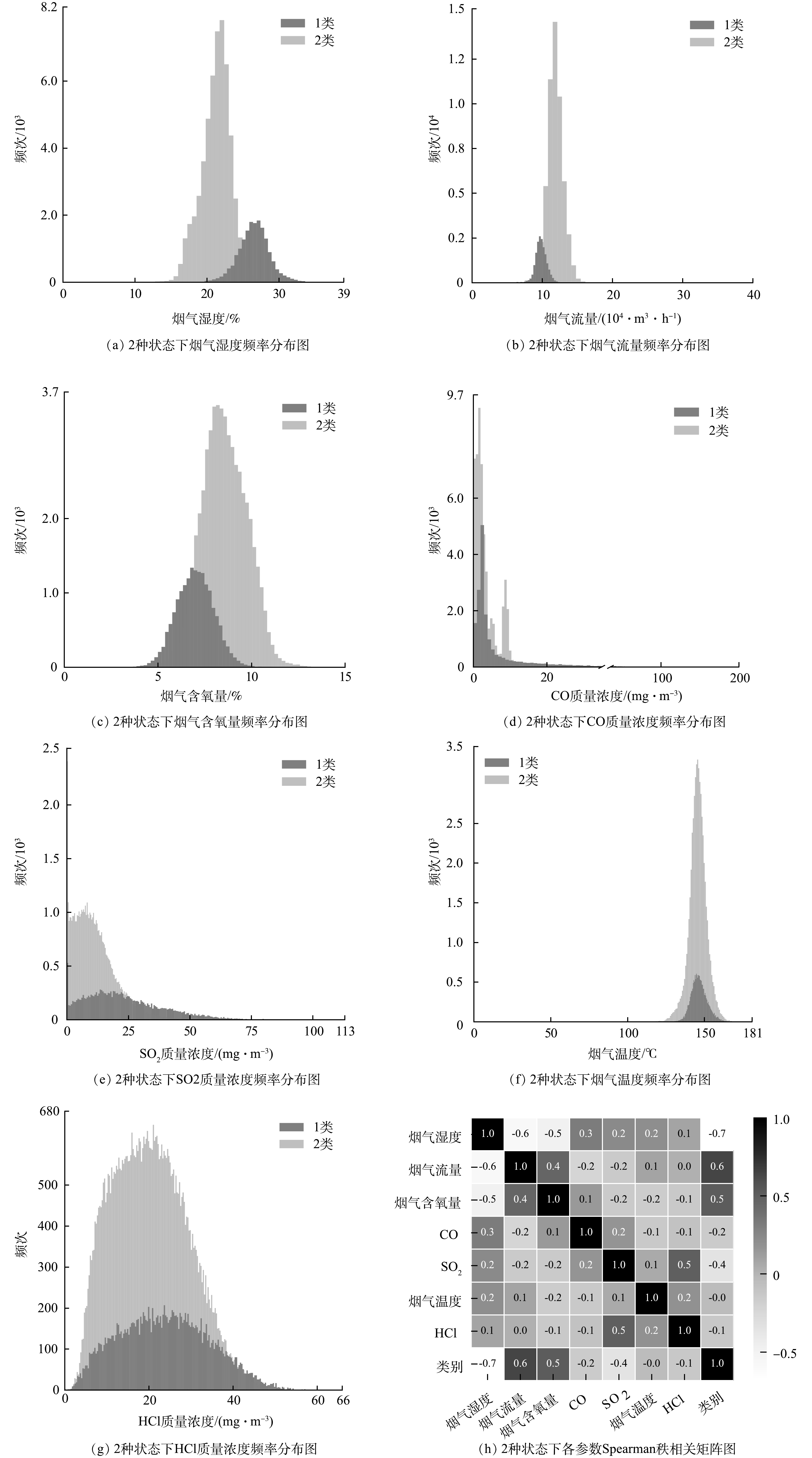
为分析焚烧系统的运行状态,采用k-Means算法对在线监测数据进行聚类。聚类前对数据特征进行Z-Score标准化,采用簇内离差平方和拐点法与轮廓系数法确定最佳分类为2类,即类别1和类别2,主要参数聚类结果和Spearman秩相关矩阵图如图2所示。由图2 (a)~图2 (g) 可以看出,3台焚烧炉可分为2种不同的运行状态。Levene检验显示各特征因子在2种类别下的质量浓度方差均不齐 (p<0.05) ,Mann-Whitney U检验结果显示各特征因子在2类状态之间存在的差异具有统计学意义 (p<0.05) 。这说明,2类状态之间差异显著。从各参数与不同类别的关系来看 (图2(h)) ,烟气湿度、烟气流量、烟气含氧量和类别的相关系数相对较高,分别为-0.7、0.6、0.5 (p<0.05) ,故3者是决定焚烧炉运行状态分类的主要参数。
根据焚烧炉燃烧运行控制原理,烟气流量是反应炉膛风量的直接指标,在实际运行过程中建议首先选取烟气流量作为炉内状态优化调整的主要指标;其次,CO是反应炉内燃烧是否充分的指标[13-14]。类别1状态下CO的排放质量浓度 (7±11.1) mg·m−3是类别2状态下的质量浓度 (3.5±3.8) mg·m−3的2倍,故可初步判定类别1的炉内状态较类别2差。结合类别1状态下烟气流量小于类别2、2类状态下温度差异小等特征,可推断出为维持焚烧系统运行温度,类别1状态降低了炉膛风量导致了类别1较差的炉内状态。
1#焚烧炉、2#焚烧炉、3#焚烧炉处于类别1状态下的小时数分别为15 233、1 352、838 h。从3台焚烧炉在不同类别下的运行时间来看,1#炉处于类别1状态下的频率明显比2#、3#焚烧炉高,其排放的污染物质量浓度也相应较高。故焚烧炉的炉内状态是影响烟气污染物排放的重要因素。
-
为进一步了解焚烧系统处于不同运行状态下其二恶英的排放特征。根据二恶英样品集样时运行状态将二恶英数据分为类别1和类别2。考虑到二恶英的记忆效应[15],采样时间段前或时间段内出现2种状态时则将样品归为类别1状态样本。类别1和类别2状态下二恶英样本数分别为31和77个。由于二恶英数据分布存在较大的变异性,采用bootstrap方法估计2种状态下二恶英的质量浓度均值[16]。Bootstrap样本数为原样本数的0.9倍,采样次数为10 000次,结果如表1所示。由表1可知,类别1状态下二恶英的质量总浓度 (∑PCDD/DFs,即17种单体质量浓度之和) 为类别2状态下的1.5倍左右,类别1状态下∑PCDD/DFS的毒性当量浓度[4]是类别2状态下1.4倍左右。Krusal-Wallis非参检验结果显示各类别下∑PCDD/DFS的质量浓度和17种单体的质量浓度均不服从正态分布 (p<0.05) ,Mann-Whitney U检验结果显示各类别下∑PCDD/DFs差异显著 (p<0.05) 。
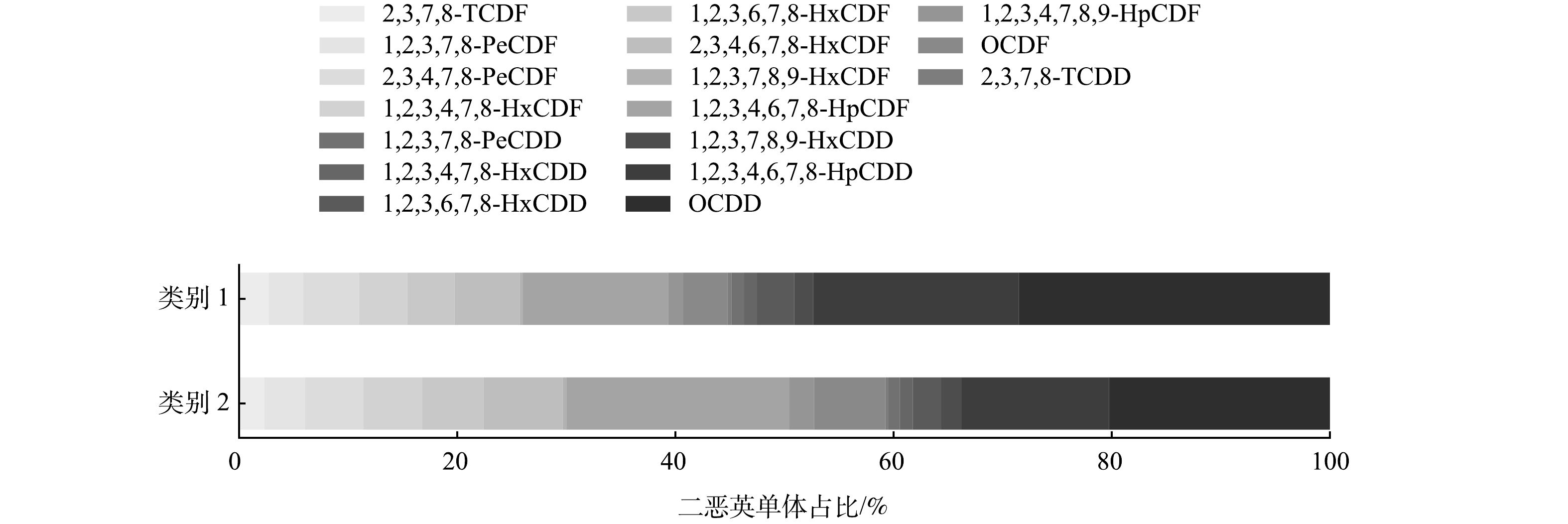
类别1状态下除2,3,7,8-TCDF和2,3,4,7,8-PeCDF单体外的其他8种PCDFs单体的质量浓度为类别2状态下的0.9~1.3倍,类别1状态下7种PCDDs单体的质量浓度为类别2状态下的1.4~2.1倍。类别1状态下PCDDS、2,3,7,8-TCDF、2,3,4,7,8-PeCDF的质量浓度明显高于类别2状态下。故从质量浓度来看,类别2具有较低的二恶英排放质量浓度。同样,2类状态下垃圾焚烧炉排放的二恶英的成分谱 (图3) 存在明显差异。
现有研究表明,PCDFS和PCDDS的比例和二恶英的主导生成机理存在联系[17-18]。当PCDFS/PCDDS>1时,以“从头合成反应”为主;当PCDFS/PCDDS<1时,则以“前驱物合成反应”为主[19-21]。前驱物反应主要生成PCDDS,从头合成反应主要生成PCDFS[5,20,22]。本研究中,焚烧炉在类别1状态下其排放的PCDFs/PCDDs比值约为0.8,在类别2状态下其PCDFS/PCDDs比值约为1.5。故类别1状态下的二恶英主要由前驱物合成反应生成;类别2状态下的二恶英主要由从头合成反应生成。从2类状态下各二恶英单体排放的质量浓度来看,类别1的PCDDs明显高于类别2。因此,焚烧炉处于不同状态时,其二恶英生成的主导机理不同,其在“从头合成反应”主导的状态下二恶英排放的质量浓度明显低于“前驱物合成”主导的状态。
根据二恶英的生成机理和2类状态下二恶英的实测结果可知,造成2类状态下二恶英不同主导机理的原因主要是:类别1状态下炉内状态较差,前驱物焚毁效率低。前驱物在烟气降温排放过程中在飞灰的表面缩聚生成二恶英,主要以PCDDS为主;类别2状态下炉内状态较好,前驱物焚毁效率高。故类别2状态的PCDDs再合成的质量浓度低。
-
焚烧炉系统在2类状态下的烟气参数频率分布见图2。由图2可知,烟气流量、烟气含氧量、CO质量浓度和烟气湿度在2类状态下分布范围存在较大的差异。从二恶英的生成机理方面来看,降低飞灰中二恶英前驱物的覆盖率和增加烟气的降温速率可减少“前驱物合成”为主导机理的二恶英的生成。降低烟气中前驱物的质量浓度,主要是增加烟气在炉膛温度大于800 ℃的炉膛反应区的停留时间和湍流度,提高前驱物的焚毁率;降低烟气在高温换热区 (800~500 ℃) 的停留时间,降低前驱物的再生成率[23-25]。因此,当焚烧炉位于类别1状态下,可通过提高烟气在炉膛反应区的时间和降低烟气在高温换热区的时间来降低烟气中二恶英前驱物的质量浓度。
类别1状态下的烟气湿度较类别2状态下高 (p<0.05) ,温度差异小。这表明,类别1状态下烟气中水分含量更高,更容易携带细颗粒物。烟气中二恶英在气相、液相和固相分布的研究结果表明[20,26],烟气中约54%的二恶英吸附于液相中的细颗粒物表面。故烟气湿度也是造成类别1状态二恶英质量浓度更高的原因之一,如2,3,7,8-TCDF和2,3,4,7,8-PeCDF等单体主要基于“从头合成”生成,但是在类别1状态下其质量浓度较类别2状态高。
综上,为降低焚烧炉烟气中二恶英排放的质量浓度,在实际运行控制中,可通过调节风量增加炉膛湍流度来提高前驱物的焚毁效率和增加炉膛氧量来提高炉膛燃烧效率等手段进行调控。在运行控制中,当炉内状态处于类别1时,以类别2状态各参数10th~90th分位作为控制目标,即首先保证烟气流量大于10.5×104 m3·h−1 (均值11.8×104 m3·h−1) ,其次烟气含氧量大于7.0% (均值8.6%)、CO质量浓度低于9.0 mg·m−3 (均值3.5 mg·m−3) 、烟气湿度低于23.7% (均值21.3%) 。由于风量的增加可能导致炉膛温度降低,故烟气温度也应作为控制指标并使其保持在140~154 ℃ (均值145.7 ℃)。
-
1) 3台焚烧炉具有显著不同的污染物排放特征,焚烧炉及烟气处理设施所处的运行状态决定了各污染物排放浓度的显著差异。
2) 3台焚烧炉的运行状态分为2类 (类别1和类别2) ,炉内状态是影响运行状态的主要因素,烟气流量是表征炉内状态的主要指标。类别1具有较差的炉内状态和较高的二恶英排放质量浓度。
3) 类别1状态下的二恶英主要由前驱物合成反应生成,类别2状态下的二恶英主要由从头合成反应生成。调整炉内状态可控制二恶英的排放。
4) 该厂焚烧炉各参数的最优控制条件为:首先应保证烟气流量大于10.5×104 m3·h−1 (均值11.8×104 m3·h−1) 。其余参数最优选择为:烟气含氧量大于7.0% (均值8.6%) 、CO质量浓度低于9.0 mg·m−3 (均值3.5 mg·m−3) 、烟气湿度低于23.7% (均值21.3%) 、烟气温度为140~154 ℃ (均值145.7 ℃) 。
Prevention and control of dioxins emission in domestic waste incineration facilities based on k-Means algorithm
- Received Date: 13/07/2022
- Available Online: 31/12/2022
-
Key words:
- domestic waste /
- incineration facilities /
- dioxins emission /
- k-Means algorithm
Abstract: In order to further explore the prevention and control of dioxins emission from domestic waste incineration facilities, pollution characteristics and control mechanisms of dioxins emitted from a domestic waste incineration power plant in South China under different operation status of incineration facilities and different furnace conditions were studied by k-Means algorithm. The results showed that three incinerators in the plant had significantly 2 different operation status (Status 1 and 2) (p<0.05), with distinct emissions of air pollutants including conventional pollutants and dioxins. The mass concentrations of CO and ∑PCDD/DFs were 2 times and 1.5 times higher, respectively, in Status 1 than Status 2. The dominant formation mechanisms of dioxins in status 1 and status 2 were the precursor synthesis reaction and the de novo synthesis reaction, respectively. To reduce the dioxins emission, the plant should firstly ensure that the smoke volume should be above 10.5×104 m3·h−1, and then guarantee that the other parameters of domestic waste incineration are in the following optimal range: flue gas oxygen content above 7%, carbon monoxide concentration below 9.0 mg·m−3, flue gas temperature between 140 ℃ and 154 ℃, and flue gas humidity below 23.7%. The incinerator should be shut down for maintenance when the limits of the optimal parameters are exceeded. The results could provide a scientific support for optimizing the incineration process and reducing dioxin emission, and also provide a theoretical basis for the identification and fine management of long-term stable operation of domestic waste incineration power plants.





 DownLoad:
DownLoad:
