-
水资源安全问题已经成为全世界关注的焦点。氟是人体必需的微量元素,但是由于地质及工业排放原因,在常规水处理过程又缺乏针对氟离子的专门处理技术,饮用水中氟离子超标会导致氟中毒以及认知障碍、焦虑、抑郁和神经损伤[1-4]。世界卫生组织(WHO)建议饮用水中氟离子浓度在0.5~1.5 mg·L−1。但是据报道,在全球范围内至少有25个国家的6 200万人受到饮用水中氟化物含量过高的影响[5]。目前,去除饮用水中氟离子的方法主要有反渗透法、离子交换法、化学沉淀法和吸附法等。吸附法具有出水水质稳定、工艺流程简单、经济实惠等优点[6],但是存在吸附时间长、会造成二级污染等问题。
介电泳是在非均匀电场中控制中性可极化微粒的运动[7]。同时,介电泳可以通过捕获吸附了污染物的吸附剂来对污染物进行去除。BATTON等[8]首次研究了利用介电泳捕获吸附重金属的羟基磷灰石,吸附了Pb2+的羟基磷灰石微粒被非均匀电场捕获。本研究采用吸附和介电泳结合的技术提高饮用水中F−的去除率,探讨了吸附剂种类及其投加量、外加电压对F−去除效果的影响,并通过SEM表征、吸附热力学等方法探究了其可能的吸附机理,为解决饮用水中氟离子的去除提供一种快速、高效的新方法。
全文HTML
-
在非均匀电场中,微粒被极化且微粒正负电荷中心处于不同的电场强度区域内,受到大小不同的作用力,从而发生位移,这种由物质的介电特性所引起的运动,称为介电泳(dielectrophoresis, DEP),也即颗粒在非均匀电场中感应出电偶极子而引起自身的运动[9-11]。1个球形微粒在非均匀电场中介电泳力的计算方法如式(1)和式(2)所示。
式中:FDEP为粒子受到的介电泳力;R为颗粒半径,m;
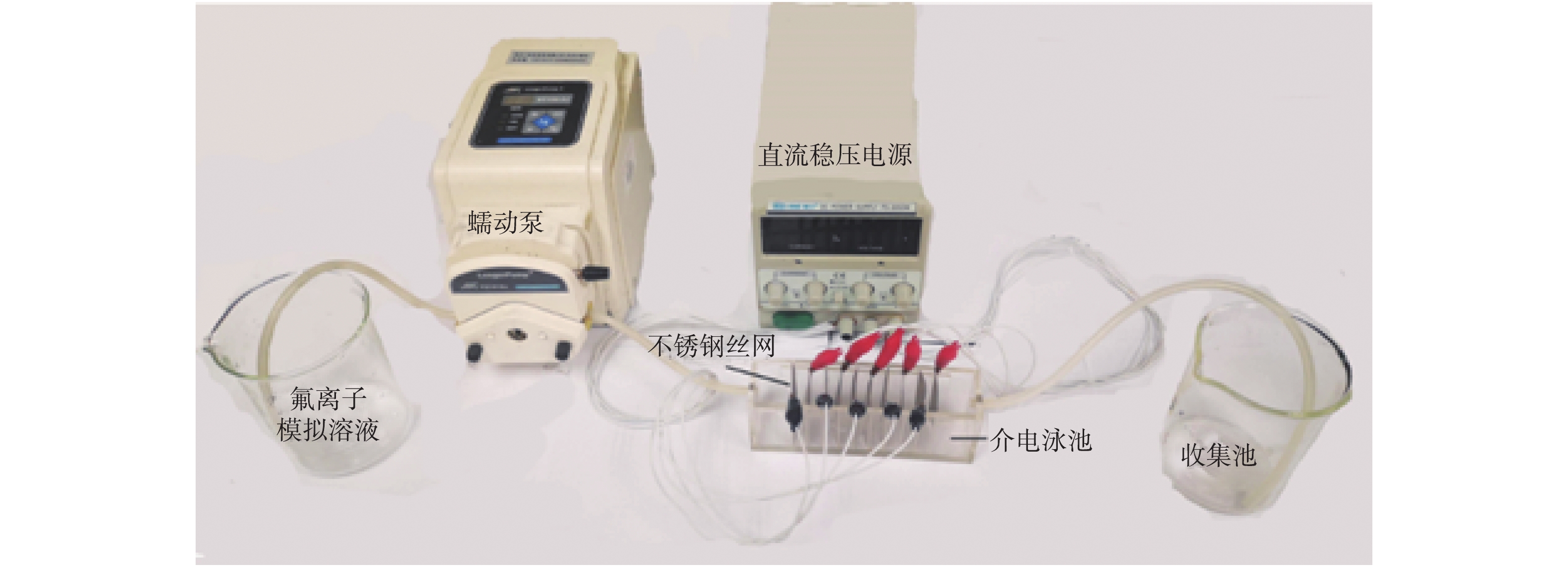
$\varepsilon _{\rm{m}} $ 为悬浮媒介的介电常数。$\varepsilon _{\rm{p}}^{\rm{*}} $ 为颗粒复合介电常数;$\varepsilon _{\rm{m}}^{\rm{*}} $ 为悬浮媒介复合介电常数;ω为电场角频率,Hz;E为电场强度,V·m−1;K(ω)为克劳修斯-莫索因子(Claussius-Mossotti),Re[K(ω)]>0,会发生正介电泳,微粒会向电场强度强的区域移动;Re[K(ω)]<0,微粒会向电场强度弱的区域移动,发生负介电泳[12]。自制介电流处理装置如图1所示。介电泳池由有机玻璃组装,间隔10 mm插入10片不锈钢丝网,正负电极交错连接。
-
PXS-270离子计(上海雷磁仪电科学仪器有限公司),232-01氟离子选择性电极(上海雷磁仪电科学仪器有限公司),MP511 pH计(上海三信仪表厂),S4800 SEM扫描电镜(日本岛津公司),Milli-Q超纯水仪器(德国默克密理博)。
实验中的主要试剂为氟化钠(国药集团药业股份有限公司)、羟基磷灰石(北京德科岛金科技有限公司)、活性炭(天津市福晨化学试剂厂)、活性氧化铝(产地郑州),均为分析纯,草木灰产自湖北,316不锈钢丝网符合国家标准要求。
-
氟离子溶液由氟化钠配置,溶液经0.45 μm滤膜过滤后,由氟离子选择性电极测定,并按照标准曲线确定浓度。在F−浓度为15 mg·L−1模拟水中加入5 g·L−1的羟基磷灰石、活性炭、草木灰、活性氧化铝,混合一段时间后,再用0.45 μm滤膜过滤,取上清液,使用离子计测定剩余F−的浓度,确定吸附效果最好的吸附剂,并模拟其吸附的热力学方程。在F−浓度为15 mg·L−1的水中加入选定的不同量的吸附剂,吸附20 min后,以流速为0.14 mL·s−1、过外加电压为15 V的介电泳装置,探讨吸附剂投加量对实验的影响。在F−浓度为15 mg·L−1的水中加入最佳的吸附剂量,在外加电压为9、11、13、15、17、19 V的情况下,溶液以流量为0.14 mL·s−1过介电泳装置,探讨外加电压的影响。
1.1. 介电泳理论和实验装置
1.2. 实验材料仪器
1.3. 实验方法
-
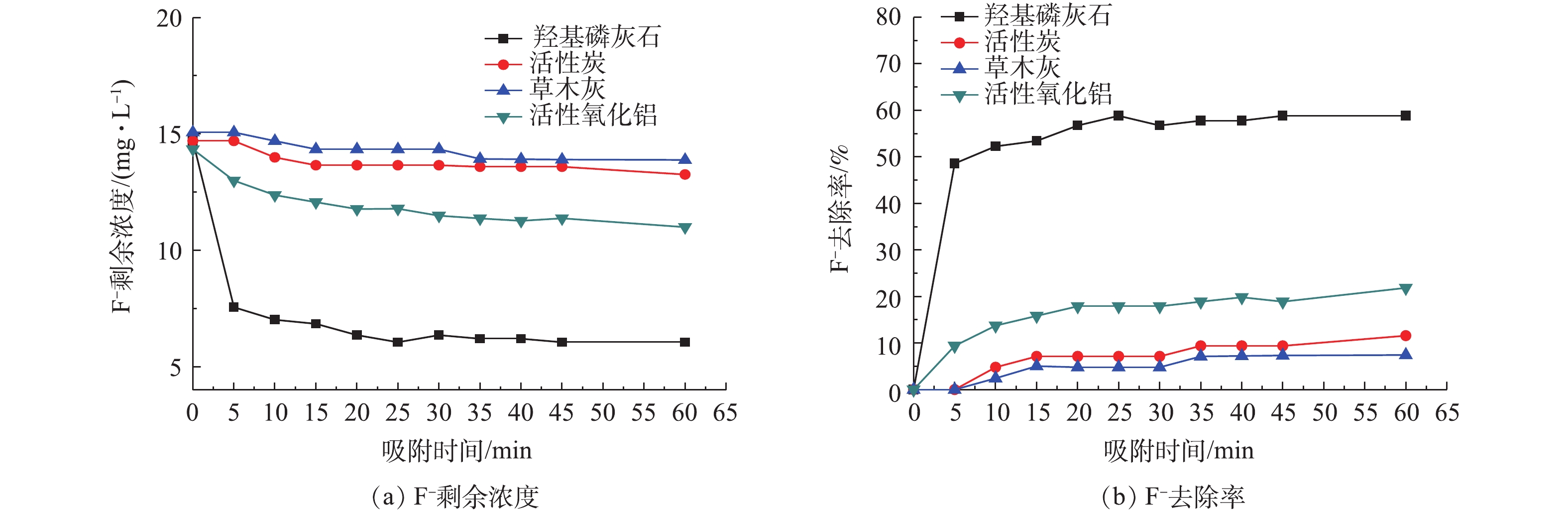
考察活性炭(GAC)、草木灰(plantash)、活性氧化铝(activated alimina)和羟基磷灰石(HAP)对F−的去除效果,结果如图2所示。由图2可知,在4种吸附剂处理后,F−的剩余浓度最终分别可降到13.65、13.32、11.00和6.05 mg·L−1,其中,羟基磷灰石对F−的去除率最高,达到了58.83%。所有吸附剂在前20 min对F−去除率均有显著提高。这是因为此时吸附剂中吸附位点的空位较多,且F−的浓度较高,能够迅速占据吸附位点[13],而在此之后,吸附位点逐渐占满,吸附剂对F−的去除率逐渐达到了平衡状态[14],吸附在60 min后趋于稳定。
-
通过实验拟合出的Langmuir吸附等温式和Freundlich吸附等温式的相应参数如表1所示。Langmuir吸附等温方程能够很好地描述羟基磷灰石对F−的吸附热力学行为,其吸附行为满足单分子层吸附模型。羟基磷灰石对F−的最大吸附量qmax为5.88 mg·g−1,远高于其他研究[15-22]的结果。因此,本研究选择羟基磷灰石作为吸附剂,并利用其去除水体中F−。
-
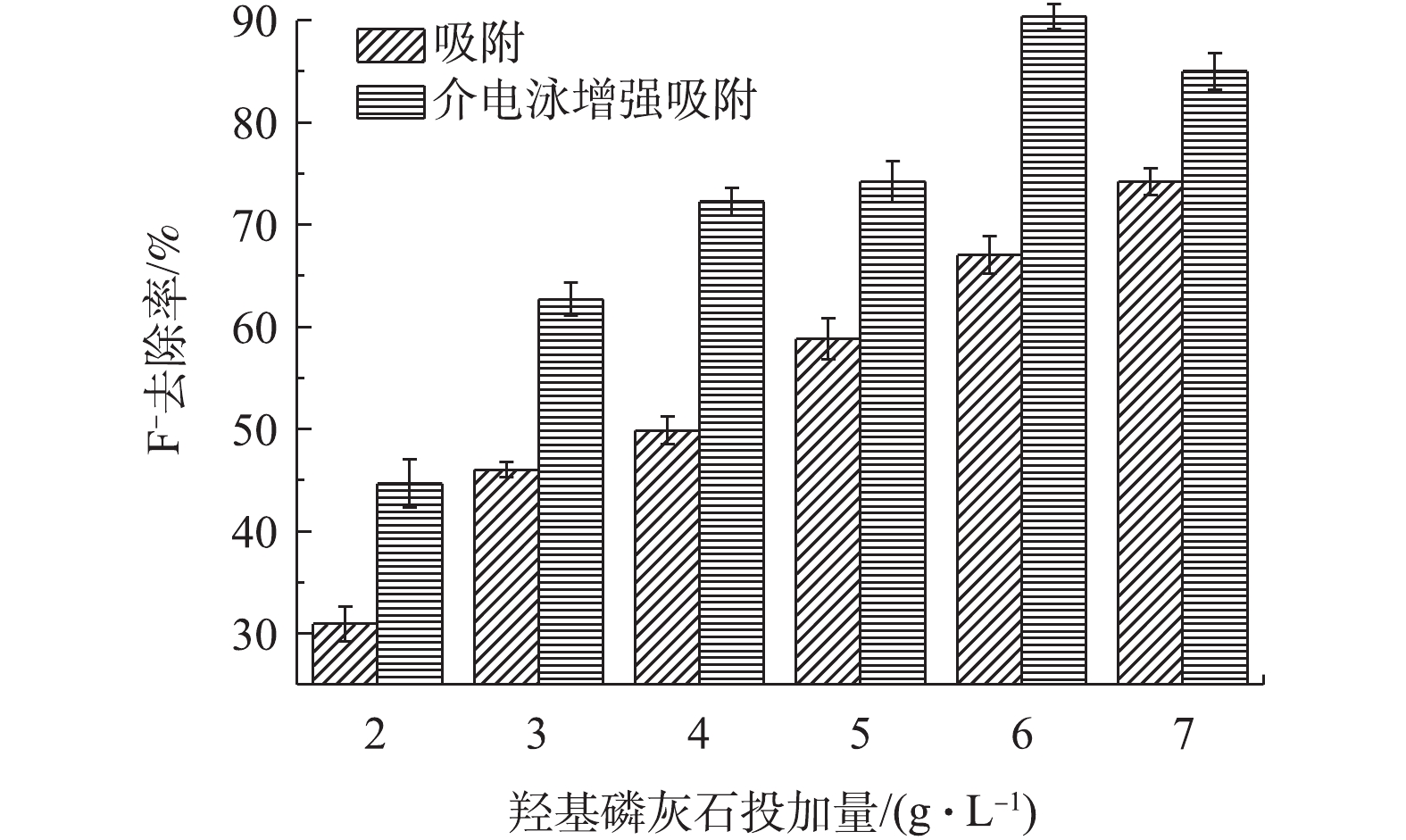
羟基磷灰石的投加量对介电泳吸附增强法去除F−的影响如图3所示。由图3可知,随着吸附剂投加量的增加,其对F−的的去除率也随之逐渐的增加;介电泳增强吸附法去除率一直高于单纯吸附;当羟基磷灰石的投加量为6 g·L−1时,介电泳增强吸附法对F−去除率的提高尤为显著。介电泳增强吸附法对F−的去除率高于单纯吸附法的原因是,在电场力的作用下,羟基磷灰石被捕获在丝网电极的表面,由于粒子间的相互介电泳作用[23],更多的F−被吸附到羟基磷灰石表面,增强了羟基磷灰石对溶液中F−的去除率。在引入介电泳后,吸附剂在6 g·L−1时吸附的F−可以达到最高,使得介电泳的效果最强;在吸附剂大于6 g·L−1时,更多的吸附剂反而可能会减弱介电泳的极化效果,导致其去除率降低[24]。
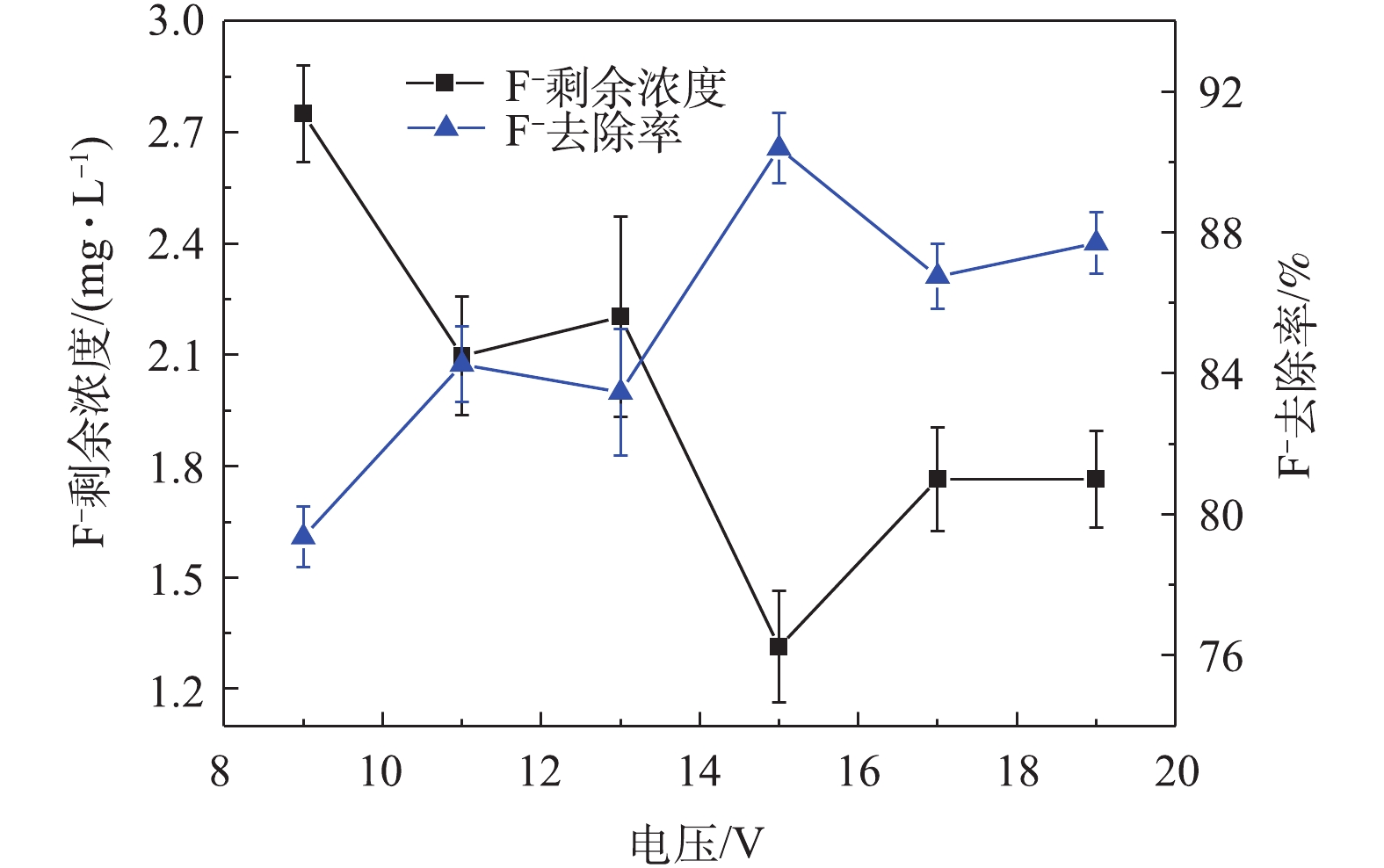
除吸附剂投加量外,施加在电极上的电压对F−的去除也有显著影响。在外加电压为15 V时,F−去除率达到了90.39%(图4)。而在外加电压为16 V时,F−去除率降低的原因是由于可极化粒子具有特征电压,在该特征电压下,粒子受到的介电泳力最大[25-27],最容易被捕获。当外加电压高于特征电压时,丝网电极表面电场过强,颗粒将离开丝网表面,向丝网空隙处迁移,被流体介质带走,故导致去除率降低[26,28]。同时,在高电压下,丝网电极的电解十分剧烈,这会影响对羟基磷灰石颗粒的捕获。
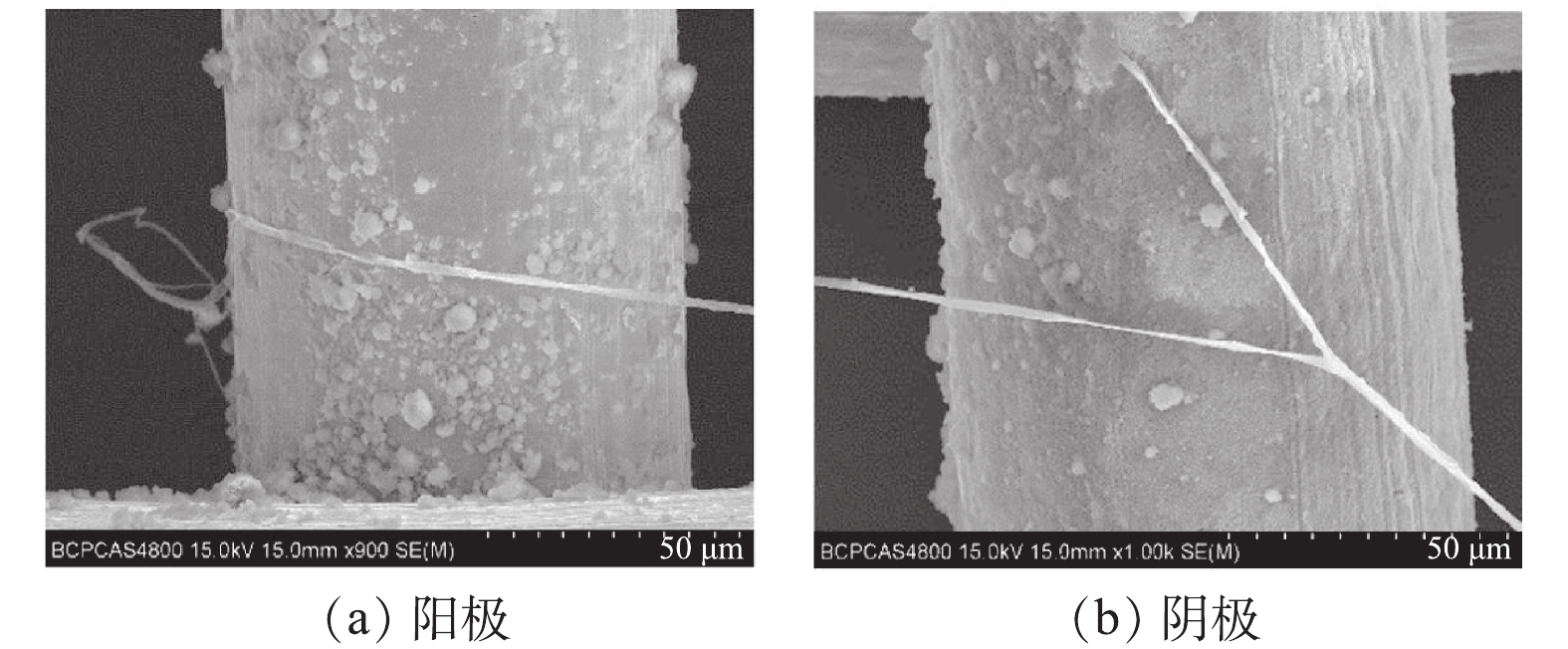
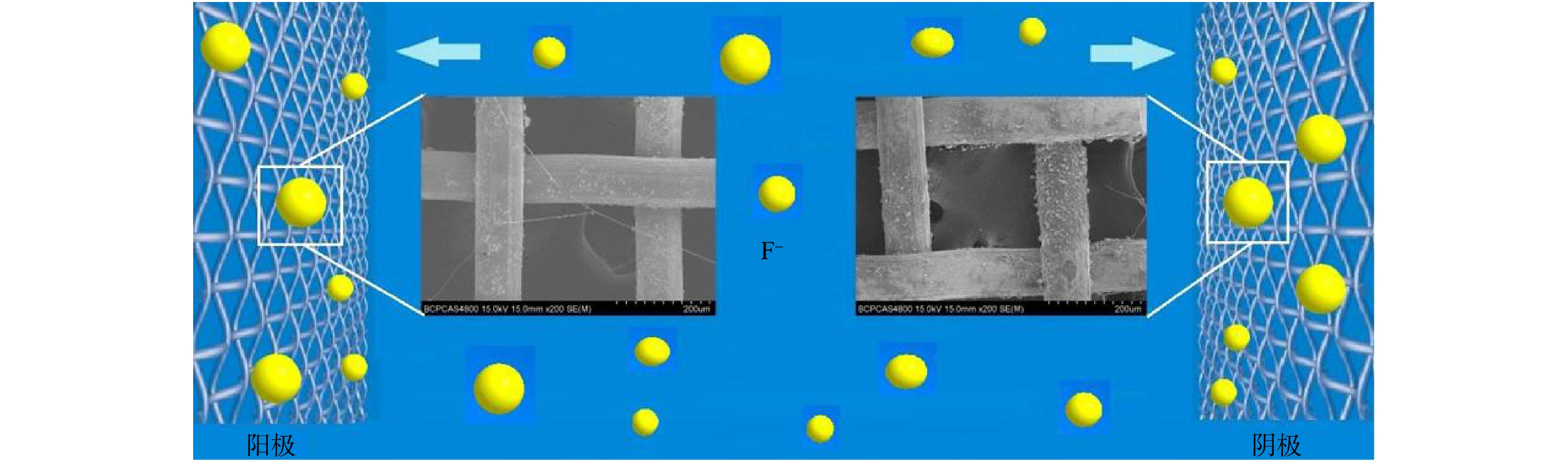
在15 V电压下,对经介电泳处理后捕获了羟基磷灰石的丝网进行自然风干,并进行SEM表征测试(图5)。在电极的阳极和阴极均有羟基磷灰石被捕获,表明发生了介电泳;而且羟基磷灰石均被捕获在电场强度最高的丝网上,证明发生了正介电泳。羟基磷灰石在介电泳作用下,以丝网电极金属丝为起点,相互连接成细长的线性结构。这可能是因为在介电场作用下,羟基磷灰石尖端带电,以电场最强的丝网电极为起点,相互吸引出现团聚与叠加[29],形成细长的线性结构。
图6为介电泳吸附增强法处理模拟水溶液中F−机理。F−先是被吸附在羟基磷灰石上,由于介电泳力的存在,模拟水经过介电泳池后,羟基磷灰石颗粒被捕获在丝网上,吸附剂被分离,在处理后的水中,吸附剂基本被去除。因此,介电泳不仅增强了吸附剂对F−的吸附,同时还减少了吸附剂悬浮物的二次污染。
2.1. 吸附剂筛选
2.2. 羟基磷灰石吸附的热力学拟合
2.3. 介电泳吸附增强法处理水中的F−
-
1)在筛选吸附剂的基础上,将介电泳技术与吸附法结合,建立了介电泳增强吸附法,能较高效地去除F−。羟基磷灰石对F−有最好的吸附效果,其饱和吸附量为5.88 mg·g−1,Langmuir吸附等温方程能很好表述吸附过程,这表明吸附满足单分子层吸附模型。
2)在羟基磷灰石的投加量6 g·L−1,外加电压15 V时,F−去除率由单纯吸附法的67.02%提高到90.39%,同时避免了吸附剂的悬浮污染。
3)初步探讨了介电泳增强吸附法去除F−的机理,丝网正负电极捕获了羟基磷灰石,发生了介电泳作用。同时,粒子间由于相互介电泳力的作用,提高了对F−的吸附率。粒子尖端相连,结合形成纳米级链状形态。




 下载:
下载: