-
矿山开发导致硫化矿物暴露于氧化环境中,产生大量的酸性矿山废水(acid mine drainage,AMD),AMD具有低pH、高重金属和硫酸盐的特点[1-3],会对矿区周围水生和土壤生态系统造成严重污染。传统处理方法为化学沉淀法[4],如石灰中和,但其存在废渣产量大、重金属含量高、金属资源浪费等问题,故限制了其大规模的应用。
硫酸盐还原菌(sulfate reducing bacteria,SRB)生物处理技术是一种有效治理AMD的方法,其主要反应过程为:SRB在还原氛围中将
${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - }$ 还原为S2−,代谢产物S2−与AMD中重金属离子形成硫化矿物[5-7]。但SRB活性易受AMD (酸、重金属)、代谢产物S2−等毒性抑制,从而导致其处理AMD效率降低。周立祥[8]和狄军贞等[9]发现,SRB最适pH为中性,在pH<5的AMD中,其处理活性较差。UTGIKAR等[10]、GUO等[11]、曹恒恒等[12]发现,Zn2+、Cu2+(≥20 mg·L−1)等重金属对SRB具有毒性抑制作用,且金属硫化物(金属离子与生物硫化物反应形成)是阻碍硫酸盐、有机物进入生物体系的屏障。LEWIS等[13]将SRB生化出水直接与AMD混合反应,发现水相中多硫化物络合物不利于金属去除,且金属沉淀物中包含未知复合物。BIJMANS等[14]报道,硫化物会抑制SRB生长,硫化物的去除可提高SRB活性。汪琦[15]采用两级循环气提工艺,有效解除了H2S对菌群(SRB、产酸菌、产甲烷菌)的毒性抑制。任立人等[16]采用两相厌氧-气提生化法,有效地解除了H2S对高含硫抗生素有机废水内SRB、产甲烷菌的毒性抑制。上述研究仅提出了对SRB活性抑制因素和单一因素的解除,鲜少涉及全面解除SRB(处理AMD)的多重毒性抑制和有效促进SRB活性的研究。本研究采用气提内循环反应器对AMD进行了处理,考察了反应器内涉硫组分的演变、产碱效率、微生物群落结构、重金属的去除,并对重金属沉淀物的纯度进行了分析;综合评估了气提内循环反应器内毒性抑制的解除效果及重金属回收,为AMD的SRB处理及有价金属回收提供应用指导和参考。
-
SRB菌种由课题组前期驯化所得。培养基的组成为 0.06 g·L−1 CaCl2·6H2O、1.0 g·L−1 NH4Cl、0.5 g·L−1 K2HPO4、0.738 g·L−1 MgSO4·7H2O、0.8 g·L−1 Na2SO4、1 g·L−1 FeSO4·7H2O、6 mL·L−1 乳酸钠(COD为2 000 mg·L−1)。SRB反应器运行控制参数为温度(25±2) ℃、pH 6.7~7.0。酸性矿山废水的水质参数为pH 3.01、21 mg·L−1 Cu2+、199 mg·L−1 Fe2+、30 mg·L−1 Zn2+、28.5 mg·L−1 Mn2+、1 098 mg·L−1
${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - }$ 。 -
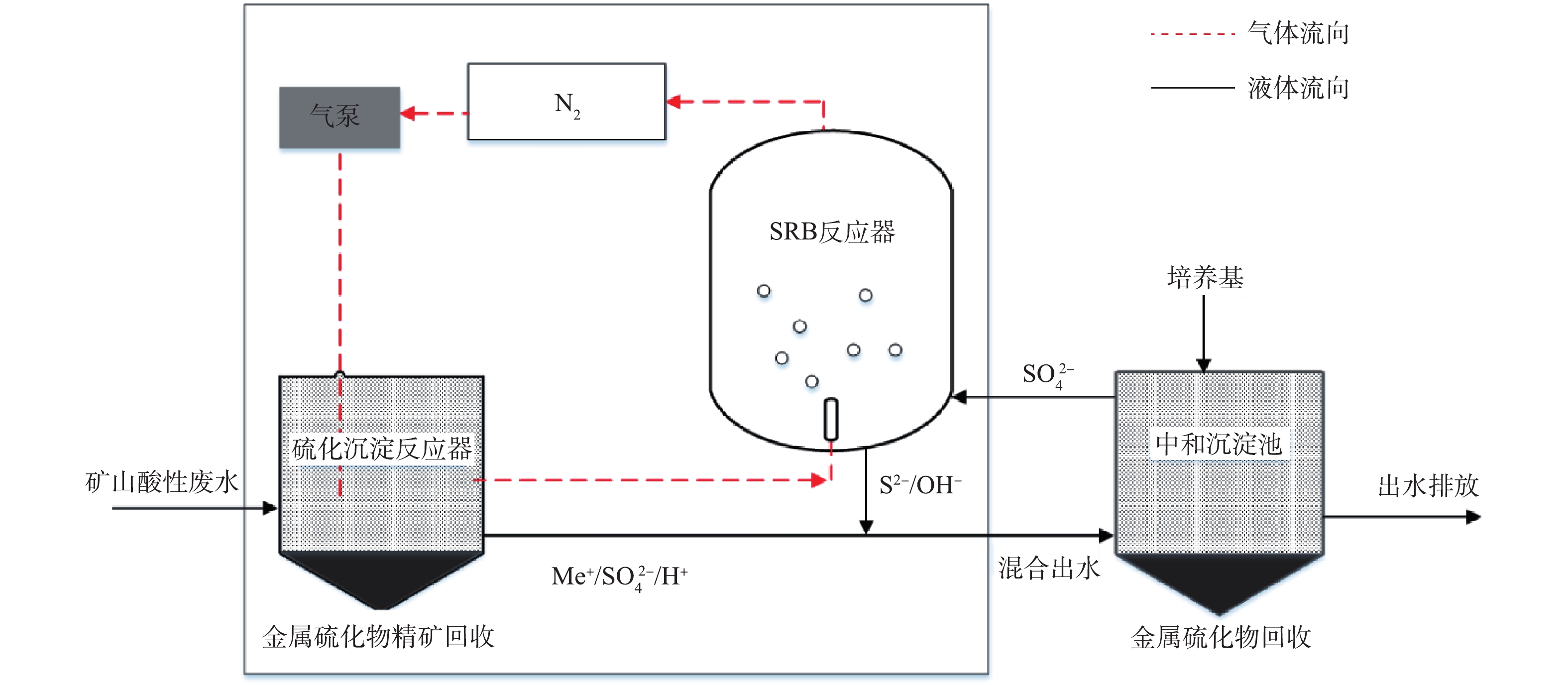
实验装置如图1所示。主要由SRB反应器(总体积4 L,其底部设有曝气装置)、硫化沉淀反应器(总体积3 L)、气泵、中和沉淀池组成;反应装置制备材料均为有机玻璃;反应器中AMD的进水量为3 L·d−1,中和排水量为3 L·d−1;在反应器运行过程中,采用气泵将循环N2(气体流量为0.005 L·min−1)引入SRB反应器,SRB代谢过程中产生的H2S被吹脱至硫化沉淀反应器;将中和沉淀池的上清液与培养基混合作为物料引入SRB反应器。传统反应器为有机玻璃SRB反应器(总体积4 L),将AMD(进水量为3 L·d−1)和培养基混合,直接引入该SRB反应器,反应过程中不进行吹脱,反应后排水量为3 L·d−1。
-
气提内循环反应器(SRB反应器)、传统反应器中菌液接种量均为20%。每隔2 h,对气提内循环反应器(SRB反应器)、传统反应器内涉硫组分(
${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - }$ 、${\rm{SO}}_3^{2 - }$ 、H2S、S2−)进行检测;每隔3 h,对气提内循环反应器(SRB反应器)、传统反应器内pH和ORP进行测定。在10、20、30、40、50、60 min和24 h时,在气提内循环反应器(硫化沉淀反应器)、传统反应器中取样,测定废水中金属离子的浓度。 -
使用pH计(上海雷磁,PHS-3C)测定pH;采用自动电位滴定仪(上海雷磁,ZD-2)测定ORP;使用硫离子浓度计(上海般特,Bante931-S)测定S2−;采用吹脱-金属离子吸收法和火焰原子吸收光谱仪(普析通用,TAS-990)测定H2S;选用 16S rDNA技术进行微生物群落结构分析;采用火焰原子吸收光谱仪(普析通用,TAS-990)测定重金属离子。
${\rm{SO}}_3^{2 - }$ 、${{\rm{S}}_2}{\rm{O}}_3^{2 - }$ 、${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - }$ 的样品预处理在4 000 r·min−1离心10 min,经0.22 μm滤膜过滤后,使用离子色谱分析仪(北京东西分析,IC-2800)并搭配色谱柱(美国Dionex,IonPacTMAS23 4×250 mm)进行测定,淋洗液配比为4.5 mmol·L−1 Na2CO3和0.8 mmol·L−1 NaHCO3,抑制电流为30 mA,淋洗液泵流速为1.0 mL·min−1。 -
从气提内循环反应器(SRB反应器)、传统反应器中取3组平行菌液,离心收集菌体,采用CTAB方法对样本的基因组DNA进行提取,之后利用琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测DNA的纯度和浓度。取适量的样本DNA于离心管中,使用无菌水稀释样本至1 ng·μL−1。以稀释后的基因组DNA为模板,引物对应区域:16S V4区引物(515F和806R)鉴定细菌多样性,使用带Barcode的特异引物、New England Biolabs公司的Phusion®带有GC缓冲液的高保真PCR预混液、高效高保真酶进行PCR。
PCR产物使用2%浓度的琼脂糖凝胶进行电泳检测;根据PCR产物浓度进行等量混样,充分混匀后,使用1×TAE浓度2%的琼脂糖胶电泳,纯化PCR产物,剪切回收目标条带。使用Thermo Scientific公司GeneJET胶回收试剂盒回收产物。
使用Thermofisher公司的Ion Plus Fragment Library Kit 48 rxns建库试剂盒进行文库的构建,构建好的文库经过Qubit定量和文库检测合格后,使用Thermofisher的Ion S5TMXL进行上机测序。
-
气提内循环反应器可有效解除代谢产物H2S对SRB的毒性抑制,并提高
${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - }$ 的去除率。气提内循环反应器与传统反应器的涉硫组分比率变化如图2所示。由图2可知,气提内循环反应器中${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - }$ 去除率为91.24%;传统反应器因不能及时排出H2S(S2−),其${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - }$ 去除率仅为36.5%。在气提内循环反应器中,${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - }$ 主要转化为${\rm{SO}}_3^{2 - }$ 和H2S(图2(a)),随着H2S的产率增加,${\rm{SO}}_3^{2 - }$ 逐渐降低,${\rm{SO}}_3^{2 - }$ 作为${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - }$ 和H2S的中间产物,成为代谢转化的限速因素。H2S作为${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - }$ 还原的最终产物,其浓度较高时会对SRB产生毒性抑制。FIRMINO等[17]、ZHAO等[18]发现H2S会导致反应器中微生物活性和硫酸盐降解率的下降。BIJMANS等[14]对生物反应器内硫化物进行了去除,发现微生物代谢活性可由13 mmol·(L·d)−1上升至51 mmol·(L·d)−1。气提内循环反应器的${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - }$ 去除率较传统反应器高,其原因是气提内循环反应器及时去除反应产物H2S,从而促进反应的进行,且解除S2−累积富集对SRB的毒性抑制。 -
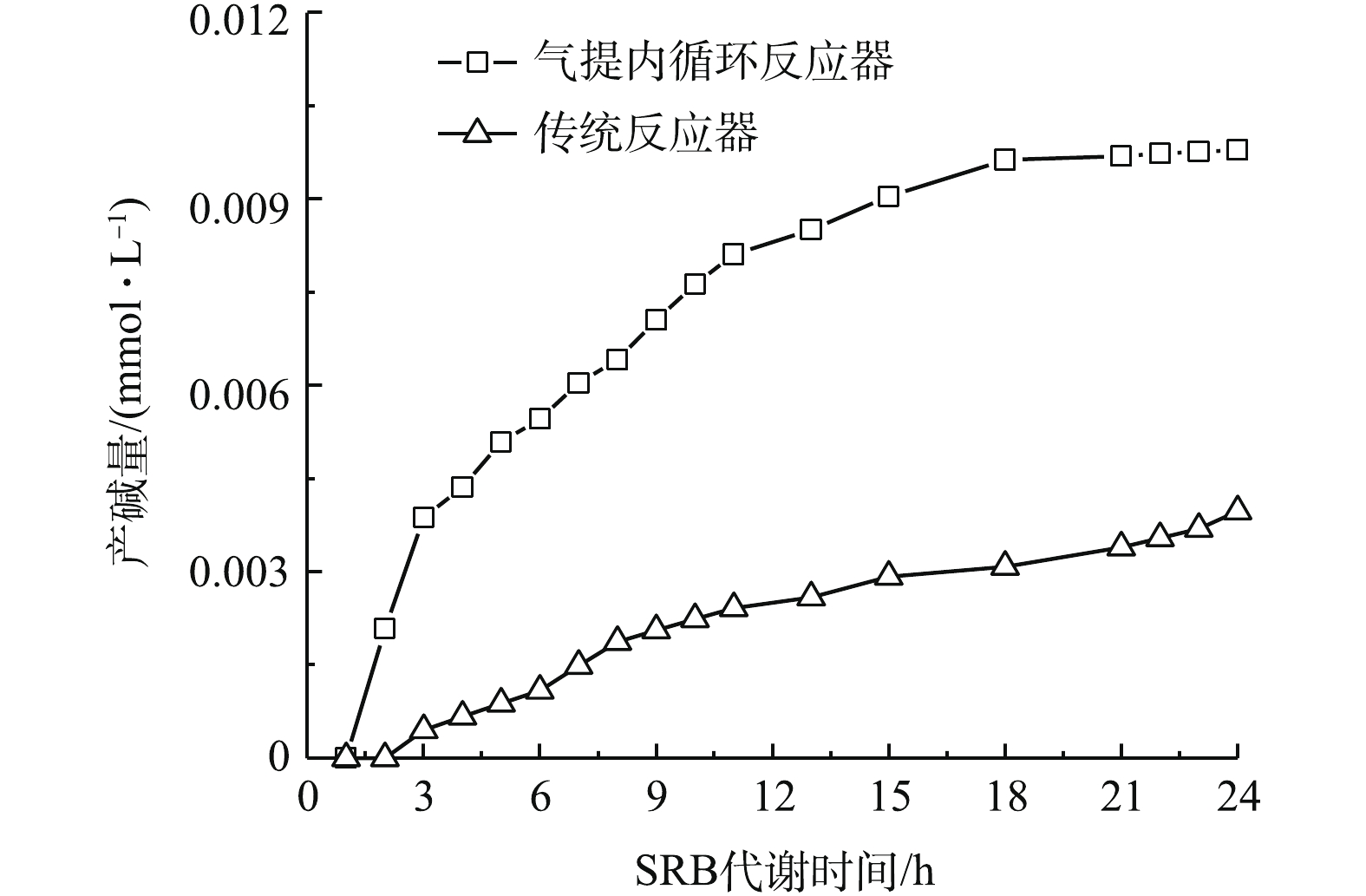
气提内循环反应器可避免AMD与SRB的直接接触所造成的毒性抑制与冲击,可实现较高的产碱效率。气提内循环反应器的产碱量变化情况如图3所示。由图3可知,气提内循环反应器的产碱量是传统反应器的3倍。在SRB代谢乳酸盐过程中会产生
${\rm{HCO}}_3^ - $ ,使得反应器内碱度逐渐增加[19],其反应机理[20]如式(1)和式(2)所示。系统中存在的Fe2+能促进各种酶的合成,缩短反应迟滞,促进SRB还原反应的进行[21-23],导致pH上升。随着反应的进行,
${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - }$ 逐渐转化为H2S,气提内循环反应器将H2S去除,不仅能使水体中OH−增加,还能避免S2−积累对SRB的毒性抑制。 -
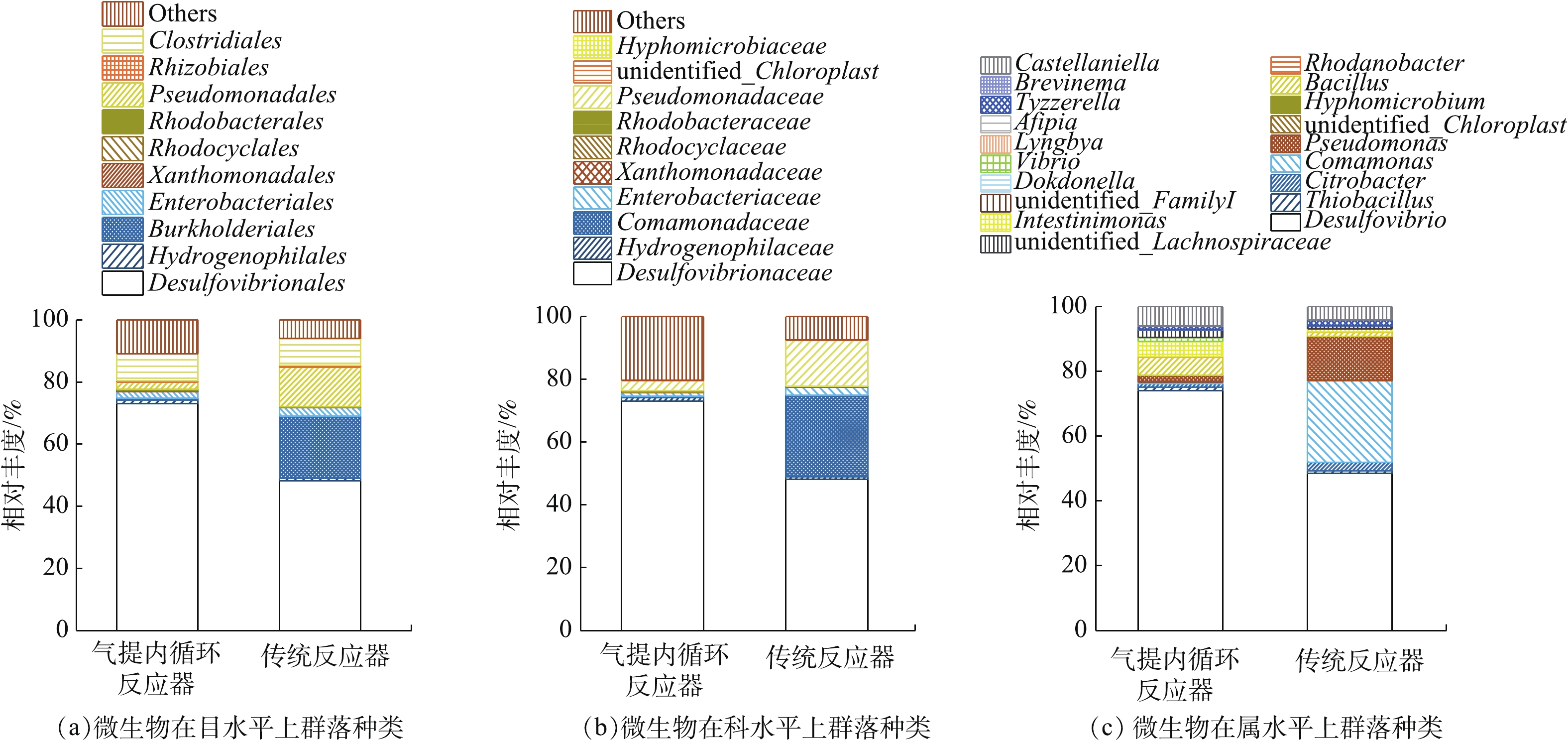
根据Barcode处理数据得到有效数据,再利用Uparse软件对所有样品的有效数据进行聚类,筛选出OTUs(operational taxonomic units,默认以97%的一致性序列聚类),并利用SSUrRNA数据库对OTUs进行物种注释分析,获得目、科、属群落组成(图4)。由图4可知,气提内循环反应器中脱硫弧菌(Desulfovibrio)在目、科、属水平上的相对丰度均为73%,传统反应器中脱硫弧菌的相对丰度仅为48%,对比2个反应器中菌属丰度,传统反应器中丛毛单胞菌(Comamonas)、柠檬酸杆菌属(Citrobacter)、假单胞菌(Pseudomonas)的相对丰度较气提内循环反应器明显增多。在适宜的环境条件下,SRB生长速度最快,能竞争到更多的营养物,使其在体系中的相对丰度较其他微生物高;当环境因素(pH、毒性物质的产生及含量等)改变时,SRB会对环境条件做出快速反应(调节体内代谢过程或改变细胞结构等),其内在生长速率也会发生变化[24]。传统反应器中pH(3.01)较低、代谢S2−积累和重金属离子的毒性抑制,均会导致SRB的竞争能力变弱、数量减少,而气提内循环反应器可解除酸、重金属及代谢S2−对SRB活性的多重抑制,充分发挥系统内优势菌属脱硫弧菌的还原能力。
-
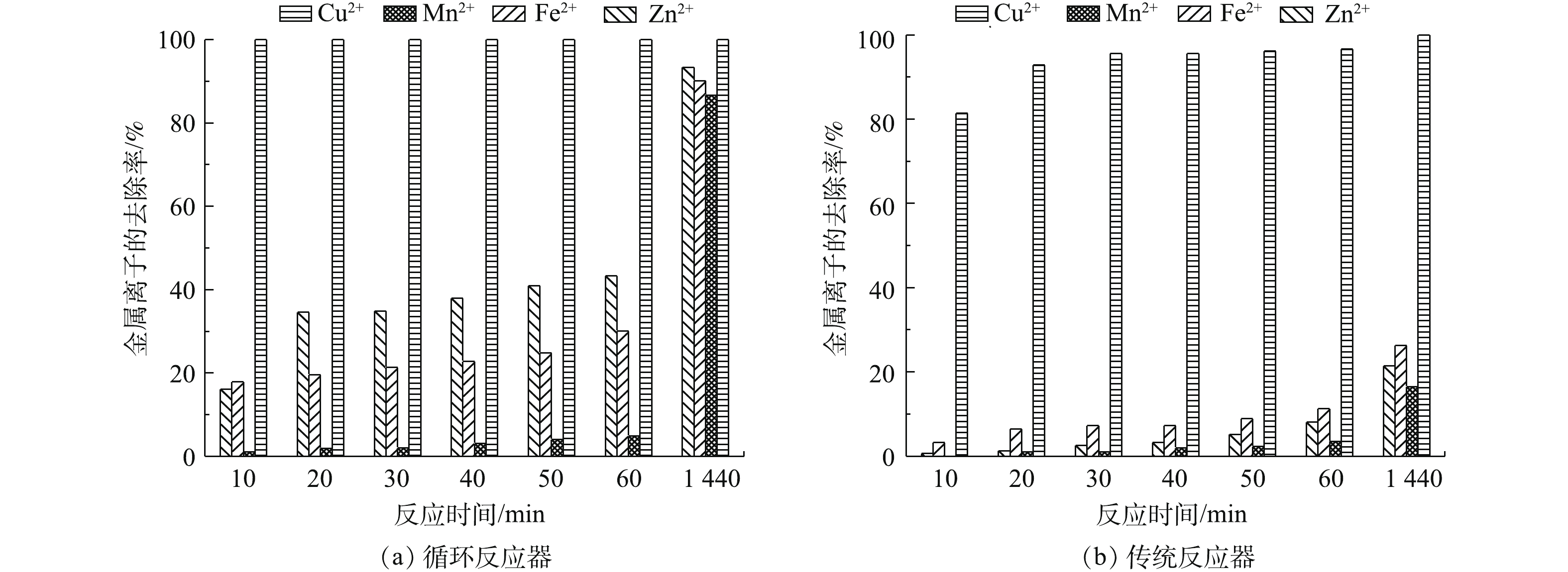
气提内循环反应器对AMD中重金属离子的去除效果较传统反应器好。气提内循环反应器和传统反应器对金属离子的去除效果如图5(a)和图5(b)所示。气提内循环反应器内Cu2+、Mn2+、Zn2+、Fe2+的去除率分别为100%、86.67%、93.34%、90.14%,Cu2+和Zn2+的出水浓度分别为0 mg·L−1和2 mg·L−1(表1),可达到《污水综合排放标准》二级标准;而在传统反应器内,Cu2+、Mn2+、Zn2+、Fe2+的去除率分别仅为96.6%、16.5%、21.4%、26.3%。反应器中Cu2+较其他金属离子容易去除的原因是,CuS的Ksp相较于ZnS、MnS、FeS等金属硫化物低,其溶度积常数顺序为MnS>FeS>ZnS>CuS[25-26];气提内循环反应器的金属去除率较传统反应器高,在气体内循环反应器中各金属的去除率为Cu2+>Zn2+>Fe2+>Mn2+,但在传统反应器中Fe2+的去除率较Zn2+高,产生该结果的原因是传统反应器内SRB酶的合成需要消耗大量的Fe2+[21]。
传统SRB反应器采用生化出水直接与重金属混合沉淀,但生化出水中除S2−外,还含有大量无效组分(如硫代硫酸根以及溶解性微生物产物、胞外多聚物等[1]),导致沉淀物中除金属硫化物外还含有其他复合物。气提内循环反应器运用目标代谢产物H2S与重金属沉淀,反应结束后,对该反应器中的沉淀物进行了XRF分析。结果表明,沉淀物中含有3.9% Cu、4.27% Zn、5.28% Mn、35.78% Fe、48.89% S,这说明目标代谢产物H2S与重金属产生的金属硫化物不含其他复合组分,且该金属硫化物的纯度可达98.12%。
-
1) H2S作为
${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - }$ 还原的最终产物,会对SRB产生毒性抑制;气提内循环反应器可有效解除H2S对SRB的毒性抑制,${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - }$ 去除率由36.5%(传统反应器)提升至91.24%。2)气提内循环反应器可避免AMD与SRB直接接触所造成的毒性抑制和冲击,实现较高的产碱效率,产碱效率是传统反应器的3倍。
3)体系中环境条件会影响脱硫弧菌属与丛毛单胞菌、柠檬酸杆菌属、假单胞菌之间的竞争;气提内循环反应器解除了多重抑制对脱硫弧菌属的活性影响,其相对丰度由传统反应器的48%提升至73%。
4)气提内循环反应器对AMD中重金属离子去除效果优于传统反应器。气提内循环反应器中Mn2+、Zn2+、Fe2+的去除率为86.67%、93.07%、90.14%,其金属硫化物的纯度可达98.12%,出水Cu2+和Zn2+浓度分别为0和2 mg·L−1,可达到《污水综合排放标准》二级标准。
基于硫酸盐还原菌的气提内循环反应器处理酸性矿山废水
Treatment of acid mine drainage by a gas stripping internal circulation reactor with sulfate reducing bacteria
-
摘要: 针对硫酸盐还原菌(SRB)处理酸性矿山废水(AMD)易受酸、重金属、代谢产物硫离子等多重毒性抑制的问题,采用气提内循环反应器对AMD进行处理,研究了反应器内涉硫组分的演变、产碱效率、微生物群落结构、重金属的去除效果。结果表明:气体内循环反应器可有效解除多重毒性抑制,体系中硫酸盐去除率由36.5%提升至91.24%;且其产碱效率提升了3倍,明显优于传统反应器,脱硫弧菌属的相对丰度也由48%提升至73%;硫化氢与重金属反应得到金属硫化物纯度可达98.12%,出水中Cu2+和Zn2+浓度分别为0和2 mg·L−1,可达到《污水综合排放标准》二级标准。以上结果可为SRB生物技术处理AMD的高效控制提供参考。Abstract: The treatment of acid mine drainage (AMD) by sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) was susceptible to multiple toxicity inhibition such as acid, heavy metal and metabolic sulfur ion. In this study, the gas stripping internal circulation reactor was used to treat AMD, the evolution of sulfur-related components in the reactor, alkali production efficiency, microbial community structure and heavy metals removal were studied. The results showed that the gas stripping internal circulation reactor could effectively eliminate multiple toxicity inhibition, the sulfate removal rate in the system increased from 36.5% to 91.24%, and its alkali production efficiency increased by 3 times, which was obviously superior to the traditional reactor, the relative abundance of Desulfovibrio increased from 48% to 73%. The purity of metal sulfide precipitated by hydrogen sulfide and heavy metals reached 98.12%, the concentrations of Cu2+ and Zn2+ in the effluent were 0 and 2 mg·L−1, respectively, which could reach the secondary standard of Integrated Wastewater Discharge Standard. This study can provide reference for the efficient control of SRB biotechnology treating AMD.
-

-
表 1 出水中重金属离子浓度
Table 1. Concentration of heavy metal ions in effluent
mg·L−1 反应器种类 Cu2+ Zn2+ Fe2+ Mn2+ 气提内循环反应器 0 2 19.61 3.8 传统反应器 0.72 23.58 146.66 23.8 -
[1] SÁNCHEZ-ANDREA I, SANZ J L, BIJMANS M F, et al. Sulfate reduction at low pH to remediate acid mine drainage[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 269: 98-109. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.12.032 [2] 陈莹, 陈炳辉, 邹琦, 等. 粤北大宝山AMD水-表层沉积物的重金属分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(1): 133-141. [3] 曹霏霏, 李红丽, 王岩. 干式厌氧消化过程挥发酸对硫酸盐还原菌的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2014, 8(3): 1169-1173. [4] ZHANG M L, WANG H X. Preparation of immobilized sulfate reducing bacteria (SRB) granules for effective bioremediation of acid mine drainage and bacterial community analysis[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2016, 92: 63-71. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2016.02.008 [5] YOREO J J D, GILBERT P U P A, SOMMERDIJK N A J M, et al. Crystallization by particle attachment in synthetic, biogenic, and geologic environments[J]. Science, 2015, 349(6247): 6760. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa6760 [6] 蒋永荣, 刘可慧, 刘成良, 等. UASB处理硫酸盐有机废水的启动[J]. 环境工程学报, 2014, 8(9): 3572-3576. [7] 李咏兰, 邱广亮, 王凯, 等. 磁性多孔微球固定化硫酸盐还原菌的研究[J]. 环境工程学报, 2011, 5(12): 2825-2829. [8] 周立祥. 生物矿化: 构建酸性矿山废水新型被动处理系统的新方法[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(6): 552-559. [9] 狄军贞, 江富, 朱志涛, 等. 混合硫酸盐还原菌处理煤矿酸性废水的固定载体研究[J]. 中国给水排水, 2015, 31(7): 100-108. [10] UTGIKAR V P, HARMON S M, CHAUDHARY N, et al. Inhibition of sulfate-reducing bacteria by metal sulfide formation in bioremediation of acid mine drainage[J]. Environmental Toxicology, 2010, 17(1): 40-48. [11] GUO J, KANG Y, FENG Y. Bioassessment of heavy metal toxicity and enhancement of heavy metal removal by sulfate-reducing bacteria in the presence of zero valent iron[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2017, 203(1): 278-285. [12] 曹恒恒, 张鸿郭, 罗定贵, 等. 重金属对硫酸盐还原菌影响[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2012, 35(12): 208-211. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2012.12.043 [13] LEWIS A, HILLE R V. An exploration into the sulphide precipitation method and its effect on metal sulphide removal[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2006, 81(3/4): 197-204. [14] BIJMANS M F, DOPSON M, ENNIN F, et al. Effect of sulfide removal on sulfate reduction at pH 5 in a hydrogen fed gas-lift bioreactor[J]. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2008, 18(11): 1809-1818. [15] 汪琦. 乙醇对硫酸盐还原-甲烷发酵效率影响的研究[J]. 环境科学, 2009, 30(3): 924-929. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2009.03.050 [16] 任立人, 张琳, 仝胜利, 等. 高含硫抗生素有机废水处理[J]. 水处理技术, 2001, 27(4): 225-228. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3770.2001.04.012 [17] FIRMINO P I M, FARIAS R S, BUARQUE P M C, et al. Engineering and microbiological aspects of BTEX removal in bioreactors under sulfate-reducing conditions[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 260: 503-512. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.08.111 [18] ZHAO F, ZHOU J D, MA F, et al. Simultaneous inhibition of sulfate-reducing bacteria, removal of H2S and production of rhamnolipid by recombinant Pseudomonas stutzeri Rhl: Applications for microbial enhanced oil recovery[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 207: 24-30. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.01.126 [19] DENG D, WEIDHAAS J L, LIN L S. Kinetics and microbial ecology of batch sulfidogenic bioreactors for co-treatment of municipal wastewater and acid mine drainage[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016, 305: 200-208. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.11.041 [20] MUYZER G, STAMS A J M. The ecology and biotechnology of sulphate-reducing bacteria[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2008, 6: 441-454. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1892 [21] 郭旭颖, 里莹, 董艳荣, 等. SRB协同自燃煤矸石处理含Fe2+、Mn2+煤矿废水研究[J]. 工业水处理, 2018, 38(6): 22-26. doi: 10.11894/1005-829x.2018.38(6).022 [22] WU P, ZHANG G M, LI J Z, et al. Effects of Fe2+ concentration on biomass accumulation and energy metabolism in photosynthetic bacteria wastewater treatment[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2012, 119: 55-59. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.05.133 [23] 徐亦寒, 孔殿超, 岳正波, 等. 针铁矿对硫酸盐还原菌分解铅矾的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 2017, 37(5): 1688-1694. [24] 宋福强. 微生物生态学[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2008. [25] SAHINKAYA E, YUCESOY Z. Biotreatment of acidic zinc- and copper-containing wastewater using ethanol-fed sulfidogenic anaerobic baffled reactor[J]. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 2010, 33(8): 989-997. doi: 10.1007/s00449-010-0423-9 [26] SAHINKAYA E, DURSUN N, OZKAYA B, et al. Use of landfill leachate as a carbon source in a sulfidogenic fluidized-bed reactor for the treatment of synthetic acid mine drainage[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2013, 48(4): 56-60. -



 下载:
下载: