-
活性污泥法作为主要的污水处理手段,已广泛应用于全国各地的污水处理厂。胞外聚合物(extracellular polymeric substances,EPS)作为活性污泥中重要组成部分,主要是聚集类微生物在代谢过程中分泌的高分子聚合物,其中蛋白质和多糖占其总量的70%~80%,而核酸、腐殖质、糖醛酸、脂类和氨基酸等物质的含量相对较低[1]。因此,EPS上的羧基、磷酰基、巯基、酚类和羟基可为有机物、重金属和抗生素等提供吸附位点[2]。与传统的去除方法相比,EPS具有环保、可再生、无毒、可降解等优点,同时可以实现污泥的资源化利用[3]。
在对EPS的诸多研究中,从活性污泥中高效提取EPS是目前研究的主要方向。常用的提取方法包括物理提取法(加热法、高速离心法、超声法)和化学提取法(酸法、碱法、EDTA法和离子交换法)。由于EPS与活性污泥絮体结合紧密,从而保护污泥絮凝体中的微生物不受外界环境变化的影响[4],因此,如何破坏EPS与活性污泥絮体的连接成为提取的关键。其中物理提取法的缺点主要是EPS产率低和蛋白质在高温下变性。化学提取法虽然提高了提取效率,但也可能污染提取的EPS或在随后的分析阶段造成影响。例如在高pH(>10)条件下,碱法导致更多的细胞裂解和大分子破坏。EDTA法中残留试剂在分光光度测定过程中对蛋白质的干扰,以及EDTA难以降解严重污染环境[5],此类方法对于污泥处理过程中EPS的常规提取不是很有效。
在本研究中,对柠檬酸钠(SC)、草酸钠(SO)、EDTA-2Na和酒石酸钾钠(SS)4种络合剂提取EPS的效果进行了比较,利用Ca2+和Mg2+作为EPS分子中不同负电荷位点连接的桥梁以稳定活性污泥絮体结构[6],通过络合剂对Ca2+、Mg2+进行络合,破坏活性污泥絮体结构进而使EPS释放[7]。再对4种络合剂提取的EPS含量和各组分特性比较,借助离子色谱仪、三维荧光光谱、红外光谱、X射线光电子能谱等表征分析手段,对相关二价阳离子浓度、EPS的光谱和能谱特性进行了表征和分析,以阐明不同络合剂提取的EPS分子结构特性。本研究结果以期为后续深入发掘络合剂对二价阳离子络合的胞外聚合物提取及应用提供参考。
-
本研究所使用的活性污泥来自于合肥市经济开发区某污水处理厂二沉池,将取得的污泥立即运回实验室保存。对污泥进行预处理操作:将取回的污泥静置30 min后在4 000 r·min−1下离心10 min,将含有悬浮杂质的上清液弃除;用0.85%的氯化钠溶液恢复至原体积,轻轻搅拌使污泥恢复悬浮状态;在6 500 r·min−1下离心10 min,弃除上清液除去悬浮杂质,重复上述操作3次,将清洗好的污泥经100 W超声5 min后完成对污泥的预处理。
-
将预处理好的污泥按以下方法提取EPS并设置对照组。取适量预处理后的污泥加入适量0.85%的氯化钠溶液作为对照组,轻轻搅拌后污泥恢复悬浮状态。在25 ℃、180 r·min−1的振荡培养箱中振荡60 min。取适量预处理后的污泥分别加入不同浓度(60、75、90、105和120 mmol·L−1)的柠檬酸钠、草酸钠、酒石酸钾钠溶液,轻轻搅拌后污泥恢复悬浮状态。通过研究发现在络合相同含量的阳离子时所需要的EDTA与柠檬酸的物质的量浓度比约为0.7:1[8],本研究将ETDA-2Na浓度梯度设为40、50、60、70、80 mmol·L−1。在25 ℃、180 r·min−1的振荡培养箱中振荡60 min。通过上述方法处理后,将样品在11 000 r·min−1、4 ℃下离心20 min,上清液通过0.45 μm滤膜后收集。
-
以蛋白质、多糖、DNA 之和来表示EPS提取总量,以牛血清白蛋白作为标准物质,用考马斯亮蓝-G250测定蛋白质[9];葡萄糖作为标准物质,用蒽酮-硫酸比色法测定多糖[10];小牛胸腺DNA作为标准物质,用二苯胺法测定DNA[11]。通过紫外可见分光光度法测定各络合剂提取EPS中蛋白质、多糖和 DNA 的吸光度。对需要测定的参数均测定3次后取平均值,带入标准曲线计算。
-
研究中使用离子色谱仪(CIC-D160型,盛瀚,青岛)测定Ca2+、Mg2+的含量;三维荧光分光光度计(F-7000,日立,日本)测定分析各样品的波长;将处理好的各样品溶液进行冷冻干燥,利用傅里叶变换红外光谱仪(Nicolet Is20,赛默飞,美国)与X射线光电子能谱分析仪(K-Alpha,Thermo Scientific,美国)测定;最后所得的数据通过Origin 2021作图。
-
有研究[12]表明,向50 mL 10 mg·L−1四环素溶液中加入100 mg EPS,在pH=6、25 ℃、180 r·min−1的振荡培养箱中振荡60 min后,吸附达到平衡。所有实验均进行3次,在进入高效液相色谱测试之前通过0.45 μm过滤器过滤。通过测试取平均值计算吸附去除率。
-
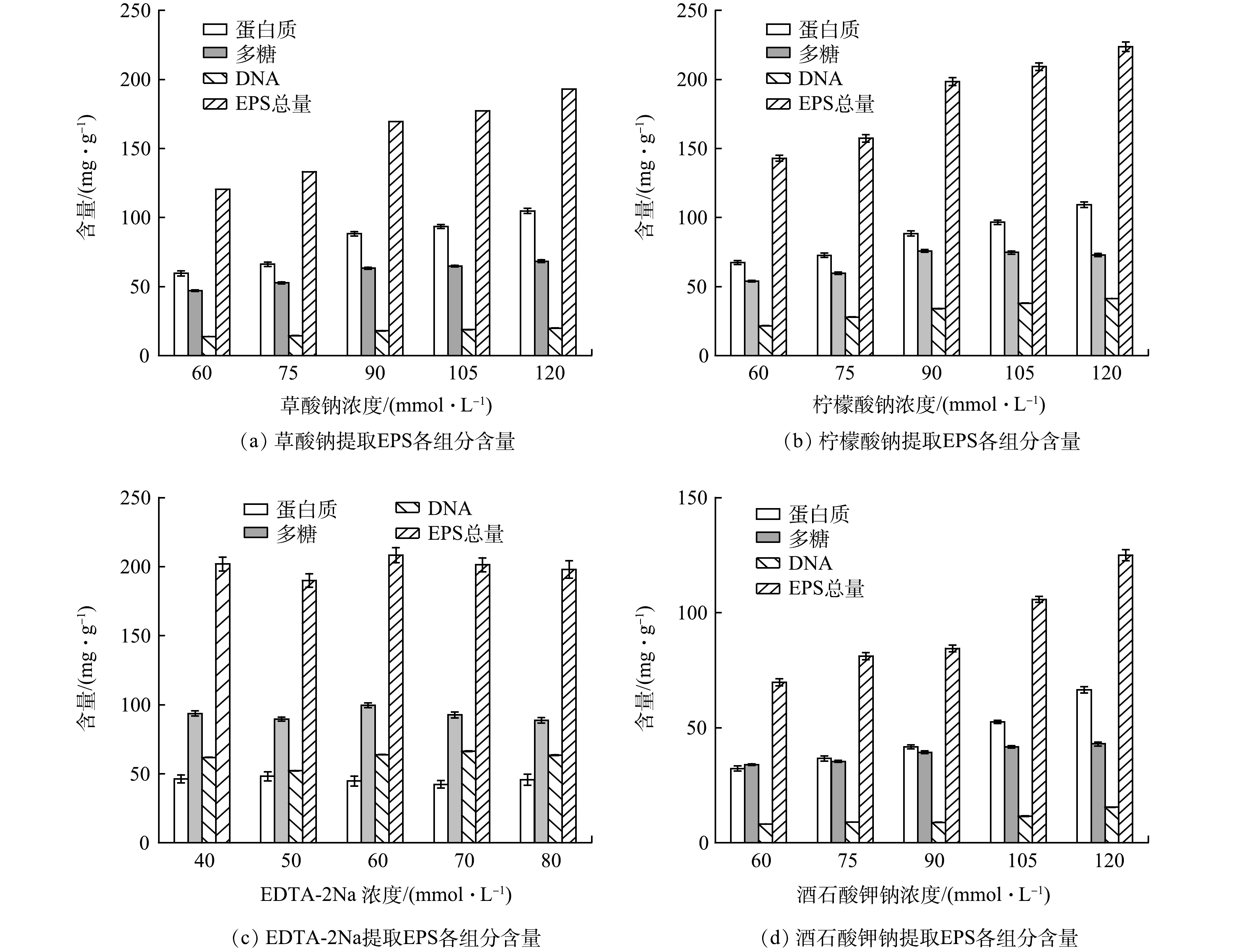
图1为各络合剂在不同提取条件下的EPS各组分含量。对照组EPS提取量为(37.01±1.78) mg·g−1(以MLSS计)。在草酸钠、柠檬酸钠、酒石酸钾钠的浓度为120 mmol·L−1时,EPS提取量最高,分别为(193.12±3.08)、(223.61±3.44)、(124.93±2.37) mg·g−1;ETDA-2Na浓度为60 mmol·L−1时,EPS提取量最高,为(208.32±5.54) mg·g−1,但DNA含量过高说明对细胞的破坏程度较大,使细胞内的蛋白质和多糖释放导致测试值过高[13];在对活性污泥微观结构研究时发现 EPS 在絮体层级(外层)和菌胶团层级(内层)的组分有所差异,在内层EPS的蛋白质含量更多[14]。络合剂通过对絮体结构进行破坏提取更多内层的蛋白质,尤其是随着柠檬酸钠和草酸钠法浓度的提高,内层EPS的提取量也随之增加,所提取的蛋白质含量最高[15]。在4种络合剂中,ETDA-2Na法提取的多糖含量最高[16]。草酸钠和酒石酸钾钠法提取的DNA含量低,这说明对细胞的损害较低[17]。柠檬酸钠法提取的DNA含量较高,可能是由于菌胶团中的细胞更替产生大量的eDNA(extracellular DNA)导致的[18]。综上所述,草酸钠法在4种络合剂中提取效率最高。
-
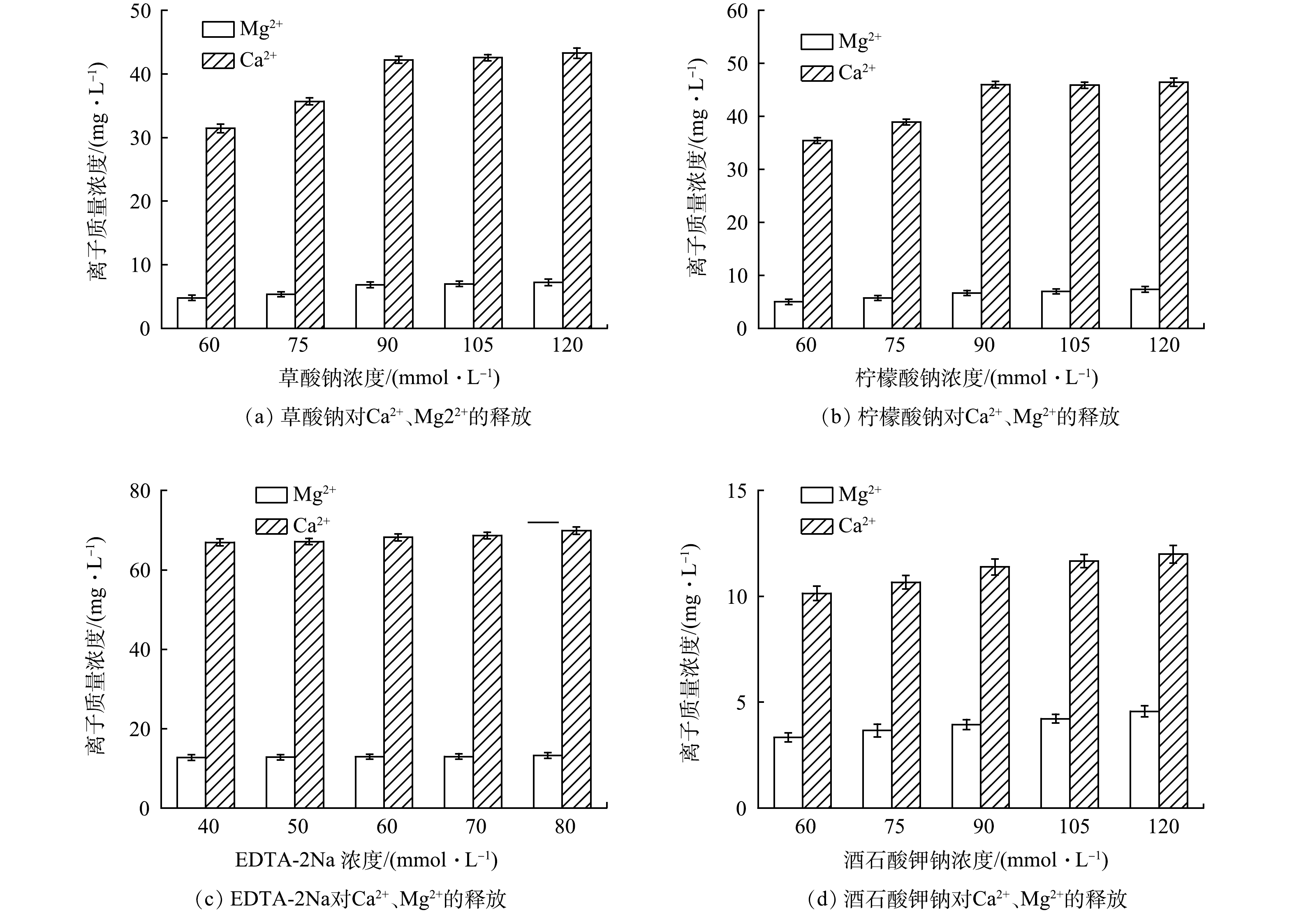
使用离子色谱仪测定不同络合剂对钙镁离子的释放效果,以说明EPS中各组分含量的差别。图2为各络合剂在不同浓度下对钙镁离子的释放效果。柠檬酸钠、草酸钠和ETDA-2Na法对钙镁离子的释放效果明显高于酒石酸钾钠法,说明这3种络合剂与钙镁离子形成络合物,从而破坏了活性污泥的絮体结构[19]。同时络合剂自身携带的钠离子通过离子交换提高这一过程EPS的释放率[20]。从钙镁离子来看,钙离子的浓度明显高于镁离子的浓度,说明钙离子比镁离子更倾向于与污泥聚合物结合[21],在EPS与细胞的桥接中发挥主要作用[22]。其中ETDA-2Na法释放的钙镁离子浓度明显高于其他络合剂。有研究表明,随着钙离子从活性污泥中的释放,胞外多糖含量也随着增加[23]。这也导致ETDA-2Na法提取的多糖含量高。随着络合剂浓度的提高,钙镁离子的浓度增长趋于平缓,可能是由于络合剂浓度过高钙离子在污泥中形成了沉淀[24],而镁离子则倾向于与蛋白质结合[25]。
-
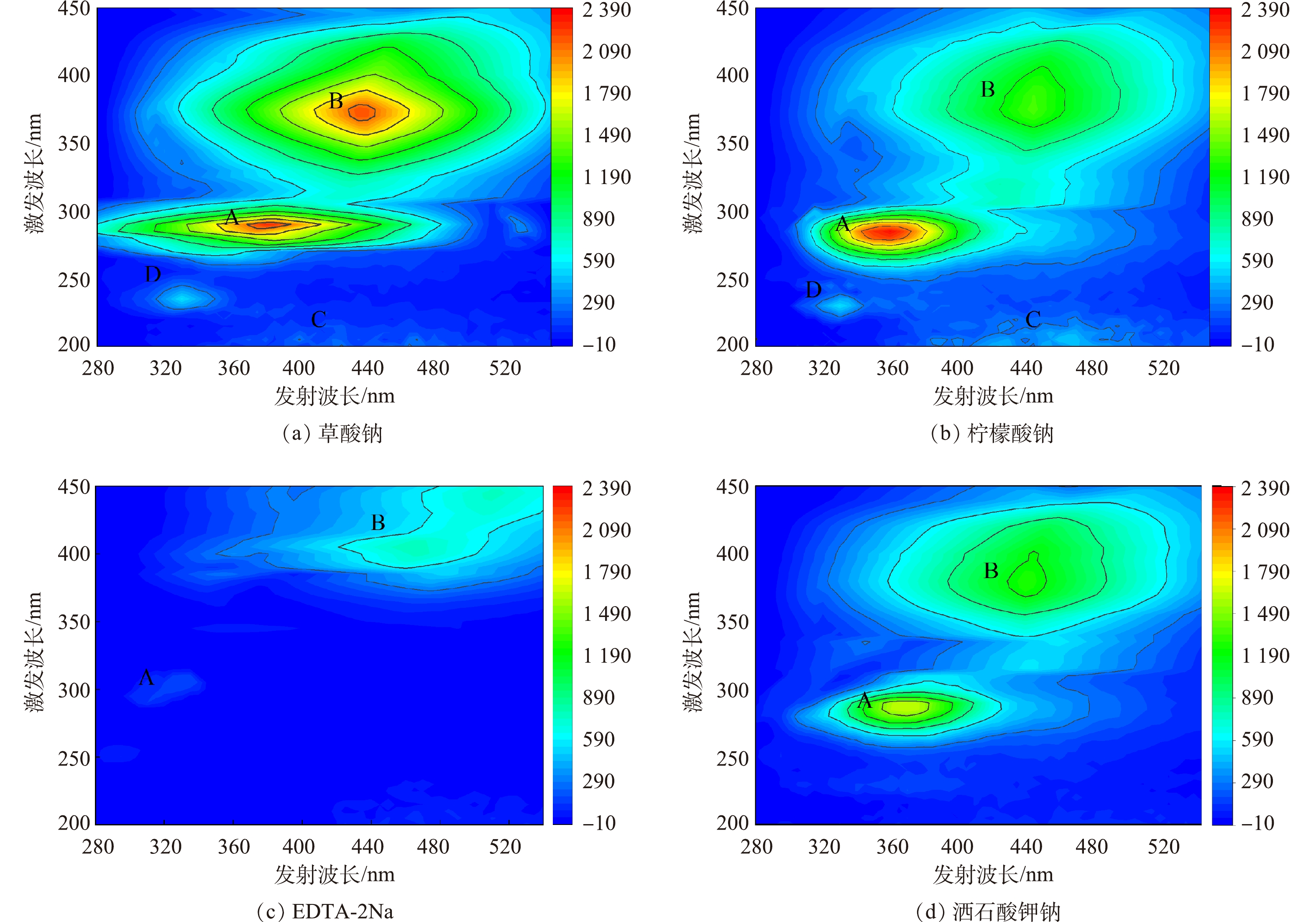
使用三维荧光光谱对各络合剂最高提取量下的EPS进行分析,去除瑞利散射[26]处理所得的数据,结果如图3所示。存在4个明显的荧光峰:色氨酸类荧光峰A(Ex/Em=275~296 nm/340~380 nm)[27];腐殖酸类荧光峰B(Ex/Em=320~370 nm/410~460 nm)[28];富里酸类荧光峰C(Ex/Em=210~240 nm/410~450nm)[29];酪氨酸类荧光峰D(Ex/Em=220~235 nm/310~340 nm)[30]。由此可知,提取的EPS组分中含有色氨酸类蛋白质、酪氨酸蛋白质、类腐殖酸和富里酸。不同络合剂提取的EPS的荧光特性存在显著差异。A、D区域为蛋白质类物质,草酸钠和柠檬酸钠法所提取EPS在A区域的荧光强度明显高于EDTA-2Na和酒石酸钾钠法。其中草酸钠和柠檬酸钠法所提取的A峰峰值是酒石酸钾钠法的1.4倍,是EDTA-2Na法的4.2~6.1倍。B、C区域为腐殖酸类物质,草酸钠提取的EPS在B区域荧光强度是柠檬酸钠法的1.4倍、EDTA-2Na法的2.8倍、酒石酸钾钠法的1.7倍。这说明草酸钠法对腐殖酸类物质也有着高的提取效率。同时,EDTA-2Na法明显破坏活性污泥中的蛋白质结构,使得相应EPS荧光强度减弱。这也很好地解释了前文中不同络合剂所提取的蛋白质含量差异。
-
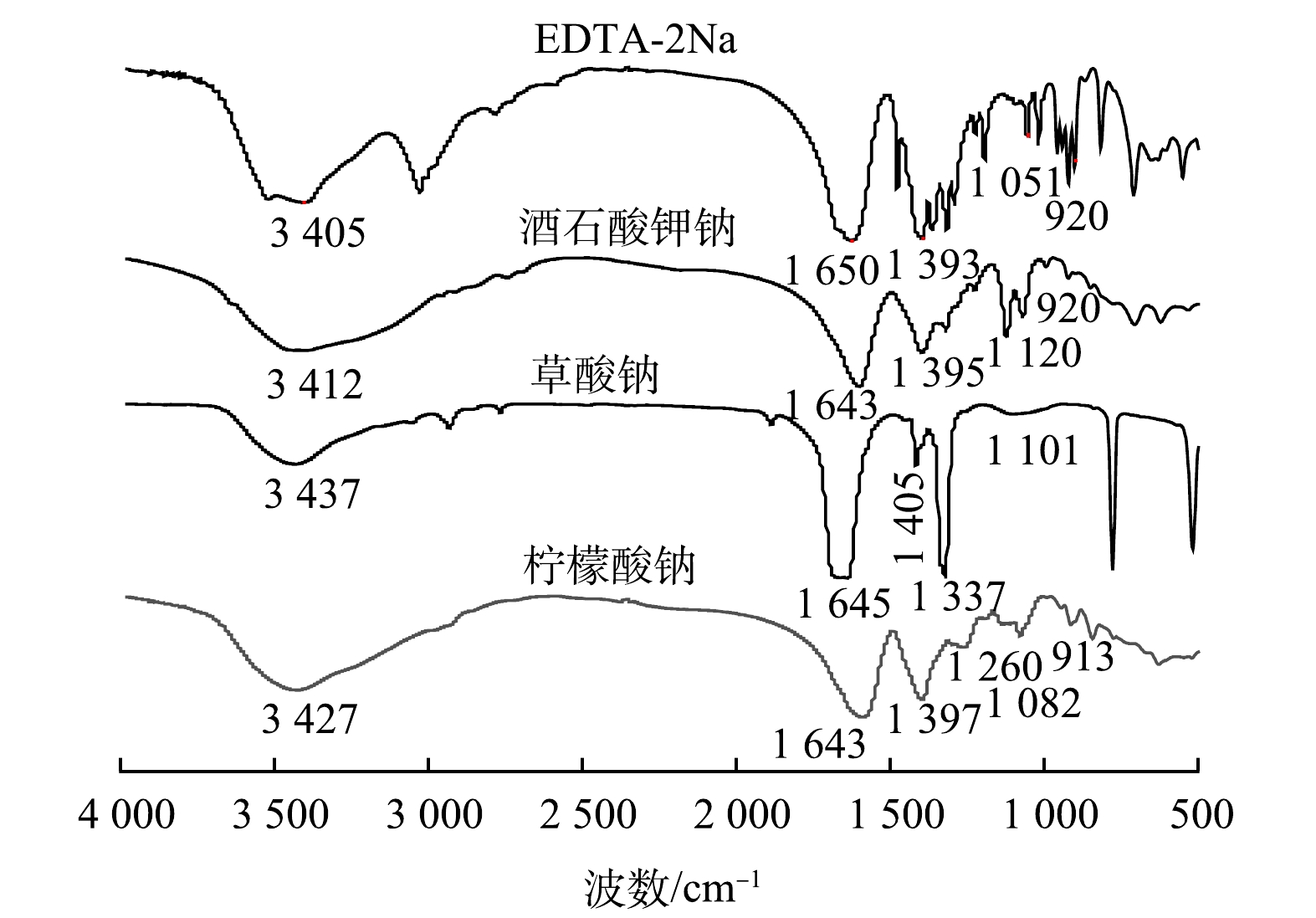
使用傅里叶红外光谱对各络合剂最高提取量下EPS进行分析,结果如图4、图5和表1所示。从图4中可以看出,4种络合剂处理的样品均在3 400 cm−1左右存在宽峰,此处属于蛋白质或多糖羟基中的O—H和N—H伸缩振动峰[31];在1 650~1 630 cm−1的峰是酰胺Ⅰ区的C=O伸缩振动峰,为典型的蛋白质类物质[32];1 410~1 390 cm−1的峰是糖醛酸中的羧酸盐基团[33];1 350~1 250 cm−1的峰主要是由氨基酸的C—O和C—H伸缩振动产生的[34];1 150~900 cm−1的峰与多糖中的C—O、C—C的伸缩振动有关,可以用来反映其多糖的含量与结构[35],EDTA-2Na法在此波段强于其余络合剂,其多糖含量最高。通过红外光谱分析表明EPS的主要组成是蛋白质和多糖。
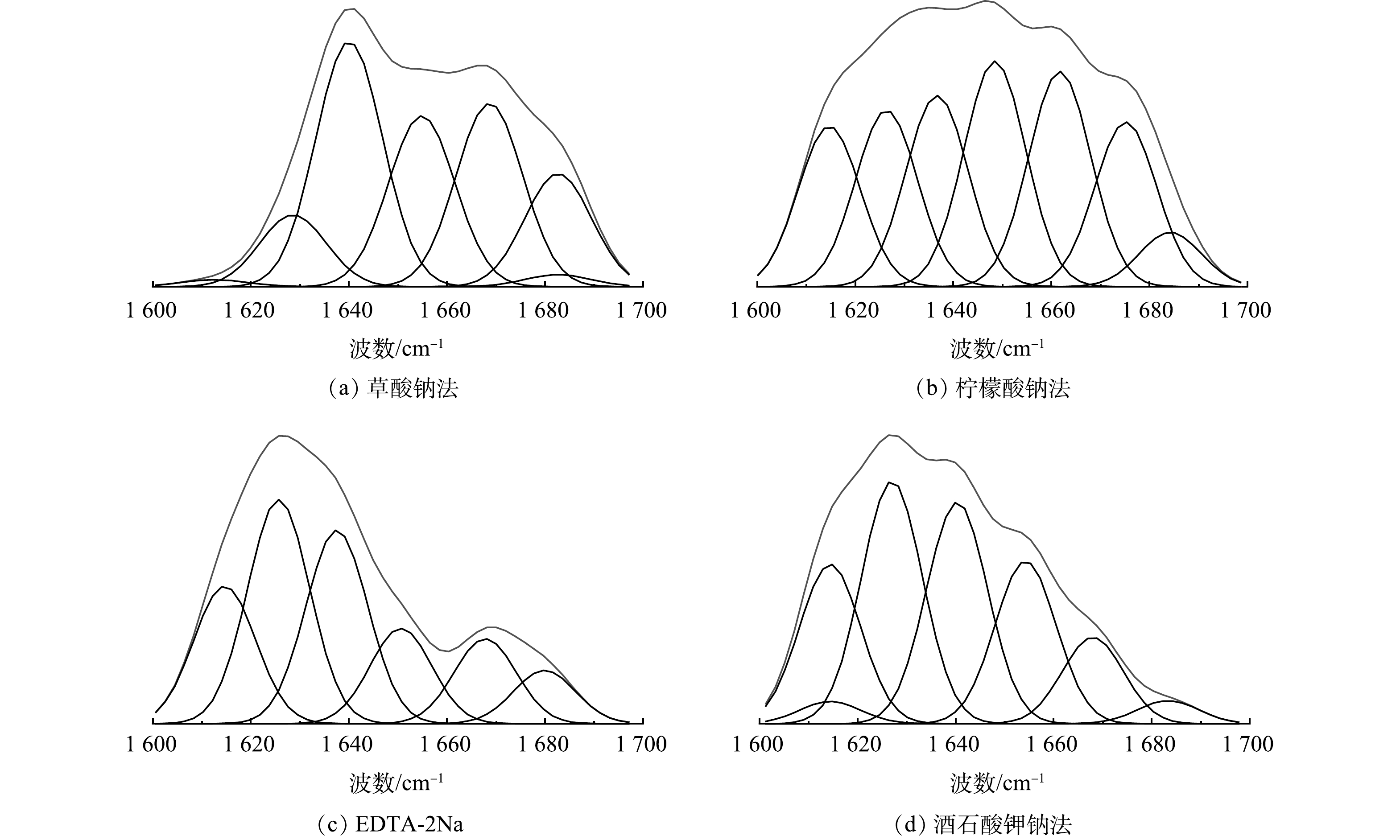
4种络合剂在最高提取量下的红外谱图峰型大致相同。在具体波峰段如酰胺Ⅰ区域(1 700~1 600 cm−1)存在较大差异,对酰胺Ⅰ区分峰拟合分析,依据已有研究将酰胺Ⅰ区划分[36]:β-折叠带(1 600~1 637 cm−1)、无规则卷曲带(1 637~1 645 cm−1)、α-螺旋带(1 646~1 660 cm−1)、β-转角带(1 661~1 680 cm−1)、反向平行β-折叠(1 681~1 700 cm−1),拟合结果如表1、图5所示[37]。α-螺旋、β-转角、β-折叠对聚集性能起正面作用,而无卷曲折叠和反向平行β-折叠对聚集性能起负面作用[38]。从分峰结果来看,4种络合剂提取的EPS的聚集有利结构均超过70%,其中柠檬酸钠法的聚集有利结构为96%、草酸钠法的有利结构为84%。α-螺旋/(β-折叠+无卷曲折叠)的比例可以反应蛋白质二级结构的紧密程度,若该值越低则蛋白质二级结构越松散[39],吸附点位越多。4种络合剂提取的EPS均有较低的 α-螺旋/(β-折叠+无卷曲折叠)值,在柠檬酸钠和草酸钠法的蛋白质二级结构中,有利结构β-转角明显高于其他络合剂提取的 EPS,更有利于后续吸附离子、抗生素。EDTA-2Na法提取的EPS蛋白质中β-折叠含量(70.4%)最高,且没有反向平行β-折叠这也与前人的研究[16]结果一致,可能是由 ETDA-2Na使EPS 中蛋白质二级结构破坏所导致的。只有酒石酸钾钠法提取的EPS蛋白质中发现了无规卷曲。以上结果表明,不同络合剂提取的EPS具有不同的蛋白质二级结构。相似百分比分析结果表明,草酸钠和柠檬酸法提取的蛋白质二级结构相似度最高。
-
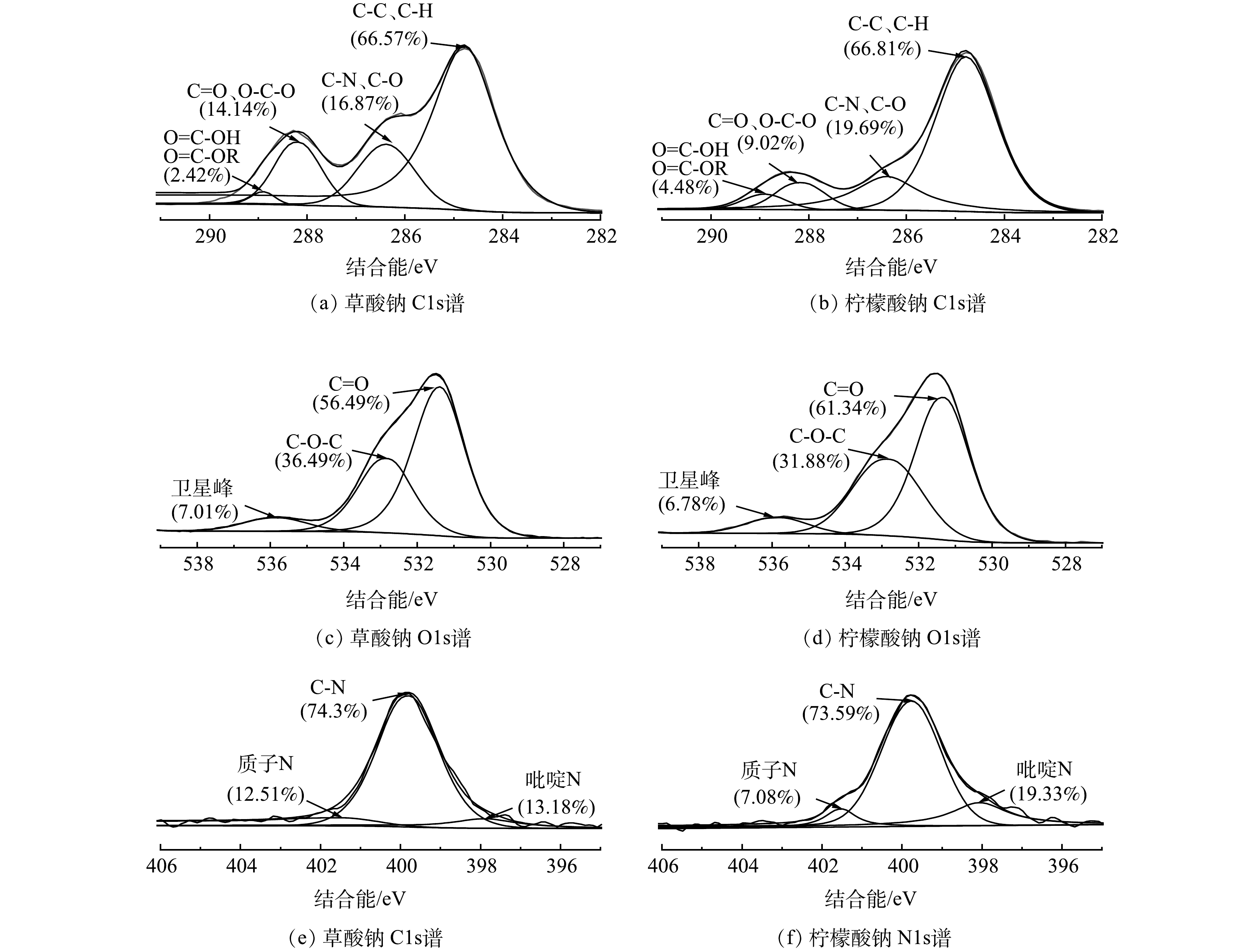
由于EPS的官能团种类丰富,需要进一步借助于 XPS确定并加以验证。由于草酸钠与柠檬酸钠法提取量高且根据上述研究发现其各项结果相似。因此,对这2种络合剂最高提取量下EPS进行XPS图谱分峰拟合比较,其结果如图6所示。
由图6(a)和图6(b)可以看出,提取的EPS中C元素主要以4种形态存在且含量相似:分别为284.8 eV处C—C、C—H占总量60%~70%[40],主要为脂质或氨基酸侧链的烃基类;286.4 eV处C—O、C—N占总量的15%~20%,来源于蛋白质中的酰胺键和醇类;288.1 eV处C=O占总量的9%~15%,来自于羧基、羰基、酰胺和半缩醛中;288.9 eV处O=C—OH、O=C—OR含量最少不到5%,其来源于酯键或羧基[41]。
由图6(c)和图6(d)可见,O元素的各官能团含量也同样相似,均以3种形态存在。存在于羧酸盐、酰胺等的O=C,占总量的55%~62%。存在于醇类、缩醛或半缩醛中的C—O—C,其含量与EPS中的多糖单体有关,柠檬酸钠法提取的多糖含量也略高于草酸钠法。最后还有少量的卫星峰[42]。
对图6(e)和图6(f)中N元素各官能团进行分析,同样其以3种形态存在。分别为位于胺基和酰胺的C—N,均占总量的70%以上,这是由络合剂提取的蛋白质中的酰胺键导致的[43]。位于碱性氨基酸或氨基糖中的质子化N(Npr)含量占到总量的7%~13%。最后还有约13%~20%的吡啶N[44]。
-
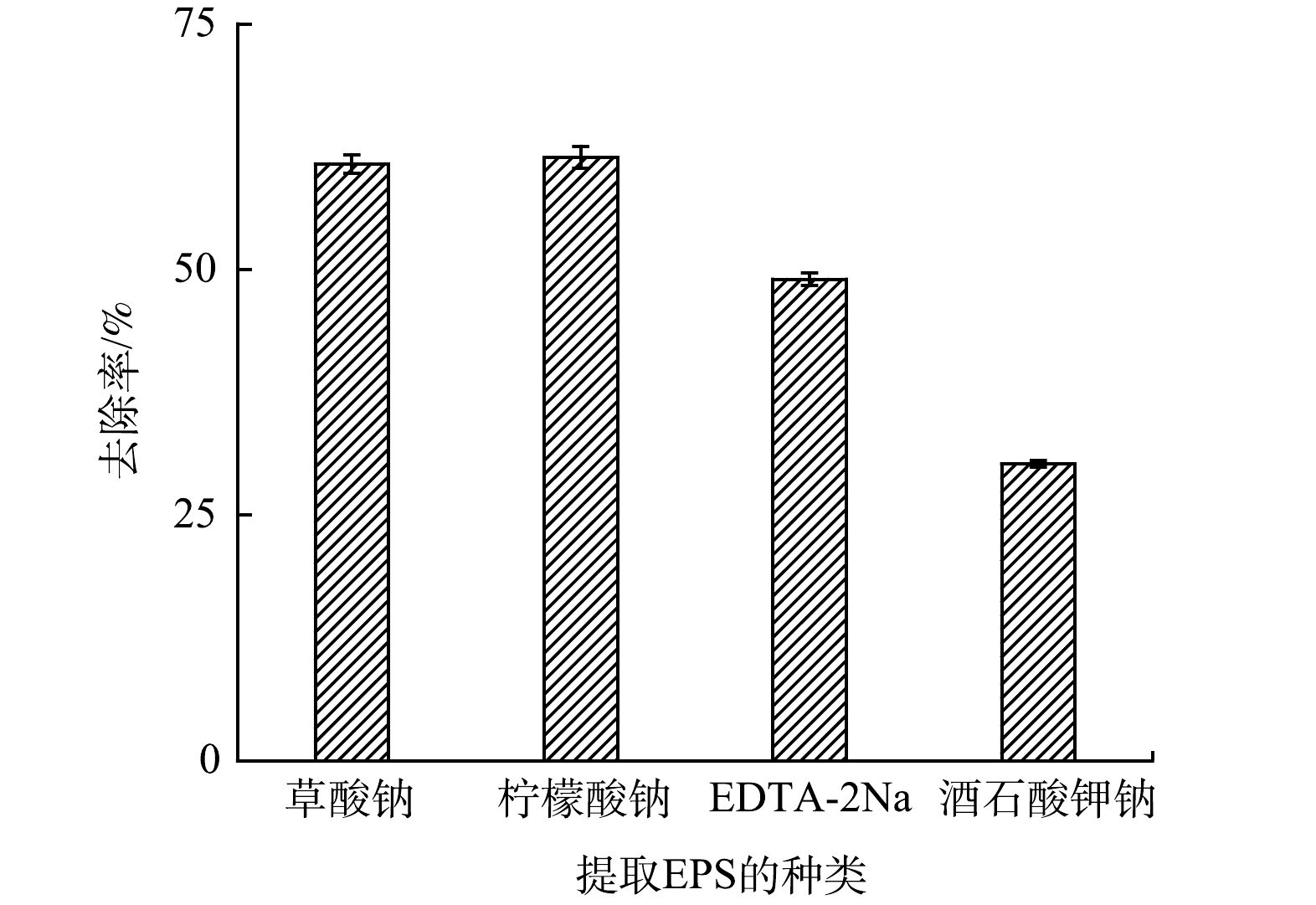
将EPS加入50 mL、pH为6的四环素溶液(10 mg·L−1)中,研究不同络合剂提取的EPS对四环素的吸附效果,结果如图7所示。草酸钠(60.74%)和柠檬酸钠法(61.41%)提取的EPS对四环素的吸附率明显高于EDTA-2Na(48.99%)和酒石酸钾钠法(30.21%)。EPS对四环素的吸附主要是羟基等活性官能团参与了四环素的吸附过程[45],其主要来自多糖和蛋白质,是EPS中主要官能团。由于不同络合剂提取的EPS中多糖、蛋白质含量各不相同,导致其对四环素去除率有所差别。
经过对4种络合剂提取的EPS组分分析,柠檬酸钠和草酸钠法三维荧光光谱实验结果表明在蛋白质的提取量上明显高于EDTA-2Na和酒石酸钾钠法。对各官能团分布特征进行分析,4种络合剂提取的EPS红外光谱的峰型相似,柠檬酸钠和草酸钠法的XPS谱图也同样反映出两者具有相似的官能团,说明不同络合剂对EPS官能团的种类无明显影响,但其吸收峰强度存在明显差异,这也与EPS各组分提取量的结果基本吻合。同时EPS的含量越高,对四环素的吸附效果越好。
-
1)采用络合剂通过络合作用去除活性污泥中二价阳离子,破坏污泥絮体结构,与常规的提取方法相比可以更高效提取EPS。
2)草酸钠和柠檬酸钠法随着浓度的提高更有利于提取内层蛋白质,从而提高EPS的提取量,但柠檬酸钠法DNA含量与草酸钠相比较高。EDTA-2Na法对EPS中的蛋白质具有较强的破坏作用;而酒石酸钾钠法提取量低、吸附效果差。
3)草酸钠法综合提取效率高,对EPS的组分和各官能团影响较小,其疏松的蛋白质二级结构为吸附提供有利条件,可以作为今后从活性污泥中提取EPS非常有效的替代方法。
不同络合剂对二价阳离子络合的胞外聚合物的提取效果比较
Comparison of the extraction effects of extracellular polymeric substances complexed with divalent cations by different complexing agents
-
摘要: 胞外聚合物(EPS)是一种环境友好的净水剂,高效提取EPS可以为吸附重金属离子及抗生素提供更多的吸附位点。本研究采用不同的络合剂去除二价阳离子以提高EPS的提取量,对柠檬酸钠(SC)法、草酸钠(SO)法、乙二胺四乙酸二钠(EDTA-2Na)法和酒石酸钾钠(SS)法提取的EPS特性进行对比。草酸钠法整体提取效率高,对EPS的组分和性质影响小,吸附效果好。柠檬酸钠和EDTA-2Na法对EPS的大分子成分造成不同程度的破坏,尤其是EDTA-2Na法明显改变了EPS的荧光特性。结合红外光谱和XPS分析证明EPS中各官能团与蛋白质、多糖等物质密切相关。研究为进一步发掘利用络合剂对二价阳离子络合提取胞外聚合物及后续应用提供理论依据和技术支持。Abstract: As an environmentally friendly water purification agent, an efficient extraction of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) can provide more adsorption sites for heavy metal ions and antibiotics. In this study, different complexing agents were used to remove divalent cations to increase the extraction amount of EPS, and a comparison was made among the properties of extracted EPS by sodium citrate (SC), sodium oxalate (SO), disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetate (EDTA-2Na) and sodium potassium tartrate (SS) methods.The results showed that the sodium oxalate method had a highly overall extraction efficiency, a low impact on the composition and properties of EPS, and a good adsorption effect.The sodium citrate method and EDTA-2Na method caused different degrees of damage to the macromolecular components of EPS, especially the EDTA-2Na method obviously changed the fluorescence properties of EPS.The combination of IR spectroscopy and XPS analysis proved that the functional groups in EPS were close correlated with proteins, polysaccharides and other substances.This study can provide a theoretical basis and technical support for the future in-depth exploration of EPS extraction by complexation of divalent cations with complexing agents and the subsequent applications.
-

-
表 1 各络合剂最高提取量条件下蛋白质二级结构的含量变化
Table 1. Changes in the content of protein secondary structure at the highest extraction volume of each complexing agent
络合剂 二级结构含量/% α-螺旋 β-折叠 β-转角 无卷曲折叠 反向平行β-折叠 草酸钠 21.28 40.32 22.84 0 15.56 柠檬酸钠 15.82 44.72 32.63 0 3.79 EDTA-2Na 12.09 70.40 17.52 0 0 酒石酸钾钠 17.73 46.22 9.42 24.13 2.51 -
[1] 林伟雄, 顾海奇, 郑诗琳, 等. 不同提取方法对活性污泥胞外聚合物吸附废水中Cd(Ⅱ)效能的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2020, 14(3): 829-834. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201906126 [2] HA J, GELABERT A, SPORMANN A, et al. Role of extracellular polymeric substances in metal ion complexation on Shewanella oneidensis: Batch uptake, thermodynamic modeling, ATR-FTIR, and EXAFS study[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2010, 4(1): 1-15. [3] WEI D, YAN T, ZHANG K Y, et al. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of extracellular polymeric substances in partial nitrification and full nitrification reactors[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 240: 171-176. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.02.115 [4] LIU Y, LI J, QIU X F, et al. Bactericidal activity of nitrogen-doped metal oxide nanocatalysts and the influence of bacterial extracellular polymeric substances (EPS)[J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A:Chemistry, 2007, 190(1): 94-100. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2007.03.017 [5] XIE M, WANG C, LIU X, et al. Characteristics of biochemical and fractal structure of activated sludge with thermochemical lysis[J]. Water Air Soil Poll, 2017, 228: 187. doi: 10.1007/s11270-017-3351-3 [6] TAN P N, HILAL N, HANKINS N P, et al. The relationship between cation ions and polysaccharide on the floc formation of synthetic and activated sludge[J]. Desalination, 2008, 227(1/3): 94-102. [7] YANG G, WANG J. Enhancing biohydrogen production from waste activated sludge disintegrated by sodium citrate[J]. Fuel, 2019, 258: 116-177. [8] KEOWMANEECHAI E, MCCLEMENTS D J. Influence of EDTA and citrate on physicochemical properties of whey protein-stabilized oil-in-water emulsions containing CaCl2[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2002, 50(24): 7145-7153. doi: 10.1021/jf020489a [9] 谢丹瑜, 康得军, 唐虹, 等. 活性污泥胞外聚合物提取方法比较与热碱法优化[J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(9): 5295-5300. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201412239 [10] LI W M, LIAO X W, GUO J S, et al. New insights into filamentous sludge bulking: The potential role of extracellular polymeric substances in sludge bulking in the activated sludge process[J]. 2020, Chemosphere, 248: 126012. [11] FRLUND B, PALMGRENR, KEIDING K, et al. Extraction of extracellular polymers from activated sludge using a cation exchange resin[J]. Water Research, 1996, 30(8): 17-49. [12] PI S, LI A, WEI W, et al. Synthesis of a novel magnetic nano-scale biosorbent using extracellular polymeric substances from Klebsiella sp. J1 for tetracycline adsorption[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017: 471-476. [13] COMTE S, GUIBAUD G, BAUDU M. Relation between extraction protocols of the activated sludge extracellular polymeric substances(EPS) and EPS complexation properties. Part I: comparison of the efficiency of eight EPS extraction properti[J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2006, 38: 237-245. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2005.06.016 [14] WANG B B, CHANG Q, PENG D C, et al. A new classification paradigm of extracellular polymeric substances(EPS)in activated sludge: Separation and characterization of exopolymers between floc level and microcolony level[J]. Water Research, 2014, 64(9): 53-60. [15] PENG L, APPELS L, SU H. Combining microwave irradiation with sodium citrate addition improves the pre-treatment on anaerobic digestion of excess sewage sludge[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2018, 213: 271-278. [16] XIAO B, LIU Y, LUO M, et al. Evaluation of the secondary structures of protein in the extracellular polymeric substances extracted from activated sludge by different methods[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2019, 80: 128-136. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2018.12.003 [17] DOMINIAK D M, NIELSEN J L, NIELSEN P H. Extracellular DNA is abundant and important for microcolony strength in mixed microbial biofilms[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2011, 13(3): 710-721. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02375.x [18] FLEMMING H C, HULLEBUSCH E, NEU T R, et al. The biofilm matrix: multitasking in a shared space[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2022, 21: 70-86. [19] FURIA T E. CRC Handbook of Food Additives. Vol. II[M]. English: CRC Press; 2nd edition, 1980. [20] DIGNAC M F, URBAIN V, RYBACKI D, et al. Chemical description of extracellular polymers: implication on activated sludge floc structure[J]. Water Science & Technology, 1998, 38(8-9): 45-53. [21] FORSTER C F, LEWIN D C. Polymer interactions at activated surfaces[J]. Effluent Water Treatment Journal, 1972, 12(10): 520-525. [22] 袁宇杰. 活性污泥胞外聚合物的高效提取及其对Cu2+、Pb2+吸附研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽建筑大学, 2022. [23] SANIN D, VESILIND P A. Bioflocculation of Activated Sludge: The Role of Calcium Ions and Extracellular Polymers[J]. Environmental Technology, 2000, 21(12): 1405-1412. doi: 10.1080/09593332208618170 [24] SAJJAD M, KIM K S. Extraction of extracellular polymeric substances from activated sludge using sodium oxalate[J]. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 2016, 13(7): 1697-1706. doi: 10.1007/s13762-016-1004-5 [25] SAJJAD M, KIM K S. Studies on the interactions of Ca2+ and Mg2+ with EPS and their role in determining the physicochemical characteristics of granular sludges in SBR system[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2015, 50(6): 966-972. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2015.02.020 [26] MORTEZA B, RASMUS B, COLIN S, et al. Handling of Rayleigh and Raman scatter for PARAFAC modeling of fluorescence data using interpolation[J]. Journal of Chemometrics, 2006, 20(3/4): 99-105. [27] YU H, SONG Y, TU X, et al. Assessing removal efficiency of dissolved organic matter in wastewater treatmen t using fluorescence excitation emission matrices with parallel factor analysis and second derivative synchronous fluorescence[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 144: 595-601. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2013.07.025 [28] LIANG Z, HAN Y Q, MEI L L, et al. Component analysis of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) during aerobic sludge granulation using FTIR and 3D-EEM technologies[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2012, 124: 455-459. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.08.059 [29] CHEN W, WESTERHOFF P, LEENHEER J A, et al. Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2003, 37(24): 5701-5710. [30] ZHANG L H, ZHAO Q N, ZHANG M S, et al. Mg2+ distribution in activated sludge and its effects on the nitrifying activity and the characteristics of extracellular polymeric substances and sludge flocs[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2020, 88: 120-128. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2019.10.002 [31] MAQUELIN K, KIRSCHNER C, CHOO-SMITH L P, et al. Identification of medically relevant microorganisms by vibrational spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 2002, 51: 255-271. doi: 10.1016/S0167-7012(02)00127-6 [32] BADIREDDY A R, CHELLAM S, GASSMAN P L, et al. Role of extracellular polymeric substances in bioflocculation of activated sludge microorganisms under glucose-controlled conditions[J]. Water Research, 2010, 44(15): 4505-4516. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.06.024 [33] GUIBAUD G, COMTE S, BDRDAS F, et al. Comparison of the complexation potential of extracellular polymeric substances(EPS) extracted from activated sludges and produced by pure bacteria strains, for cadmium, lead and nickel[J]. Chemosphere, 2005, 59(5): 629-638. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.10.028 [34] JIA F X, YANG Q, LIU X H, et al. Stratification of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) for aggregated anammox microorganisms[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(6): 3260-3268. [35] BARTH A, ZSCHERP C. What vibrations tell us about proteins[J]. Qarterly Reviews of Biophysics, 2002, 35(4): 369-430. doi: 10.1017/S0033583502003815 [36] LONG G H, JI Y, PAN H B, et al. Characterization of thermal denaturation structure and morphology of soy glycinin by FTIR and SEM[J]. International Journal of Food Properties, 2015, 18(4): 763-774. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2014.908206 [37] GULER G, VOROBEV M M, VOGEL V, et al. Proteolytically-induced changes of secondary structural protein conformation of bovine serum albumin monitored by Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) and UV-circular dichroism spectroscopy[J]. Spectrochim Acta A, 2016, 161: 8-18. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2016.02.013 [38] LIAO B Q, ALLEN D G, LEPPARD G G, et al. Interparticle interactions affecting the stability of sludge flocs[J]. Journal of Colloid & Interface Science, 2002, 249(2): 372-380. [39] HOU X, LIU S, ZHANG Z. Role of extracellular polymeric substance in determining the high aggregation ability of anammox sludge[J]. Water Research, 2015, 75: 51-62. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2015.02.031 [40] AHIMOU F, BOONAERT C J P, ADRIAENSEN Y, et al. XPS analysis of chemical functions at the surface of Bacillus subtilis[J]. Colloid Interface Science, 2007, 309(1): 49-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2007.01.055 [41] 王彬斌, 于滨玮, 何锋, 等. 基于二价阳离子去除的胞外聚合物提取方法特性比较[J]. 环境科学学报, 2022, 42(10): 303-313. [42] XU H, LV H, LIU X , et al. Electrolyte cations binding with extracellular polymeric substances enhanced microcystis aggregation: Implication for microcystis bloom formation in eutrophic freshwater lakes[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016: acs. est. 6b00129. [43] 赵伟. 典型有机酸络合体系中重金属的螯合吸附分离特性及解络强化[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2018. [44] 刘文静. 呼伦贝尔褐煤黄腐酸非酸性基团分布规律研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2019. [45] LI A, PI S, WEI W, et al. Adsorption behavior of tetracycline by extracellular polymeric substrates extracted from Klebsiella sp. J1[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(24): 25084-25092. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-7726-6 -



 下载:
下载: