-
电除尘器作为工业烟气净化的主要设备之一,由于其总除尘效率高、本体阻力低、处理烟气量大、耐高温强腐蚀性气体以及运行维护费用低等优点,广泛应用在电力、冶金、建材等工业领域[1]。理论上,电除尘器可以高效捕集任何粒径的气溶胶粒子,但在实际工业应用中,对亚微米粒子和超细粒子(粒径小于0.1 μm)的捕集效率并不理想[2-5]。为了提高电除尘器对细颗粒物的捕集效率,开发新型电极电除尘器是采取的主要措施之一[6]。基于电风效应对细颗粒物运动状态的影响,减缓收尘电极附近的湍流现象,提出的多孔收尘电极电除尘器是其中之一,其电极结构特征是多孔板型式的收尘极板,在较低的比集尘面积条件下,对细颗粒物有较高的捕集效率。为引导该新型电除尘器设计选型,研究微细颗粒物在其电场内部沉降过程与除尘性能尤为重要。
由于对电除尘通道内各种电气、流动和粒子参数进行实测存在困难,数值模拟方法广泛应用在电除尘器通道内电气特性、流场特性和粒子运动特性的研究。GAO等[7]利用数值模拟方法描述双区电除尘器的物理过程,通过实验验证了该数值模型的准确性,并建立了双区电除尘器除尘性能与影响因素之间的定量关系。DONG等[8]对尖端放电极形式的电除尘器进行了气固两相流的数值研究,详细分析了进口气流速度、负电晕电压、放电极上的尖端位置对气流流线分布的影响。ZHU等[9]利用数值模拟方法研究了波型板电除尘器和平行板电除尘器中微粒的捕集过程,研究发现波型板电除尘器比平行板电除尘器具有更强的电场特性,并且对离子风流动具有更强的抵抗能力。目前,采用数值模拟方法对该新型电极电除尘器的研究内容鲜见报道,而且对其除尘性能及颗粒沉降规律尚不清晰。
多项研究表明,新型电极可从多方面提高电除尘器除尘性能。本研究采用数值模拟方法研究荷电粒子在多孔收尘电极电除尘器内迁移与沉降规律,并以平板电极为基础,结合多孔板电极利用数值模拟软件Comsol Multiphysics探究2种不同收尘极结构下电除尘器通道内的电气特性、流场特性和粒子运动特性,以揭示多孔收尘电极电除尘器的提效机理,并为该新型电极电除尘器的选型设计提供参考。
-
忽略尘粒与气体对电场影响,电场电晕放电控制方程可简化为泊松方程与电流连续方程[2],如式(1)~式(4)。
式中:E为电场强度,V∙m−1;J为电流密度,A∙m−2;φ为电压,V;ε0为真空介电常数,8.85×10−12 C2∙(N∙m2)−1;μion为离子迁移率,m2∙(V∙S)−1;Dion为离子扩散系数,m2∙s;ρion为空间电荷密度,C∙m−3;uf为流体速度,m∙s−1。
-
电除尘器内的流场被称为电流场,含有大量气体离子电荷与颗粒荷电后电荷,流体本身也受电场力作用,已有研究[10-13]表明,采用时均Navier-Stokes方程和雷诺应力标准湍流模型[14]对电除尘器内电流场可进行有效的求解。时均Navier-Stokes方程与标准κ-ε湍流模型可以写成式(5)~式(10)。
式中:uf为流体速度,m∙s−1;ρf为流体密度,kg∙m−3;p为气体静压,Pa;μ为层流黏性系数,kg∙(m∙s)−1;μT为湍流黏性系数,kg∙∙(m∙s)−1;I为单位矩阵;湍流动能κ与湍流耗散系数ε;Pk为湍动能每单位耗散净产出。常数分别为:Cμ=0.09,σκ=1.00,σε=1.30,Cε1=1.44,Cε2=1.92。
-
电除尘器中粒子荷电有2种荷电机制:电场荷电与扩散荷电[2]。龙正伟等[15]从计算精度和计算效率两方面分析使用Lawless[16]模型模拟粒子荷电过程满足计算需求。因此,颗粒的总荷电速率可以表示为式(11)~式(17)。
式中:kB是玻尔兹曼常数;Tion是离子温度;Rf和Rd是无量纲场荷电率及扩散荷电率;εrp为粒子的相对介电常数;fa是联系电场荷电率与扩散和电率的一个功能函数公式(18)。
-
描述颗粒运动方法有欧拉模型与拉格朗日模型,前者适合计算宏观的运动,而后者适合研究单颗粒的运动。本研究为了解多孔电极电除尘器内部单颗粒的运动特性,采用拉格朗日运动模型对粒子沉降规律进行描述。进入电除尘器的颗粒在荷电后受到电场力作用,同时受到曳力及重力作用。对电除尘器进行二维模拟,忽略颗粒在竖直方向受到的重力,由牛顿第二定律,颗粒的运动方程见式(19)。
式中:up是颗粒运动速度,m∙s−1;uf是流体运动速度,m∙s−1;CD是流体曳力系数;ρp是颗粒密度,kg∙m−3;dp是颗粒直径,m,q是颗粒荷电量,C;流体曳力系数CD是颗粒雷诺数Rep的函数,满足公式(20)[17]。
式中:Rep表示气流中颗粒运动特征的无量纲准数,可由式(21)计算[18]。
式中:Cc为肯宁汉修正系数,计算方法[19]如式(22)~式(23)所示。
式中:dp为粒子直径,m;kB为玻尔兹曼常数,1.38×10−23 J∙K−1;T为气体温度,K;p为气体压强,Pa;d为气体分子有效直径,干空气分子有效直径约为3.70×10−10 m;λ为气体分子平均自由程,在1个大气压和20 ℃条件下约为6.60×10−8 m。
-
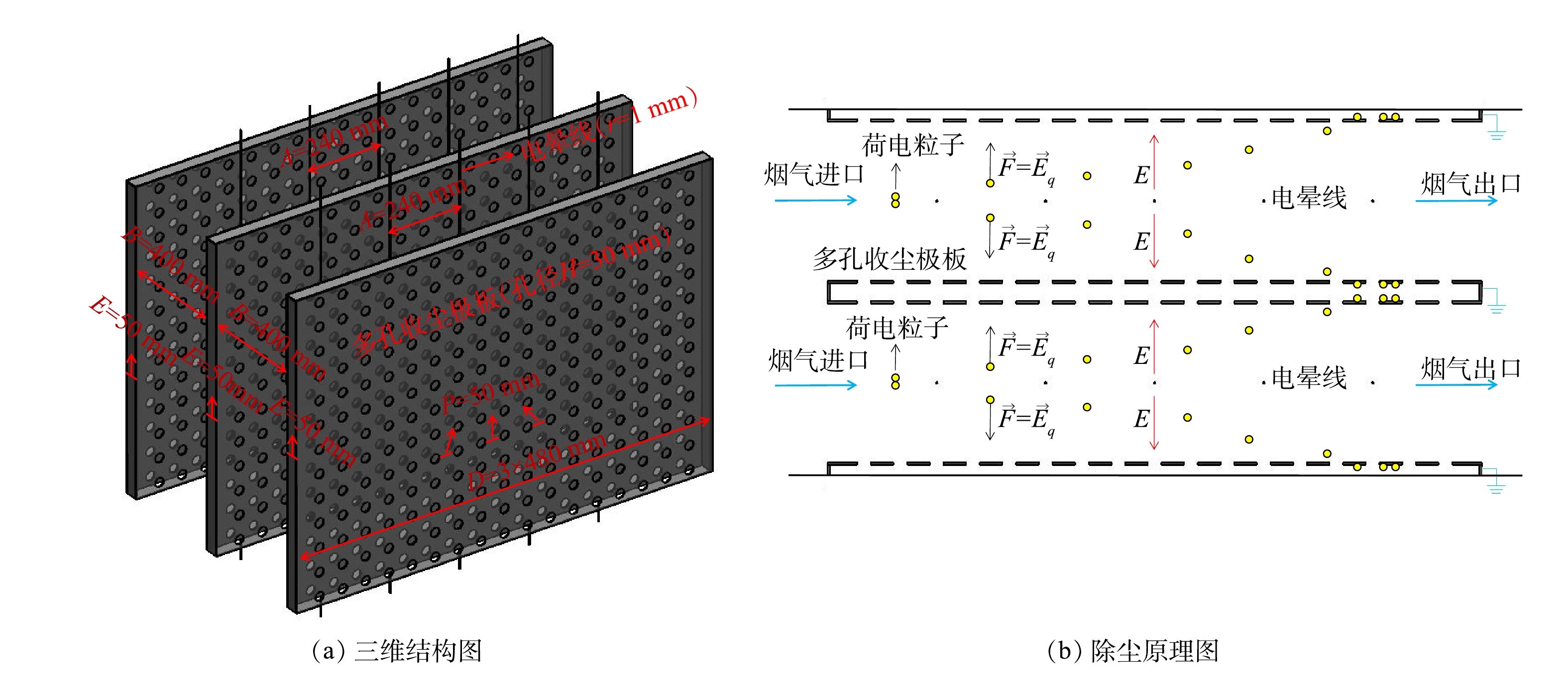
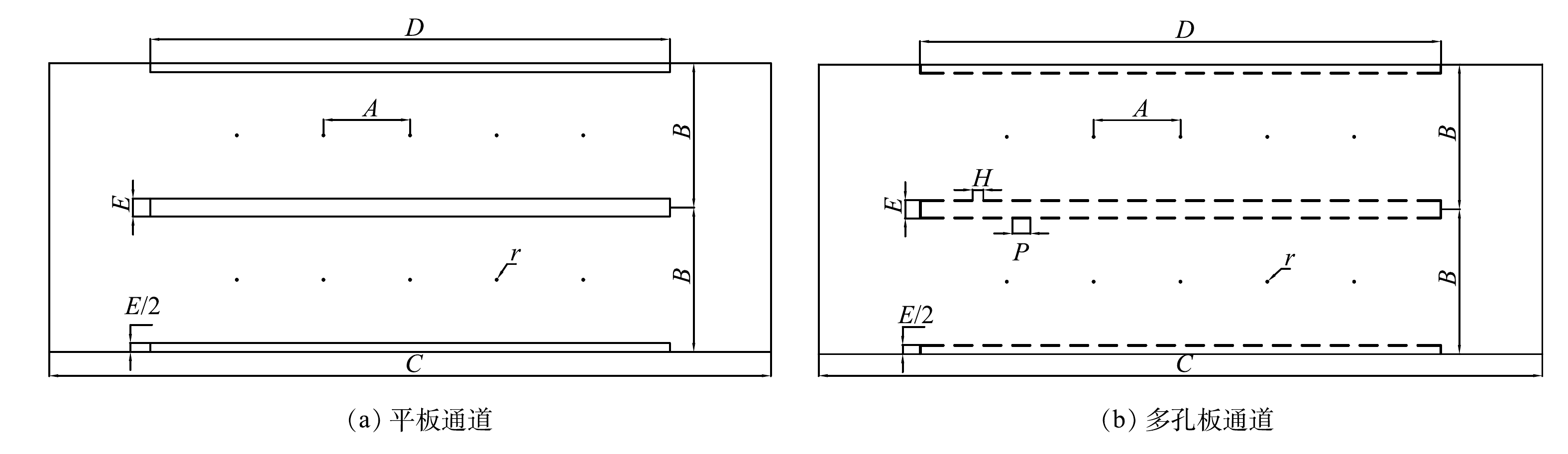
为指导该新型电除尘器设计选型,多孔电极几何尺寸按照工业电除尘器电极尺寸构建。由于电除尘器中微细颗粒重力可以忽略不计[2],故采用电除尘器除尘部分二维特征结构。本研究以平板电极电除尘双通道为参照,分析多孔电极对微细颗粒物的提效机理,通道中相邻5根电晕线及其周边区域为模拟区域。图1给出了2种收尘极板电除尘通道的剖面简图,圆孔在立面以相同的孔间距均匀分布,多孔在立面开孔率为17.2%。图2给出了除尘通道三维结构示意图与除尘原理图,通道基本尺寸与计算参数取值汇总在表1中。
电除尘器运行参数根据工业电除尘器的常见运行条件选择。外加电压为65 kV;入口气体流速为1.00 m∙s−1;流体温度293.15 K;密度1.24 kg∙m−3;层流粘性系数为1.88×10−5 kg∙(m∙s)−1;入口释放颗粒个数为5 000个;颗粒密度2 200 kg∙m−3;相对介电常数为5。
-
电除尘器模拟采用的边界条件汇总在表2。其中,电晕极表面的电势为运行电压,离子空间电荷密度根据Kaptzov假设[20]并结合Peek定律[21]来调整,由此计算得到的场强值等于表面场强大小。
-
由于几何模型曲率半径相差较大,对模型采用三角形网格单元离散化。电晕线和收尘板附近的网格被细化,其中电晕线表面网格最大尺寸为0.2 mm;收尘板表面网格最大尺寸为2 mm。计算域中的最大单元尺寸为20 mm;平板电极结构有77 124个域单元;多孔板电极结构有174 844个域单元,对计算域网格进行收敛测试以确认网格大小符合计算要求,可以获得独立于网格的数值解。
-
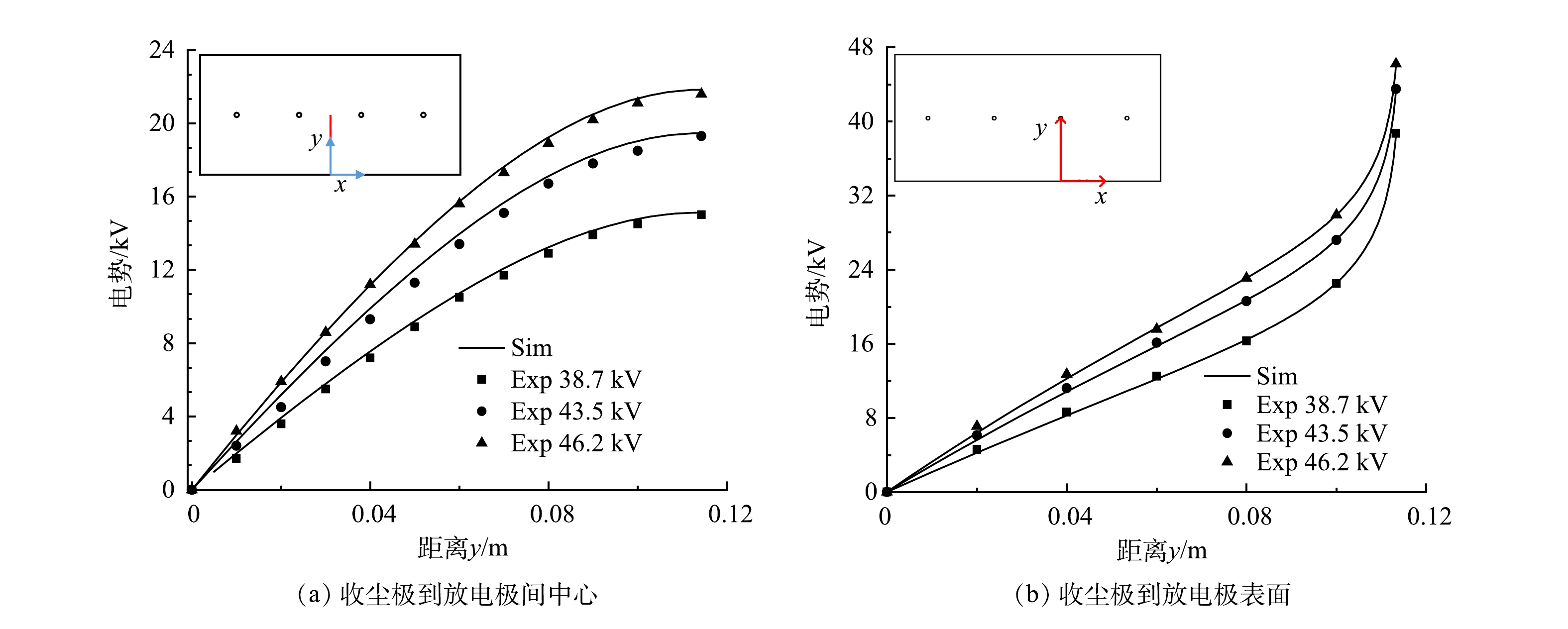
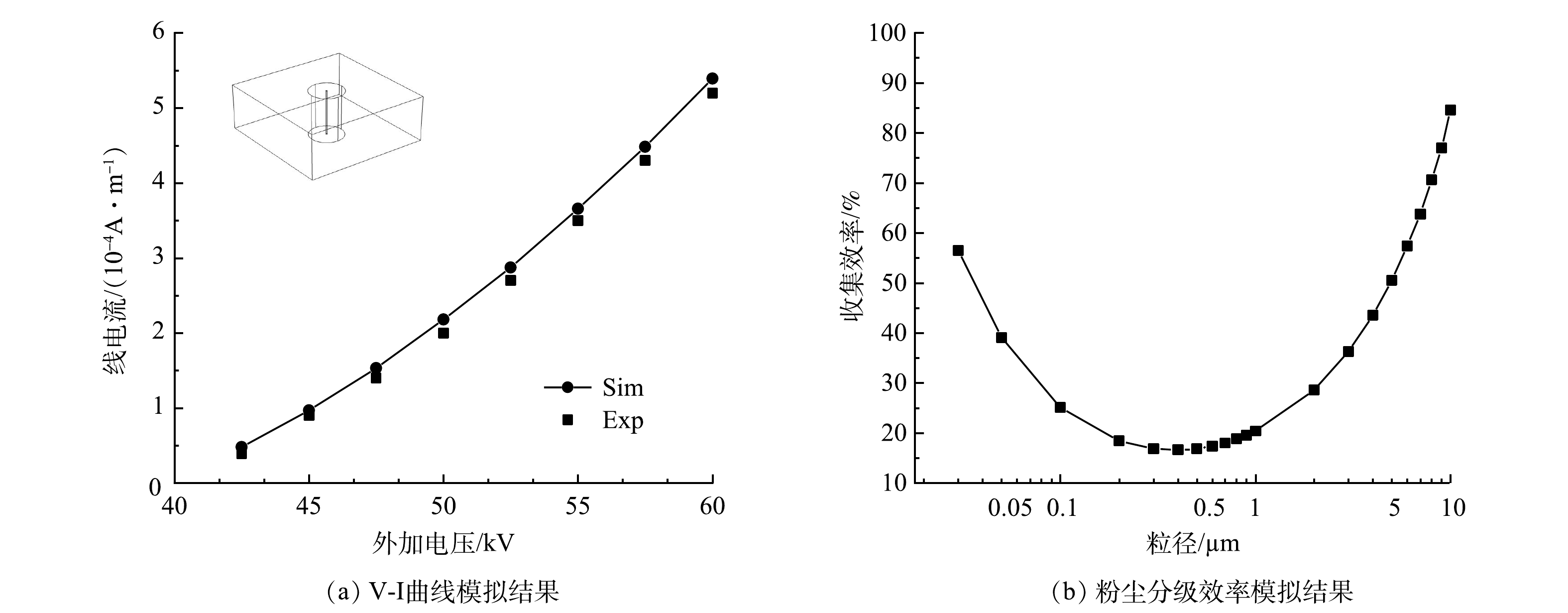
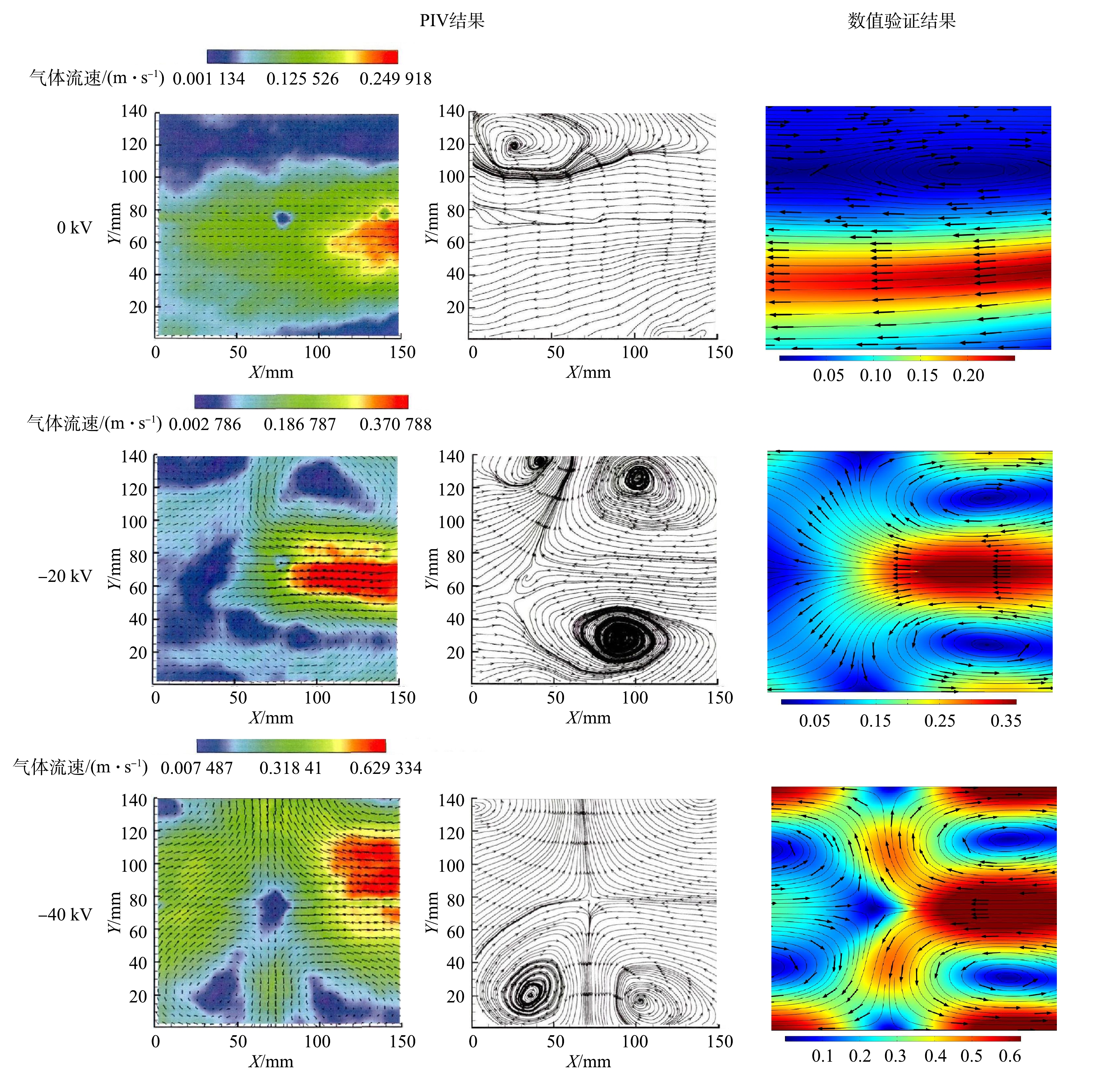
为了验证数值模型的准确性,将模拟结果与多组实验数据进行对比,其中极间电势分布验证按照Penny、Matick实验模型[22]建立电场通道长为0.609 6 m;板间距0.228 6 m;线间距0.152 4 m;线径1.016 0 mm几何模型。伏安曲线验证按照Lawless、Sparks实验模型[23]建立极板尺寸0.228 6 m×0.100 0 m;板间距0.228 6 m;线径为1.590 0 mm几何模型。电流体验证按照文献[24-25]实验模型建立断面尺寸200 mm×200 mm;极板尺寸400 mm×200 mm;板间距200 mm;电晕线直径为0.150 0 mm几何模型。图3给出了外加电压为38.7、43.5、46.2 kV时数值计算结果与Penny、Matick电势分布实验数据对比。图4(a)为实验条件为温度615 K;压力0.86 atm;外加电压处于42.5~60 kV的V-I曲线模拟结果与Lawless、Sparks实验数据对比。图4(b)为粉尘分级效率捕集曲线。图5给出了实验条件为室温22 ℃、相对湿度约为50%、气体流速为0.200 m∙s−1时,外加电压分别为0、−20、−40 kV时电流体模拟结果与PIV实验结果的对比。
图3和图4(a)的结果表明,本研究的数值结果与实验得到的结果符合较好,且所选择的静电模块和稀物质传递模块可以对电场和空间电荷进行准确的描述。图4(b)的粉尘穿透曲线与众多研究者的结果[5]一致,在0.1~1 μm范围内会出现除尘效率的最低点,本研究对电除尘器粒子的收集效率预测具有准确性。图5电流场计算结果与PIV实验结果基本一致,电流场计算模型与实验模型符合较好。
-
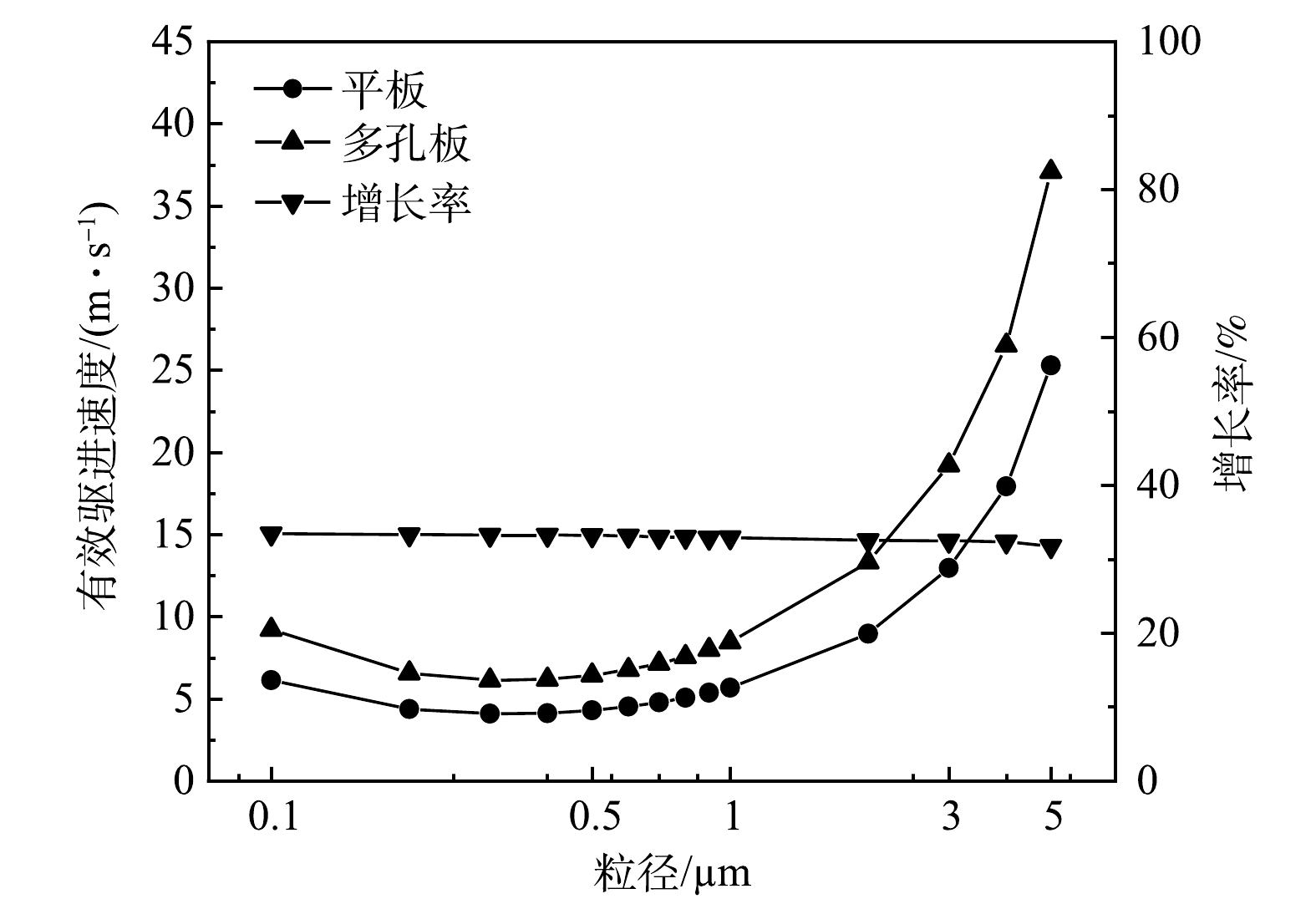
为探究极板开孔后对电除尘器除尘性能影响,对比分析了平板与多孔板电极中处于0.1~5 μm范围内颗粒的有效驱进速度,结果如图6所示。当粒径处于0.1~5 μm,2种电极结构下有效驱进速度随粒径变化的趋势一致,曲线均呈现马蹄形,最低点均在粒径0.3 μm处。这是因为,在0.1~1.0 μm范围内颗粒双荷电机制均处于下限,颗粒荷电量不高导致其受电场力作用有限,此时曳力引入肯宁汉系数所致。结果表明,多孔板电极中颗粒有效驱进速度较平板电极中颗粒有效驱进速度提升30%,在与平板电极结构几何尺寸相同的条件下,多孔板电极结构增大了收尘面积并提高微细粒子有效驱进速度,可降低电除尘器运行成本。
-
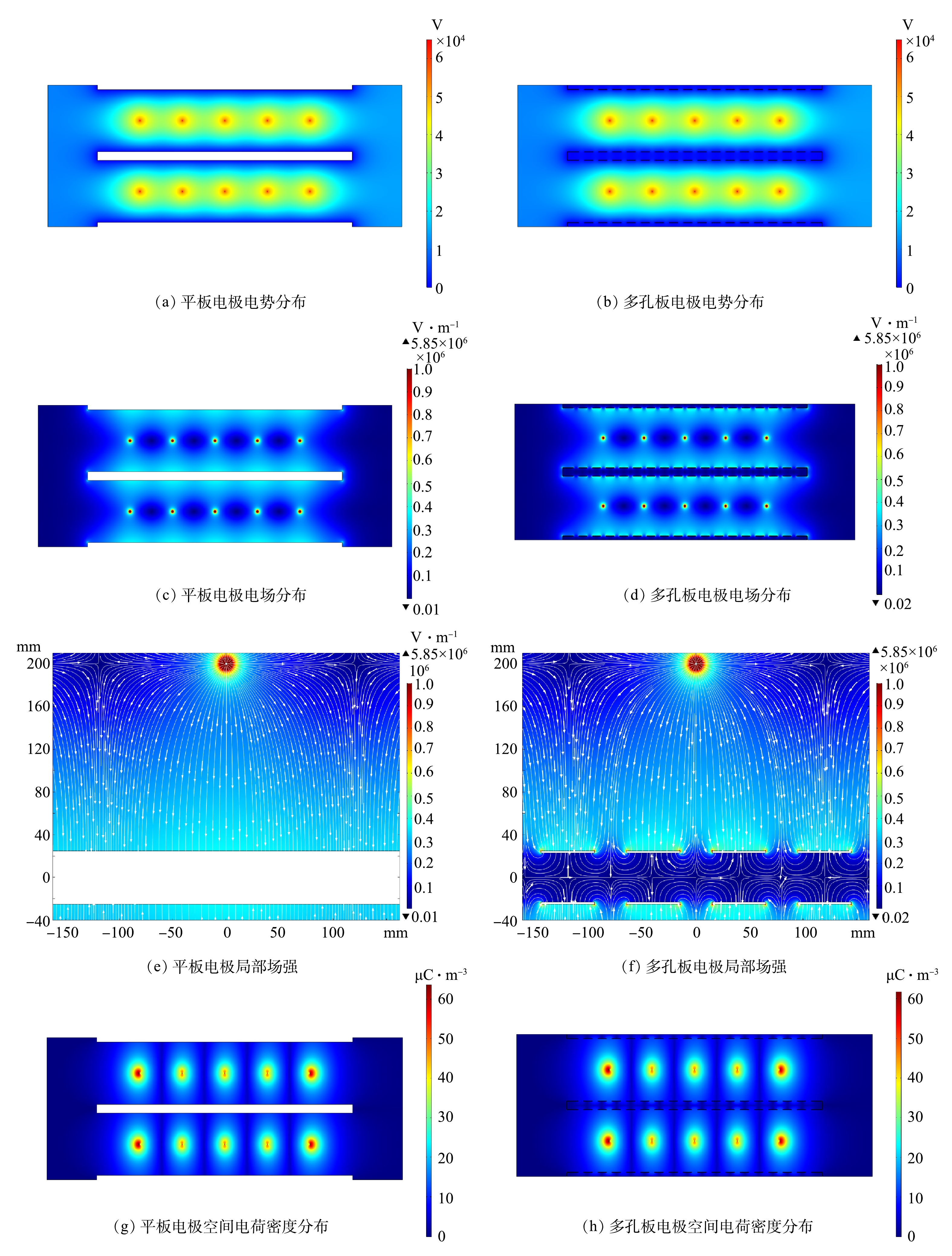
图7给出了2种板型下电气特性分布的数值结果,2种电极结构下的电势、电场强度与空间电荷密度分布相似,电势与空间电荷密度均在电晕线表面最高,远离电晕线时下降;电晕线表面的电场强度最大,电晕线表面至收尘极板,电场强度呈现先减小后缓慢增大的趋势,这与OGLESBY[26]描述结果一致。结果表明,收尘板表面电场强度随电晕线距离的减小而增大,圆孔只会影响多孔板附近的电场分布。根据图7(e)和图7(f)所示,板表面电场强度分布与导线和圆孔的位置有关,电场强度在孔边缘达到最大值,电场穿过圆孔分布在多孔板的背面区域,背面区域的电势、空间电荷密度和电场强度随远离多孔板而迅速降低。
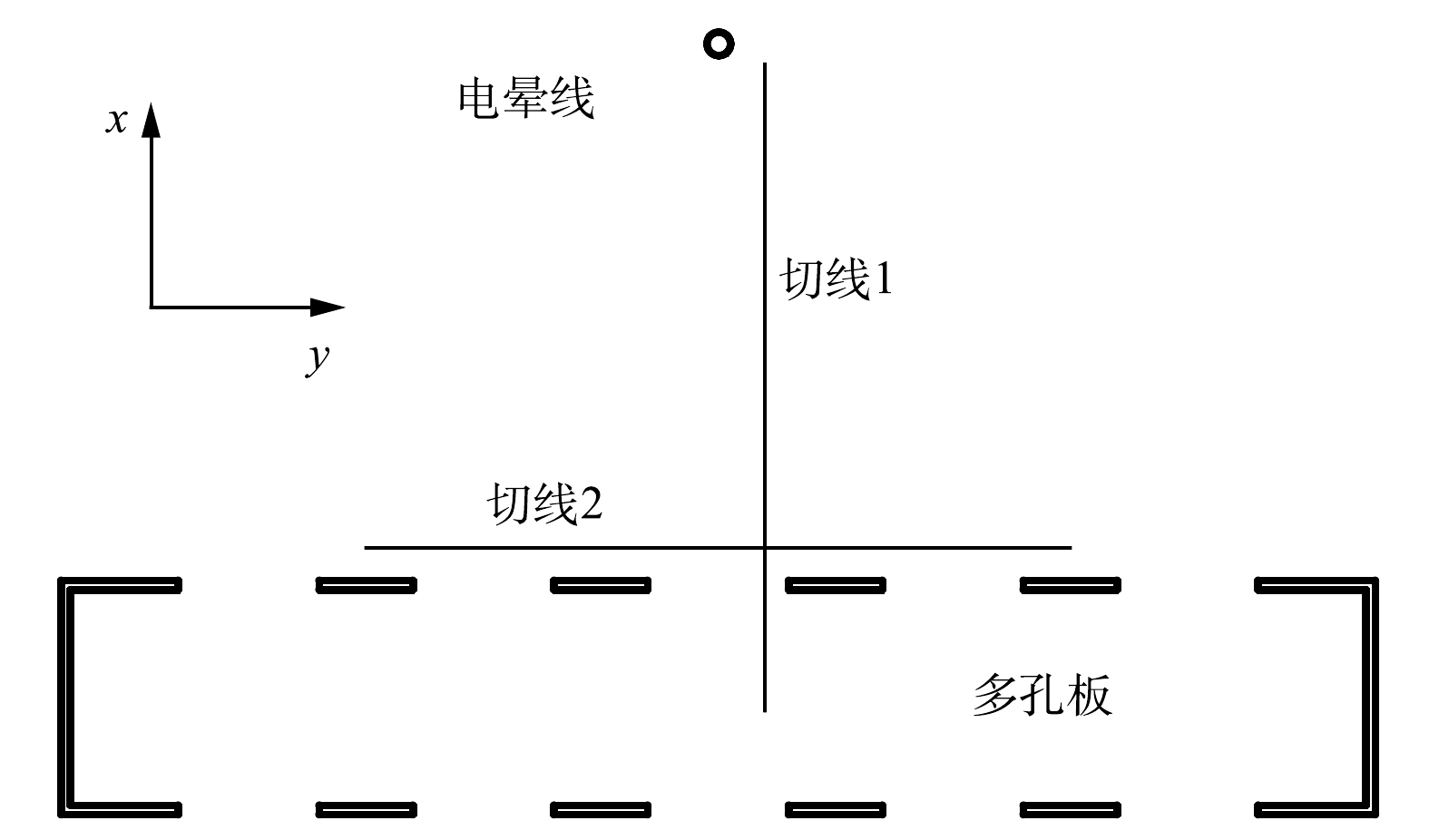
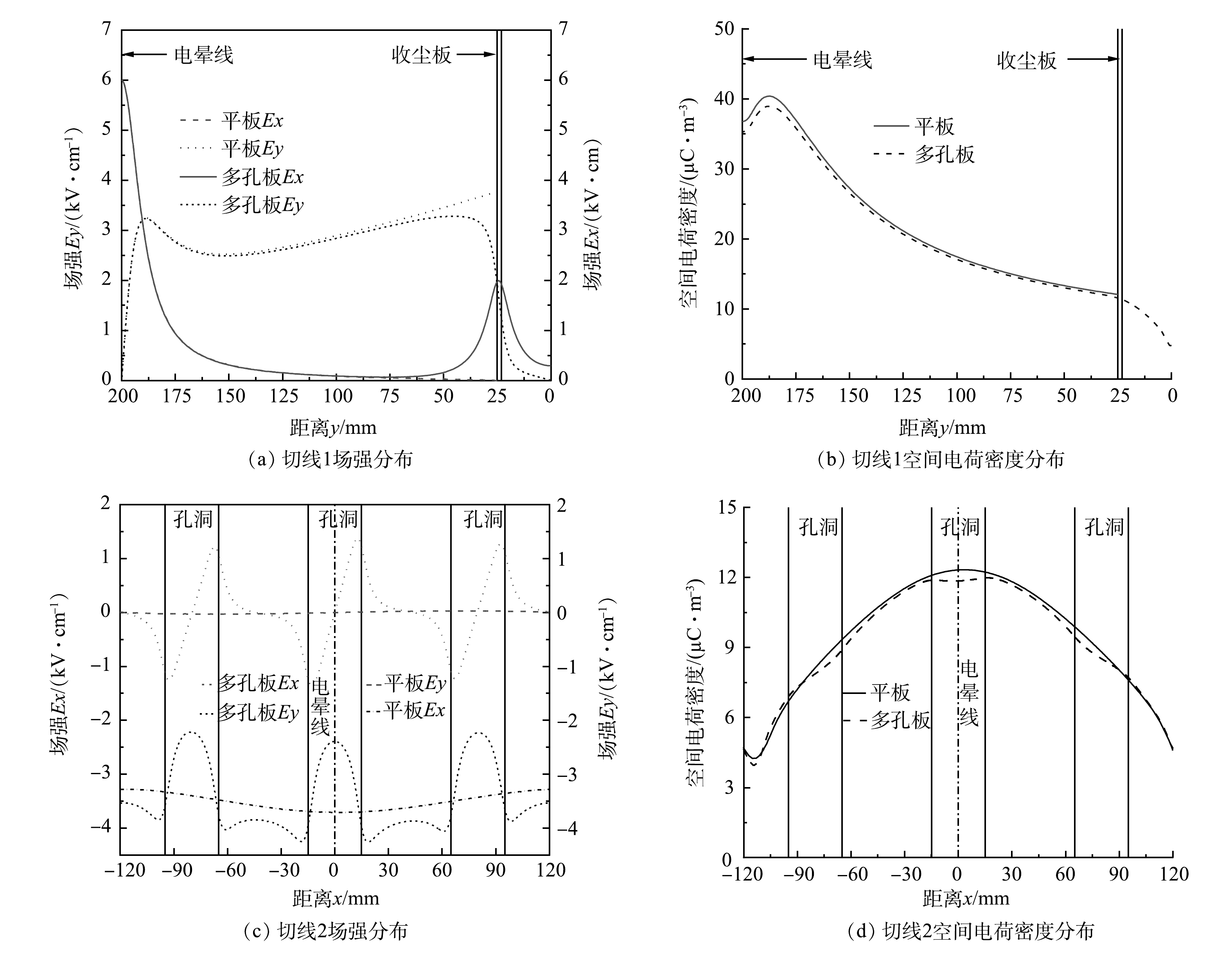
如图8所示,选取2条切线上的电场数据作定量分析。其中,切线1位于x=10 mm,穿过圆孔距离多孔板实体截面右侧边缘5 mm处;切线2位于y=30 mm,距离多孔板实体截面5 mm处。根据图9(a)与图9(b),2种电极结构沿切线1空间电荷密度分布曲线在线板间区域重合,场强延伸曲线在大多数区域重合,但在收尘板附近存在不同,电场竖直分量Ey减小,水平分量Ex增大,并在圆孔位置处电场水平分量Ex出现最大值,进入多孔板背面后迅速减小。以上结果表明,圆孔显著提高了电场通道中距板表面25 mm内电场强度。
图9(c)与图9(d)比较了2种电极沿切线2的电场特性分布,圆孔对空间电荷密度分布并无影响。平板结构下Ex接近于零,而多孔结构下Ex存在以孔间距为周期的波动,振幅约为3.00 kV·cm−1,接近电晕线时振幅略微增加。Ex在圆孔左、右边缘处分别达到最小值与最大值,在圆孔和板实体截面中心为0,Ex通过板实体截面中心或圆孔中心时改变方向,方向总是指向板实体截面最近的中心位置。以上结果表明,在与板面相邻区域中,Ex具有相同的特性,这有助于颗粒在多孔板三个侧面上沉积。在平板电极结构下,与电晕线相对的板表面处Ey有最大值,随远离电晕线减小,平均值为3.51 kV·cm−1;收尘板开孔后,圆孔位置的Ey减小,而多孔板实体截面的Ey增加,平均值为3.42 kV·cm−1,多孔板附近的电场强度因开孔而增加。
-
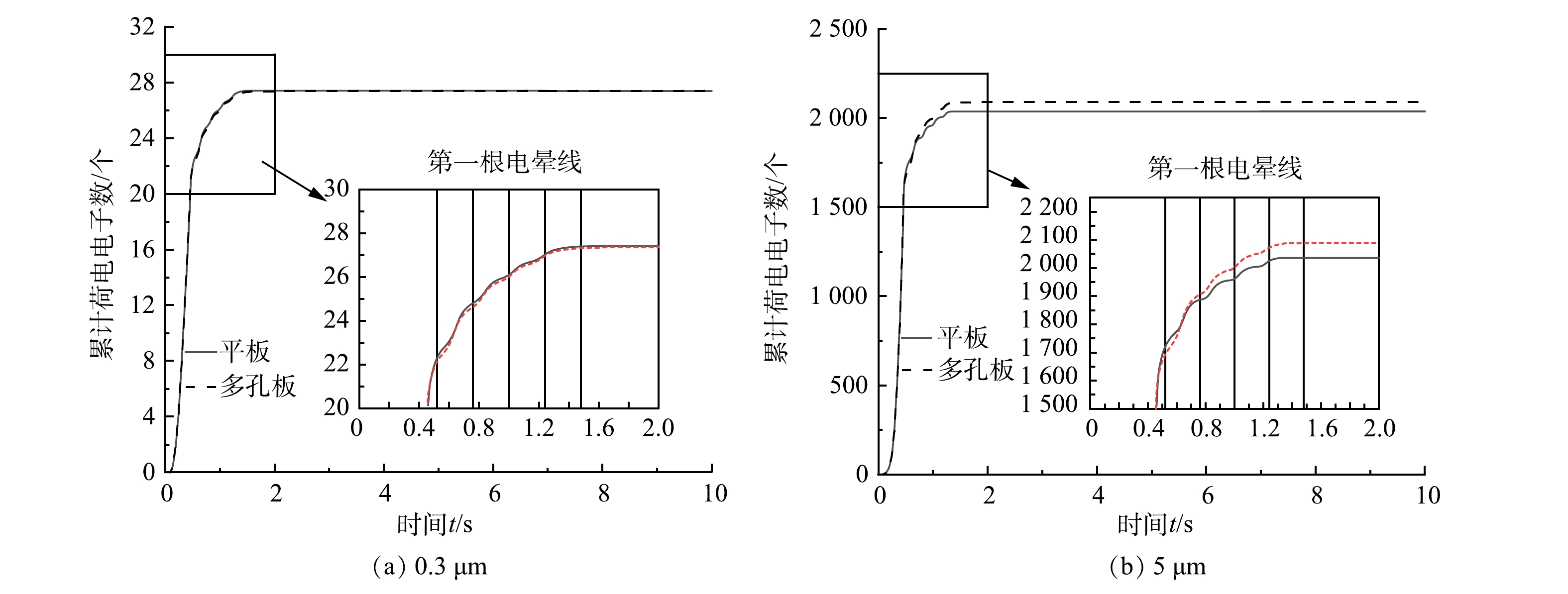
模拟结果表明,2种板型通道内0.1~5 μm粒径的粒子荷电总数相近,荷电总数增长趋势在1 μm左右发生突变,这与粒子荷电机制有关[27-28]。由于电场中离子电流引起的粒子荷电过程随粒子直径减小而使其荷电有效性降低,对于粒径大于1 μm的颗粒由电场荷电起主导作用;当粒径处于0.1~1 μm范围内,颗粒由电场荷电和扩散荷电共同作用,电场荷电不再起主导作用。电场荷电粒子的饱和荷电量与颗粒粒径的平方成正比,因而当颗粒粒径处于1 μm时,粒子荷电总量发生突变。
图10比较了0.3和5 μm颗粒的粒子荷电过程,粒子自进入通道内至第1根电晕线位置的0.5 s内,获得荷电总量80%左右电荷。这是由于,粒子靠近电晕线,场强增加使粒子开始快速荷电;当粒子远离电晕线时,场荷电速率降低;场荷电停止时,粒子进行扩散荷电。粒子所得电荷越高,使得离子与粒子间的库仑力增大产生排斥,离子很难扩散到粒子表面,此时粒子达到最大电荷量。粒子最终电荷量与其直径相关,5 μm粒子最终电荷荷电量是0.3 μm粒子的43倍。平板电极中0.3 μm粒子平均需要1.68 s获得27.408个电荷达到饱和电荷量,多孔板电极中0.3 μm粒子需要8.47 s获得27.409个电荷达到饱和电荷量,这表明多孔板电极延长了粒子最终荷电时间,但并不影响粒子荷电总量。
-
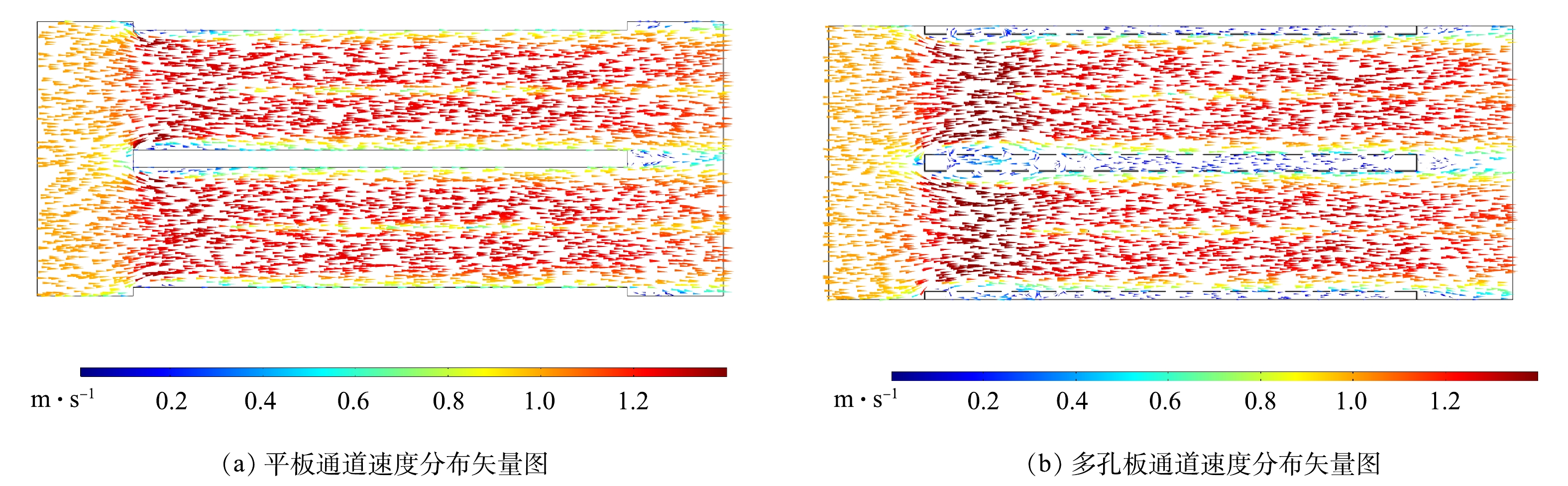
图11是2种板型下通道内速度分布矢量图,流场结构分布在大部分区域相似,但在收尘极板前端和尾端出现了阻流和气流死区现象,这是由于几何模型考虑了收尘极板厚度所致。在多孔板结构下,部分气流会进入多孔板空腔内部,由于空腔内气流流速较低,可增加粉尘在电场内的停留时间从而提高除尘性能。
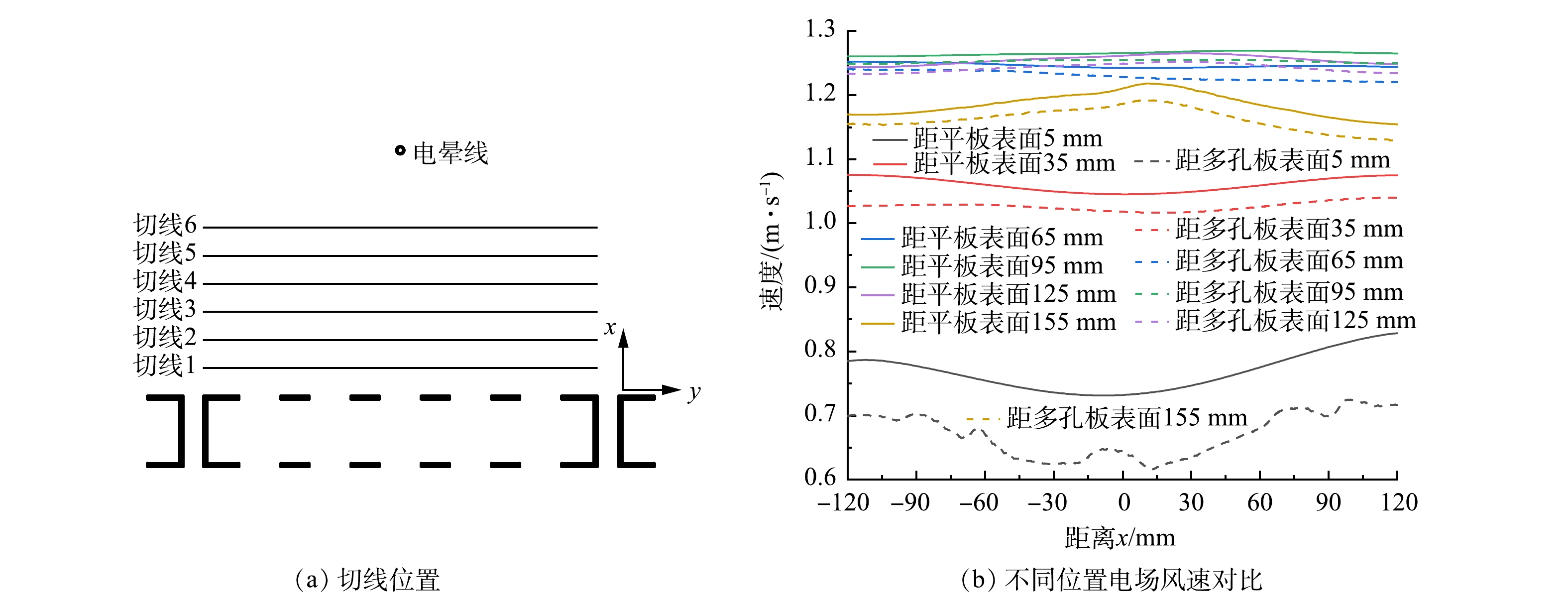
如图12(a)所示,选取几何模型中心位置多孔板表面5、35、65、95、125、155 mm处的切线对流场进行分析。据图12(b)显示,2种结构通道内电场风速差别不大,靠近电晕线处的电场风速水平分量较高,远离电晕线后降低,但多孔板表面水平方向电场风速小于平板表面水平方向电场风速,板表面5 mm处相较于平板结构降低了12.5%。这是由于极板开孔后,相比于平板电极,通道内气流流通面积增大,在一定的气体流量下,降低了板面电场风速;同时,在通道进口处,多孔板结构对气流产生阻挡作用,气体流经孔板表面产生涡旋减弱了板表面电场风速。结果表明,多孔板可有效抑制二次扬尘的不利影响。
-
上述结果表明,粒子在2种板型板表面外区域的迁移沉降过程基本一致。选取了0.3和5 μm粒子在多孔板表面与空腔中的运动轨迹进行分析,结果如图13所示。图中绿线、红线、蓝线、灰线分别表示沉降在板正面、背面、侧面和逃逸颗粒的运动轨迹。由图13(a)和图13(b)可以看出,粒子被多孔收尘极板捕获可能性与进入通道内初始位置相关,粒子进入电场的位置决定粒子沉降的位置,入口距板表面较近的粒子更容易被捕集,未沉降至孔板的粒子最终随气流流出。由图13(c)和图13(d)可知,粒子运动轨迹整体可分为多孔板前端、中端和尾端,部分粒子在多孔板前端随气流运动形成涡旋,最终沉降至板表面。这是由于前端产生的局部阻流作用所致;位于中端的粒子随气流进入多孔板空腔,在电场力的作用下,粒子最终会沉降至多孔板空腔内背面与侧面;位于尾端空腔内的粒子部分随气流从圆孔流出沉降至多孔板表面。上述结果表明,多孔板解构改变了颗粒在极板附近沉降轨迹,颗粒会沉降至多孔板正面、背面与侧面,进入空腔内的颗粒不会再次返回通道内流出。
-
1)电除尘器气固两相流模型计算值与实验值吻合较好。
2) 极板开孔后不会对空间电荷密度与颗粒荷电过程产生影响,但会显著提高电场通道中距板表面25 mm内电场强度。
3)粒径范围处于0.1至5 μm内的粒子被多孔收尘极板捕获可能性与粒子进入通道内初始位置相关,被捕集的荷电粒子沉降在多孔板的正面、侧面与背面,随气流进入多孔板空腔内的粒子最终沉降在多孔板壁面上,不会再次返回电场通道内随气流流出。
4)模拟结果表明相较于平板,多孔收尘极板可增大板表面电场强度,减缓气流对收尘极板表面冲刷作用,并提高微细粒子的有效驱进速度,极板开孔后可以有效提高电除尘器的除尘性能。
多孔收尘电极电场中荷电粒子的沉降规律及其除尘性能预测
Sedimentation law of charged particles in electric field of porous dust collecting electrode and prediction of dust removal performance
-
摘要: 为了探究多孔收尘电极电除尘器的除尘性能,采用COMSOL Multiphysics建立电除尘器气固两相流数值模型,对多孔收尘电极电除尘器中的颗粒荷电沉降过程进行数值模拟,研究其电场、流场分布及粒子荷电、运动和沉降过程。结果表明,电除尘器气固两相流模型计算值与实验值符合良好。多孔收尘电极电除尘器能够有效提高微细粒子有效驱进速度约30%。极板开孔后显著提高了电场通道中距板表面25 mm内电场强度,开孔不会对空间电荷密度与颗粒荷电过程产生影响;多孔板结构表面5 mm处电场风速水平分量相较于平板结构降低了12.5%,消弱了气流对收尘区域的冲刷作用,进入多孔板空腔内的粒子最终沉降在多孔板壁面上。本研究结果可为多孔收尘电极电除尘器对微细粒子提效捕集的机理探究及新型电除尘器的选型设计提供参考。
-
关键词:
- 多孔收尘电极电除尘器 /
- 数值模拟 /
- 气固两相流 /
- 微细粒子 /
- 有效驱进速度
Abstract: In order to explore the dust removal performance of the Porous-dust-collecting-electrode electrostatic precipitators(PDCE-ESPs), COMSOL Multiphysics was used to establish a numerical model of the gas-solid two-phase flow of the electrostatic precipitators, and the particle charge sedimentation process in the PDCE-ESPs was numerically simulated in this study. The distributions of electric and flow fields and the charging, motion, and precipitation of particles in this specific structure were studied. The results showed that the calculated value of the gas-solid two-phase flow model of the electrostatic precipitators was in good agreement with the experimental value. The PDCE-ESPs can effectively increase the effective driving speed of fine particles by about 30%. After opening the plate, the electric field intensity within 25 mm from the plate surface in the electric field channel was significantly increased, and the opening had no effect on the space charge density and particle charge process. The horizontal component of electric field wind speed at 5 mm on the surface of porous plate structure decreased by 12.5% compared with that of flat plate structure, which weakened the scouring effect of air flow on dust collecting area, and the particles entering the cavity of porous plate eventually settle on the wall of porous plate. The results can explain the mechanism of the PDCE-ESPs for improving the trapping of fine particles, and provide a reference for the selection and design of the new type of electrostatic precipitators. -

-
表 1 2种板型几何参数
Table 1. Geometric parameters of two plate types
板型 线间距A/mm 板间距B/mm 通道长度C/mm 极板长度D/mm 空腔厚度E/mm 线径r/mm 孔径H/mm 孔间距P/mm 平板 240 400 2 000 1 440 50 1 — — 多孔板 240 400 2 000 1 440 50 1 30 50 表 2 边界条件设置
Table 2. Boundary condition setting
位置 流场 颗粒 电场 空间电荷 入口 $ {U}_{x}={U}_{0} $ $ {U}_{x}={U}_{0} $ $\dfrac{\text{∂}\text{ϕ} }{\text{∂}{n} }\text{=0}$ $\dfrac{\text{∂}{\text{ρ} }_{\text{ion} } }{\text{∂}{n} }\text{=0}$ 出口 压力出口 冻结 $\dfrac{\text{∂}\text{ϕ} }{\text{∂}{n} }\text{=0}$ $\dfrac{\text{∂}{\text{ρ} }_{\text{ion} } }{\text{∂}{n} }\text{=0}$ 收尘极 无滑移 冻结 φ=0 $\dfrac{\text{∂}{\text{ρ} }_{\text{ion} } }{\text{∂}{n} }\text{=0}$ 放电极 无滑移 反弹 φ= $ {\text{φ}}_{0} $ Peek law 圆孔边界 无滑移 冻结 φ=0 $\dfrac{\text{∂}{\text{ρ} }_{\text{ion} } }{\text{∂}{n} }\text{=0}$ -
[1] 安连锁, 王金平, 郦建国, 等. 中国燃煤电厂电除尘技术发展及应用综述[J]. 中国电力, 2018, 51(4): 115-123. [2] WHITE H J. Industrial electrostatic precipitation[M]. MA: Addison Wesley, 1963. [3] ZHAO H, CHEN K Y, LIU Z, et al. Coordinated control of PM2.5 and O3 is urgently needed in China after implementation of the “Air pollution prevention and control action plan”[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 270: 129441-129441. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129441 [4] 刘艳梅, 闫静, 徐文帅, 等. 超低排放改造后燃煤电厂常规大气污染物排放特征[J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(6): 1967-1975. [5] 郝吉明, 段雷, 易红宏, 等. 燃烧源可吸入颗粒物的物理化学特征[M]. 科学出版社, 2008. [6] CHOI H Y, Park Y G, Ha M Y, et al. Numerical simulation of the wavy collecting plate effects on the performance of an electrostatic precipitator[J]. Powder Technology, 2021, 382: 232-243. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2020.12.070 [7] GAO M, ZHU Y, YAO X, et al. Dust removal performance of two-stage electrostatic precipitators and its influencing factors[J]. Powder Technology, 2019, 348: 13-23. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2019.03.016 [8] DONG M, ZHOU F, SHANG Y, et al. Numerical study on electrohydrodynamic flow and fine-particle collection efficiency in a spike electrode-plate electrostatic precipitator[J]. Powder Technology, 2019, 351: 71-83. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2019.03.046 [9] ZHU Y, GAO M, CHEN M, et al. Numerical simulation of capture process of fine particles in electrostatic precipitators under consideration of electrohydrodynamics flow[J]. Powder Technology, 2019, 354: 653-675. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2019.06.038 [10] KALLIO G A, STCOK D E. Interaction of electrostatic and fluid dynamic fields in wire-plate electrostatic precipitators[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1992, 240(1): 133-166. [11] LIANG W J. The characteristics of ionic wind and its effect on electrostatic precipitator[J]. Quality Assurance Journal, 1994, 5(4): 241-245. [12] HANS J S, STEFFEN S, HANS B. On the modelling of the Electro-Hydrodynamic flow field in electrostatic precipitators[J]. Flow, Turbulence and Combustion, 2002, 68(1): 63-89. doi: 10.1023/A:1015666116174 [13] CHUN Y N, ChANG J S, BEREZIN A A, et al. Numerical modeling of near corona wire electrohydrodynamic flow in a wire-plate electrostatic precipitator[J]. IEEE Trans. Dielect. Elect. Insul, 2007, 14(1): 119-124. doi: 10.1109/TDEI.2007.302879 [14] YAMAMOTO T. Effects of turbulence and electrohydrodynamics on the performance of electrostatic precipitators[J]. Journal of Electrostatics, 1989, 22(1): 11-22. doi: 10.1016/0304-3886(89)90106-X [15] LONG Z W, YAO Q. Evaluation of various particle charging models for simulating particle dynamics in electrostatic precipitators[J]. Journal of Aerosol Science, 2010, 41(7): 702-718. doi: 10.1016/j.jaerosci.2010.04.005 [16] WAWLESS P A. Particle charging bounds, symmetry relations, and an analytic charging rate model for the continuum regime[J]. Journal of Aerosol Science, 1996, 27(2): 191-215. doi: 10.1016/0021-8502(95)00541-2 [17] 周栋梁, 李水清, 靳星, 等. 电场、流场耦合作用下脱除细颗粒物的实验和数值模拟[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2016, 36(2): 453-458. [18] OUNIS H, AHMADI G, MCLAUGHLIN J B, et al. Brownian diffusion of submicrometer particles in the viscouse sublayer[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1991, 143: 66-277. [19] FRIEDLANSER S K, WILLIAM H M. Smoke, Dust and Haze: Fundamentals of Aerosol Behavior[J]. Phys. Today, 1977, 30(9): 58-58. doi: 10.1063/1.3037714 [20] KAPTZOV N A, Elektricheskie invlentiia v gazakh i vakuumme[M]. OGIZ, Moscow, 1947. [21] PEEK F W, Dielectric phenomena in high voltage engineering[M]. 3rd ed McGraw-Hill, New York, 1929. [22] PENNEY G W, MATICK R E. Potentials in D-C corona fields[J]. American Institute of Electrical Engineers, Part I:Communication and Electronics, Transactions of the, 1960, 79(2): 91-99. [23] LAWLESS P A, SPARKS L E. A mathematical model for calculating effects of back corona in wire‐duct electrostatic precipitators[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1980, 51(1): 242-256. doi: 10.1063/1.327416 [24] 沈欣军. 电除尘器内细颗粒物的运动规律及其除尘效率研究[D]. 浙江大学, 2015. [25] 沈欣军, 郑钦臻, 宁致远, 等. 燃煤电厂电除尘PM10和PM2.5的排放控制Ⅳ: 采用二维PIV除尘[J]. 科技导报, 2014(33): 43-50. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2014.33.005 [26] AHMED K. Computation and measurement of corona current density and V-I characteristics in wires-to-plates electrostatic precipitator[J]. Journal of Electrostatics, 2016, 81: 1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.elstat.2016.02.005 [27] 张建平, 陈思艺, 王帅, 等. 扩散荷电对两种ESP除尘性能影响的对比分析[J]. 环境工程, 2019, 37(8): 143-147. [28] 高梦翔, 姚鑫, 朱勇, 等. 双区静电除尘器的数值模拟研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2018, 38(10): 3698-3703. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.10.012 -



 下载:
下载: