-
常温常压下饱和蒸汽压大于133.32 Pa、常压下沸点在50~260 ℃的有机化合物统称为挥发性有机物(VOCs)[1]。VOCs是产生PM2.5和O3的重要前体物,进而引起霾和光化学烟雾[2]。大多数VOCs具有毒性和刺激性,例如化工行业应用广泛的苯系物[3],严重危害人群健康。因此,研发高效的VOCs控制技术刻不容缓。催化氧化技术通常在小于350 ℃的温度下即可将VOCs完全氧化为CO2和H2O,具有高效清洁的优势[4]。开发高性能低成本的催化剂是催化氧化技术的关键[5]。
对VOCs催化氧化催化剂的研究目前主要集中在非贵金属氧化物催化剂和负载型贵金属催化剂。非贵金属氧化物催化剂成本低廉,但催化性能相对较差[6]。相比之下,负载型贵金属催化剂由于具有催化性能高、使用寿命长的优点而应用广泛,例如Pt基催化剂催化氧化芳香烃[7-9]。目前,关于负载型贵金属催化剂的研究集中于降低贵金属含量和提高催化性能两个方面[2]。采用活性载体负载贵金属,不仅可以提高贵金属的分散度,而且贵金属与载体之间的相互作用可以影响催化性能[10-12]。MENG等[13]在meso-Co3O4上负载了Pt纳米颗粒,发现贵金属与载体之间的相互作用提升了表面氧浓度,强化了催化剂的氧化还原性能,因此Pt/meso-Co3O4催化剂具有优异的乙炔氧化性能。Co3+具有良好的得电子能力[14-17],由于氧化铈具有优良的储氧能力,通常作为催化剂中的助剂[18-20]。张烁[21]发现,Co0.9Ce0.1Ox催化剂具有良好的丙烷催化氧化性能,在Co3O4中掺杂Ce氧化物可以提升催化剂的表面Co3+比例和氧迁移能力。贵金属颗粒的分散度和粒径是影响催化性能的重要指标[22]。国内外关于贵金属颗粒的分散度和粒径对催化性能影响的研究主要集中于通过改变制备方法控制贵金属颗粒的分散度和粒径[13, 23-25]。浸渍法、共沉淀法、热分解法、化学还原法等工艺是当前用于生产负载型贵金属催化剂的常见工艺,直接浸渍法和沉淀法的缺点是不能制备粒径可控的贵金属[26]。MAO等[26]通过Pt2 (dba)3分解,制备了粒径分布窄的Pt纳米颗粒,将其负载于活性炭上,其催化邻氯硝基苯氢化反应的性能良好。RAMIREZ等[27]在温和的化学条件下通过分解Pt2(dba)3 获得了形状和尺寸均匀的Pt纳米颗粒,催化性能优异。然而,针对Pt纳米颗粒与Co-Ce载体之间的相互作用对催化性能的影响,尤其是不同制备方法之间的对比研究相对较少。
本研究以应用广泛的甲苯作为目标污染物,分别采用铂纳米胶体浸渍法和氯铂酸浸渍法,将Pt纳米颗粒负载在Co0.9Ce0.1Ox载体上;通过ICP-OES、XRD、HRTEM、H2-TPR、XPS等表征手段,研究制备方法对Pt/Co0.9Ce0.1Ox催化剂的氧化还原性能、催化氧化性能等的影响,为设计高效VOCs氧化催化剂提供参考。
-
实验所用试剂主要有硝酸钴(Co(NO3)3·6H2O)、硝酸铈(Ce(NO3)3·6H2O)、一水合柠檬酸(C6H8O7·H2O)、乙醇(C2H6O)、正戊烷(C5H12)、氯铂酸(H2PtCl6·6H2O)、醋酸钠(CH3COONa)、二亚苄基丙酮(C17H14O)、四氯铂酸钾(K2PtCl4)和碳酸丙二醇酯(C4H6O3),均为分析纯。
-
采用柠檬酸络合法制备Co0.9Ce0.1Ox催化剂。将含有14.48 g硝酸钴、1.74 g硝酸铈和12.61 g柠檬酸的溶液在室温下混合。其中,柠檬酸和金属盐的摩尔比为1.5∶1,钴和铈元素的摩尔比为9∶1。在80 ℃的水浴中搅拌溶液,直到溶液凝胶化。凝胶经过12 h的干燥后,在450 ℃下煅烧4 h,得到的黑色固体命名为Co0.9Ce0.1Ox。
采用铂纳米胶体浸渍法负载Pt纳米颗粒。在50 ℃下,将K2PtCl4溶液加入60 mL含有2.8 g乙酸钠和2.36 g双二苯亚甲基丙酮的乙醇溶液。得到的混合物在冷凝器中于90 ºC回流后,静置24 h,用去离子水和戊烷洗涤过滤后,将得到的固体在真空下干燥得到Pt2(dba)3。将Pt2(dba)3固体加入100 mL澄清的碳酸丙二醇(PC)中,并将得到的混合物置于500 mL装有搅拌器的高压釜中。用H2置换釜内空气6次后,在4.0 MPa和25 ℃下向釜内通入H2,获得含有铂纳米胶体的棕色溶液。采用铂纳米浸渍法将溶液中的铂纳米胶体吸附在Co0.9Ce0.1Ox上,在350 ℃下煅烧,得到的固体标记为0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N。其中,N表示纳米铂胶体浸渍法,0.5表示Pt质量分数为0.5%。作为比较,采用以上方法制备Pt质量分数为0.1%的样品,标记为0.1Pt/CoCeOx-N。
将0. 0325 g氯铂酸六水合物(H2PtCl6)溶于3 mL去离子水中,获得H2PtCl6溶液。将2.44 g 的Co0.9Ce0.1Ox载体置于烧杯中,缓慢加入H2PtCl6溶液,超声搅拌约1 h至吸附平衡,静置24 h后,用去离子水清洗,直到滤液中用AgNO3溶液检测不出氯离子。然后在450 ℃下煅烧4 h,得到的固体标记为0.5Pt/CoCeOx-I。其中,I代表氯铂酸浸渍法,0.5代表铂的质量分数为0.5%。
-
采用固定床反应器进行催化性能评估。将0.1 g催化剂放置在石英管中,用石英纤维棉将两端密封。气体总流速为150 mL·min−1,氧气的体积分数为20%,甲苯的体积分数为0.06%,反应空速(GHSV)为90 000 mL·g−1·h−1。经过30 min的吹扫,在达到稳定状态时,用FT-IR气体分析仪(DX4000,芬兰Gasmet公司)记录气体体积流量。反应后的0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N催化剂标记为0.5Pt/CoCeOx-NU,反应后的0.5Pt/CoCeOx-I催化剂标记为0.5Pt/CoCeOx-IU。
采用适量氮气通过洗气瓶携带反应气体中体积分数为5%的水蒸气,为了防止水蒸气冷凝,采用伴热带进行加热气体管道。采用固定床反应器进行催化剂耐久性实验,将反应温度升至350 °C 保持25 h以上。采用FT-IR气体分析仪(Gasmet DX4000,芬兰)检测出口的甲苯质量流量。
-
采用电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES)测定催化剂的Pt含量;采用(Micromeritics ASAP 2460,美国麦克仪器公司)比表面分析仪进行N2吸附/脱附实验测定催化剂的比表面积和孔容;采用Brunauer-Emmett-Teller(BET)方程计算催化剂的比表面积;采用(X'Pert Pro,荷兰Panalytical公司)XRD衍射仪分析催化剂的晶体结构;采用(2100F,日本电子株式会社) TEM电子显微镜分析催化剂的微观结构和晶格衍射图像;采用H2程序升温还原法(H2-TPR)测试催化剂的氧化还原特性;采用(Escalab 250,美国Thermo公司)光电子能谱仪分析催化剂表面元素价态。
-
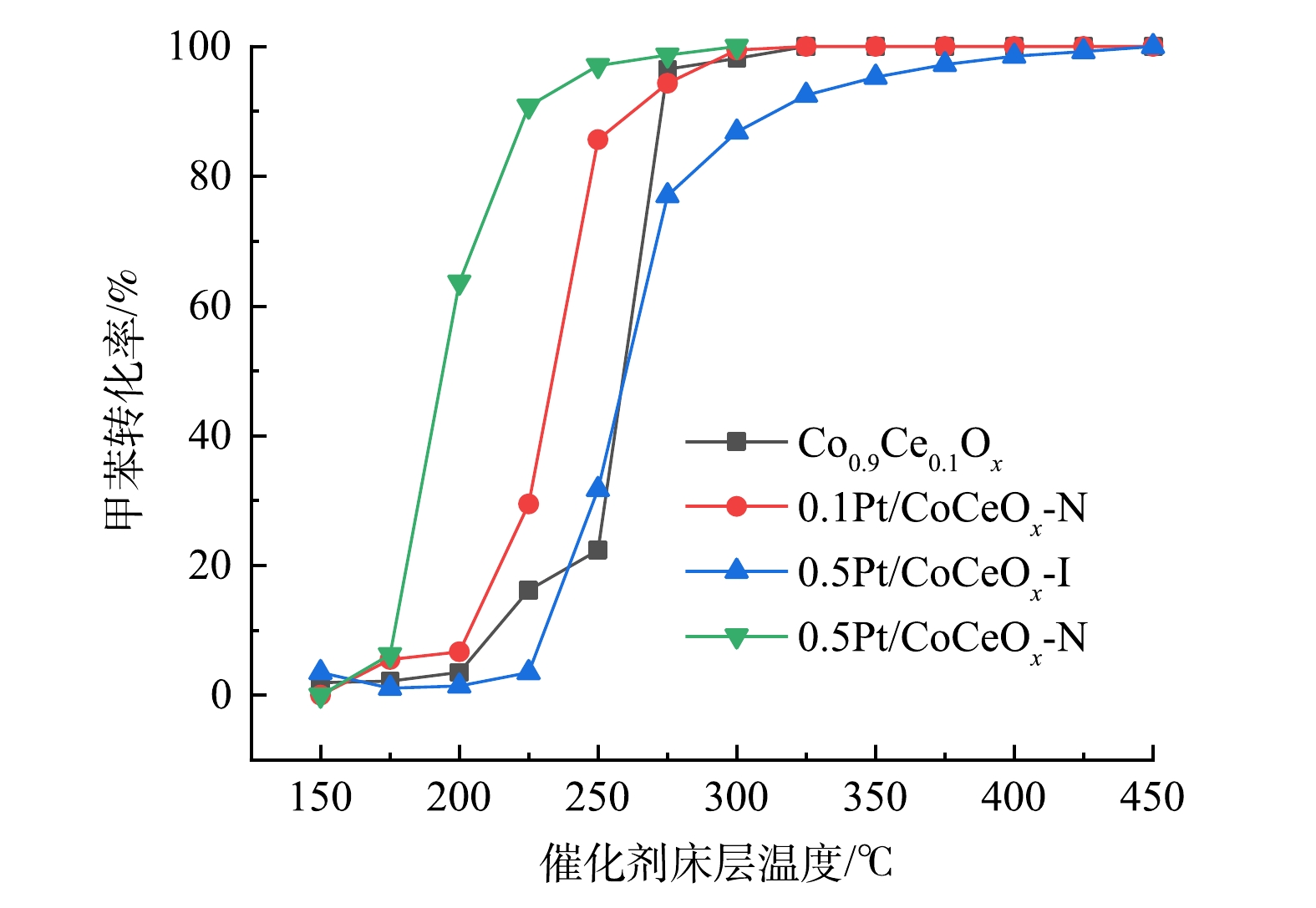
在空速为90 000 mL·g−1·h−1、甲苯的体积分数为0.06%、氧气的体积分数为20%条件下,不同催化剂上的甲苯转化率与反应温度的关系如图1所示。表1总结了转化率为50%和90%时的温度,分别标记为T50和T90。Co0.9Ce0.1Ox、0.5Pt/CoCeOx-I、0.1Pt/CoCeOx-N和0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N催化剂的T50分别为259、260、243、192 ℃。与Co0.9Ce0.1Ox相比,0.1Pt/CoCeOx-N和0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N催化剂的T50分别下降了25和67 ℃,而0.5Pt/CoCeOx-I催化剂的T50略有上升。这说明铂纳米胶体浸渍法负载的Pt纳米颗粒增强了催化剂的活性。由于0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N催化剂的负载量提高,所以,性能提升效果有所增强。相反,氯铂酸浸渍法负载的Pt 纳米颗粒几乎没有提升催化性能。上述催化性能变化的差异表明,不同制备方法对催化剂的甲苯氧化活性具有不同影响。为阐明影响机制,进行进一步表征。
如图2所示,引入体积分数为5%的水蒸气后,Co0.9Ce0.1Ox 的T50上升4 ℃、T90上升19 ℃、0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N的T50上升4 ℃、T90上升20 ℃。催化性能的降低可能是水蒸气在催化剂表面的竞争吸附所致。此外,对比Co0.9Ce0.1Ox和0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N催化剂的抗水性能,并未表现出明显差异,这表明水蒸气在Pt及载体上的吸附可能无选择性。将0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N催化剂置于固定床反应器中,升温至 350 ℃保持25 h,甲苯转化率一直保持在 99%以上,没有活性下降的趋势,这表明催化剂耐久性良好。
-
催化剂的Pt质量分数、比表面积和孔隙大小如表2所示。根据ICP-OES的结果,0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N、0.1Pt/CoCeOx-N和0.5Pt/CoCeOx-I催化剂的Pt质量分数分别为0.55%、0.11%和0.41%,分别与设计值接近。Co0.9Ce0.1Ox、0.5Pt/CoCeOx-I、0.1Pt/CoCeOx-N和0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N催化剂的比表面积分别为71.8、56.8、76.6和45.5 m2·g−1,孔径分别为8.9、8.9、9.6、11.4 nm。负载Pt 纳米颗粒后,0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N和0.5Pt/CoCeOx-I催化剂的比表面积下降,孔容减小。一方面,负载的Pt 纳米颗粒有可能堵塞微孔孔道,造成比表面积大幅下降,同时孔容略有下降;另一方面负载前驱体后的煅烧有可能增大孔容及比表面积。本研究表征结果表明,前者具有占主导地位的可能,因而平均孔径表现出增加的趋势。
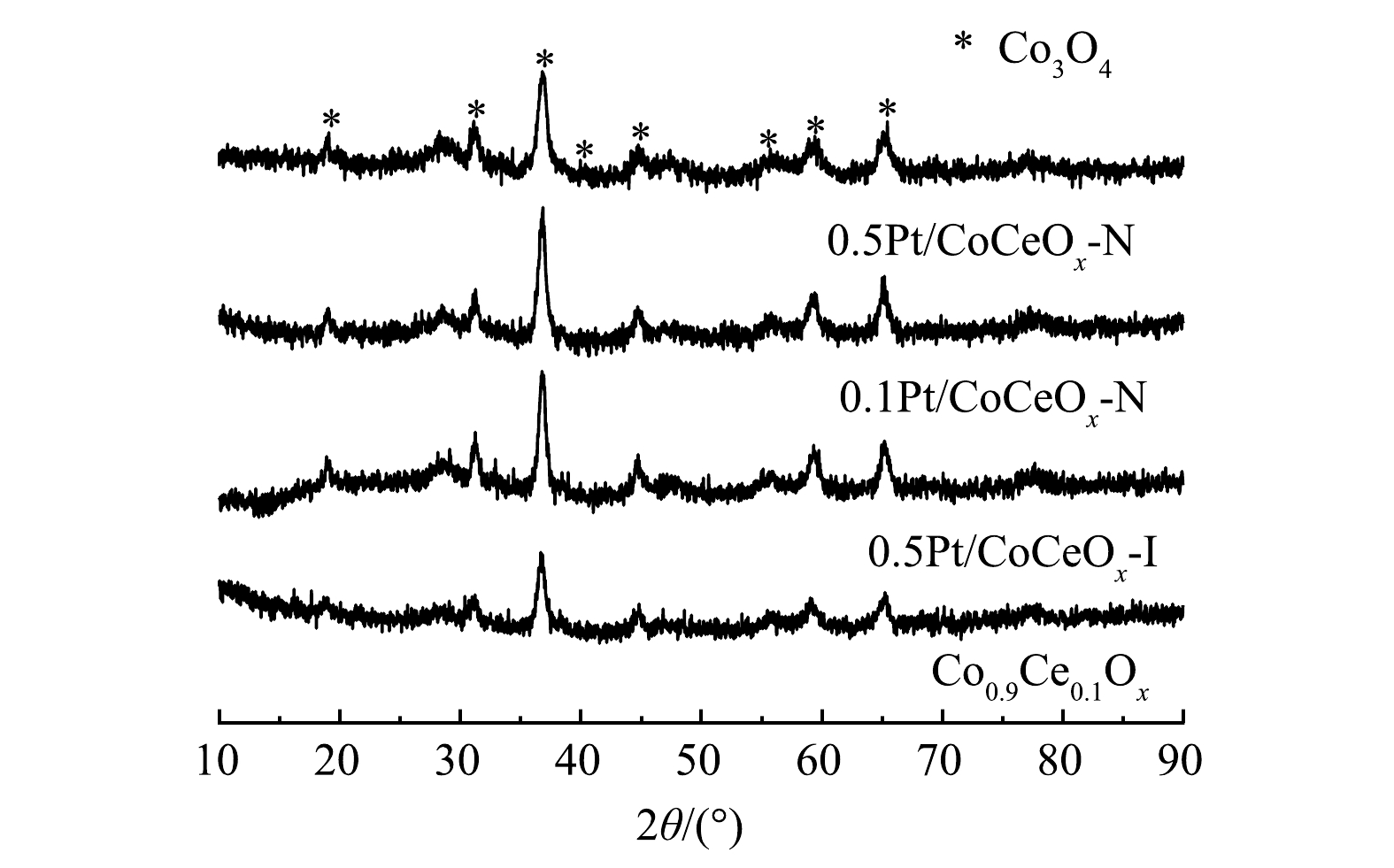
XRD结果如图3所示,0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N、0.1Pt/CoCeOx-N和0.5Pt/CoCeOx-I催化剂在2θ=19°、31°、36.7°、44.8°、59.5°和65.4°(JCPDS#43-1003)均表现出典型的尖晶石Co3O4衍射峰,未观察到其他相的特征峰。这表明Ce以非晶态形式存在或高度分散,且负载Pt纳米颗粒对Co0.9Ce0.1Ox晶体结构无显著影响。如表2所示,ICP-OES证明了Pt物种的存在。XRD光谱没有显示出Pt或PtOx的衍射信号,RUI等[28]发现,XRD表征结果中检测不到Pt或PtOx的特征峰表明Pt在TiO2上分散良好,因此,这可能是因为Pt负载量低或者高度分散。
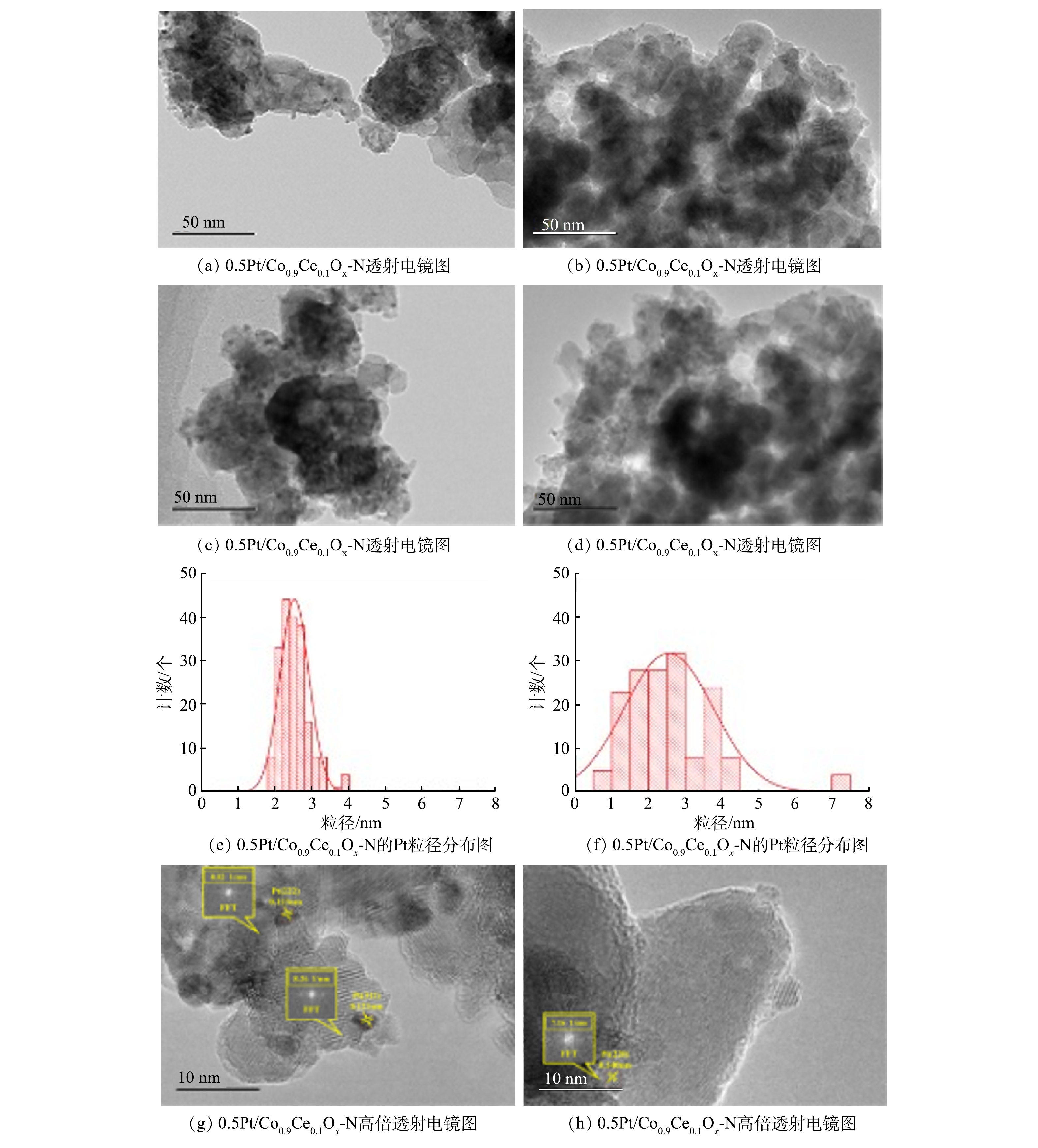
图4为TEM结果。如图4(a)所示,铂纳米胶体浸渍法制备的Pt纳米颗粒大部分在形状和尺寸上均匀,无明显团聚。这说明,采用Pt2(dba)3前驱体还原制备的Pt胶体有效地抑制了Pt纳米颗粒的生长,可以在温和的条件下获得规则的Pt纳米结构。从图4(b)中可以看出,氯铂酸浸渍法制备的Pt纳米颗粒尺寸差异较大且分散不均匀,出现轻微团聚现象。这可能是导致0.5Pt/CoCeOx-I催化性能低于未负载的Co0.9Ce0.1Ox催化剂的原因。通过测量200个铂颗粒的粒径得出,0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N图4(e)和0.5Pt/CoCeOx-I图4(f)的Pt纳米颗粒平均尺寸都约为2.5 nm。但是,0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N的Pt纳米颗粒尺寸分布在2~4 nm,粒径分布窄。而0.5Pt/CoCeOx-I的Pt纳米颗粒尺寸超过2~4 nm的范围,粒径分布宽。HANSEN等[29]发现,均匀的Pt纳米颗粒尺寸,有利于活性组分Pt表面积的提升和活性位点的增多,因此有利于催化性能的提升。图4(g)显示,0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N中最常观察到的晶面间距对应于零价铂。而图4(h)显示,0.5Pt/CoCeOx-I中仅能观察到个别零价铂。
图5(b)和图5(c)为反应后样品的TEM结果。与反应前的催化剂相比,反应后0.5Pt/CoCeOx-NU和0.5Pt/CoCeOx-IU催化剂上的Pt未出现明显团聚。TEM 结果表明,不同制备方法可导致Pt纳米颗粒尺寸、分散度和Pt0比例的差异。为了深入研究Pt 纳米颗粒尺寸、分散度和零价铂比例对催化剂催化性能的影响,进行进一步的表征。
-
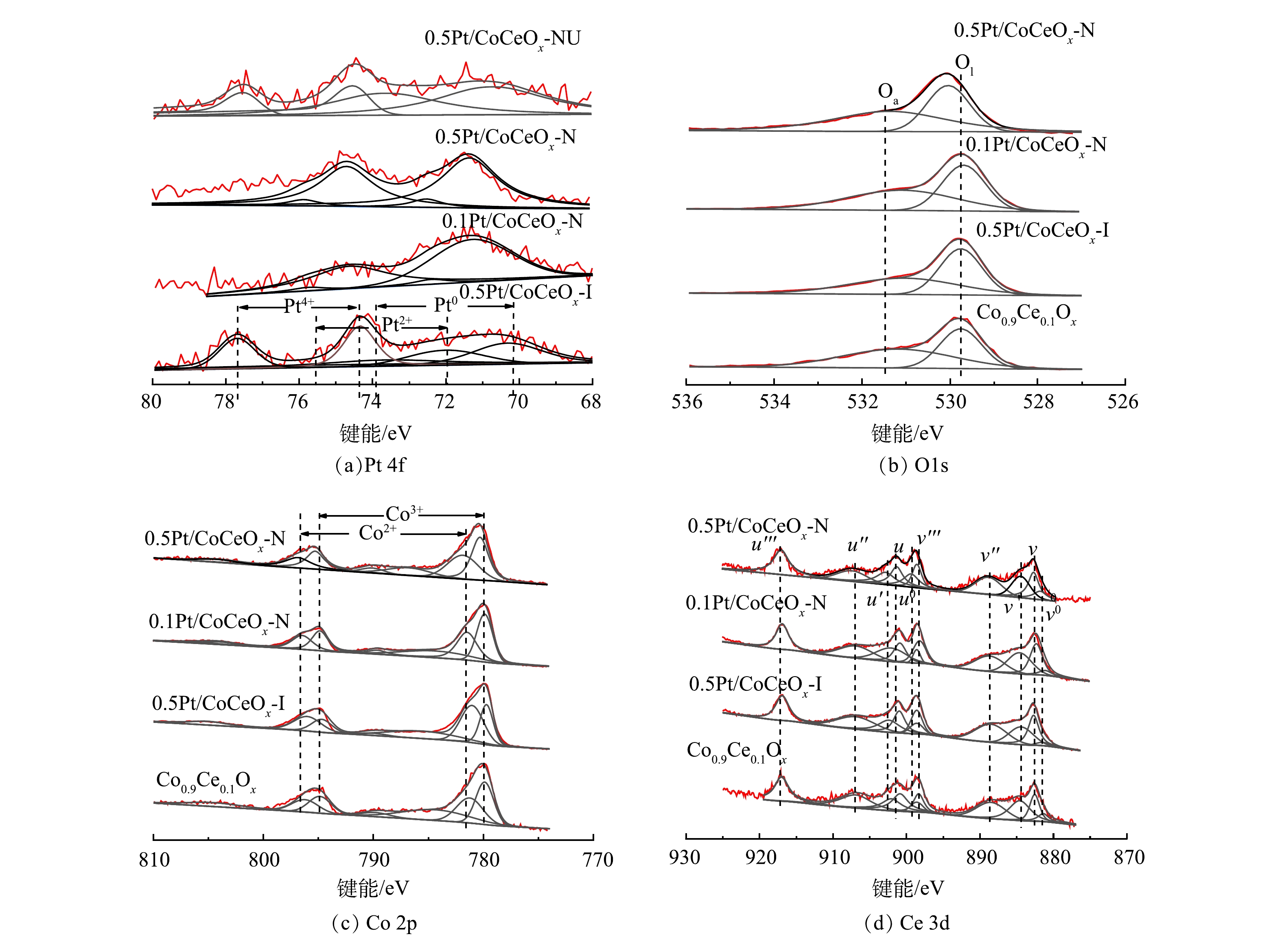
如图6(a)所示,0.5Pt/CoCeOx-I的Pt 4f5/2峰可以分解为70.5-72.0 eV、72.1-72.9 eV和74.4-75.0 eV这3个峰,分别归属于Pt0、Pt2+和Pt4+。每种催化剂中,Pt的不同价态的比例如表3所示,催化剂0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N 和0.1Pt/CoCeOx-N的Pt0/(Pt0+PtOx)分别为91.55%和93.37%,而催化剂0.5Pt/CoCeOx-I仅为38.29%。SEO等[30]研究发现,在氧化还原过程中,Pt的氧化过程是一个失电子过程,零价态Pt可以不断被氧化为Pt2+和Pt4+,失去的电子转移至表面氧物种,形成O2−,能够参与氧化反应,因此0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N 和0.1Pt/CoCeOx-N催化剂的高比例零价Pt有利于表面氧浓度提升。如图6(a)所示,反应后的0.5Pt/CoCeOx-NU催化剂表面的铂除了Pt0之外,还产生少量Pt4+,部分证实了上述猜测。
图6(b)为样品的O1s XPS图谱。位于528-530 eV的峰属于晶格氧(O2-),表示为Ol,峰值为530.7-531.4 eV的峰归属于表面吸附氧(O2−),表示为Oa。采用等WANG [31]报道的积分峰面积法确定催化剂的Oa/(Oa+Ol)比例,如式(1)所示。
式中:Al和Aa分别表示晶格氧和表面氧物种的光电子峰面积。
如表3所示,Co0.9Ce0.1Ox、0.5Pt/CoCeOx-I、0.1Pt/CoCeOx-N和0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N催化剂的Oa/(Oa+Ol)比例分别为53.50%、49.60%、53.90%和58.54%。0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N和0.1Pt/CoCeOx-N催化剂的Oa/(Oa+Ol)比例分别比Co0.9Ce0.1Ox提升5.41%和0.4%,证明Pt纳米胶体浸渍法提升了催化剂的表面氧浓度。随着Pt负载量提高,表面氧浓度提升的幅度有所增强。相反,氯铂酸浸渍法的Oa/(Oa+Ol)比例下降了3.9%,说明表面氧浓度降低。彭若斯等[11]研究了Pt/CeO2催化剂催化氧化甲苯的反应机制,发现贵金属与载体间的强相互作用活化了 CeO2晶格氧,加速了氧循环,为反应提供了更多的表面氧物种,进一步提高了甲苯催化氧化效率。因此,本研究中,铂纳米胶体浸渍法制备的Pt纳米颗粒负载在Co0.9Ce0.1Ox载体上,提升了表面氧浓度,有利于气态氧的吸附活化,从而提高催化剂对甲苯氧化的催化活性。
图6(c)为Co 2p XPS图谱,通过去卷积,将归属于Co 2p3/2和Co 2p1/2的自旋轨道分裂的2个主峰分解成2个峰。位于780eV和795eV的峰属于Co3+,位于782eV和797eV的峰属于Co2+。如表3所示,Co0.9Ce0.1Ox、0.5Pt/CoCeOx-I、0.1Pt/CoCeOx-N和0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N催化剂的Co3+/(Co2++Co3+)比例分别为56.79%、39.92%、52.87%和55.11%,可以看出,负载Pt之后,催化剂的Co3+/(Co2++Co3+)比例均有一定程度的降低。与未负载的Co0.9Ce0.1Ox催化剂相比, 0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N和0.1Pt/CoCeOx-N催化剂的Co3+/(Co2++Co3+)略微下降了1.68%和2.91%。而0.5Pt/CoCeOx-I催化剂的Co3+/(Co2++Co3+)大幅下降了16.87%。Co3+含量降低,导致需要保持平衡的电荷数减少,因此用于平衡电荷的缺陷和空位减少,削弱了催化剂的催化氧化性能。
如图6(d)所示,通过去卷积,Ce 3d XPS可以划分为10个峰。U′′(916.1 eV)、V′′(897.6 eV)、U(900.3 eV)、V(881.9 eV)、U′′(906. 9 eV)和V′′(888.5 eV)对应于Ce4+,U′(901.9 eV)、U0(898.6 eV)、V′(883.9 eV)和V0(880.6 eV)属于Ce3+。如表2所示,Co0.9Ce0.1Ox、0.5Pt/CoCeOx-I、0.1Pt/CoCeOx-N和0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N催化剂的Ce3+/(Ce4++Ce3+)比例分别为31.23%、27.10%、31.44%和33.56%。Ce3+有利于表面氧物种的生成,因此0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N催化剂的表面氧浓度提升。
-
H2-TPR结果如图7所示, Co0.9Ce0.1Ox催化剂的还原峰大致分为3个主峰和1个肩峰。TENG等[32]和WU等[33]研究发现,钴相的还原峰可划分为3部分。因此,位于265 ℃的峰代表与CeO2强相互作用的Co3+还原为Co2+,位于330 ℃的主峰和305 ℃的肩峰代表与CeO2弱相互作用的Co3O4还原为CoO再还原为金属Co的连续相变,位于464 ℃的峰代表与CeO2强相互作用的Co2+还原为Co0,证明催化剂表面同时存在Co2+和Co3+,与XPS结果吻合。Co3O4还原反应如式(2)和(3)所示。
负载Pt后,H2-TPR图谱上出现了位于100 ℃附近的新还原峰,PENG等[34]研究了Pt/CeO2催化氧化甲苯,发现了由于PtOx的还原,负载Pt后H2-TPR图谱上出现了的新还原峰,因此位于100 ℃附近的新还原峰归属于PtOx的还原。此外,如表4所示,100 ℃附近的新还原峰的耗氢量大于理论耗氢量,因此该还原峰还包含了与CeO2强相互作用的Co3+还原为Co2+。如表4所示,0.5Pt/CoCeOx-I、0.1Pt/CoCeOx-N和0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N催化剂的与CeO2强相互作用的Co3+还原为Co2+的峰位置分别为265、194、130和107 ℃,总耗氢量分别为13 085.2、13 021.0、13 150.6、13 583.9 μmol·g−1。与未负载的催化剂Co0.9Ce0.1Ox相比,催化剂0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N和0.1Pt/CoCeOx-N的此峰向低温偏移明显,分别偏移158和135 ℃。孙西勃[35]研究发现,与纯CeO2催化剂相比,Pt/CeO2催化剂的还原峰向低温偏移,这归因于Pt与CeO2之间的相互作用活化了CeO2的晶格氧。陈炳旭等[19]研究发现 Pt 可以使 H2溢流至附近的 Ce-O 键,从而促进 CeO2 在更低温度被还原。Co3+的氧化还原温度下降了158 ℃,提升了催化剂的氧化还原性能,提供了更多可被还原的活性位点,增大了耗氢量。因此,0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N催化剂的Co3+还原为Co2+还原温度最低,一方面可能是由于氢溢流促进钴在更低温度被还原;另一方面铂纳米胶体浸渍法制备的Pt 纳米颗粒与Co0.9Ce0.1Ox之间存在相互作用,提升了载体Co0.9Ce0.1Ox表面氧迁移速率,从而提高了表面氧浓度,有利于钴氧化物在更低温度下被还原。负载Pt后,0.5Pt/CoCeOx-I催化剂的低温还原峰向低温偏移了71 ℃,偏移温度和耗氢量小于0.1Pt/CoCeOx-N和0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N催化剂,这说明与氯铂酸浸渍法相比,铂纳米胶体浸渍法制备的Pt纳米颗粒与Co0.9Ce0.1Ox载体之间的相互作用对催化剂的氧化还原性能的强化作用更明显。
-
1)铂纳米胶体浸渍法制备的Pt纳米颗粒尺寸均匀分布在2~4 nm,高活性零价Pt比例高达93.37%。
2) 0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N催化剂的Pt纳米颗粒与Co-Ce载体之间存在相互作用,提升了催化剂的表面氧浓度,使得Co3+的还原温度降低了158 ℃,强化了催化剂的氧化还原性能。
3)与氯铂酸浸渍法制备的0.5Pt/CoCeOx-I催化剂相比,0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N催化剂的T50下降了68 ℃,具有优异的甲苯催化氧化性能。
2种制备方法对Pt/Co-Ce催化氧化甲苯性能的影响
Effects of two preparation methods on the performance of Pt/Co-Ce catalytic oxidation of toluene
-
摘要: 针对高效催化氧化甲苯催化剂的开发,采用2种不同制备方法制备Pt纳米颗粒并负载在Co-Ce载体上,以实现甲苯的高效脱除;并通过ICP-OES、XRD、HRTEM、H2-TPR、XPS等研究了制备方法对Pt/Co-Ce催化氧化甲苯性能的影响。结果表明,铂纳米胶体浸渍法制备的Pt纳米颗粒尺寸均匀分布在2~4 nm,高活性零价Pt比例高达93.37%。Pt纳米颗粒与Co-Ce载体之间存在相互作用,提升了催化剂的表面氧浓度,使得Co3+的还原温度降低了158 ℃,强化了催化剂的氧化还原性能。因此,0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N催化剂具有优异的甲苯催化氧化性能,与氯铂酸浸渍法制备的0.5Pt/CoCeOx-I催化剂相比,T50下降了68 ℃。本研究结果可为高性能的VOCs催化氧化催化剂的设计提供参考。Abstract: In order to develop an efficient catalytic oxidation catalyst for toluene, Pt nanoparticles were prepared and loaded on Co-Ce support by different preparation methods to achieve efficient removal of toluene. The effects of the preparation method on the catalytic performance of Pt/Co-Ce were investigated by ICP-OES, XRD, HRTEM, H2-TPR, and XPS techniques. The results showed that the Pt nanoparticles prepared by Pt nanocolloid impregnation method were uniformly distributed in the size of 2-4 nm, and the proportion of zero-valent Pt was as high as 93.37%. The interaction between Pt nanoparticles and Co-Ce support enhanced the surface oxygen concentration of the catalyst, which decreased the reduction temperature of Co3+ by 158 °C and strengthened the redox performance of the catalyst. Therefore, the 0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N catalyst has excellent catalytic oxidation performance for toluene, and the T50 decreases by 68 °C compared with the 0.5Pt/CoCeOx-I catalyst prepared by the chloroplatinic acid impregnation method, respectively. This study can provide a reference for the design of high-performance catalysts for the oxidation of VOCs.
-
Key words:
- Toluene /
- catalytic oxidation /
- preparation method /
- Platinum /
- Cobalt /
- Cerium
-
表 1 Pt/ Co0.9Ce0.1Ox 和 Co0.9Ce0.1Ox催化剂的催化性能
Table 1. The catalytic performance of Pt/ Co0.9Ce0.1Ox and Co0.9Ce0.1Ox catalysts.
供试样品 T50 /℃ T90 /℃ Co0.9Ce0.1Ox 259 287 0.5Pt/CoCeOx-I 260 314 0.1Pt/CoCeOx-N 234 257 0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N 192 225 表 2 Pt/ Co0.9Ce0.1Ox 和 Co0.9Ce0.1Ox催化剂的和结构特性
Table 2. The structural data of Pt/ Co0.9Ce0.1Ox and Co0.9Ce0.1Ox catalysts
供试样品 ICP测得Pt质量分数 设计Pt质量分数 SBET /(m2·g−1) 孔容/(cm3·g−1) 孔径/nm Co0.9Ce0.1Ox − − 71.8 0.158 8.9 0.5Pt/CoCeOx−I 0.41% 0.5% 56.8 0.132 8.9 0.1Pt/CoCeOx−N 0.11% 0.1% 76.6 0.169 9.6 0.5Pt/CoCeOx−N 0.55% 0.5% 45.5 0.113 11.4 表 3 XPS表面元素分布表征结果
Table 3. Surface characterization results from XPS
供试样品 Pt0/(Pt0+PtOx) Oa/(Oa+Ol) Co3+/(Co2++Co3+) Ce3+/(Ce4++Ce3+) Co0.9Ce0.1Ox / 53.50% 56.79% 31.23% 0.5Pt/CoCeOx-I 38.29% 49.60% 39.92% 27.10% 0.1Pt/CoCeOx-N 93.37% 53.90% 52.87% 31.44% 0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N 91.55% 58.54% 55.11% 33.56% 表 4 Pt/ Co0.9Ce0.1Ox 和 Co0.9Ce0.1Ox催化剂的氧化还原性能
Table 4. Catalytic performance of Pt/ Co0.9Ce0.1Ox and Co0.9Ce0.1Ox> catalysts
样品 总氢耗量/(μmol·g−1) 第一个峰的理论氢耗量/(μmol·g−1) 第一个峰的氢耗量/(μmol·g−1) Co0.9Ce0.1Ox 13 085.2 / / 0.5Pt/CoCeOx-I 13 021.0 51.3 107.1 0.1Pt/CoCeOx-N 13 150.6 <<10.2 90.4 0.5Pt/CoCeOx-N 13 583.9 <<51.3 104.6 -
[1] MOZAFFAR A, Zhang Y L. Atmospheric volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in China: a review[J]. Current Pollution Reports, 2020, 6(3): 250-63. doi: 10.1007/s40726-020-00149-1 [2] HE C, CHENG J, ZHANG X, et al. Recent advances in the catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds: A review based on pollutant sorts and sources[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2019, 119(7): 4471-4568. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00408 [3] PAULIS M, PEYRARD H, MONTES M. Influence of chlorine on the activity and stability of Pt/Al2O3 catalysts in the complete oxidation of toluene[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2001, 199(1): 30-40. doi: 10.1006/jcat.2000.3146 [4] HUANG HB, XU Y, FENG QY, et al. Low temperature catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds: A review[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2015, 5(5): 2649-2669. [5] REN QM, FENG ZT, MO SP, et al. 1D-Co3O4, 2D-Co3O4, 3D-Co3O4 for catalytic oxidation of toluene[J]. Catalysis Today, 2019, 332: 160-167. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2018.06.053 [6] 赵海楠, 王健, 刘国才, 等. 氧化还原共沉淀法制备的二元锰氧化物催化剂催化氧化苯的效果[J]. 环境工程学报, 2020, 14(3): 701-708. [7] NIKAWA T, NAYA S, KIMURA T, et al. Rapid removal and subsequent low-temperature mineralization of gaseous acetaldehyde by the dual thermos-catalysis of gold nanoparticle-loaded titanium(IV) oxide[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2015, 326: 9-14. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2015.03.005 [8] 安霓虹. 负载型铂催化剂上甲醛的CO低温催化氧化反应性能研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2012. [9] 李雨馨. 微波辅助乙二醇法制备高性能碳载铂催化剂[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2019. [10] 刘菊荣, 苏晨光, 董雅鑫, 等. Pd-Na/Al2O3催化剂的表征及室温下催化氧化甲醛的性能[J]. 环境工程学报, 2020, 14(8): 2203-2210. [11] 彭若斯. 二氧化铈负载铂催化剂催化氧化甲苯的性能与反应机理研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2017. [12] 王奇. 介孔Co3O4负载贵金属Pt催化剂对乙炔氧化消除的研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2018. [13] MENG M, ZHA Y Q, LUO J Y, et al. A study on the catalytic synergy effect between noble metals and cobalt phases in Ce-Al-O supported catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis A-General. 2006, 301(2): 145-151. [14] WANG Q, LIU J, LI YH, et al. Mesoporous Co3O4 supported Pt catalysts for low-temperature oxidation of acetylene[J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(30): 18592-18600. doi: 10.1039/C7RA02266B [15] CARABINEIRO SAC, CHEN X, KONSOLAKIS M, et al. Catalytic oxidation of toluene on Ce-Co and La-Co mixed oxides synthesized by extirpating and evaporation methods[J]. Catalysis Today, 2015, 244: 161-171. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2014.06.018 [16] FAURE B, ALPHONSE P. Co-Mn-oxide spinel catalysts for CO and propane oxidation at mild temperature[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2016, 180: 715-725. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.07.019 [17] 张维东. 纳米钴氧化物催化剂的合成及对丙烷的完全催化氧化研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2017. [18] 喻成龙, 杨文亭, 夏良海, 等. Mn-Ce复合氧化物微球的制备及其催化氧化甲苯性能[J]. 环境工程学报, 2020, 14(6): 1554-1562. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201908016 [19] 陈柄旭. 非热等离子体改性Pt/CeO2催化氧化甲苯性能的研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2019. [20] 冯振涛. 铈基催化剂的可控制备及其催化降解甲苯机理研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2019. [21] ZHANG S, LIU S J, ZHU X C, et al. Low temperature catalytic oxidation of propane over cobalt-cerium spinel oxides catalysts[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 479: 1132-1140. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.02.118 [22] GUO YL, WEN MC, LI GY, et al. Recent advances in VOC elimination by catalytic oxidation technology onto various nanoparticles catalysts: A critical review[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2021: 281. [23] 谭伟, 袁震, 蒋进元, 等. 不同形貌MnO2及其负载Au催化剂的制备与CO和甲苯催化氧化性能研究[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2018, 8(2): 142-148. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2018.02.019 [24] LIOTTA LF. Catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds on supported noble metals[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2010, 100(3/4): 403-412. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2010.08.023 [25] SANTOS VP, CARABINEIRO SAC, TAVARES PB, Oxidation of CO, ethanol and toluene over TiO2 supported noble metal catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2010, 99(1/2): 198-205. [26] MAO J Z, YAN X H, GU H Z, et al. Hydrogenation of o-chloronitrobenzene by platinum nanoparticles on activated carbon[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2009, 30(3): 182-194. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(08)60095-9 [27] RAMIREZ E, ERADES L, PHILIPPOT K, et al. Shape control of platinum nanoparticles[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2007, 17(13): 2219-2228. doi: 10.1002/adfm.200600633 [28] RUI Z B, CHEN L Y, CHEN H Y, et al. Strong metal-support interaction in Pt/TiO2 Induced by mild HCHO and NaBH4 solution reduction and its effect on catalytic toluene combustion[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2014, 53(41): 15879-15888. [29] HANSEN TK, HOJ M, HANSEN BB, et al. The effect of Pt particle size on the oxidation of CO, C3H6, and NO over Pt/Al2O3 for diesel exhaust aftertreatment[J]. Topics in Catalysis, 2017, 60(17/18): 1333-44. doi: 10.1007/s11244-017-0818-9 [30] SEO P W, CHOI H J, HONG S I, et al. A study on the characteristics of CO oxidation at room temperature by metallic Pt[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 178(1-3): 917-925. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.02.025 [31] WANG M M, CHEN D Y, LI N J, et al. Nanocage-shaped Co3-xZrxO4 solid-solution supports loaded with Pt nanoparticles as effective catalysts for the enhancement of toluene oxidation[J]. Small, 2020, 16(51): 9. [32] TENG F, CHEN M, LI G, et al. High combustion activity of CH4 and catalluminescence properties of CO oxidation over porous Co3O4 nanorods[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2011, 110: 133-140. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.08.035 [33] WU H, PANTALEO G, DI CARLO G, et al. Co3O4 particles grown over nanocrystalline CeO2: Influence of precipitation agents and calcination temperature on the catalytic activity for methane oxidation[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2015, 5(3): 1888-1901. [34] PENG R S, SUN X B, LI S J, et al. Shape effect of Pt/CeO2 catalysts on the catalytic oxidation of toluene[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 306: 1234-1246. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.08.056 [35] 孙西勃. 二氧化铈纳米棒负载纳米贵金属催化氧化甲苯研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2017. -




 下载:
下载: