-
污水处理行业的臭气主要产生于污水处理厂和污水收集管网泵站等环节,相关治理技术主要有吸收法、吸附法、燃烧法和生物法等[1]。其中,生物除臭技术因其环保、高效、低成本等优点在污水处理厂臭气处理领域得以应用[2]。生物滤柱与生物洗涤塔、生物滤池和生物滴滤塔等生物除臭技术相比,具有占地面积小、运行费用低、处理效率高和管理方便等特点[3-5],但在冬季低温条件下微生物代谢活性受到抑制,极易出现处理效果差、运行不稳定等问题。通过填料投加以增大滤柱有效生物量来提高处理效果是生物滤柱研究中较为重要的强化策略之一[6]。
生物除臭技术中的填料通常具备较好的持水性、良好的透气性和优异的比表面积,有利于微生物膜的形成和微生物的新陈代谢[7]。屈艳芬等[8]采用混合肥料、聚苯乙烯胶球体、活性炭、沸石为混合填料进行除臭实验,取得了良好的处理效果。端艳等[9]采用陶粒作为生物滤池中的填料,发现其对COD和氨氮有良好的去除效果。肖作义等[10]将树皮、活性炭和多孔空心球按照6:2:1的比例混合填充,对NH3和H2S的去除效果较好。刘桂臣等[11]考察了沸石-无烟煤双层滤料生物滤池处理污水的效果,结果表明,可获得良好的出水水质。单一填料生物除臭工艺的运行时间较长时会出现堵塞、透气性变差等问题[12],因此,开发高效、稳定的复合填料以提高生物滤柱的微生物量,成为强化低温环境下滤柱除臭运行效能的重要方式。
本研究通过搭建模拟喷淋-生物滤柱臭气处理工艺,以蜂窝煤渣、活性炭、蜂窝沸石和陶粒构建复合填料强化生物滤柱处理效能,选择污水处理厂主要恶臭气体硫化氢(H2S)和氨气(NH3)作为目标污染物,分析闽南地区(以厦门为例)冬季低温条件下混合填料生物滤柱对2种恶臭气体的去除效果,探究系统成功运行后,复合填料表面生物膜微生物的群落结构变化,并进行物料衡算以综合评估复合填料-生物滤柱的臭气处理效能,为冬季气候条件下闽南地区污水处理厂的臭气高效快速处理提供技术参考。
-
1)接种污泥。实验采用厦门某污水处理厂曝气池活性污泥。接种污泥的TSS为12.29 g·L−1,VSS为7.68 g·L−1,pH为7.68。
2) H2S气体。在密闭瓶中加入硫化亚铁固体,再将一定含量的10%稀硫酸溶液通过蠕动泵以一定流速通入瓶中,使之发生化学反应产生H2S;通过调节蠕动泵控制产气量,使产生的气体质量浓度保持在(5.0 ± 0.6) mg·L−1。
3) NH3气体。通过投加25%氨水模拟NH3的产生,通过流量计调节投加氨水的量,使生物滤柱反应器进水中氨氮质量浓度保持在(35.0 ± 1.5) mg·L−1。
4)喷淋水。以模拟生活污水作为喷淋水源,其组分及质量浓度如下。氯化铵,14.28 mg·L−1;磷酸二氢钾,28.15 mg·L−1;尿素,19.20 mg·L−1;无水氯化钙,8.31 mg·L−1;硫酸镁,33.91 mg·L−1;无水乙酸钠,21.11 mg·L−1;葡萄糖,192.00 mg·L−1;(NH4)6Mo7O2,0.18 mg·L−1;FeSO4·7H2O,1.50 mg·L−1;ZnSO4·7H2O:0.12 mg·L−1;MnCl2·2H2O:0.12 mg·L−1;CoCl2·6H2O:0.15 mg·L−1;CuSO4·5H2O:0.03 mg·L−1。
5)复合填料。该实验选用的复合填料是蜂窝煤渣、活性炭、蜂窝沸石和陶粒。参考已报道文献[10, 12-13],将生物滤柱复合填料的体积投配比设置为4∶4∶1∶1,混合后构建复合填料。蜂窝煤渣取用学校食堂废弃的蜂窝煤渣,干燥、粉碎,过80目标准筛;活性炭的粒径为2~4 mm,蜂窝沸石的粒径为2~4 mm,陶粒粒径为4~6 mm。
-
本次实验地点位于华侨大学厦门校区,实验装置如图1所示。环境温度维持在8~14 ℃。取用厦门某污水处理厂曝气池的活性污泥为生物滤柱提供所需微生物。为准确判断混合填料挂膜情况,每3 d检测1次生物滤池反应器出水COD,确定微生物对营养物质的吸收与利用情况[14]。实验装置主要由H2S发生装置、喷淋装置和生物滤柱组成。生物滤柱为圆柱形,尺寸为φ70 mm×1 700 mm,滤柱有效容积为6.50 L。复合填料置入生物滤柱中,填料区填充高度约为700 mm,体积填充比为0.4。生物滤柱底部连接微曝气装置,反应器启动时开始进行曝气。
-
阶段1是驯化挂膜阶段,运行时间为15 d。本实验采用直接驯化挂膜法[15-16],往生物滤柱中填入活性污泥直至将填料区完全浸没,48 h后再将泥浆排出,然后将模拟生活污水通入反应器中,此过程不通入臭气。每隔3 d在反应器的进水、出水口取样以测定COD含量。
阶段2是H2S气体处理阶段(运行路径①),运行时间为30 d。H2S气体从H2S发生装置由空气泵抽至喷淋装置底部的进气口,再经喷淋后输送至生物滤柱底部的进水口;经过填料区后,残余气体由顶部出气口排出。其中,H2S进气量由空气流量计调节控制;在此阶段中,每隔3 d测定1次进出H2S质量浓度和进出水中SO42−的质量浓度。
阶段3是H2S和NH3混合臭气处理阶段,运行时间为30 d。在第2阶段的基础上,开启氨水释放装置(路径①与路径②同时开启),NH3经喷淋后进入生物滤柱,每隔3 d测定1次进出H2S质量浓度和进出水中NH3-N质量浓度。
-
采用重铬酸钾法测定COD[17];采用纳氏试剂分光光度法测定氨氮(NH3-N)质量浓度[18];采用硫化氢气体检测仪测定H2S质量浓度;采用铬酸钡分光光度法测定SO42−的质量浓度[19]。
-
为探究处理臭气对复合填料生物膜上微生物群落组成多样性和变化情况的影响,分别取接种污泥、运行阶段1、运行阶段2、运行阶段3结束运行后的复合填料上生物膜污泥样品进行分析。每个样品平行取样3次,混合均匀后分别标记为In0、Bio1、Bio2、Bio3。从生物滤柱中取得复合填料层的填料,从其表层提取生物膜污泥样品,在10 000 r·min−1下离心10 min,使得污泥固液分离。然后,使用快速DNA试剂盒(MoBio Laboratories)从污泥沉积物中提取基因组DNA,操作步骤按照试剂盒中提供的使用说明书进行。利用Qubit3.0 DNA检测试剂盒对基因组DNA精确定量,以确定聚合酶链反应(PCR)应加入的DNA量。使用引物(515F和806R)对污泥细菌16S DNA的V3-V4区域进行PCR扩增。利用Gene Tools Analysis Software (Version4.03.05.0, SynGene)对PCR产物进行浓度对比后,按照等质量原则计算各样品所需体积,将各PCR产物进行混合。使用E.Z.N.A.®GelExtractionKit凝胶回收试剂盒回收PCR混合产物,TE缓冲液洗脱回收目标DNA片段。后续建库按照NEBNext®UltraTM DNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina®标准流程进行建库操作,完成后在高通量测序平台Hiseq或Miseq进行上机测序,并通过广东美格基因科技有限公司分析平台(www.magichand.online)对扩增产物进行高通量测序分析。根据MiSeq测序结果检测到的OTU,使用RDP数据库(http://rdp.cme.msu.edu/misc/resources.jsp)进行微生物分类分析,包括科和属级别。每个样本的微生物多样性由Mothur软件计算(http://www.mothur. org/wiki/Schloss_SOP#Alpha_diversity),包括Chao1指数,richness指数;通过Matlab软件实现PCA主成分分析。最后,通过STAMP软件评估微生物群落相对丰度(科、属级别的比较分析)。
-
进出水中溶解性有机物(COD)的变化有助于明确微生物对反应器中有机物质的吸收和降解特性[20]。复合填料-生物滤柱在启动运行阶段(阶段1)15 d的COD变化见表1。在启动运行的前9 d内,生物滤柱对COD的去除率较低(57%~64%);从第12天开始,生物滤柱对COD的去除率逐渐稳定在80%以上,说明生物滤柱内微生物可充分利用进水营养液中的碳源作为自身营养物质。在生物膜上微生物代谢达到平衡后,挂膜成功。这与现有报道[20]情况相符。
-
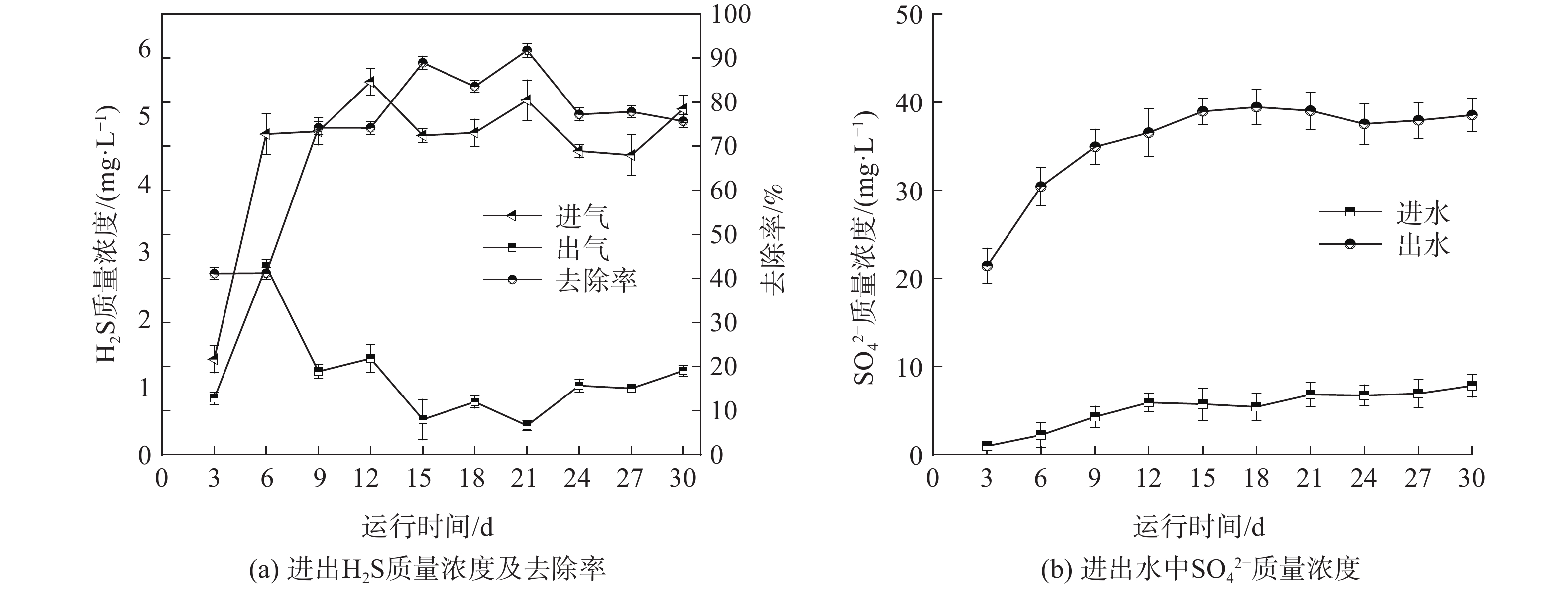
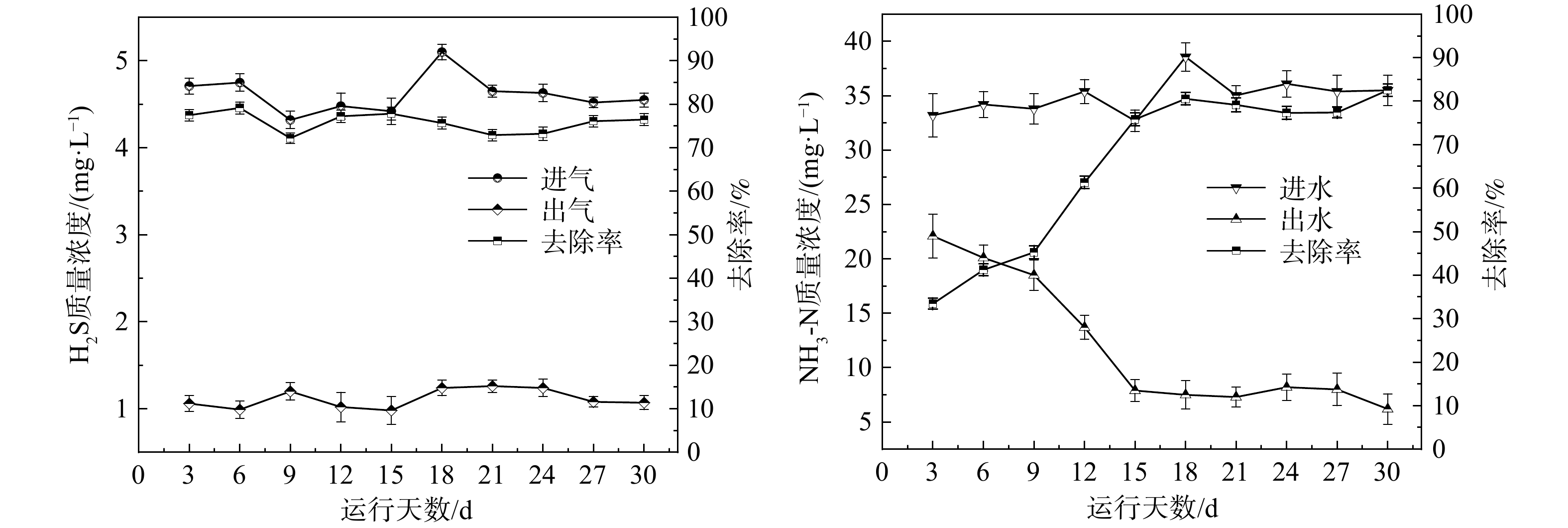
复合填料-生物滤柱反应器对H2S的降解效果如图2所示(运行阶段2)。图2(a)为复合填料-生物滤柱反应器对H2S气体的去除效果。在运行6 d后,H2S的进气质量浓度为4.42~5.51 mg·L−1,出气质量浓度降至0.99~1.66 mg·L−1。在此过程中,H2S的去除率仅为约40%。从第9天开始,H2S的去除率逐渐升高至70%以上,并保持稳定,最大去除率可达91.77%。图2(b)为运行阶段2进出水中SO42−的质量浓度变化(已扣除进水组分中SO42−的质量浓度)。其中,出水SO42−的质量浓度达到21.44~49.44 mg·L−1,远高于进水SO42−的质量浓度,这说明复合填料-生物滤柱硫氧化菌(sulfur-oxidizing bacteria,SOB)得到富集,将H2S转化为SO42−[21]。SO42−的质量浓度可间接反映去除H2S功能菌的富集程度,即随着运行时间的增长,硫氧化菌的富集程度提高,这是H2S对硫氧化菌培养驯化的结果。
-
运行阶段3是复合填料-生物滤柱同步去除H2S和NH3的运行阶段。在阶段2的基础上向生物滤柱通入氨水模拟NH3的进入,运行时间为30 d。图3(a)为此运行阶段生物滤柱反应器进出H2S质量浓度的变化及其去除率。在阶段3运行的30 d里,H2S的去除率一直稳定在70%以上,说明生物滤柱对H2S的去除效果良好且运行稳定。图3(b)为进出水NH3-N质量浓度及其去除率。在前15 d内,NH3-N的去除率逐步上升。从第15 d开始,去除率一直稳定在70%以上,其中最大去除率达到82.53%。这与殷峻等[22]研究结果相符,说明生物滤柱可实现对H2S和NH3-N的同步去除,且去除效果良好、运行稳定。
-
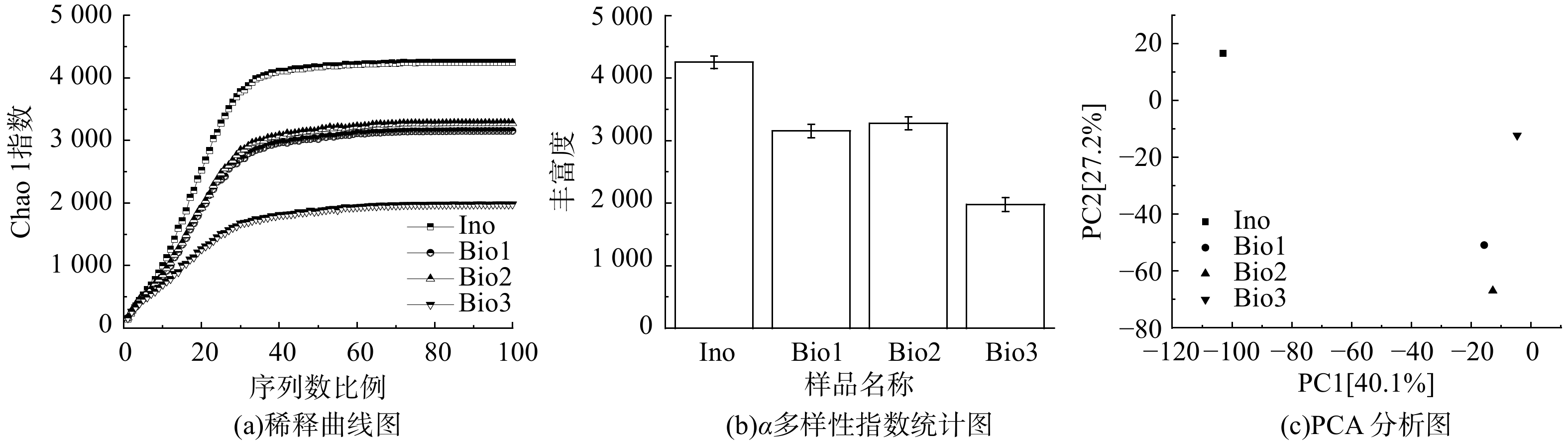
图4(a)为4个样本的稀释曲线。随着样本量的增加,样本稀释曲线趋于平缓,即说明本次实验取样合理,样本测序数据量能反应污泥样品中的总体微生物[23]。
复合填料-生物滤柱内生物膜的微生物群落组成多样性指数如图4(b)所示。样本的物种丰富度随运行天数的增加整体呈下降趋势。这可能是由于驯化与挂膜培养过程中微生物生存环境和营养源的改变所致。样本Bio2的物种丰富度与样本Bio1相差不大,说明通入H2S对微生物物种丰富度的影响较小;而样本Bio3的物种丰富度小于样本Bio2,这可能由于高负荷H2S和NH3环境会对微生物群落产生抑制作用,降低了微生物丰富度[24]。
主成分分析(principal component analysis,PCA)主要用于考察样本间最主要的差异特征,样本在坐标系中的距离远近可最大程度地还原样本间的实际差异。图4(c)为4个样本的PCA分析图,可观察到接种污泥样本In0与其他3个样本在坐标系中距离较远,微生物物种差异性较大。这说明通入臭气后,生物滤柱反应器中的微生物种群有较大变化,即臭气(H2S、NH3)的进入对复合填料生物膜菌群结构起到重要的重塑作用,进而改变微生物群落功能,使之具备脱硫除氮能力。而样本Bio1和样本Bio2在坐标系中距离相近,样本Bio3相比较下较远,说明通入H2S并运行30 d后的反应器内微生物种群变化不明显。在进入氨气后,反应器内微生物种群变化较为明显,说明单一臭气(H2S)对复合载体生物膜菌群结构的影响小于混合臭气,加入氨气后反应器内微生物种群的变化更为明显。这表明混合臭气(H2S+NH3)对微生物菌群具有更显著的筛选与驯化作用。这也是Bio3样品丰富度降低(图2)的主因,亦与前述报道[24]相符。
-
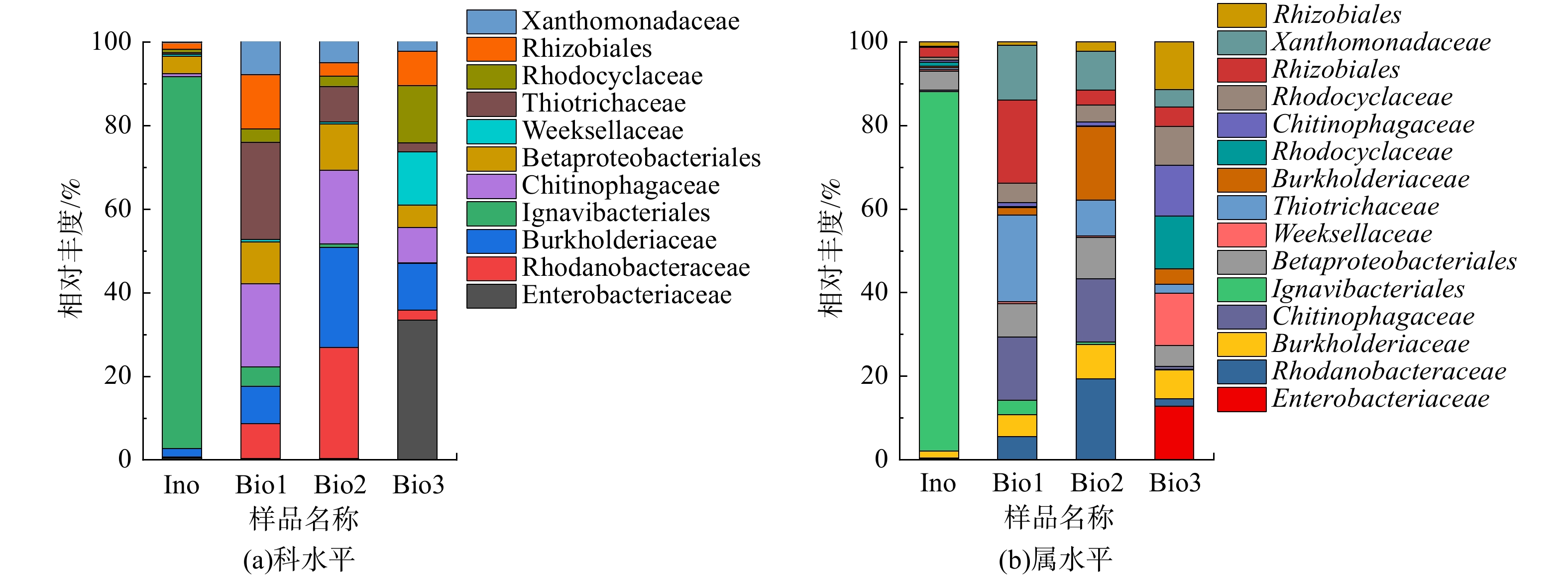
对4个样本在科水平的微生物群落组成(相对丰度>0.01%)进行了分析,其结果见图5(a)。由图5(a)可见,4个样本的物种组成相似,但相对丰度占比存在明显区别。Ignavibacteriales的相对丰度在通入H2S后呈现明显下降趋势,Ignavibacteriales科属于绿硫细菌 (green sulfur bacteria,GSB),但是没有硫氧化能力[22],故通入H2S后,其丰度下降,并逐渐被具有硫氧化能力的硫氧化菌及其他硫氧化菌取代。而Rhizobiales、Thiotrichaceae和Chiitinophagaceae在通入H2S后相对丰度上升,是除H2S优势功能菌和有机物降解菌。通入H2S运行30 d后,Burkholderiaceae和Rhodanobacteraceae的相对丰度升高,为除H2S优势功能菌。加入NH3进入反应器至运行结束,Rhodocyclaceae、Weeksellaceae和Enterobacteriaceae的相对丰度上升,而Xanthomonadceae、Thiotrichaceae和Rhodanobacteraceae的相对丰度下降。NH3的加入,使脱氮优势菌丰度上升,与除H2S优势菌竞争营养物质,从而导致部分除H2S优势菌的丰度下降,NH3的存在会对部分脱硫微生物产生抑制作用,亦是污泥样品Bio3与Bio2产生菌群差异性的主因(图4(c))。综上所述,Rhodocyclaceae、Weeksellaceae和Enterobac是H2S与NH3混合臭气处理阶段的优势微生物。
图5(b)为4个样本在属水平的微生物群落组成(相对丰度>0.01%)。接种污泥样本In0中Ignavibacteriales(88.90%)的相对丰度最高,通入臭气后呈现明显下降趋势。这说明H2S对Ignavibacteriales
有抑制作用,通入H2S会导致其丰度下降,逐渐被其他除臭优势菌取代,这与图5(a)呈现的分析结果一致。在通入H2S后,Thiothrix的相对丰度从0.38%上升至23.22%,Ferruginibacter的相对丰度从0.40%上升至19.16%,菌属Thiothrix和Ferruginibacter与H2S降解相关[25-26]。在通入H2S运行30 d后,Burkholderiaceae、Tahibacter相对丰度从1.57%、8.38%分别上升至13.75%和26.61%,这说明Burkholderiaceae、Tahibacter对H2S的生物降解/转化有积极的贡献作用,与已有报道[27-28]结果一致。从加入NH3至反应器运行结束,Dinghuibacter、Cloacibacterium和Kosakonia的相对丰度显著上升,分别从0.61%、0.48%和0.32%上升至7.65%、12.8%和33.42%,而Burkholderiaceae、Tahibacter和Ferruginibacter的相对丰度显著下降。这说明Dinghuibacter、Cloacibacterium和Kosakonia为氨氮去除相关功能菌[29-31]。 -
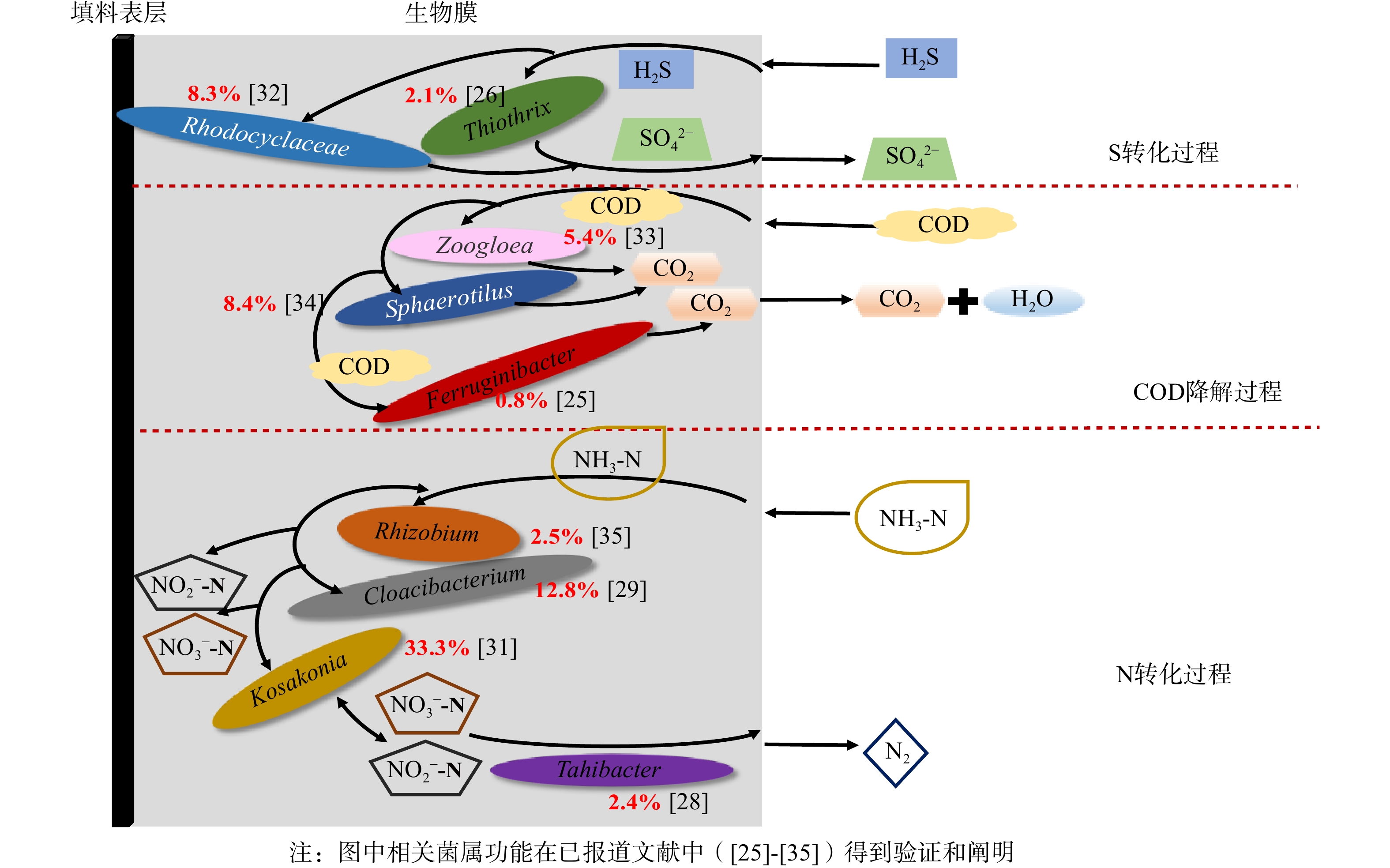
复合填料表层生物膜内除臭微生物群落中的核心菌属成员及其对H2S、NH3的转化作用见图6。Thiothrix是硫化物氧化丝状菌属,以H2S为能源,可将H2S氧化为硫粒积累在菌体内,在缺乏营养时又将硫粒氧化为SO42−,从而获得能量。Rhodocyclaceae属于紫色非硫细菌 (purple nonsulfur bacteria,PNSB),可将硫化物氧化成SO42−。H2S喷淋后生成氢硫酸(H2S),扩散进入生物膜后被Thiothrix[26]和Rhodocyclaceae[32]氧化为SO42−,从而将H2S从水中去除。Thiothrix在Bio1的相对丰度(图5(b))为23.22%(高于In0中的0.38%),这可能是由于H2S的存在造成Thiothrix在生物膜中的富集,从而加快去除H2S。而Bio3中Rhodocyclaceae的相对丰度从接种污泥的0.50%上升至8.30%,是运行阶段3中去除H2S的优势功能菌。水中的有机物质被有机物降解菌Zoogloea、Sphaerotilus和Ferruginibacter降解为CO2和H2O。Zoogloea和Sphaerotilus属在接种污泥In0中的相对丰度仅为0.31%和1.75%,在Bio3中上升到5.36%和8.38%,对COD的降解具有积极贡献[33-34]。Ferruginibacter属的相对丰度从In0的0.40%上升至19.16%,这与COD降解密切相关[25]。生物膜中的Rhizobium[35]和Kosakonia[31]是具有固氮作用的菌属;Cloacibacterium[29]可促进硝酸盐还原酶和亚硝酸盐还原酶的产生,并将水中的氨氮转化为硝酸盐和亚硝酸盐,再通过Tahibacter在有氧条件下将硝酸盐和亚硝酸盐还原为N2[28],从而达到脱氮的效果。Cloacibacterium在In0中的相对丰度为0.40%,在Bio3中因NH3的加入而上升至12.81%;Kosakonia的相对丰度从0.48%上升至33.43%,是运行阶段3中去除氨氮的重要贡献者。
填料的选择与复合填料-生物滤柱的除臭效能密切相关。蜂窝煤渣含有Ca、Al、Fe、Mg等多种成分,结构疏松、微孔多、比表面积大,因而具有较好的吸附性能,同时对磷和氨氮也有一定的去除效果[36-37]。活性炭对有机物的吸附能力强、过滤速度快,同时具有较大的比表面积,有利于生物膜的生长[38-39]。沸石具有发达的孔隙结构、巨大的比表面积及稳定的物理和化学性质,是优良的吸附剂和生物载体,同时还兼具较强的氨氮吸附能力,可强化对氨氮的去除效果[39-40]。陶粒具有生物附着性强、挂膜性能良好、水流流态佳、大孔隙结构发达、表面粗糙等优点,微生物不仅可在其表面生长,还可在其孔隙内附着生长,为自养和异养菌提供良好的生长环境,是较好的生物挂膜载体[41-42]。
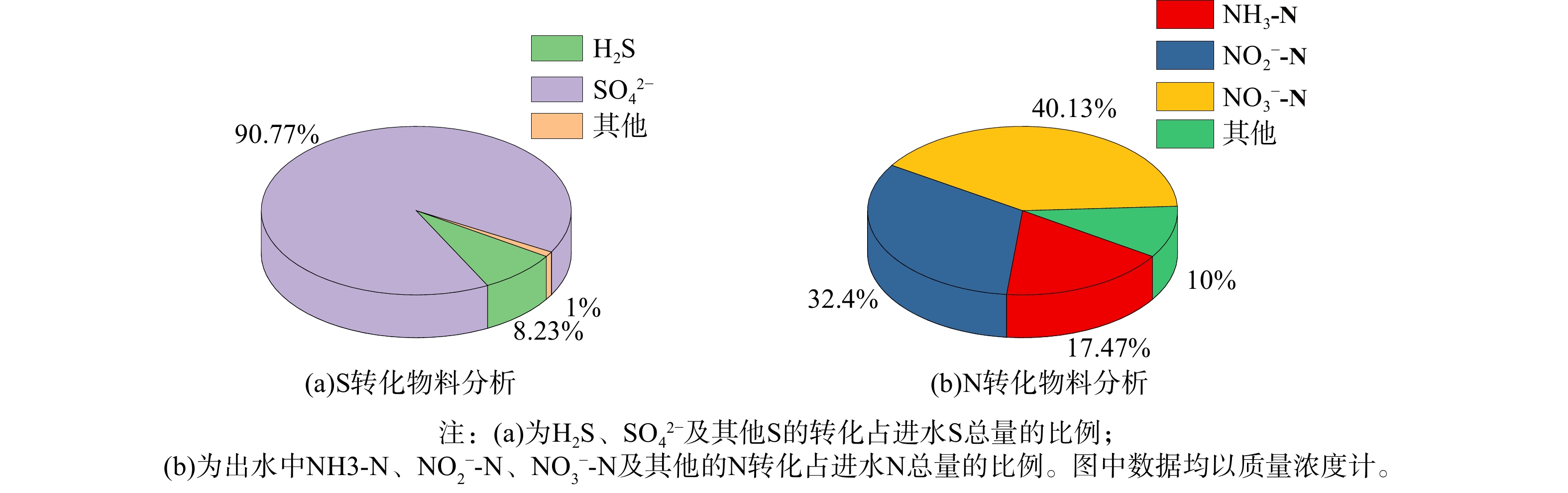
复合填料-生物滤柱反应器中的硫和氮物料衡算分析见图7。在硫素转化方面,90.77%的H2S被转化为SO42−,表明生物滤柱中S转化功能菌的富集对H2S的去除具有重要作用;在氮素转化方面,72.53 %的NH3-N被转化为硝酸盐和亚硝酸盐,,表明此时复合填料生物膜兼具N素去除的重要功能。
与已报道相似文献对比,方媛媛等[13]采用陶粒、火山岩、沸石和轮胎颗粒4种材料以体积比1∶1∶1∶1混合的填料,在23℃下对氨氮的去除率可达到92.6%;聂中林等[43]以沸石-陶粒为填料在曝气生物滤池中对氨氮的去除率达到94.6%;肖作义等[10]在实验温度为21~35 ℃时,发现以树皮、活性炭和多孔空心球(体积比为6∶2∶1)为填料的生物滤池对H2S和NH3的最大去除率为99.24%和97.53%。本研究采用蜂窝煤渣、活性炭、蜂窝沸石和陶粒体积比为4∶4∶1∶1的组合填料-生物滤柱,在实验温度为8 ℃~14 ℃时,对H2S和NH3的最大去除率可达91.77%和82.53%。相比于其他研究,本研究中组合填料-生物滤柱的去除效果可能稍显不足,鉴于低温条件下微生物活性受到抑制,本研究已达到预期处理效果。
-
1)在厦门市冬季低温条件下,通过蜂窝煤渣、活性炭、蜂窝沸石和陶粒4种填料构建了复合填料-生物滤柱生物除臭工艺,运行15 d即可实现成功挂膜,且对H2S和NH3的最大去除率为91.77%和82.53%,工艺运行高效稳定。
2)在低温条件下,复合填料生物膜中菌属Thiothrix、Rhodocyclaceae、Zoogloea、Sphaerotilus、Ferruginibacter、Rhizobium、Cloacibacterium、Kosakonia、Tahibacter对物质降解协作密切,是生物除臭的优势功能微生物。其中,Thiothrix和Rhodocyclaceae属与H2S去除相关;Rhizobium、Cloacibacterium、Kosakonia与Tahibacter属对NH3的去除与转化具有重要贡献作用;有机物降解菌Zoogloea、Sphaerotilus和Ferruginibacter是水相溶解态COD去除的主要贡献者。
闽南地区低温下复合填料强化生物滤柱除臭及微生物分析
Efficiency and microbial analysis of deodorization process of biofilter enhanced by composite filler under low temperature in Southern Fujian
-
摘要: 通过搭建复合填料-生物滤柱反应装置,在厦门冬季低温环境下开展复合填料(蜂窝煤渣、活性炭、蜂窝沸石和陶粒)强化生物滤柱除臭研究,分析了除臭微生物群落组成特性。复合填料-生物滤柱装置在启动运行15 d时其COD去除率达到85%以上且保持稳定,对H2S和NH3的最大去除率可分别达到91.77%和82.53%,表明挂膜成功。菌群分析结果表明:以H2S、NH3等臭气喷淋液为基质的生物滤柱驯化挂膜过程会降低微生物的丰度和多样性;菌属Thiothrix、Ferruginibacter、Burkholderiaceae、Tahibacter、Dinghuibacter、Cloacibacterium和Kosakonia是除臭过程的优势功能微生物和臭气成分降解的贡献者。本研究阐明了复合填料生物膜内功能菌属对H2S、NH3等臭气喷淋液有机质的生物降解/转化机制,并进行了物料平衡分析;复合填料-生物滤柱装置对H2S与NH3的平均去除率分别达到90.77%和72.53%,具有良好的生物除臭效果与运行稳定性。本研究可为南方低温季节的污水臭气治理提供技术参考和理论支撑。Abstract: The deodorization performance of the composite filler (honeycomb cinder, activated carbon, honeycomb zeolite and ceramsite) enhanced biological filter was studied under low temperature environment in Xiamen in winter, through the establishment of a compound filler-biological filter reaction device. After 15 days of operation, the chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal efficiency of the composite packing biological filter column device reached more than 85% and remained stable. The maximum removal efficiencies of H2S and NH3 could reached 91.77% and 82.53%, respectively, indicating that the film was successfully attached. The results of bacterial community analysis showed that the domestication and membrane hanging process of biofilter column based on odor spray liquid such as H2S and NH3 would reduce the abundance and diversity of microorganisms. The genera of thiothrix, ferraginibacter, burkholderiaceae, tahibacter, dinghuibacter, cloacibacterium and kosakonia were the dominant functional microorganisms in the deodorization process and contributed to the degradation of odor components. In this study, the biodegradation / transformation mechanism of organic matter in odor spray liquid such as H2S and NH3 by functional bacteria in composite filler biofilm was clarified, and the material balance analysis was carried out. During operation, the average removal efficiencies of H2S and NH3 by the system reached 90.77% and 72.53%, respectively, indicating that the process had good biological deodorization effect and operation stability. This study can provide reference for the application of biological waste gas / odor treatment process in low-temperature season or cold area.
-
污水处理行业的臭气主要产生于污水处理厂和污水收集管网泵站等环节,相关治理技术主要有吸收法、吸附法、燃烧法和生物法等[1]。其中,生物除臭技术因其环保、高效、低成本等优点在污水处理厂臭气处理领域得以应用[2]。生物滤柱与生物洗涤塔、生物滤池和生物滴滤塔等生物除臭技术相比,具有占地面积小、运行费用低、处理效率高和管理方便等特点[3-5],但在冬季低温条件下微生物代谢活性受到抑制,极易出现处理效果差、运行不稳定等问题。通过填料投加以增大滤柱有效生物量来提高处理效果是生物滤柱研究中较为重要的强化策略之一[6]。
生物除臭技术中的填料通常具备较好的持水性、良好的透气性和优异的比表面积,有利于微生物膜的形成和微生物的新陈代谢[7]。屈艳芬等[8]采用混合肥料、聚苯乙烯胶球体、活性炭、沸石为混合填料进行除臭实验,取得了良好的处理效果。端艳等[9]采用陶粒作为生物滤池中的填料,发现其对COD和氨氮有良好的去除效果。肖作义等[10]将树皮、活性炭和多孔空心球按照6:2:1的比例混合填充,对NH3和H2S的去除效果较好。刘桂臣等[11]考察了沸石-无烟煤双层滤料生物滤池处理污水的效果,结果表明,可获得良好的出水水质。单一填料生物除臭工艺的运行时间较长时会出现堵塞、透气性变差等问题[12],因此,开发高效、稳定的复合填料以提高生物滤柱的微生物量,成为强化低温环境下滤柱除臭运行效能的重要方式。
本研究通过搭建模拟喷淋-生物滤柱臭气处理工艺,以蜂窝煤渣、活性炭、蜂窝沸石和陶粒构建复合填料强化生物滤柱处理效能,选择污水处理厂主要恶臭气体硫化氢(H2S)和氨气(NH3)作为目标污染物,分析闽南地区(以厦门为例)冬季低温条件下混合填料生物滤柱对2种恶臭气体的去除效果,探究系统成功运行后,复合填料表面生物膜微生物的群落结构变化,并进行物料衡算以综合评估复合填料-生物滤柱的臭气处理效能,为冬季气候条件下闽南地区污水处理厂的臭气高效快速处理提供技术参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验原料及其特征
1)接种污泥。实验采用厦门某污水处理厂曝气池活性污泥。接种污泥的TSS为12.29 g·L−1,VSS为7.68 g·L−1,pH为7.68。
2) H2S气体。在密闭瓶中加入硫化亚铁固体,再将一定含量的10%稀硫酸溶液通过蠕动泵以一定流速通入瓶中,使之发生化学反应产生H2S;通过调节蠕动泵控制产气量,使产生的气体质量浓度保持在(5.0 ± 0.6) mg·L−1。
3) NH3气体。通过投加25%氨水模拟NH3的产生,通过流量计调节投加氨水的量,使生物滤柱反应器进水中氨氮质量浓度保持在(35.0 ± 1.5) mg·L−1。
4)喷淋水。以模拟生活污水作为喷淋水源,其组分及质量浓度如下。氯化铵,14.28 mg·L−1;磷酸二氢钾,28.15 mg·L−1;尿素,19.20 mg·L−1;无水氯化钙,8.31 mg·L−1;硫酸镁,33.91 mg·L−1;无水乙酸钠,21.11 mg·L−1;葡萄糖,192.00 mg·L−1;(NH4)6Mo7O2,0.18 mg·L−1;FeSO4·7H2O,1.50 mg·L−1;ZnSO4·7H2O:0.12 mg·L−1;MnCl2·2H2O:0.12 mg·L−1;CoCl2·6H2O:0.15 mg·L−1;CuSO4·5H2O:0.03 mg·L−1。
5)复合填料。该实验选用的复合填料是蜂窝煤渣、活性炭、蜂窝沸石和陶粒。参考已报道文献[10, 12-13],将生物滤柱复合填料的体积投配比设置为4∶4∶1∶1,混合后构建复合填料。蜂窝煤渣取用学校食堂废弃的蜂窝煤渣,干燥、粉碎,过80目标准筛;活性炭的粒径为2~4 mm,蜂窝沸石的粒径为2~4 mm,陶粒粒径为4~6 mm。
1.2 实验装置与步骤
1.2.1 实验装置
本次实验地点位于华侨大学厦门校区,实验装置如图1所示。环境温度维持在8~14 ℃。取用厦门某污水处理厂曝气池的活性污泥为生物滤柱提供所需微生物。为准确判断混合填料挂膜情况,每3 d检测1次生物滤池反应器出水COD,确定微生物对营养物质的吸收与利用情况[14]。实验装置主要由H2S发生装置、喷淋装置和生物滤柱组成。生物滤柱为圆柱形,尺寸为φ70 mm×1 700 mm,滤柱有效容积为6.50 L。复合填料置入生物滤柱中,填料区填充高度约为700 mm,体积填充比为0.4。生物滤柱底部连接微曝气装置,反应器启动时开始进行曝气。
1.2.2 实验步骤
阶段1是驯化挂膜阶段,运行时间为15 d。本实验采用直接驯化挂膜法[15-16],往生物滤柱中填入活性污泥直至将填料区完全浸没,48 h后再将泥浆排出,然后将模拟生活污水通入反应器中,此过程不通入臭气。每隔3 d在反应器的进水、出水口取样以测定COD含量。
阶段2是H2S气体处理阶段(运行路径①),运行时间为30 d。H2S气体从H2S发生装置由空气泵抽至喷淋装置底部的进气口,再经喷淋后输送至生物滤柱底部的进水口;经过填料区后,残余气体由顶部出气口排出。其中,H2S进气量由空气流量计调节控制;在此阶段中,每隔3 d测定1次进出H2S质量浓度和进出水中SO42−的质量浓度。
阶段3是H2S和NH3混合臭气处理阶段,运行时间为30 d。在第2阶段的基础上,开启氨水释放装置(路径①与路径②同时开启),NH3经喷淋后进入生物滤柱,每隔3 d测定1次进出H2S质量浓度和进出水中NH3-N质量浓度。
1.3 分析方法
采用重铬酸钾法测定COD[17];采用纳氏试剂分光光度法测定氨氮(NH3-N)质量浓度[18];采用硫化氢气体检测仪测定H2S质量浓度;采用铬酸钡分光光度法测定SO42−的质量浓度[19]。
1.4 微生物群落分析
为探究处理臭气对复合填料生物膜上微生物群落组成多样性和变化情况的影响,分别取接种污泥、运行阶段1、运行阶段2、运行阶段3结束运行后的复合填料上生物膜污泥样品进行分析。每个样品平行取样3次,混合均匀后分别标记为In0、Bio1、Bio2、Bio3。从生物滤柱中取得复合填料层的填料,从其表层提取生物膜污泥样品,在10 000 r·min−1下离心10 min,使得污泥固液分离。然后,使用快速DNA试剂盒(MoBio Laboratories)从污泥沉积物中提取基因组DNA,操作步骤按照试剂盒中提供的使用说明书进行。利用Qubit3.0 DNA检测试剂盒对基因组DNA精确定量,以确定聚合酶链反应(PCR)应加入的DNA量。使用引物(515F和806R)对污泥细菌16S DNA的V3-V4区域进行PCR扩增。利用Gene Tools Analysis Software (Version4.03.05.0, SynGene)对PCR产物进行浓度对比后,按照等质量原则计算各样品所需体积,将各PCR产物进行混合。使用E.Z.N.A.®GelExtractionKit凝胶回收试剂盒回收PCR混合产物,TE缓冲液洗脱回收目标DNA片段。后续建库按照NEBNext®UltraTM DNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina®标准流程进行建库操作,完成后在高通量测序平台Hiseq或Miseq进行上机测序,并通过广东美格基因科技有限公司分析平台(www.magichand.online)对扩增产物进行高通量测序分析。根据MiSeq测序结果检测到的OTU,使用RDP数据库(http://rdp.cme.msu.edu/misc/resources.jsp)进行微生物分类分析,包括科和属级别。每个样本的微生物多样性由Mothur软件计算(http://www.mothur. org/wiki/Schloss_SOP#Alpha_diversity),包括Chao1指数,richness指数;通过Matlab软件实现PCA主成分分析。最后,通过STAMP软件评估微生物群落相对丰度(科、属级别的比较分析)。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 复合填料-生物滤柱的运行效能
2.1.1 驯化挂膜阶段
进出水中溶解性有机物(COD)的变化有助于明确微生物对反应器中有机物质的吸收和降解特性[20]。复合填料-生物滤柱在启动运行阶段(阶段1)15 d的COD变化见表1。在启动运行的前9 d内,生物滤柱对COD的去除率较低(57%~64%);从第12天开始,生物滤柱对COD的去除率逐渐稳定在80%以上,说明生物滤柱内微生物可充分利用进水营养液中的碳源作为自身营养物质。在生物膜上微生物代谢达到平衡后,挂膜成功。这与现有报道[20]情况相符。
表 1 运行阶段1(启动阶段)复合填料-生物滤柱对COD去除效率的变化Table 1. Change of COD removal efficiency of composite packing biological filter column in operation stage 1 (start-up stage)运行天数/d 进水COD/(mg·L−1) 出水COD/(mg·L−1) COD去除率/% 3 160 68 57.50 6 168 60 64.29 9 180 64 64.44 12 250 28 88.80 15 228 28 87.72 2.1.2 单一H2S处理阶段
复合填料-生物滤柱反应器对H2S的降解效果如图2所示(运行阶段2)。图2(a)为复合填料-生物滤柱反应器对H2S气体的去除效果。在运行6 d后,H2S的进气质量浓度为4.42~5.51 mg·L−1,出气质量浓度降至0.99~1.66 mg·L−1。在此过程中,H2S的去除率仅为约40%。从第9天开始,H2S的去除率逐渐升高至70%以上,并保持稳定,最大去除率可达91.77%。图2(b)为运行阶段2进出水中SO42−的质量浓度变化(已扣除进水组分中SO42−的质量浓度)。其中,出水SO42−的质量浓度达到21.44~49.44 mg·L−1,远高于进水SO42−的质量浓度,这说明复合填料-生物滤柱硫氧化菌(sulfur-oxidizing bacteria,SOB)得到富集,将H2S转化为SO42−[21]。SO42−的质量浓度可间接反映去除H2S功能菌的富集程度,即随着运行时间的增长,硫氧化菌的富集程度提高,这是H2S对硫氧化菌培养驯化的结果。
2.1.3 H2S与NH3混合臭气处理阶段
运行阶段3是复合填料-生物滤柱同步去除H2S和NH3的运行阶段。在阶段2的基础上向生物滤柱通入氨水模拟NH3的进入,运行时间为30 d。图3(a)为此运行阶段生物滤柱反应器进出H2S质量浓度的变化及其去除率。在阶段3运行的30 d里,H2S的去除率一直稳定在70%以上,说明生物滤柱对H2S的去除效果良好且运行稳定。图3(b)为进出水NH3-N质量浓度及其去除率。在前15 d内,NH3-N的去除率逐步上升。从第15 d开始,去除率一直稳定在70%以上,其中最大去除率达到82.53%。这与殷峻等[22]研究结果相符,说明生物滤柱可实现对H2S和NH3-N的同步去除,且去除效果良好、运行稳定。
2.2 组合填料微生物组成及多样性分析
2.2.1 微生物群落组成多样性分析
图4(a)为4个样本的稀释曲线。随着样本量的增加,样本稀释曲线趋于平缓,即说明本次实验取样合理,样本测序数据量能反应污泥样品中的总体微生物[23]。
复合填料-生物滤柱内生物膜的微生物群落组成多样性指数如图4(b)所示。样本的物种丰富度随运行天数的增加整体呈下降趋势。这可能是由于驯化与挂膜培养过程中微生物生存环境和营养源的改变所致。样本Bio2的物种丰富度与样本Bio1相差不大,说明通入H2S对微生物物种丰富度的影响较小;而样本Bio3的物种丰富度小于样本Bio2,这可能由于高负荷H2S和NH3环境会对微生物群落产生抑制作用,降低了微生物丰富度[24]。
主成分分析(principal component analysis,PCA)主要用于考察样本间最主要的差异特征,样本在坐标系中的距离远近可最大程度地还原样本间的实际差异。图4(c)为4个样本的PCA分析图,可观察到接种污泥样本In0与其他3个样本在坐标系中距离较远,微生物物种差异性较大。这说明通入臭气后,生物滤柱反应器中的微生物种群有较大变化,即臭气(H2S、NH3)的进入对复合填料生物膜菌群结构起到重要的重塑作用,进而改变微生物群落功能,使之具备脱硫除氮能力。而样本Bio1和样本Bio2在坐标系中距离相近,样本Bio3相比较下较远,说明通入H2S并运行30 d后的反应器内微生物种群变化不明显。在进入氨气后,反应器内微生物种群变化较为明显,说明单一臭气(H2S)对复合载体生物膜菌群结构的影响小于混合臭气,加入氨气后反应器内微生物种群的变化更为明显。这表明混合臭气(H2S+NH3)对微生物菌群具有更显著的筛选与驯化作用。这也是Bio3样品丰富度降低(图2)的主因,亦与前述报道[24]相符。
2.2.2 微生物群落组成分析
对4个样本在科水平的微生物群落组成(相对丰度>0.01%)进行了分析,其结果见图5(a)。由图5(a)可见,4个样本的物种组成相似,但相对丰度占比存在明显区别。Ignavibacteriales的相对丰度在通入H2S后呈现明显下降趋势,Ignavibacteriales科属于绿硫细菌 (green sulfur bacteria,GSB),但是没有硫氧化能力[22],故通入H2S后,其丰度下降,并逐渐被具有硫氧化能力的硫氧化菌及其他硫氧化菌取代。而Rhizobiales、Thiotrichaceae和Chiitinophagaceae在通入H2S后相对丰度上升,是除H2S优势功能菌和有机物降解菌。通入H2S运行30 d后,Burkholderiaceae和Rhodanobacteraceae的相对丰度升高,为除H2S优势功能菌。加入NH3进入反应器至运行结束,Rhodocyclaceae、Weeksellaceae和Enterobacteriaceae的相对丰度上升,而Xanthomonadceae、Thiotrichaceae和Rhodanobacteraceae的相对丰度下降。NH3的加入,使脱氮优势菌丰度上升,与除H2S优势菌竞争营养物质,从而导致部分除H2S优势菌的丰度下降,NH3的存在会对部分脱硫微生物产生抑制作用,亦是污泥样品Bio3与Bio2产生菌群差异性的主因(图4(c))。综上所述,Rhodocyclaceae、Weeksellaceae和Enterobac是H2S与NH3混合臭气处理阶段的优势微生物。
图5(b)为4个样本在属水平的微生物群落组成(相对丰度>0.01%)。接种污泥样本In0中Ignavibacteriales(88.90%)的相对丰度最高,通入臭气后呈现明显下降趋势。这说明H2S对Ignavibacteriales
有抑制作用,通入H2S会导致其丰度下降,逐渐被其他除臭优势菌取代,这与图5(a)呈现的分析结果一致。在通入H2S后,Thiothrix的相对丰度从0.38%上升至23.22%,Ferruginibacter的相对丰度从0.40%上升至19.16%,菌属Thiothrix和Ferruginibacter与H2S降解相关[25-26]。在通入H2S运行30 d后,Burkholderiaceae、Tahibacter相对丰度从1.57%、8.38%分别上升至13.75%和26.61%,这说明Burkholderiaceae、Tahibacter对H2S的生物降解/转化有积极的贡献作用,与已有报道[27-28]结果一致。从加入NH3至反应器运行结束,Dinghuibacter、Cloacibacterium和Kosakonia的相对丰度显著上升,分别从0.61%、0.48%和0.32%上升至7.65%、12.8%和33.42%,而Burkholderiaceae、Tahibacter和Ferruginibacter的相对丰度显著下降。这说明Dinghuibacter、Cloacibacterium和Kosakonia为氨氮去除相关功能菌[29-31]。 2.3 微生物除臭机理分析
复合填料表层生物膜内除臭微生物群落中的核心菌属成员及其对H2S、NH3的转化作用见图6。Thiothrix是硫化物氧化丝状菌属,以H2S为能源,可将H2S氧化为硫粒积累在菌体内,在缺乏营养时又将硫粒氧化为SO42−,从而获得能量。Rhodocyclaceae属于紫色非硫细菌 (purple nonsulfur bacteria,PNSB),可将硫化物氧化成SO42−。H2S喷淋后生成氢硫酸(H2S),扩散进入生物膜后被Thiothrix[26]和Rhodocyclaceae[32]氧化为SO42−,从而将H2S从水中去除。Thiothrix在Bio1的相对丰度(图5(b))为23.22%(高于In0中的0.38%),这可能是由于H2S的存在造成Thiothrix在生物膜中的富集,从而加快去除H2S。而Bio3中Rhodocyclaceae的相对丰度从接种污泥的0.50%上升至8.30%,是运行阶段3中去除H2S的优势功能菌。水中的有机物质被有机物降解菌Zoogloea、Sphaerotilus和Ferruginibacter降解为CO2和H2O。Zoogloea和Sphaerotilus属在接种污泥In0中的相对丰度仅为0.31%和1.75%,在Bio3中上升到5.36%和8.38%,对COD的降解具有积极贡献[33-34]。Ferruginibacter属的相对丰度从In0的0.40%上升至19.16%,这与COD降解密切相关[25]。生物膜中的Rhizobium[35]和Kosakonia[31]是具有固氮作用的菌属;Cloacibacterium[29]可促进硝酸盐还原酶和亚硝酸盐还原酶的产生,并将水中的氨氮转化为硝酸盐和亚硝酸盐,再通过Tahibacter在有氧条件下将硝酸盐和亚硝酸盐还原为N2[28],从而达到脱氮的效果。Cloacibacterium在In0中的相对丰度为0.40%,在Bio3中因NH3的加入而上升至12.81%;Kosakonia的相对丰度从0.48%上升至33.43%,是运行阶段3中去除氨氮的重要贡献者。
填料的选择与复合填料-生物滤柱的除臭效能密切相关。蜂窝煤渣含有Ca、Al、Fe、Mg等多种成分,结构疏松、微孔多、比表面积大,因而具有较好的吸附性能,同时对磷和氨氮也有一定的去除效果[36-37]。活性炭对有机物的吸附能力强、过滤速度快,同时具有较大的比表面积,有利于生物膜的生长[38-39]。沸石具有发达的孔隙结构、巨大的比表面积及稳定的物理和化学性质,是优良的吸附剂和生物载体,同时还兼具较强的氨氮吸附能力,可强化对氨氮的去除效果[39-40]。陶粒具有生物附着性强、挂膜性能良好、水流流态佳、大孔隙结构发达、表面粗糙等优点,微生物不仅可在其表面生长,还可在其孔隙内附着生长,为自养和异养菌提供良好的生长环境,是较好的生物挂膜载体[41-42]。
复合填料-生物滤柱反应器中的硫和氮物料衡算分析见图7。在硫素转化方面,90.77%的H2S被转化为SO42−,表明生物滤柱中S转化功能菌的富集对H2S的去除具有重要作用;在氮素转化方面,72.53 %的NH3-N被转化为硝酸盐和亚硝酸盐,,表明此时复合填料生物膜兼具N素去除的重要功能。
与已报道相似文献对比,方媛媛等[13]采用陶粒、火山岩、沸石和轮胎颗粒4种材料以体积比1∶1∶1∶1混合的填料,在23℃下对氨氮的去除率可达到92.6%;聂中林等[43]以沸石-陶粒为填料在曝气生物滤池中对氨氮的去除率达到94.6%;肖作义等[10]在实验温度为21~35 ℃时,发现以树皮、活性炭和多孔空心球(体积比为6∶2∶1)为填料的生物滤池对H2S和NH3的最大去除率为99.24%和97.53%。本研究采用蜂窝煤渣、活性炭、蜂窝沸石和陶粒体积比为4∶4∶1∶1的组合填料-生物滤柱,在实验温度为8 ℃~14 ℃时,对H2S和NH3的最大去除率可达91.77%和82.53%。相比于其他研究,本研究中组合填料-生物滤柱的去除效果可能稍显不足,鉴于低温条件下微生物活性受到抑制,本研究已达到预期处理效果。
3. 结论
1)在厦门市冬季低温条件下,通过蜂窝煤渣、活性炭、蜂窝沸石和陶粒4种填料构建了复合填料-生物滤柱生物除臭工艺,运行15 d即可实现成功挂膜,且对H2S和NH3的最大去除率为91.77%和82.53%,工艺运行高效稳定。
2)在低温条件下,复合填料生物膜中菌属Thiothrix、Rhodocyclaceae、Zoogloea、Sphaerotilus、Ferruginibacter、Rhizobium、Cloacibacterium、Kosakonia、Tahibacter对物质降解协作密切,是生物除臭的优势功能微生物。其中,Thiothrix和Rhodocyclaceae属与H2S去除相关;Rhizobium、Cloacibacterium、Kosakonia与Tahibacter属对NH3的去除与转化具有重要贡献作用;有机物降解菌Zoogloea、Sphaerotilus和Ferruginibacter是水相溶解态COD去除的主要贡献者。
-
表 1 运行阶段1(启动阶段)复合填料-生物滤柱对COD去除效率的变化
Table 1. Change of COD removal efficiency of composite packing biological filter column in operation stage 1 (start-up stage)
运行天数/d 进水COD/(mg·L−1) 出水COD/(mg·L−1) COD去除率/% 3 160 68 57.50 6 168 60 64.29 9 180 64 64.44 12 250 28 88.80 15 228 28 87.72 -
[1] 付小娟. 污水处理和固废处理行业的臭气治理技术分析[J]. 山西化工, 2021, 41(6): 241-242. [2] 余鹏举, 曹先贺, 王宏志, 等. 微生物在恶臭污染治理中的研究及应用[J]. 微生物学通报, 2021, 48(1): 165-179. [3] 张玉生, 程磊. 污水处理系统除臭技术应用进展[J]. 能源与环境, 2021(6): 72-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9064.2021.06.026 [4] 马军, 邱立平. 曝气生物滤池及其研究进展[J]. 环境工程, 2002, 20(3): 7-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8942.2002.03.001 [5] WANG C R, LI J, WANG B Z, et al. Development of an empirical model for domestic wastewater treatment by biological aerated filter[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2006, 41(4): 778-782. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2005.09.015 [6] 王硕, 时文歆, 王燕, 等. 低温污水生物处理技术研究现状与展望[J]. 生物技术通报, 2015, 31(5): 48-53. [7] 邢家乐, 耿荣海, 张丹迟, 等. 影响生物除臭法性能的主要因素分析及工程解决方案[C]//天津: 中国环境科学学会2021年科学技术年会——环境工程技术创新与应用分会场. 2021: 433-437. [8] 屈艳芬, 叶锦韶, 尹华. 城市污水厂恶臭的生物过滤处理系统设计和运行[J]. 中国给水排水, 2007, 23(4): 35-38. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4602.2007.04.010 [9] 端艳, 陆少鸣, 江荻. 悬浮陶粒曝气生物滤池在城镇污水处理中的挂膜启动[J]. 水处理技术, 2018, 44(2): 88-92. [10] 肖作义, 段耀庭, 赵鑫, 等. 混合填料在生物滤池中除臭效果研究[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2020, 27(6): 88-94. [11] 刘桂臣, 蒋白懿, 徐箴. 沸石-无烟煤生物滤池联合处理微污染水试验研究[J]. 供水技术, 2008, 2(5): 8-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9353.2008.05.003 [12] 刘宝玉, 张欣, 杨华军, 等. 不同填料组合对生物滤池去除H2S的影响[J]. 天津建设科技, 2020, 30(1): 31-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-3197.2020.01.009 [13] 方媛瑗, 戴国飞, 杨平, 等. 不同填料组合对污水中氮磷去除效果的研究[J]. 应用化工, 2020, 49(10): 2475-2477. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2020.10.016 [14] DORADO A D, LAFUENTE J, GABRIEL D, et al. Interaction between sorption and biodegradation in a biofilter packed with activated carbon[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2012, 66(8): 1743-1750. doi: 10.2166/wst.2012.384 [15] 郭兵兵, 何凤友, 牟桂芝, 等. 生物填料塔工艺净化恶臭废气的研究[J]. 石油炼制与化工, 2004, 35(10): 45-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2399.2004.10.011 [16] STRIKAUSKA S Z D, BERZINS A, et al. Biodegradation of ammonia by two stage biofiltration system[J]. Emviromental Engineering & Policy, 1998, 1(3): 175-179. [17] 娄红杰, 张先松, 姜兴剑, 等. 烘箱消解-重铬酸钾滴定法测定水质中化学需氧量[J]. 化学分析计量, 2020, 29(6): 42-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-6145.2020.06.010 [18] 张改亲. 纳氏试剂分光光度法测试水中氨氮要点分析[J]. 山西化工, 2021, 41(3): 45-46. [19] 周琴, 周良. 铬酸钡分光光度法测定水中硫酸盐含量[J]. 四川环境, 2019, 38(6): 125-127. [20] 武福平, 齐海英, 丁俊宏, 等. 活性炭-石英砂生物过滤处理微污染窖水的挂膜试验研究[J]. 水处理技术, 2011, 37(7): 70-72. [21] 刘国新, 吴海珍, 孙胜利, 等. 市政污泥接种焦化废水好氧降解能力及微生物群落演替的响应分析[J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(9): 3807-3815. [22] 殷峻, 方士, 陈英旭. 生物滤塔处理低浓度H2S和NH3混合气体[J]. 中国给水排水, 2003, 19(13): 114-116. [23] 徐瑛, 孙永明, 郑涛, 等. 高通量测序技术辅助筛选脱硫菌[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(5): 1808-1814. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2014.05.035 [24] TU X, LI J, FENG R, et al. Comparison of removal behavior of two biotrickling filters under transient condition and effect of ph on the bacterial communities[J]. Plos One, 2016, 11(5): e0155593. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155593 [25] WEN Y, JIN Y, WANG J, et al. MiSeq sequencing analysis of bacterial community structures in wastewater treatment plants[J]. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 2015, 24(4): 1809-1815. [26] BRIGMON R L, MARTIN H W, ALDRICH H C. Biofouling of groundwater systems by Thiothrix spp[J]. Current Microbiology, 1997, 35(3): 169-174. doi: 10.1007/s002849900233 [27] MOTL N, SKIBA M A, KABIL O, et al. Structural and biochemical analyses indicate that a bacterial persulfide dioxygenase-rhodanese fusion protein functions in sulfur assimilation[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2017, 292(34): 14026-14038. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.790170 [28] MAKK J, HOMONNAY Z G, KEKI Z, et al. Tahibacter aquaticus gen. nov., sp nov., a new gammaproteobacterium isolated from the drinking water supply system of Budapest (Hungary)[J]. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 2011, 34(2): 110-115. doi: 10.1016/j.syapm.2010.11.001 [29] SHAHID M, AMEEN F, MAHESHWARI H S, et al. Colonization of Vigna radiata by a halotolerant bacterium Kosakonia sacchari improves the ionic balance, stressor metabolites, antioxidant status and yield under NaCl stress[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 2021, 158: 103809. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2020.103809 [30] LV Y Y, WANG J, CHEN M H, et al. Dinghuibacter silviterrae gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from forest soil[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2016, 66(4): 1785-1791. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.000940 [31] CHO D H, RAMANAN R, HEO J, et al. Enhancing microalgal biomass productivity by engineering a microalgal-bacterial community[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2015, 175: 578-585. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.10.159 [32] CHUNG J, SHIN S, OH J. Characterization of a microbial community capable of reducing perchlorate and nitrate in high salinity[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2009, 31(7): 959-966. doi: 10.1007/s10529-009-9960-1 [33] LV Y, WAN C, LEE D-J, et al. Microbial communities of aerobic granules: Granulation mechanisms[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2014, 169: 344-351. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.07.005 [34] EPRINTSEV A T, WU T L, SELIVANOVA N V, et al. Obtaining homogenous preparations of succinate dehydrogenase isoforms from the D-507 strain of Sphaerotilus natans[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Microbiology, 2012, 48(6): 541-545. doi: 10.1134/S0003683812060038 [35] WANG F, WANG H, SUN C, et al. Conventional bioretention column with Fe-hydrochar for stormwater treatment: Nitrogen removal, nitrogen behaviour and microbial community analysis[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 334: 125252. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125252 [36] 吴秋仙, 刘学伟. 蜂窝煤渣对磷吸附特性探讨[J]. 水产养殖, 2019, 40(4): 41-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2091.2019.04.009 [37] 吴秋仙. 蜂窝煤渣对氨氮吸附特性探讨[J]. 水产养殖, 2014, 35(1): 21-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2091.2014.01.005 [38] 张尊举, 董春艳. 陶粒-沸石-活性炭组合填料生物滤池的研究[J]. 中国环境管理干部学院学报, 2013, 23(5): 63-66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-813X.2013.05.018 [39] 叶治安, 周娜, 郭长红, 等. 沸石活性炭复合滤料串级生物滤池处理厂矿企业生活区污水的实验研究[J]. 水处理技术, 2017, 43(12): 111-114. [40] 郭文东. 煤砂滤料用于降浊除蚤的可行性试验研究[J]. 辽宁化工, 2018, 47(11): 1092-1094. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0935.2018.11.007 [41] 丁绍兰, 杨倩, 谢林花, 等. 核桃壳-陶粒填料曝气生物滤池去除氨氮的研究[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2018, 40(1): 1-5. [42] BARBER A, LALONDE K, MUCCI A, et al. The role of iron in the diagenesis of organic carbon and nitrogen in sediments: A long-term incubation experiment[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2014, 162: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2014.02.007 [43] 聂中林, 马赫, 梁鹏, 等. 不同填料曝气生物滤池处理微污染河水的效果[J]. 中国给水排水, 2020, 36(17): 41-48. -







 下载:
下载: