-
石油工业是我国的重要支柱产业之一,油田联合站是油田原油集输和处理的中枢[1]。在联合站中,各区块来油通过原油稳定系统将分离出的轻烃组分回收进入轻烃厂,处理后的原油组分通过联合站处理再进行外输[2-4]。在联合站的日常操作运行中,各种拱顶罐呼吸阀、干化池等存在油气逸散的风险。另外,储罐在运行过程中可能因腐蚀、雷击、油罐失效、人为损坏等意外因素导致油罐罐壁破损[5-6],从而泄漏和蒸发出大量易燃易爆、有毒的油气混合物。这些混合物即挥发性有机物 (volatile organic compounds,VOCs) 。VOCs的泄漏不仅会污染环境,还会严重威胁企业安全和人群健康、安全和环境 (Health、Safety、Environment,HSE) [7-10]。“十四五”规划提出,要强化多污染物协同控制和区域协同治理,加快VOCs排放综合整治,到2025年,VOCs排放总量下降10%以上[11-12]。经调研,油田联合站的多个环节 (如原油储罐及轻烃储罐、除油罐、净化罐、沉降罐、敞开液面) 存在VOCs排放问题,因此,有必要开展油田联合站VOCs排放的扩散规律研究。
目前,VOCs扩散规律分析方法主要有:现场测试[13-14]、风洞实验[15-16]和数值模拟[17-20]。其中,基于计算流体力学 (computational fluid dynamics,CFD) 及其Fluent软件的数值模拟方法的可操作性强,已在航天、汽车、能源、化工、材料、生物医药等诸多领域广泛应用[21]。KOUNTOURIOTIS等[22]通过数值模拟,在风速、风向、温度、油气扩散源位置等多种影响因素下,研究了不同成分的汽油挥发出的VOCs扩散规律,并发现在扩散源附近的VOCs浓度远远高于爆炸极限。基于风洞平台实验验证和Fluent数值模拟,建立了基于单膜传质理论的油气蒸发过程当量膜厚数值模拟计算方法,以及基于Stefan-Fuchs方程、Clausius-Clapeyron方程及若干准则数的非稳态蒸发单相传质的数值模拟方法,揭示了在各操作条件下油罐非稳态石油蒸发和油罐排放气在大气环境中的扩散行为及其内在机理,以及影响因素间的关联性[15,23-24]。
本课题组通过CFD 数值模拟和风洞实验平台研究了某石化企业的实体罐区发生溢油事故后油气蒸发的扩散规律,掌握了罐区VOCs浓度的变化特征[25]。然而,针对油田联合站内多排放源的VOCs扩散规律研究仍未出现。本研究以某油田大型联合站多点排放源为对象,通过CFD数值模拟和现场调研数据相结合,以探究正常工况下VOCs扩散机理及储罐裂缝处VOCs泄漏扩散的叠加效应。本研究结果可与前期针对大型罐区VOCs扩散数值模拟[25]成果相结合形成系列成果,为石油石化行业的运行管理及VOCs排放控制提供参考。
-
(1) 基本控制方程
油气扩散的流动基本控制方程包括质量守恒方程、动量守恒方程、能量守恒方程和组分运输方程[25]。控制方程的通用形式见式 (1) ,其展开形式见式 (2) 。
式中:ρ为混合气体密度,kg·m−3;u为速度矢量;Φ为通用变量;Г为广义扩散系数;S为广义源项;ν为运动粘度,Pa·s。
(2) 湍流方程
在风速的影响下,联合站内的VOCs流体处于湍流状态,而表达湍流状态的Realizable k-ε模型可很好地描述站内的气流扰动和VOCs扩散情况[25-26]。因此,本研究选用该模型,具体方程见式 (3) ,式中Cl的计算见公式 (4) 。对于特定方程Φ、Г、S代表的具体形式如表1所示。
式中:湍流方程中的ρ为气体密度,kg·m−3;u为速度矢量;Sk、Sε为用户定义的源项;Pk为由层流速度梯度而产生的湍流动能,m2·s−2;Gk为由平均速度梯度引起的湍流动能,m2·s−2;μ为VOCs的动力黏度,Pa·s;μt为湍流粘度,Pa·s;K为湍流动能,m2·s−2;Gb为由浮力而产生的湍流动能,m2·s−2;ε为耗散率,m2·s−3;η为有效因子;YM为在可压缩湍流中过渡扩散产生的波动,m2·s−2;C1ε、C2、C3ε为经验常数;σk、σ为k方程和ε方程对应的普朗德数;xi、μi中的下标i、j表示各自x、y、z方向的分值,m·s−1。
-
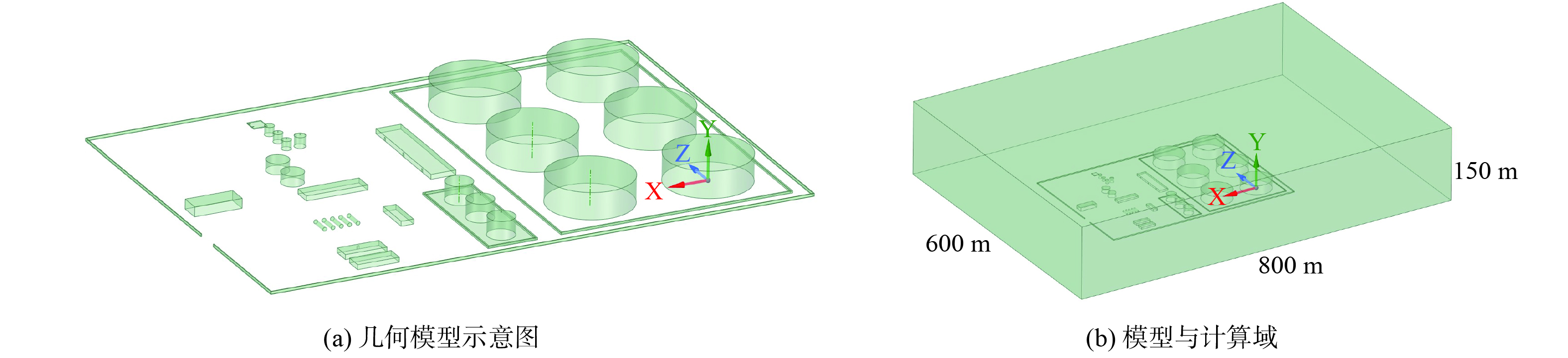
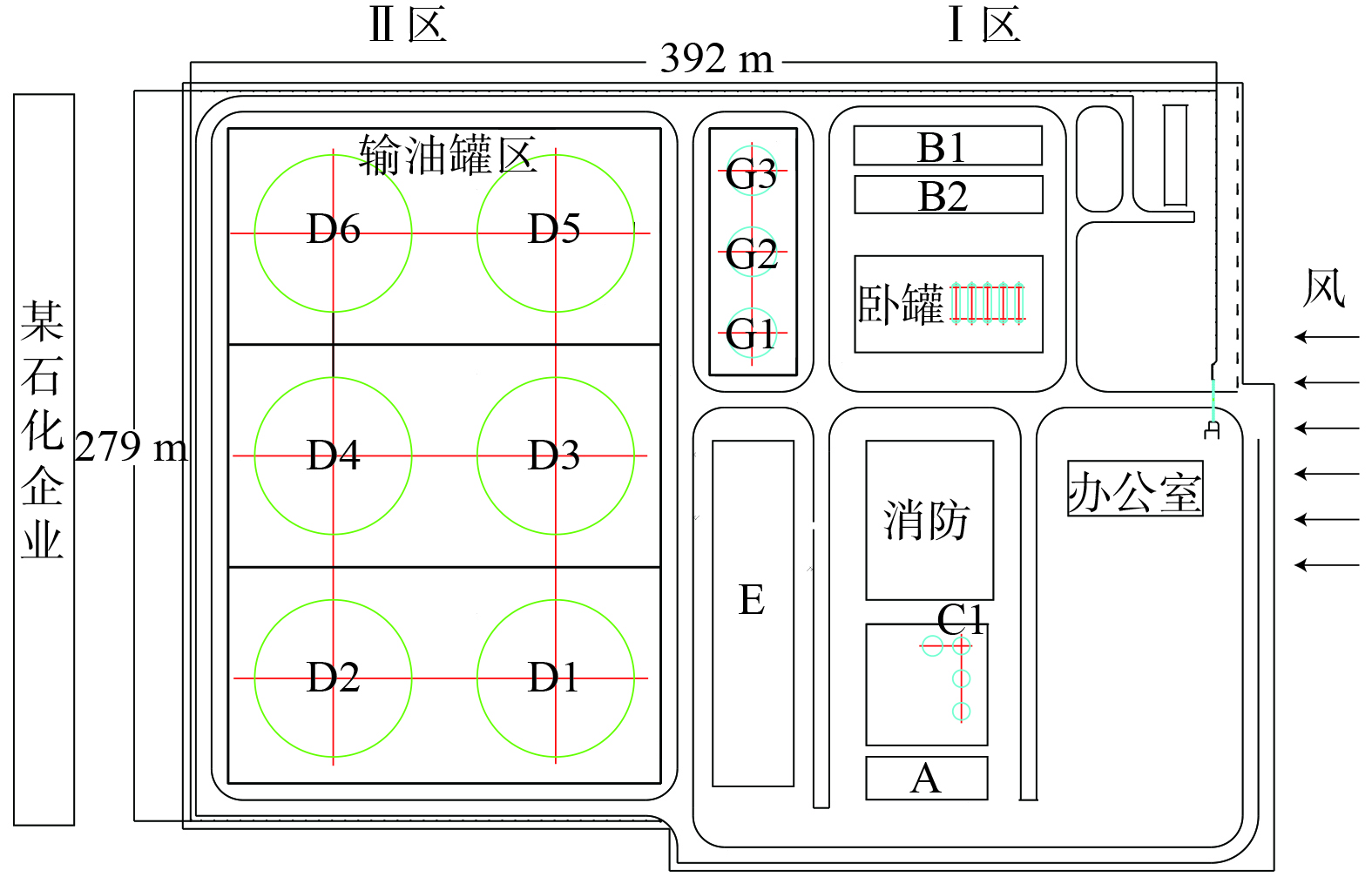
以某油田大型联合站为研究对象,进行了实地考察。该联合站主要承担该油田2个区块的来油、脱水、净化和外输等工作。年外输净化油为2×105 m3,年回注量约为9.5×104 m3。为便于后续的模拟分析,对联合站内的建筑进行编号 (图1) 。其中,Ⅰ区主要包括3个3 000 m3拱顶罐G1~G3 (G1、G2为沉降罐,G3为净化罐) ,B1、B2为输油泵房,E为配套设施 (包括计量室、加药室、转油泵房、配电室等) ,A为干化池,C1为300 m3拱顶罐 (除油罐) ;Ⅱ区为输油罐区,主要包括6个5 000 m3 原油外浮顶储罐D1-D6。场站的平面尺寸为长392 m、宽279 m,呼吸阀的高度0.5 m、直径0.2 m。储罐的具体尺寸 (含高度) 和参数见表2。
原油外浮顶储罐D区为新建罐区,技术管控水平高、密封条件好,各个排放源均符合标准。联合站的VOCs多排放源包括:正在工作的G2沉降罐呼吸阀、G3净化罐呼吸阀;泵房B2地漏 (VOCs从泵房排风扇和大门排出) 、E中的转油泵房的工作泄漏 (从E的3个大门排出) 、污油箱及干化池A;正在工作的C1除油罐呼吸阀。拱顶罐呼吸阀的VOCs排放主要源于储罐进出油的大呼吸和小呼吸损耗。干化池A没有完全密闭处理,池中油泥排放VOCs会直接扩散。输油首站中的储罐均为外浮顶罐,泄漏较少。联合站左侧为某石化企业,其余三侧为开阔地形,对VOCs扩散行为影响较小,因此,本研究主要考虑从Ⅰ区到Ⅱ区的风向。
通过模拟联合站不同风速 (2 m·s−1、4 m·s−1、6 m·s−1) 条件下正常工况时的泄漏,以探究联合站主要泄漏源泄漏对站内输油罐区Ⅱ区和左方位石化企业的影响。另外,考虑到Ⅰ区拱顶罐出现破裂,模拟了G2沉降罐VOCs从罐壁裂缝处排放扩散及叠加情况。其中,罐壁破裂口的大小为长2 m、宽0.5 m。
本研究聚焦联合站内VOCs扩散规律和对输油罐区 (Ⅱ区) 、某石化企业的扩散影响。为便于数值模拟,忽略联合站外某石化企业可能产生影响。建立与现场尺寸1∶1的联合站三维几何模型图 (图2 (a) ) 。外部计算域示意图为图2 (b) 。
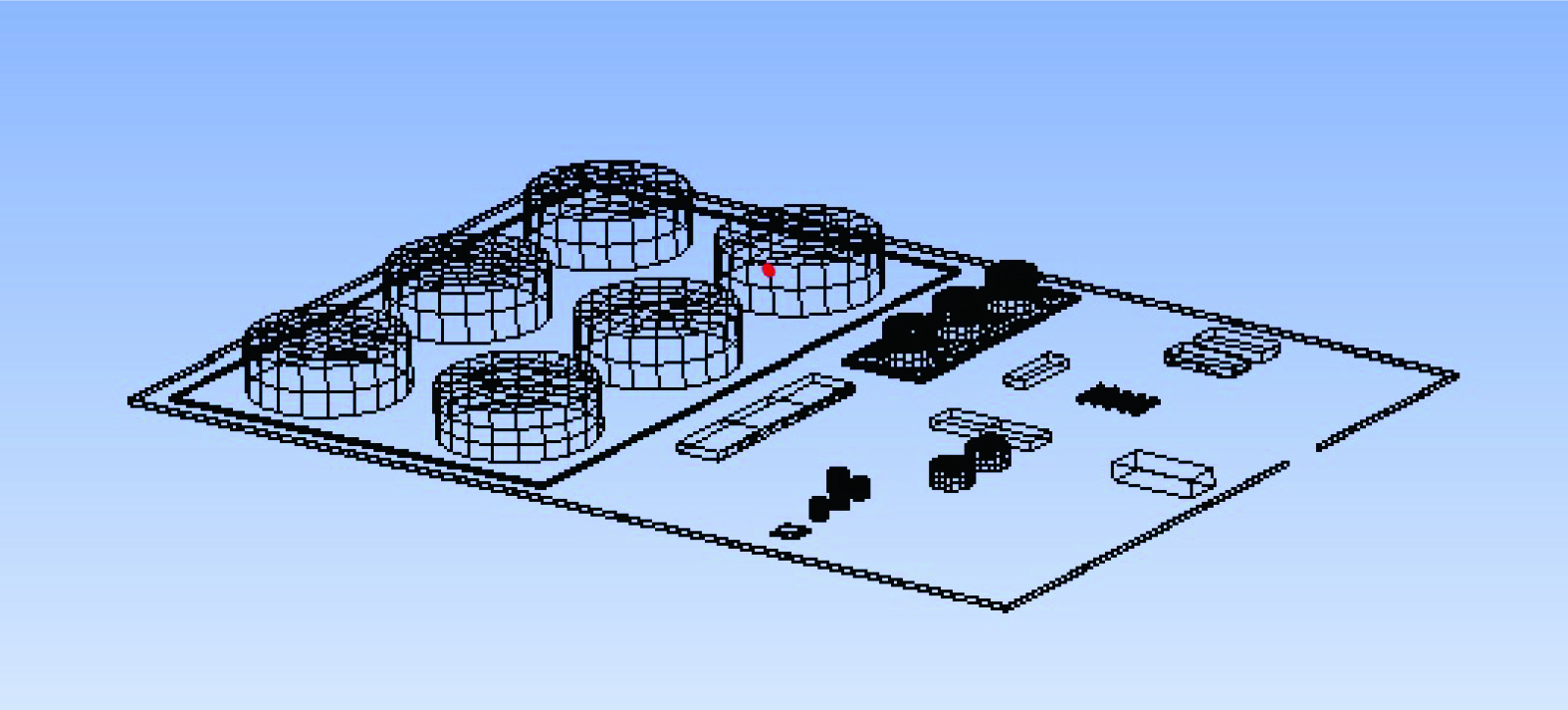
由于联合站建筑和油罐较多、模型较为复杂,非结构网格能适应这种复杂模型,采用Ansys meshing软件划分三维网格 (图3) 。流场的风速沿x轴反方向进入,即从联合站Ⅰ区到Ⅱ区的风向。入口边界设置为速度入口边界条件,出口边界设置为压力出口边界条件。VOCs扩散源设置为质量流率边界条件,质量流率为联合站现场实测值。其中,网格交界面设置为内部边界,其他边界均设置为绝热固壁边界。
-
当环境风为4 m·s−1时,对距离G3罐顶部高2 m处的位置进行风速监测,具体无关性验证结果如表3。风速会随网格数量的变化而变化。当网格数量从746 528增加到2 005 657时,沿x方向速度发生显著变化;当网格数量增加到200万左右时,风速不再发生变化。这说明网格数量已经符合计算要求,后面的网格数量划分参照选取200万左右的数量。
-
(1) 排放组分的代表性
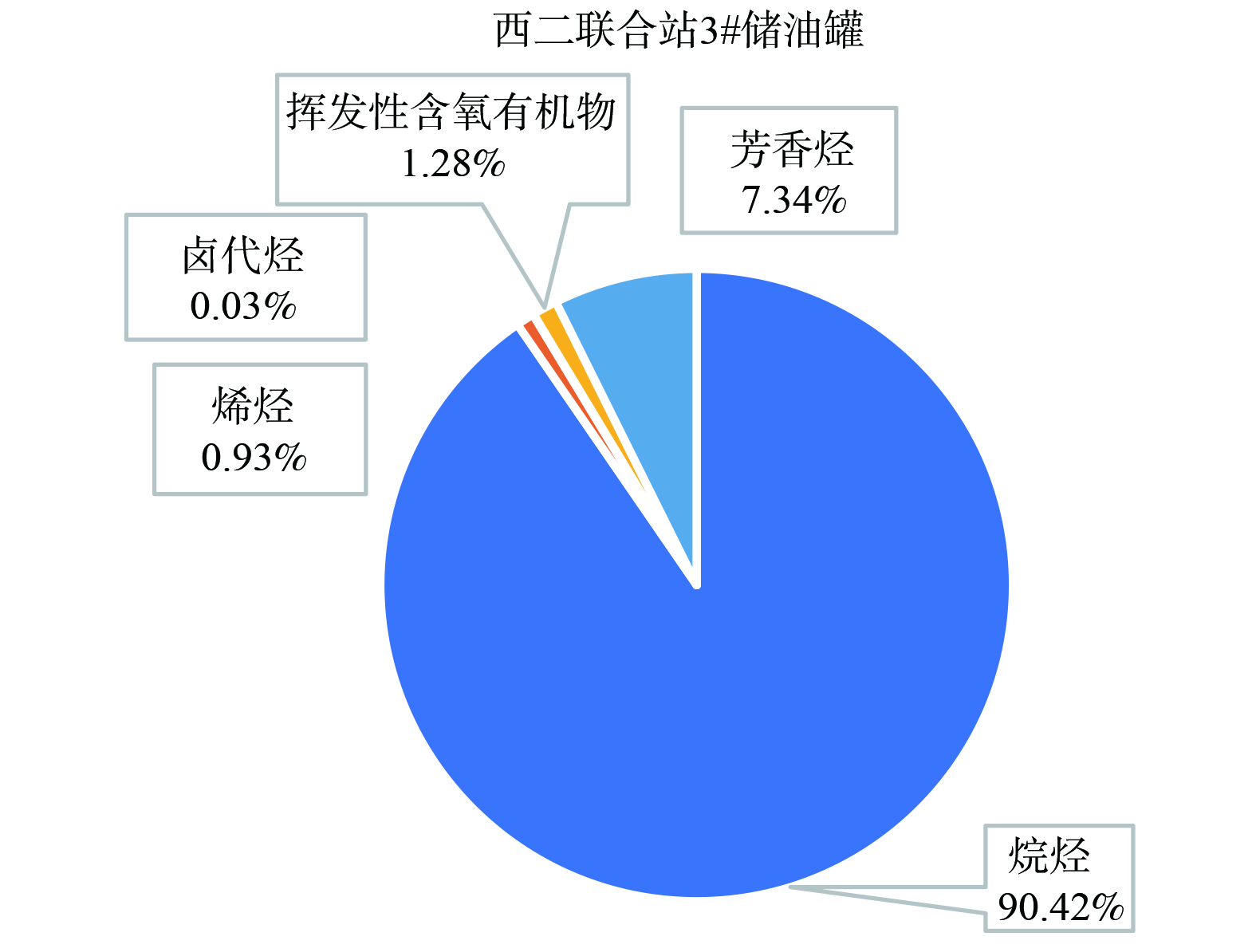
为验证排放组分的代表性,在联合站内采集净化罐排放的VOCs样品并进行全组分分析 (共118组分) , (图4) 。在12个全组分中含量占比最高的是烷烃,这表明该油田全组分以烷烃为主。在烷烃中,占比依次为甲基环己烷、正辛烷、正庚烷、十一烷、癸烷、正己烷、二甲基庚烷、正戊烷、环己烷等烷烃,含量取平均值后,与正己烷含量相近。因此,选取正己烷为代表模拟该联合站的VOCs扩散规律。
(2) 数值模拟的准确性
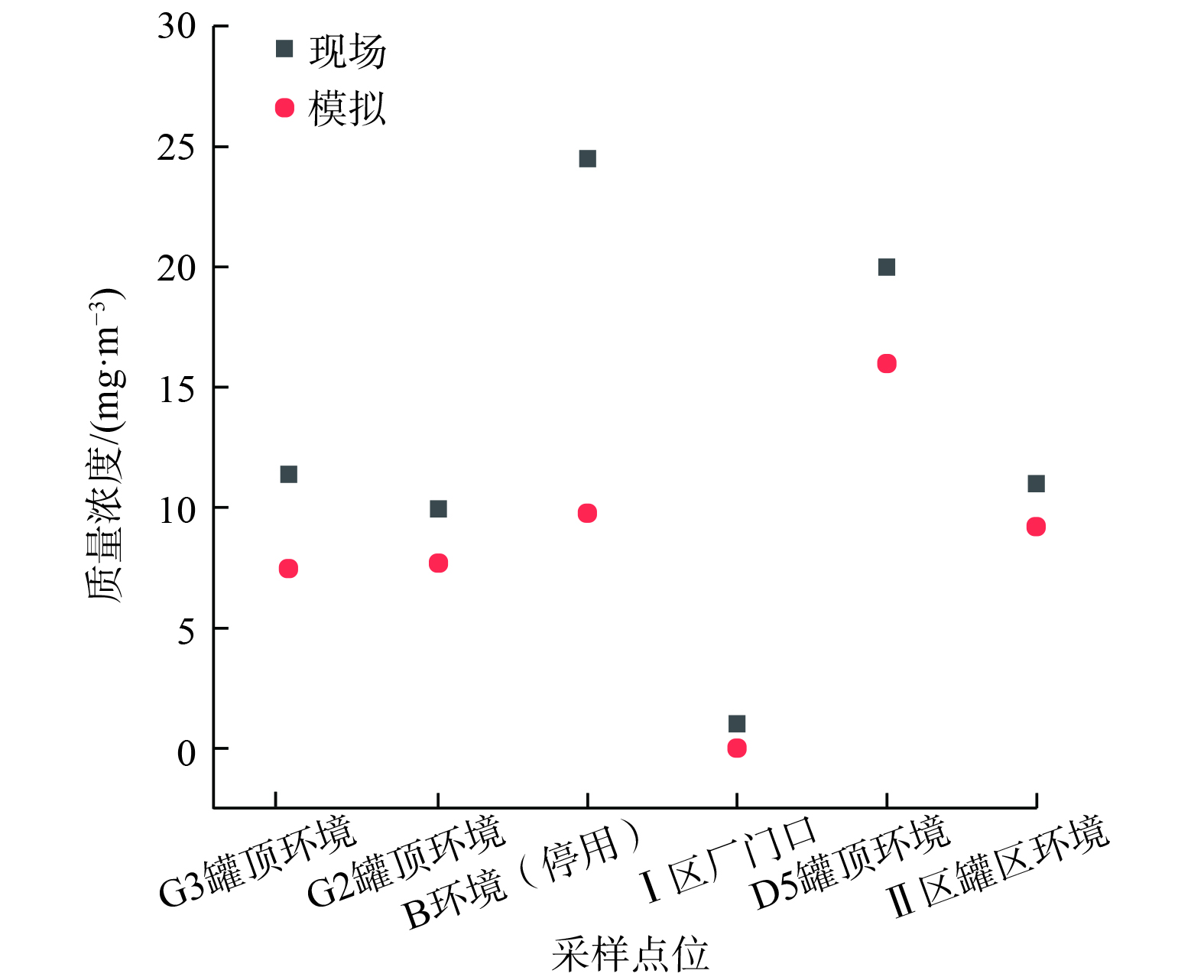
为了验证数值模型的可行性和准确性,通过2种方法进行验证。首先,前期研究[17,25]中已采用风洞实验进行了数值模拟常用方法的论证。另外,通过便携式气相色谱仪、风速仪、高纯氢气发生器、多路温度测试仪、低噪音空气泵、旋涡式气泵和干式螺杆真空泵等现场测试仪器实测了多点排放数据,并进行验证。其中,数据测量多次取平均值 (表4) ,进行相关的数值模拟结果与实测数据如图5所示。模拟结果与实测数据大部分比较接近,故该数值模型的构建参数设置可行。存在部分相差较大的数据是由于:1) 不管是现场还是模拟流场都属于非定常流动,一定程度上存在湍流的不确定性,即物理参数 (如流场中风速) 在一定范围内波动,不同时刻的实测值略有不同;2) 风速仪和取样器的检测探头从量油口深入罐内后,会对罐内的流场和浓度场产生一定扰动。
-
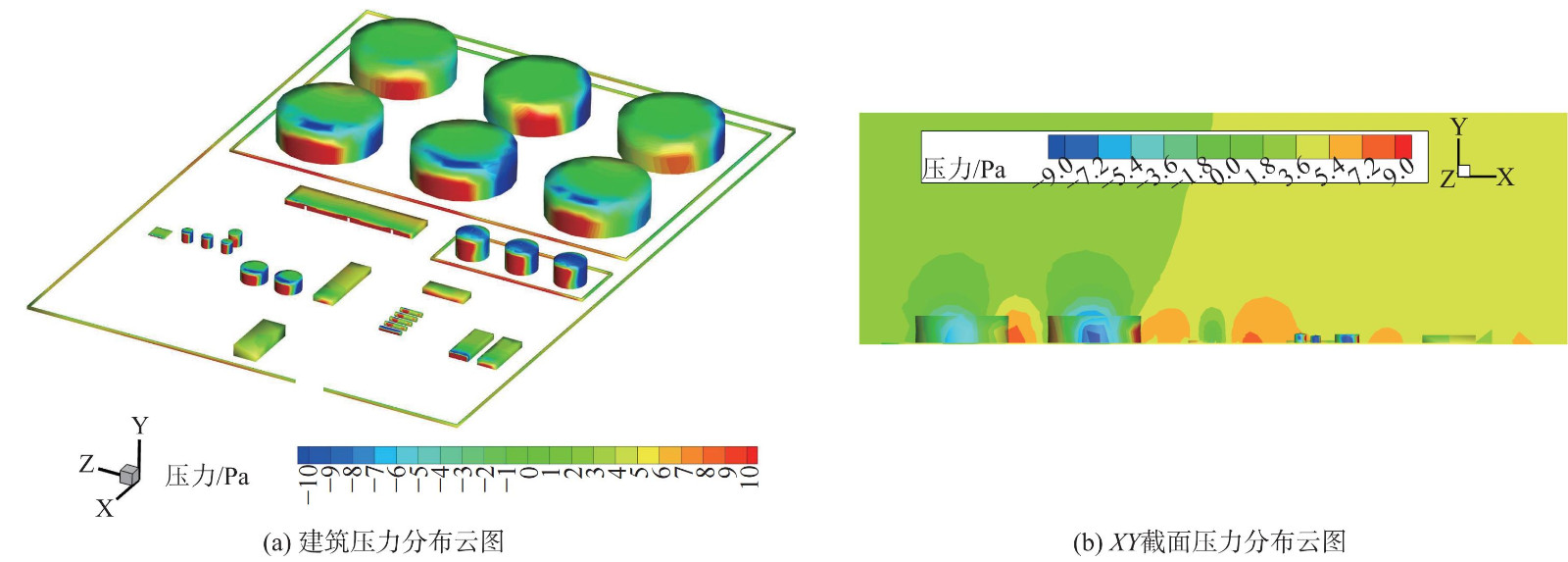
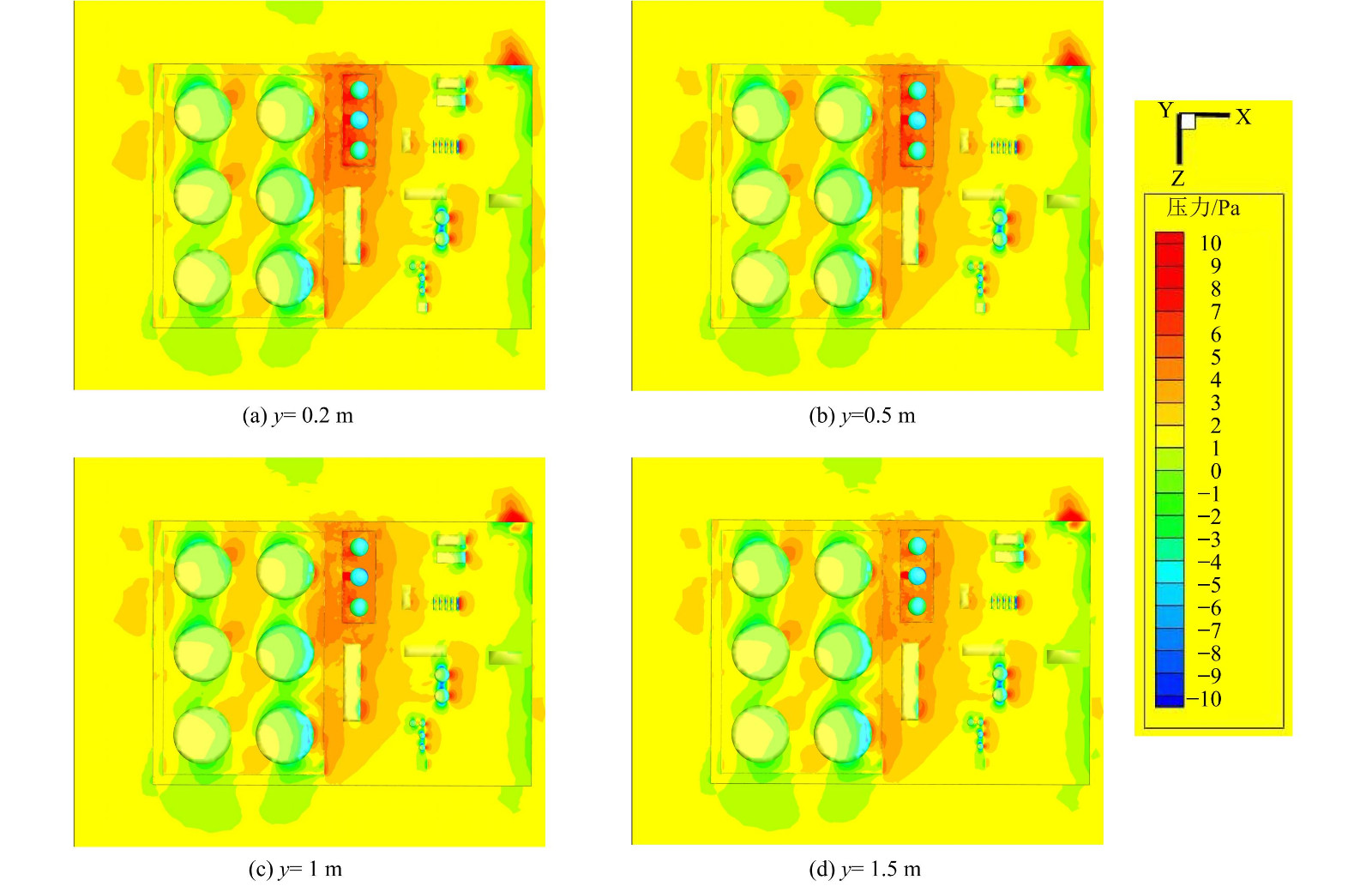
图6 (a) 为当风速为2 m·s−1 (沿x轴反方向) 时联合站的压力分布云图。在罐区多排放源的排放下,Ⅰ区和Ⅱ区的前排储罐、防火堤和办公区的迎风侧被气流直接撞击,动能转换为压力势能,压力达到该风速下的最大压力。而建筑的两边和背风侧压力最小且为负压,这是由于部分气流在撞击储罐后,移入空腔区,气流加速,沿储罐两侧向后方流动,出现绕流现象。该现象为湍流运动且雷诺数 (Re) 足够大,加大了储罐前方区域及背风侧空腔区域的回流,使压力迅速减小。罐顶部前沿有明显的负压区。这是由于在压差的作用下,罐顶上方的气流速度增大,使储罐顶部的压力减小,从而形成负压。Ⅰ区和Ⅱ区的后排储罐由于前排储罐的阻挡,受到气流直接撞击的面积减少,相应的红色正压区减少。该结果与文献[16,25]的结果符合,也符合图6 (b) 所示联合站所在xy截面的压力云图。
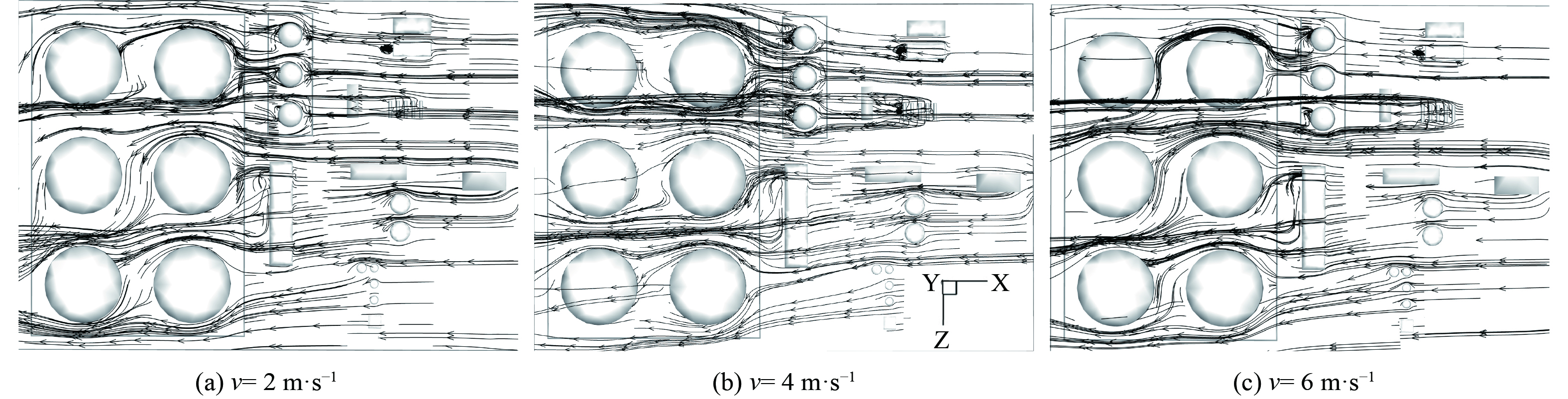
不同风速下联合站内气流流动轨迹如图7所示。油气多排放溯源主要分布在联合站Ⅰ区 (G、B、C1、A、E) ,流场的风向从联合站Ⅰ区到Ⅱ区,因此,本研究主要分析从Ⅰ区到Ⅱ区的建筑对气流的扰动。图7表明,由于Ⅰ区高度不一的建筑对气流存在阻碍作用,部分气流会在建筑的背风侧囤积并形成小漩涡,如B区和G区。另外部分气流从B区顶部穿过到达G区,由于B区和G区高度不同,在G区储罐形成分流,在背风侧也形成涡流。当风速从2 m·s−1依次变为6 m·s−1时,由于风速变大,G1罐的背风侧涡流变大,并且前方气流协同涡流气流汇合流向联合站D区[25]。另外,经过Ⅰ区的气流由于Ⅰ区卧式罐的阻挡,会有一部分经过G区储罐流向Ⅱ区。在风速2 m·s−1时,由于“卡门涡街”效应,G区储罐背风侧会形成多个漩涡,当风速增大至4 m·s−1,背风侧的小漩涡会汇合形成一个涡流,VOCs容易在此聚集,应加强日常防控。
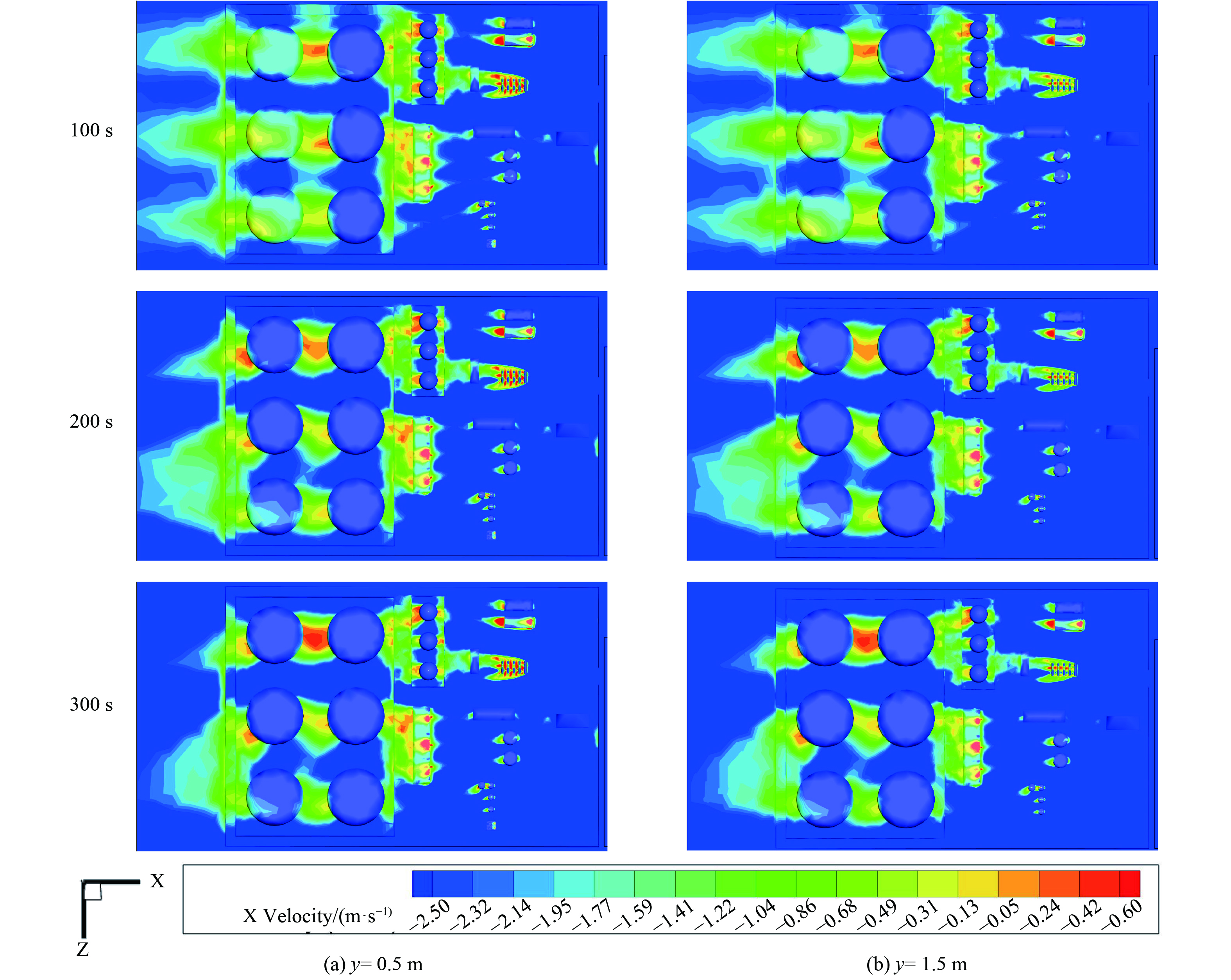
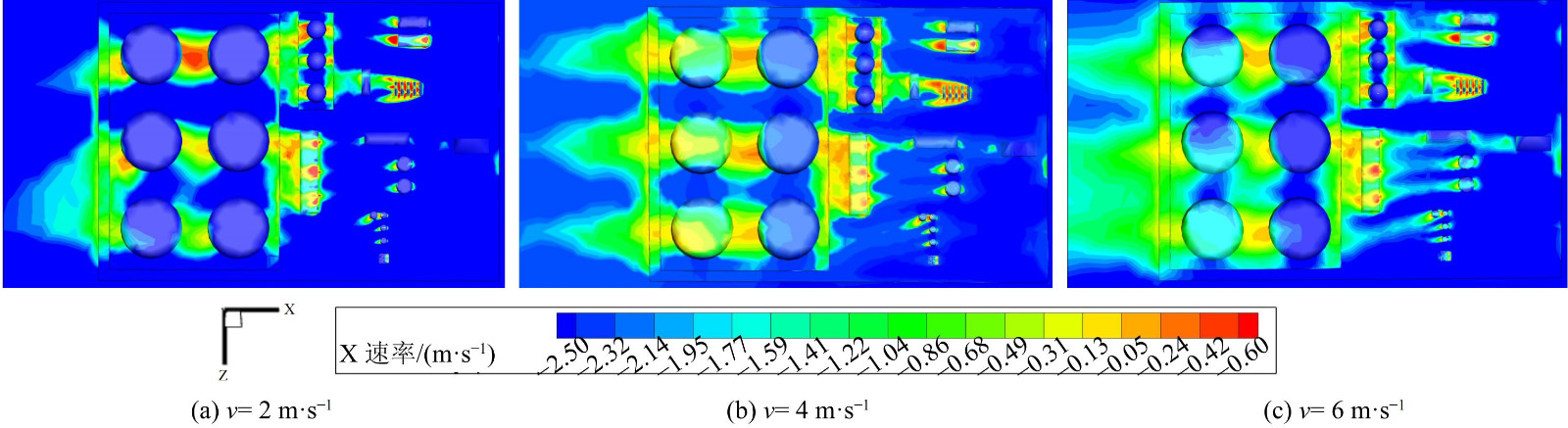
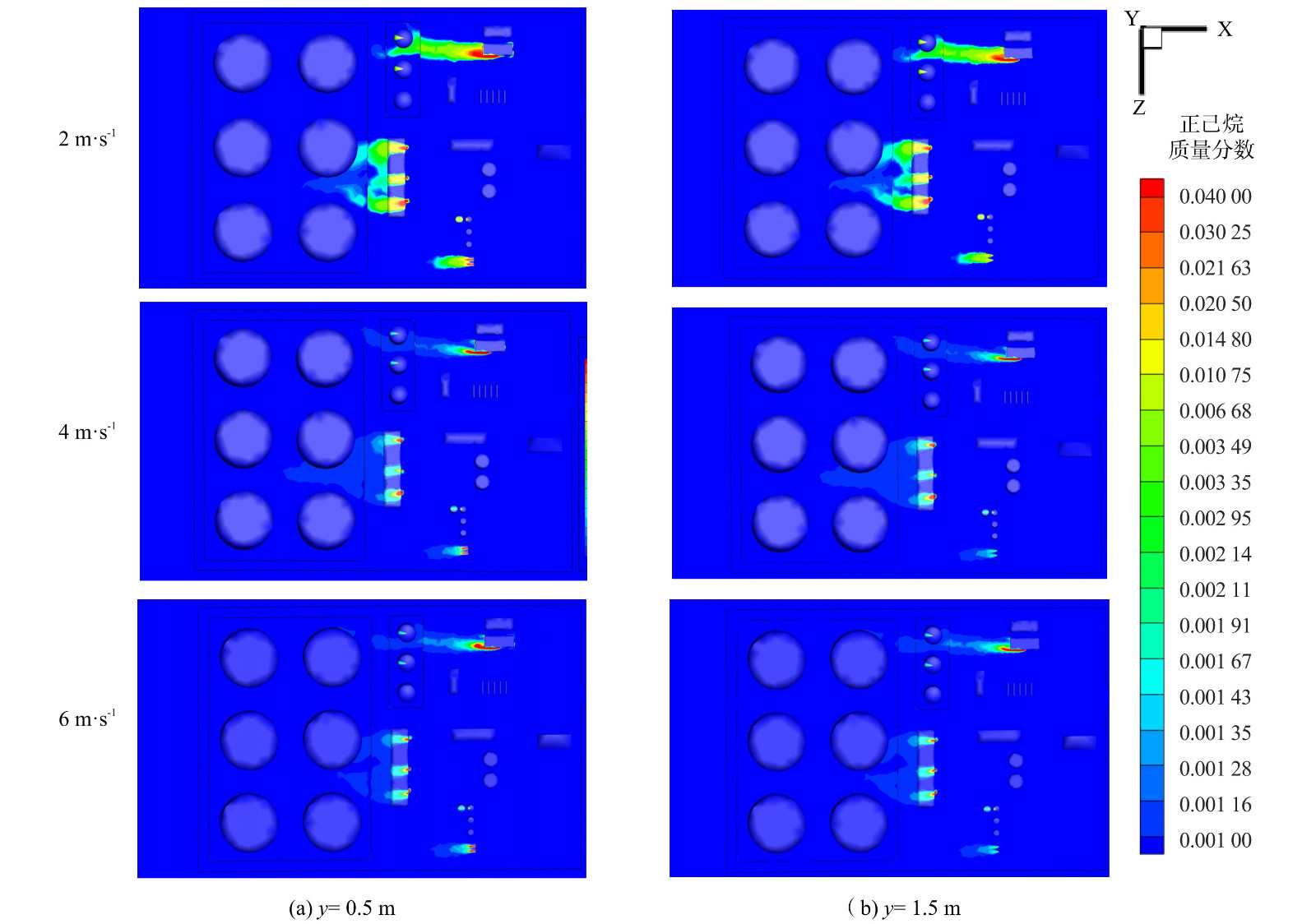
图8为当风速为2 m·s−1时,联合站内不同高度随时间变化的速度分布云图。图9为不同风速下,t=300 s,y= 0.5 m时联合站xz截面的速度分布云图。以排放源G区为例,当气流撞击迎风侧后气流加速,沿储罐两侧向后方流动,但由于G区和两层防火堤的阻挡,Ⅱ区的D5罐到达的垂直气流减少。相反,D1罐和D3罐由于前面为高度为3.5 m的计量室,远小于Ⅱ区罐的高度,故受到的垂直气流相对D5罐多。另外,在Ⅰ区Ⅱ区的建筑后方,由于建筑背风侧存在涡流,会有明显的红色反方向速度。尤其在B、E、G1罐、D5罐后方,应注意VOCs在此处的叠加。值得注意的是,G区和D区的罐间速度远大于罐前迎风侧。这是由于来流在建筑物迎风面拐角处压力增大,使切变气流在迎风面发生分离,来流在建筑两侧分流。在气流临近建筑物拐角处时,与前方来流汇合,这部分区域属于位移区,分离流在此处的风速增高。另外,随着高度的增大,在联合站的xz平面的整体风速下降,只有Ⅱ区的高罐迎风侧和罐间风速无明显差别。这说明低位风速的变化受建筑物影响较多。
-
在浓度场中,VOCs多排放源主要分布在联合站Ⅰ区 (G、B、C1、A、E) ,取联合站的xz截面,得到该截面300 s时VOCs质量浓度分布云图 (图10) 。由于重力和涡流的作用,VOCs扩散呈现整体向下趋势,上风向的建筑和防火堤对VOCs扩散造成阻碍,而罐间、A、B、E和防火堤背风侧都积聚了一定量的VOCs,其质量分数为0.001 67~0.04。正己烷的爆炸极限体积分数为1%~7%,此处VOCs质量分数在爆炸极限范围内。D区储罐为5 000 m3内浮顶罐,G区为3 000 m3拱顶罐,B区为3.5 m高的泵房。由于存在高度差距,当B区的气流在经过G1罐顶时,VOCs在此被阻挡,且由于漩涡引起的强气流向G1罐的后上方流动,抵达不到后方D区的防火堤,叠加效应不是很明显。而E区VOCs浓度在环境风的裹挟下,在风速为2 m·s−1时已跨过E区和D区前方的防火堤抵达D区。因此,应注意B区后方和D区与E区之间的VOCs聚集,容易引起火灾爆炸,日常巡检应重点关注此处VOCs情况。
-
当Ⅰ区G2罐罐壁发生意外裂缝,出现油气泄漏时,在6 m·s−1风速和多排放源的影响下,会出现VOCs叠加效应。图11为不同高度下联合站内压力分布云图。联合站的整体建筑迎风侧为正压区,背风侧、罐间和储罐顶部出现不同程度的负压区,与上述压力场 (图6) 类似。但是当排放源G2罐罐壁出现裂缝时,G2罐背风侧出现了明显的类似矩形的正压区。这可能是由于G2罐的背风侧泄漏,导致G2罐的背风侧压差减小,风速在G2罐的背风侧停滞,出现明显的VOCs叠加效应。另外,图11中其余压力场大于无泄漏时的压力场,尤其G区背风侧。这说明G2罐事故泄漏源对于压力场的叠加效应主要发生在G区,并以G区为中心点呈点射状向外逐步减弱。
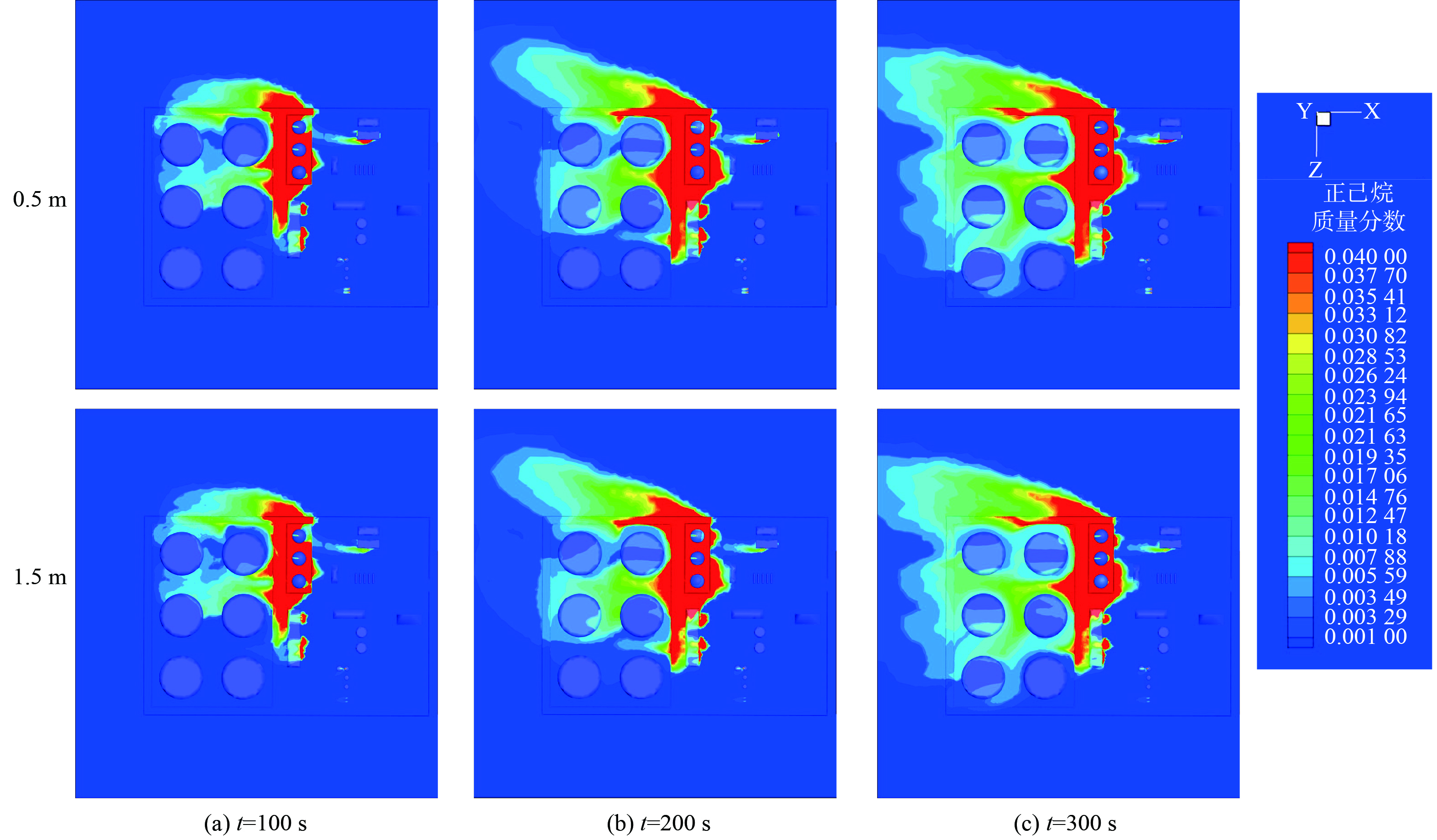
取在y=0.5 m和1.5 m高度处的不同时刻VOCs质量分数分布云图如图12所示。VOCs浓度随高度的变化与上述浓度场一致。随着VOCs扩散时间的增加,以排放源G2罐罐壁作为中心泄漏源,高浓度VOCs扩散呈由点向外放射性扩大,出现大面积的红色高浓度区,主要偏向于下风向的扩散。另外,一方面由于“卡门涡街”的效应,另一方面由于在G区罐背风侧会出现由漩涡汇合形成的强气流,故G2罐的VOCs扩散强度大于单独事故泄漏源和正常工况下 (即无事故泄漏源) 的扩散强度,出现“1+1>2”的叠加效应。并且,在强气流的作用下,会裹挟泄漏的VOCs向D5罐的上方侧扩散,应尤其注意G区和D区上前方位的VOCs积聚。值得注意的是,在泄漏源下风向的Ⅱ区和某石化企业的VOCs浓度容易处于爆炸极限范围内,应注意火灾爆炸的风险。
-
1) 在正常工况条件下,联合站内多排放源的受风速影响,内储罐迎风侧的压力达到最大,罐间和背风侧由于出现绕流和回流,出现大面积的负压区域,且有明显的反方向速度。另外,在重力和涡流的影响下,VOCs呈整体向下运动趋势,容易造成罐间和背风侧的VOCs聚集,且在漩涡引起的强气流作用下,Ⅱ区和某石化企业容易达到爆炸极限。但由于联合站内排放源之间的距离大于扩散范围,VOCs叠加效果不明显。
2) 通过对联合站Ⅰ区的排放源G2罐罐壁破损泄漏时进行模拟,发现在事故罐后方会出现红色正压区,且VOCs扩散会呈点射状向下风向扩散。加上“卡门涡街”效应和漩涡引起的强气流,多排放源的VOCs扩散会出现“1+1>2”的叠加效应。叠加后的VOCs质量浓度会明显增强,油气爆炸危险区域加速扩展。另外,Ⅱ区和某石化企业会处在爆炸极限范围内,应注意火灾爆炸的风险。
3) 本研究考虑条件为从联合站Ⅰ区到Ⅱ区的风向。但联合站常年风向不定,若联合站风向为Ⅱ区到Ⅰ区,按本模拟方法可推断处联合站内多排放源的VOCs扩散会对联合站Ⅰ区的影响较大,并严重影响作业区工作人员的健康与生产作业安全,且应注意火灾爆炸的风险。
某油田大型联合站多排放源VOCs扩散的数值模拟
Numerical simulation of VOCs diffusion from multiple emission sources at a large combined station in an oilfield
-
摘要: 油田联合站是油田的重要组成部分,存在油气 (VOCs) 排放的可能,有必要对其扩散规律进行研究,以制定相关污染防控及安全措施。以某典型联合站为例,建立1:1的实际模型,结合现场调研测试和数值模拟,重点分析了联合站正常工况下多排放源的VOCs扩散机理及储罐裂缝处VOCs泄漏扩散的叠加效应。结果表明:在风速影响下,罐间和背风侧由于出现绕流和回流,容易达到爆炸极限;在重力和涡流的作用下,联合站内的背风侧会出现VOCs聚集,但叠加效应不明显;当储罐发生罐壁破损时,在事故罐后方出现正压区,在涡流和强气流的影响下,叠加后的VOCs浓度会明显增强,并呈点射状向下风向扩散,油气爆炸危险区域加速扩展。本研究成果可为联合站设计、运行管理及制定安全环保措施提供参考。
-
关键词:
- 油田联合站 /
- 油气(VOCs)扩散 /
- 储罐泄漏 /
- 数值模拟 /
- 叠加效应
Abstract: Oil field joint station is an important part of oil field, there is the possibility of oil and gas (VOCs) emission, it is necessary to carry out research on the oil vapor emission laws of oilfields. Therefore, taking a typical united station as an example, a 1:1 practical model was established. Combined with on-site investigation, testing and numerical simulation, an investigation of the oil vapor diffusion mechanism under normal conditions and the superposition effect of oil vapor leakage and diffusion at the crack of the storage tank was conducted emphatically. The results showed that: under the influence of wind speed, the oil vapor could easily reach the explosion limit due to the circumfluence and backflow between the tanks and the leeward side; under the action of gravity and eddy current, oil vapor would accumulate on the leeward side, but the superposition effect was not obvious; When the tank wall was damaged and leaked, a positive pressure area would appear behind the accident tank. Under the influence of eddy current and strong airflow, the superimposed oil vapor concentration would be significantly enhanced, and will spread to the downwind in a point-like manner, accelerating the extension of oil vapor explosion danger area. The results of this study can provide reference for the design, operation management and safety and environmental protection measures of the joint station. -

-
表 1 通用方程 (3) 中各参数的具体形式
Table 1. Detailed form of each parameter in general equation (3)
方程 广义变量Φ值 广义扩散系数Г值 广义源项S 质量守恒方程 1 0 0 动量守恒方程 ${u_i}$ $\mu $ $ - \partial p/\partial x+{S_i}$ 能量守恒方程 $T$ $ k/c $ ${S_T}$ 组分运输方程 ${C_S}$ ${D_S}\rho $ ${S_S}$ 表 2 G区储罐的尺寸
Table 2. Dimension of oil storage tank in area G
储罐
位号储罐
直径/m储罐
高度/m公称
容积/m3最大液体
高度/m平均液体
高度/mG1 17 13.15 3 000 12 10.68 G2 17 13.2 3 000 12 9 G3 17 13.14 3 000 12 9 表 3 数值模拟网格无关性检验结果
Table 3. Results of grid independence test for numerical simulation
网格数量 沿x方向的速度/ (m·s−1) 746 528 3.14 1 461 100 3.23 2 005 657 3.64 3 009 842 3.64 表 4 某油田联合站现场测试数据
Table 4. Data from field test of an united station
区域 采样点位 VOCs质量浓度/(mg·m−3) 采样时刻 风速/(m·s−1) I区 G3罐顶环境 11.40 14:45 2.0 G2罐顶环境 9.95 14:40 2.0 B环境 (停用) 24.50 15:15 0.5 I区厂门口 0.95 18:05 1.5 Ⅱ区 D5罐顶环境 20.00 11:51 3.2 Ⅱ区罐区环境 11.00 16:15 3.0 -
[1] 祁甲民. 基于多源测量数据融合的三维建模技术研究[D]. 郑州: 河南工业大学, 2018. [2] LI T, ZHU J, ZHANG W. Cascade utilization of low temperature geothermal water in oilfield combined power generation, gathering heat tracing and oil recovery[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2012, 40: 27-35. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2012.01.049 [3] LI Z, LIANG Y, WANG G, et al. A method for optimising pump configuration and operation in oilfield water injection network[J]. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 2021, 88: 1105-1110. [4] LI Z, GUO Y, XU N, et al. Integration of a novel distributed water and energy system in the oilfield[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2022, 186: 350-361. doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2022.08.008 [5] 张秀玲, 宋翠红, 刘春杨. 储油罐油气扩散规律的理论研究[J]. 中国石油和化工标准与质量, 2011, 31(7): 248-249. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4076.2011.07.213 [6] TAMADDONI M, SOTUDEH-GHAREBAGH R, NARIO S, et al. Experimental study of the VOC emitted from crude oil tankers[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2014, 92(6): 929-937. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2013.10.005 [7] 黄维秋. 油气回收基础理论及其应用[M]. 北京: 中国石化出版社, 2011: 244-253. [8] ATKINSON G, COWPE E, HALLIDAY J, et al. A review of very large vapour cloud explosions: Cloud formation and explosion severity[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2017, 48: 367-375. doi: 10.1016/j.jlp.2017.03.021 [9] MILAZZO M F, ANCIONE G, LISI R. Emissions of volatile organic compounds during the ship-loading of petroleum products: Dispersion modelling and environmental concerns[J]. Journal of environmental management, 2017, 204: 637-650. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.09.045 [10] CIRIMELLO P G, OTEGUI J L, RAMAJO D, et al. A major leak in a crude oil tank: Predictable and unexpected root causes[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2019, 100: 456-469. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2019.02.005 [11] SIMAYI M, SHI Y, XI Z, et al. Emission trends of industrial VOCs in China since the clean air action and future reduction perspectives[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2022, 826: 153994. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153994 [12] WU T, CUI Y, LIAN A, et al. Vehicle emissions of primary air pollutants from 2009 to 2019 and projection for the 14th Five-Year Plan period in Beijing, China[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2023, 124: 513-521. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2021.11.038 [13] GOEURY C, HERVOUET J-M, BAUDIN-BIZIEN I, et al. A Lagrangian/Eulerian oil spill model for continental waters[J]. Journal of hydraulic Research, 2014, 52(1): 36-48. doi: 10.1080/00221686.2013.841778 [14] 刘泽阳. 联合站典型源VOCs排放规律研究及应用[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2019. [15] HUANG W Q, HUANG F Y, FANG J, et al. A calculation method for the numerical simulation of oil products evaporation and vapor diffusion in an internal floating-roof tank under the unsteady operating state[J]. Journal Of Petroleum Science And Engineering, 2020, 188: 106867. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2019.106867 [16] 黄维秋, 陈风, 吕成, 等. 基于风洞平台实验的内浮顶罐油气泄漏扩散数值模拟[J]. 油气储运, 2020, 39(4): 425-433. [17] DEAVES D, GILHAM S, MITCHELL B, et al. Modelling of catastrophic flashing releases[J]. Journal of hazardous materials, 2001, 88(1): 1-32. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3894(01)00284-9 [18] ZHANG T, LI G, YU Y, et al. Atmospheric diffusion profiles and health risks of typical VOC: Numerical modelling study[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 275: 122982. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122982 [19] BELLEGONI M, OVIDI F, LANDUCCI G, et al. CFD analysis of the influence of a perimeter wall on the natural gas dispersion from an LNG pool[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2021, 148: 751-764. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2021.01.048 [20] OKAMOTO K, ICHIKAWA T, FUJIMOTO J, et al. Prediction of evaporative diffusion behavior and explosion damage in gasoline leakage accidents[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2021, 148: 893-902. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2021.02.010 [21] KOZO F. Progress and future prospects of CFD in aerospace—Wind tunnel and beyond[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2005, 41(6): 455-470. doi: 10.1016/j.paerosci.2005.09.001 [22] ALEXANDROS K, ALEIFERIS P G, CHARALAMBIDES A G. Numerical investigation of VOC levels in the area of petrol stations[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 470: 1205-1224. [23] 黄维秋, 吕成, 郭淑婷, 等. 油气排放及回收的研究进展[J]. 石油学报(石油加工), 2019, 35(2): 421-432. [24] HUANG W Q, WANG S, JING H B, et al. A calculation method for simulation and evaluation of oil vapor diffusion and breathing loss in a dome roof tank subjected to the solar radiation[J]. Journal Of Petroleum Science And Engineering, 2020, 195: 107568. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2020.107568 [25] 许雪, 陈风, 黄维秋, 等. 基于风洞平台实验的大型罐区溢油事故后的油气扩散模拟[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(12): 3946-3956. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202101099 [26] ALEXANDER M, LORENZO M, VAGESH D N. Comparison of k-ε models in gaseous release and dispersion simulations using the CFD code FLACS[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2019, 130: 306-316. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2019.08.016 -



 下载:
下载: