-
随着经济的发展,环境污染问题日益严重. 在众多污染物里抗生素危害极大,它会诱导产生抗药菌和抗药基因,从而危害人和动物的健康. 其中,四环素(tetracycline)作为一种典型的抗生素,广泛应用于医药工业中,经常在废水中被监测到 [1]. 在过去几年中,物理化学技术,如氧化[2]、膜技术[3]和光催化[4]已被应用于处理抗生素废水. 其中,半导体光催化被认为是一种有效、绿色、节能的技术,而获得了广泛的关注.
二氧化钛(TiO2)作为典型的光催化剂,因其无毒、稳定性好和成本低,而被广泛应用[5]. 它有两种主要的晶型:锐钛矿、金红石. 其中,锐钛矿被广泛认为拥有良好的光催化性能[6];金红石的带隙宽度稍小于锐钛矿, 在光催化产H2中比锐钛矿效果更好[7]. 然而, Kawahara等认为混合晶型的TiO2比单一晶型拥有更高的光催化活性[8]. 为解决TiO2的带隙宽度大,可见光下效果差,光生电子和空穴复合速度快,光催化活性低等劣势. 研究者们采用复合其他材料来改善这些缺点. Wang等制备了TiO2/g-C3N4复合材料, 提高了光生载流子的迁移效率,减少复合率,增强了光催化降解四环素的效果[9];Hajipour 等用一种简单沉淀法制备出了TiO2/CuO复合材料,减小了带隙宽度,使材料可以在可见光下快速降解阿莫西林[10]; Ali 等将SBA 15和TiO2进行复合,使得TiO2的比表面积变大,反应活性位点增加,光催化性能提升[11].
碳量子点(CQDs)是一种碳基零维材料,被广泛用于光催化、生物传感和生物成像等技术领域[12-14]. CQDs可以作为复合材料的电子库,提高光生电子-空穴对的分离,拥有上转换光致发光特性,与其他半导体复合后可提高材料对可见光的利用率. 表面的官能团可以通过在光催化剂表面提供更高的吸附容量来增强光催化活性[15]. Wang等的研究表明,锐钛矿相二氧化钛在与碳量子复合后,在光催化下的产H2能力是以前的9. 7倍,复合材料表现出极高的光催化活性[16]; Muhammad等发现,当初始溶液pH 11时,CQD/TiO2对甲基橙废水的降解率是TiO2的3倍[17].
本研究研制了一种全新的CQDs/TiO2:首先制备了锐钛矿与金红石混相的TiO2,以葡萄糖为碳源制备了CQDs,后将两者合成了CQDs/TiO2纳米复合材料. 在可见光条件下降解四环素废水. 探究了不同条件下,复合材料对四环素废水的降解性能,并探究降解机理.
-
四异丙醇钛、乙醇、葡萄糖、氢氧化钠、氨水、四环素、对苯醌、四氯化碳、异丙醇、草酸铵、去离子水,0. 22 μm滤膜,透析袋(3500 MW),所用试剂均为分析纯.
-
TiO2纳米颗粒的制备 先将四异丙醇钛(4 mL)与乙醇(20 mL)混合,磁力搅拌1 h,超声30 min.与含H2O(4 mL)和乙醇(10 mL)的溶液混合,并将混合物保持在恒速下搅拌(1 h). 将混合物在水热反应釜中以180 ℃加热12 h. 收集的粉末用水和乙醇清洗,90 ℃干燥后在530 ℃下煅烧5 h.
CQDs的制备方法 首先,0.15 g葡萄糖加入40 mL水中,加入一定浓度的氨水并搅拌. 将溶液转移至100 mL聚四氟乙烯反应器中,然后以180 ℃在干燥箱中加热10 h. 再将其冷却至室温,用0.22 μm微孔膜去除大颗粒物质,通过透析袋(3500 MW)透析2 d,去除杂质离子. 即可得CQDs溶液,通过冷冻干燥可得到CQDs粉末.
CQDs/TiO2的制备方法. 先前制备的TiO2(0.64 g)分散于CQDs溶液中,加入20 mL蒸馏水,超声30 min,磁力搅拌3 h,使其混合均匀. 随后将溶液在烘箱中80 ℃干燥10 h,用去离子水离心洗涤4次并再次干燥,即获得CQDs/TiO2. 用不同葡萄糖含量(0.1 g、0.15 g、0.2 g)合成的复合材料分别记作为CT1、CT2、CT3.
-
采用X射线衍射仪(日本D/Max 2500)进行催化剂的晶体结构分析; X射线光电子能谱仪(美国Thermo Scientific K-Alpha)研究了催化剂中各种元素的表面化学成分和价态;透射电子显微镜 (日本JEOL JEM-F200)观察了材料形貌和晶格间距;全自动比表面及孔隙度分析仪(康塔Autosorb-IQ-MP)探究了复合材料的比表面积;傅里叶红外变换光谱仪(德国Bruker VERTEX70)分析了材料的化学键和官能团;紫外-可见分光光度计(日本Shimadzu UV-3600i Plus)探究了光学特征.
-
50 mg催化剂分散到50 mL四环素水溶液(10 mg·L−1)中. 在光催化实验开始之前,溶液在黑暗中搅拌30 min,以达到吸附-解吸平衡. 之后,开启氙灯,光催化反应开始. 定期从上清液中取出试样,并在12000 r·min−1下离心3 min,以去除固体颗粒,使用紫外-可见分光光度计测定四环素浓度.
为了评估纳米复合材料和嵌入在TiO2表面CQDs的稳定性,进行5次循环重复测试. 每次光催化反应后,以6000 r·min−1的转速离心4 min,收集光催化剂,用去离子水清洗,后在烘箱中60 ℃干燥,收集的光催化剂在相同条件下重复实验4次.
-
淬灭实验常用于探究光催化机理. 在其他条件不变的情况下,加入异丙醇(IPA,5 mmol)、四氯化碳(CCl4,5 mmol)、苯醌(BQ,1.5 mmol)、草酸铵(AO,5 mmol)分别作·OH、 e-、·O2-、h+的清除剂[18-21].
-
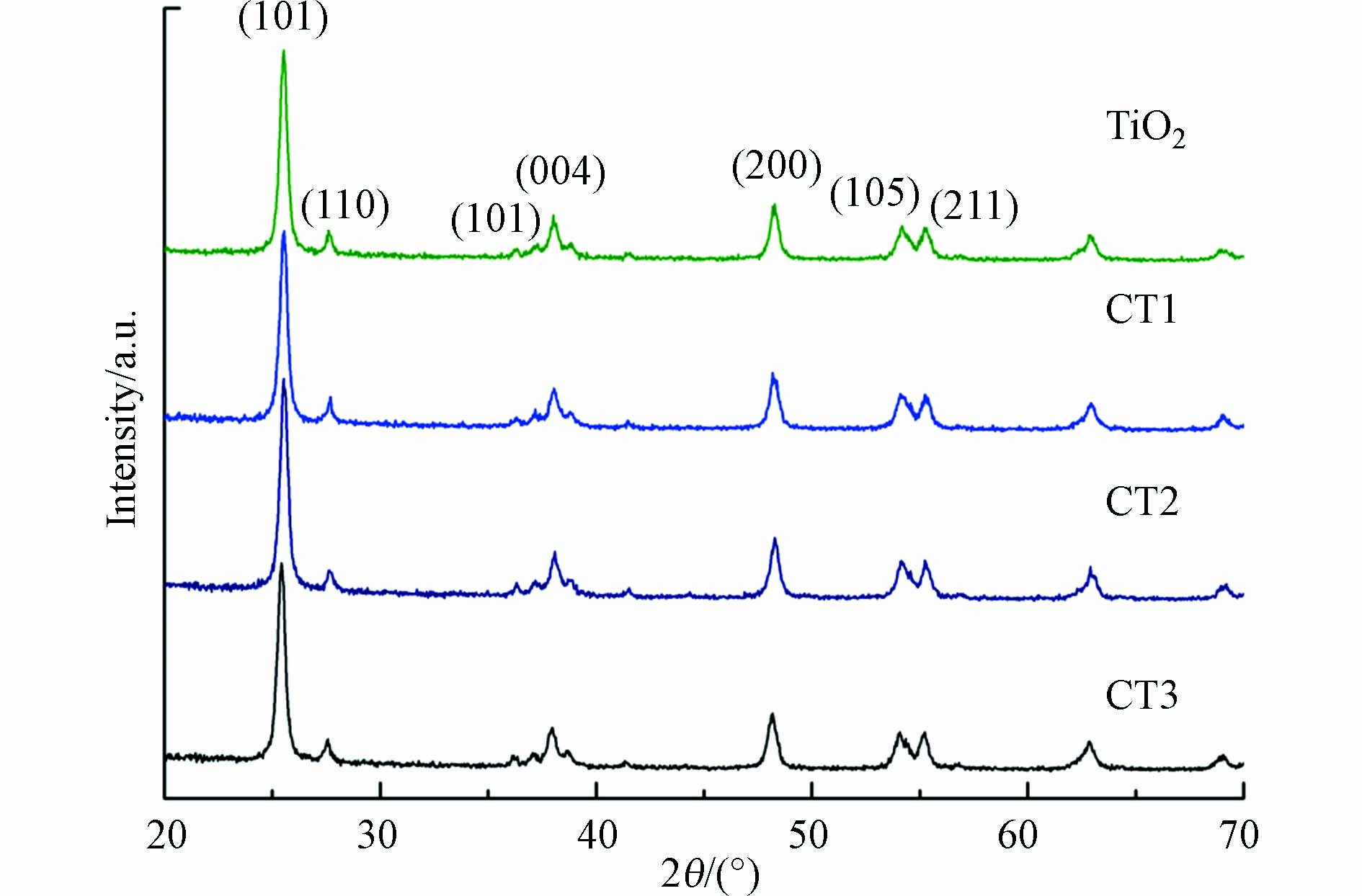
XRD分析如图1所示,对比PDF卡片,在TiO2和不同配比的CQDs/TiO2复合材料谱图中均检测到对应的晶面信息. 其中属于锐钛矿的峰有:25.3°(101)、37. 8°(004)、48.0°(200)、54.0°(105)、55.1°(211),属于金红石的峰有:27.4°(110)、36.1°(101). 证明混相TiO2制备成功. TiO2与CQDs/TiO2的峰形都没有明显的变化,说明CQDs的负载没有改变TiO2的晶体结构. 复合材料峰的位置几乎未发生偏移,这表明CQDs分散在TiO2表面,没有进入TiO2晶格[22]. 在复合材料的XRD图中没有检测到CQDs的衍射峰,表明掺杂没有导致生成其他物质. 也与CQDs掺杂量较低、结晶度差有关.
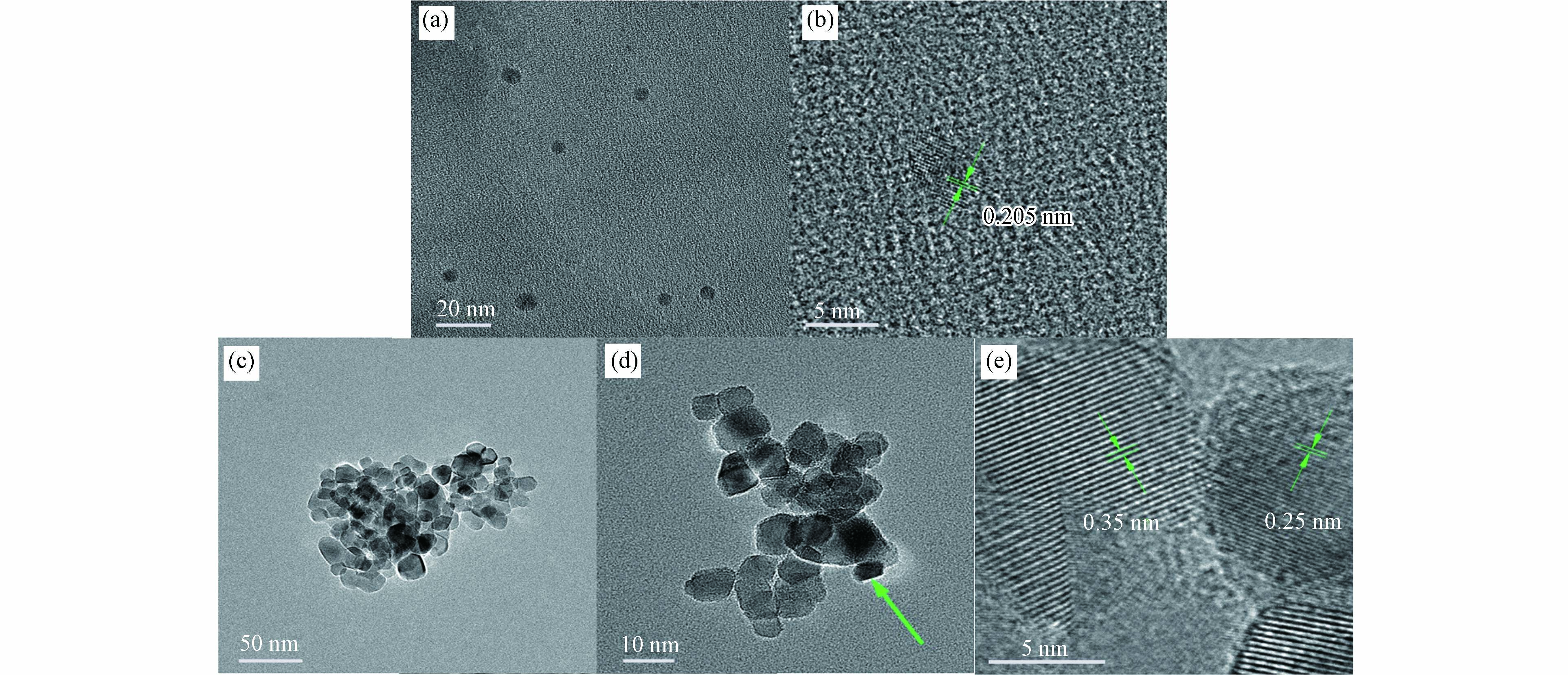
通过TEM和HR-TEM分析了CQDs和CQDs/TiO2纳米复合材料的形态外观. 图2a为通过水热法获得的CQDs的TEM图像. 这些制备的碳点呈球状,通过对此TEM图像测量后,发现直径为3.4 nm到5 nm. 图2b中显示CQDs的高分辨率HR-TEM图像,经过测量,晶格间距约为0.205 nm,对应的是石墨碳的(102)晶面[23]. 图2c为CQDs/TiO2纳米复合材料的TEM图像. 当负载在TiO2表面时,CQDs形态为如图2d所示,绿色箭头指向CQDs. 值得注意的是,添加CQD对TiO2的比表面积有影响,但对其孔径几乎没有影响(表1),这意味着CQDs位于TiO2的表面,而不是其孔中,这与图2d观察到的形貌相同. 在图2e中,晶面间距为0.345 nm对应于TiO2锐钛矿的(101)晶面[24],而为0.25 nm晶面间距对应着石墨烯的100晶面[25],表明CQDs/TiO2成功复合.
通过X射线光电子能谱(XPS)研究了合成材料中各元素的表面化学成分和价态. 图3a显示,复合材料含有碳、氧、钛和氮元素. C1s的XPS光谱(图3b)主要包含4个特征峰,位于288.2、286.05、284.6 eV.
分别归属于C=O、C—O和C—C&C=C,这证明了复合材料CQDs/TiO2中碳量子点的存在[25]. 在O1s的XPS光谱(图3c)中,特征峰529.7、531.4、532.3 eV分别归因于Ti-O、C—O和O—H键,揭示了CQD和TiO2纳米颗粒通过形成Ti—O—C键结合在一起[25]. 此外,在Ti2p的高分辨XPS图像(图3d)中Ti2p3/2和Ti2p1/2的特征峰位于458.4 eV和464.2 eV,与纯TiO2相比有轻微位移,这表明TiO2和CQDs之间强烈的相互作用.
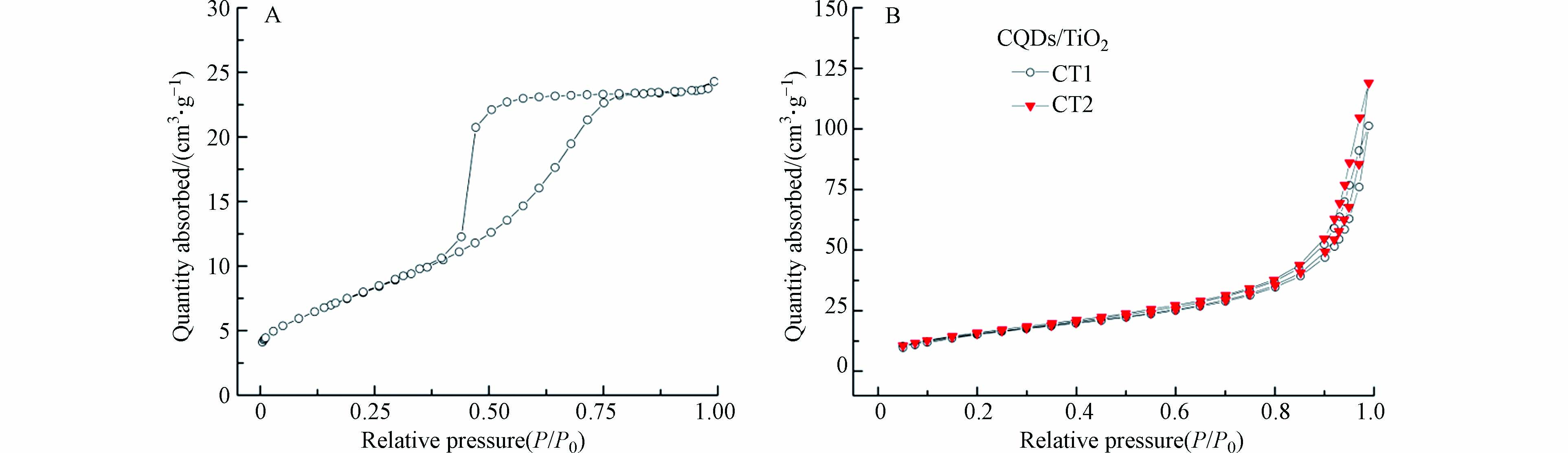
BET. 氮吸附分析用于研究材料的结构特性,图4为材料的N2吸附-脱附等温线图. 根据IUPAC分类,TiO2和CQDs/TiO2均为IV型吸附等温线,TiO2为H2型回滞环(图4A),而CQDs/TiO2为H3型回滞环(图4B). 表1中,CQDs的负载略微减少了复合材料的孔体积,但大幅度地增加了材料的比表面积,这与其表面的特殊官能团有关,从而提供了更多的表面活性中心,有利于污染物的降解,使得CQDs/TiO2表现出优异的降解性能.
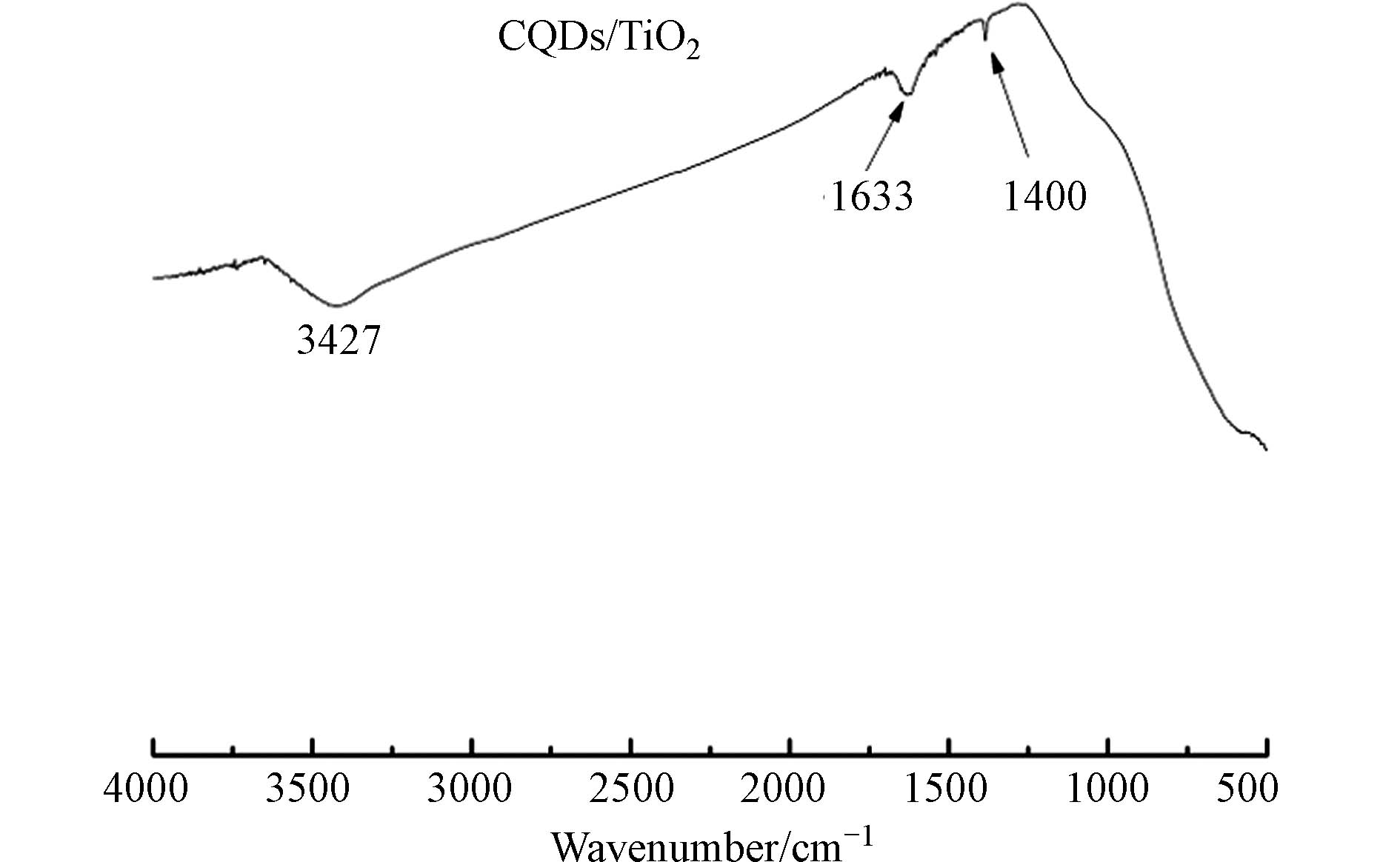
FTIR 分析. 利用CQDs/TiO2 (CT2)的FTIR光谱(图5)研究了复合材料化学键的组成和官能团. 3427、1633、1400 cm−1处有明显的特征峰. 其中,3427 cm−1对应—OH的伸缩振动吸收峰,是由于对水吸附造成的现象;1633 cm−1是C=O的振动峰,1400 cm−1是C=C键的对称拉伸振动峰,属于碳量子点的拉伸振动峰[26],这表明CQDs成功负载在TiO2.
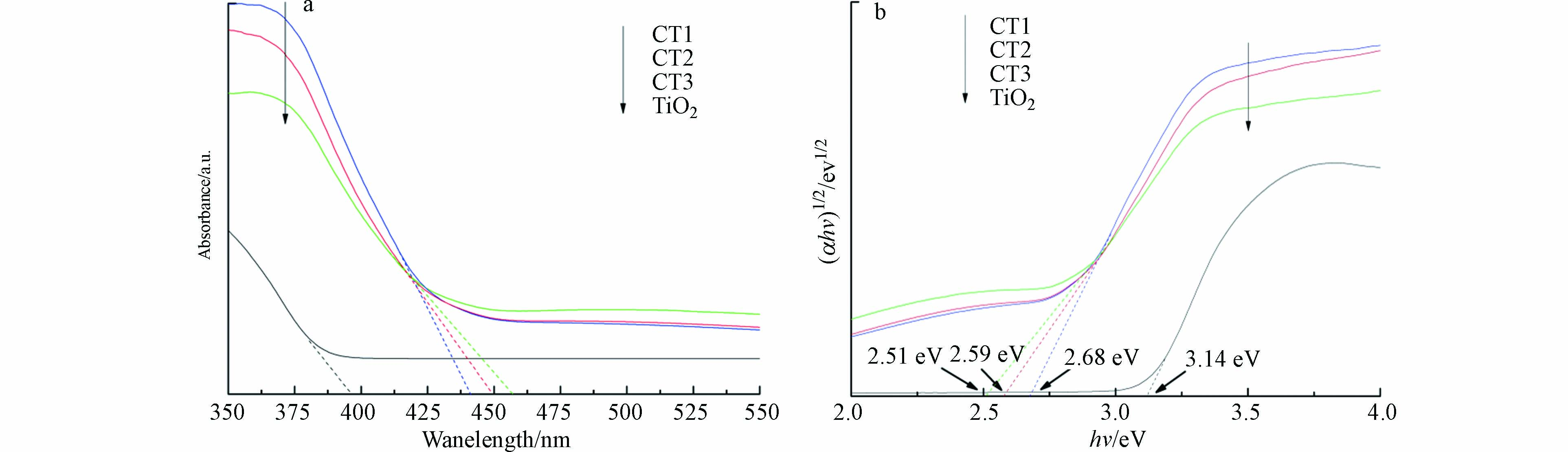
UV-vis DRS漫反射. 为了探究CQDs/TiO2的光学性质,通过UV-vis DRS对复合材料进行表征(图6). 其中,图6a中吸收带关系为TiO2(395 nm)<CT1(441 nm)<CT2(450 nm)<CT3(457 nm). 很明显CQDs的负载显著地延长了光吸收,复合材料的吸收带边缘出现了明显的红移现象[27],说明CQDs/TiO2更容易实现电子跃迁,拓宽了光的吸收范围,增强了材料在可见光下的催化效果;图6b中通过Tauc公式,按照间接带隙半导体直接计算,绘制(αhv)1/2-hv曲线图,估算的带隙宽度关系为TiO2(3.14 eV)>CT1(2.68 eV)>CT2(2.59 eV)>CT3(2.51 eV). 结果表明,掺杂降低了带隙宽度,对比单一材料,复合材料对可见光的响应能力更强. 实验发现当碳量子点掺杂量增高时,吸收边带增大,CQDs/TiO2的带隙能变窄[28]. 但实际的光催化能力并没有增加,这是因为过多的CQDs沉积在TiO2上,使复合材料的比表面积减小,阻碍光催化反应的进行而造成的.
-
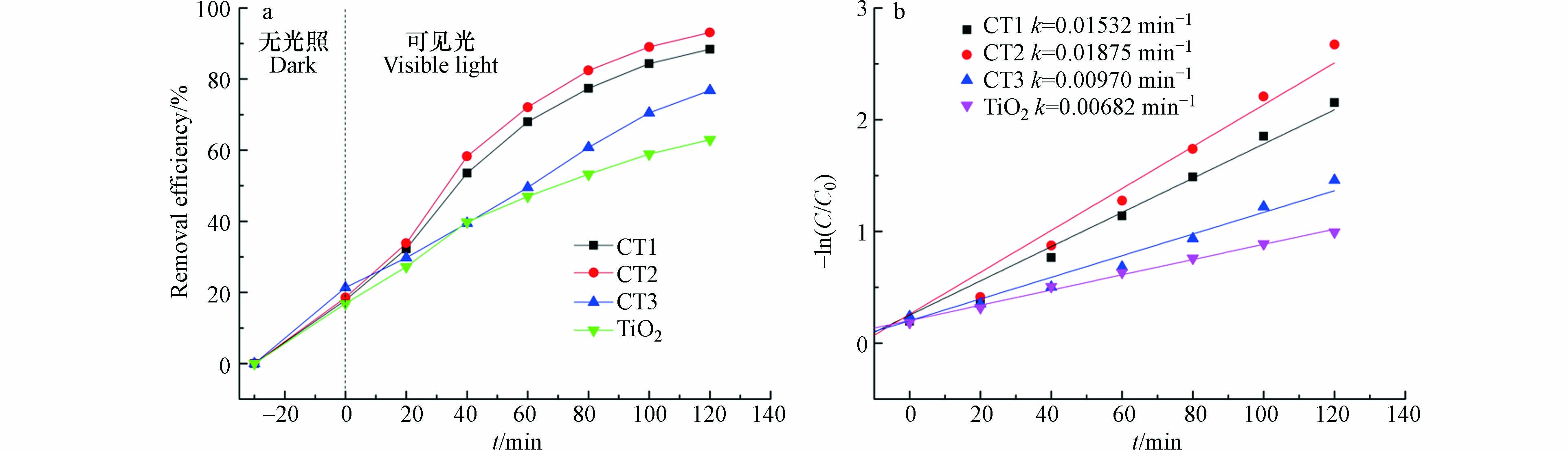
掺杂量的影响. 如图7a所示,显示了在光照条件下,四环素的降解率随时间的变化曲线(pH=5.6,四环素浓度10 mg·L−1,光照强度为300 W). 将1 mg·L−1的催化剂投入溶液中,光照120 min后,纳米复合材料的降解率均高于TiO2,且CT2的降解率最高,达到了93.1%,而TiO2仅为62.9%. CQDs/TiO2的降解效果优于纯TiO2,体现了CQDs/TiO2复合材料优异的光催化性能. 结果表明,添加一定量的CQDs(CT2)可以提高CQDs/TiO2的光催化性能. 当掺杂量过多时(CT3),复合材料的降解率反而下降. 是因为CQDs相对TiO2粒径较小,当大量覆盖在材料表面时,会减小二氧化钛的有效受光面积,电子和空穴的复合速率加快,导致光催化反应降低. 由-ln(C/C0)与降解时间t之间的线性关系可以推断,四环素的光降解动力学拟合曲线遵循准一级动力学模型. 图7b是根据反应时间绘制的反应速率图,为了获得速率常数,进行了线性拟合. 经计算,TiO2光催化剂的恒定速率为0.00682 min−1,而CT2为0.01875 min−1,是TiO2的2. 75倍,效果极佳.
四环素初始浓度的影响. 从图8a可以直观看出,随着四环素浓度的增加,其降解效率逐渐降低(pH=5.6,催化剂投加量1 mg·L−1,光照强度为300 W). 当初始浓度为5、10、15、20、25 mg·L−1时,降解率分别为99.5%、93.1%、88.6%、82.3%、75.5%. 图8b显示了各个浓度的反应速率,反应速率也随着浓度的增加而增加,浓度越低反应速率越快,其中5 mg·L−1的速率远大于其他高浓度. 这是因为当初始浓度较低时,四环素分子与其降解的中间产物(如脱水四环素、差向四环素)之间,对光催化活性物质(如·O2-、·OH)的争夺较弱,从而让更多的活性物质与四环素反应,使去除效率增高. 当较高浓度时,四环素会和其中间产物产生反应竞争[29],导致没有足够多的活性物质与四环素反应,反应速率降低.
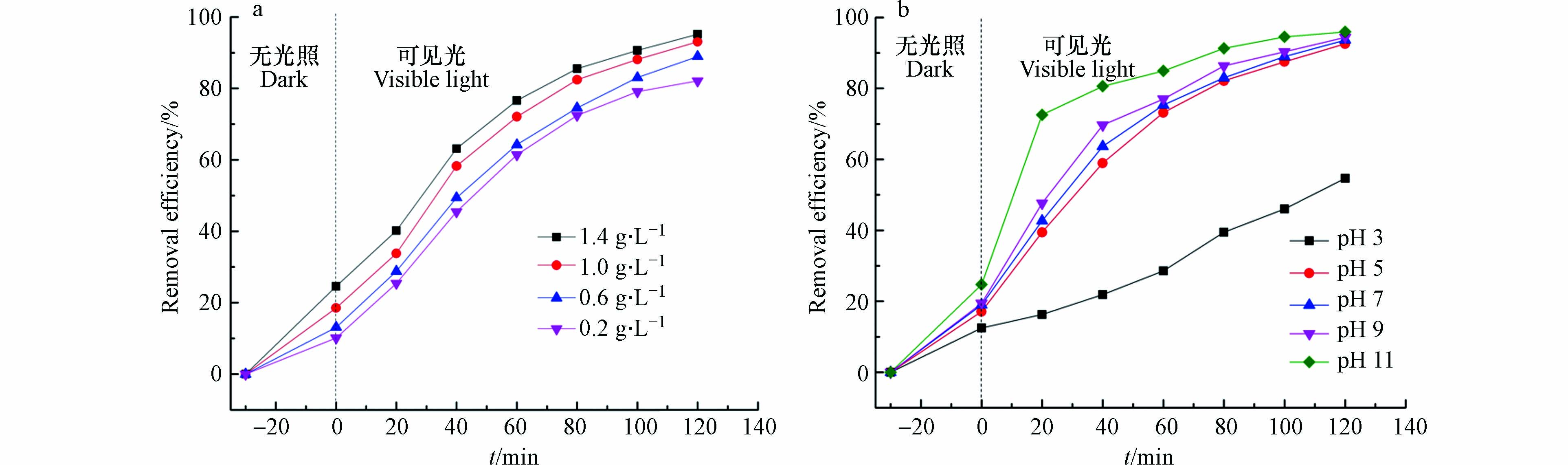
催化剂投加量的影响. 在25 ℃,pH为5.6,光照强度为300 W的条件下,分别以不同的CQDs/TiO2投加量(0.2—1.4 g·L−1)处理10 mg·L−1的四环素溶液,结果如图9a所示. 四环素去除率随着催化剂投加量的增加而增加,当投加量从1 g·L−1增加到1.4 g·L−1时,降解率仅从93.1%轻微增加到95.2%,这是因为高浓度的催化剂彼此之间发生团聚,表面积减小,反应速率减慢;催化剂量增多,也会造成它们相互叠加,到达复合材料表面的光照强度减弱,使去除率没有达到预期水平.
溶液初始pH的影响. pH是影响光催化反应的重要因素. 以CT2为例研究了pH对CQDs/TiO2降解四环素的影响(四环素浓度为10 mg·L−1,催化剂投加量为1 mg·L−1,光照强度为300 W). 在图9b中显示了溶液pH对四环素降解率的影响,当pH从3升高到11时,降解率从54.6%增加到95.9%. 可以看出,在碱性条件有利于四环素的降解. 这是由于pH值较大时,溶液中大量的OH-转化为·OH[30],而·OH恰好是与四环素反应的最主要活性物质之一(后面通过实验证明),所以四环素的降解效率有了很大提高. 在酸性条件中,四环素带正电荷,与CQDs/TiO2的正电荷相互排斥,两者之间巨大的静电斥力阻碍了污染物的吸附. 而且反应生成的·O2-容易与溶液中丰富的H+结合,消耗了大量反应活性物质,从而影响反应速率[30]. 因此当pH值较低时,CQDs/TiO2对四环素的降解效率低.
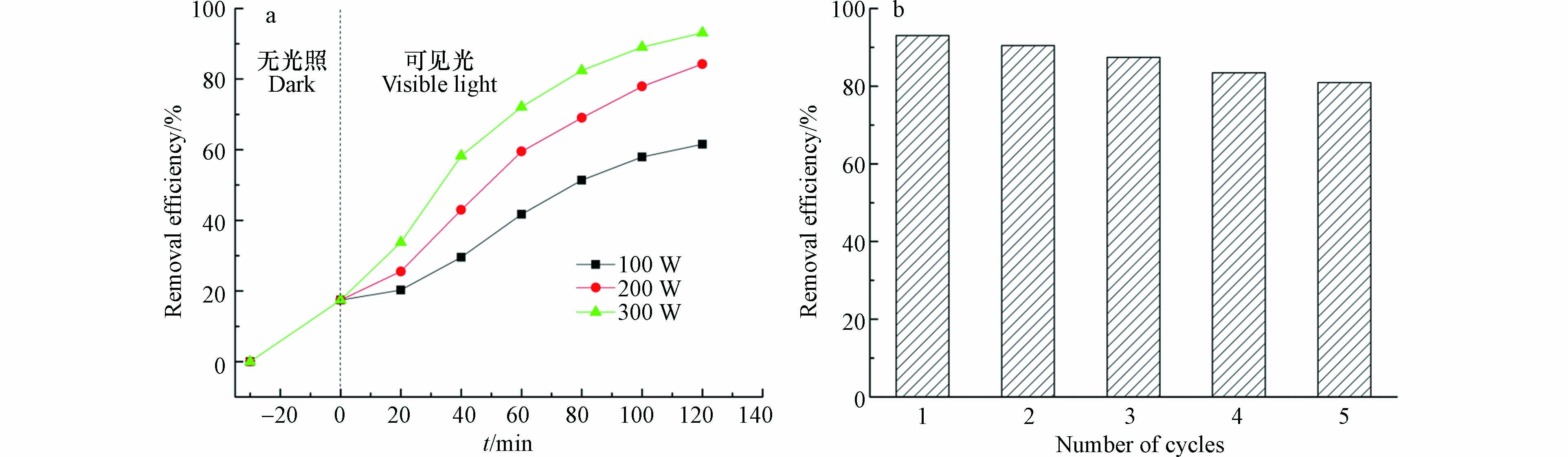
光照强度的影响及稳定性分析. 利用可调节功率电源对氙灯进行功率调节,分别为100、200、300 W. 图10a描绘了不同输入功率下降解率的变化趋势(pH=5.6,四环素浓度为10 mg·L−1,催化剂投加量为1 mg·L−1). 如图所示,当氙灯的功率为从100 W增加到300 W时,降解率从61.5%增加到了93.1%. 降解效率随着氙灯的输入功率的增加而提高,这归因于高的输入功率会产生离子风,导致水中与污染物反应的活性物质的数量增加[31]. ARA等通过构建数学模型证明了·OH、·O2-的产率和光照强度有关[32],光照强度越高这些活性物质的产率就越高. 图10b中,CQDs/TiO2在5个周期后降解率仍能达到80%以上,损失的少量活性可能是Ti—O—C键的断裂造成的[33]. 显然,CQDs/TiO2不仅具有优异的性能,还是一种环保,可循环利用的优质光催化剂.
-
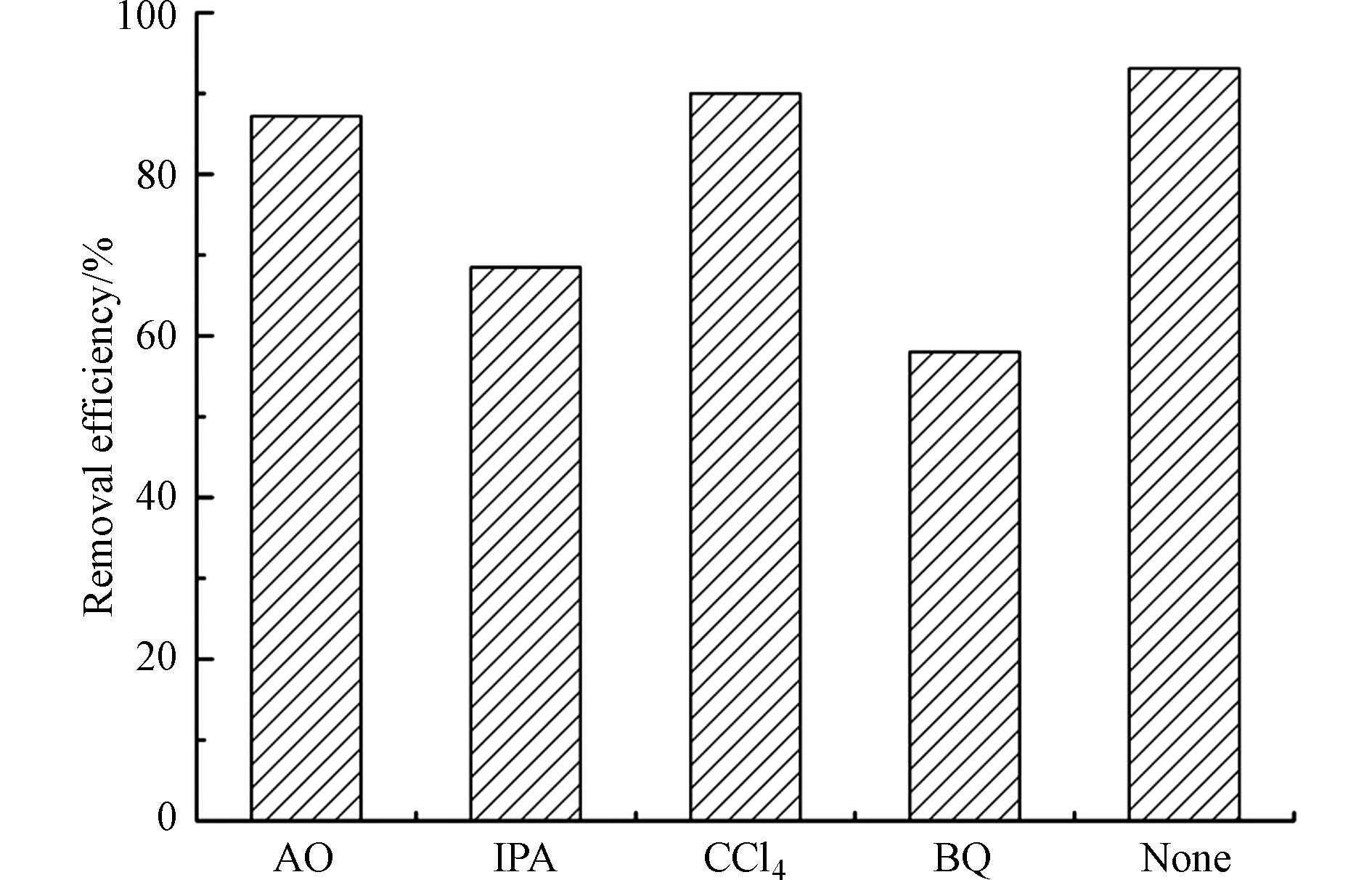
为了检测CQDs/TiO2在四环素光降解过程中的主要活性物质,进行了淬灭实验(图11). 在分别添加对苯醌、异丙醇、四氯化碳、草酸铵的溶液中,四环素的光催化降解性能从93.1%分别降低到58.0%、68.5%、90.0%和87.2%. 很明显对苯醌和异丙醇对降解过程影响最大,这就说明·OH、 ·O2-是四环素降解过程中最重要的两个活性物种. 主要涉及反应的公式如下(1—7):
其中,(4)、(5)反应产生的HO2·、H2O2活性较弱,对反应的影响可以忽略不记.
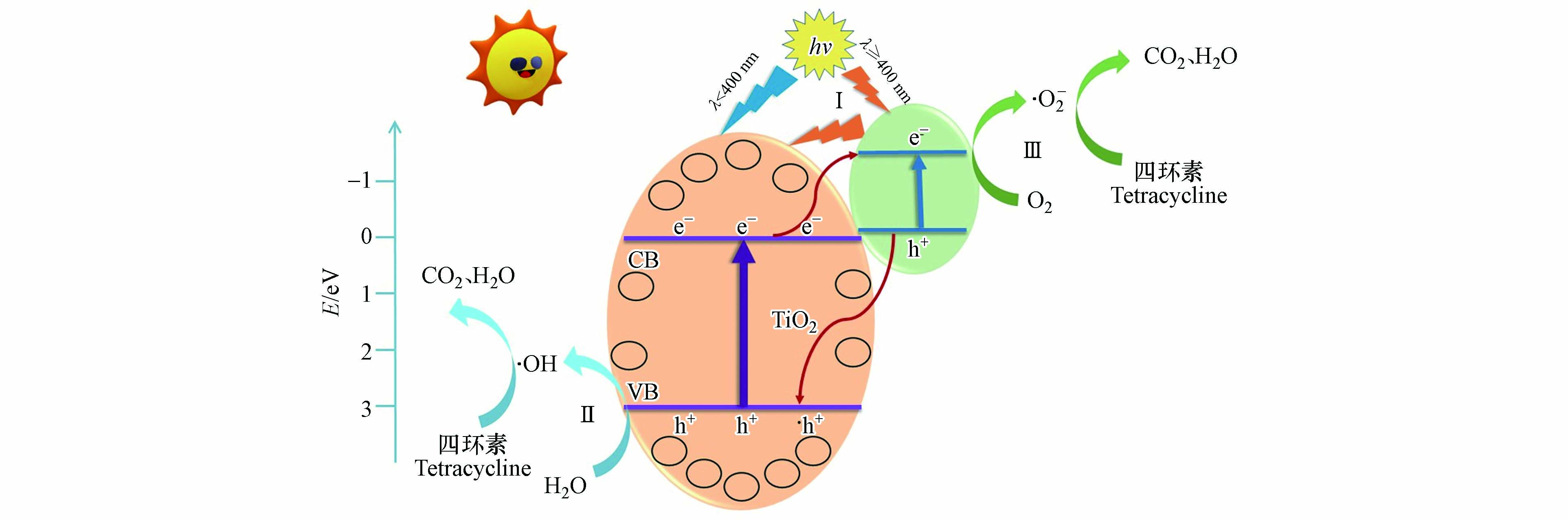
根据以上结果,分析了CQDs/TiO2降解四环素过程中的反应机制(图12). 光线照射到催化剂时,因CQDs的上转换光致发光特性[34],进一步激发了TiO2(过程Ⅰ),产生光生电子和空穴. 此外,CQDs还可以作为电子储存器. 在共轭π键的作用下,它可以捕获从TiO2的导带中迁移的电子. TiO2导带中的电子会转移到CQDs上,与氧分子反应,产生·O2-(过程Ⅲ). 同时,CQDs价带上的空穴会迁移到TiO2的表面,然后与H2O反应,生成·OH(过程Ⅱ). 这些高活性的自由基拥有很强的氧化能力,可以与吸附在TiO2表面的四环素分子发生反应,最终生成CO2和H2O.
-
(1)运用了一种简便新颖的水热超声法,用混合相的TiO2为原料,制备了全新CQDs/TiO2. CQDs负载在TiO2纳米颗粒表面,不仅增大材料的比表面积,增强了可见光的利用率,而且有助于电子和空穴的分离. 在模拟光照120 min后,CQDs/TiO2(CT2)对四环素的降解速率是TiO2的2.75倍.
(2)探究了CQDs掺杂量、溶液初试浓度、催化剂投加量、溶液pH、光照强度对CQDs/TiO2复合材料光催化降解四环素的影响. 其中,过大的掺杂量与过低的pH均不利于光催化的进行,这可为后续处理抗生素废水的研究提供帮助.
(3)该催化剂具有良好的重复使用性和稳定性,5次重复性实验后活性只轻微下降. 通过淬灭实验,得到·OH、·O2-为CQDs/TiO2在四环素光降解过程中的两个主要活性物质. 分析了CQDs/TiO2在可见光下光降解四环素的反应机制.
CQDs/TiO2复合材料的制备及光催化降解抗生素
Preparation of CQDs/TiO2 composites and photocatalytic degradation of antibiotic wastewater
-
摘要: 以四异丙醇钛和葡萄糖为原料,制备全新的CQDs/TiO2复合材料并用于降解四环素废水. 使用XRD、XPS、TEM、HR-TEM、BET、FT-IR、UV-vis DRS等方法进行表征,探究了在不同掺杂量、溶液初始浓度、催化剂投加量、pH、光照强度等条件下的降解效果. 实验结果表明,在pH=5. 6、催化剂投加量1 g·L−1、四环素溶液浓度10 mg·L−1,光照120 min后,CQDs/TiO2对四环素的去除率可达93.1%,复合材料大幅度提升了降解效率. 通过淬灭实验,发现降解过程主要起作用的活性物种为·OH、·O2−,并分析了CQDs/TiO2降解四环素的反应机制. 进行5次循环利用实验,降解率仍能达到80%以上,表现出CQDs/TiO2是一种稳定、可循环利用的复合材料.Abstract: Novel CQDs/TiO2 composites were prepared from titanium tetraisopropoxide and glucose and used to degrade tetracycline wastewater. XRD, XPS, TEM, HR-TEM, BET, FT-IR, and UV-vis DRS were used for characterization. The degradation effects were also investigated under different doping amounts, initial concentration of the solution, catalyst dosing, pH, and light intensity. The experimental results showed that the removal rate of tetracycline by CQDs/TiO2 could reach 93.1% at pH=5. 6, catalyst dosage of 1 g·L−1, tetracycline solution concentration of 10 mg·L−1, and 120 min of light exposure, and the composite material substantially improved the degradation efficiency. Through quenching experiments, it was found that the main active species acting in the degradation process were ·OH and ·O2−, and the reaction mechanism of CQDs/TiO2 in degrading tetracycline was analyzed. Five recycling experiments were carried out and the degradation rate still reached over 80%, demonstrating that CQDs/TiO2 is a stable and recyclable composite material.
-
Key words:
- CQDs/TiO2 /
- photocatalysis /
- tetracycline /
- wastewater treatment.
-

-
表 1 不同材料的比表面积、孔径
Table 1. Specific surface area and pore size of different materials
样品
Samples比表面积/(m2·g−1)
Specific surface area平均孔径/nm
Average pore sizeTiO2 29.66 10.46 CT1 57.66 10.12 CT2 59.28 10.1 CT3 50.06 10.16 -
[1] LIU X H, LU S Y, MENG W, et al. Occurrence, source, and ecological risk of antibiotics in Dongting Lake, China [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2018, 25(11): 11063-11073. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-1290-1 [2] KURNIAWAN T A, LO W H, CHAN G Y S. Radicals-catalyzed oxidation reactions for degradation of recalcitrant compounds from landfill leachate [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2006, 125(1): 35-57. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2006.07.006 [3] QIU G L, CHEN H, SRINIVASA RAGHAVAN D S, et al. Removal behaviors of antibiotics in a hybrid microfiltration-forward osmotic membrane bioreactor for real municipal wastewater treatment [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 417: 129146. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.129146 [4] YANG X R, CHEN Z, ZHAO W, et al. Recent advances in photodegradation of antibiotic residues in water [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 405: 126806. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.126806 [5] BAYAN E M, PUSTOVAYA L E, VOLKOVA M G. Recent advances in TiO2-based materials for photocatalytic degradation of antibiotics in aqueous systems [J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2021, 24: 101822. [6] MURDOCH M, WATERHOUSE G I N, NADEEM M A, et al. The effect of gold loading and particle size on photocatalytic hydrogen production from ethanol over Au/TiO2 nanoparticles [J]. Nature Chemistry, 2011, 3(6): 489-492. doi: 10.1038/nchem.1048 [7] LI R G, WENG Y X, ZHOU X, et al. Achieving overall water splitting using titanium dioxide-based photocatalysts of different phases [J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2015, 8(8): 2377-2382. [8] KAWAHARA T, OZAWA T, IWASAKI M, et al. Photocatalytic activity of rutile-anatase coupled TiO2 particles prepared by a dissolution-reprecipitation method [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2003, 267(2): 377-381. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9797(03)00755-0 [9] WANG W, LIU X L, FANG J J, et al. TiO2@g-C3N4 heterojunction with directional charge migration behavior for photodegradation of tetracycline antibiotics [J]. Materials Letters, 2019, 236: 622-624. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2018.11.025 [10] HAJIPOUR P, ESLAMI A, BAHRAMI A, et al. Surface modification of TiO2 nanoparticles with CuO for visible-light antibacterial applications and photocatalytic degradation of antibiotics [J]. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(23): 33875-33885. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.08.300 [11] ALI A, SHOEB M, LI Y, et al. Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of antibiotic drug and dye pollutants by graphene-ordered mesoporous silica (SBA 15)/TiO2 nanocomposite under visible-light irradiation [J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2021, 324: 114696. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114696 [12] HENG Z W, CHONG W C, PANG Y L, et al. An overview of the recent advances of carbon quantum dots/metal oxides in the application of heterogeneous photocatalysis in photodegradation of pollutants towards visible-light and solar energy exploitation [J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2021, 9(3): 105199. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.105199 [13] LI T X, LI Z, HUANG T Z, et al. Carbon quantum dot-based sensors for food safety [J]. Sensors and Actuators A:Physical, 2021, 331: 113003. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2021.113003 [14] YUE J, ZHANG K, YU H, et al. Mechanism insights into tunable photoluminescence of carbon dots by hydroxyl radicals [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2019, 54(8): 6140-6150. doi: 10.1007/s10853-018-03254-1 [15] CHEN P, WANG F L, CHEN Z F, et al. Study on the photocatalytic mechanism and detoxicity of gemfibrozil by a sunlight-driven TiO2/carbon dots photocatalyst: The significant roles of reactive oxygen species [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2017, 204: 250-259. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.11.040 [16] WANG J, GAO M M, HO G W. Bidentate-complex-derived TiO2/carbon dot photocatalysts: in situ synthesis, versatile heterostructures, and enhanced H2 evolution [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(16): 5703. doi: 10.1039/c3ta15114j [17] SHAFIQUE M, MAHR M S, YASEEN M, et al. CQD/TiO2 nanocomposite photocatalyst for efficient visible light-driven purification of wastewater containing methyl orange dye [J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2022, 278: 125583. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2021.125583 [18] ZHUANG J D, DAI W X, TIAN Q F, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of RhB over TiO2 bilayer films: Effect of defects and their location [J]. Langmuir, 2010, 26(12): 9686-9694. doi: 10.1021/la100302m [19] LIU Y, YUAN X Z, WANG H, et al. Solvothermal synthesis of graphene/BiOCl0.75Br0.25 microspheres with excellent visible-light photocatalytic activity [J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(42): 33696-33704. doi: 10.1039/C5RA02852C [20] CHEN Y, LIU K R. Preparation and characterization of nitrogen-doped TiO2/diatomite integrated photocatalytic pellet for the adsorption-degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride using visible light [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 302: 682-696. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.05.108 [21] LI T T, ZHANG S J, MENG S G, et al. Amino acid-assisted synthesis of In2S3 hierarchical architectures for selective oxidation of aromatic alcohols to aromatic aldehydes [J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(11): 6457-6466. doi: 10.1039/C6RA28560K [22] LYU J Z, ZHOU Z, WANG Y H, et al. Platinum-enhanced amorphous TiO2-filled mesoporous TiO2 crystals for the photocatalytic mineralization of tetracycline hydrochloride [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 373: 278-284. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.03.096 [23] ZHAN Y, SHANG B, CHEN M, et al. One-step synthesis of silica-coated carbon dots with controllable solid-state fluorescence for white light-emitting diodes [J]. Small (Weinheim an Der Bergstrasse, Germany), 2019, 15(24): e1901161. doi: 10.1002/smll.201901161 [24] MAHATO D, KHARWAR Y P, RAMANUJAM K, et al. S, N co-doped graphene quantum dots decorated TiO2 and supported with carbon for oxygen reduction reaction catalysis [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(41): 21549-21565. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.04.013 [25] CONG Y, LI X K, QIN Y, et al. Carbon-doped TiO2 coating on multiwalled carbon nanotubes with higher visible light photocatalytic activity [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2011, 107(1/2): 128-134. [26] LI F, TIAN F, LIU C J, et al. One-step synthesis of nanohybrid carbon dots and TiO2 composites with enhanced ultraviolet light active photocatalysis [J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(11): 8389-8396. doi: 10.1039/C4RA14865G [27] WANG J, WANG C F, CHEN S. Amphiphilic egg-derived carbon dots: Rapid plasma fabrication, pyrolysis process, and multicolor printing patterns [J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed. in English), 2012, 51(37): 9297-9301. doi: 10.1002/anie.201204381 [28] PHANG S J, TAN L L. Recent advances in carbon quantum dot (CQD)-based two dimensional materials for photocatalytic applications [J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2019, 9(21): 5882-5905. [29] XU Y G, LIU J, XIE M, et al. Construction of novel CNT/LaVO4 nanostructures for efficient antibiotic photodegradation [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 357: 487-497. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.09.098 [30] HUNGE Y M, YADAV A A, KANG S W, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline antibiotics using hydrothermally synthesized two-dimensional molybdenum disulfide/titanium dioxide composites [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2022, 606: 454-463. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2021.07.151 [31] FENG J W, ZHENG Z, SUN Y B, et al. Degradation of diuron in aqueous solution by dielectric barrier discharge [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 154(1/2/3): 1081-1089. [32] RANJBARI A, DEMEESTERE K, VERPOORT F, et al. Novel kinetic modeling of thiabendazole removal by adsorption and photocatalysis on porous organic polymers: Effect of pH and visible light intensity [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 431: 133349. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.133349 [33] SHARMA S, DUTTA V, SINGH P, et al. Carbon quantum dot supported semiconductor photocatalysts for efficient degradation of organic pollutants in water: A review [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 228: 755-769. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.292 [34] YU X J, LIU J J, YU Y C, et al. Preparation and visible light photocatalytic activity of carbon quantum dots/TiO2 nanosheet composites [J]. Carbon, 2014, 68: 718-724. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2013.11.053 -



 下载:
下载: