-
在煤炭开采和使用过程中会生产大量煤矸石、粉煤灰等固体废弃物,这些固废的堆存既占用土地又会造成严重的环境污染. 当前,煤基固废作为大宗固废,其利用方式主要有如下几种:一是直接利用,如作为填筑材料用于筑路、回填,或者制备型煤用于燃烧;二是制备建材或者其他材料,如利用煤矸石制备水泥和建筑材料[1];三是提取有价元素,粉煤灰中富含铝、镓、锂等有价元素,可以通过提取工艺对其进行回收[2]. 由于受处理成本和效率的制约,目前煤基固废的综合利用率仍不到53.1%[3]. 推进煤基固废减量化、资源化规模利用,将其由燃料化应用向高值材料化应用方面转变是双碳背景下可持续发展的必然要求. 由于部分煤基固废中碳含量较高,将其作为制备炭材料的原料之一,可实现其高值化利用,因此利用碳含量高的煤基固废制备多孔炭意义重大.
另一方面,中国人民共和国生态环境部于2023年发布的《2021年中国生态环境统计年报》数据显示,2021年全国废水中重金属(总砷、总铅、总镉、总汞、总铬)排放量为50.5 t[4]. 其中,铬作为废水中的典型重金属,在环境中主要以六价铬和三价铬的形式存在. 六价铬具有急性毒性、难降解、迁移性强、易富集和致癌性等特点,其毒性是三价铬的500倍[5]. 与有机物不同,重金属不能通过生物降解,在人体内积累到一定浓度后会危害身体健康,而且含铬废水还会对水生生物群落造成严重威胁(如图1所示)[6 − 8]. 因此如何降低废水中六价铬的浓度是目前亟需解决的难题之一. 多孔炭作为炭材料的一种,其表面活性官能团和重金属之间存在物理和化学作用,可以有效去除水体中的重金属[9 − 10]. 基于此,本文综述了煤基多孔炭制备和改性方法以及其对重金属吸附性能的研究进展,并针对目前的局限性和挑战对改性多孔炭吸附重金属未来的发展方向进行了展望.
-
多孔炭是富碳物质在无氧或缺氧条件下生成的一类稳定、难溶、高度芳香化的物质,是一类具有发达孔隙和大比表面积的多孔材料. 煤炭资源储量丰富,具有较高的机械性能和化学稳定性以及易于降解[11]等特点,且价格相对低廉,因此被广泛用作制备多孔炭材料的原料. 目前制备煤基多孔炭常用的原料主要有煤(包括无烟煤、烟煤和褐煤)、煤焦油、沥青和煤基固废(如煤泥、煤气化渣、煤矸石)等. 研究人员发现,选用不同变质程度的煤为原料并采用物理活化法均可制备煤基活性炭,而且制得的煤基活性炭比表面积最大可达532 m2·g−1,孔体积可达0.395 cm3·g-1[12]. 所制备的活性炭具有良好吸附性能,可用于废水中有机污染物如亚甲基蓝和重金属等污染物的吸附. 除了煤以外,煤基固废如煤矸石、煤泥、煤气化渣等也可以作为制备多孔炭的原料. 这些固废由于来源和产生途径不同,因此理化性质有一定的差异. 如:煤泥中主要含有煤粉、煤炭颗粒及岩石颗粒等[13];煤矸石主要成分则为Al2O3、SiO2和C,同时还含有一些矿物元素如Fe、K、Ca、Mg、Ti等[14];煤气化渣是原煤气化过程中产生的固体废弃物,其主要由二氧化硅、氧化铝、氧化铁、氧化钙和残碳等组成[15].
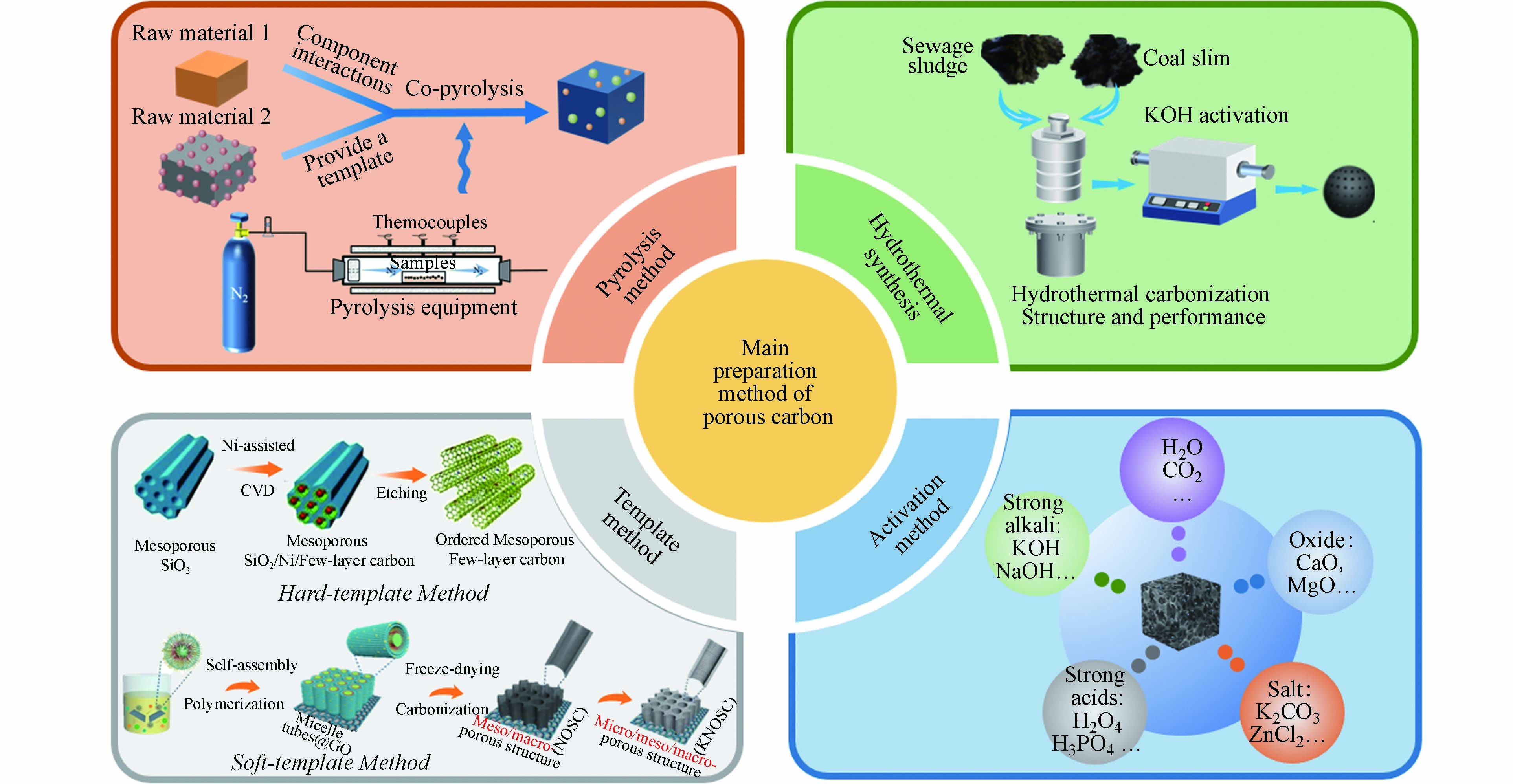
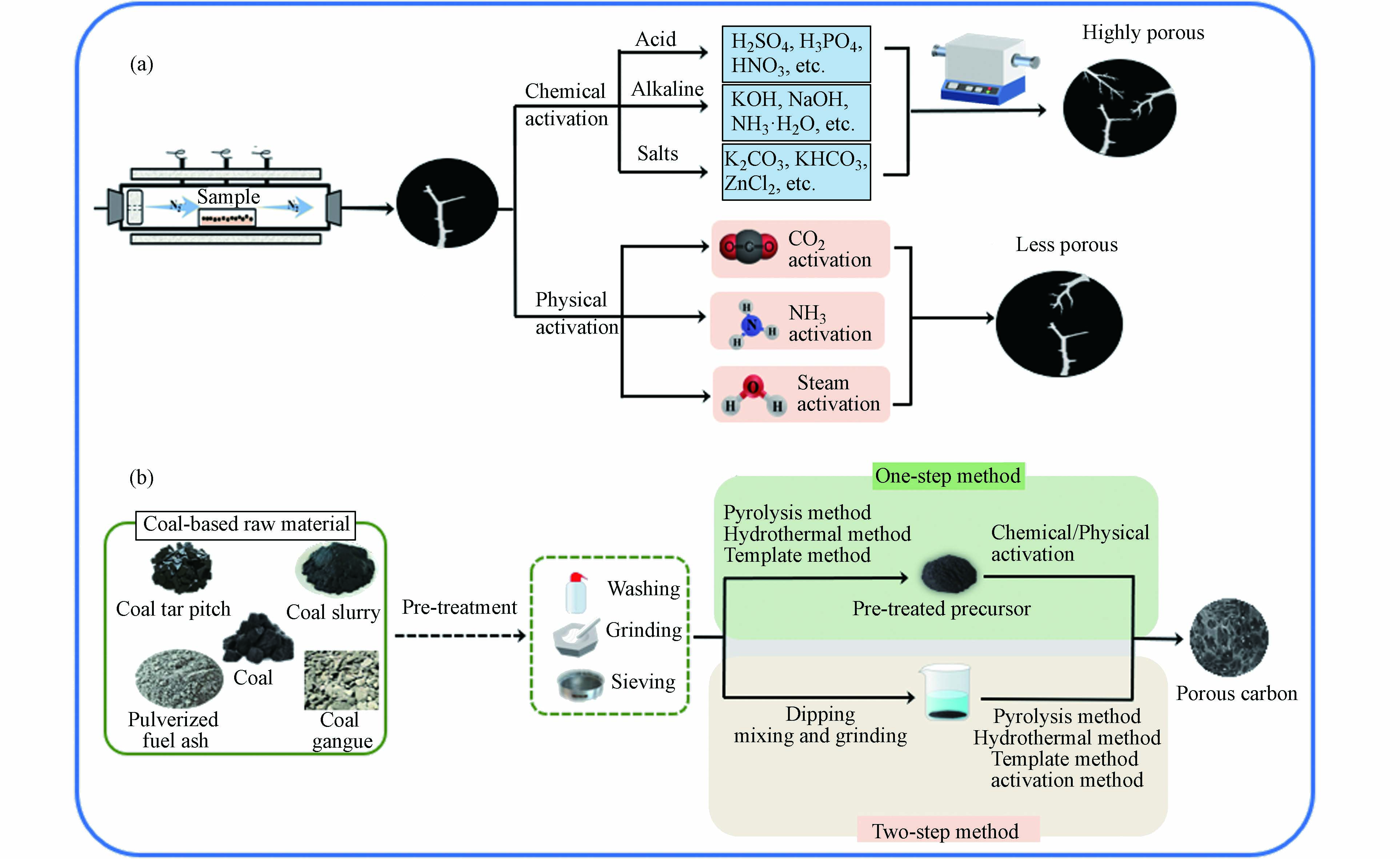
作为吸附材料,多孔炭吸附能力的强弱取决于其比表面积和孔径,因此调控多孔炭孔结构可有效提升其吸附性能. 根据国际理论与应用化学联合会(IUPAC)分类方法,将活性炭的孔结构分为:微孔(<2 nm)、中孔(2—50 nm)、大孔(>50 nm)[16],其中增加微孔数量可以增大表面积从而促进物理吸附;增加中孔数量可以有利于直接吸附尺寸较大的分子,促进污染物扩散并加快吸附速率[17],同时为物质进入微孔提供通道. 针对不同的目标对象,对于多孔炭的孔隙结构有着不同的要求. 在气体吸附中微孔起主要作用,而若是应用于水处理中尤其是需要吸附具有较大尺寸的重金属离子,则是具有较发达的中孔结构最为合适[18]. 目前,制备多孔炭材料常见的方法有热解法[19]、水热法[20]、模板法[21]和活化法[11]等(如图2所示). 这些制备方法还可以相互联用进而制备出性能更佳的多孔炭. 如模板法与活化法联用,可有效调控活性炭不同尺度孔结构的分布. 何孝军等[22]以煤沥青为原料、纳米Fe2O3为模板和KOH作为活化剂成功合成了具有层次孔结构的多孔炭,而且发现活化剂的加入可以有效提高多孔炭材料的比表面积和孔体积. 表1总结了几种含碳资源经不同工艺制备煤基多孔炭的相关参数[23 − 37]. 从表1中可以看出,以煤基固废为原料经适宜的制备方式和改性手段也可制备出性能优异的多孔炭;这不仅可以实现煤基固废的资源化利用,同时还可大幅降低吸附剂制备成本,符合双碳背景下固废清洁高效低碳利用发展理念. 因此,多种制备方法联用是未来合成具有分级孔结构的多孔炭的重要发展方向之一.
-
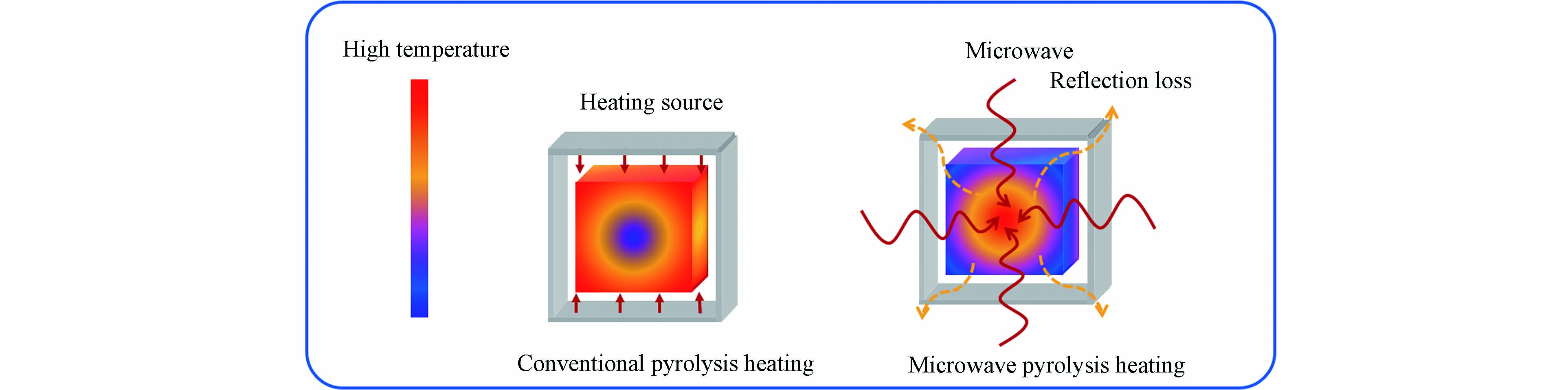
热解作为目前较为成熟的热化学转化技术,是原料在惰性气氛(氮气或者氩气)下加热发生水分子蒸发、高分子降解和高温分解等一系列物理化学反应,进而除去碳源中非碳元素和易挥发成分,最终得到多孔炭材料的一种技术. 目前热解法主要分为常规热解和微波热解. 常规热解是指热量通过传导、对流和辐射的途径传递到材料表面,原料的受热过程是由外至内;这种加热方法存在传热效率低、热损高和反应时间长的问题,成本较高. 与常规热解不同,微波热解是将电场能转化为热能从而对原料进行加热,因此其热量从原料的内部向外部扩散[38 − 39]. 图3为这两种不同热解方式的加热原理示意图[39]. 目前国内外学者对生物质热解技术已进行了大量研究,有学者通过微波热解技术制备了生物基多孔炭[40 − 41]. 由于原煤不能单独采用微波加热完成热解,因此学者们使用不同的微波吸收剂辅助煤在微波场下热解[42],另外,目前关于微波热解制备煤基多孔炭的研究相对较少,还处于探索阶段.
-
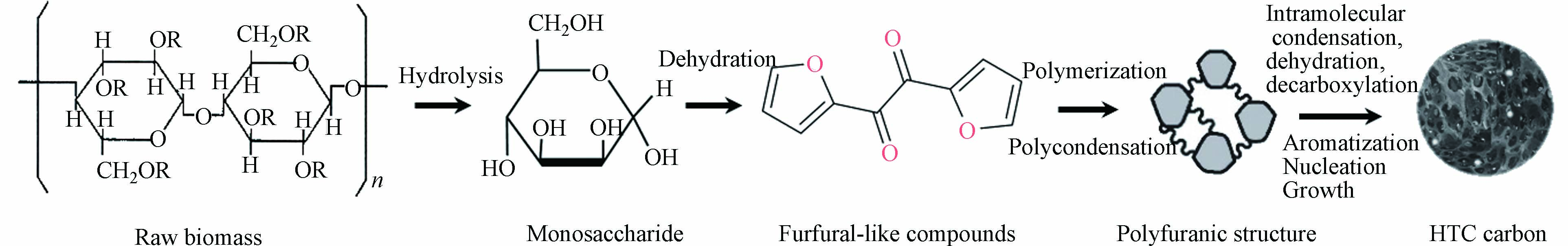
水热碳化技术(HTC)是1931年诺贝尔奖获得者Bergius提出的将纤维素类生物质通过相对较低的温度(150—300 ℃)和自生压力的水热条件下转化为煤样材料的一种绿色技术,该方法是一种模拟天然成煤机理的快速炭化方法[43]. 图4是水热碳化法合成多孔炭的路线示意图[44]. 在该过程中,主要发生水解、脱水、聚合和芳构化反应等一系列化学反应. 目前有研究人员利用秸秆类生物质或污泥等与煤或煤基固废进行共水热碳化,研究发现,在此过程中煤基原料的加入会对水热碳化起到促进作用. 作者课题组前期利用高硫煤泥和污泥进行共水热碳化制备原位硫氮掺杂多孔炭,发现在共水热碳化过程中两者存在协同作用,共水热碳化有利于提高水热炭的碳含量和水热炭质量产率[45]. 和传统的多孔炭吸附剂相比,水热炭的比表面积相对较小,孔隙也不太发达,但表面含有大量含氧官能团(—OH、C=O、O—C=O等),使水热炭表面显负电性,利于吸附水中重金属离子等带正电荷的污染物[46].
-
模板法也是制备多孔炭非常重要的方法之一,通过模板法制备多孔炭可以更好的调控其孔径分布和孔体积,从而获得具有高比表面积和更均匀孔径分布的有序碳结构. 模板法根据其模板自身组分和性质可分为软模板和硬模板两种. 其中,软模板法是利用含碳物质和嵌段共聚物(模板剂)制备具有有序结构的材料,然后经高温热解使模板剂分解蒸发而在碳材料内部留下适当的孔的一种方法[47]. 硬模板法是将碳前驱体引入到具有有序孔结构模板(沸石、二氧化硅和阳极氧化铝等)的孔道中,经高温碳化后再利用酸或碱处理去除模板后制备得到多孔炭材料[48]. 硬模板法制备过程相对复杂且制备所得的多孔炭比表面积相对较低,但对于多孔炭结构的调控较软模板法精准. 相较于硬模板法,软模板法不用洗去模板剂,但模板剂成本较高[49].
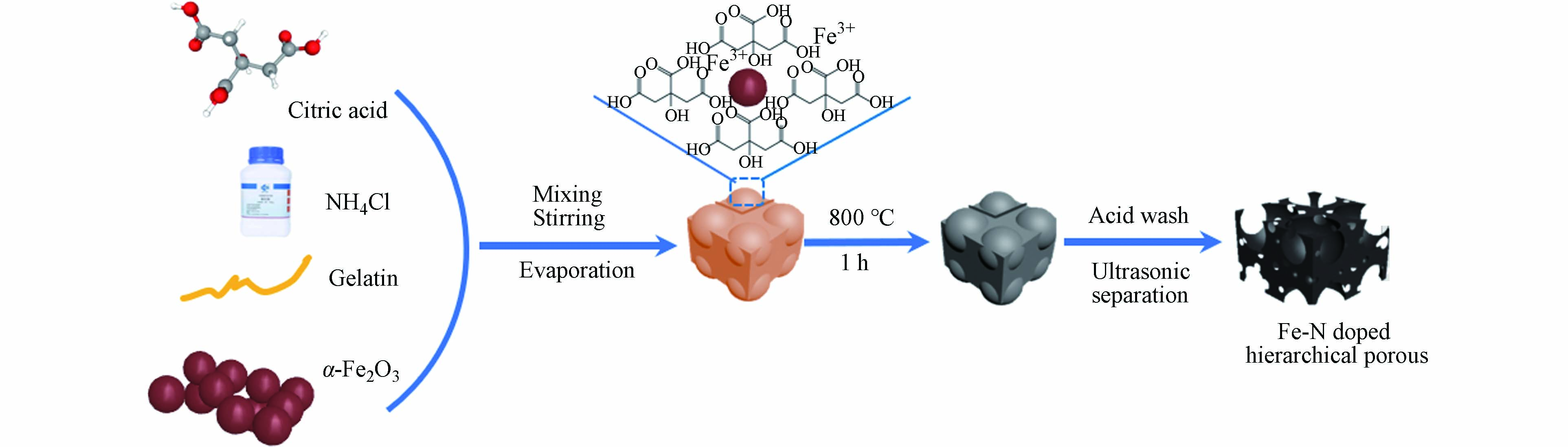
当前,关于模板法制备多孔炭的研究备受关注. 有研究者利用Fe2O3纳米颗粒充当模板来构建分级多孔结构(图5为三维互连的Fe-N掺杂分级多孔炭材料制备示意图),所制备的碳材料具有理想的孔结构和比表面积(1644 m2·g−1)[50]. He等[51]以KMnO4氧化后的煤沥青为原料,NaCl为绿色模板,制备了一种新型的富氧三维多孔炭,该材料表现出较高的比电容(在0.5 A·g−1下为306 F·g−1)和优异的循环稳定性(10000次循环后比电容保持率为99.7%). 此外,将模板法与活化法联用可进一步提高碳材料的比表面积、孔体积和微孔率. 邱介山[52]、何孝军[53 − 54]等以煤沥青、煤焦油等煤基衍生物为碳源,模板法联用KOH活化法制备了具有较好孔隙结构的煤基活性炭. Jiang等[55]以ZnO为模板,采用碳化和KOH活化联合的方式制备了煤沥青基多孔炭,该多孔炭具有大的比表面积(2059.43 m2·g−1)和分级孔结构(主要是微孔和中孔). 由此可见,模板法联用活化法是制备煤基活性炭很具前景的一种方法.
-
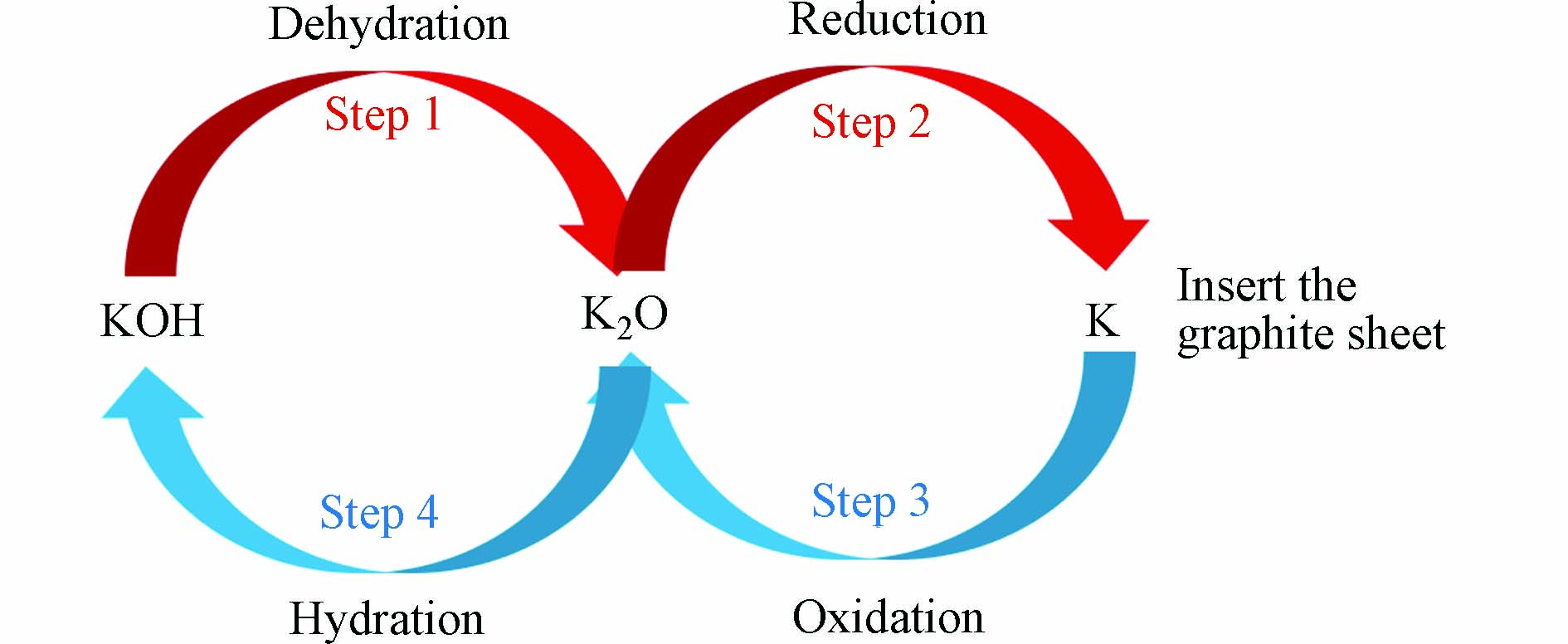
在多孔炭材料的制备工艺中,活化法常与其他制备工艺联用. 活化主要起三个作用:开放原来的闭塞孔、扩大原有孔隙和形成新的孔隙. 根据活化剂的不同,可分为物理活化和化学活化(如图6所示[11,17,56]). 物理活化是通过CO2 [57 − 58]、水蒸气[59]、氨气[60]以及空气或其混合气体等氧化性气体,在高温下选择性氧化样品非晶区的部分组分和晶区结构上的活性位点,从而生成孔隙结构[61]. 化学活化则是利用化学试剂通过浸渍或混合等方式和原料之间反应生成气体从而产生更多孔道,进而制备出具有较大比表面积和孔体积的多孔炭[62]. 目前,具有代表性的活化剂有KOH、H3PO4、KHCO3等. 图7为化学活化过程中KOH活化反应机理示意图,在此过程中,主要有四个步骤,分别为脱水反应,还原反应,氧化反应,水合反应,反应总方程如公式(1)所示[63]:
活化法制备多孔炭的工艺包括炭化过程以及活化过程,根据活化步骤可以分为一步活化法和两步活化法(如图6(b)所示). 一步活化法是将原料先与化学试剂浸渍或者混合再进行高温炭化,或者原料在高温管式炉先炭化再改变气氛直接进行物理活化. 以煤沥青(CTP)为碳源,KOH为活化剂,采用一步碳化活化法可制备出高性能分级多孔炭材料[64]. Liu等[65] 将二茂铁、宁夏焦煤和KOH通过一步法制备出了磁性多孔炭. 由于KOH的活化作用和磁性组分的引入,使多孔碳材料的比表面积最大可达1188 m2·g−1,总孔隙率达到0.50 cm3·g−1. Zhu等[66]以准东煤和FeCl3为原料,利用CO2 为活化剂一步法制备出了磁性煤基多孔炭,所制备的多孔炭具有分级孔结构,其微孔和中孔体积分别达到0.282 cm3·g−1和0.222 cm3·g−1,并且研究结果显示Fe元素不仅对中孔的发展起促进作用,而且还可以使其在外加磁场的作用下加速固液分离,提高吸附剂的重复利用率. 两步活化法是指将通过热解、水热或模板法等得到的初始碳化体再通过物理/化学活化法进行活化的一种方法,也是目前最为常见的活化方式. 由于炭化过程可以形成初始的孔隙结构,其初始优异的孔隙结构是活化过程的基础[67],因此两步活化可以有效提高多孔炭比表面积和孔隙.
另外,需要提及的是,作为典型的含碳固废,煤基固废普遍存在灰分含量高的特点. 煤基固废中高含量的无机矿物质对多孔炭的制备影响较为复杂. 当前,对于煤基炭材料中矿物质的影响,大多是通过对比脱除矿物质所前后所制备的炭材料的孔结构、性能等的差异来揭示其内在影响机制[68]. 一般认为原料中灰分过高不利于活化反应的进行[69],且矿物质的存在会影响其孔的形成,降低比表面积. 如:徐园园等[70]通过水蒸气活化脱灰前后的新疆煤制备煤基活性炭,发现脱灰后产物的比表面积从1285 m2·g−1增加到了1373 m2·g−1,表明煤基多孔炭的结构与其内在矿物质有关,脱除矿物质后会增加其比表面积,进而使其吸附性能增强. 但也有研究者认为矿物质又会作为自模板,促进孔的形成[71 − 72]. 如:高碳、高灰分的煤基固废煤液化残渣,其内在矿物质主要是硅铝酸盐等物质. 以煤液化残渣为碳源和模板剂、KOH为活化剂,通过自模板法一步炭化可制备出同时含有微孔、介孔和大孔的分级多孔炭(比表面积为1787 m2·g−1)[71],在此过程中煤液化残渣中的矿物质与KOH反应形成可溶性盐,经洗涤后在矿物质的原始位置形成了孔隙,同时KOH还具有活化作用[72].
由于多孔炭的孔结构分布、表面官能团含量及类型等都会影响其应用效果,因此比表面积并不是唯一判断多孔炭性能优劣的标准. 有研究显示,一步活化法得到多孔炭是微孔、介孔和大孔同时存在的多级孔结构,而两步活化法制备的多孔炭材料只含有微孔和少量介孔[73],而且一步活化法制备的活性炭的表面官能团较两步活化法制备的活性炭的表面官能团含量较高[74]. 由于不同来源 煤基固废理化性质差异较大,而且所制备的多孔炭材料可能会应用于吸附、催化和储能等多个领域,因此煤基固废多孔炭制备工艺应根据其相应的应用性能要求做出合适的选择.
-
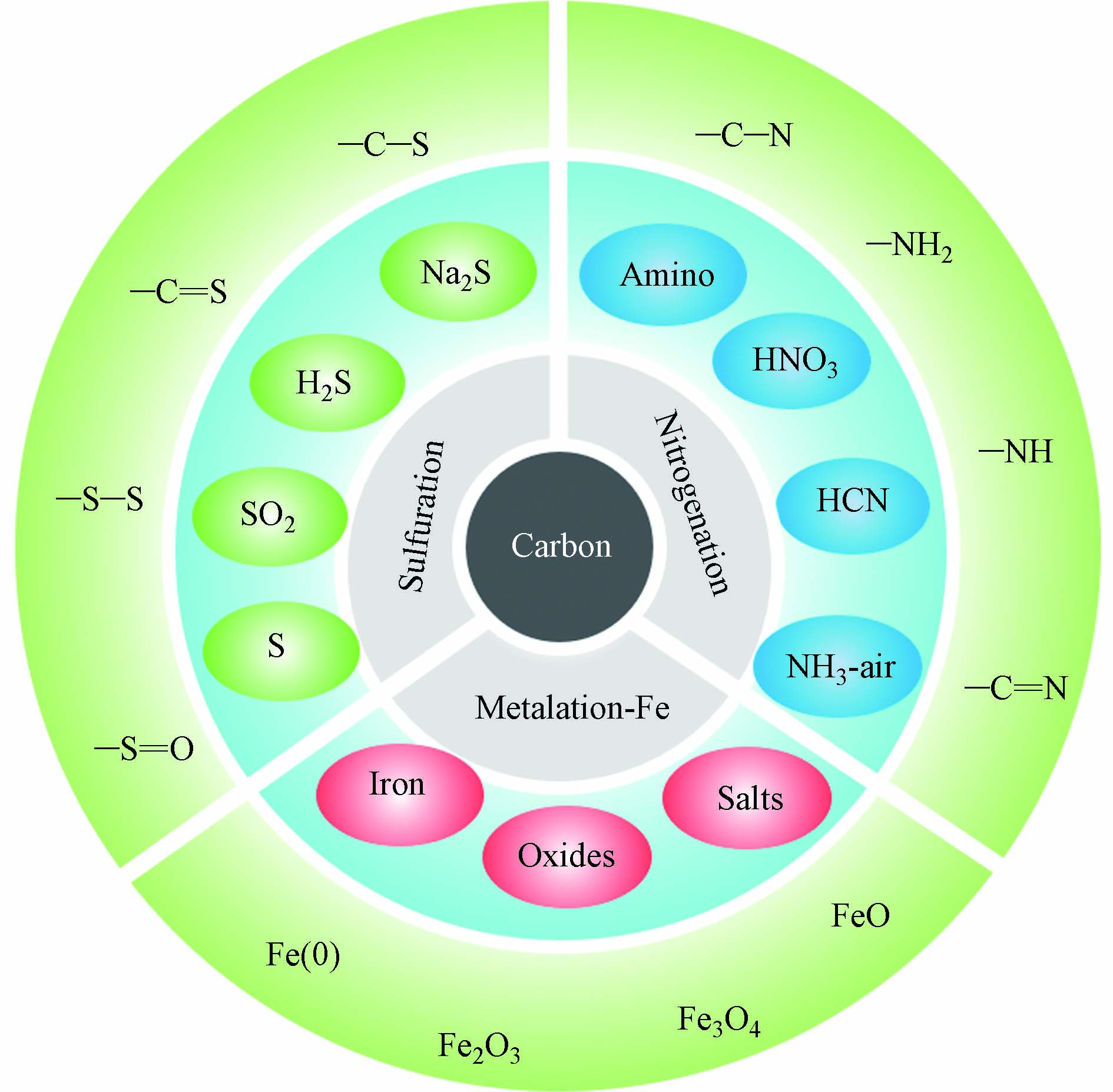
除多孔炭孔结构以外,重金属离子与吸附剂表面官能团之间的物理和化学作用也会影响其对重金属的吸附性能[75 − 76]. 丰富的表面活性官能团对于多孔炭材料的表面化学性质和重金属的吸附起着至关重要的作用[77]. 目前关于杂原子掺杂对多孔炭的改性研究已有很多报道(见表2)[27,28,76,78 − 85]. 杂原子掺杂可以通过增加特定官能团改善多孔炭吸附剂表面性能,增强其表面化学性质和结构稳定性[77,86 − 87],从而使多孔炭材料在吸附重金属时具有更好的选择性[88 − 92]. 在炭材料表面引入非金属元素氮、硫或金属元素铁等杂原子后,这些杂原子都可以在炭表面形成不同官能团(如图8所示),进而增强其对重金属的吸附能力.
-
在元素周期表中,氮原子与碳原子邻位,其原子半径与碳原子接近,掺杂氮原子后对碳材料的晶格畸变影响较小[93],而且因为氮原子的价电子层比碳原子多一个电子,氮原子能够做为电子供体,提高氮掺杂碳材料的电导率[94],因此氮是炭材料杂原子掺杂的理想元素之一. 氮掺杂通常是通过碳与氨、尿素或胺等反应来实现. 图9为典型的氮元素改性多孔炭示意图,通过氮掺杂,可以将含氮官能团引入碳表面,进而增强多孔炭对重金属的吸附能力[17].
材料中掺杂的氮元素通常被分为化学氮和结构氮. 化学氮是指以功能型表面官能团形式存在于材料上的氮,比如胺基和亚硝基. 结构氮则是指直接与碳骨架相连的氮原子,比如吡啶型氮、吡咯型氮和石墨型氮. 根据Lewis酸碱理论,表面含有碱性官能团可以增强活性炭表面与重金属离子的反应. 含氮官能团的存在可使多孔炭材料更易与重金属离子结合,使得金属离子可以更加均匀的分散在炭材料表面[95];因此,增加多孔炭材料表面含氮官能团可以明显改善其表面的亲水性,提高其对重金属离子的吸附性能. 掺杂氮的活性炭对Cu(Ⅱ) 的吸附实验结果表明,掺氮后具有较高的初始吸附速率和吸附容量[78]. 此外,研究还发现吸附性能不仅与结构表面含氮总量有关,还与特定氮官能团类型密切相关,氮元素的存在形式会影响重金属离子吸附性能. 如:以吡咯氮和胺基的形式存在的氮可以与重金属离子发生结合作用,对重金属离子的去除起促进作用,而石墨型氮却不能很好的与重金属离子结合[96].
-
硫作为一种富含电子的活性元素,也是常见的掺杂元素之一. 引入硫原子可以在碳原子附近诱导出许多有利于反应的活性位点[97 − 98]. 近年来,硫掺杂除用于多孔炭材料的改性外,也常用于氧化石墨烯、碳纳米管、层状双金属氢氧化物和凹凸棒石等材料. 与氮原子掺杂手段相似,也可以通过加热或酸处理等方式实现硫原子掺杂. 碳与单质硫、SO2、H2S、Na2S、K2S和二甲基二硫化物等硫化剂反应,会在炭吸附剂表面引入含硫官能团(如C—S、C=S或S=O),或是以噻吩和氧化硫种SOx 的形式存在于碳面边缘区域或缺陷部位[99]. 根据掺杂和炭化的先后顺序,可分为原位掺杂和后处理两种. 原位掺杂是指在炭化过程中掺杂硫原子,后处理是指在炭化后对碳骨架进行修饰. 硫原子的掺杂不仅可以在多孔炭表面形成含硫官能团,还会改变多孔炭的孔结构. 合适的处理条件下掺杂硫原子会使表面积和孔体积增加,并避免可能会出现的含硫颗粒堵塞孔隙进而造成表面积和孔隙体积减少的现象发生[100].
在硫掺杂多孔碳对重金属吸附方面,有研究表明硫掺杂碳材料中丰富的含硫基团(如C—SO3—C、C—SO2—C和C—S—C等)可通过与重金属离子形成强的共价键而实现对重金属离子的去除[101]. 另外,金属硫化物纳米材料通过硫与重金属离子之间的软硬酸碱效应,也表现出对重金属离子吸附特异的选择性[102]. 类石墨烯碳载层状双金属氢氧化物在掺杂硫原子后可提高对Cd(Ⅱ) 和Co(Ⅱ) 的吸附性能[101]. 此外,何静等[103]通过水热反应合成了硫掺杂凹凸棒石复合材料并将其用于吸附Pb(Ⅱ)和Cu(Ⅱ). 研究发现,经5次再生实验后吸附率分别达68.7%和55.78%[97]. Zhang等[104]以硫代硫酸钠为硫源制备了硫掺杂材料,并用于去除水溶液中的四环素-六价铬复合污染物;通过再生实验证明所制备的材料对污染物有较高的去除效率,而且还可以重复使用. 但是,需要指出的是,由于C—S键的强度弱于C—C键,因此掺杂硫后的碳材料稳定性较差[97]. 因此,关于硫掺杂碳材料可能引起的潜在危害以及其性能优化方面的研究还有待进一步深入.
-
在多孔炭制备过程中,添加金属、金属盐及其氧化物也可以在炭化和活化过程中调控多孔炭孔结构,提升其吸附性能. 这些添加剂可以在保留多孔炭原本较高比表面积和丰富有机官能团的同时实现对多孔炭的改性. 目前,铁原子掺杂的工艺主要有浸渍法和原位合成法. 浸渍法是将活性炭与含铁溶液混匀浸渍再经过一系列后续处理,最终得到铁掺杂多孔炭. 原位合成法是直接利用铁源或者在原料中添加铁离子,经过活化得到负载铁离子的活性炭产物[105].
研究人员发现加入铁元素可以催化活化过程,在炭化过程中可催化气化反应并有助于中孔的形成[106]. 如褐煤与铁、镍、钴的乙酞丙酮化物在一定条件下混合活化后,制得的多孔炭中孔率会明显提升,而且这几种金属中铁的效果最佳[107]. 另外,研究还发现,Fe3O4可以促进孔隙发育[81]、提高其表面积和表面官能团(Fe—O、Fe—OOH、C—O和O—H)[108],而零价铁则具有强还原性和迁移性能好等特点,并且磁铁矿负载多孔炭还可以使其具有磁性便于固液分离[109]. 此外,研究还发现,由三氯化铁负载煤(铁含量为3%)衍生的多孔炭具有分级孔结构(其微孔和中孔体积最高)[66],负载三氯化铁可以提升其对六价铬的吸附量[110]. 这可能是由于材料表面的Fe(Ⅱ) 将Cr(Ⅵ) 还原为Cr(Ⅲ) [111]. 此外,考虑到吸附材料需要回收利用,有研究者将由Fe3O4 改性合成的磁性吸附剂在0.1 mol·L−1的NaOH溶液进行解吸处理,循环4次后才发现其对Cr(Ⅵ) 的去除性能开始呈缓慢降低趋势,说明该材料具有较好的可重复使用性[108,112]. 另外,利用赤泥进行改性后的多孔炭对Cr(Ⅵ) 也表现出较好的吸附和还原性能,并且还可以通过外加磁场进行回收,从而进一步降低了成本[81]. 此外,董建华[113]采用真空煅烧还原法处理吸附Cr(Ⅵ) 后的铁掺杂多孔炭,发现具有一定的再生效果;但由于其局限性,目前利用该方法尚未实现其完全再生. 另外,需要指出的是,由于材料表面负载的零价铁在与Cr(Ⅵ) 反应后会生产成CrxFe1-x(OH)3和FeCr2O4的钝化层,从而降低材料利用效率、阻碍反应的进行,因此有研究者在铁掺杂的基础上对其进行硫化改性. 硫化改性后,会形成FeSx,可协同提高零价铁的电子传递能力和吸附材料对水体中Cr(Ⅵ) 的吸附、还原能力[114]. 如:刘丽等[115]通过用硫代硫酸钠对零价铁进行改性,发现硫化后的材料对Cr(Ⅵ) 的去除量是之前的3倍;硫原子掺杂后使得材料在碱性条件下对Cr(Ⅵ) 的去除能力明显提升,弥补了其他材料在碱性条件下对Cr(Ⅵ) 去除效率低的不足[116]. 由此可见,铁原子掺杂多孔炭在水污染修复领域具有较大的应用潜力[109].
通过上述分析可知,氮原子掺杂可以使吸附剂表面富含碱性官能团,通过生成吡咯氮和胺基的形式增强重金属离子之间结合作用,从而提高其对重金属的吸附容量. 硫改性后的多孔炭,不仅可以改变其表面的电荷分布,还能与重金属离子形成强烈的共价键[117]. 此外,金属元素铁不仅可以对多孔炭赋磁改性,还能够催化炭化和活化过程,增加中孔率,进而提高其对具有较大尺寸的重金属离子的吸附性能. 由此可见,硫氮及铁元素掺杂改性后的碳材料在重金属废水净化处理中都有良好的应用前景.
-
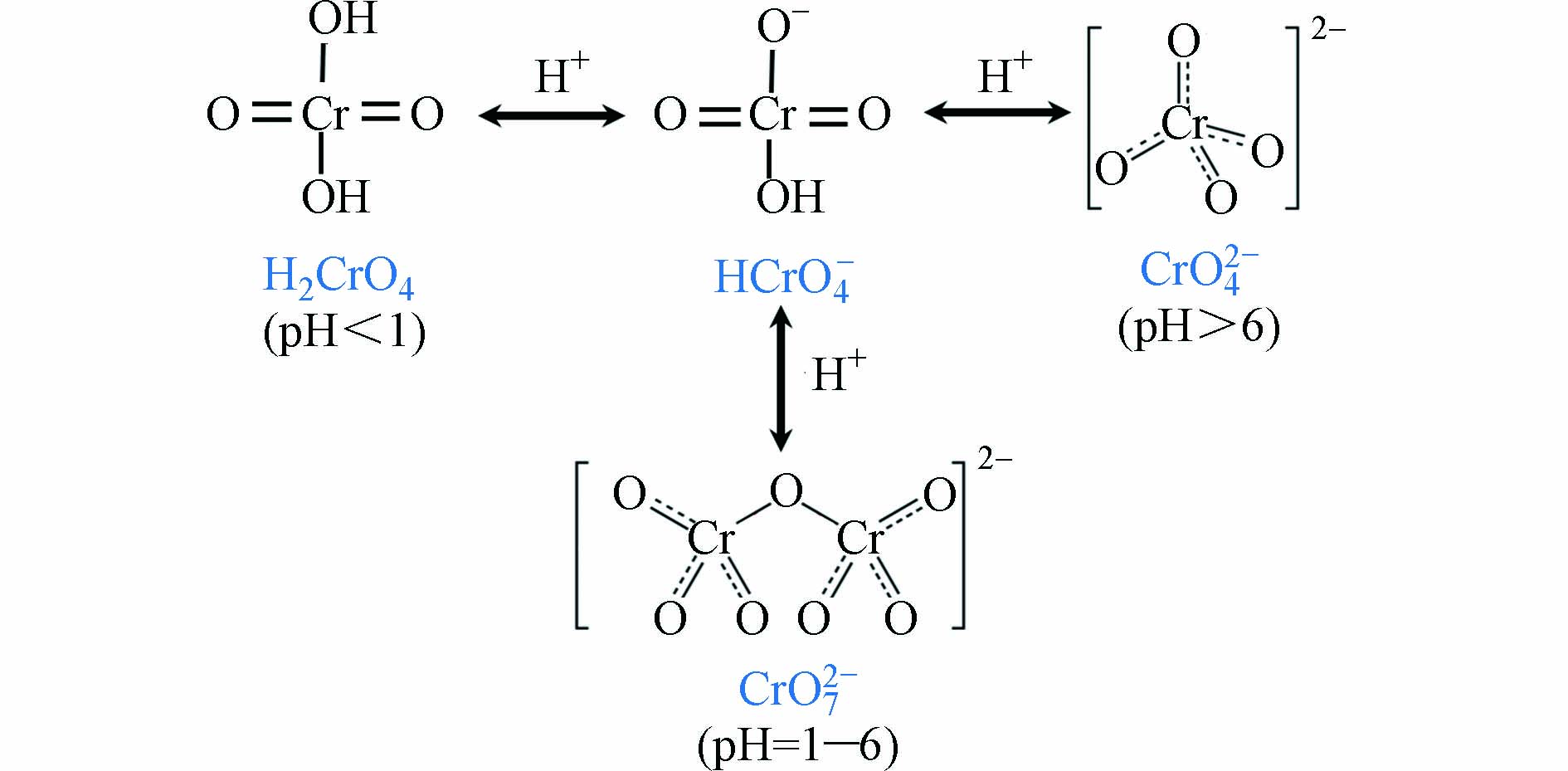
废水中重金属离子种类较多,是一个相对复杂的复合体系. 废水中的重金属离子除汞、砷、铅外,铬因具有高毒性和致癌性,因此也一直是环境领域关注的焦点. 铬离子在水体中主要以六价铬和三价铬两种形式存在,其中六价铬又主要以HCrO4-、Cr2O72-和CrO42-形态存在(见图10),其毒性、氧化能力和迁移能力都比三价铬更强.
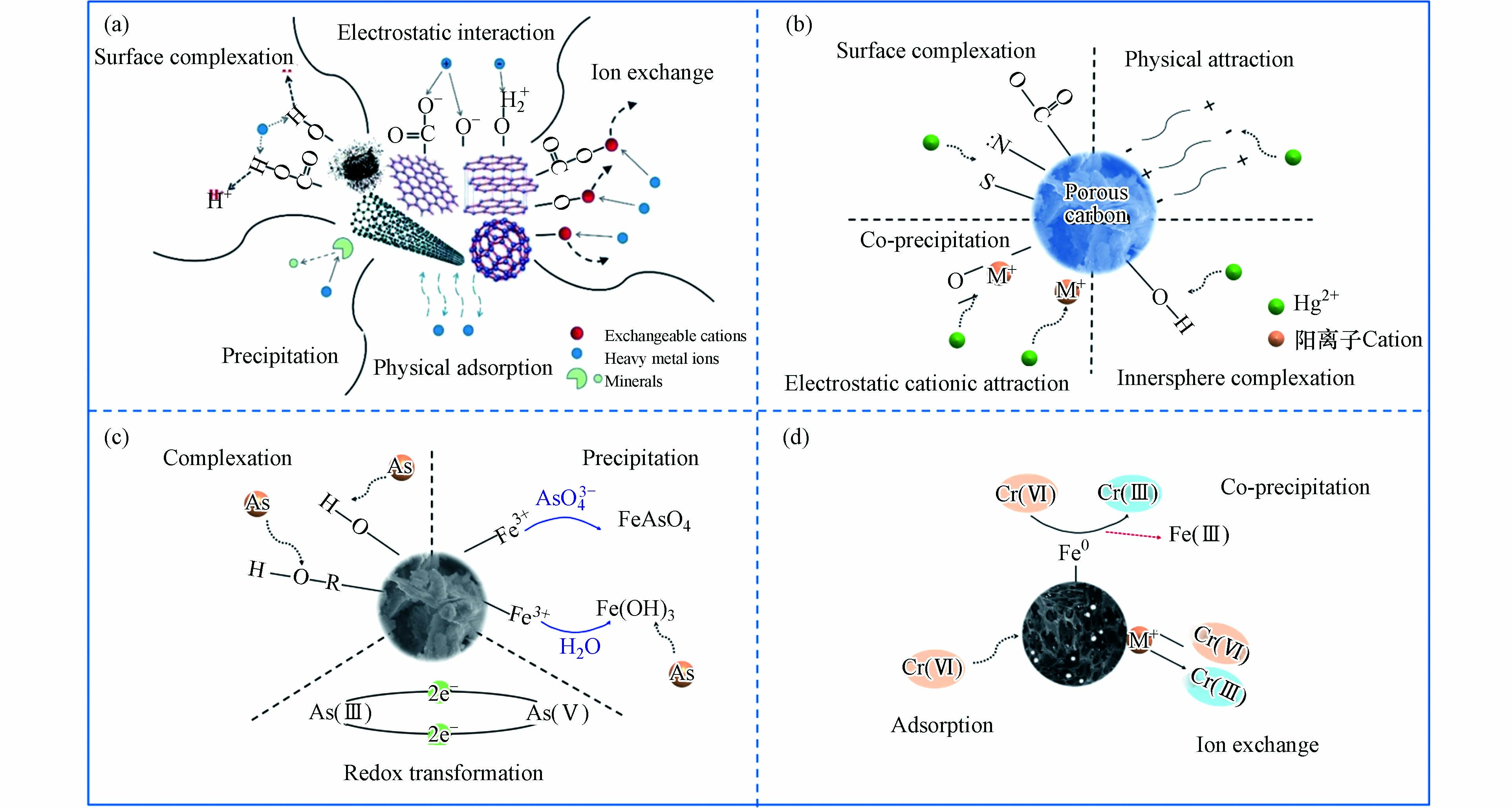
多孔炭可以通过与重金属离子发生吸附反应从而降低其在水中的浓度[119]. 目前关于多孔炭用于废水中重金属吸附的研究较多,尤其是对环境危害比较大的Hg、As、Cr等重金属的吸附研究更多,其吸附机理如图11所示. 大量研究结果表明,去除废水中重金属离子的机理主要为:静电作用、离子交换作用、表面络合作用、沉淀作用和吸附作用(如图11(a)所示)[17] 5种机理. 不同的吸附剂和吸附条件都会影响Cr(Ⅵ) 的吸附性能,而且吸附机理也不尽相同,下面将围绕影响煤基多孔炭去除Cr(Ⅵ) 的因素、多孔炭对六价铬的吸附机理和多孔炭吸附真实废水中的六价铬三个方面内容进行综述.
-
多孔炭自身的理化性质及其结构等都会影响其对重金属的吸附效果. 除此之外,如溶液的初始pH值、重金属离子的初始浓度、吸附剂的投加量和复杂体系中离子间的相互作用等也会对吸附效果产生影响.
-
溶液的初始pH值是影响重金属吸附过程的重要因素之一,它不仅会影响吸附剂表面化学性质,还会影响重金属离子的存在形态和官能团的络合行为[17]. 在一定的pH范围内,大部分金属吸附量会随着pH的增加而增加,当pH达到一定值后,吸附量又随着pH的增加而降低. 其主要原因是电荷零点的pH值(pHzpc)和介质pH之间的关系,影响表面带电性质[8]. 在pH值为1.0—3.0的条件下,多孔炭对Cr(Ⅵ)可以达到较好的吸附效果[122](如表3所示[24,118,122 − 125]). 因为多孔炭的零电荷点多为中性,因此当pH值为2.0—7.0时,多孔炭表面带正电荷;由于Cr(Ⅵ) 常以Cr2O72-、CrO42-和HCrO4-等阴离子形式存在于水溶液中,带正电荷的多孔炭和阴离子形式存在的Cr(Ⅵ )在异性电荷相吸的作用下对吸附起到促进作用,同时强酸性溶液中大量的H+ 能中和活性炭表面负电荷,有利于Cr2O72- 、HCrO4- 扩散[126]和吸附与还原[127].
-
温度是物理化学过程中最常见的参数之一,对重金属的吸附和去除有重要影响[128]. 煤质活性炭对Cr(Ⅵ) 去除率随温度的升高均有明显提升,相同条件下将温度从25 ℃升温至70 ℃,吸附率将会从50.20%提高到75.83%[122],温度和去除率呈正相关,这也表明这一过程为吸热过程[110,129]. 一方面可能是因为随温度升高,离子扩散速率加快,多孔炭对Cr(Ⅵ) 的吸附速率也加快,吸附容量也相应提高;另一方面可能是随温度升高,吸附反应的活化能降低,从而使吸附反应更容易进行[122].
-
研究发现,Cr(Ⅵ) 去除效率和吸附容量随吸附剂用量而变化,这是由于改变吸附剂的投加量可以改变吸附的活性位点和官能团总量. Wu等[130]通过实验发现,当吸附剂投加量由1 g·L−1增加至3.5 g·L−1时,Cr(Ⅵ) 的去除率从50.1%提高到97.2%,但是Cr(Ⅵ) 的吸附量从50.0 mg·g−1降低到27.8 mg·g−1. 在溶液中Cr(Ⅵ) 的含量不变的条件下,吸附剂量增加可以提供更多的吸附位点,从而去除率逐渐增加,直至其稳定;但是由于Cr(Ⅵ) 含量是恒定的、有限的,随着吸附的活性位点增加,单位吸附剂的利用效率会降低[130 − 131],因此吸附剂投加量与吸附率呈正相关,而与吸附容量呈负相关.
-
通过热力学分析可以判断反应是否能够发生,而动力学则是研究反应速率快慢的问题. 对于吸附热力学而言,常用的吸附等温线模型包括Freundlich、Langmuir和D-R等. 而常见的吸附动力学模型则包括伪一级动力学模型、伪二阶动力学模型和粒子内扩散模型[132 − 133],而且还可以通过标准差(SD)和系数(R2)来评估每个模型的适用性. 研究发现,SD越低、R2 越高,则表明动力学模型的适合性越好.
仇雅丽等[24]利用赤泥和煤制备多孔炭材料吸附水中其吸附Cr(Ⅵ),发现该吸附过程符合 Freundlich吸附机制,其吸附动力学可用准一级或准二级动力学方程描述. 杨慧芬等[123]利用赤泥和煤泥通过碳热还原法制备磁性多孔炭材料,并用于吸附水中六价铬;其吸附动力学和等温吸附研究表明,此材料对水中Cr(Ⅵ) 的吸附以化学吸附为主的,最大吸附量为86.88 mg·g−1,Cr(Ⅵ) 在吸附材料表面的吸附过程接近单层吸附. 另外,Beksissa等[118]研究了表面二阶动力学模型,为Cr(Ⅵ)在褐煤制备的活性炭上的吸附速率提供了最佳拟合. 从文献报道来看,多孔炭材料吸附水中六价铬的热力学多数符合Langmuir模型,吸附方式以化学吸附为主. 但是对于动力学模型却没有较好的统一(见表4),这可能是因为原料和制备工艺的不同导致多孔炭结构和性能具有差异性.
-
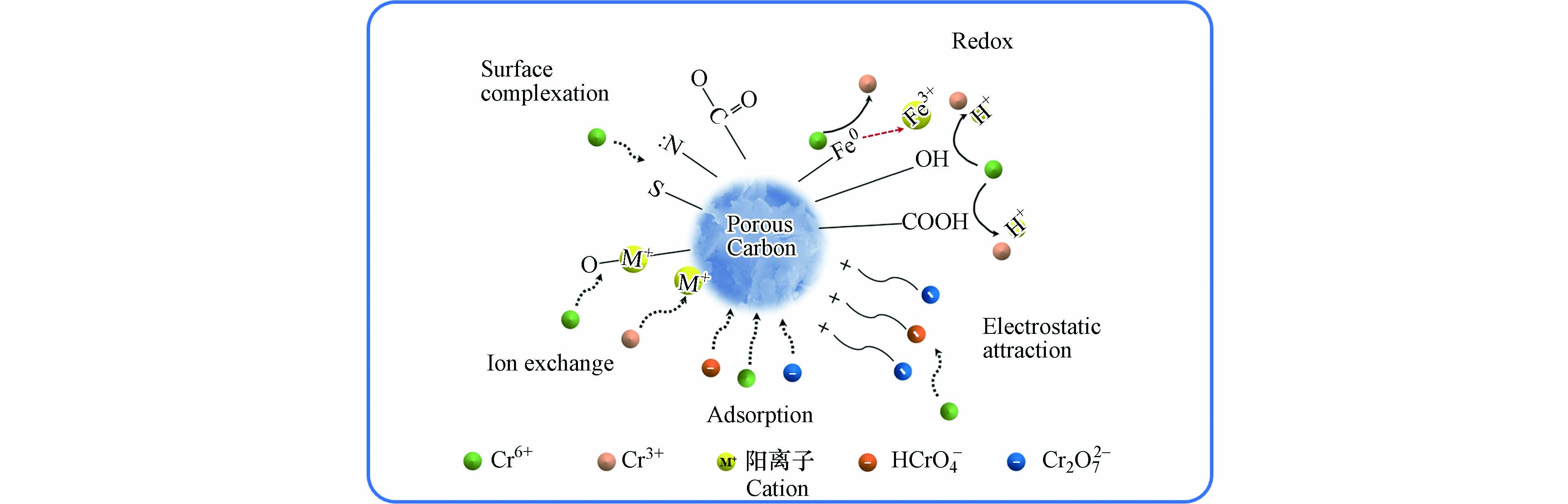
改性后的多孔炭表面负载有丰富的活性官能团,这些官能团与重金属之间的络合、氧化还原作用等都会对吸附一定影响,因此,改性后的多孔炭对重金属离子具有更好的吸附选择性. 如:sp3杂化的吡咯氮具有富电子结构,使其容易给电子从而与具有氧化性的Cr(Ⅵ) 发生氧化还原作用[135];巯基对Pb(Ⅱ)离子具有良好亲和性,可以与Pb(Ⅱ)离子形成稳定的络合物[136]等. 在吸附过程中,影响吸附效果的因素有很多,另外不同材料制备的多孔炭对重金属Cr(Ⅵ) 的吸附机理也不同. 研究发现,煤与赤泥共热解制备的铁炭复合材料对Cr(Ⅵ) 也有良好的吸附效果,而且当赤泥与煤的质量比为1:3、炭化温度为800 ℃、炭化时间为60 min时制备的铁炭复合材料对Cr(Ⅵ) 吸附效果最好,并且在溶液pH=3.0时可同时达到Cr(Ⅵ) 的最好吸附效果和铁的最低溶出量[28]. 此外,利用金属氧化物对多孔炭进行表面改性也可显著改善其对Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附性能. 通过负载纳米零价铁对多孔活性炭球进行改性,改性后的材料比表面积达1032.09 m2·g−1,可有效去除废水中Cr(Ⅵ) ,且在循环利用5次后其对Cr(Ⅵ) 的去除率仍在60%以上[137]. 多孔炭吸附Cr机理也主要包括离子交换、氧化还原、表面络合、静电吸引和表面吸附作用(如图12 所示)[124,130,138].
煤基多孔炭吸附Cr(Ⅵ) 的过程主要为物理吸附和化学吸附共同作用,并通过静电相互作用、氧化还原、表面络合[139]和离子交换的形式结合(公式 (2)—(3))[108],煤基多孔炭丰富的孔隙和表面官能团对于Cr(Ⅵ) 的去除非常重要[122,133,140].
研究发现,表面上存在的电荷对多孔炭吸附Cr(Ⅵ) 起重要作用,当pH < pHzpc时,多孔炭上的官能团发生质子化,从而通过静电作用将带负电荷的HCrO 4− 和Cr2O72− 吸附到多孔炭上;然而,由于带负电荷的多孔炭对阴离子Cr(Ⅵ) 有静电排斥作用,因此,随着溶液pH从2.2逐渐升高至8.0,Cr(Ⅵ) 的吸收显著下降[133]. 除了静电作用之外,络合作用在吸附过程中也起着非常重要. 如C=C、C=O和C—O—C对Cr(Ⅵ) 有一定的还原作用或者与Cr(Ⅵ) 发生络合作用[81,141].
前期研究发现,利用煤矸石可制备出分层多孔炭吸附剂,制备的吸附剂对Cr(Ⅵ) 具有良好的吸附性能,吸附容量为320.5 mg·g−1,而且对Cr(Ⅵ) 的吸附主要为化学吸附[125]. 煤矸石吸附Cr(Ⅵ) 主要是通过氧化还原作用,这是因为在酸性条件下煤矸石中的菱铁矿和黄铁矿变为Fe(Ⅱ)、S和H2S等还原性物质,Cr(Ⅵ) 被还原成Cr(Ⅲ),Fe(Ⅱ) 和S、H2S 被Cr(Ⅵ) 分别氧化成Fe(Ⅲ) 和SO42− [142]. 此外,研究还发现在多孔炭表面负载Fe0或铁的氧化物后对Cr(Ⅵ) 具有良好的络合(见公式(4))[143]和还原作用,铁炭材料表面的Fe0 将Cr(Ⅵ) 还原成Cr(Ⅲ),随后生成Fe(Ⅱ)/Fe(Ⅲ)和铬离子反应,见公式 (5)—(8) [21,143 − 144]. 同时伴随着H+的消耗,溶液pH的升高致使Fe–Cr氢氧化物沉淀在铁炭材料上,在此过程中发生的反应见公式 (9)—(10) [111].
通过文献报道可知,多孔炭吸附Cr(Ⅵ) 的机理可归纳为:Cr(Ⅵ) 先通过静电作用吸附到材料表面,其中部分Cr(Ⅵ) 被C—O [111]或者质子化官能团还原为Cr(Ⅲ) ;其次,通过与溶液中的阳离子如H+ 、Al3+ 和Zn2+ 等发生离子交换反应,或表面官能团发生络合反应(主要是—COOH、C—O和—OH)等方式将大量Cr(Ⅲ) 吸附到材料上,而剩余的Cr(Ⅲ) 和Fe(Ⅲ) 生成共沉淀产物或者被释放到溶液中[138,145].
-
实际含铬废水与模拟的含铬废水有所不同,两者的理化性质和共存离子存在情况有一定的差异. 一般认为,真实废水中存在的其他重金属和阴离子(如硫酸盐、钙、镁、铜、镉、铁等离子)会在一定程度上干扰Cr(Ⅵ) 的吸附[146]. 王华斌[81]发现1.0 g赤泥改性后的多孔炭能够净化0.3 L实际的电镀废水,低于模拟含Cr(Ⅵ) 废水处理量(0.8 L). Pholosi等[146] 比较了合成废水和实际废水中Cr(Ⅵ) 的去除率,发现用磁性松果复合材料吸附时,Cr的去除率分别为43.18%和35.03%,去除率降低的原因一方面可能是真实废水中的阴、阳离子和Cr(Ⅵ) 活性位点之间存在竞争,另一方面可能也与多孔炭对Cr(Ⅵ) 的选择性有关. 然而,也有研究表明共存的Ca2+、Na+ 等阳离子或Cl-、NO3-等阴离子并不会对铬的去除率产生负面影响,共存离子存在时,对Cr(Ⅵ) 的吸附性能仅下降不到2%[108]. 总体来看,目前研究者还主要是通过模拟含铬废水来研究多孔材料对六价铬的吸附性能和机理,关于多孔炭对真实含铬废水中Cr的去除性能及机理还有待进一步研究.
-
在煤炭开采和加工过程中产生的煤矸石、煤泥、煤气化渣等煤基固废,可通过热解、水热碳化以及模板法和活化法等方法制备多孔炭. 在制备过程中,原料的理化性质、制备方法及工艺(升温速率、终温及时间)等在一定程度上都会影响多孔炭性能. 此外,氮、硫、铁等杂原子掺杂也会影响多孔炭的性能. 氮、硫原子作为炭材料常见的掺杂元素,目前常见的掺杂方式主要有原位掺杂和后处理两种. 引入氮、硫原子后可以通过改变材料表面的电子特征和官能团来提升材料的吸附性能,如在碳结构中引入硫原子后会在碳原子附近诱导出丰富的活性位点. 另外,金属元素也可以通过物理和化学两方面作用改性多孔炭,其中物理作用改性原理是由于金属或其化合物与原料混合时会占有一定的空间,因此在对活性炭进行酸洗后处理时,金属会被洗去,从而形成孔隙;化学作用改性原理则是因为在原料中添加金属或其化合物后,会起到增加表面活性点的作用,从而改善其炭化特性、表面活性、反应速率和反应历程. 需要提及的是,铁元素掺杂可以催化多孔炭的活化过程,促进大、中孔的发育,但是对于微孔的形成影响并不大;材料表面负载零价铁后将有助于Cr(Ⅵ) 还原为Cr(Ⅲ) 进而降低其毒性.
利用多孔炭材料处理水体中的重金属时,影响重金属吸附效果的因素主要有pH值、吸附剂的用量、重金属的初始浓度以及环境温度等. 多孔炭对Cr(Ⅵ) 的吸附机理主要包括静电作用、氧化还原反应、离子交换作用和表络合作用等,基本符合Langmuir等温模型和化学吸附. 由于原料和多孔炭制备方法的差异性,使其吸附动力学模型各不相同. 废水中的重金属离子种类繁多、存在形态多样,且各种离子之间存在一定的相互作用,因此实际废水体系中重金属离子和多孔炭之间的作用机理更为复杂. 明确多孔炭与重金属之间的选择吸附性关系以及重金属离子吸附效率与多孔炭结构之间的构效关系,开发绿色、环保、低碳、高效的重金属吸附技术是未来废水中重金属离子去除的重要研究方向之一.
煤基固废多孔炭的制备及其对废水中六价铬的去除性能研究进展
Progress in preparation and modification of coal-based porous carbon and the adsorption performance of Cr(Ⅵ) in waste water
-
摘要: 推进煤炭清洁高效利用是助力双碳目标的重要途径之一,而煤基固废高值化利用是煤炭清洁高效利用过程中很重要的一个方面,利用煤基固废制备多孔炭可实现煤基固废高值化利用. 本文综述了以各种煤基固废为原料制备多孔炭和多孔炭改性的方法,并介绍了煤基多孔炭对六价铬的吸附性能研究进展. 目前,煤基固废制备多孔炭的方法主要有热解、水热碳化、模板法和活化法;而掺杂改性则主要是通过浸渍或者原位合成等手段对多孔炭进行氮、硫、铁等原子的掺杂. 多孔炭对水中六价铬有良好的吸附性能,其吸附机理主要包括静电作用、氧化还原反应、离子交换作用和表面络合作用等. 由于废水中的重金属离子种类繁多、存在形态多样,且各种离子之间存在一定的相互作用,因此实际废水体系中重金属离子和多孔炭之间的作用机理较为复杂. 明确多孔炭与重金属之间的选择吸附性关系以及重金属离子吸附效率与多孔炭结构之间的构效关系,开发绿色、环保、低碳、高效的重金属吸附技术是未来废水中重金属离子去除的重要研究方向之一.Abstract: Promoting the clean and efficient utilization of coal is an important way to achieve carbon peaking and carbon neutrality goals. High-value utilization of coal-based solid waste is an important aspect for clean and efficient utilization of coal. Preparation of porous carbon from coal-based solid waste is one of the effective ways to achieving high-value utilization of coal-based solid waste. This paper reviews the preparation of porous carbon from various coal-based solid wastes and the modification of porous carbon, and presents the progress of research on the adsorption performance of coal-based porous carbon for Cr(Ⅵ). At present, the main methods for preparing porous carbon from coal-based solid waste are pyrolysis, hydrothermal carbonization, template and activation etc. And through impregnation or in situ synthesis, heteroatoms such as N, S and Fe can be doped into the porous carbon. Porous carbon has good adsorption properties for Cr(Ⅵ) in water, and its adsorption mechanism mainly includes electrostatic interaction, redox reaction, ion exchange and surface complexation. For the actual wastewater, there are many types of heavy metals, as well as their existence forms, so the certain interactions between various ions are complex, and the mechanism of action between heavy metal ions and porous carbon are not very clear. In the future, the constitutive relationship between heavy metal ion adsorption efficiency and porous carbon structure needs to be clarified. Furthermore, developing green, environmentally friendly, low-carbon and efficient heavy metal adsorption technologies is also one of the important tasks for the removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater.
-
Key words:
- porous carbon /
- preparation methods /
- doping modification /
- adsorption /
- Cr(Ⅵ).
-

-
图 11 (a)重金属的5种吸附机制[17];(b) Hg的吸附机理示意图[81];(c) As的吸附机理示意图[120 − 121];(d) Cr的吸附机理示意图[81]
Figure 11. (a) Five sorption mechanisms for heavy metals[17]; (b) schematic diagram of the sorption mechanism for Hg [81]; (c) schematic diagram of the sorption mechanism for As [120 − 121]; (d) schematic diagram of the sorption mechanism for Cr [81]
表 1 各种煤基多孔炭的制备参数及孔结构参数
Table 1. Preparation parameters and pore structure parameters of various coal-based porous carbon
原料
Material制备参数
Preparation parameters孔结构参数
Hole structure parameters参考文献
References制备方式
Method温度/℃
Temperature时间/min
Time活化剂/模板剂
Activator/ Template比表面积/(m2·g−1)
Specific surface area孔体积/(cm3·g−1)
Pore volume褐煤1 化学氧化法(H3PO4) 500 420 未使用活化剂/模板剂 5.46 0.079 [23] 褐煤2 常规热解 800 60 未使用活化剂/模板剂 242.73 0.186 [24] 褐煤3 活化法,水蒸汽等离子体改性 800 120 MgCO3 1989 1.09 [25] 烟煤 活化法 800 120 NH3 1235 0.58 [26] 无烟煤1 常规热解 700 120 KOH 3550.7 — [27] 无烟煤2 活化法 880 180 水蒸气 993.5 0.5086 [28] 煤泥 活化法 485 90 ZnCl2 918.15 0.511 [29] 煤沥青1 活化法 800 60 KOH 1649 1.0 [30] 煤沥青2 活化法 800 60 KOH 2168 1.14 [31] 煤沥青3 模板法 700 120 NaCl 332 0.422 [32] 煤焦油+沥青 常规热解 900 120 未使用活化剂/模板剂 3305 1.66 [33] 煤气化粗渣 活化法 700 360 CO2 862.76 0.684 [34] 煤气化细渣 活化法 750 80 KOH 2481 1.711 [35] 煤矸石 活化法 850 180 K2CO3 1160 0.512 [36] 煤矸石+松木屑 热解法 500 60 未使用活化剂/模板剂 80.725 0.094 [37] —,文献中未提及. —, not mentioned in the literature. 表 2 多孔炭杂原子掺杂改性
Table 2. Porous carbon modified by heteroatom doping
掺杂原子
Atomic type添加剂
Additives研究结果
Research results参考文献
References氮原子 氨气 活性炭表面固定的吡啶氮、胺基、吡咯氮等官能团,提高Cu(Ⅱ) 离子的吸附速率和容量. [78] 甲壳素 较高的温度以石墨型氮的形态存在,相比前者,在较低温度主要是以吡咯氮和胺基的形式存在. [76] g-C3N4 g-C3N4 的引入能够显著提高催化剂的比表面积,提高铁纳米颗粒在碳载体材料上的均匀分散程度. [79] 铁原子 Fe3O4 Fe3O4有利于多孔炭材料中孔的形成和发育、催化孔隙的生成,其中添加质量分数10%的Fe3O4 产生的中孔率高达76.0%. [80] 磁铁矿 磁铁矿的存在可以增加炭化和活化速率,形成大的比表面积和高的孔体积,并且促进了活性炭中微孔和中孔数量的增加. [28] 赤泥 赤泥中的Fe2O3 先还原成Fe3O4,再进一步还原成Fe0;Fe0 将Cr(Ⅵ) 还原成Cr(Ⅲ) 再进行吸附. [24] 赤泥 赤泥改性水热炭中形成Fe3O4 和Fe0 磁性成分,对Cr(Ⅵ) 展现出较好的化学还原和吸附效果. [81] 磁铁矿 磁铁矿在pH≥5.5时对Pb(Ⅱ) 具有很好的吸附效果,这是因为较高的pH值有利于磁铁矿表面去质子化导致其表面负电荷位点增多,与带正电荷的Pb(Ⅱ) 之间产生强烈静电引力而提升吸附性能. [82] 硫原子 SO2、H2S SO2改性后的活性炭可提高对Cd(Ⅱ) 约70%的吸附容量;吸附Pb(Ⅱ) 时,随着活性炭中硫含量的增加,对Pb(Ⅱ) 的吸附量增加. [83 − 84] 废旧聚苯硫醚 所制备的材料是微孔与介孔复合材料且主要孔型为微孔,对于Cd(Ⅱ) 吸附量24.69 mg·g−1. 其比表面积为466.69 m2·g−1,微孔体积为0.1469 cm3·g−1,平均孔径为2.3287 nm. [85] 表 3 部分煤基多孔炭吸附六价铬的最佳条件
Table 3. Optimal conditions for the adsorption of hexavalent chromium on some coal-based porous carbon
原料
Material吸附方式
Adsorption
methods吸附参数
Adsorption Parameters吸附性能
Adsorption properties参考文献
ReferencespH 初始浓度/
(mg·L−1)
Concentration时间/h
Time投加量/
(g·L−1)
Dosage温度/℃
Temperature吸附量/
(mg·g−1)
Capacity去除率/%
Removal rate商业煤质活性炭 静态吸附 1 200 12 1 25 151.88 75.83 [122] 褐煤 1 20 4 3.5 25 5.6* 98 [118] 煤泥 2 50 24 4 25 9.32 74.56* [24] 煤泥 2 100 1 3 25 99.87 86.88 [123] 煤矸石 5 100 24 0.2 35 9.2 91 [124] 煤矸石 动态吸附 2 15.8 Φ=10 mm*
H=5 mm45 320.51 [125] *, 根据文献提供的数据进行计算所得. *, calculations based on data provided in the literature. 表 4 煤基多孔炭吸附六价铬的动力学和热力学模型
Table 4. Kinetic and isotherm models for the adsorption of hexavalent chromium on coal-based porous carbon
原料
Material动力学模型
Kinetic model热力学模型
Isotherm吸附方式
Adsorption method吸附量/(mg·g−1)
Maximum adsorption
capacity参考文献
References煤泥 准二级动力学模型 Langmuir 化学吸附 86. 88 [123] 煤矸石 拟二阶动力学模型 Langmuir 化学吸附 55.08 [131] 煤矸石 拟二阶动力学模型 Langmuir 化学吸附 320.51 [125] 煤矸石+油菜秸秆 拟二阶动力学模型 Langmuir 化学吸附 9.2 [124] 粉煤灰 准二级动力学模型 — 物理吸附和化学吸附 1.394 [134] 酸化后的褐煤 二级动力学模型 Freundlich — 5.6* [118] 褐煤 准一级或准二级动力学模型 Freundlich — 12.965 [24] *, 根据文献提供的数据进行计算所得;—, 文献中未提及.
*, calculations based on data provided in the literature; —, not mentioned in the literature. -
[1] 孙志军, 李贞, 赵俊吉, 等. 山西省典型煤电基地煤基固废综合利用研究与资源化分析[J]. 中国煤炭, 2021, 47(4): 70-80. SUN Z J, LI Z, ZHAO J J, et al. Comprehensive utilization study and resource recycling analysis of coal based solid waste in Shanxi typical coal power base[J]. China Coal, 2021, 47(4): 70-80 (in Chinese).
[2] REZAEI H, SHAFAEI S Z, ABDOLLAHI H, et al. Spent-medium leaching of germanium, vanadium and lithium from coal fly ash with biogenic carboxylic acids and comparison with chemical leaching[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2023, 217: 106038. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2023.106038 [3] 张吉雄, 张强, 周楠, 等. 煤基固废充填开采技术研究进展与展望[J]. 煤炭学报, 2022, 47(12): 4167-4181. ZHANG J X, ZHANG Q, ZHOU N, et al. Research progress and prospect of coal based solid waste backfilling mining technology[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(12): 4167-4181 (in Chinese).
[4] 2021年中国生态环境统计年报_中华人民共和国生态环境部[EB/OL 2023-07-01
[5] 袁飞. 华宁煤基多孔炭制备与粉体成型及对Cr(Ⅵ)吸附性能研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2022. YUAN F. Preparation and powder forming of Huaning coal based porous carbon and its adsorption properties study for Cr(Ⅵ)[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2022 (in Chinese).
[6] 施周, 邓林. 水中重金属离子吸附材料的研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 建筑科学与工程学报, 2017, 34(5): 21-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2049.2017.05.003 SHI Z, DENG L. Research progresses and trends in materials for adsorption of heavy metal ions in aqueous phase[J]. Journal of Architecture and Civil Engineering, 2017, 34(5): 21-30 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2049.2017.05.003
[7] NADAROGLU H, KALKAN E, DEMIR N. Removal of copper from aqueous solution using red mud[J]. Desalination, 2010, 251(1/2/3): 90-95. [8] AHMARUZZAMAN M. Industrial wastes as low-cost potential adsorbents for the treatment of wastewater laden with heavy metals[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2011, 166(1/2): 36-59. [9] STRELKO V, MALIK D J, STREAT M. Characterisation of the surface of oxidised carbon adsorbents[J]. Carbon, 2002, 40(1): 95-104. doi: 10.1016/S0008-6223(01)00082-3 [10] XIE R Z, JIN Y, CHEN Y, et al. The importance of surface functional groups in the adsorption of copper onto walnut shell derived activated carbon[J]. Water Science and Technology:a Journal of the International Association on Water Pollution Research, 2017, 76(11/12): 3022-3034. [11] 牛桃霞. 多孔碳材料的制备及其吸附性能研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2018. NIU T X. Preparation and adsorption properties study of porous carbon materials[D]. Xi'an: Northwest University, 2018 (in Chinese).
[12] PUREVSUREN B, LIOU Y H, DAVAAJAV Y, et al. Investigation of adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous phase onto coal-based activated carbons[J]. Journal of the Chinese Institute of Engineers, 2017, 40(4): 355-360. doi: 10.1080/02533839.2017.1308273 [13] 陈春瑞, 王鹏程, 杨凤玲, 等. 煤泥浓密膏体流变特性测试方法研究进展[J]. 中国煤炭, 2022, 48(5): 60-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-530X.2022.05.011 CHEN C R, WANG P C, YANG F L, et al. Research progress on testing methods of rheological properties of coal slime dense paste[J]. China Coal, 2022, 48(5): 60-67 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-530X.2022.05.011
[14] 杜韫哲, 柳一灵, 沈伟, 等. 山西省部分地区煤矸石基础理化性质研究[J]. 煤炭加工与综合利用, 2023(4): 80-83. doi: 10.16200/j.cnki.11-2627/td.2023.04.019 DU Y Z, LIU Y L, SHEN W, et al. The basic physical and chemical properties of coal gangue in some typical areas of Shanxi Province[J]. Coal Processing & Comprehensive Utilization, 2023(4): 80-83 (in Chinese). doi: 10.16200/j.cnki.11-2627/td.2023.04.019
[15] 张丽宏, 金要茹, 程芳琴. 煤气化渣资源化利用[J]. 化工进展, 2023, 42(8): 4447-4457. doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2022-1845 ZHANG L H, JIN YAO R, CHENG F Q. Resource utilization of coal gasification slag[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2023, 42(8): 4447-4457 (in Chinese). doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2022-1845
[16] 韩露. 山西典型煤种制备超级活性炭的正交试验研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2008. HAN L. Preparation of super-activated carbon from typical Shanxi coals by the method of orthogonal design[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2008 (in Chinese).
[17] YANG X D, WAN Y S, ZHENG Y L, et al. Surface functional groups of carbon-based adsorbents and their roles in the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions: A critical review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 366: 608-621. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.02.119 [18] CIOFU F. Activated carbon (charcoal) obtaining. application[J]. Fiabilitate şi Durabilitate, 2015, suppl(1): 98-103. [19] 程彬海. 有机固体废物热解制备功能多孔碳材料中氮的增效机制研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2019. CHENG B H. Mechanism elucidation of nitrogen in functional porous carbon materials prepared by pyrolysis of organic solid waste[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2019 (in Chinese).
[20] 杨晓阳, 王宝凤, 宋旭涛, 等. 污泥与高硫煤共水热碳化过程中硫氮形态转化规律[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(11): 5211-5219. YANG X Y, WANG B F, SONG X T, et al. Migration of sulfur and nitrogen during co-hydrothermal carbonization process of sewage sludge and high-sulfur coal[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(11): 5211-5219 (in Chinese).
[21] WANG C S, YAN B, ZHENG J J, et al. Recent progress in template-assisted synthesis of porous carbons for supercapacitors[J]. Advanced Powder Materials, 2022, 1(2): 100018. doi: 10.1016/j.apmate.2021.11.005 [22] HE X J, ZHAO N, QIU J S, et al. Synthesis of hierarchical porous carbons for supercapacitors from coal tar pitch with nano-Fe2O3 as template and activation agent coupled with KOH activation[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2013, 1(33): 9440-9448. doi: 10.1039/c3ta10501f [23] 张崎. 煤基吸附剂的制备及其去除废水中重金属的研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉科技大学, 2016. ZHANG Q. Preparation of coal based sorbent and its application for the removal of heavy metal from wastewater[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2016 (in Chinese).
[24] 仇雅丽, 李长明, 王德亮, 等. 赤泥/煤基铁炭材料的制备及其脱除废水Cr(Ⅵ)的性能[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(7): 3216-3225. QIU Y L, LI C M, WANG D L, et al. Preparation of red mud/coal based material and its performance to remove Cr(Ⅵ) in waste water[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(7): 3216-3225 (in Chinese).
[25] DONG D, ZHANG Y S, XIAO Y, et al. Oxygen-enriched coal-based porous carbon under plasma-assisted MgCO3 activation as supercapacitor electrodes[J]. Fuel, 2022, 309: 122168. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.122168 [26] SUN F, GAO J H, YANG Y Q, et al. One-step ammonia activation of Zhundong coal generating nitrogen-doped microporous carbon for gas adsorption and energy storage[J]. Carbon, 2016, 109: 747-754. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2016.08.076 [27] SHI M, XIN Y F, CHEN X X, et al. Coal-derived porous activated carbon with ultrahigh specific surface area and excellent electrochemical performance for supercapacitors[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 859: 157856. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.157856 [28] ZHANG J. Preparation and characterization of magnetic coal-based activated carbon in the presence of Fe3O4[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2011, 393/394/395: 1355-1358. [29] ZHANG G, YANG H F, JIANG M L, et al. Preparation and characterization of activated carbon derived from deashing coal slime with ZnCl2 activation[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2022, 641: 128124. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.128124 [30] WEI Q H, QIN F F, MA Q X, et al. Coal tar- and residual oil-derived porous carbon as metal-free catalyst for nitroarene reduction to aminoarene[J]. Carbon, 2019, 141: 542-552. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2018.09.087 [31] QIN F F, TIAN X D, GUO Z Y, et al. Asphaltene-based porous carbon nanosheet as electrode for supercapacitor[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6(11): 15708-15719. [32] MA X Q, XIAO N, XIAO J, et al. Nitrogen and phosphorus dual-doped porous carbons for high-rate potassium ion batteries[J]. Carbon, 2021, 179: 33-41. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2021.03.067 [33] QIN B, WANG Q, ZHANG X H, et al. One-pot synthesis of interconnected porous carbon derived from coal tar pitch and cellulose for high-performance supercapacitors[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2018, 283: 655-663. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2018.06.201 [34] 亢玉红, 冯博洪, 李珍妮, 等. 煤气化废渣基活性炭吸附对二甲苯动力学与热力学研究[J]. 离子交换与吸附, 2020, 36(1): 49-57. KANG Y H, FENG B H, LI Z N, et al. Adsorption thermodynamics and kinetics of p-xylene on activated carbon prepared by coal gasificationwaste residue[J]. Ion Exchange and Adsorption, 2020, 36(1): 49-57 (in Chinese).
[35] XU Y T, CHAI X L. Characterization of coal gasification slag-based activated carbon and its potential application in lead removal[J]. Environmental Technology, 2018, 39(3): 382-391. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2017.1301569 [36] 邓晓虎, 乐英红, 高滋. K2CO3活化煤矸石制备活性炭吸附剂[J]. 应用化学, 1997, 14(3): 49-52. DENG X H, YUE Y H, GAO Z. Preparation of active carbon adsorbents from elutrilithe via K2CO3 activation[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 1997, 14(3): 49-52 (in Chinese).
[37] QIU B B, DUAN F. Synthesis of industrial solid wastes/biochar composites and their use for adsorption of phosphate: From surface properties to sorption mechanism[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2019, 571: 86-93. [38] QUAN C, ZHOU Y Y, WANG J W, et al. Biomass-based carbon materials for CO2 capture: A review[J]. Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2023, 68: 102373. doi: 10.1016/j.jcou.2022.102373 [39] ALLENDE S, BRODIE G, JACOB M V. Breakdown of biomass for energy applications using microwave pyrolysis: A technological review[J]. Environmental Research, 2023, 226: 115619. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.115619 [40] 李宇轩, 张纯, 刘辉, 等. 微波辅助热解制备铁氮/生物炭及其芬顿催化活性[J]. 有色金属科学与工程, 2022, 13(6): 34-41. LI Y X, ZHANG C, LIU H, et al. Preparation of Fe-N/biochar by microwave-assisted pyrolysis and its Fenton catalytic activity[J]. Nonferrous Metals Science and Engineering, 2022, 13(6): 34-41 (in Chinese).
[41] 李京书, 张媛媛, 王兰慧, 等. 污泥热解生物炭中重金属与磷的转化行为研究进展[J]. 能源环境保护, 2023, 37(2): 30-38. doi: 10.20078/j.eep.20230307 LI J S, ZHANG Y Y, WANG L H, et al. Review on transformation behavior of heavy metals and phosphorus in sewage sludge pyrolysis biochar[J]. Energy Environmental Protection, 2023, 37(2): 30-38 (in Chinese). doi: 10.20078/j.eep.20230307
[42] 陈太平. 准东煤微波热解并向功能性碳材料转化的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2020. CHEN T P. Microwave pyrolysis of Zhundong coal and its transformation to functional carbon materials[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020 (in Chinese).
[43] 靳庆壮. 生物质水热碳化废水循环利用过程中水热炭的形成机制研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2021. JIN Q Z. Study on the formation mechanism of hydrochar in the recycling process of biomass hydrothermal carbonization wastewater[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2021 (in Chinese).
[44] GONG Y T, XIE L, CHEN C H, et al. Bottom-up hydrothermal carbonization for the precise engineering of carbon materials[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2023, 132: 101048. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2022.101048 [45] YANG X Y, WANG B F, SONG X T, et al. Co-hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge and coal slime with sulfuric acid for N, S doped hydrochar[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 354: 131615. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131615 [46] 雷艳秋. 生物质基碳材料的制备及在环境与能源中的应用[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学, 2017. LEI Y Q. The biomass-based carbon material prepartion and application in environment and energy[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University, 2017 (in Chinese).
[47] PAVLENKO V, KHOSRAVI H S, ŻÓŁTOWSKA S, et al. A comprehensive review of template-assisted porous carbons: Modern preparation methods and advanced applications[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:R:Reports, 2022, 149: 100682. doi: 10.1016/j.mser.2022.100682 [48] 苏丽. 功能化多孔碳材料的制备及其电化学性能研究[D]. 秦皇岛: 燕山大学, 2021. SU L. Preparation and electrochemical properties of functionalized porous carbon materials[D]. Qinhuangdao: Yanshan University, 2021 (in Chinese).
[49] ZHANG W, CHENG R R, BI H H, et al. A review of porous carbons produced by template methods for supercapacitor applications[J]. New Carbon Materials, 2021, 36(1): 69-81. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5805(21)60005-7 [50] TIAN P F, ZANG J B, SONG S W, et al. In situ template reaction method to prepare three-dimensional interconnected Fe-N doped hierarchical porous carbon for efficient oxygen reduction reaction catalysts and high performance supercapacitors[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 448: 227443. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.227443 [51] HE X J, ZHANG H B, ZHANG H, et al. Direct synthesis of 3D hollow porous graphene balls from coal tar pitch for high performance supercapacitors[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(46): 19633-19640. doi: 10.1039/C4TA03323J [52] 周颖, 宋晓娜, 舒成, 等. 模板法煤沥青基中孔炭的制备及其电化学性能[J]. 新型炭材料, 2011, 26(3): 187-191. ZHOU Y, SONG X N, SHU C, et al. The electrochemical properties of templated and activated mesoporous carbons produced from coal pitch[J]. New Carbon Materials, 2011, 26(3): 187-191 (in Chinese).
[53] WU T T, JIN B Y, LI H Q, et al. Foam-like porous carbons with ultrahigh surface area from petroleum pitch and their supercapacitive performance[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2021, 783: 139058. doi: 10.1016/j.cplett.2021.139058 [54] HE X J, LI X J, WANG X T, et al. Efficient preparation of porous carbons from coal tar pitch for high performance supercapacitors[J]. New Carbon Materials, 2014, 29(6): 493-502. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5805(14)60150-5 [55] JIANG Y C, HE Z F, DU Y Y, et al. In-situ ZnO template preparation of coal tar pitch-based porous carbon-sheet microsphere for supercapacitor[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 602: 721-731. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2021.06.037 [56] SRIVASTAVA A, GUPTA B, MAJUMDER A, et al. A comprehensive review on the synthesis, performance, modifications, and regeneration of activated carbon for the adsorptive removal of various water pollutants[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2021, 9(5): 106177. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.106177 [57] 贺新福, 张小琴, 安得宁, 等. 低阶型煤热解半焦制备活性炭的试验研究[J]. 煤炭技术, 2017, 36(4): 290-293. HE X F, ZHANG X Q, AN D N, et al. Study on preparation of activated carbon from briquette char[J]. Coal Technology, 2017, 36(4): 290-293 (in Chinese).
[58] 田叶顺, 任文, 王国袖, 等. 微波加热CO2活化法制备生物质活性炭及其脱硫性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(12): 5774-5784. TIAN Y S, REN W, WANG G X, et al. Study on preparation and desulfurization characteristics of biomass activated carbon by microwave heating CO2 activation method[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(12): 5774-5784 (in Chinese).
[59] 侯志勇, 郝亮亮, 沈小瑞, 等. 煤气化细渣制备吸附材料研究进展[J]. 洁净煤技术, 2021, 27(增刊2): 201-205. HOU Z Y, HAO L L, SHEN X R, et al. Research progress on preparation of adsorption materials from coal gasification fine slaget[J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2021, 27(Sup 2): 201-205 (in Chinese).
[60] WANG L W, SHA L, ZHANG S H, et al. Preparation of activated coke by carbonization, activation, ammonization and thermal treatment of sewage sludge and waste biomass for SO2 absorption applications[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2022, 231: 107233. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2022.107233 [61] 虞军伟. 碳基常压储氢材料的制备及其微观结构调控[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2021. YU J W. Preparation and microstructure control of carbon-based atmospheric hydrogen storage materials[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2021 (in Chinese).
[62] LU C L, XU S P, GAN Y X, et al. Effect of pre-carbonization of petroleum cokes on chemical activation process with KOH[J]. Carbon, 2005, 43(11): 2295-2301. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2005.04.009 [63] LILLO-RÓDENAS M A, JUAN-JUAN J, CAZORLA-AMORÓS D, et al. About reactions occurring during chemical activation with hydroxides[J]. Carbon, 2004, 42(7): 1371-1375. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2004.01.008 [64] WANG Z H, CAO Q F, GUO F J, et al. Preparation and electrochemical properties of low-temperature activated porous carbon from coal tar pitch[J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2023, 135: 109855. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2023.109855 [65] LIU Y, ZHU Z S, CHENG Q, et al. One-step preparation of environment-oriented magnetic coal-based activated carbon with high adsorption and magnetic separation performance[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2021, 521: 167517. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2020.167517 [66] ZHU Y W, WANG Y J, WANG T Y, et al. One-step preparation of coal-based magnetic activated carbon with hierarchically porous structure and easy magnetic separation capability for adsorption applications[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2023, 569: 170480. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2023.170480 [67] 王李炜. 污泥与生物质制备活性焦脱硫性能的研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2022. WANG L W. Study on desulfurization performance of activated coke prepared from sludge and biomass[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2022 (in Chinese).
[68] 张傲. 氧解残煤微波制备多孔炭及吸波应用[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2019. ZHANG A. Preparation of porous carbon by microwave irradiation from oxidized coal and its microwave absorbing application[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2019 (in Chinese).
[69] 于馨凝, 华哲生, 杨洋, 等. Ca(NO3)2改性对煤基多孔炭结构及甲苯吸附性能的影响[J]. 煤炭学报, 2021, 46(12): 4063-4070. YU X N, HUA Z S, YANG Y, et al. Effects of Ca(NO3)2 pretreatment on structure of coal-based porous carbon and its adsorption properties for toluene[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(12): 4063-4070 (in Chinese).
[70] 徐园园, 陆倩, 木沙江, 等. 煤基多孔炭的制备及其在超级电容器中的应用[J]. 煤炭转化, 2016, 39(1): 76-81. XU Y Y, LU Q, MU S J, et al. Preparation of coal-based porous carbon and utilization in supercapacitor[J]. Coal Conversion, 2016, 39(1): 76-81 (in Chinese).
[71] WANG X L, LI Y Z, YANG C, et al. Self-template porous carbon by direct activation of high-ash coal liquefaction residue for high-rate supercapacitor electrodes[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2021, 45(3): 4782-4792. doi: 10.1002/er.6096 [72] 王相龙. 煤液化残渣制备多孔炭及其电容性能研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆大学, 2021. WANG X L. Capacitive properties of porous carbons prepared from coal liquefaction residue[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang University, 2021 (in Chinese).
[73] 仇微微. 杂原子掺杂碳微球的制备及其电化学性能研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2020. QIU W W. Preparation and electrochemical properties of heteroatom-doped carbon spheres [D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2020 (in Chinese).
[74] 阚渝姣. 废旧电路板基活性炭的制备及吸附性能研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2018. KAN Y J. Study on the preparation and adsorption property of activated carbon from waste circuit boards [D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2018 (in Chinese).
[75] BIAN Y, BIAN Z Y, ZHANG J X, et al. Effect of the oxygen-containing functional group of graphene oxide on the aqueous cadmium ions removal[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2015, 329: 269-275. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.12.090 [76] WANG H Y, GAO B, WANG S S, et al. Removal of Pb(Ⅱ), Cu(Ⅱ), and Cd(Ⅱ) from aqueous solutions by biochar derived from KMnO4 treated hickory wood[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2015, 197: 356-362. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2015.08.132 [77] LYU H H, GAO B, HE F, et al. Ball-milled carbon nanomaterials for energy and environmental applications[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2017, 5(11): 9568-9585. [78] KASNEJAD M H, ESFANDIARI A, KAGHAZCHI T, et al. Effect of pre-oxidation for introduction of nitrogen containing functional groups into the structure of activated carbons and its influence on Cu (Ⅱ) adsorption[J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2012, 43(5): 736-740. doi: 10.1016/j.jtice.2012.02.006 [79] 徐朝权. 铁氮共掺杂多孔碳材料的制备及其氧还原性能研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆大学, 2018. XU Z Q. The preparation and application of Fe and N co-doped porous carbon catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang University, 2018 (in Chinese).
[80] 邢雯雯, 周铁桥, 张军, 等. 煤基磁性活性炭的制备[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2009, 31(1): 83-87. XING W W, ZHOU T Q, ZHANG J, et al. Preparation of magnetic coal-based activated carbon[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2009, 31(1): 83-87 (in Chinese).
[81] 王华斌. 金属盐及赤泥改性水热炭吸附重金属的性能与机理研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2020. WANG H B. Performance and mechanism study on engineered hydrochar modified by metal salts or industrial red mud for heavy metals immobilization[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2020 (in Chinese).
[82] NASSAR N N. Rapid removal and recovery of Pb(Ⅱ) from wastewater by magnetic nanoadsorbents[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 184(1/2/3): 538-546. [83] MACı́AS-GARCı́A A, GÓMEZ-SERRANO V, ALEXANDRE-FRANCO M F, et al. Adsorption of cadmium by sulphur dioxide treated activated carbon[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2003, 103(1/2): 141-152. [84] MACı́AS-GARCı́A A, VALENZUELA-CALAHORRO C, ESPINOSA-MANSILLA A, et al. Adsorption of Pb2+ in aqueous solution by SO2-treated activated carbon[J]. Carbon, 2004, 42(8/9): 1755-1764. [85] 苏文韬, 蔡铭, 车美红, 等. 由聚苯硫醚废料制备硫掺杂多孔碳处理含重金属废水[J]. 工业技术创新, 2022, 9(3): 83-90. SU W T, CAI M, CHE M H, et al. Preparing the sulfur-doped porous carbon from polyphenylene sulfide waste to treat wastewater contained heavy metals[J]. Industrial Technology Innovation, 2022, 9(3): 83-90 (in Chinese).
[86] WANG B, GAO B, FANG J N. Recent advances in engineered biochar productions and applications[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2017, 47(22): 2158-2207. doi: 10.1080/10643389.2017.1418580 [87] GARCı́A T, MURILLO R, CAZORLA-AMORÓS D, et al. Role of the activated carbon surface chemistry in the adsorption of phenanthrene[J]. Carbon, 2004, 42(8/9): 1683-1689. [88] BAI J, SUN H M, YIN X J, et al. Oxygen-content-controllable graphene oxide from electron-beam-irradiated graphite: Synthesis, characterization, and removal of aqueous lead [Pb(Ⅱ)][J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(38): 25289-25296. [89] ZHOU Y M, GAO B, ZIMMERMAN A R, et al. Sorption of heavy metals on chitosan-modified biochars and its biological effects[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2013, 231: 512-518. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2013.07.036 [90] CAZETTA A L, VARGAS A M M, NOGAMI E M, et al. NaOH-activated carbon of high surface area produced from coconut shell: Kinetics and equilibrium studies from the methylene blue adsorption[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011, 174(1): 117-125. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2011.08.058 [91] HU X, DING Z H, ZIMMERMAN A R, et al. Batch and column sorption of arsenic onto iron-impregnated biochar synthesized through hydrolysis[J]. Water Research, 2015, 68: 206-216. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2014.10.009 [92] ZHANG J, ZHANG N, TACK F M G, et al. Modification of ordered mesoporous carbon for removal of environmental contaminants from aqueous phase: A review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 418: 126266. [93] 黄美苓. 多孔碳复合材料的制备及吸附六价铬的研究[D]. 济南: 济南大学, 2017. HUANG M L. The preparation of porous carbon composite materials and the adsorption of hexavalent chromium[D]. Jinan: University of Jinan, 2017 (in Chinese).
[94] 王帅晴, 杨思文, 李娜, 等. 元素掺杂生物质碳材料在电化学储能中的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2023, 42(8): 4296-4306. doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2022-1797 YANG S W, LI N, et al. Research progress of element doped biomass carbon materials for electrochemical energy storage[J]. Chemical Progress, 2023, 42(8): 4296-4306 (in Chinese). doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2022-1797
[95] LI F B, QIAN Q L, YAN F, et al. Nitrogen-doped porous carbon microspherules as supports for preparing monodisperse nickel nanoparticles[J]. Carbon, 2006, 44(1): 128-132. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2005.06.049 [96] GAO Y J, CHEN X, ZHANG J G, et al. Chitin-derived mesoporous, nitrogen-containing carbon for heavy-metal removal and styrene epoxidation[J]. ChemPlusChem, 2015, 80(10): 1556-1564. doi: 10.1002/cplu.201500293 [97] MA G X, NING G Q, WEI Q. S-doped carbon materials: Synthesis, properties and applications[J]. Carbon, 2022, 195: 328-340. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2022.03.043 [98] 朱俊生, 丁晓波, 曹景沛, 等. 褐煤基多孔炭/CoNi2S4复合材料的制备及电容特性研究[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2021, 49(1): 20-26. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(21)60006-3 ZHU J S, DING X B, CAO J P, et al. Preparation of lignite-based porous carbon/ CoNi2S4 composite materials and their capacitance performance[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2021, 49(1): 20-26 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(21)60006-3
[99] ZHENG Y F, CHEN K M, JIANG K P, et al. Progress of synthetic strategies and properties of heteroatoms-doped (N, P, S, O) carbon materials for supercapacitors[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2022, 56: 105995. doi: 10.1016/j.est.2022.105995 [100] SHEN Y, CHEN B L. Sulfonated graphene nanosheets as a superb adsorbent for various environmental pollutants in water[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(12): 7364-7372. [101] 毛玉婷. GS@LDO吸附水中污染物的机制研究及其工程应用[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2022. MAO Y T. Study on the adsorption mechanism of pollutants by GS@LDO and its engineering application[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2022 (in Chinese).
[102] 黄雪琼. 硫掺杂Fe3O4纳米吸附剂的制备及其对水中重金属离子Pb(Ⅱ)的去除及性能研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2018. HUANG X Q. Synthesis of novel magnetic sulfur-doped Fe3O4 nanoparticles and their application for efficient removal of Pb(Ⅱ)[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2018 (in Chinese).
[103] 何静. 新型硫掺杂凹凸棒的可控制备及其对MB、Pb2+、Cu2+的吸附性能研究[D]. 兰州: 西北民族大学, 2019. HE J. Controllable preparation of new sulfur-doped attapulgite composites and their adsorption properties for MB, Pb2+ and Cu2+ [D]. Lanzhou: Northwest University for Nationalities, 2019 (in Chinese).
[104] ZHANG Y Z, HE R, ZHAO J. Removal mechanism of tetracycline-Cr(Ⅵ) combined pollutants by different S-doped sludge biochars: Role of environmentally persistent free radicals[J]. Chemosphere, 2023, 317: 137856. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.137856 [105] 段昕辉. 废煤基活性炭再生制备载铁复合材料及除砷机理研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2012. DUAN X H. Preparation of iron-loaded composite by regeneration of waste coal-based activated carbon and study on arsenic removal mechanism[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2012 (in Chinese).
[106] 范明霞, 童仕唐. 活性炭孔隙结构对重金属离子吸附性能的影响[J]. 功能材料, 2016, 47(1): 1012-1016. FAN M X, TONG S T. Effect of pore structure of activated carbon on heavy metal ions adsorption performance[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2016, 47(1): 1012-1016 (in Chinese).
[107] YOSHIZAWA N, YAMADA Y, SHIRAISHI M, et al. Dispersion properties of metal oxide nanoparticles supportedin mesoporous activated carbons[J]. TANSO, 1998, 1998(181): 8-13. doi: 10.7209/tanso.1998.8 [108] CHU T T H, NGUYEN M V. Improved Cr (VI) adsorption performance in wastewater and groundwater by synthesized magnetic adsorbent derived from Fe3O4 loaded corn straw biochar[J]. Environmental Research, 2023, 216(Pt 4): 114764. [109] 杨妍, 刘国涛, 余庆慧, 等. 多孔炭材料改性纳米零价铁的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2021, 40(增刊2): 198-202. YANG Y, LIU G T, YU Q H, et al. Research progress of nano-zero-valent iron modified by porous carbon materials [J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2021, 40(Sup 2): 198-202 (in Chinese).
[110] 李改平. 煤基吸附剂的制备及其吸附Cr6+的研究[D]. 青岛: 山东科技大学, 2011. LI G P. The preparation of coal based sorbents and study on Cr6+ adsorption[D]. Qingdao: Shandong University of Science and Technology, 2011 (in Chinese).
[111] HU S J, LIU C S, BU H L, et al. Efficient reduction and adsorption of Cr(VI) using FeCl3-modified biochar: Synergistic roles of persistent free radicals and Fe(II)[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2024, 137: 626-638. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2023.03.011 [112] 沈玲芳. 生物质基磁性炭定向制备及其对水体中Pb(Ⅱ)、Cr(Ⅵ)的去除机理研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江科技学院, 2022. SHEN L F. Preparation of magnetic biochar and its removal mechanism of Pb(Ⅱ) and Cr(Ⅵ) from aqueous solution[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University of Science & Technology, 2022 (in Chinese).
[113] 董建华. 铁掺杂生物质炭对六价铬的还原-吸附去除行为机制研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2020. DONG J H. Mechanism study on reduction assisted adsorption removal of hexavalent chromium by iron-doped biochar[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, 2020 (in Chinese).
[114] BIN Q, LIN B, ZHU K, et al. Superior trichloroethylene removal from water by sulfide-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron/graphene aerogel composite[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 2020, 88: 90-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2019.08.011 [115] 刘丽, 梁乐缤, 时悦, 等. 硫掺杂零价铁去除Cr(Ⅵ)的机理及环境影响因素[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2021, 40(5): 1079-1087. LIU L, LIANG L B, SHI Y, et al. Sulfidation enhanced Cr(VI) reduction by zerovalent iron under different environmental conditions: A mechanistic study[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2021, 40(5): 1079-1087 (in Chinese).
[116] 刘丽. 生物炭负载硫化零价铁去除水体中Cr(Ⅵ)的机理研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2021. LIU L. Research on removal mechanism of Cr(Ⅵ) from water by biochar supported sulfide-modified zero-valent iron[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2021 (in Chinese).
[117] MA L J, WANG Q, ISLAM S M, et al. Highly selective and efficient removal of heavy metals by layered double hydroxide intercalated with the MoS4(2-) ion[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(8): 2858-2866. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b00110 [118] BEKSISSA R, TEKOLA B, AYALA T, et al. Investigation of the adsorption performance of acid treated lignite coal for Cr (VI) removal from aqueous solution[J]. Environmental Challenges, 2021, 4: 100091. doi: 10.1016/j.envc.2021.100091 [119] 于树芳. 活性炭吸附去除水中砷的效能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2014. YU S F. Study on removel eeffectioncy of arsenic from aquous solution by activated carbon adsorption[D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2014 (in Chinese).
[120] 殷慧卿, 郭成, 胡笳, 等. 生物质基材料吸附水中砷离子的研究进展[J]. 化学工业与工程, 2022, 39(4): 71-82. doi: 10.13353/j.issn.1004.9533.20216003 YIN H Q, GUO C, HU J, et al. Adsorption of arsenic ions from water by biomass derived materials: A review[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering, 2022, 39(4): 71-82 (in Chinese). doi: 10.13353/j.issn.1004.9533.20216003
[121] 李莹莹, 朱永建, 陈国梁, 等. 磁性生物炭对高砷煤矿酸性废水的净化处理[J]. 矿业工程研究, 2022, 37(1): 70-78. LI Y Y, ZHU Y J, CHEN G L, et al. Purification of high arsenic acid mine wastewater by magnetic biochar[J]. Mineral Engineering Research, 2022, 37(1): 70-78 (in Chinese).
[122] 单鑫, 陈荟蓉, 禹洪丽, 等. 不同炭材料吸附Cr(Ⅵ)的热力学研究[J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(3): 1109-1115. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.20160317 SHAN X, CHEN H R, YU H L, et al. Study of thermodynamics for adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ) by different carbon materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2016, 10(3): 1109-1115 (in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.20160317
[123] 杨慧芬, 姜美苓, 高春庆, 等. 赤铁矿渣—煤泥铁碳基复合材料的制备及除Cr(Ⅵ)性能研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2023(1): 269-275. YANG H F, JIANG M L, GAO C Q, et al. Preparation of iron-carbon based composite material with hematite residue and coal slime and removal of Cr(Ⅵ) in aqueous solution[J]. Metal Mine, 2023(1): 269-275 (in Chinese).
[124] ZHAO R H, WANG B, ZHANG X Y, et al. Insights into Cr(VI) removal mechanism in water by facile one-step pyrolysis prepared coal gangue-biochar composite[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 299: 134334. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134334 [125] WU J X, YAN X L, LI L, et al. High-efficiency adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ) and RhB by hierarchical porous carbon prepared from coal gangue[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 275: 130008. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130008 [126] 范明霞, 赵春玲. pH值、离子强度和共存离子对活性炭吸附Cr(Ⅵ)的影响[J]. 化学工程师, 2017, 31(10): 25-27. FAN M X, ZHAO C L. Effect of pH, ion strength and coexistence ion for Cr(VI) adsorption on activated carbon[J]. Chemical Engineer, 2017, 31(10): 25-27 (in Chinese).
[127] 王鲁敏, 邓昌亮, 殷军港, 等. 硝化褐煤对铬离子溶液的吸附研究[J]. 环境化学, 2001, 20(1): 54-58. WANG L M, DENG C L, YIN J G, et al. Study on adsorption of nitrify lignite forchromium-ion solution[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2001, 20(1): 54-58 (in Chinese).
[128] 刘美丽, 牛其建, 俞洋洋, 等. 碳基材料负载纳米零价铁去除六价铬的研究进展[J]. 环境科学研究, 2022, 35(3): 768-779. LIU M L, NIU Q J, YU Y Y, et al. Progress in removal of hexavalent chromium by carbon-based materials loaded with nano zero-valent iron[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2022, 35(3): 768-779 (in Chinese).
[129] 吴吉昀, 冯博, 陈燕, 等. 粉煤灰-硅藻土复合材料对选矿废水中Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附行为研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2022, 42(4): 125-129. WU J Y, FENG B, CHEN Y, et al. Adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ) in mineral processing wastewater by fly ash-diatomite composite[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2022, 42(4): 125-129 (in Chinese).
[130] WU Z Y, ZHANG H, ALI E, et al. Synthesis of novel magnetic activated carbon for effective Cr(Ⅵ) removal via synergistic adsorption and chemical reduction[J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2023, 30: 103092. [131] ZHANG X, LI M, SU Y G, et al. A novel and green strategy for efficient removing Cr(Ⅵ) by modified kaolinite-rich coal gangue[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2021, 211: 106208. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2021.106208 [132] KAZAK O. Fabrication of in situ magnetic activated carbon by co-pyrolysis of sucrose with waste red mud for removal of Cr(Ⅵ) from waters[J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2021, 24: 101856. [133] QU J H, WANG Y X, TIAN X, et al. KOH-activated porous biochar with high specific surface area for adsorptive removal of chromium (Ⅵ) and naphthalene from water: Affecting factors, mechanisms and reusability exploration[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 401: 123292. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123292 [134] 任贵宁. 赤泥吸附剂的制备及对溶液中磷和铬(Ⅵ)的吸附研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2016. REN G N. Preparation of red mud adsorbent and its using on adsorption of phosphate and Cr(Ⅵ)[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2016 (in Chinese).
[135] 江钰. 不同构型富氮生物炭与典型重金属的相互作用机制[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2021. JIANG Y. Interaction mechanism between different configurations of nitrogen-rich biochars and typical heavy metals[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2021 (in Chinese).
[136] 张力文, 李德亮. 改性粉煤灰吸附重金属Pb2+和Cu2+的机理探讨[C]//2018中国环境科学学会科学技术年会论文集(第三卷). 合肥, 2018: 966-974. ZHANG L W, LI D L. Exploration of the mechanism of heavy metal Pb2+ and Cu2+ adsorption by modified fly ash[C]. Proceedings of the 2018 Annual Scientific and Technical Conference of the Chinese Society of Environmental Sciences (Volume III), Hefei, 2018: 966-974.
[137] SONG Y, WANG L C, LV B L, et al. Removal of trace Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by porous activated carbon balls supported by nanoscale zero-valent iron composites[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2020, 27(7): 7015-7024. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-07027-4 [138] 张建, 马锋锋, 郝爱红, 等. 改性生物炭对水中Cr(Ⅵ)的去除研究进展[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2020, 43(12): 38-46. ZHANG J, MA F F, HAO A H, et al. Research progress of Cr(Ⅵ) removal from water by modified biochar[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 43(12): 38-46 (in Chinese).
[139] WANG Q Y, LI L P, TIAN Y, et al. Shapeable amino-functionalized sodium alginate aerogel for high-performance adsorption of Cr(VI) and Cd(II): Experimental and theoretical investigations[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 446: 137430. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.137430 [140] WANG H, WANG W C, ZHOU S, et al. Adsorption mechanism of Cr(Ⅵ) on woody-activated carbons[J]. Heliyon, 2023, 9(2): e13267. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13267 [141] YANG H F, LI Z F, FU P, et al. Cr(Ⅵ) removal from a synthetic solution using a novel carbonaceous material prepared from oily sludge of tank bottom[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 249: 843-850. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.03.065 [142] 黎艳, 窦亚芳, 肖文理, 等. 煤矸石还原酸性废水中Cr(Ⅵ)的机理分析[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2022, 42(6): 30-35. LI Y, DOU Y F, XIAO W L, et al. Mechanism analysis of Cr(Ⅵ) reduction by coal gangue in acidic wastewater[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2022, 42(6): 30-35 (in Chinese).
[143] KUMARI M, PITTMAN C U, MOHAN D. Heavy metals [chromium (Ⅵ) and lead (II)] removal from water using mesoporous magnetite (Fe3O4) nanospheres[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2015, 442: 120-132. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2014.09.012 [144] WANG H B, CAI J Y, LIAO Z W, et al. Black liquor as biomass feedstock to prepare zero-valent iron embedded biochar with red mud for Cr(Ⅵ) removal: Mechanisms insights and engineering practicality[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 311: 123553. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123553 [145] SHI Y Y, SHAN R, LU L L, et al. High-efficiency removal of Cr(Ⅵ) by modified biochar derived from glue residue[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 254: 119935. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119935 [146] PHOLOSI A, NAIDOO E B, OFOMAJA A E. Batch and continuous flow studies of Cr(Ⅵ) adsorption from synthetic and real wastewater by magnetic pine cone composite[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2020, 153: 806-818. doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2019.11.004 -



 下载:
下载: