-
随着冶金、采矿、核能和化学制造业的快速发展,大量有毒重金属离子释放到自然环境中,对地表和地下环境构成了严重威胁[1-2]。具有高毒性和强渗透性的重金属离子容易在生物体中不断积累。其中大部分已知的重金属都具有剧毒或致癌作用[3-4],例如,镉会导致高血压,引起心脑血管疾病,还会破坏骨钙,引起肾功能失调[5-6]。因此,有效地从环境中去除有害重金属离子仍然是一项非常重要但又具有挑战性的环境污染治理工程。
迄今为止,去除重金属离子的技术主要包括吸附[7-8]、化学沉淀法、膜过滤、离子交换、光催化降解、混凝、氧化还原和溶剂萃取等。在这些方法中,吸附技术因其成本低廉、操作简单、实用性强、环境友好以及吸附剂再生简单等原因,已成为最普遍和有效的技术之一[9-10]。
纳米级零价铁(nZVI)是一种环境友好的材料,具有出色的迁移率、高反应活性、低毒性、可控制的粒径和丰富的表面活性部位,因此被用作消除重金属离子的有效吸附剂。尽管nZVI(零价铁)具有去除污染物的功效,但在实际应用中仍然存在一些局限性,例如易聚集、不稳定、易氧化和二次污染[11-12]。为了解决上述问题,常用的改性方法有表面改性nZVI[13-14]、多孔材料负载nZVI[15-17]和无机黏土矿物负载nZVI[18]。其中负载nZVI的多孔材料因其高比表面积、空隙结构和独特的性能而备受关注。研究人员将nZVI固定在多孔固体载体材料上不仅抑制nZVI的氧化和聚集,还增加了表面积和稳定的脱除部位,更有效地从环境中去除污染物。在众多nZVI基材料中,石墨族材料优异的理化性质及吸附重金属离子的能力引起了广泛的研究兴趣。本文重点介绍了石墨基负载nZVI复合材料去除几种常见的重金属离子(例如Cr、Pb、U、Cu、Co和Cd等)的研究。
-
石墨基nZVI复合材料对环境中重金属离子的吸附能力都较强,表1以Cr(Ⅵ)离子为例列出了不同材料的吸附热力学参数和吸附效果,由表1可知,负载nZVI的复合材料的吸附性能和理化性能较nZVI均有明显提高。
-
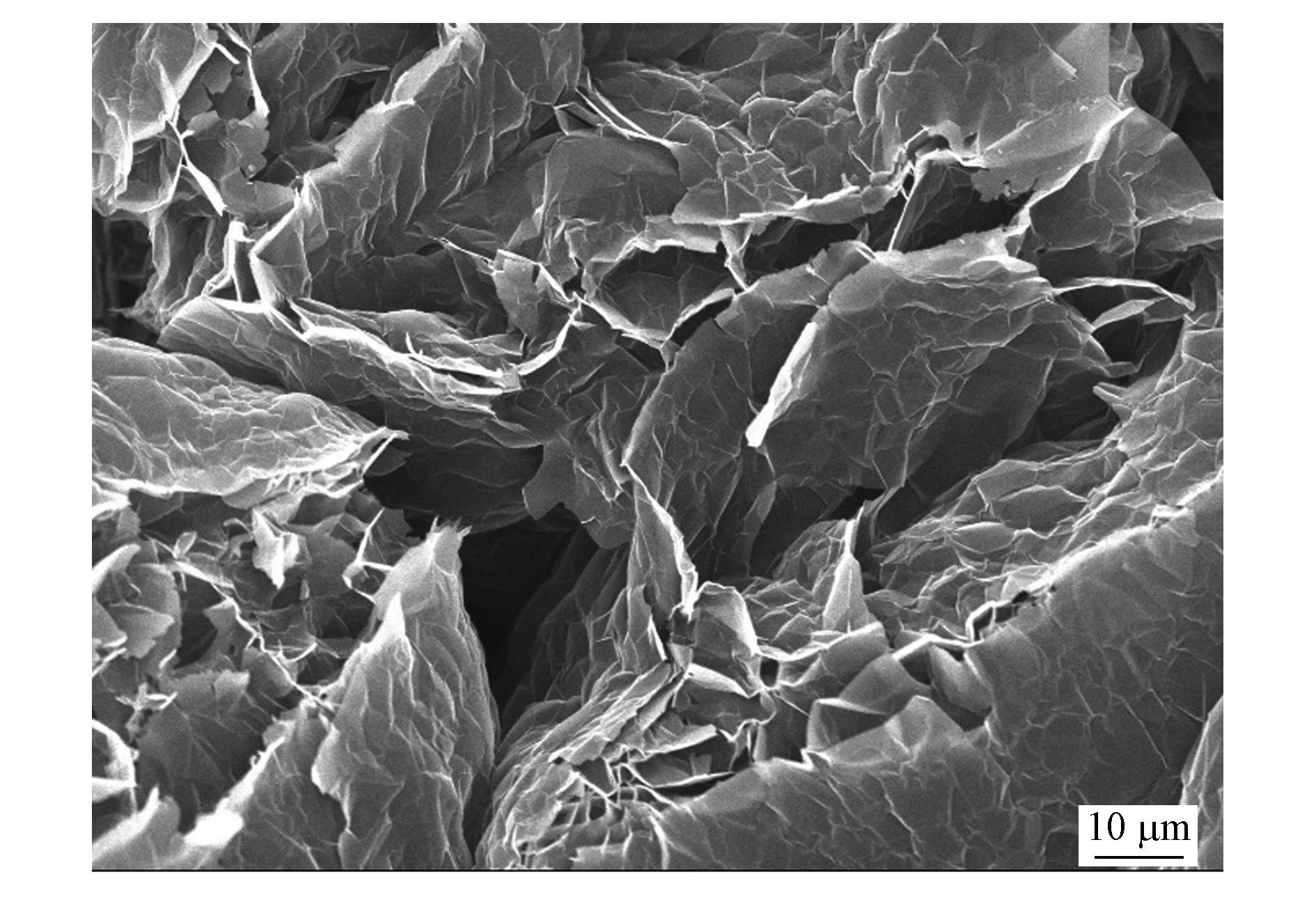
石墨烯(graphene)是一种新型2维碳材料,具有较大的比表面积,易于与其他材料结合,而且具有优良性能的层状结构和选择性吸附能力[26-29]。为了改善nZVI电子传递效率、提高还原效率和增强分散性,Jabeen等[20]制备了零价纳米铁(nZVI)掺杂的石墨烯复合材料。图1是G-nZVI和nZVI的SEM图,G-nZVI的比表面积为170.0 m2·g−1,而nZVI的比表面积仅为56.0 m2·g−1。随着比表面积增大,对Cr(Ⅵ)的最大吸附量从148.0 mg·g−1增加到162.0 mg·g−1。还有研究将Fe3O4/石墨烯作为载体,将nZVI颗粒均匀分散在Fe3O4纳米颗粒之间或石墨烯基面[30]。该材料对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除率达到83.8%。可以看出石墨烯与nZVI结合比表面积明显增大,同时吸附能力增强。近几年研究发现,石墨烯还有两种衍生产物,一种是对石墨烯进行氧化得到的氧化石墨烯[31];另一种是将氧化石墨烯还原得到的还原氧化石墨烯。
-
氧化石墨烯(GO)具有高表面积和易进行功能化的表面。但是还是存在一些局限性,越来越多的GO基纳米复合材料吸引着环境应用领域的关注[32-35]。Yu等[36]利用液相氧化还原法合成氧化石墨烯/膨润土负载零价纳米铁的复合材料,结合氧化石墨烯的片状结构和膨润土的层状结构有效地分散纳米铁颗粒,对铅离子的去除效率几乎达到100%。还有Mandal等[37]将石墨烯和零价纳米铁与生物炭结合(CTBC-GO/nZVI)用于固定土壤中的铜。实验表明,CTBC-GO/nZVI对铜的固定化效果优于原生生物炭和GO-BC。并在使用14 d后,依旧有效去除铜65.0%以上。说明这类复合材料较好地解决了nZVI的易氧化和团聚的问题,在实际运用中具有一定价值。
-
还原氧化石墨烯(rGO)是一种具有超薄二维结构的纳米材料,rGO表面所携带的官能团能够通过产生静电斥力提高Fe0颗粒的分散性;而且rGO具有较大的比表面积,能够为污染物的吸附提供更多接触点[22,38-39]。董军等[40]制备了还原氧化石墨烯负载零价铁复合材料(rGO-nZVI),nZVI和rGO-nZVI复合材料的SEM和XRD如图2所示,nZVI呈球形,分散于rGO片状颗粒上。比表面积有显著提高,提供了更多的反应位点和更高的反应活性,几乎可以完全去除Cr(Ⅵ)。Zhang等[41]在这基础上制备了三元纳米复合材料,加入了聚吡咯(PPy),PPy和Fe0的加入解决了rGO选择性差和吸附量低的问题,对铀离子的去除率达到95.0%以上。Chen等[42]制备的零价铁-聚苯胺-石墨烯气凝胶复合材料(Fe-PANI-GA)在pH=5.5时,Fe-PANI-GA对U(Ⅵ)的最大去除能力达350.5 mg·g−1。以上研究结构表明,rGO-nZVI基三元纳米复合材料对重金属离子有较强的吸附能力。
-
膨胀石墨内部孔隙发达,结构松散(如图3)。极易吸附油类、有机分子及疏水性物质,同时也对重金属离子也有一定的吸附性[43],在废水处理领域是一种不可替代优良吸附剂。 Xu等[23,44]将nZVI负载到膨胀石墨(EG)上,制备出复合材料(EG-nZVI),比表面积高达296.0 m2·g−1,并且含有亚微米级的零价铁颗粒,能有效去除铬离子(Cr(Ⅵ))和铅离子(Pb(Ⅱ)),对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除率为98.8%,对Pb(Ⅱ)的去除率是nZVI的1.4倍。此外,EG可以有效抑制nZVI的表面形成不良的氢氧化亚铁沉淀,大大提高了EG-nZVI对重金属的去除能力。
-
探索石墨基负载nZVI复合材料吸附重金属离子的机理研究是解释反应过程的关键,有利于吸附条件和解吸再生条件的优化。常见的反应机制包括吸附、氧化还原、离子交换和沉淀,吸附和还原过程是石墨基负载nZVI复合材料与重金属离子最主要的作用机制。
-
吸附是典型的去除重金属离子的过程,吸附机理一般包括物理吸附和化学吸附。石墨基负载nZVI复合材料因表面丰富的反应位点和官能团使它们有效去除重金属离子。为确定主要机理,采用光谱分析、表面络合模型和理论计算等方法对吸附行为进行了研究。
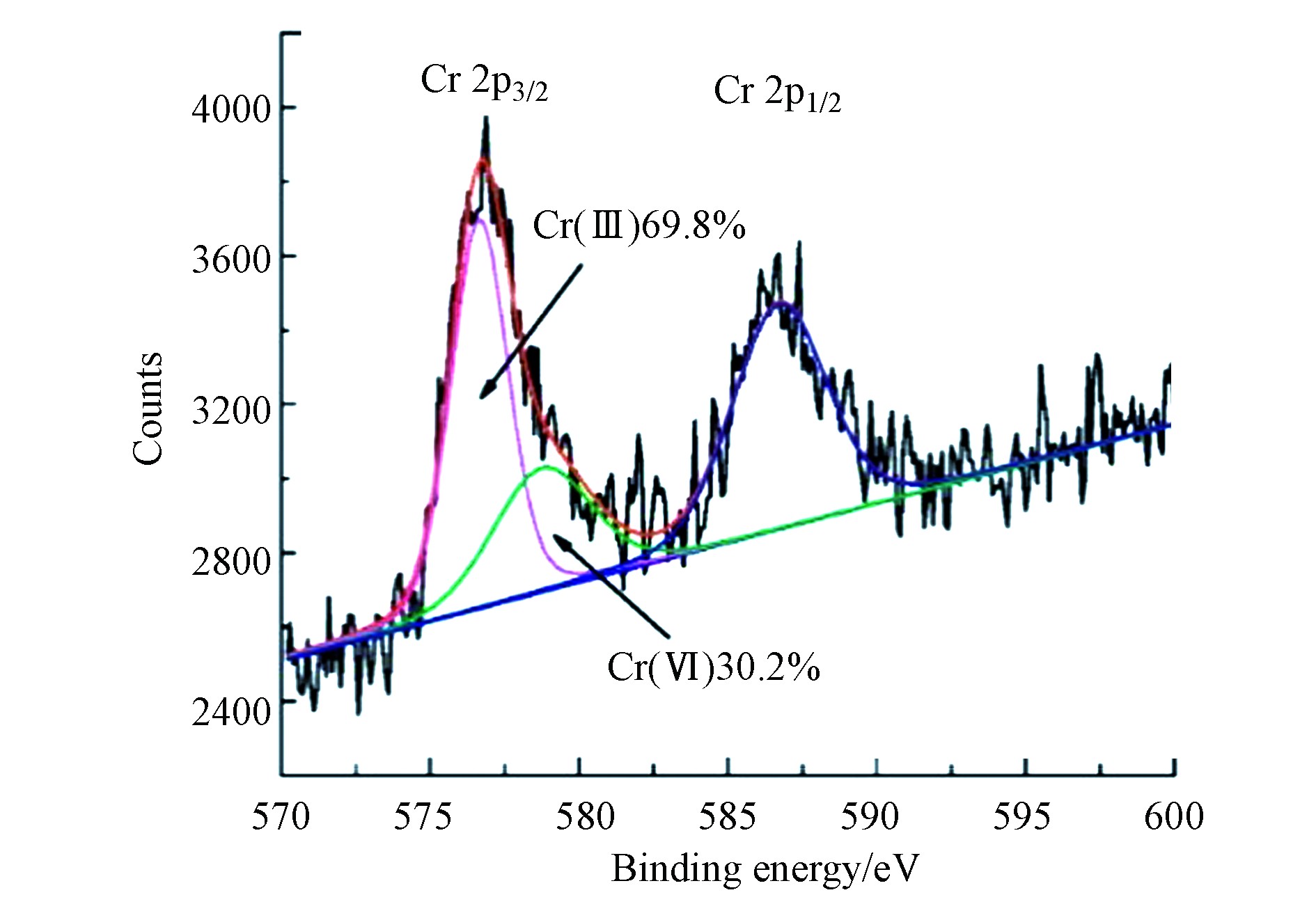
不同的重金属离子的吸附机理有较大区别。对于铬离子,rGO-nZVI和G-nZVI去除Cr(Ⅵ)涉及了吸附和还原[45],如图4所示的Cr2p区域中,X射线光电子能谱被分解为两个组分,在579.4 eV处存在Cr(Ⅵ),在576.6 eV处存在Cr(Ⅲ),表明Cr(Ⅵ)在rGO-nZVI表面富集且Cr(Ⅵ)被还原为Cr(Ⅲ)。然而,Li等[46]发现rGO-nZVI吸附Cd(Ⅱ)是通过静电相互作用和比表面键,而不是氧化还原过程造成的。
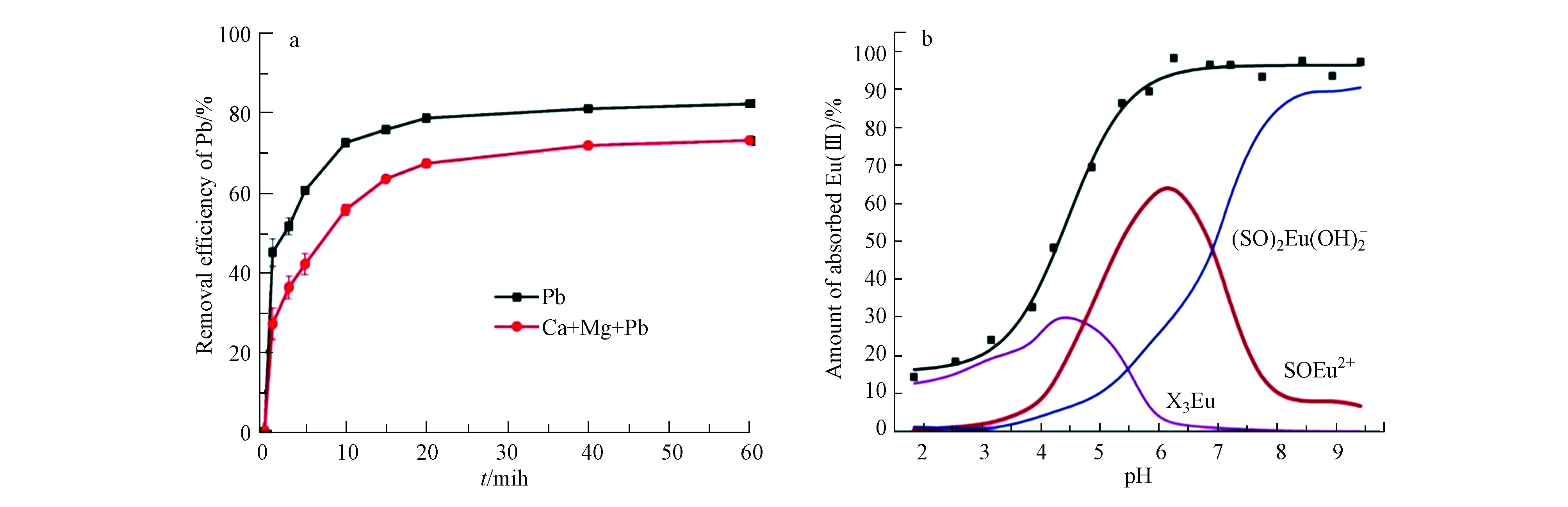
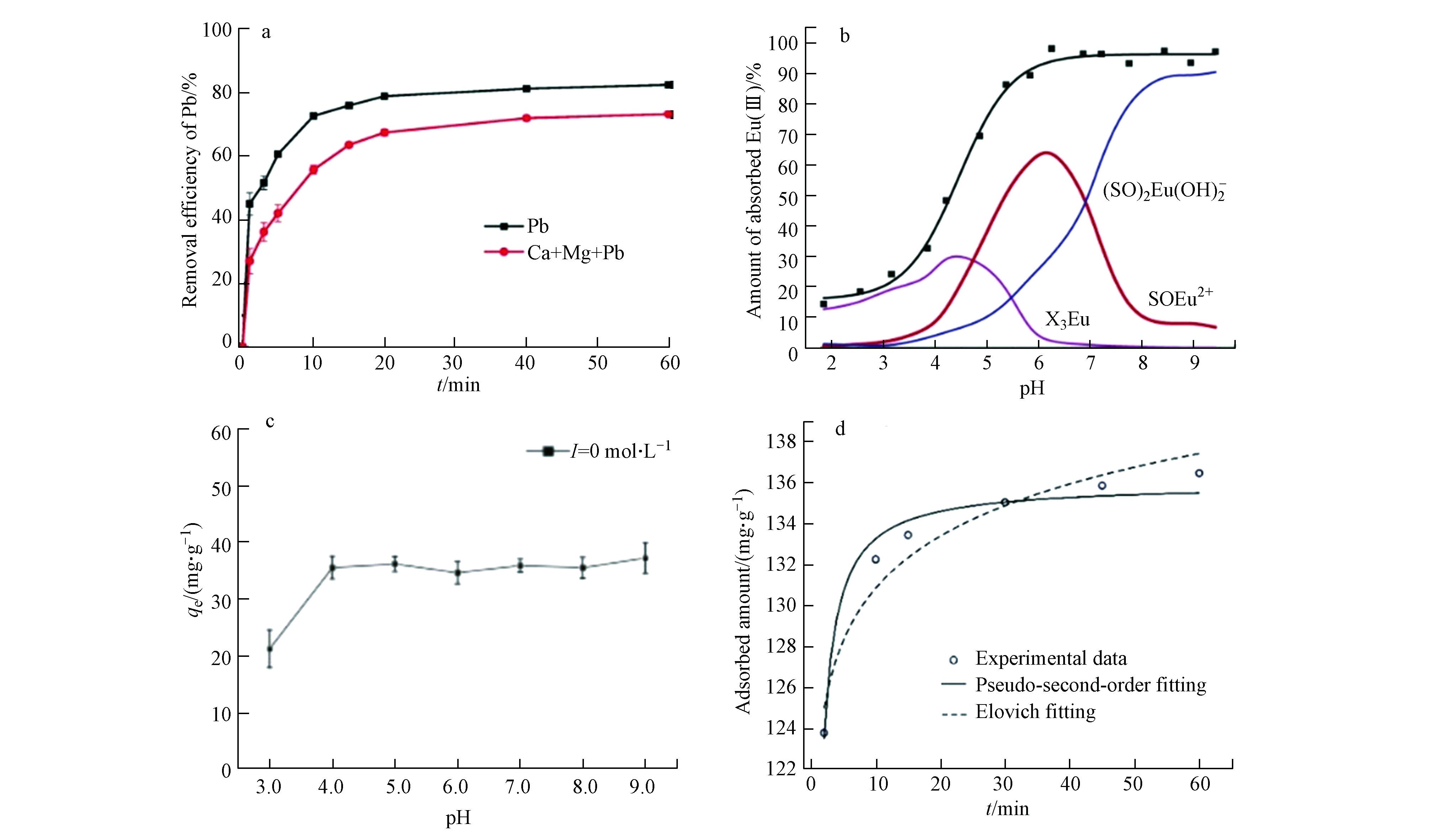
此外,石墨基负载nZVI复合材料吸附重金属离子具有一些明显的特点,如吸附过程均表现为先快后慢。图5是rGO-nZVI吸附Pb(Ⅱ)的机理[47],最初是rGO上的nZVI的外表面对Pb(Ⅱ)快速的物理吸附,然后是较慢的化学吸附,铅离子通过形成化学键粘附在石墨烯片表面,完成了对铅离子的吸附,然后再对吸附在材料表面的Pb(Ⅱ)进行还原。另外,吸附具有选择性,如当Ca(Ⅱ)和Mg(Ⅱ)作为Pb(Ⅱ)的竞争性离子时[48],如图6a,rGO-nZVI任对Pb(Ⅱ)吸附表现出较高选择性。而在实际应用中,反应体系包含多种共存的重金属离子,复杂的相互作用应该是相当繁琐的。为了进一步了解重金属离子在nZVI基材料上的相互作用机理,Zhu等[49]利用表面络合建模研究rGO-nZVI对Eu(Ⅲ)的吸收行为。拟合结果如图6b可知,吸附行为可以通过阳离子交换中心(XNA)和表面络合中心(SOH)的扩散层模型进行模拟。结果表明,当pH<4.5时,rGO-nZVI对Eu(Ⅲ)的吸附主要是阳离子交换反应;当pH>5.0时,rGO-nZVI主要吸附(SO)2Eu(OH)2-内层络合物。在废水处理中,多数情况下,往往是几种吸附作用的结果
-
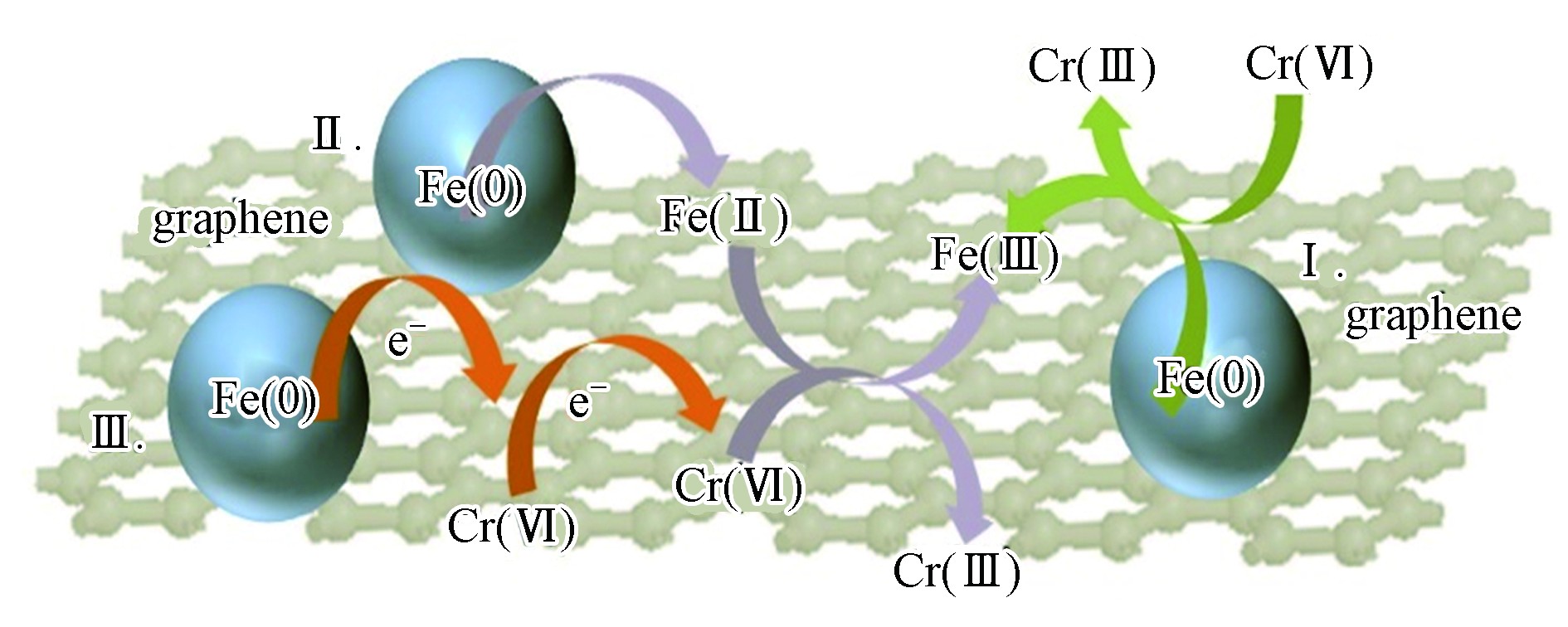
一般情况下,nZVI作为许多重金属离子的电子供体,nZVI基材料与重金属离子之间重要的相互作用便是氧化还原反应,存在的还原机理有两种:(1)nZVI基材料直接还原重金属离子;(2)重金属离子吸附在nZVI基材料上,引起其表面价态的变化,使吸附的重金属离子从高价逐渐减少到低价。在一些文献[23,25,29,39,45]中发现nZVI在还原Cr(Ⅵ)的反应中起了重要作用,通常分为3种路径,如图7所示,路径I是nZVI直接将电子转移还原Cr(Ⅵ)。路径II是表面形成的Fe(Ⅱ)与Cr(Ⅵ)之间自发的还原反应。路径Ⅲ是石墨基材料与nZVI之间可能存在电子转移行为,石墨基材料作为介质,有效地从nZVI转移电子还原Cr(Ⅵ),从而延缓了nZVI的表面钝化。这些研究表明,Fe(0)、Fe(Ⅱ)和Fe(Ⅲ)可能同时参与了Cr(Ⅵ)的还原反应,直至Cr(OH)3沉淀物和Cr3+-Fe3+共沉积物覆盖石墨基材料表面。
Li等[50]研究G-nZVI去除U(Ⅵ)的还原机理,可能发生的反应如下(1)—(4),同样,铁的3种价态物参与了还原反应,表明nZVI在还原反应中起着不可替代的主导作用。
综上所述,nZVI在吸附和还原反应中起着非常重要的作用。事实上,在环境应用中,各种材料之间可能存在吸附过程、还原过程、氧化过程甚至其他特殊的相互作用。然而,主要的相互作用归因于一种或两种。因此,需要通过更加真实的反应条件来了解重金属离子与nZVI基材料的相互作用机理。
-
一般来说,在溶液pH、接触时间、温度、吸附剂用量等条件下,吸附重金属离子的反应机理可以通过间歇吸附实验来验证。随着环境的变化,材料的性质、重金属离子的形式和吸附行为也发生改变。因此,评价重金属离子在废水中的环境效应具有重要意义。
-
溶液pH不仅影响材料的表面电荷,还会改变重金属离子的存在形式,从而影响nZVI基材料与重金属离子之间的相互作用。比如,带正电的吸附剂表面很容易吸附带负电荷的重金属离子;当pH<pHPZC(零电荷点)时,吸附剂带正电荷,而当pH>pHPZC时,吸附剂带负电荷。对于铬离子,无论溶液pH值如何,主要存在形式都是带负电荷。因此,带正电的吸附剂可以成功吸附Cr(Ⅵ)。如图8中a和b所示的石墨基负载nZVI复合材料[23,39],在酸性溶液中,Cr(Ⅵ)去除率几乎达到100%,但在碱性溶液中,Cr(Ⅵ)去除率明显下降。然而对于钴离子来说,在不同pH值下,钴的相对形态主要以Co2+、Co(OH)+、Co(OH)2和Co(OH)3-的形式存在。如图8c所示[18],当pH 3.0时,G-nZVI吸附剂表面带正电荷,排斥力阻碍了Co2+离子的迁移,吸附量较低,随着pH值的升高,静电斥力减小,在pH值为4.0—9.0时,对Co(Ⅱ)的吸附量维持在较高水平,故溶液pH对石墨基负载nZVI复合材料吸附重金属离子有着不可忽视的影响。整体来说,地下水的pH值一般在5.0—9.0之间,石墨基负载nZVI复合材料对Cr(Ⅵ)、Co(Ⅱ)、U(Ⅵ)、Pb(Ⅱ)、As(Ⅲ)等重金属离子的吸附均可在pH=5.0—9.0范围内进行。
-
为了考察重金属离子在石墨基负载nZVI复合材料上吸附的反应速率和实际应用潜力,应用准一级、准二级动力学模型探讨了接触时间对金属离子吸附的影响。根据复合材料与重金属离子相互作用机理,吸附速率随时间由快变慢,最终达到吸附平衡。不同的吸附材料达到吸附平衡的时间通常是不一样的,但大多符合准二级动力学模型,这表明主要的吸附机理是化学吸附,即吸附剂和吸附物之间通过共享或交换电子进行吸附。Kumarathilaka等[25]采用新型淀粉稳定纳米零价铁-石墨烯复合材料(G-nZVI)去除Cr(Ⅵ)。如图8d所示,准二阶非线性模型较好地描述了Cr(Ⅵ)吸附过程的动力学过程。预测出吸附容量约为137.0 mg·g−1。Zhang等[52]发现准二级模型较好地拟合了U(Ⅵ)在Fe-Ni/氧化石墨烯复合材料(Fe-Ni/GO)上的吸附动力学,进一步表明吸附过程不是物理吸附,而是化学吸附。因此,化学吸附在控制吸附速率中起着重要作用,同样对Pb(Ⅱ)[47]、Cd(Ⅱ)[46]和Eu(Ⅲ)[49]的吸附来说,随时间变化的吸附过程均表现为先快后慢的过程,可用准二级模型拟合较好描述。
-
温度可以改变反应体系的能量、去除率和吸附量,吸附等温线是描述温度对吸附行为影响的曲线,对优化吸附剂的应用至关重要。常用Langmuir、Freundlich、Temkin和Dubinin-Radushkevich模型描述了去除过程的吸附等温线。Langmuir模型是假设金属离子在均匀的表面上以单层吸附方式吸附,吸附剂之间不发生相互作用。而Freundlich模型本质上是经验模型,可以在非均相吸附剂表面上发生多层吸附。Kumarathilaka等[25]利用Langmuir、Freundlich、Temkin和Dubinin-Radushkevich等4种等温线模型拟合Cr(Ⅵ)在G-nZVI的去除,相关系数R2分别为0.962、0.949、0.948和0.789,R2值较的高的Langmuir等温线模型是描述G-nZVI吸附Cr(Ⅵ)的更好的匹配模型。同时,溶液温度的研究也可以表达重要的热力学参数值,如吉布自由能(ΔG0)、熵(ΔS0)和焓(ΔH0)。根据热力学参数,Chen等[42]表明零价铁-聚苯胺-石墨烯气凝胶三元复合材料(Fe-PANI-GA)吸附U(Ⅵ)是吸热反应。而且ΔG值为负值并随温度的升高而下降,说明吸附过程是自发的,表明材料具有良好的吸附稳定性。
-
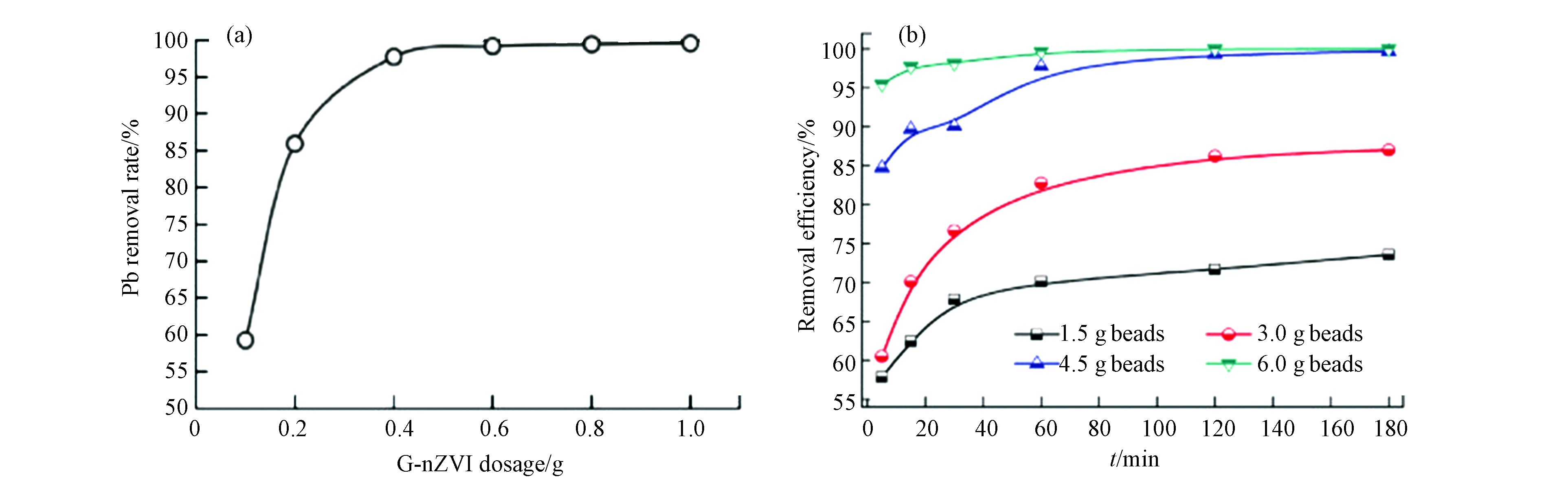
吸附剂用量也是影响去除率的关键因素之一,最佳吸附剂用量可以其更有经济应用价值。可以通过采用最佳吸附剂用量来提高重金属离子的去除效率。如图9a所示,为了最大化去除效率和经济性,陈等[53]选择G-nZVI投入量为0.6g去除Pb(Ⅱ),去除效率高达95.0%以上。另一项研究中,采用不同投加量的还原氧化石墨烯-海藻酸钠-零价纳米铁(GA-nZVI)去除吸附Cr(Ⅵ)[54],如图9b显示,当GA-nZVI用量从1.5 g增加到4.5 g时,去除效率从73.6%提高到99.7%。当添加6.0gGA-nZVI时,1 h内Cr(Ⅵ)的去除率接近100%。但过量添加GA-nZVI对进一步改善效果有限,且不经济。故使用了3.0 g的GA-nZVI。
综上所述,环境条件对石墨基负载nZVI复合材料吸附重金属离子有明显的影响,其去除能力与溶液pH、接触时间、温度和吸附剂用量等因素密切相关。实际应用中的水环境条件通常非常复杂,导致重金属离子在水环境中的渗透和迁移也是复杂的、非线性的,因此,应充分研究不同环境条件下新型纳米材料对污染物的吸附性能和潜在反应机理,为进一步研究水界面吸附行为提供参考。
-
在石墨基负载nZVI复合材料吸附重金属离子过程中,石墨基材料和nZVI的相互作用明显影响各种重金属离子在废水中的毒性、积累、粘附和迁移,在污染物去除和环境原位修复方面显示出巨大的潜力。到目前为止大多数的研究表明,石墨基负载nZVI复合材料吸附重金属离子的最佳pH值为4.0至7.0,符合水环境范围(pH=5.0—9.0),吸附实验和理论研究也证实了自然环境中这类复合材料上的吸附过程大多是还原反应和单层分子吸附,且大多数性能优良的石墨基负载nZVI复合材料可在室温表现出较大的吸附容量和去除性能。
石墨基负载nZVI复合材料有望成为重金属离子的高效吸附剂和还原剂,用于环境修复,为有效去除水溶液中的环境污染物提供了一种简便可行的途径。虽然该技术到目前还没有得到广泛应用,但随着对重金属离子的环境行为、修复机理的深入研究,以及经济绿色合成新型纳米材料技术形成和回收纳米材料技术的进步,石墨基负载nZVI复合材料在重金属离子治理领域将会实现规模化推广和商业化应用。
石墨基复合材料负载零价纳米铁吸附重金属离子的研究进展
Research progress on adsorption of heavy metal ions by graphite based composites supported with nano zero valent iron
-
摘要: 工业废水中重金属的存在威胁着环境和人类健康,有效去除环境中的重金属离子具有重要意义。论文简要介绍了近年来石墨基复合材料负载纳米零价铁(nZVI)去除废水中重金属离子的研究,探讨了多种石墨基负载nZVI复合材料对重金属离子的吸附特性和环境条件对吸附性能的影响因素,并对其未来的研究和应用进行了总结和展望。Abstract: The presence of heavy metals in industrial wastewater threatens the environment and human health, and it is of great significance to effectively remove heavy metal ions in the environment. The paper briefly introduced the recent research on graphite-based composite materials loaded with nano-zero-valent iron (nZVI) to remove heavy metal ions from surface and underground wastewater, and discussed the adsorption characteristics of various graphite-based composite materials on heavy metal ions and environmental conditions for adsorption The influencing factors of performance, and its future research and application are summarized and prospected.
-
Key words:
- graphite-based composites /
- nano zero valent iron /
- adsorption /
- heavy metal ions /
- research progress
-

-
图 8 (a)pH对EG-nZVI去除Cr(Ⅵ)的影响[23];(b)pH对rGO-nZVI去除Cr(Ⅵ)的影响[39];(c)pH对G-nZVI去除Co(Ⅱ)的影响[18];(d)Cr(Ⅵ)的伪二阶动力学模型和Elovich动力学模型[25]
Figure 8. (a) Effect of pH on Cr (Ⅵ) removal by EG-nZVI[23]; (b) Effect of pH on Cr (Ⅵ) removal by rGO-nZVI[39]; (c) Effect of pH on Co (Ⅱ) removal by G-nZVI[18]; (d) Effect of pH on the removal of As (Ⅴ) and As (Ⅲ) by rGO-nZVI[51]
表 1 石墨基负载nZVI复合材料对Cr(Ⅵ)离子的吸附热力学参数和吸附效果等主要参数对比
Table 1. comparison of adsorption thermodynamic parameters and adsorption efficiency of graphite-based nZVI composites for Cr(Ⅵ) ion
吸附剂
Adsorbent比表面积/(m2 ·g−1)
Specific surface area温 度
Temperature最适pH
Optimal pH吸附/(mg ·g−1)
Adsorption去除率/%
Removal rate参考文献
ReferencesnZVI 33.5 — 5.0 47.2 — [19] G-nZVI 170.0 室温 4.2 162.0 — [20] G-nZVI — 室温 3.0 — 95.0↑ [21] rGO-nZVI 118.0 室温 5.0 187.2 — [22] EG-nZVI 296.0 室温 3.0 — 98.8 [23] GO-nZVI/BC — 室温 2.0 490.2 — [24] 淀粉+G-nZVI 525.0 室温 3.0 143.3 — [25] -
[1] HUSSAIN M A, ZAMAN S, ABBAS A, et al. Sodium hyroxyethylcellulose adipate: An efficient and reusable sorbent for cadmium uptake from spiked high-hardness ground water [J]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 2018, 13: 2766-2777. [2] YU S J, LIU Y, AN Y J, et al. Rational design of carbonaceous nanofiber/Ni-Al layered double hydroxide nanocomposites for high-efficiency removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 242: 1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.06.031 [3] XU L, HUO X, LIU Y, et al. Hearing loss risk and DNA methylation signatures in preschool children following lead and cadmium exposure from an electronic waste recycling area [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 246: 125829. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.125829 [4] SHAH S, JEONG K S, PARK H, et al. Environmental pollutants affecting children's growth and development: Collective results from the MOCEH study, a multi-centric prospective birth cohort in Korea [J]. Environment International, 2020, 137: 105547. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.105547 [5] NWOKOCHA C R, PALACIO J, RATTRAY V R, et al Protective effects of apocynin against cadmium toxicity and serum parameters; evidence of a cardio-protective influence[J]. Inorganica Chimica Acta, 2020, 503: 119411. [6] JARUP L, AKESSON A. Current status of cadmium as an environmental health problem. [J]. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2009, 238(3): 201-208. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2009.04.020 [7] KHAN Z H, GAO M L, QIU W W, et al. Mechanisms for cadmium adsorption by magnetic biochar composites in an aqueous solution [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 246: 125701. [8] MASHKOOR F, NASAR A. Magsorbents: Potential candidates in wastewater treatment technology – A review on the removal of methylene blue dye [J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2020, 500: 166408. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2020.166408 [9] WU Y H, PENG H W, LIU Y, et al. Environmental remediation of heavy metal ions by novel-nanomaterials: A review [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 246: 608-620. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.12.076 [10] ZOU Y D, WANG X X, KHAN A, et al. Environmental Remediation and Application of Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron and Its Composites for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions: A Review [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(14): 7290-7304. [11] 陈海军, 黄舒怡, 张志宾, 等. 功能性纳米零价铁的构筑及其对环境放射性核素铀的富集应用研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(6): 560-574. CHEN H J, HUANG S Y, ZHANG Z B, et al, Synthesis of Functional nanoscale zero-valent iron composites for the application of radioactive uranium enrichment from environment: A review[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2017, 75(6): 560-574(in Chinese).
[12] 张玉荣, 吴杰, 朱慧杰, 等. 纳米铁负载材料应用研究 [J]. 河南城建学院学报, 2012, 21(1): 35-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7046.2012.01.010 [13] LI M Q, MU Y, SHANG H, et al. Phosphate modification enables high efficiency and electron selectivity of nZVI toward Cr(Ⅵ) removal [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2020, 263: 118364. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118364 [14] LIU J, LIU A, ZHANG W X. The influence of polyelectrolyte modification on nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI): Aggregation, sedimentation, and reactivity with Ni(Ⅱ) in water [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 303: 268-274. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.05.132 [15] WANG M, CHENG W, WAN T, et al. Mechanistic investigation of U(Ⅵ) sequestration by zero-valent iron/activated carbon composites [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 362: 99-106. [16] GOSWAMI A, KADAM R G, TUCEK J, et al. Fe(0)-embedded thermally reduced graphene oxide as efficient nanocatalyst for reduction of nitro compounds to amines [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 382: 122469. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122469 [17] HUANG L H, ZHOU S J, JIN F, et al. Characterization and mechanism analysis of activated carbon fiber felt-stabilized nanoscale zero-valent iron for the removal of Cr(Ⅵ) from aqueous solution [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2014, 447: 59-66. [18] XING M, XU L J, WANG J L. Mechanism of Co(Ⅱ) adsorption by zero valent iron/graphene nanocomposite. [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016, 301: 96-286. [19] MONTESINOS V N, QUICI N HALAC E B, et al. Highly efficient removal of Cr(Ⅵ) from water with nanoparticulated zerovalent iron: Understanding the Fe(Ⅲ)–Cr(Ⅲ) passive outer layer structure [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 244: 569-575. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.01.093 [20] JABEEN H, CHANDRA V, JUNG S, et al. Enhanced Cr(Ⅵ) removal using iron nanoparticle decorated graphene. [J]. Nanoscale, 2011, 3(9): 3583-3585. doi: 10.1039/c1nr10549c [21] 袁永海, 尹昌慧, 施意华, 等. 石墨烯负载零价纳米铁材料的合成及去除水中Cr(Ⅵ)的研究 [J]. 中国无机分析化学, 2017, 7(2): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2017.02.001 YUAN Y H, YIN C H, SAHI Y H, et al. Synthesis of Graphene-sopported Nano Fe(0) and Removal of Cr(Ⅵ) from Aqueous Solution. Chinese [J]. Journal of Inorganic Analyital Chemistry, 2017, 7(2): 1-5(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2017.02.001
[22] LI J, CHEN C L, ZHANG R, et al. Nanoscale zero-valent iron particles supported on reduced graphene oxides by using a plasma technique and their application for removal of heavy-metal ions. [J]. Chemistry, An Asian Journal, 2015, 10(6): 1410-1417. doi: 10.1002/asia.201500242 [23] XU C B, YANG W J, LIU W J, et al. Performance and mechanism of Cr(VI) removal by zero-valent iron loaded onto expanded graphite [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2018, 67: 14-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2017.11.003 [24] SHANG J G, GAO J, XI J T, et al. Immobilization of Cr(Ⅵ) from solution by a graphene oxide‐nZVI/biochar composite [J]. Water Environment Research, 2019, 91(7): 565-572. doi: 10.1002/wer.1059 [25] KUMARATHILAKA P, JAYAWEERA V, WIJESEKARA H, et al. Insights into Starch coated nanozero valent iron-graphene composite for Cr(Ⅵ) removal from aqueous medium [J]. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2016, 2016: 1-10. [26] 王灿. 石墨烯负载零价纳米铁去除水中砷的研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2014. WANG C, Removal of As(Ⅲ) and As(Ⅴ) from aqueous solutionsusing nanoscale zero valent iron-reduced graphite oxidemodified composites[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2014(in Chinese).
[27] ZHANG K, DWIVEDI V, CHI C Y, et al. Graphene oxide/ferric hydroxide composites for efficient arsenate removal from drinking water [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 182(1-3): 162-168. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.06.010 [28] 郭绍雄, 李悦, 胡增荣, 等. 石墨烯增强铜基复合材料的研究进展 [J]. 热加工工艺, 2019, 49(6): 17-31. GUO S X, LI Y, HU Z R, et al. Research progress of graphene reinforced copper matrix composites [J]. Hot Working Technology, 2019, 49(6): 17-31(in Chinese).
[29] 冯新, 刘志烽, 万俊杰, 等. 纳米铁/石墨烯插层复合材料制备及Cr 6+去除 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2019, 42(1): 15-22. FENG X, LIU Z F, WAN J J, et al. Synthesis of nano zero-valent iron intercalated graphene and removal of Cr6+ [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 42(1): 15-22(in Chinese).
[30] LV X S, XUE X Q, JIANG G M, et al. Nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) assembled on magnetic Fe3O4/graphene for chromium (Ⅵ) removal from aqueous solution [J]. Journal of colloid and Interface Science, 2014, 417: 51-59. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2013.11.044 [31] SHAO D D, HOU G S, LI J X, et al. PANI/GO as a super adsorbent for the selective adsorption of uranium(Ⅵ) [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 255: 604-612. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.06.063 [32] GUO J, WANG R Y, TJIU W W, et al. Synthesis of Fe nanoparticles@graphene composites for environmental applications [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2012, 225-226: 63-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.04.065 [33] NG S W, NOOR N, ZHAENG Z J. Graphene-based two-dimensional Janus materials [J]. NPG Asia Materials, 2018, 10: 217-237. doi: 10.1038/s41427-018-0023-8 [34] MEHRABI N, MASUD A, AFOLABI M, et al. Magnetic graphene oxide-nano zero valent iron (GO–nZVI) nanohybrids synthesized using biocompatible cross-linkers for methylene blue removal [J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(2): 963-973. doi: 10.1039/C8RA08386J [35] 张一铭. 氧化石墨基复合材料的制备及铀吸附性能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2019. ZHANG Y M, Preparation and adsorption properties of uranium on graphene oxide composite material[D]. Haerbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2019(in Chinese).
[36] YU C, SHAO J C, SUN W J, et al. Treatment of lead contaminated water using synthesized nano-iron supported with bentonite/graphene oxide [J]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 2020, 13(1): 3474-3483. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2018.11.019 [37] MANDAL S, PU S Y, HE L L, et al. Biochar induced modification of graphene oxide & nZVI and its impact on immobilization of toxic copper in soil [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 259: 113851. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113851 [38] SUN Y B, DING C C, CHENG W C, et al. Simultaneous adsorption and reduction of U(Ⅵ) on reduced graphene oxide-supported nanoscale zerovalent iron [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 280: 399-408. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.08.023 [39] REN L M, DONG J, CIN Z F, et al. Reduced graphene oxide-nano zero value iron(rGO-nZVI) micro-electrolysis accelerating Cr(Ⅵ) removal in aquifer [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2018, 73(11): 96-106. [40] 董军, 任黎明, 迟子芳, 等. 氧化石墨烯负载纳米零价铁(rGO-nZⅥ)去除地下水中Cr(Ⅵ)的XPS谱学表征 [J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2017, 37(1): 250-255. DONG J, REN L M, CHI Z F, et al. Analysis of XPS in the removal of Cr(Ⅵ) from groundwater with rGO-nZⅥ [J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2017, 37(1): 250-255(in Chinese).
[41] ZHANG Y M, ZHANG H S, LIU Q, et al. Polypyrrole modified Fe0-loaded graphene oxide for the enrichment of uranium(VI) from simulated seawater [J]. Dalton Transactions, 2018, 47: 12984. doi: 10.1039/C8DT02819B [42] CHEN L L, FENG S J, ZHAO D L, et al. Efficient sorption and reduction of U(Ⅵ) on zero-valent iron-polyaniline-graphene aerogel ternary composite [J]. Journal of Colloid And Interface Science, 2017, 490: 197-206. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2016.11.050 [43] 徐珊, 于艳, 曹宝月, 等. 膨胀石墨负载氧化锌吸附废水中的Cr(Ⅵ) [J]. 水处理技术, 2019, 45(11): 76-79,84. XU S, YU Y, CAO B Y, et al. Adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ) in wastewater by expanded graphite supported zinc oxide [J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 2019, 45(11): 76-79,84(in Chinese).
[44] 徐从斌, 杨文杰, 孙宏亮, 等. 膨胀石墨负载零价铁的合成及其对水中Pb(Ⅱ)去除效果与机制 [J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(1): 41-47. doi: 10.15541/jim20170157 XU C B, YANG W J, SUN H L, et al. Performance and mechanism of Pb(Ⅱ) removal by expanded graphite loaded with zero-valent iron [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(1): 41-47(in Chinese). doi: 10.15541/jim20170157
[45] LI X Y, AI L H, JIANG J. Nanoscale zerovalent iron decorated on graphene nanosheets for Cr(Ⅵ) removal from aqueous solution: Surface corrosion retard induced the enhanced performance [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 288: 789-797. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.12.022 [46] LI J, CHEN C L, ZHU K, et al. Nanoscale zero-valent iron particles modified on reduced graphene oxides using a plasma technique for Cd(II) removal [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 288: 389-394. doi: 10.1016/j.jtice.2015.09.010 [47] JABEEN H, KEMP K C, CHANDRA V. Synthesis of nano zerovalent iron nanoparticles – Graphene composite for the treatment of lead contaminated water [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2013, 130(30): 429-435. [48] XIAO X F, WANG Q Q, OWENS G, et al. Reduced graphene oxide/iron nanoparticles used for the removal of Pb (Ⅱ) by one step green synthesis [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface ence, 2019, 557: 598-607. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.09.058 [49] ZHU H J, GAO H Y, HUANG X M, et al. The uptake of europium by reduced graphene oxide-supported nanoscale zerovalent iron investigated by batch and modeling techniques [J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2015, 3(4): 2974-2980. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2015.10.014 [50] LI Z J, WANG L, YUAN L Y, et al. Efficient removal of uranium from aqueous solution by zero-valent iron nanoparticle and its graphene composite [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 290(jun.15): 26-33. [51] WANG C, LUO H J, ZHANG Z L, et al. Removal of As(Ⅲ) and As(Ⅴ) from aqueous solutions using nanoscale zero valent iron-reduced graphite oxide modified composites [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 268(15): 124-131. [52] ZHANG Q, ZHAO D L, DING Y, et al. Synthesis of Fe–Ni/graphene oxide composite and its highly efficient removal of uranium(Ⅵ) from aqueous solution [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 230: 1305-1315. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.05.193 [53] 陈祝炳, 袁永海, 尹昌慧, 等. 石墨烯负载纳米铁对废水中铅的去除 [J]. 矿产与地质, 2017, 31(4): 808-811. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2017.04.024 [54] LV X S, ZHANG Y L, FU W Y, et al. Zero-valent iron nanoparticles embedded into reduced graphene oxide-alginate beads for efficient chromium (Ⅵ) removal [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2017, 506: 633-643. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2017.07.024 -




 下载:
下载: