-
降尘是我国城市空气污染的主要因子之一[1-2],兼具“污染源”与“传播媒介”双重作用[3],也是多种污染物的载体和反应床,其中重金属类的污染尤为突出[4]。降尘中重金属可通过呼吸、皮肤接触及手-口摄入等多种途径进入人体[5],引起人体机能功能性障碍和不可逆性损伤,甚至产生“致癌、致畸、致突变”的三致效应[6],对人体健康构成严重威胁。因此,降尘中重金属的污染与防治问题已引起国内外学者的广泛关注。明确降尘中重金属的污染表征、时空分布特征分析、来源解析等研究对城市大气环境精准治理具有重要意义。
对于工业城市而言,由于其排放的降尘中重金属种类多、排放量大、污染源类型复杂,往往导致城市大气重金属污染较为严重[7],亟需开展工业城市大气的重金属污染防治工作。明确大气降尘中重金属来源是开展大气环境精准防治工作的重要理论基础。降尘中重金属源解析方法包括以污染源为研究对象的扩散模型和以污染区域为研究对象的受体模型[8],其中受体模型已受到广泛使用。如杨弘等[9]采用主成分分析法(Principal Component Analysis,PCA)识别了太原市大气颗粒物中重金属主要来源。Ma等[10]通过绝对主成分得分多元线性回归受体模型(Absolute Principal Component Scores-Multivariate Linear Regression,APCS-MLR)对垃圾焚烧厂周边土壤重金属来源进行识别和贡献分配。Yan等[11]采用正定矩阵因子分析模型(Positive Matrix Factorization,PMF)对厦门市大气降尘中稀土元素进行来源解析。PMF模型是美国环境保护署推荐使用的源解析方法之一,其通过相关矩阵和协方差矩阵对多维变量进行降维,是一种十分有效的重金属源解析方法。目前,PMF模型已广泛用于大气颗粒物中重金属的来源解析[11-12]。
济南市作为我国典型的老工业城市,集聚了以冶炼、化工、机械等为主体的重工业集群,产业结构重型化,钢铁锻造冶炼、煤炭燃烧以及机动车尾气排放等会释放大量的粉尘及颗粒物,造成大气中重金属的污染源类型复杂。庞绪贵等[13]采用因子分析法对济南城区大气降尘及污染端元进行分析,结果表明企业燃煤、汽车尾气和交通污染是济南大气降尘污染的主要来源。赵西强等[14]采用主成分分析对济南近地表大气降尘元素进行源解析,结果表明土壤粉尘、燃煤、建筑尘及汽车尾气排放是降尘元素的主要贡献因子。由此可见,不同源解析方法得到的源解析结果有较大差异。
为明确济南市大气降尘中重金属的分布特征和来源解析,本研究采集了济南市大气降尘为研究对象,分析降尘中重金属Mn、Fe、Co、Ni、Cu、Zn、As和Pb含量,通过PMF模型对济南市降尘中重金属进行来源解析。研究结果以期为济南市大气重金属污染的精准防治工作提供数据支撑和科学依据。
-
济南市地处山东省中西部(N36°40′,E117°00′),北跨黄河,南依泰山,属于温带半湿润季风气候,地势南高北低,形成半盆地地貌。综合考虑济南市的气候特征、地形地貌特点、工业分布情况、道路交通条件等,在全市共布设35个大气降尘采样点和3个土壤背景点(鹊山水库S11、S12、S13)(图1)。于2019年8月晴朗无风天气下使用毛刷采集公交站台、公告栏、植物叶面、居民楼窗台等中低位置的降尘,装入干净的聚乙烯自封袋中,编号密封保存,并详细记录每个采样点周围的环境特征信息。
-
将样品去除落叶、石块等杂质后自然风干备用。降尘中重金属全量采用强酸(高氯酸:硝酸=1∶4)消解[15]。称取降尘样品(0.2000±0.0005) g于硬质玻璃消解管中,加入8 mL浓硝酸(Merck)和2 mL高氯酸(GR),将消解管置于电热板消解仪中,消解程序为:温度升至50 ℃保持3 h,升温至75 ℃后保持1 h,升温至100 ℃并保持1 h,升温至125 ℃后保持1 h,升温至150 ℃保持3 h,升温至175 ℃保持2 h,升温至190 ℃并保持3 h。待样品温度冷却至室温后加入10 mL体积分数为1%稀硝酸,置于消解仪中,100 ℃保持1 h。待样品温度再次冷却至室温后将溶液移至50 mL离心管中,溶液经过0.22 μm水系滤头过滤后采用电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, ICP-MS, Agilent, 7500cx)测定消解液中重金属Mn、Fe、Co、Ni、Cu、Zn、As、Pb全量,重金属Mn、Fe、Co、Ni、Cu、Zn、As、Pb的仪器检测限分别为0.05、4.12、0.01、0.09、0.16、0.42、0.03、0.28 μg·L−1。样品分析过程中,采用土壤成分分析标准物质(GSS-6,中国地质科学院地球物理化学勘察研究所)对方法回收率进行监控,其重金属Mn、Fe、Co、Ni、Cu、Zn、As、Pb的回收率分别为98.7%、89.5%、87.3%、102%、96.9%、87.3%、100%、117%;平行样(3组)中各元素相对误差均低于10%;试剂空白均未检出。
-
地累积指数(Geoaccumulation Index,Igeo)用于分析沉积物中重金属元素污染程度的定量化指标,目前也被广泛应用于土壤和降尘中重金属的污染评价研究。其计算公式为[16-17]:
式中,Cn为大气降尘中重金属元素n的实际测量值(mg·kg−1);Bn为该元素的地球化学背景值(mg·kg−1),本研究采用济南市土壤元素地球化学背景值,k为修正系数,依据造岩运动可能引起背景值波动而设定(取1.5)。地累积指数根据指数大小分为7个等级:Igeo≤0表示无污染;0<Igeo≤1表示轻度污染;1<Igeo≤2表示中度污染;2<Igeo≤3表示中度-重度污染;3<Igeo≤4表示重度污染;4<Igeo≤5表示重度-极度污染;5<Igeo表示极度污染。
-
本研究采用正定矩阵因子分析模型(PMF)对济南大气降尘中重金属进行源解析。PMF是一个多元因子的分析工具,样品数据矩阵(X)分解为因子贡献矩阵(G)和因子成分矩阵(F)。PMF模型的基本方程为[11]:
式中,Xij为第i个样品中第j种元素的含量;Gik为第k个因子对第i个样品的贡献率;Fkj为第k个因子中第j种元素的含量;Eij为第i个样品中第j种元素的残差;p为因子个数。
PMF模型需要对样品含量及不确定度进行迭代计算,计算样品含量的不确定度,公式如下:
式中,Uij为第i个样品中第j种元素的不确定度;MDL为元素的检出限;c为元素含量;δ为相对标准偏差。
PMF模型通过多以迭代计算得到较小的目标函数Q值,以得到最优的因子贡献矩阵(G)和因子成分矩阵(F)的解。其计算方程如下:
式中,Q为目标函数;n和m分别为样品数量和元素种类数量。模型运算过程中根据信噪比(Signal/Noise, S/N)和Q值多次计算,确定最优结果。
-
重金属分布特征采用ArcMap 10.2中的反距离加权法(Inverse Distance Weighted, IDW)法进行插值分析。地累积指数热图采用ClustVis进行绘制。来源解析采用EPA PMF 5.0进行计算,Circos Table Viewer v0.63进行绘图。
-
济南市大气降尘中重金属Mn、Fe、Co、Ni、Cu、Zn、As和Pb浓度平均值分别为501.4、29884.6、8.2、24.8、44.3、153.9、12.5 、40.1 mg·kg−1,均低于全国大气降尘中重金属平均值(表1)。值得注意的是,济南市降尘中部分重金属元素(如Mn、Ni、Cu、Zn和Pb)显著低于全国工业区平均值和部分非工业城市(如杭州、南京和厦门),这可能与济南市的土壤重金属背景值有关。土壤重金属背景值能够反映一定时间区域范围内未明显受到现代社会工业化污染和破坏的土壤原来固有的元素含量水平[29]。相较于土壤对照值,济南市降尘中重金属Mn、Fe、Co、Ni、Cu、Zn、As和Pb的超标倍数分别为0.5、0.6、0.2、0.3、2.7、2.7、0.1、2.2倍,其中Cu、Zn和Pb的超标倍数显著(P<0.05)高于其余重金属元素的超标倍数,表明济南市大气降尘中Cu、Zn和Pb元素受到人类活动影响的可能性较大。赵西强等[14]分析了济南市近地表大气降尘中重金属地球化学特征,结果显示济南市大气降尘中重金属Ni、Zn、As、Pb浓度分别为26.0、119.0、9.5、38.0 mg·kg−1,其中Zn和Pb元素富集程度分别为1.83和1.81,其结果与本研究一致。庞绪贵等[13]研究结果也表明,济南市大气降尘中Cu、Pb、Zn和Cd等重金属的富集程度较高,受到不同程度人为污染。
通过进一步分析,济南市降尘中各重金属元素浓度分布存在明显的空间差异,受外来污染源影响的可能性较大。钢城区作为降尘重金属分布的“热点”区域(图2),其降尘中Mn、Fe、Co、Cu和As浓度平均值分别为1172.4、73577.3、17.0、139.7 、32.3 mg·kg−1,显著高于其他区县降尘中重金属浓度。这可能与钢城区发达的钢铁冶炼加工产业有关。而Zn和Pb在历下区、槐荫区等人口密集区域最高浓度可达351.5 mg·kg−1和114.0 mg·kg−1。这可能是由于该区域为济南市城市主干道,交通污染源和人为活动对区域大气降尘中重金属Zn和Pb的贡献率较大[30]。此外,市区内大量的热电厂、化工厂、机械厂等企业燃煤排放也可能导致区域降尘中的Zn和Pb浓度较高[14]。商河县降尘中重金属Mn、Fe、Co、Ni、Cu、Zn、As和Pb浓度处于较低水平,平均值分别为429.3、19045.9、6.5 、20.8、35.2、113.1、12.8 、24.0 mg·kg−1,这可能是由于商河县以农业生产为主,其对降尘中重金属的贡献率较低。
-
济南市大气降尘中各重金属元素的地累积指数(Igeo)平均值大小为Zn>Cu>Pb>Fe>Mn>Ni>Co>As(图3)。其中,Zn、Cu和Pb的Igeo平均值均大于1,分别为1.17、1.06和1.01,表明Cu、Zn和Pb污染程度总体属于中度污染,且部分样品中Cu、Zn和Pb的Igeo大于2,属于中度-重度污染水平,Cu、Zn和Pb为中度-重度污染的样品数量比例分别为8.6%、20.0%和8.6%。赵西强等[14]研究结果表明,济南市近地表大气降尘中Zn的Igeo变化范围为−2.02—3.48,Pb的Igeo变化范围为−1.81—2.75,均以轻度污染为主。李少洛[31]的研究结果也表明,济南市降尘中Cu、Pb的Igeo范围分别为0.79—1.35、0.86—1.21,均属于轻度污染-中度污染,但Zn的Igeo范围高达2.30—2.63,属于中度-重度污染水平。这表明济南市降尘中Cu、Zn、Pb均受到不同程度污染,这与本研究结果一致。而Mn、Fe、Co、Ni和As的Igeo平均值均小于0,分别为−0.12、−0.05、−0.46、−0.30和−0.65,表明Mn、Fe、Co、Ni和As总体为无污染。但值得注意的是,部分样品存在Mn、Fe、Co、Ni和As的Igeo大于0,为轻度污染水平,其样品数量比例分别为20.0%、22.9%、8.6%、20.0%和11.4%。整体而言,济南市大气降尘重金属的污染程度较轻,其中Cu、Zn和Pb为主要污染物,对降尘中重金属污染的贡献程度较高。
-
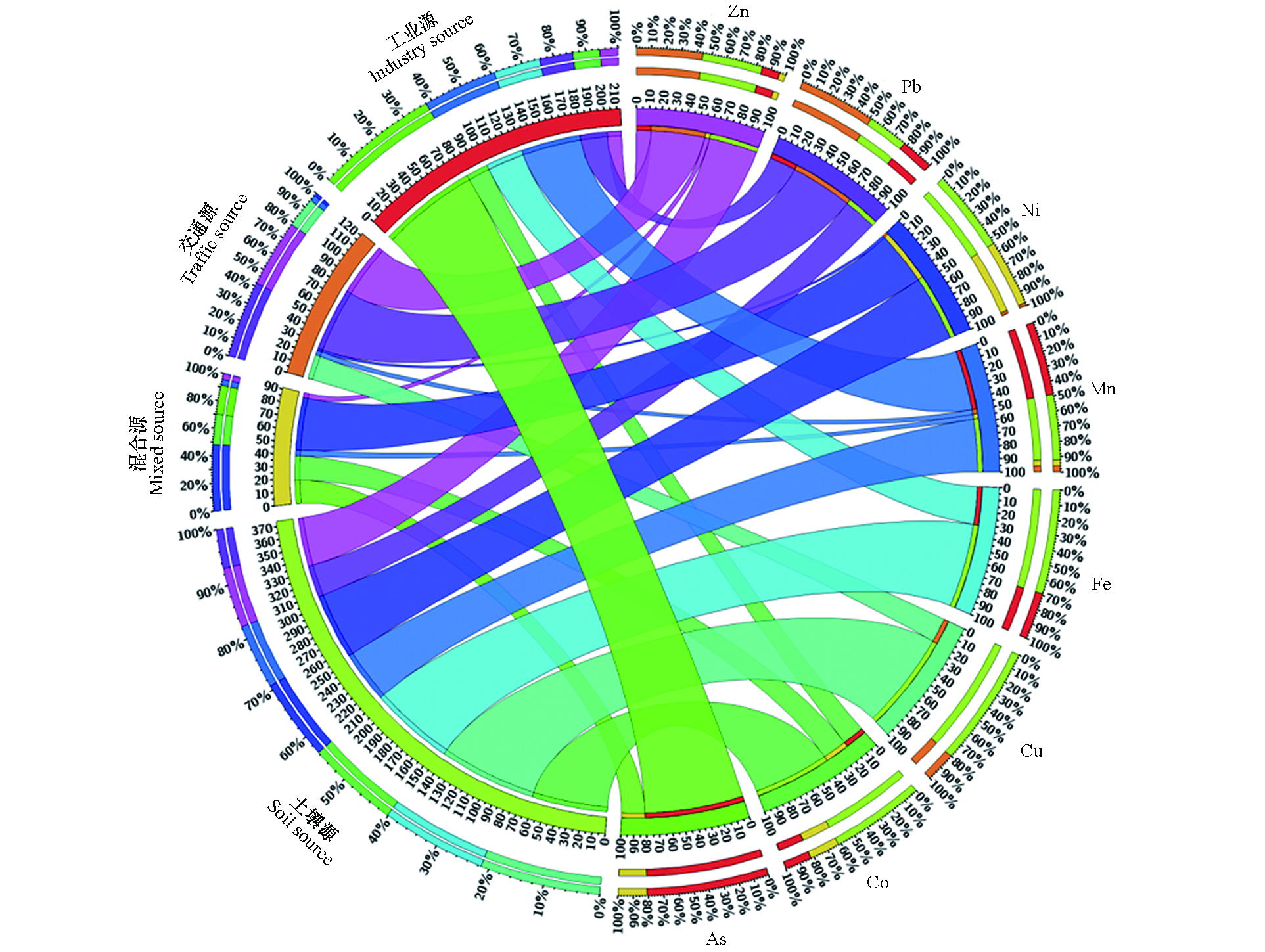
本研究在PMF模型完成20次概率矩阵分解后,通过济南市重金属来源辨识的基础上,确定了4个主要贡献源,其中Co、Cu、Fe、Mn和Ni作为典型的地壳元素,可作为土壤源的主要指示元素[13,31];Zn和Pb则是汽车尾气排放和车轮胎磨损的主要指示元素[32];工业燃煤产生的As对济南市大气环境影响较大[13],因此本研究中降尘中重金属来源分别为土壤源、工业源、交通源和混合源,贡献率分别为46.8%、26.6%、15.2%和11.4%(图4)。虽然人为的生产生活过程中一定程度上影响了降尘中重金属的分布,但风化母质的土壤源依然是降尘中重金属的主要来源。李少洛[31]对济南市春季降尘中无机成分进行PMF来源解析,结果也表明,土壤尘是济南市降尘中无机元素的主要贡献源,贡献率为39.2%。庞绪贵等[13]通过因子分析结果表明,企业燃煤、汽车尾气排放和交通污染对降尘中重金属的贡献率约占60.4%,是济南市大气降尘重金属污染的主要来源。通过进一步分析表明,重金属Co、Cu、Fe主要来自土壤源,占比分别为61.6%、80.1%和69.4%。Mn主要来自于土壤源和工业源的贡献。Ni主要来自于土壤源和混合源。交通源对降尘中Pb和Zn的贡献率较高,分别为51.4%和44.4%。As则主要来自于工业源,其贡献率可达81.3%。由此可见,在济南市大气环境治理过程中,对于工业源应加强重金属As和Mn排放控制,对于交通源可侧重于对Pb和Zn的监测,其他混合源则对降尘中Ni的贡献较大。
-
(1)本研究分析了济南市降尘中重金属污染概况,重金属Cu、Zn和Pb超过对应的土壤背景值2.7倍、2.7倍和2.2倍,表明济南市大气降尘中Cu、Zn和Pb元素受到人类活动影响的可能性较大。其中Cu主要集中分布于钢城区,而Zn和Pb则集中分布在历下区和槐荫区等人口密集区。
(2)污染评价结果表明,济南市降尘中重金属Zn、Cu和Pb的Igeo平均值均大于1,属于中度污染,且Cu、Zn和Pb为主要污染物,对降尘环境污染的贡献程度较高。其余重金属的Igeo平均值均小于0,表现为无污染水平。
(3)通过PMF解析得到济南市降尘中重金属主要存在4个贡献源,分别为土壤源、工业源、交通源和混合源,贡献率分别为46.8%、26.6%、15.2%和11.4%。其中,重金属Co、Cu、Fe主要来自土壤源,Mn主要来自于土壤源和工业源的贡献,Ni主要来自于土壤源和混合源,交通源对降尘中Pb和Zn的贡献率较高,As则主要来自于工业源。本研究结果可为济南市大气环境精准管控提供理论支撑。
典型工业城市大气降尘中重金属分布特征及其来源解析---以济南市为例
Distribution characteristic and source apportionment of heavy metals in atmospheric dust in a typical industrial city -- A case study of Jinan
-
摘要: 污染源解析是城市大气环境精准防治的重要基础。为探究典型工业城市大气降尘中重金属污染分布特征和污染源解析,本研究在济南市域内采集了35个大气降尘样品,分析了样品中重金属浓度及其空间分布特征,采用正定矩阵因子分析模型(Positive Matrix Factorization,PMF)解析降尘中重金属来源。研究结果表明,降尘中Mn、Fe、Co、Ni、Cu、Zn、As和Pb浓度平均值分别为501.4、29884.6、8.2、24.8、44.3、153.9、12.5、40.1 mg·kg−1,其中Zn、Cu和Pb的地累积指数(Geoaccumulation Index,Igeo)分别为1.17、1.06和1.01,属于中度污染;钢铁冶炼较为发达的钢城区降尘中Mn、Fe、Co、Cu和As浓度显著高于其他区县,其浓度平均值分别为1172.4、73577.3、17.0、139.7、32.3 mg·kg−1,而Zn和Pb在历下区、槐荫区等人口密集区域最高浓度可达351.5 mg·kg−1和114.0 mg·kg−1;PMF分析结果表明,济南市降尘重金属主要存在4个贡献源,分别为土壤源、工业源、交通源和混合源,贡献率分别为46.8%、26.6%、15.2%和11.4%。其中,重金属Co、Cu、Fe主要来自土壤源,Mn主要来自于土壤源和工业源的贡献,Ni主要来自于土壤源和混合源,交通源对降尘中Pb和Zn的贡献率较高,As则主要来自于工业源。本研究结果可为济南市大气环境精准防控政策的制定提供理论依据。Abstract: The sources apportionment of heavy metals in atmospheric dust is an important basis for accurate prevention and control of urban atmospheric environment. To explore the source and contribution of heavy metals in atmospheric dust in a typical industrial city, this study collected 35 atmospheric dust samples from Jinan city, the concentrations and spatial distribution of heavy metals were analyzed. The Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) model was utilized to analyze the source of heavy metals in atmospheric dust. The results showed that the average concentrations of Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, As and Pb in atmospheric dust samples were 501.4, 29884.6, 8.2, 24.8, 44.3, 153.9, 12.5, 40.1 mg·kg−1, respectively. The average geoaccumulation index (Igeo) of Zn, Cu and Pb in the atmospheric dust were 1.17, 1.06 and 1.01, respectively, presenting moderate pollution level. The concentrations of Mn, Fe, Co, Cu and As in Gangcheng district with developed steel smelting were higher than that in other district, with the average values of 1172.4, 73577.3, 17.0, 139.7, 32.3 mg·kg−1, respectively. The highest concentrations of Zn and Pb reached 351.5 mg·kg−1 and 114.0 mg·kg−1, respectively in Lixia and Huaiyin district with the densely populated areas. PMF analysis showed that there were four main sources of heavy metals in the atmospheric dust in Jinan, including soil sources, industrial sources, traffic sources and other sources, and the contribution rates were 46.8%, 26.6%, 15.2% and 11.4%, respectively. Co, Cu and Fe mainly came from soil sources, Mn mainly came from soil sources and industrial sources, Ni mainly came from soil sources and mixed sources, traffic sources mainly contributed to Pb and Zn in atmospheric dust, and As mainly came from industrial sources. The results of this study could provide a theoretical basis for the formulation of precise prevention and control policies of atmospheric environment in Jinan.
-
Key words:
- industrial city /
- atmospheric dust /
- heavy metals /
- PMF model /
- source apportionment
-

-
表 1 济南市及全国部分城市大气降尘中重金属浓度
Table 1. The heavy metals concentrations of atmospheric dust in Jinan and other cities
城市
CitiesMn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn As Pb 济南 501.4 29884.6 8.2 24.8 44.3 153.9 12.5 40.1 抚顺[18] — — — 26.9 81.3 619.7 — 98.5 沈阳[19] — — — 38.2 41.2 149.8 6.5 38.5 西安[20] 569.3 — 27.0 34.1 65.4 523.0 12.7 120.2 兰州[21] 501.5 19227.1 — 40.6 82.2 369.2 — 130.3 杭州[22] 741.1 21149.0 7.0 27.8 223.6 1820.4 — 363.7 天津[23] 380.2 — — 37.1 201.1 736.4 25.7 82.5 厦门[24] 723.0 43733.0 11.2 40.4 444.4 4495.0 — 160.0 焦作[25] — — 9.6 40.3 67.6 1111.5 35.0 155.6 南京[26] 645.8 23703.0 9.9 44.1 183.7 683.2 4.9 123.4 北京[27] — — 13.3 46.9 158.9 741.3 — 154.8 全国-工业区[28] — — — 50.1 332.7 2319.0 369.4 861.7 全国-非工业区[28] — — — 42.5 116.1 603.6 38.2 171.0 济南土壤对照点 334.3 18408.5 7.0 19.1 12.0 42.0 11.1 12.5 注:“—”表示无数据. The data were not available. -
[1] 代杰瑞, 祝德成, 庞绪贵, 等. 济宁市近地表大气降尘地球化学特征及污染来源解析[J]. 中国环境科学, 2014, 34(1): 40-48. DAI J R, ZHU D C, PANG X G et al. Geochemical characteristics and pollution sources identification of the near-surface atmosphere dust-fall in Jining City[J] Chian Environmental Science, 2014, 34(1): 40-48 (in Chinese).
[2] TANG R, MA K, ZHANG Y, et al. The spatial characteristics and pollution levels of metals in urban street dust of Beijing, China [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2013, 35: 88-98. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2013.03.016 [3] 雷凯, 卢新卫, 王利军. 宝鸡市街尘中铅的污染与评价 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2007, 30(11): 43-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2007.11.016 LEI K, LU X W, WANG L J. Lead pollution and its assessment in urban street dust of Baoji City [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 30(11): 43-45(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2007.11.016
[4] 王明仕, 李晗, 王明娅, 等. 中国降尘重金属分布特征及生态风险评价 [J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2015, 29(12): 164-169. WANG M S, LI H, WANG M Y, et al. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment on dust heavy metals in China [J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2015, 29(12): 164-169(in Chinese).
[5] GOPE M, MASTO R E, GEORGE J, et al. Bioavailability and health risk of some potentially toxic elements (Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn) in street dust of Asansol, India [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2017, 138: 231-241. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.01.008 [6] 蔡睿, 卜俊国, 许嘉俊, 等. 重金属暴露及其致癌分子机制的研究进展 [J]. 医学综述, 2014, 20(10): 1786-1789. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2014.10.020 CAI R, BU J G, XU J J, et al. Recent progress in the molecular carcinogenic mechanism of heavy metal exposure [J]. Medical Recapitulate, 2014, 20(10): 1786-1789(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2014.10.020
[7] 刘星, 聂春光. 中国工业经济发展与工业污染排放的变化 [J]. 统计与决策, 2007(4): 65-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6487.2007.04.024 LIU X, NIE C G. China’s industrial development and the change of industrial pollution emission [J]. Statistics & Decision, 2007(4): 65-67(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6487.2007.04.024
[8] 董騄睿, 胡文友, 黄标, 等. 基于正定矩阵因子分析模型的城郊农田土壤重金属源解析 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2015, 35(7): 2103-2111. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2015.07.031 DONG L R, HU W Y, HUANG B, et al. Source appointment of heavy metals in suburban farmland soils based on positive matrix factorization [J]. China Environmental Science, 2015, 35(7): 2103-2111(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2015.07.031
[9] 杨弘, 张君秋, 王维, 等. 太原市大气颗粒物中重金属的污染特征及来源解析 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2015, 31(2): 24-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2015.02.005 YANG H, ZHANG J Q, WANG W, et al. The elemental pollution characteristics and source apportionment of atmospheric particulate in Taiyuan [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2015, 31(2): 24-28(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2015.02.005
[10] MA W C, TAI L Y, et al. Contamination source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil around municipal solid waste incinerator: A case study in North China [J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 631/632: 348-357. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.011 [11] YAN Y, CHI H F, LIU J R, et al. Provenance and bioaccessibility of rare earth elements in atmospheric particles in areas impacted by the optoelectronic industry [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 263: 1143-1149. [12] JI H, TAN J C, DUAN F H, et al. Source apportionment of size segregated fine/ultrafine particle by PMF in Beijing [J]. Atmospheric Research, 2014, 139: 90-100. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2014.01.007 [13] 庞绪贵, 王晓梅, 代杰瑞, 等. 济南市大气降尘地球化学特征及污染端元研究 [J]. 中国地质, 2014, 41(1): 285-293. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.01.023 PANG X G, WANG X M, DAI J R, et al. Geochemical characteristics and pollution sources identification of the atmospheric dust-fall in Jinan City [J]. Geology in China, 2014, 41(1): 285-293(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.01.023
[14] 赵西强, 王增辉, 王存龙, 等. 济南市近地表大气降尘元素地球化学特征及污染评价 [J]. 物探与化探, 2016, 40(1): 154-159. ZHAO X Q, WANG Z H, WANG C Z, et al. Geochemical characteristics and pollution assessment of near-surface atmospheric dust in Jinan [J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 40(1): 154-159(in Chinese).
[15] LEE C S, LI X D, SHI W Z, et al. Metal contamination in urban, suburban, and country park soils of Hong Kong: A study based on GIS and multivariate statistics [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2006, 356: 45-61. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.03.024 [16] 姚峰, 包安明, 阴俊齐, 等. 新疆准东煤田土壤重金属来源与污染评价 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2013, 33(10): 1821-1828. YAO F, BAO A M, YIN J Q, et al. Soil heavy metal sources and pollution assessment in the coalfield of East Junggar Basin in XinJiang [J]. China Environmental Science, 2013, 33(10): 1821-1828(in Chinese).
[17] 李娟娟, 马金涛, 楚秀娟, 等. 应用地积累指数法和富集因子法对铜矿区土壤重金属污染的安全评价 [J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2006(12): 135-139. LI J J, MA J T, CHU X J, et al. Application of index of geo-accumulation and enrichment factor in safety assessment of heavy-metal contamination in soil of copper refining [J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2006(12): 135-139(in Chinese).
[18] 李晓丹. 抚顺市大气降尘中重金属污染评价与防治对策研究 [J]. 黑龙江环境通报, 2017, 41(1): 10-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-263X.2017.01.005 LI X D. Study on heavy metal pollution assessment of atmospheric dust and control measures in Fushun City [J]. Heilongjiang Environmental Journal, 2017, 41(1): 10-13(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-263X.2017.01.005
[19] 刘春跃. 沈阳城市降尘中典型重金属污染物特征分析及风险评价[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳大学, 2020. LIU C Y. Characteristic analysis and risk assessment of typical heavy metal pollutants in urban dust in Shenyang City[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang University, 2020 (in Chinese).
[20] 解成祥. 西安市各功能区大气降尘中重金属与多环芳烃污染特征及评价[D]. 西安: 陕西师范大学, 2019. XIE C X. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of PAHs in dustfall from different functional areas in Xi’an[D]. Xi’an: Shaanxi Normal University, 2019 (in Chinese).
[21] 李萍, 薛粟尹, 王胜利, 等. 兰州市大气降尘重金属污染评价及健康风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(3): 1021-1028. LI P, XIE L Y, WANG S L, et al. Pollution evaluation and health risk assessment of heavy metals from atmospheric deposition in Lanzhou [J]. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(3): 1021-1028(in Chinese).
[22] 焦荔, 沈建东, 姚琳, 等. 杭州市大气降尘重金属污染特征及来源研究 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2013, 35(1): 73-76,80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2013.01.016 JIAO L, SHEN J D, YAO L, et al. Pollution characteristics and sources of heavy metals in atmospheric dustfall of Hangzhou [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2013, 35(1): 73-76,80(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2013.01.016
[23] 李越洋, 姬亚芹, 王士宝, 等. 天津市春季道路降尘PM2.5中重金属污染特征及健康风险评价 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2018, 31(5): 853-859. LI Y Y, JI Y Q, WANG S B, et al. Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of PM2.5-bound heavy metals in road dust deposition during spring in Tianjin City [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2018, 31(5): 853-859(in Chinese).
[24] 赵莉斯, 于瑞莲, 胡恭任, 等. 厦门市大气降尘中重金属形态分布及生物有效性 [J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(4): 805-811. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.04.2016071101 ZHAO L S, YU R L, HU G R, et al. Speciation and bioavailability of heavy metals in the atmospheric dustfall of Xiamen City [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(4): 805-811(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.04.2016071101
[25] 王明仕, 刘艳萍, 曹景丽, 等. 焦作市采暖期大气降尘重金属的分布特征和健康风险评估 [J]. 地球与环境, 2018, 46(1): 59-65. WANG M S, LIU Y P, CAO J L, et al. Distribution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in atmospheric dust-fall in Jiaozuo City, Henan Province, China [J]. Earth and environment, 2018, 46(1): 59-65(in Chinese).
[26] 田春晖, 杨若杼, 古丽扎尔·依力哈木, 等. 南京市大气降尘重金属污染水平及风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(7): 3118-3125. TIAN C H, YANG R Z, GULIZHAER Y L H M, et al. Pollution levels and risk assessment of heavy metals from atmospheric deposition in Nanjing [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(7): 3118-3125(in Chinese).
[27] 熊秋林, 赵文吉, 束同同, 等. 北京降尘重金属污染水平及其空间变异特征 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2016, 29(12): 1743-1750. XIONG Q L, ZHAO W J, SHU T T, et al. Heavy metal pollution levels and spatial variation characteristics of dust deposition in Beijing [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2016, 29(12): 1743-1750(in Chinese).
[28] 何予川, 王明娅, 王明仕, 等. 中国降尘重金属的污染及空间分布特征 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2018, 27(12): 2258-2268. HE Y C, WANG M Y, WANG M S, et al. Pollution and spatial distribution characteristics of heavy metals of dustfall in China [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2018, 27(12): 2258-2268(in Chinese).
[29] 雷国建, 陈志良, 刘千钧, 等. 广州郊区土壤重金属污染程度及潜在生态危害评价 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2013, 33(S1): 49-53. LEI G J, CHEN Z L, LIU Q J, et al. The assessments of polluted degree and potential ecological hazards of heavy metals in suburban soil of Guangzhou city [J]. China Environmental Science, 2013, 33(S1): 49-53(in Chinese).
[30] 张桂芹, 谭路遥, 张怀成, 等. 济南城市主干道降尘重金属污染特征及生态风险评价 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2020, 29(1): 156-164. ZHANG G Q, TAN L Y, ZHANG H C, et al. Heavy metal pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of dust falling on urban main road in Jinan [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2020, 29(1): 156-164(in Chinese).
[31] 李少洛. 济南市降尘污染特征及组分来源解析[D]. 济南: 山东建筑大学, 2019. LI S L. Characteristics and source analysis of dust pollution in Jinan City[D]. Jinan: Shandong Jianzhu University, 2019.
[32] 孙友敏, 李少洛, 陈春竹, 等. 济南市机动车排气污染特征及对市区PM2.5的影响 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(4): 1384-1391. SUN Y M, LI S L, CHEN C J, et al. Study on characteristics of vehicle exhaust and the influence on PM2.5 in Jinan City [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2018, 38(4): 1384-1391(in Chinese).
-




 下载:
下载: