-
我国《水污染防治行动计划》明确规定,在重点的湖泊(水库)等水质要求敏感的区域排放的污水必须达到城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准(GB 18918-2002)一级A排放要求[1]。虽然目前我国污水处理设施在数量上已达4 000多个,但在处理能力以及处理设施上的发展并不平衡。目前部分城镇污水处理厂在出水一级A提标改造中对氮磷的去除效果并不十分理想,需要进一步研发新技术以改进现有技术,提高脱氮除磷效率[2]。藻菌共生体系是利用藻类和细菌2类生物之间在协同作用处理污水的一种生态系统[3]。污水中的有机物经好氧菌分解产生
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N、$ {\rm{PO}}_4^{3 - } $ 和CO2等无机物,为藻类提供营养,合成自身细胞组织;藻类光合作用释放的O2又可供好氧菌继续氧化有机物[4]。藻菌共生体系能有效去除污水中含碳、氮、磷等的污染物,具有运行成本低、无二次污染以及藻、菌生物资源可再利用的特点,在城镇污水处理研究中受到广泛关注并得到了实际应用[5]。碳源是藻类与菌类进行生命活动时不可或缺的条件之一。藻类可利用无机碳源进行光合作用合成有机碳[6],菌类利用有机或无机碳源为细胞生长提供能量以及合成碳骨架[7],因此,外在碳源的缺乏直接影响藻菌共生体系的稳定生长及其污水处理效率。然而,我国城镇污水处理厂的进水COD普遍偏低,部分进水甚至低于100 mg·L−1。因此,在藻菌共生体系等生物处理工艺运行中可考虑通过补充合适的碳源来进一步提升脱氮除磷效率[8]。
本研究以某城镇污水厂中鉴定出的优势脱氮除磷藻种短带鞘藻(Oedogonium brevicingulatum)为藻源,以该厂好氧池中活性污泥为菌源,构建并优化了短带鞘藻-活性污泥共生体系。从乙酸钠、葡萄糖、碳酸钠和碳酸氢钠4种外加碳源中筛选出最适宜该体系的外加碳源,对其脱氮除磷处理效果进行了评价,并使用其处理某城镇污水,以期为该藻菌共生技术的实际应用提供技术参数[9]。
全文HTML
-
在前期研究中,采用PCR-DGGE分子生物学方法筛选并鉴定某污水处理厂中的优势藻种为丝状短带鞘藻(Oedogonium brevicingulatum)[10]。从中国科学院武汉水生所国家淡水藻库购置的纯种短带鞘藻作为实验所用藻种。接种前用超纯水将藻细胞清洗3次,随后在无菌操作台中用接种环将藻细胞接种于含300 mL改良BG11培养基的锥形瓶中,摇匀,并用透气膜封口。将锥形瓶置于光照恒温培养箱中培养,培养条件设置为:温度(25±1) ℃、光照强度6 000 lx、光暗比12 h∶12 h[11]。每天定时摇瓶3次,防止藻类贴壁生长。
实验所用活性污泥取自某城市污水处理厂A2O处理工艺中的好氧池。将取回的活性污泥曝气24 h以去除杂质,再用葡萄糖、可溶性淀粉、NH4Cl、K2HPO4、KH2PO4按照C∶N∶P为100∶5∶1的比例配置营养盐培养活性污泥,每天更换营养盐3次,曝气间歇时间为12 h∶12 h。
-
实验前期,对某城镇污水处理厂二沉池进水的主要污染物进行了为期1年的跟踪监测并计算年平均值,
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N、TN、TP和COD分别为15.4、21.5、1.5和102.4 mg·L−1,按照该污水厂主要污染物的年平均进水浓度,分别采用NH4Cl、KNO3、K2HPO4和葡萄糖来配置实验用模拟城镇污水。在反应器运行期间,采用该城镇污水厂二沉池4月份的实际进水,主要污染物进水水质指标
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N、TN、TP和COD平均值分别为16.5、27.5、1.4和87.4 mg·L−1。实验过程中水温控制在(25±1) ℃[12],pH控制在7.0~8.0[13-14]。 -
实际污水处理采用课题组研究设计的固定化藻菌共生生物膜反应器[15]。该反应器的总高度为0.5 m,总容积为17 L,通体由透明有机玻璃制成,固定化材料为聚乙烯弹性立体填料,生物反应区的高度为0.25 m,有效直径为0.25 m。反应器结构实物图见图1。
-
用恒重的定量滤纸过滤并称量一系列不同湿重梯度的短带鞘藻,然后将短带鞘藻和滤纸置于103~105 ℃的烘箱中烘至恒重,利用差减法得出藻的干重质量,再分别以藻湿重和藻干重为横、纵坐标来绘制藻的干、湿重关系标准曲线,得到式(1);短带鞘藻叶绿素的测定采用丙酮提取法[16],取一系列不同湿重的藻体,分别测定总叶绿素含量,作出总叶绿素—藻湿重标准曲线,得到式(2)。
用量筒准确量取100 mL混合均匀的活性污泥混合液后过滤,将载有活性污泥的滤纸移入103~105 ℃的烘箱内烘至恒重,利用差减法求得活性污泥干重质量,最后将活性污泥干重质量除以体积确定活性污泥浓度。培养过程中每2~3 d对出水中的沉淀物在光学显微镜下进行观察。当视野中观察到累枝虫(Epistylislacustris)伴随钟虫(Vorticellidae)一起出现时,表明出水活性污泥的培养进入成熟期且可用于后续的实验。
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N的测定采用纳氏试剂分光光度法(GB 7479-1887);TN、TP的测定分别采用便携式总氮测定仪(深昌鸿PWN-810 B)和钼酸铵分光光度法(GB 11893-1989);COD的测定采用微波消解滴定法(GB 11914-1989);pH采用便携式pH计(雷磁PHS-3E)测定。 -
采用Monod动力学方程(式(3))建立短带鞘藻和活性污泥生长动力学模型,描述稳态时碳酸氢钠限制条件下对短带鞘藻和活性污泥生长的影响。
式中:μ为比生长速率,d−1;μm为最大比生长速率,d−1;S为限制性碳酸氢钠浓度,mg·L−1;KS为半饱和常数,mg·L−1。根据该动力学方程可分别求出短带鞘藻和活性污泥的动力学参数。
1.1. 藻种、活性污泥来源与培养
1.2. 实验污水进水水质
1.3. 固定化藻菌共生生物膜反应器
1.4. 检测指标与方法
1.5. Monod动力学模型
-
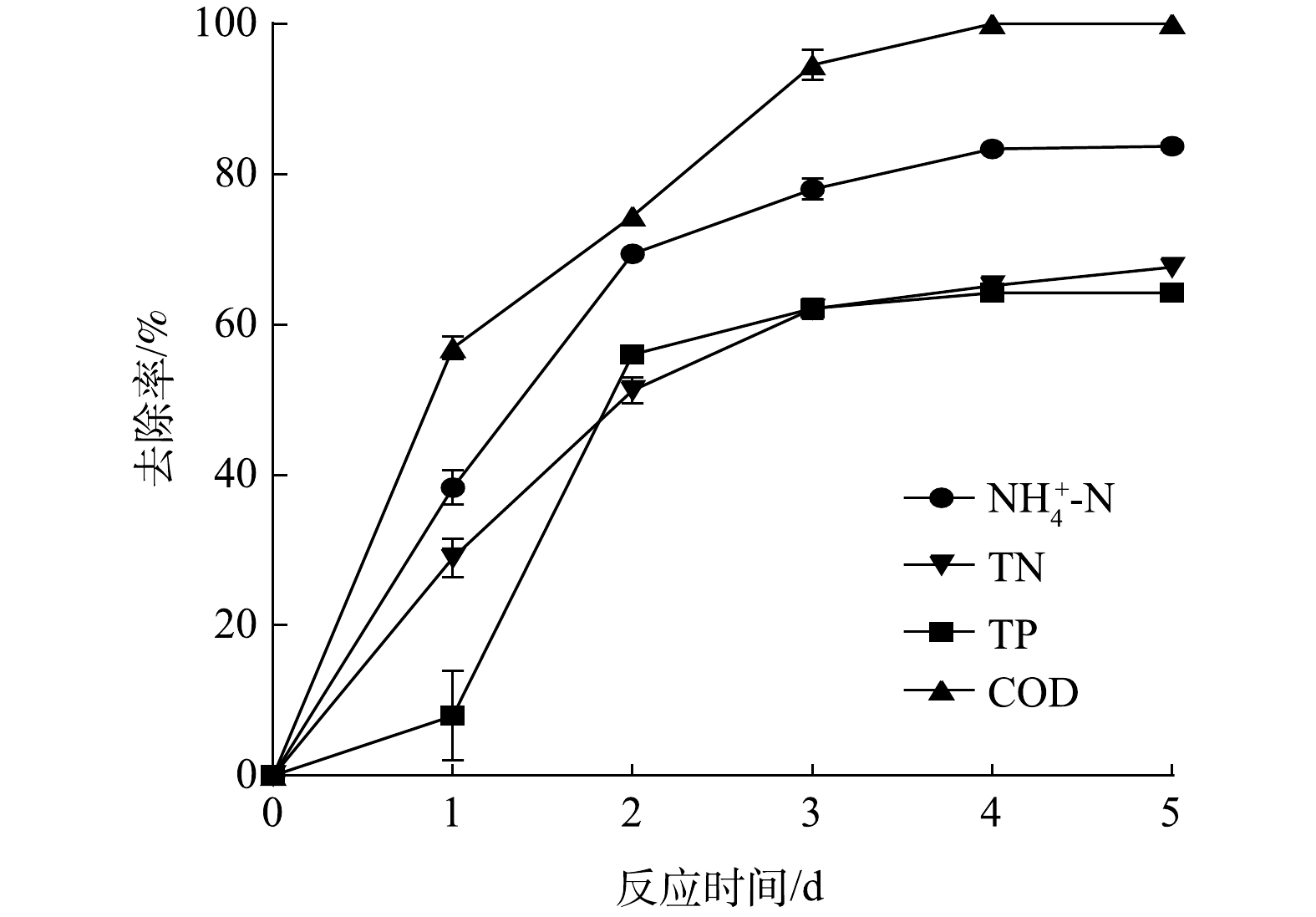
在5 d的实验周期中,首先对短带鞘藻-活性污泥共生体系进行工艺参数优化[17]。考察了初始藻菌干重比(1∶1、2∶1、3∶1、5∶1)、初始生物量(0.2、0.3、0.4、0.5 g·L−1)、曝气量(0、0.2、0.4、1 L·min−1)和曝气间歇时间(1、3、6、24 h)对短带鞘藻-活性污泥共生体系脱氮除磷的影响。结果表明,在初始藻菌比为3∶1,初始生物量0.3 g·L−1,曝气量0.2 L·min−1和曝气间歇时间6 h∶6 h的条件下,短带鞘藻-活性污泥共生体系对各污染物去除率最优。如图2所示,在实验第5天时,
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N、TN、TP和COD的去除率分别为83.7%、67.6%、64.7%和100%。 -
碳源是藻类与菌类进行生命活动时不可或缺的因素之一。目前由于雨污分流不彻底,污水管网收集不充分,城镇污水处理厂进水普遍存在COD偏低的问题,部分进水小于100 mg·L−1[18]。在本研究中,某城镇污水厂在A2O工艺运行中通过比较葡萄糖和乙酸钠后,加入了乙酸钠来提升脱氮除磷效率。因此,为进一步提升藻菌共生体系的脱氮除磷效率,解决进水碳源不足的问题,可考虑通过补充合适的外加碳源。本研究考察了2种有机碳源(乙酸钠、葡萄糖)和2种无机碳源(碳酸钠、碳酸氢钠)对短带鞘藻-活性污泥共生体系去除氮磷和COD的影响。如图3(a)和图3(b)所示,外加有机碳源(乙酸钠和葡萄糖)的实验组对
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N和TN的去除速率高于外加无机碳源(碳酸钠和碳酸氢钠)的实验组,其中葡萄糖为外加碳源的实验组脱氮效率最高。该体系中氮的去除主要靠藻菌共同作用,藻类通过吸收氮素将其合成为自身细胞,菌类硝化作用将氨氮转化为亚硝酸盐和硝酸盐后通过反硝化作用将硝态氮和亚硝态氮转化为氮气[19]。有机碳源的加入增强了菌类的活性,进而提高了脱氮效率[20]。与脱氮的效果不同,如图3(c)所示,当外加碳源为无机碳时,对TP的去除效果更好且TP< 0.5 mg·L−1,达到一级A排放标准。在第6 h时,外加碳源为碳酸氢钠的实验组先于碳酸钠TP达到一级A标准,且相比于外加碳源为葡萄糖和乙酸钠的实验组其对TP的去除率分别提高了6.0%和14.4%。在该藻菌体系中,藻对磷的同化吸收和表面吸附为主要的除磷途径,无机碳源更容易被藻类利用[21],新细胞合成速率加快,除磷效率得到提高。在本研究中,如图3(d)所示,4个实验组在第6 h时COD的去除率虽均能达到100%,但是,添加无机碳源的实验组在6 h内对COD的去除率更高。综合评价,碳酸氢钠是该体系的最适外加碳源。
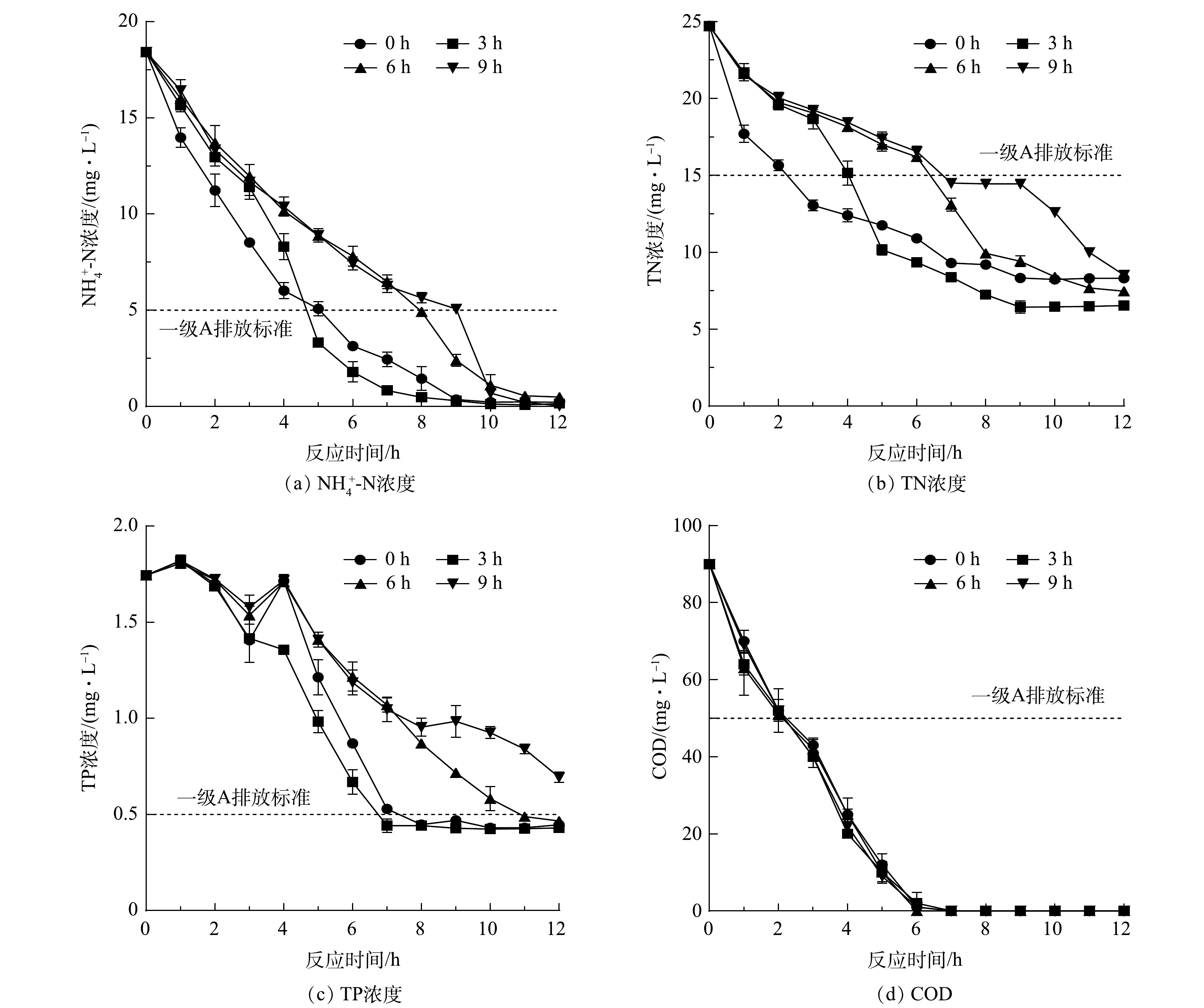
进一步考察了碳酸氢钠初始浓度对该藻菌共生体系去除氮、磷和COD的影响。由图4(a)、图4(b)可知,当初始碳酸氢钠初始浓度为100 mg·L−1时,对
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N和TN的去除率最高,分别为98.7%和78.6%。初步分析,投加碳酸氢钠改变了体系初始$ {\rm{HCO}}_3^ - $ 浓度,进而导致初始pH也不同。如图5所示,当初始碳酸氢钠浓度为75~125 mg·L−1时,pH维持在7.1~8.8,适合藻菌体系的生长,随着碳酸氢钠投加量的增加175 mg·L−1的实验组pH达到9.4~10.3,过高的pH不利于藻菌体系脱氮[22]。如图4(c)所示,各实验组在0~4 h里TP的浓度波动较大,随后TP浓度开始持续降低,直至平稳。造成上述现象的主要原因:一方面是由于碳酸氢钠的加入使pH发生变化,部分藻菌共生体表面附着的磷溶入水中造成TP浓度的短暂升高;另一方面是体系在脱氮除磷的过程中会使氮磷比发生变化,从而引起藻类向水中释放磷以维持自身细胞生长[23]。在12 h实验周期结束时,碳酸氢钠初始浓度为100 mg·L−1和125 mg·L−1的实验组TP浓度达到一级A标准,分别为0.42 mg·L−1和0.48 mg·L−1。COD的去除效果如图4(d)所示,在4个实验组中并未表现出明显的差异,均能达到一级A排放标准。外加碳酸氢钠的投加时间对体系脱氮的影响如图6(a)和图6(b)所示,在体系脱氮过程中,藻菌生物体利用污水中的碳源作为能源支撑同化吸收以及分解转化水中的氮素。加入碳酸氢钠后,短带鞘藻持续吸收水中的氮元素以合成自身细胞等物质,因此,在补充碳源后的数小时内
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N和TN的浓度开始快速下降。如图6(c)所示,TP浓度在0~3 h内出现波动,这可能是因为藻在最初的延滞生长期吸收磷并储存于体内,随着环境变化和生长需要会将体内部分的磷释放出来[24]。如图6(d)所示,外加碳酸氢钠的投加时间对体系去除COD的影响不大。而第3 h由于碳源的加入短带鞘藻的活性增强,快速吸收水中以及藻中释放出来的磷。综合考虑各污染物的去除情况,在第3 h补充碳酸氢钠的实验组有着更好的脱氮除磷性能,在实验周期12 h时结束时,出水中${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N、TN、TP和COD分别为0.14、6.54、0.43和0 mg·L−1。 -
为确定碳酸氢钠对共生体系中短带鞘藻和活性污泥去除氮、磷与COD的影响,分别设置了单藻和单泥实验组。由图7(a)可以看出,短带鞘藻加碳酸氢钠实验组在实验第4 h时
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N浓度最先达到一级A标准。活性污泥加碳酸氢钠实验组与单泥实验组在对TN、TP的去除效果如图7(b)、图7(c)所示,二者并未表现出明显差异,且在12 h实验周期结束时,活性污泥加碳酸氢钠实验组和单泥实验组中TP的浓度分别为0.82 mg·L−1和0.72 mg·L−1,均未达到一级A排放标准。这是由于加入碳酸氢钠后,活性污泥中的硝化菌逐渐成为优势菌种,加快吸收水中的${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N,并将其氧化为硝酸盐或亚硝酸盐,但厌氧条件下反硝化菌缺少有机碳源的补充,硝态氮还原成氮气的过程缓慢;在对TP的去除上,好氧状态下活性污泥中的聚磷菌吸收正磷酸盐,但在厌氧状态下会向水体中释磷[25]。而短带鞘藻利用外加的碳酸氢钠作为碳源,持续吸收水体中的氮磷和有机物来合成自身细胞,相比于活性污泥外加碳酸氢钠的实验组其对TN和TP的去除率分别提高了11.5%和42.4%。相较于其他实验组,短带鞘藻外加碳酸氢钠实验组达到一级A排放标准的时间更短且效果更好。如图7(d)所示,各实验组在对COD的去除效果上未表现出明显差异。 -
采用Monod动力学方程(式(3))计算拟合,获得外加碳酸氢钠后短带鞘藻和活性污泥生长动力学参数。短带鞘藻和活性污泥都能较好的拟合Monod模型(R2分别为0.943和0.862),此外 ,短带鞘藻的比生长速率(μm)为0.276 d−1,大于活性污泥(0.144 d−1);而半饱和常数(Ks)为0.77 mg·L−1,远低于活性污泥的15.28 mg·L−1,这表明短带鞘藻对碳酸氢钠的亲和性要优于活性污泥。因此,该体系外加碳酸氢钠后更多地促进了短带鞘藻的生长,提升了脱氮除磷的效果。
-
将某城镇污水厂进水加入到课题组研究设计的藻菌共生生物膜反应器中连续运行30 d。以脱氮除磷效果为评价指标,初步评价了该体系在反应器中对实际城镇污水的处理效果。在反应器运行的0~10 d里,设置水力停留时间(HRT)为8 h,如图8所示,
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N、TP的浓度波动较大,均不能达到一级A标准。因此,在11~20 d,将HRT调整为12 h,${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N、TP及COD的出水波动明显较前10 d平稳,但出水中${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N、TP和TN仍无法稳定达标。虽然继续延长反应器的HRT可有效增加反应器对污染物的去除效率[26],但HRT过长会增加污水处理的成本,因此,在反应器运行的最后10 d中设置HRT为12 h,另投加前期实验中筛选出的最佳外加碳源碳酸氢钠100 mg·L−1来提高反应器的处理效率。结果表明,出水中的${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N、TP、TN和COD分别为3.7、13.0、0.4和34.2 mg·L−1,均达到一级A排放标准。
2.1. 短带鞘藻-活性污泥共生体系的构建
2.2. 外加碳源对藻菌共生体系脱氮除磷效果的促进
2.3. 外加碳酸氢钠短带鞘藻和活性污泥脱氮除磷效果的影响
2.4. Monod动力学评价外加碳酸氢钠对短带鞘藻和活性污泥脱氮除磷效果的影响
2.5. 外加碳酸氢钠对藻菌共生生物膜反应器处理实际城镇污水的影响
-
1)构建了短带鞘藻-活性污泥共生体系,并确定了最佳工艺条件为初始藻菌干重比3∶1、初始生物量0.3 g·L−1、曝气量0.2 L·min−1和曝气间歇时间6 h∶6 h,在此条件下,对
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N、TN、TP和COD的去除率分别为83.7%、67.6%、64.7%和100%。2)筛选出最适宜的外加碳源为碳酸氢钠。在12 h的实验周期中,3 h往短带鞘藻-活性污泥共生体系投加100 mg·L−1的碳酸氢钠,该体系对
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N、TN和TP的去除率分别提高了15.6%、6.3%和10.0%,实验周期结束时出水中${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N、TN、TP和COD分别为0.14、6.54、0.43和0 mg·L−1,各污染物浓度均达到一级A排放标准。3)外加碳酸氢钠主要促进了共生体系中短带鞘藻的生长。
4)当投加碳酸氢钠为100 mg·L−1、HRT为12 h时,固定化藻菌共生反应器出水中的氮、磷及COD均能达到一级A排放标准且运行稳定。






 下载:
下载: