-
二噁英(dioxin)是一类持久性有机污染物(persistent organic pollutants,POPs),由于氯原子的取代数目和位置不同[1],它包括75 种多氯二苯并二噁英(polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin,PCDDs)和135种多氯二苯并呋喃(polychlorinated dibenzofuran,PCDFs)。二噁英主要来源于废弃物焚烧等热处置过程和氯化化学工业过程而产生的副产物[2-5]。其中17种(2, 3, 7, 8 位全部被氯原子取代)二噁英类化合物被认为对人类健康有巨大的危害[6-8]。二噁英类化合物具有致癌、致畸、致突变作用[9],由于具有疏水性、亲脂性和高化学稳定性[10],能够通过沉降到水、土壤及沉积物等不同环境基质中,经过生物积累等作用进入人体[11-14],威胁人类的生命健康。因此1998年世界卫生组织(WHO)规定人体每日允许二噁英摄入量为1—40 pg·kg−1 [15]。2001年二噁英被列入《关于持久性有机污染物的斯德哥尔摩公约》首批POPs清单。随后,世界各国对其在环境中的排放限值作出了规定。欧盟将二噁英排放标准定为0.1 ng-TEQ·
$ {\text{m}}_{\text{N}}^{\text{-}\text{3}} $ [16],我国在《危险废物焚烧污染控制标准》(GB18484-2001)中规定二噁英排放限值为0.5 ng-TEQ·$ {\text{m}}_{\text{N}}^{\text{-}\text{3}} $ ,在《生活垃圾焚烧污染控制标准》(GB 18485-2014)中将二噁英排放限值提升为0.1 ng-TEQ·$ {\text{m}}_{\text{N}}^{\text{-}\text{3}} $ ,监测二噁英的排放水平已成为环境监测的重要指标。PCDD和PCDF的化学结构式:

由于二噁英在环境中的含量很低,同时其所处的基质对检测分析影响相对较大,若要保证目标单体检测的灵敏度和准确度,不能直接用气相色谱-质谱仪器进行检测分析。必须对其进行样品前处理,去除基质中的干扰物,同时富集浓缩二噁英后才能进入仪器进行定性定量分析。目前对于二噁英的样品前处理技术分为提取和净化两个步骤。其中二噁英的主要提取技术主要为索氏提取法[17-21, 22]和加速溶剂萃取法[21, 23]。索氏提取法(Soxhlet extraction, SE)是传统的提取方法,具有设备要求低和操作简单的特点,但是索氏提取法耗时长(16—48 h),有机溶剂消耗量大(160—350 mL)[24-26]。因此,Rübel 等[27]提出了一种全新的萃取方法——加压溶剂萃取法(Pressurized liquid extraction, PLE),也称为加速溶剂萃取(Accelerated solvent extraction, ASE)。该方法是通过提高温度(50—200 ℃)和增加压力(1000—3000 psi)来对基质中的有机物进行自动萃取。提高温度不仅能够加快分子的扩散速率,还可以增加水的溶解度,有利于萃取溶剂进入“水封微孔”提取目标物。增加压力可以迫使萃取溶剂进入样品基体间隙中,提取出其中的目标物。基于高温高压条件,萃取溶剂能与样品充分接触,继而提高了萃取效率。表1汇总了部分文献报道的不同基质中二噁英的提取技术的应用。可以看出,与索氏提取相比,用ASE提取二噁英耗时短(0.8—1 h),有机溶剂消耗少(15—160 mL)。为了实现快速在线检测,目前已有文献报道将加速溶剂萃取技术应用于样品在线分离检测系统中,并研制出了微型化的装置[28-31]。微池加速溶剂萃取的提取时间更短(15—60 s)、萃取溶剂更少(125 µL)。综上所述,加速溶剂萃取法具有有机溶剂用量少、萃取时间短、样品回收率高等突出优点,被美国环保局(EPA)推荐为固体废弃物中的二噁英检测的标准方法[32],我国也在《饲料中二噁英及二噁英类多氯联苯的测定同位素稀释-高分辨气相色谱/高分辨质谱法》(GB/T 28643-2012)和《食品中二噁英及其类似物毒性当量的测定》(GB 5009.205-2013)中推荐ASE作为饲料和食品中二噁英的提取方法。
本文主要综述了在不同基质中应用加速溶剂萃取技术提取二噁英的研究情况,其中包括环境基质(水体[33-34]、土壤及底泥沉积物[35-42]、大气及废气[43-47])、生物基质(生物[48,69-73]、人体血浆[49,79-82])、食品基质(食物[50,86-91]、饲料[51,88-90])等,为进一步发展该技术应用于不同基质中二噁英的检测提供参考。
-
二噁英能与水中的悬浮固体颗粒结合,水体中悬浮颗粒物中的二噁英可以通过滤膜后用ASE进行提取。Castro 等[33]用玻璃纤维滤膜过滤湖水水样后,将玻璃纤维滤膜转移至ASE萃取池中(33 mL)进行两次萃取,两次的提取溶剂分别为甲醇和正己烷,以75 ℃,1500 psi,100%溶剂冲洗量,提取和加热时间均为5 min。甲醇相的提取液再用正己烷提取,并且过硅胶柱净化,结合高分辨气相色谱与高分辨质谱(HRGC/HRMS)进行检测。结果测得该湖的水样中二噁英含量为163.3—2773.5 fg·L−1。Youn 等[34]用玻璃纤维滤膜和两种不同的C18固相萃取盘过滤水样,将目标物保留在固相萃取盘中,在ASE萃取池(22 mL)中加入硅藻土、富集了目标物的固相萃取盘、玻璃纤维滤膜,在压力为1500 psi,温度为150 ℃的条件下,用甲苯对目标物提取7 min,进行两个循环。将得到的提取液浓缩后用自动化多层硅胶柱净化待检测。结果表明,回收率在61%—98%之间,能够满足EPA1613和JISK0312方法的要求。该方法能够用于水样中二噁英的高通量分析,并且相比于传统的抽滤水样-索氏提取-硅胶柱净化的方法,将分析时间缩短至3 d。Vandermarken等[94] 比对三十年间比利时沿海地区的悬浮颗粒物中二噁英的浓度,采集海水中的悬浮颗粒物,将其加入到ASE萃取池中(33 mL),用1∶1(V/V)的正己烷∶丙酮在125 ℃,1500 psi,60%溶剂冲洗量,提取时间为10 min,加热时间为6 min的条件下进行两次循环萃取,结合Calux 生物测定法检测,结果表明通过近年来不断减少二噁英排放量,该海域中二噁英的浓度远低于三十年前。
-
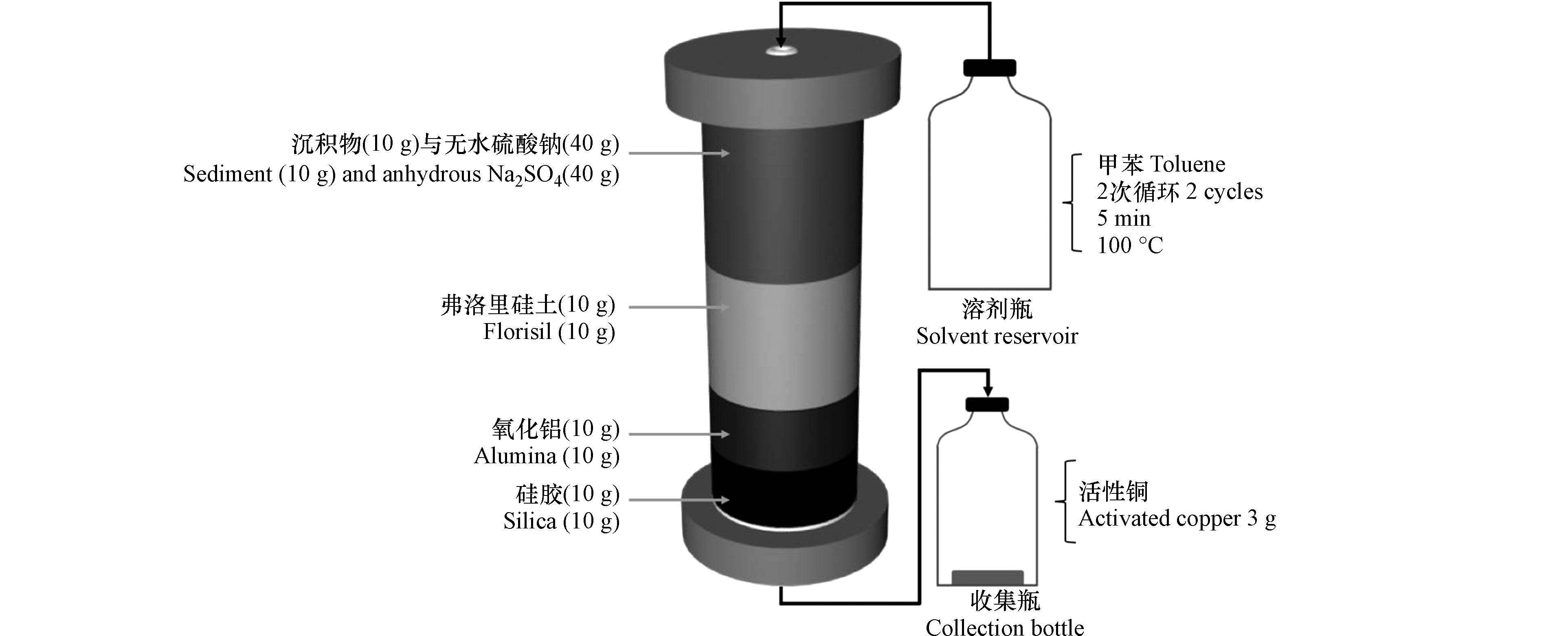
排放进入大气的二噁英通过大气干沉降和湿沉降转移到地表,进而进入土壤和水体中,导致土壤和水体受到污染[53]。底泥沉积物是水体中二噁英最主要的“汇”,而其中二噁英能够通过迁移分配等方式再次进入水体,对水体的生态系统造成危害。因此对土壤及底泥沉积物中二噁英的检测非常有必要。Chang 等[54]对地震、海啸后的土壤中二噁英的含量进行检测。在ASE萃取池(66 mL)中加入土壤样品,萃取温度为160 ℃,用甲苯作为提取溶剂,加热时间和静态萃取时间分别为8 min 和20 min,吹扫150 s,进行两次循环。将ASE过程中获得的提取液过亚砜/银离子柱进行净化,再经洗脱液淋洗,可得到纯化的二噁英。结合气相色谱-多光子电离-飞行时间质谱(GC/MPI/TOFMS)检测。测得地震和海啸后的土壤中二噁英含量较高,为0.01—11.64 pg·g−1-TEQ。该方法从提取(1 h)、净化、检测(45 min)阶段都缩短了二噁英的分析周期,在3 d之内能完成7个土壤样品的检测,为发生自然灾害后的土壤中二噁英的检测提供安全快速高效的分析方法。对于沉积物中二噁英的提取,Chuang 等[55]将沉积物样品与硅藻土混合,并在萃取池(33 mL)中自下而上填充氧化铝(分离二噁英与多氯联苯),含10% AgNO3的二氧化硅(去除含硫化合物)和酸性二氧化硅(去除碱性化合物)。二氯甲烷作为提取溶剂连续提取3个循环,每次循环提取时间为10 min,温度为100 ℃,吹扫时间为60 s,溶剂冲洗量为100%。结合免疫化学法(ELISA)和气相色谱/高分辨率质谱(GC / HRMS)分析,沉积物中的二噁英回收率可达116% ± 11%。该方法通过ASE-ELISA将样品处理量提升3倍以上,并且成本大大降低。Aguial 等[56]将沉积物样品与无水硫酸钠混合置于ASE萃取池(100 mL)中,分别由下至上加入用甲苯预先清洗的二氧化硅,氧化铝和弗洛里硅土(Florisil),萃取池内部吸附剂填充如图1。该萃取在100 ℃和1500 psi(溶剂冲洗量为50%)的条件下,进行2个循环。该方法用于分析表层沉积物中的二噁英回收率为84%。该法对于沉积物类的较脏样品中的二噁英有较好提取和净化能力,将提取和净化步骤合二为一,大大节省了前处理时间,每个样品的前处理时间降至2.5 h,还将有机溶剂的使用量减少到100 mL以下,为以后检测二噁英开辟了一条快速高效便捷的道路。
-
大气及粉尘中的二噁英一般采用大流量主动采样器采集。Klees 等[57]用索氏提取法和加速溶剂萃取法对街道粉尘中的二噁英的提取做了对比。首先将一部分采集到的街道粉尘样品放置到ASE萃取池(22 mL)中,温度范围为100—160 ℃,以甲苯作为萃取溶剂在110 bar的压力下,加热和提取时间为5 min,吹扫时间为60 s,溶剂冲洗量为60%,得到的萃取液氮吹浓缩。另一部分的样品则经过索氏提取的方法提取。根据EN 1948-2的方法,将ASE和SE的萃取液过硅胶柱净化,用气相色谱-高分辨质谱(GC/HRMS)检测。结果测得采用ASE法的二噁英回收率在96%—121%之间,而采用索氏提取法的二噁英回收率在81%—112%之间。经过比对,ASE 在对于粉尘中二噁英的提取能够替代索氏提取法,表现出较高回收率和提取效率,且大大节省了样品前处理时间。中国科学院生态环境研究中心张庆华课题组[58-59] 根据美国EPA TO-9A中的方法对天津市空气中的二噁英进行采样,用玻璃纤维滤膜(GFF)和聚氨酯泡沫(PUF)分别采集颗粒物相和气相中的二噁英。将GFF和PUF装入ASE萃取池中,萃取条件为100 ℃、1500 psi,以丙酮为萃取溶剂进行两次循环提取。根据美国 EPA 1613B 的方法萃取液经过浓缩过硅胶柱后用HRGC/HRMS检测。样品的回收率在32.9%—124%和25.3%—150%之间,符合1613B的要求。2017年该课题组采用与上述相同的ASE条件,样品的前处理基于EPA 1613B方法,结合气相色谱/三重四极杆质谱(GC-MS/MS)对北京周边的大气样品进行分析。样品的加标回收率在43%—103%之间,大气中二噁英的毒性当量(TEQ)平均值为0.10 pg·m−3 WHO-TEQ2005[38]。该检测方法具有灵敏度高、重现性好、成本低等特点,有较好的推广性。
-
目前,高效地检测飞灰中的二噁英仍然存在一定的难度,由于飞灰本身结构的复杂性,加大了二噁英提取的难度。为提高飞灰中二噁英组分的提取效率,需要预先用HCL对飞灰进行消解,并且选择合适的压力、温度等提取条件。Windal 等[60]采用超临界流体萃取法(SFE)和加速溶剂萃取法(ASE)分别提取飞灰中二噁英并与索氏提取法进行对比。萃取前用1 mol·L−1的HCl(8 mL)对飞灰消解2 h。SFE过程是将用HCl消解的粉煤灰与海沙混合,然后放入萃取池(10 mL)中。萃取器温度设定为150 ℃,压力设定为400 bar。在萃取之前,将甲苯添加到样品池中,并在30 min动态萃取之前进行1 h或3 h的静态萃取。ASE过程是将提取的甲苯收集在小瓶中,预填充10 mL甲苯。ASE的萃取温度设定为150 ℃,压力设定为50 bar,动态萃取为1 h或2 h。结果表明,索氏提取对于低碳含量的粉煤灰中二噁英组分的提取效率较高,但对于高碳含量的粉煤灰中二噁英组分提取效率较低。与索氏提取相比SFE对基质的纯净程度要求更高一些,SFE对于纯净程度高的基质样品中二噁英的提取效果更好。ASE可以在80 ℃下2 h内获得与索氏提取相似的回收率。将温度提高到150 ℃,ASE的回收率为110%—160%。对于提取飞灰中的二噁英来说,ASE可达到与索氏提取法相当的回收率,并且提取时间缩短了20倍,效率更高.
-
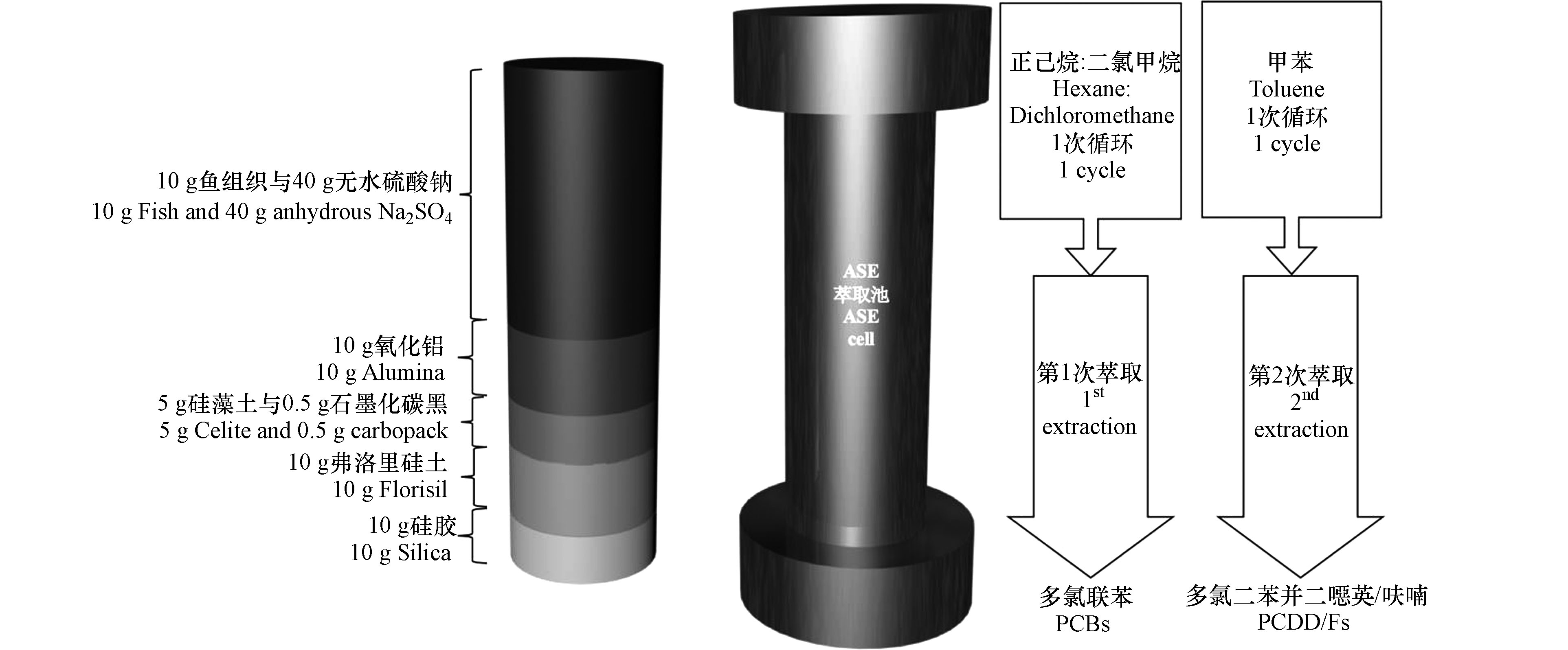
对于鱼组织等复杂的生物基质中二噁英的提取,通常的方法是先提取再通过净化柱净化两步完成样品前处理。Subedi 等[61]分析鱼组织中的二噁英时,将氧化铝、硅藻土和石墨化碳黑(carbopack)、Florisil和硅胶等净化材料与鱼肉组织一起加入到萃取池中(如图2),鱼组织置于萃取池顶部。ASE过程中提取溶剂提取鱼组织中的二噁英的同时,净化材料吸附鱼肉基体中的干扰物,从而实现了提取和净化一步完成。提取条件是用1∶1(V/ V)的二氯甲烷∶正己烷(1个循环)提取样品,然后再利用甲苯(1个循环)提取。每个样品的萃取条件为100 ℃、1500 psi、1个循环、5 min静态提取时间、吹扫290 s和75%的溶剂冲洗量。该方法能将鱼组织中的 PCDD/Fs 和 PCBs 在萃取池中通过两次不同条件的萃取分离出来,并且 PCDD/Fs 的回收率高,可达到85%。该方法将加速溶剂萃取与净化同时进行,提取过程自动操作,压缩了实验步骤,减少了样品前处理时间,提高了样品分析的效率。
-
长期接触二噁英会对人体造成严重危害,特别是会干扰内分泌系统的正常工作。为了分析血液中的二噁英浓度水平,Zhang 等[62]将采集到的血浆与硅藻土混合加入到ASE系统中,以120 ℃为萃取温度,正己烷/二氯甲烷/丙酮(45:45:10,V/V)为萃取溶剂,提取时间为5 min进行3个循环,萃取液经无水硫酸钠除水后过硅胶柱净化,采用GC-HRMS检测。二噁英的加标回收率在36%—108%之间。Todaka 等[63]采集患有Yusho病的病人血浆经过15 h的冷冻干燥后放置在ASE系统中用压力为2000 psi,温度为120 ℃,提取时间为10 min,吹扫180 s,提取溶剂为丙酮和正己烷的混合溶液(1∶3,V/V),进行2次循环,提取液过硅胶柱除脂,采用 HRGC/HRMS 检测。结果显示病人血液中二噁英含量比正常人含量高3.5倍。该方法耗时短、灵敏度高,对于血浆二噁英的检测具有较好的实用性。
-
Clarkson 等[6]对英格兰北部城市的树皮进行采样,将树皮研磨碎,用ASE提取树皮中的二噁英。在150 ℃,1500 psi下,用甲苯静态提取8 min进行3次循环,萃取液经过硅胶柱净化,结合 GC-MS/MS 检测。该法的回收率在70%—95%之间。说明该法对于树皮等固体样品的提取也能快速高效,对于草本植物中二噁英的检测具有参考性,可以更好地了解环境中二噁英的来源、分布、迁移等环境行为。
-
食物样品中含有大量的脂肪组织,用ASE提取时脂肪组织与目标物同时萃取出来,对后续检测存在干扰,所以需要对萃取液进行再处理才能用于分析。Lorenzi等[91]将牛奶与硅藻土混合后加入到ASE系统中,用甲苯在135 ℃和1500 psi 的条件下进行两次循环萃取,萃取液用重量分析法确定脂肪含量,以得到ASE的萃取效率,结果表明ASE的回收率能达到美国EPA 1613B 的要求。Wiberg 等[65]将鱼肉、鸡肉和猪肉组织等处理后装到ASE的萃取池(100 mL)中,用硫酸钠填补萃取池中的空隙,在100 ℃,提取时间为5 min,以庚烷为萃取溶剂进行两个循环,对萃取液浓缩后过硅胶柱净化,利用 GC-HRMS 检测。结果测得样品中二噁英的回收率在81%—97%之间,比传统食物样品中二噁英的提取节省了时间和溶剂的消耗。
-
Bernsmann 等[51]将索氏提取法与ASE对草、面粉等粗饲料和其它类别饲料中二噁英的提取作了比较。将饲料样品放入 ASE 的萃取池(100 mL)中,同时在池中加入硅胶,提取温度为120 ℃,压力为1500 psi,萃取液过硅胶柱净化,结合 HRGC/HRMS 检测。结果表明,在ASE萃取池中高压、高温的环境下硅胶的脂肪保留能力较低,饲料原料的脂肪含量低于5%才能用该法提取二噁英。由于粗饲料中蜡的含量较高,高温高压下会溶解,导致ASE不适于粗饲料中二噁英的提取。目前提取粗饲料中的二噁英可以用振荡提取的方式[92],回收率在80.6%—93.5%之间,能满足要求。但是其它类别的饲料中ASE与索氏提取法的总 WHO-TEQ 分别为0.48 pg·g−1和0.50 pg·g−1,提取回收率在63%—102%之间。在其它类别饲料样品中二噁英的提取,ASE的结果与索氏提取并无差别,而且节省了提取时间和溶剂的消耗,是更优的提取手段。
-
Kleinhenz 等[64]检测了腌制猪肉等肉类食物香料中二噁英的含量。将处理好的香料加入ASE系统中,正己烷作为萃取溶剂,在100 ℃和100 bar下,静态提取时间为10 min进行两次循环,萃取液过硅胶柱净化,结合 GC-HRMS 检测。结果测得香料中二噁英的检出限低于0.03 ng WHO-PCDD/PCDF-TEQ/kg,定量限低于0.10 ng WHO-PCDD/PCDF-TEQ/kg,回收率在82.6%—105.6%之间。该法检测香料中二噁英含量时,可以降低HRGC/HRMS的检出限,并且得到较高回收率。
-
我国对于固体废弃物的处理以填埋为主,因此固废中二噁英含量的检测十分重要。周全法课题组 [66-67]对废线路板中的二噁英含量进行检测,并比对了ASE与索氏提取法。将粉碎处理后的废线路板粉末加入ASE萃取池(34 mL)中,萃取温度为190 ℃,压力为1500 psi,60 mL甲苯为萃取溶剂,加热和静态萃取时间分别为9 min和10 min,进行3次循环。而索氏提取法则用300 mL甲苯提取16 h以上。两个方法的萃取液均过硅胶柱净化,结合HRGC-HRMS检测。结果测得ASE和索氏提取法的回收率分别为54.3%—113.0%和28.3%—77.7%,满足国标要求。两种方法相比,ASE的回收率更高,说明高温高压对该样品的萃取效率和渗透性的准确性更高,尽管ASE的平均相对偏差值略差于索氏提取法,但是均在国标要求的范围内。所以对于废线路板类的复杂样品中二噁英的提取,ASE缩短提取时间并节省有机溶剂的消耗,且回收率更优异,能为以后此类样品中二噁英的检测建立快速高效的分析方法提供参考。
-
目前,加速溶剂萃取技术提取二噁英的应用已经遍及公共安全、地质勘探、环境检测、食品卫生、生物制药等领域,加速溶剂萃取技术在二噁英检测的样品前处理过程中体现出了明显的优势和巨大的应用潜力。对于绝大多数固体样品基质中的二噁英,均可以用ASE对二噁英进行提取,并且提取的回收率能够满足要求。与传统的索氏提取方法相比,ASE萃取时间大大减少。另一方面,加速溶剂萃取仪器具有高通量的优点,可降低样品前处理过程的内在成本(包括:时间、溶剂、人工、实验室空间等)。在ASE应用研究中,值得关注的是,加速溶剂萃取池中可同时加入净化材料,既萃取二噁英的同时也进行了净化,避免了萃取溶液要过净化柱的步骤,将提取和净化两个步骤合二为一,大大缩短了样品前处理时间,而且也减少了有机溶剂的使用。但是,加速溶剂萃取池体内壁大多为不锈钢材料,对于酸碱性样品的提取还存在一定局限性,今后在加速溶剂萃取仪器池体制作方面应适当考虑对含酸、碱性基质的样品的适用性,以便使该技术得到更广泛的应用。
加速溶剂萃取技术应用于二噁英检测的研究进展
Research progress of accelerated solvent extraction (ASE) technology in the detection of dioxins
-
摘要: 加速溶剂萃取技术通过提高温度和压力对混合基质中的有机物进行自动萃取。由于其具备有机溶剂用量少、萃取快速、样品回收率高等优点,可被应用于二噁英分析的样品前处理过程中。二噁英样品的提取效率与样品基质性质相关,为保证提取回收率必须选择合适的提取条件。本文从不同基质的角度综述了加速溶剂萃取技术在二噁英检测中的研究进展,同时展望了该技术未来的发展趋势。Abstract: Accelerated solvent extraction (ASE) technique extracts organic substances in mixed matrices at elevated pressure and temperature simultaneously. The technique could be used as sample pretreatment before dioxins analysis because it achieves high extraction efficiency with a less quantity of solvent within a short time. The extraction efficiency of dioxins is related to the properties of sample matrix. Therefore, in order to ensure the extraction recovery, the appropriate extraction conditions must be selected. This paper reviewed the progress of ASE technology in dioxin extraction and detection from different matrices. At the same time, the potential trend of this technology was also proposed.
-
Key words:
- accelerated solvent extraction /
- dioxin /
- sample pretreatment
-

-
表 1 不同基质中二噁英提取技术的应用
Table 1. Application of dioxin extraction technology in different matrices
样品基质
Sample
matrix萃取技术
Extraction
technology萃取时间/h
Extraction
time萃取溶剂体积/mL
Extraction solvent
volume回收率/%
Recovery仪器分析方法
Instrumental
analysis method文献
Ref.土壤 索氏提取 18 250 68.0—85.0 GC/HRMS [25] 废气 索氏提取 24 350 80.0—97.0 HRGC/HRMS [19] 母乳 索氏提取 24 250 50.0—120.0 GC/HRMS [22] 血清 索氏提取 48 160 66.2—95.2 HRGC/HRMS [52] 烟道气 索氏提取 19 300 33.0—113.0 HRGC/HRMS [84] 底泥 索氏提取 16 250 55.0—86.0 HRGC/HRMS [74] 底泥 索氏提取 48 350 52.0—104.0 HRGC/HRMS [68] 鱼组织 索氏提取 24 — 60.0—120.0 GC/HRMS [75] 松叶 索氏提取 24 — 46.0—116.0 HRGC/HRMS [76] 水体 索氏提取 24 — 32.0—127.0 GC/HRMS [77] 复合饲料 振荡提取 1 45 80.6—93.5 HRGC/HRMS [92] 底泥 ASE 1 180 93.2—115.6 HRGC/HRMS [35] 底泥 ASE 0.5 120 42.0—120.0 HRGC/HRMS [78] 粉尘 ASE 0.2 35 96.0—121.0 HRGC/HRMS [57] 水体 ASE 0.2 — 61.0—98.0 GC/HRMS [34] 生肉 ASE 0.8 160 40.0—119.0 HRGC/HRMS [93] 土壤 ASE 0.2 15 50.0—81.0 GC/MS [25] 土壤 ASE 0.7 — 60.6—117.0 GC/MS [83] 大气 ASE 0.5 — 55.7—94.1 HRGC/HRMS [85] 肉类 ASE 0.2 — 81.0—97.0 GC/HRMS [65] 树皮 ASE 0.4 — 70.0—95.0 GC-MS/MS [6] 鱼组织 ASE 0.3 — 59.0—114.0 HRGC/HRMS [69] -
[1] DE-JONG A P J M, LIEM A K D. Gas chromatography—mass spectrometry in ultra trace analysis of polychlorinated dioxins and related compounds [J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 1993, 12(3): 115-124. doi: 10.1016/0165-9936(93)88011-S [2] TAN P F, HURTADO I, NEUSCHÜTZ D, et al. Thermodynamic modeling of PCDD/Fs formation in thermal processes [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2001, 35(9): 1867-1874. [3] FOCANT J F, PIRARD C, PAUW D E. Automated sample preparation-fractionation for the measurement of dioxins and related compounds in biological matrices: A review [J]. Talanta, 2004, 63(5): 1101-1113. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2004.05.025 [4] HUTZINGER O, FIEDLER H. From source to exposure: Some open questions [J]. Chemosphere, 1993, 27(1-3): 121-129. [5] HEGER H J, ZIMMERMANN R, BLUMENSTOCK M, et al. On-line real-time measurements at incineration plants: PAHs and a PCDD/F surrogate compound at stationary combustion conditions and during transient emission puffs [J]. Chemosphere, 2001, 42(5-7): 691-696. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(00)00243-5 [6] CLARKSON P J, LARRAZABAL-MOYA D, STATON I, et al. The use of tree bark as a passive sampler for polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and furans [J]. International Journal of Environmental & Analytical Chemistry, 2002, 82(11-12): 843-850. [7] CONCEJERO M, RAMOS L, JIMÉNEZ B, et al. Suitability of several carbon sorbents for the fractionation of various sub-groups of toxic polychlorinated biphenyls, polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans [J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2001, 917(1-2): 227-237. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9673(01)00667-7 [8] NAKAO T, AOZASA O, OHTA S, et al. Assessment of human exposure to PCDDs, PCDFs and Co-PCBs using hair as a human pollution indicator sample I: Development of analytical method for human hair and evaluation for exposure assessment [J]. Chemosphere, 2002, 48(8): 885-896. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00156-X [9] REINER E J. The analysis of dioxins and related compounds [J]. Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 2010, 29(4): 10368-559. doi: 10.1002/mas.20255 [10] MALAVIA J, ABALOS M, SANTOS F J, et al. Ion-trap tandem mass spectrometry for the analysis of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans, and dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls in food [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2007, 55(26): 10531-10539. doi: 10.1021/jf0719858 [11] HAYWARD D G, ARCHER J C, ANDREWS S, et al. Application of a high-resolution quadrupole/orbital trapping mass spectrometer coupled to a gas chromatograph for the determination of persistent organic pollutants in cow’s and human milk [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2018, 66(44): 11823-11829. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b03721 [12] ORGANTINI K L, MYERS A L, JOBST K J, et al. Quantitative analysis of mixed halogen dioxins and furans in fire debris utilizing atmospheric pressure ionization gas chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 87(20): 10368-10377. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b02463 [13] BRUCE-VANDERPUIJE P, MEGSON D, JOBST K, et al. Background levels of dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls (dlPCBs), polychlorinated, polybrominated and mixed halogenated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs, PBDD/Fs & PXDD/Fs) in sera of pregnant women in Accra, Ghana [J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2019, 673: 631-642. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.060 [14] 李晓明, 张莉娜, 牟靖芳, 等. 高分辨气相色谱-质谱法同时测定食用油中二噁英和呋喃的多氯(溴)代二苯并衍生物的含量 [J]. 理化检验(化学分册), 2014, 50(2): 235-240. LI S M, ZHANG L N, MOU J F, et al. Simultaneous determination of polychloro(bromo)-dibenzo derivatives of dioxin and furan in edible oil by HRGC-MS [J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis(Part B: Chemical Analysis), 2014, 50(2): 235-240(in Chinese).
[15] 刘媛媛. 国内外二噁英检测标准制修订现状与进展 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2014, 36(1): 80-83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2014.01.017 LIU Y Y. Current status and advances of dioxin detection standards modification at home and abroad [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2014, 36(1): 80-83(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2014.01.017
[16] World Health Organization. Consultation on Assessment of the Health Risk of Dioxins: Re-evaluation of the Tolerable Daily Intake (TDI) [R]. (ICP/EHH018 VD96), Geneva, Switzerland, 1998. [17] MYERS A L, MABURY S A, REINER E J. Analysis of mixed halogenated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans (PXDD/PXDFs) in soil by gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (GC–MS/MS) [J]. Chemosphere, 2012, 87(9): 1063-1069. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.02.013 [18] LIU H X, ZHANG Q H, CAI Z W, et al. Separation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers, polychlorinated biphenyls, polychlorinated dibenzo- p-dioxins and dibenzo-furans in environmental samples using silica gel and florisil fractionation chromatography [J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2006, 557(1): 314-320. [19] 饶钦全, 王晖, 蔡卫义. 自动净化-高分辨气相色谱/高分辨质谱测定废气中二噁英 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2018, 34(3): 112-117. RAO Q Q, WANG H, CAI W Y. Determination of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in exhaust gas by automatic clean-up system and high resolution gas chromatography/high resolution mass spectrometry [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2018, 34(3): 112-117(in Chinese).
[20] ORGANTINI K L, MYERS A L, JOBST K J, et al. Comprehensive characterization of the halogenated dibenzo-p-dioxin and dibenzofuran contents of residential fire debris using comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography coupled to time of flight mass spectrometry [J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2014, 1369: 138-146. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2014.09.088 [21] WANG P, SHANG H T, LI H H, et al. PBDEs, PCBs and PCDD/Fs in the sediments from seven major river basins in China: Occurrence, congener profile and spatial tendency [J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 144: 13-20. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.08.045 [22] LI J G, ZHANG L, WU Y N, et al. A national survey of polychlorinated dioxins, furans (PCDD/Fs) and dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls (dl-PCBs) in human milk in China [J]. Chemosphere, 2009, 75(9): 1236-1242. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.01.073 [23] 吴嘉嘉, 张兵, 董姝君, 等. 同位素稀释气相色谱/三重四极质谱法测定二噁英同类物 [J]. 分析化学, 2011, 39(9): 1297-1301. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2040(10)60467-7 WU J J, ZHANG B, DONG S J, et al. Determination of ultratrace polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans by gas chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry [J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2011, 39(9): 1297-1301(in Chinese). doi: 10.1016/S1872-2040(10)60467-7
[24] BAUTZ H, POLZER J, STIEGLITZ L. Comparison of pressurised liquid extraction with Soxhlet extraction for the analysis of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans from fly ash and environmental matrices [J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 1998, 815(2): 231-241. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9673(98)00453-1 [25] RICHTER B E, EZZELL J L, KNOELES D E, et al. Extraction of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans from environmental samples using accelerated solvent extraction (ASE) [J]. Chemosphere, 1997, 34(5-7): 975-987. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(97)00400-1 [26] 王宇珊, 黄道建, 陈继鑫, 等. 某垃圾焚烧厂投产前后周边土壤二噁英的分布[J]. 环境科学研究, 2020, 33(8): 1938 - 1945. https://doi.org/10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2020.02.14. WANG Y S, HUANG D J, CHEN J X, et al. Distribution of PCDD/Fs in Soil before and after a Municipal Solid Waste Incinerator’ Operating[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2020, 33(8): 1938 - 1945 (in Chinese).
[27] RÜBEL A, BIERL R. Routine analysis of vinicultural relevant fungicides, insecticides and herbicides in soil samples using enhanced solvent extraction (ESE) [J]. Fresenius Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 1999, 364(7): 648-650. doi: 10.1007/s002160051405 [28] RAMOS L, VREULS J J, TH-BRINKMAN U A. Miniaturised pressurised liquid extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from soil and sediment with subsequent large-volume injection-gas chromatography [J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2000, 891(2): 275-286. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9673(00)00652-X [29] KRISTENSON M E, ANGIOI S, VREULS R J J, et al. Miniaturised pressurised liquid extraction of chloroanilines from soil with subsequent analysis by large-volume injection-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry [J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2004, 1058(1): 243-249. [30] 周延生, 刘文民, 赵景红, 等. 加压溶剂萃取和在线检测可吸入固体颗粒物(PM10)中16种多环芳烃 [J]. 分析化学, 2005, 33(9): 1231-1234. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3820.2005.09.008 ZHOU Y S, LIU W M, ZHAO J H, et al. Determination of 16 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in atmospheric particulate matters by on-line micro-pressurized liquid extraction coupled with capillary gas chromatography [J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2005, 33(9): 1231-1234(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3820.2005.09.008
[31] 周延生, 王涵文, 关亚风. 加压溶剂萃取法萃取大气颗粒物中的烷烃 [J]. 分析化学, 2004, 32(8): 983-987. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3820.2004.08.001 ZHOU Y S, WANG H W, GUAN Y F. Determination of alkanes in atmospheric particulate matter with pressurized liquid extraction [J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2004, 32(8): 983-987(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3820.2004.08.001
[32] Method 3545. USEPA SW-846.3rd ed., Update III: U. S. GPO, Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Waste[S], Washington D. C., 1995, 7: 1-12. [33] CASTRO J J, DEVILLER G, GHIANI M, et al. PCDD/F and PCB multi-media ambient concentrations, congener patterns and occurrence in a Mediterranean coastal lagoon (Etang de Thau, France) [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2007, 156(1): 123-135. [34] YOUN Y Y, PARK D H, LEE Y H, et al. High-throughput method of dioxin analysis in aqueous samples using consecutive solid phase extraction steps with the new C18 UltraflowTM pressurized liquid extraction and automated clean-up [J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 118: 124-129. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.07.023 [35] 李翔, 张垚, 孙毅之, 等. 加速溶剂萃取-流体控制系统净化-高分辨气相色谱/高分辨质谱定量测定底泥中的二噁英 [J]. 色谱, 2006, 26(4): 347-350. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-8713.2006.04.006 LI X, ZHANG Y, SUN Y Z, et al. Determination of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzo furans in sediment by accelerated solvent extraction, fluid management systems and high resolution gas chromatography/high resolution mass spectrometry [J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2006, 26(4): 347-350(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-8713.2006.04.006
[36] 刘巧娜, 王丽婧, 赵兴茹, 等. 洞庭湖底泥中二噁英污染现状及水动力对其分布的影响 [J]. 环境化学, 2015, 34(4): 741-747. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.04.2014092204 LIU Q N, WANG L J, ZHAO X R, et al. Occurrence of PCDD/Fs in sediments of Dongting Lake and the effect of hydrodynamic on their distribution [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 34(4): 741-747(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.04.2014092204
[37] YASUYUKI Z, SHUNJI H, AKIHIRO F, et al. Rapid automatic identification and quantification of compounds in complex matrices using comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography coupled to high resolution time-of-flight mass spectrometry with a peak sentinel tool [J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2013, 778: 54-62. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2013.03.049 [38] 孙慧中, 王璞, 田菲菲, 等. 气相色谱/三重四极杆质谱法测定环境样品中二噁英 [J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(7): 1688-1691. SUN H Z, WANG P, TIAN F F, et al. Determination of dioxins in environmental samples by gas chromatography / triple quadrupole mass spectrometry [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(7): 1688-1691(in Chinese).
[39] KIM E J, OH J E, CHANG Y S. Effects of forest fire on the level and distribution of PCDD/Fs and PAHs in soil [J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2003, 311(1-3): 177-189. doi: 10.1016/S0048-9697(03)00095-0 [40] WATANABE E Y, LI X, IMASAKA T, et al. Gas chromatography/femtosecond multiphoton ionization/time-of-flight mass spectrometry of dioxins [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2010, 82(15): 6519-6525. doi: 10.1021/ac1009063 [41] VOS J D, GORST-ALLMAN P, ROHWER E. Establishing an alternative method for the quantitative analysis of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans by comprehensive two dimensional gas chromatography–time-of-flight mass spectrometry for developing countries [J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2011, 1218(21): 3282-3290. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2011.03.050 [42] KINGUCHI O, KOBAYASHI T, SAITOH K, et al. Pressurized liquid extraction of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, polychlorinated dibenzofurans and coplanar polychlorinated biphenyls from contaminated soil [J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2006, 1108(2): 176-182. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2006.01.013 [43] SAITO K, TAKEKUMA M, OGAWA M, et al. Extraction and cleanup methods of dioxins in house dust from two cities in Japan using accelerated solvent extraction and a disposable multi-layer silica-gel cartridge [J]. Chemosphere, 2003, 53(2): 137-142. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00305-9 [44] HAJIZADEH Y, ONWUDILI J A, WILLIAMS P T. Removal potential of toxic 2378-substituted PCDD/F from incinerator flue gases by waste-derived activated carbons [J]. Waste Management, 2011, 31(6): 1194-1201. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2011.01.011 [45] HAJIZADEH Y, ONWUDILI J A, WILLIAMS P T. Effects of gaseous NH3 and SO2 on the concentration profiles of PCDD/F in flyash under post-combustion zone conditions [J]. Waste Management, 2012, 32(7): 1378-1386. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2012.02.007 [46] HAJIZADEH Y, ONWUDILI J A, WILLIAMS P T. Williams. PCDD/F formation from oxy-PAH precursors in waste incinerator flyash [J]. Chemosphere, 2011, 85(11): 1672-1681. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.07.078 [47] CUNLIFFE A M, WILLIAMS P T. Influence of temperature on PCDD/PCDF desorption from waste incineration flyash under nitrogen [J]. Chemosphere, 2006, 66(6): 1146-1152. [48] BAYARRI S, BALDASSARRI L T, IACOVELLA N, et al. PCDDs, PCDFs, PCBs and DDE in edible marine species from the Adriatic Sea [J]. Chemosphere, 2001, 43(4-7): 601-610. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(00)00412-4 [49] 沈斌, 施丽丽, 董晶剑, 等. 二噁英暴露对成年男性血清类固醇激素的影响 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2018, 38(6): 2345-2352. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.06.039 SHEN B, SHI L L, DONG J J, et al. Effect of dioxin exposure on serum steroid hormones in adult male [J]. China Environmental Science, 2018, 38(6): 2345-2352(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.06.039
[50] LIN Y J, FENG C, XU Q, et al. A validated method for rapid determination of dibenzo-p-dioxins/furans (PCDD/Fs), polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in human milk: focus on utility of tandem solid phase extraction (SPE) cleanup [J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2016, 408(18): 4897-4906. doi: 10.1007/s00216-016-9576-y [51] BERNSMANN T, FÜRST P. Comparison of acceleerated solvent extraction (ASE) with integrated sulphuric acid clean up and soxhlet extraction for determination of PCDD/PCDF, dioxin-like PCB and indicator PCB in feeding stuffs[C]. Organohalogen Compounds, 2004, 66: 157-161. [52] 徐洁, 张素坤, 任明忠, 等. 血清中二噁英测定方法的优化 [J]. 环境化学, 2013, 32(6): 1032-1037. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2013.06.017 XU J, ZHANG S K, REN M Z, et al. Development of GC-MS method for analysis of PCDD / Fs in serum [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2013, 32(6): 1032-1037(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2013.06.017
[53] 李雁, 郭昌胜, 侯嵩, 等. 固体废物焚烧过程中二噁英的排放和生成机理研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(4): 746-759. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018110103 LI Y, GUO C S, HOU S, et al. The formation mechanisms and emission of dioxin during the solid waste incineration process [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(4): 746-759(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018110103
[54] CHANG Y C, IMASAKA T. Simple pretreatment procedure combined with gas chromatography/multiphoton ionization/mass spectrometry for the analysis of dioxins in soil samples obtained after the Tōhoku earthquake [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 85(1): 349-354. doi: 10.1021/ac3028917 [55] CHUANG J C, VAN-EMON J M, SCHROCK M E. High-throughput screening of dioxins in sediment and soil using selective pressurized liquid extraction with immunochemical detection [J]. Chemosphere, 2009, 77(9): 1217-1223. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.09.010 [56] AGUIAL L, WILLIAMS E S, BROOKS B W, et al. Development and application of a novel method for high‐throughput determination of PCDD/Fs and PCBs in sediments [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2014, 33(7): 1529-1536. doi: 10.1002/etc.2579 [57] KLEES M, HIESTER E, BRUCKMANN P, et al. Determination of polychlorinated biphenyls and polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans by pressurized liquid extraction and gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry in street dust samples [J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2013, 1300: 17-23. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2013.03.056 [58] DING L, LI Y M, WANG P, et al. Seasonal trend of ambient PCDD/Fs in Tianjin City, northern China using active sampling strategy [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2012, 24(11): 1966-1971. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(11)61058-9 [59] DING L, LI Y M, WANG P, et al. Spatial concentration, congener profiles and inhalation risk assessment of PCDD/Fs and PCBs in the atmosphere of Tianjin, China [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2013, 58(9): 971-978. doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5694-5 [60] WINDAL I, MILLER D J, DE-PAUW E, et al. Supercritical fluid extraction and accelerated solvent extraction of dioxins from high-and low-carbon fly ash [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2000, 72(16): 3916-3921. doi: 10.1021/ac9914972 [61] SUBEDI B, USENKO S. Enhanced pressurized liquid extraction technique capable of analyzing polychlorodibenzo-p-dioxins, polychlorodibenzofurans, and polychlorobiphenyls in fish tissue [J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2012, 1238: 30-37. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2012.03.037 [62] ZHANG L, ZHONG Y X, LIU X, et al. Determination of polychlorinated dibenzo‐p‐dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans, and dioxin‐like polychlorinated biphenyls in human serum using programmable‐temperature vaporization gas chromatography with high‐resolution mass spectrometry [J]. Journal of Separation Science, 2017, 40(17): 3453-3461. doi: 10.1002/jssc.201700465 [63] TODAKA T, HIRAKAWA H, HORI T, et al. Concentrations of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, polychlorinated dibenzofurans, and non-ortho and mono-ortho polychlorinated biphenyls in blood of Yusho patients [J]. Chemosphere, 2007, 66(10): 1983-1989. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.07.069 [64] KLEINHENZ S, JIRA W, KARL H S. Dioxin and polychlorinated biphenyl analysis: automation and improvement of clean-up established by example of spices [J]. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, 2006, 50(4-5): 362-367. [65] WIBERG K, SPORRING S, HAGLUND P, et al. Selective pressurized liquid extraction of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans and dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls from food and feed samples [J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2007, 1138(1-2): 55-64. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2006.10.074 [66] 蔡璐, 赵文杰, 周全法. 加速溶剂萃取法与索氏提取法对废线路板中二噁英测定的影响 [J]. 分析化学, 2017, 45(5): 687-692. doi: 10.11895/j.issn.0253-3820.160767 CAI L, ZHAO W J, ZHOU Q F. Determination of dioxin in waste printed circuit boards by accelerated solvent extraction and soxhelt extraction [J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 45(5): 687-692(in Chinese). doi: 10.11895/j.issn.0253-3820.160767
[67] 黄蓉, 毕承路, 赵文杰, 等. 废线路板粉末中二噁英含量的测定 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2016, 32(6): 130-134. HUANG R, BI C L, ZHAO W J, et al. Determination of dioxin content in the waste circuit boards powder [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2016, 32(6): 130-134(in Chinese).
[68] ANTUNES P, VIANA P, VINHAS T, et al. Optimization of pressurized liquid extraction (PLE) of dioxin-furans and dioxin-like PCBs from environmental samples [J]. Talanta, 2008, 75(4): 916-925. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2007.12.042 [69] ZHAO X R, CUI T T, GUO R, et al. A clean-up method for determination of multi-classes of persistent organic pollutants in sediment and biota samples with an aliquot sample [J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2019, 1047: 71-80. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2018.10.011 [70] CUI L L, WANG S S, YANG X P, et al. Fatty acids, polychlorinated dibenzo- p -dioxins and dibenzofurans, and dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls in paired muscle and skin from fish from the Bohai coast, China: Benefits and risks associated with fish consumption [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 639: 952-960. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.195 [71] GARNER A J, PAGANO J J. Trends of polychlorinated dioxins, polychlorinated furans, and dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls in Chinook and Coho salmonid eggs from a Great Lakes tributary [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 247: 1039-1045. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.01.117 [72] HAN Y, LIU W, ZHU W, et al. Sources of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans, and biphenyls in Chinese mitten crabs [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 196: 522-530. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.01.018 [73] 王璞, 王亚韡, 李英明, 等. 青海湖湟鱼(Gymnocypris przewalskii)中PCBs和PCDD/Fs的分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2006, 25(6): 669-673. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2006.06.001 WANG P, WANG Y W, LI Y M, et al. PCBs and PCDD/Fs in scale-less carp (Gymnocypris przewalskii)from the Qinghai Lake [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2006, 25(6): 669-673(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2006.06.001
[74] METELKOVA L, ZHAKOVSKAYA Z, KUKHAREVA G, et al. Occurrence of PCDD/PCDFs, dioxin-like PCBs, and PBDEs in surface sediments from the Neva River and the Eastern Gulf of Finland (Russia) [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2019, 26(8): 7375-7389. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-1945-y [75] ÁBALOS M, BARCELÓ D, PARERA J, et al. Levels of regulated POPs in fish samples from the Sava River Basin. Comparison to legislated quality standard values [J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2019, 647: 20-28. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.371 [76] CHEN P, XIAO X, MEI J, et al. Characteristic accumulation of PCDD/Fs in pine needles near an MSWI and emission levels of the MSWI in Pearl River Delta: A case study [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 181: 360-367. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.04.098 [77] NGUYEN D D, TSAI C L, HSU Y C, et al. PCDD/Fs and dl-PCBs concentrations in water samples of Taiwan [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 173: 603-611. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.01.087 [78] GAO L R, HUANG H T, LIU L D, et al. Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans, and dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls in sediments from the Yellow and Yangtze Rivers, China [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(24): 19804-19813. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-5175-2 [79] CHEN X, CHEN J S, ZHANG L, et al. Levels of PCDDs, PCDFs and dl-PCBs in the blood of childbearing-aged women living in the vicinity of a chemical plant in Tianjin: A primary study [J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 118(1): 1-4. [80] BAO Y, ZHANG L, LIU X, et al. Dioxin-like compounds in paired maternal serum and breast milk under long sampling intervals [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2020, 194: 110339. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110339 [81] ZHANG Z, ZHOU M, HE J, et al. Polychlorinated dibenzo-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzo-furans exposure and altered lung function: The mediating role of oxidative stress [J]. Environment International, 2020, 137: 105521. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.105521 [82] YU D Z, LIU X F, LIU X, et al. Polychlorinated Dibenzo-p-Dioxins, Polychlorinated Dibenzofurans, and Dioxin-Like Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Umbilical Cord Serum from Pregnant Women Living Near a Chemical Plant in Tianjin, China [J]. International of Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2019, 16(12): 2178. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16122178 [83] LI W, LI C Q, CHEN Z S, et al. Characteristic and potential sources of polychlorinated dibenzo‐p‐dioxins and dibenzofurans in agricultural soils in Beijing, China [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2014, 33(9): 2004-2012. doi: 10.1002/etc.2646 [84] ZHANG C C, LI X X, ZHOU Z G. Spatial and temporal variation, source profile of PCDD/Fs in the atmosphere of a municipal waste incinerator in China [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 184: 109615. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109615 [85] HAO Y F, LI Y M, WANG T, et al. Distribution, seasonal variation and inhalation risks of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans, polychlorinated biphenyls and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the atmosphere of Beijing, China [J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2018, 40(5): 1907-1918. doi: 10.1007/s10653-017-9961-2 [86] LORENZI V, ANGELONE B, FERRETTI E, et al. PCDD/Fs, DL-PCBs, and NDL-PCBs in Dairy Cows: Carryover in Milk from a Controlled Feeding Study [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2020, 68(7): 2201-2213. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b08180 [87] FRANCHINA F A, LAZZARI E, SCHOLL G, et al. Assessment of a New GC-MS/MS System for the Confirmatory Measurement of PCDD/Fs and (N)DL-PCBs in Food under EU Regulation [J]. Foods, 2019, 8(8): 302. doi: 10.3390/foods8080302 [88] SUN H, WANG P, LI H, et al. Determination of PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like PCBs in food and feed using gas chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry [J]. Science China-chemistry, 2017, 60(5): 670-677. doi: 10.1007/s11426-016-9017-9 [89] WANG L, DING G, ZHOU Z, et al. Level and characteristics of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in feed and feed additives [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences-China, 2017, 51(1): 324-331. [90] DAM G T, PUSSENTE I C, SCHOLL G, et al. The performance of atmospheric pressure gas chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry compared to gas chromatography–high resolution mass spectrometry for the analysis of polychlorinated dioxins and polychlorinated biphenyls in food and feed samples [J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2016, 1477: 76-90. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2016.11.035 [91] LORENZI V, GHIDINI S, ANGELONE B, et al. Three years of monitoring of PCDD/F, DL-PCB and NDL-PCB residues in bovine milk from Lombardy and Emilia Romagna regions (Italy): Contamination levels and human exposure assessment [J]. Food Control, 2016, 68: 45-54. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.03.034 [92] PISKORSKA-PLISZYNSKA J, MALAGOCKI P, FURGA B, et al. Application of the AhR reporter gene assay for the determination of PCDD/Fs and DL-PCBs in feed samples [J]. Journal of Veterinary Research, 2017, 61(4): 473-481. doi: 10.1515/jvetres-2017-0066 [93] MARTIN B S, PIZARRO-ARÁNGUIZ N, GARCÍA-MENDOZA D, et al. A four-year survey in the farming region of Chile, occurrence and human exposure to polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans, and dioxin -like polychlorinated biphenyls in different raw meats [J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2016, 537: 1278-1286. [94] VANDERMARKEN T, GAO Y, BAEVENS W, et al. Dioxins, furans and dioxin-like PCBs in sediment samples and suspended particulate matter from the Scheldt estuary and the North Sea Coast: comparison of CALUX concentration levels in historical and recent samples [J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2018, 626: 109-116. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.084 -



 下载:
下载: