-
湖滨湿地是河流与湖泊的交互地带,是生物多样性丰富的地带和最广泛的栖息地,承担着重要的生态服务功能,同时也是重金属富集和转换的场所[1]。重金属作为典型的环境污染物之一,具有毒性大、难降解和生物富集等特点[2-3]。虽然被誉为“地球之肾”的湿地可以通过自身的物理、化学和生物作用对重金属进行吸附、固定和转化,但是当湿地系统内重金属达到一定浓度时就会对湿地系统及其动植物和微生物产生严重的生态毒性[4-5]。Yin等[6]研究指出,生物体过量摄入重金属会抑制自身生长,严重的甚至会导致器官衰变、机体失活;朱源等[7]研究指出,栖息地重金属污染是威胁候鸟生存的重要环境因素之一;马康等[8]研究发现,湿地沉积物释放的重金属可在植物体内富集,高浓度的重金属在植物体内将产生毒性效应,导致植物死亡,从而降低植物群落多样性。因此,研究湖滨湿地重金属污染状况、评价其生态风险对于湖滨湿地生态系统安全和生物多样性保护具有积极意义。
目前,滇池流域沉积物重金属研究多以滇池湖底沉积物和入湖河流沉积物为研究对象,缺乏对滇池河口湿地重金属污染状况的调查。李贝等[9]研究指出,滇池大多数表层沉积物中重金属含量高于当地土壤背景值;李仁英等[10]研究指出,盘龙江口滇池沉积物重金属污染都在中等程度以上;刘勇等[11]研究指出,滇池沉积物金属元素累积的主要因素是流域内工农业发展及污染物输入,且滇池北部沉积物中重金属污染有加重趋势;肖冬冬等[12]研究表明,滇池流域河流表层沉积物重金属出现随流向累积的现象。随着社会经济发展,晋宁已成为昆明市的一个区,城市居民增加,原来的农业用地已逐渐转变为城市用地,人类活动更加剧烈[13],东大河沿途接纳的污染物也相应增加,更容易在河口湖滨湿地富集和转换[14-15],对东大河湿地沉积物重金属研究可以反映城市化过程对河口湿地重金属污染的影响。东大河湿地是东大河与滇池交接的生态敏感带,生物多样性丰富,又是候鸟越冬湿地之一,而目前尚未有研究系统地对东大河湿地重金属污染情况进行调查。本文测定了东大河湿地表层沉积物重金属Zn、Cu、Ni、Pb、Cr的含量,并对其污染特征展开研究,以期为东大河湿地重金属污染防治提供参考。
-
东大河是滇池南端主要入湖河流之一,发源于昆明市晋宁区宝峰街道双龙河谷,流经宝峰小河口、双龙、昆阳储英等多个地区后,于晋宁区昆阳街道东大河湿地汇入滇池。东大河湿地位于昆明市晋宁区滇池南岸湖滨带(24°40′18.46″—24°41′09.14″N,102°36′55.39″—102°38′04.67″E),总面积约114 hm2,是云南晋宁南滇池国家湿地公园的主要组成部分[16]。东大河湿地是东大河入湖口处陆地与湖泊水体的缓冲区,是滇池湖滨“四退三还一护”生态建设中逐步建成的人工湿地[17-18]。东大河湿地内部水域特征差异显著,湿地中部是东大河流经的中心区域,水道密布、纵横交错;湿地东部是渔场“退渔”后的恢复重建区,水域开阔;湿地西部呈条带状,只有一条狭长且相对封闭的水道相连。东大河湿地周边广泛分布着农田和居民区,主要有河嘴村、兴旺村、大河村、墩子村等4个村庄及其耕地,由于湿地面积大、水鸟物种丰富、环境优美等原因,现已成为昆明市民休憩放松的重要场所[19-20]。
-
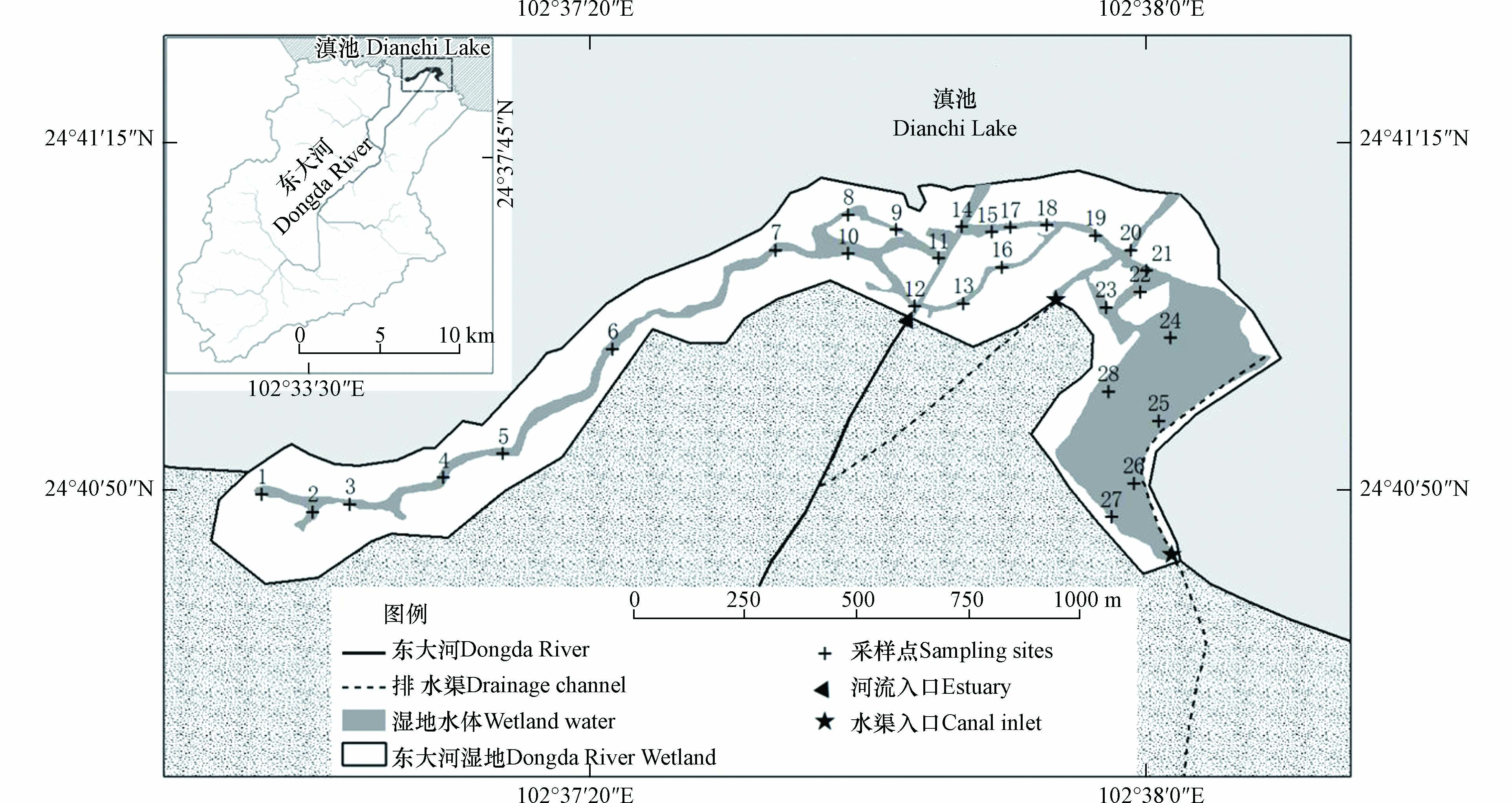
2020年11月在东大河湿地不同水域特征下按湿地中部、东部、西部设置采样点进行湿地表层沉积物的采集,湿地西部水道相对封闭,沿水道约100—150 m间隔设置1个采样点,湿地中部水道密集,水交换速率较快,沿水道约50—100 m间隔设置1个采样点,湿地东部水域开阔,约100—150 m间隔设置1个采样点,此外在人类活动频繁的停靠站、水域环境差异较大的区域增加1—2个采样点,共设置了28个采样点,1—8号为西部样点,9—23号为中部样点,24—28号为东部样点,具体位置如图1所示。
在设置的采样点通过抓斗采泥器采集湿地表层(0—10 cm)沉积物样品,各样品平行采集3次,用聚乙烯自封袋密封,于当天运回实验室,并将样品全部移转至用去离子水清洗干净的搪瓷盘内,除去样品中的枝棒、叶片等异物,均匀摊开后置于无阳光直射的地方自然风干。风干后的样品用玛瑙研磨钵研磨,过200目筛后的样品用四分法分取,保存于牛皮纸袋中备用。沉积物重金属Zn、Cu、Ni、Pb、Cr含量分析在云南师范大学低纬高原环境变化云南省高校重点实验室进行。根据国家标准HJ491-2019《土壤和沉积物铜、锌、铅、镍、铬的测定 火焰原子吸收分光光度法》对样品进行消解,取0.2 g样品于聚四氟乙烯坩埚中,依次加入HCl-HNO3-HF-HClO4加热消解,定容25 mL后用耶拿contr AA700原子吸收光谱仪测定[21]。实验所用试剂均为优级纯,实验过程中每批样品均随机抽取两个样品做平行试验,保证结果误差<5%,同时每批样品增加两个空白样品,并采用水系沉积物(GBW07305a GSD-5a)作为质量控制样品,保证标准样品回收率在80%—120%之间,原子吸收光谱仪标准曲线采用GSB 04国家标准样品标绘,拟合优度达到0.999以上,保证实验的准确性。
-
重金属含量统计采用Excel和SPSS 26软件进行处理,相关图件的制作在Origin 2021和ArcGIS 10.7软件中完成。
目前国内外对水体沉积物重金属风险评价的方法有地质累积指数法、污染负荷指数法、潜在生态风险指数法、沉积物富集系数法等[22]。每种评价方法都有各自的优缺点,因此在进行评价时通常采用多种方法配合使用。本研究根据沉积物学原理,采用地质累积指数法和潜在生态风险指数法对沉积物重金属的污染风险进行评价。
-
地质累积指数由德国沉积学学者Muller提出[23],用于定量分析水体沉积物重金属污染状况,适用于单一重金属污染评价[24–26],计算公式为:
式中,
$ {I}_{\mathrm{g}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{o}} $ 是某样点地质累积指数,$ {C}_{n} $ 是沉积物中重金属n的含量,k是修正指数(一般取1.5),$ {B}_{n} $ 是环境背景值,这里参考中国南方水系沉积物背景值。$ {I}_{geo} $ 越高代表重金属n的污染程度越严重,Forstner等将地质累积指数划分为7个级别,如表1所示。 -
潜在生态风险指数由瑞典学者Hakanson提出[27],该方法综合考虑了污染物种类、含量、毒性等,可以进行更全面的评价,被广泛应用于沉积物污染评价[28–30],计算公式为:
式中,RI是某采样点沉积物多种重金属综合潜在生态危害指数,分成4个等级,如表2所示,k是重金属种类数,
$ {\mathrm{E}}_{\mathrm{r}}^{\mathrm{i}} $ 是重金属i的潜在生态危害系数,分成5个等级,如表2所示,$ {T}_{r}^{i} $ 为重金属i的毒性系数,$ {C}_{f}^{i} $ 是重金属i的污染系数,$ {C}_{实测}^{i} $ 是重金属i的实测含量,$ {C}_{n}^{i} $ 为重金属i的环境背景值;$ {T}_{r}^{i} $ 取徐争启等校正后的毒性系数,如表3所示,$ {C}_{n}^{i} $ 参考中国南方水系沉积物背景值,如表3所示。 -
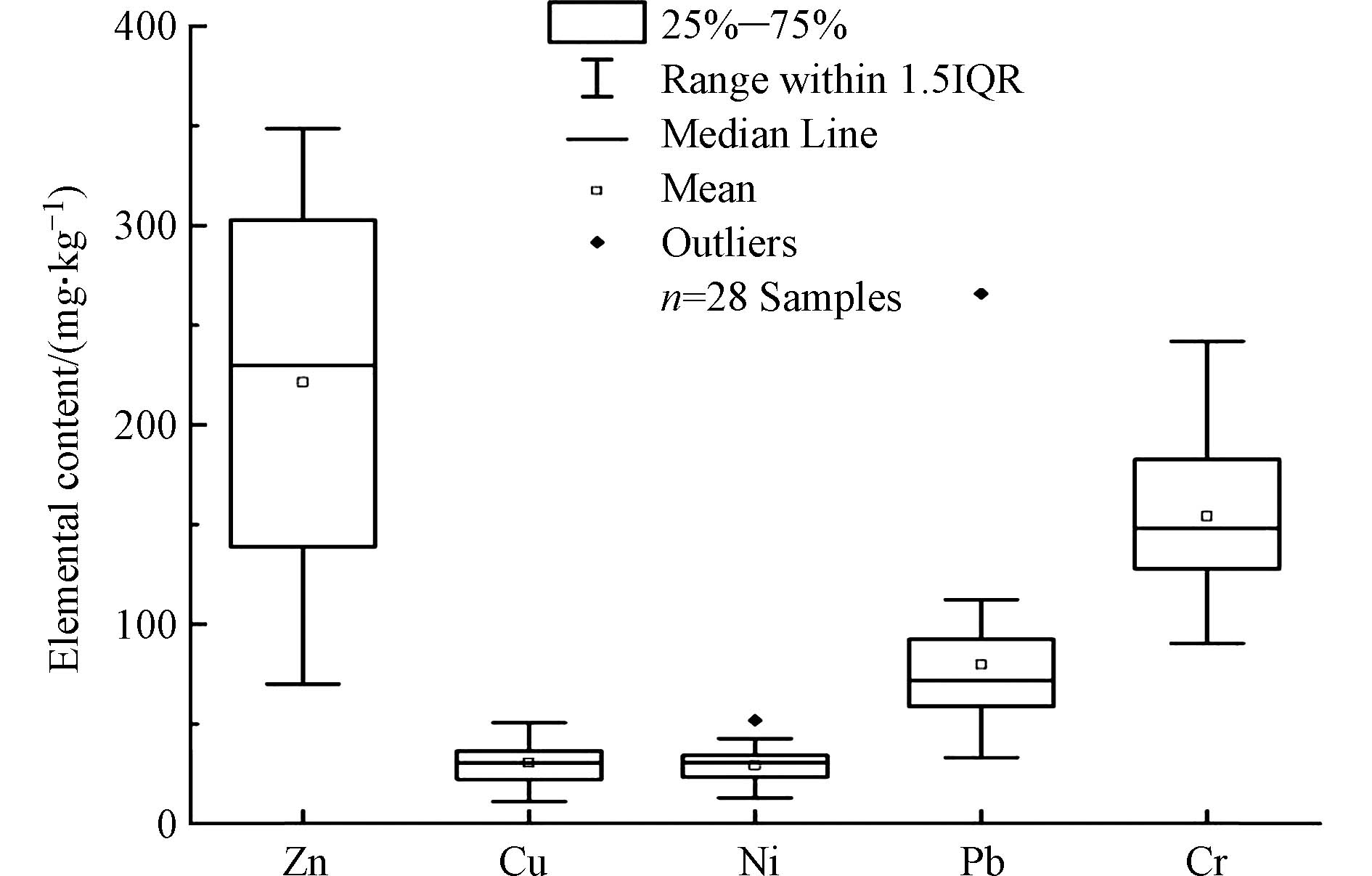
研究检测了东大河湿地沉积物中锌(Zn)、铜(Cu)、镍(Ni)、铅(Pb)、铬(Cr)等5种重金属,其含量分别是70.07—348.56、11.09—50.72、12.91—51.81、33.23—265.87、90.36—241.87 mg·kg−1,其平均浓度分别是221.38、30.40、29.19、79.73、154.00 mg·kg−1,如表4所示,统计特征如图2所示。东大河湿地属于滇池水系,地处中国云南,因此东大河湿地沉积物背景值选择云南省A层土壤重金属背景值和中国南方水系沉积物背景值为参考值[31-32]。东大河湿地沉积物Zn、Cu、Ni、Pb、Cr的平均浓度分别是云南省土壤背景值(80.5、33.6、33.4、36.0、57.6 mg·kg−1)的2.8、0.9、0.9、2.2、2.7倍,分别是中国南方水系沉积物背景值(81.0、25.0、29.0、32.3、67.0 mg·kg−1)的2.7、1.2、1.0、2.5、2.3倍,超过中国南方水系沉积物背景值的采样点比例分别是96.43%、71.43%、57.14%、100.00%、100.00%。由以上分析可知,东大河湿地沉积物中5种重金属均存在不同程度的富集,Pb、Cr、Zn的富集相对较高,Cu、Ni的富集较低,可能与东大河沿途接纳了大量城乡污水相关。相关研究表明,污水排放是河流沉积物重金属污染的重要来源,城乡面积大的区域河流沉积物的重金属含量更高,河流沉积物重金属浓度出现从上游到下游升高的总趋势[22,33-34]。
变异系数是反映总体各单位标志值的差异程度或离散程度的指标,是反映数据分布状况的指标之一[35]。相关研究表明,当沉积物重金属变异系数大于20%,表明人类活动是影响重金属变化的主要驱动因子[36–38]。东大河湿地沉积物Zn、Cu、Ni、Pb、Cr的变异系数分别是39.21%、29.78%、28.91%、51.93%、22.94%,变异程度呈Pb>Zn>Cu>Ni>Cr,其中Pb、Zn的变异系数大于36%,属强变异,Ni、Cu、Cr的变异系数在16%—35%之间属中等变异。东大河湿地沉积物5种重金属的变异系数均大于20%,说明湿地的重金属可能受人类活动影响较大。东大河主要流经林地、农业用地和城镇用地,下游流经晋宁城区,人类活动强烈,可能是东大河湿地重金属变异系数高的原因之一。
与国内其他湖泊湿地沉积物重金属相比较(表5),东大河湿地Cr浓度高于当地背景值,且高于云南其他湿地沉积物含量,略低于太湖竺山湾湿地和巢湖,说明东大河湿地的Cr元素累积相对较高,需要重视。研究区Zn浓度低于重金属污染较为严重的草海湖滨带,与滇池宝丰湿地的浓度相当,介于太湖和巢湖之间,且明显高于当地背景值,说明东大河湿地Zn元素同样有较高的累积量。研究区Pb浓度与滇池及周边湿地相当,高于当地背景值,明显高于阳宗海、太湖和巢湖等的浓度,说明滇池沿岸Pb浓度可能普遍偏高,在滇池范围内出现累积。研究区Cu、Ni浓度相比于滇池及周边湿地要低,与巢湖含量相当,远低于受污染的太湖竺山湾湿地,与背景值相当,说明东大河湿地Cu、Ni累积含量较低。
-
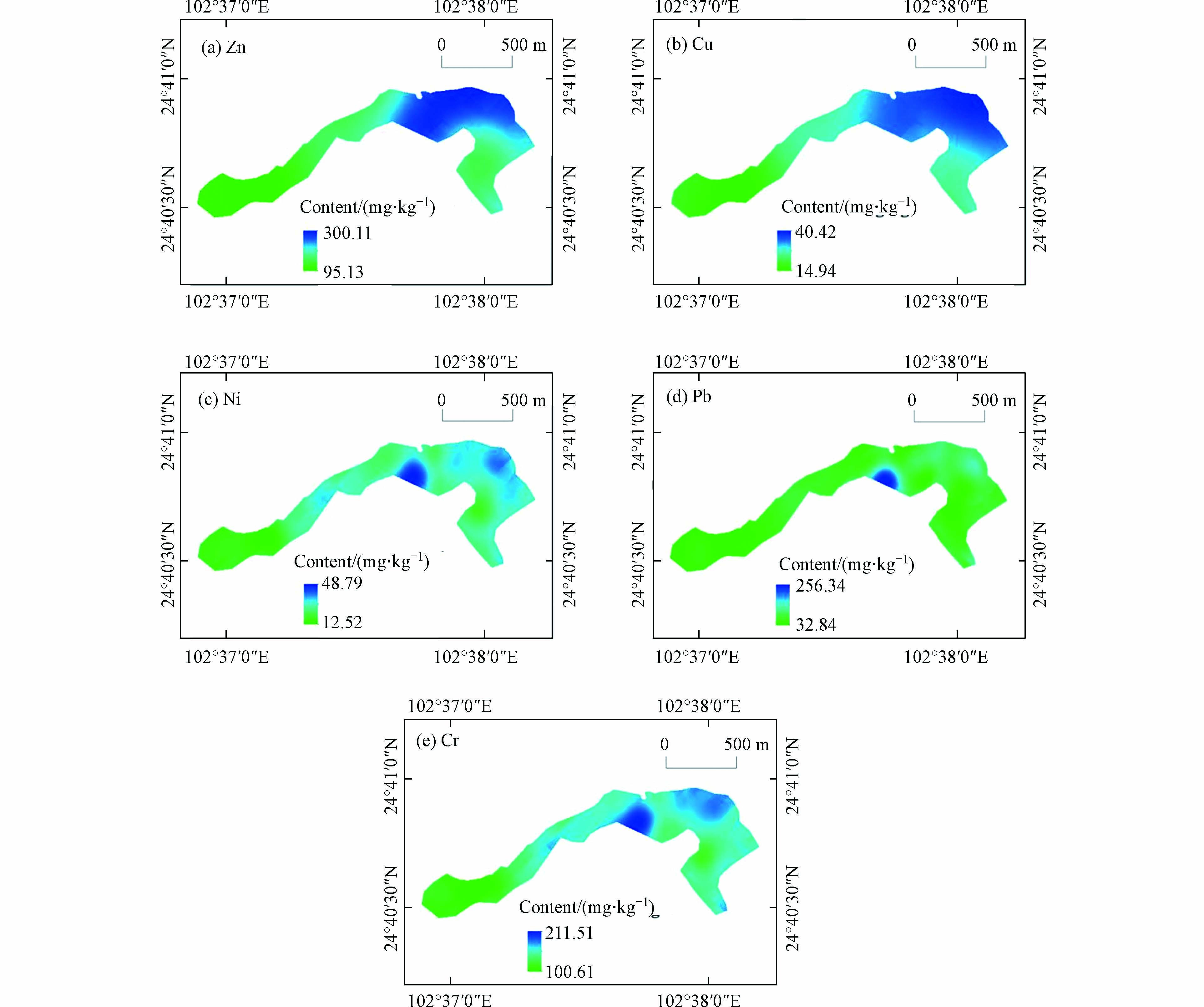
根据各样点重金属含量检测值,采用GIS空间插值的方法呈现重金属空间分布特征,在ArcGIS10.7中使用地统计Kriging空间插值法绘制了东大河湿地表层沉积物重金属空间分布图,如图3所示。东大河湿地沉积物5种重金属空间分布格局各不相同,均出现局部富集的高浓度区域。
Zn的高浓度区域集中分布在湿地中部,主要沿东大河主河道分布,湿地西部和湿地东部Zn浓度相对较低,湿地西部由东向西Zn浓度有明显的降低趋势。相关研究表明,沉积物Zn的来源有电力和热力生产、煤炭开采、洗选和燃烧、化工制造业和新兴电子业、机械工业生产,与交通排放、刹车装置、汽车轮胎磨损密切相关[33,45]。东大河湿地Zn的空间布局表明,东大河沿途接纳了工业生产、交通运输中产生的Zn污染在入湖口处发生聚集,导致东大河湿地沉积物Zn浓度升高。
Cu的高浓度区域主要分布在水道密集的湿地中部,与主河道、排水渠所在位置高度吻合,Cu浓度呈现由湿地中部向东西两侧降低的特征。相关研究表明,沉积物Cu来源有电、热力生产;煤炭生产和使用;新兴电子和机械工业生产[45],如电镀加工过程[33];普遍存在于化肥和农药中,从东大河湿地Cu的空间布局可以看出,Cu污染可能来自排污口废水排放和东大河周围工农业活动等复合污染[22]。
Ni、Pb、Cr含量空间分布格局较为相似,高浓度区域出现在相近的区域,主要分布在湿地中部主河道和排水渠区域,零星分布在湿地东部和西部,西部样点人为干扰明显,此处是湿地公园游船观光区域,游客相对较多,游船篙竿对表层沉积物扰动频繁;湿地东部高值区分布在湿地外围,实地考察发现,湿地东部的外围环绕着一条相对独立的排水渠,与湿地东部广阔的水域有个别缺口连通;经检测,湿地东部外围排水渠样点的重金属浓度明显高于湿地东部开阔水域,因此外围排水渠可能是湿地东部重金属的来源之一。相关研究表明,Cr普遍存在于化肥和农药中[22],与合金制品制造有关[33];农业区的Pb污染主要来自施肥[36],此外还有秸秆焚烧和森林火灾[46],城镇区域的Pb污染来源主要有生活污水、工业排放和交通排放,如轮胎磨损、刹车片摩擦和汽油的燃烧等[36,45,47];Ni的来源有汽车尾气[47]、工业生产等,如电镀加工过程有关[33]。从东大河湿地Ni、Pb、Cr的空间布局可以看出,东大河湿地沉积物Ni、Pb、Cr的来源主要是来自河流纳污,在河流、水渠的入口处富集[15];西部样点偏高可能存在两方面的原因,一是该区域游客较多,存在外源输入的可能,二是该区域沉积物经常受到篙竿的扰动,经过多次扰动后,该区域的表层沉积物颗粒更细,吸附能力更强,导致重金属在表层富集,因此该点周边的重金属含量出现偏高的现象[48-49]。
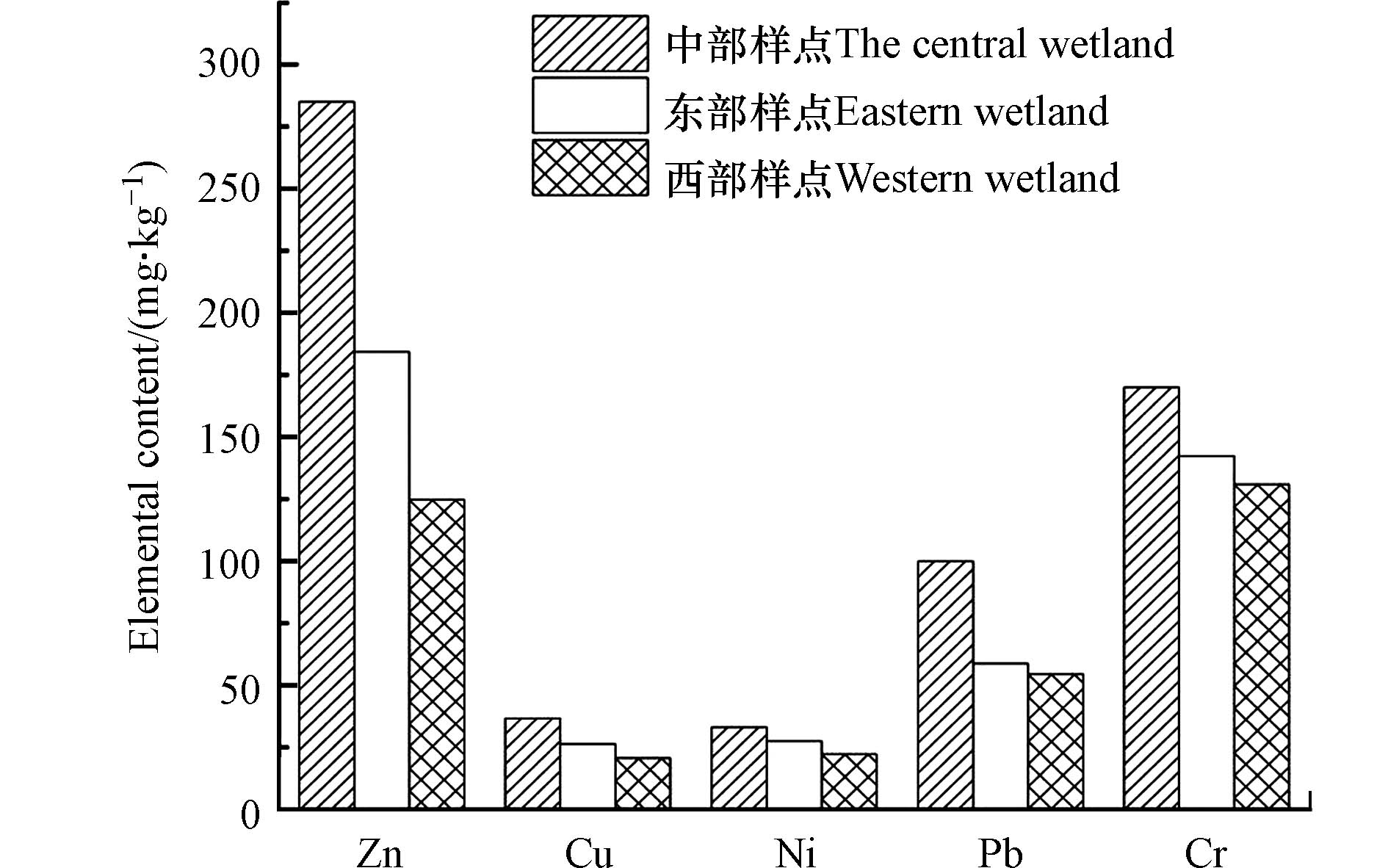
已有研究表明,在全国范围内云南省农田土壤重金属的平均含量较高,Zn、Cu、Pb、Cr的全省平均含量分别达到93.49、32.56、35.74、74.43 mg·kg−1,由于云南省地处欧亚板块与印度洋板块的碰撞结合带,成矿条件优越,矿床资源丰富,矿产资源开采、冶炼是重金属污染的重要来源[50-51]。多矿种共伴生是矿产资源基本特征之一,由于伴生矿重金属污染具有相同的来源,伴生矿重金属污染通常具有空间相似性,矿床中铜铅锌常组合出现,因此铜、铅、锌多具有相似的空间分布特征[52-53]。东大河湿地位于东大河河流入湖口处,远离矿区,但5种重金属的空间分布具有明显的规律性和相似性,均在湿地水体入口附近积累,5种重金属的平均含量均呈现出湿地中部>东部>西部的特征,如图4所示。
根据东大河湿地沉积物重金属的空间分布特征推测,其成因主要有两个,一是东大河水体中各种污染物进入湿地后由于吸附作用逐渐沉淀在沉积物中;二是湿地内部水道纵横交错,河水流速变缓,沉积物容易淤积,重金属污染物会附着在沉积物中,从而造成了局部样点重金属富集现象[14]。
-
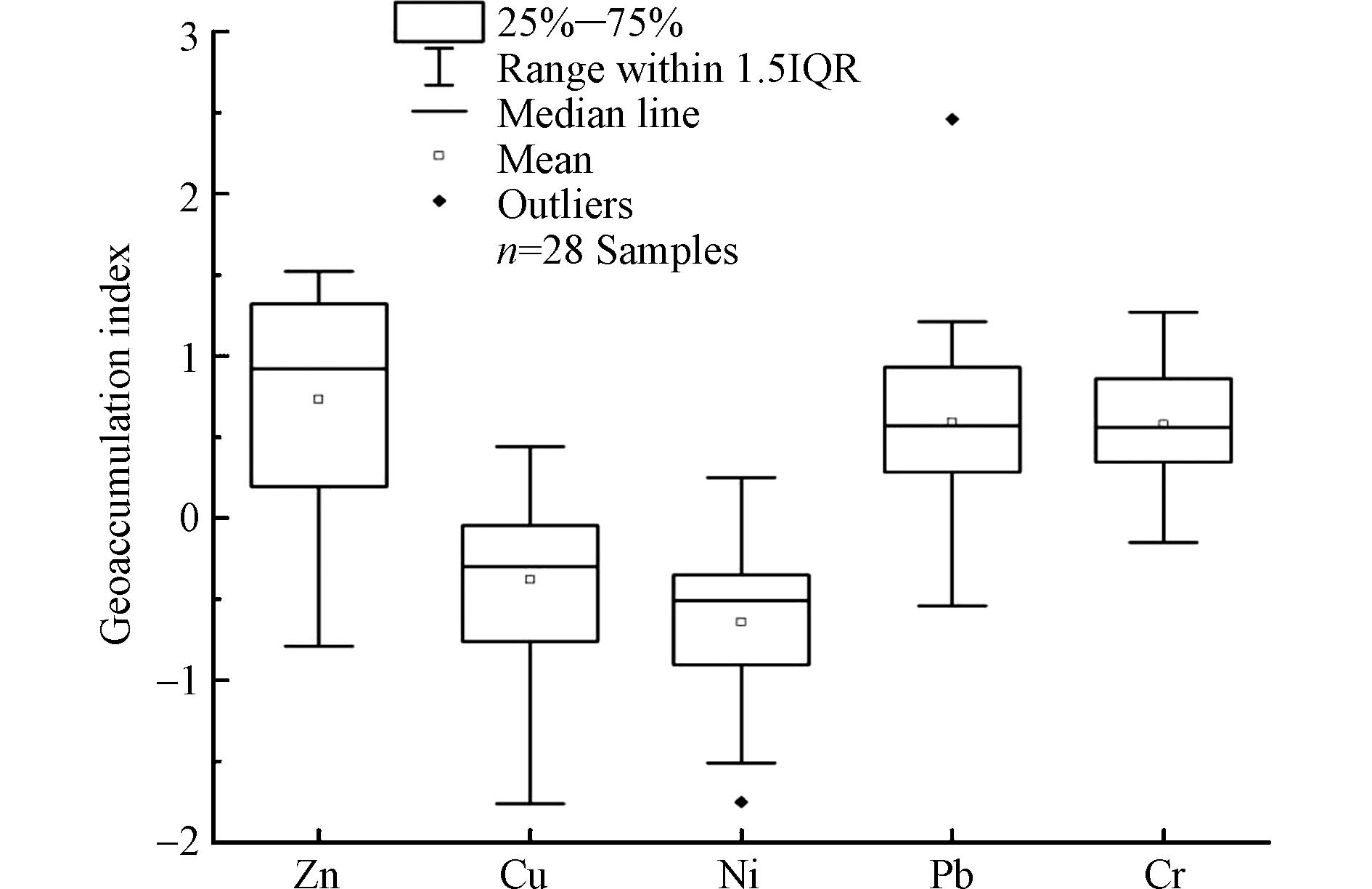
根据东大河湿地沉积物重金属含量的测定结果,按照式(1)计算5种重金属的地质累积指数,如表6所示。从表6中可以看出,东大河湿地沉积物中5种重金属的地质累积指数由大到小依次为:Zn>Pb>Cr>Cu>Ni,平均值分别是0.87、0.72、0.62、-0.30、-0.58。研究区域Ni的平均含量为无污染,除河流入口处的12号样点属于轻度污染外,其他样点均为无污染;Cu整体上也处于无污染状态,21%(6个样点)达到轻度污染,79%(22个样点)为无污染;Cr的平均含量为轻度污染,86%(24个样点)属于轻度污染,7%(2个样点)处于无污染,7%(2个样点)达到偏中度污染;Pb的平均含量为轻度污染,71%(20个样点)属于轻度污染,14%(4个样点)处于无污染,11%(3个样点)达到偏中度污染,4%(1个样点)达到中度污染;Zn的平均含量为轻度污染,43%(12个样点)达到偏中度污染,36%(10个样点)为轻度污染,21%(6个样点)处于无污染,如图5所示。由上分析可知,东大河湿地河流、排水渠入口处的个别样点达到中度污染、偏中度污染,其余大部分样点为轻度污染或者是无污染。
-
按照式(2)计算5种重金属的潜在生态风险指数,如表7所示。从表7可以看出,东大河湿地沉积物单一重金属潜在生态风险指数(
$ {E}_{r}^{i} $ )由大到小依次为:Pb>Cu>Ni>Cr>Zn,平均值分别是12.34、6.08、5.03、4.60、2.73。东大河湿地沉积物5种重金属中,除12号样点的Pb达到中等生态危害外,其他样点重金属均为轻微生态危害。东大河湿地沉积物5种重金属的综合潜在生态危害指数(RI)介于14.11—68.41之间,平均值为30.79,所有样点的综合潜在生态危害指数均低于150,属于轻微生态危害,表明Zn、Cu、Ni、Pb、Cr的5种重金属整体上对东大河湿地生态环境影响较低。湿地3个区域的平均RI值由大到小依次为:湿地中部>湿地东部>湿地西部,东大河湿地中部的潜在生态危害最大,与湿地中部重金属含量最高的空间布局一致。从东大河湿地沉积物5种重金属综合潜在生态危害指数的构成比例可知,Pb是东大河湿地沉积物重金属潜在生态危害贡献率最高的元素(占40.09%),其次是Cu、Ni(分别占19.75%、16.35%),然后是Cr(占14.93%),贡献率最小的是Zn,只占8.88%。由此可以反映出,毒性系数高的元素对生态的危害较大,即使东大河湿地沉积物中Ni、Cu浓度含量不高,但是其潜在生态危害远比毒性低、浓度高的Zn要大。 -
(1)东大河湿地沉积物中Zn、Cu、Ni、Pb、Cr的含量分别是70.07—348.56、11.09—50.72、12.91—51.81、33.23—265.87、90.36—241.87 mg·kg−1,平均浓度分别是云南省土壤背景值的2.8、0.9、0.9、2.2、2.7倍,分别是中国南方水系沉积物背景值的2.7、1.2、1.0、2.5、2.3倍,超过中国南方水系沉积物背景值的采样点比例分别是96.43%、71.43%、57.14%、100.00%、100.00%,变异系数分别是39.21%、29.78%、28.91%、51.93%、22.94%,变异程度呈Pb>Zn>Cu>Ni>Cr。
(2)东大河湿地沉积物5种重金属空间分布格局各不相同,均出现局部富集的高浓度区域,具有明显的规律性和相似性,5种重金属的平均含量均呈现出湿地中部>东部>西部的特征。东大河湿地沉积物5种重金属均在湿地水体入口附近积累,在人类活动频繁的区域和排水渠连通区出现高值区,人类活动是影响东大河湿地沉积物重金属差异的主要驱动因子。
(3)东大河湿地沉积物中5种重金属的地质累积指数由大到小依次为:Zn>Pb>Cr>Cu>Ni,河流和排水渠入口处的个别样点达到中度污染和偏中度污染,其余大部分样点为轻度污染或者是无污染;东大河湿地沉积物单一重金属潜在生态风险指数(
$ {\mathrm{E}}_{\mathrm{r}}^{\mathrm{i}} $ )由大到小依次为:Pb>Cu>Ni>Cr>Zn,除12号样点的Pb达到中等生态危害外,其他样点重金属均为轻微生态危害,5种重金属的综合潜在生态危害指数为30.79,属轻微生态危害,湿地3个区域的综合潜在生态危害指数由大到小依次为:湿地中部>湿地东部>湿地西部。针对东大河湿地重金属污染问题应重点控制Zn、Pb、Cr等污染物质,针对东大河湿地重金属生态风险问题应重点关注Pb、Cu、Ni等高毒性元素,特别是Pb元素,它不仅是高毒性元素,而且地质累积指数也较高,是综合潜在生态危害的主要贡献元素。
滇池东大河湿地沉积物重金属空间分异特征及生态风险评价
Spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Dongda River wetland in Dianchi Lake
-
摘要: 湖滨湿地是重金属富集和转换的场所。为了解滇池东大河湿地沉积物重金属的污染特征及环境风险,根据东大河湿地的水域特征采集了28个沉积物样品,采用原子吸收光谱仪火焰法测定Zn、Cu、Ni、Pb、Cr的含量,并分析其空间分布特征,使用地质累积指数法和潜在生态风险指数法评价了湿地沉积物重金属的生态风险。结果表明,东大河湿地沉积物Zn、Cu、Ni、Pb、Cr的质量浓度分别是70.07—348.56、11.09—50.72、12.91—51.81、33.23—265.87、90.36—241.87 mg·kg-1。东大河湿地沉积物5种重金属的空间分布格局具有明显的规律性和相似性,5种重金属的平均含量均呈现出湿地中部>东部>西部的特征,在湿地水体入口附近积累,在人类活动频繁的区域和排水渠连通区出现高值区,人类活动是影响东大河湿地沉积物重金属差异的主要驱动因子。东大河湿地沉积物5种重金属在河流和排水渠入口处的个别样点达到中度污染和偏中度污染,其余大部分样点为轻度污染或无污染;单一重金属潜在生态风险指数表明Pb在河流入口附近达到中等生态危害,其他样点重金属均为轻微生态危害,综合潜在生态危害指数为轻微生态危害,湿地3个区域的综合潜在生态危害指数由大到小依次为:湿地中部>湿地东部>湿地西部。Abstract: The lakeside wetland is a place where heavy metals are enriched and converted. In order to understand the pollution characteristics and environmental risks of heavy metals in the sediments of the Dongda River Wetland in Dianchi Lake, 28 sediment samples were collected according to the water characteristics of Dongda River wetland. For the samples, the content of Zn, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Cr was determined by the flame method of atomic absorption spectrometer, and the spatial distribution characteristics of heavy metals in the sediments were analyzed. In addition, the ecological risk of heavy metals in wetland sediments was evaluated by geoaccumulation index method and potential ecological risk index method. The results indicated that the contents of Zn, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Cr in Dongda River wetland are respectively 70.07—348.56, 11.09—50.72, 12.91—51.81, 33.23—265.87 and 90.36—241.87 mg·kg-1. The spatial distribution patterns of five heavy metals in Dongda River Wetland sediments have obvious regularities and similarities. The average content of the five heavy metals all present the characteristics of the central>the eastern>the western parts of the wetland. Heavy metals accumulate near the entrance of wetland water, and high-value areas appear in the areas of frequent human activities and drainage channels. Human activities are the main driving factors affecting the difference of heavy metals in the sediments in Dongda River wetland. 5 kinds of heavy metals in the sediments of Dongda River wetland detect moderately polluted and moderately to strongly at individual sample points at the entrance of rivers and drains, and most of the remaining samples points are unpolluted to moderately polluted or practically unpolluted. Pb of the single potential ecological risk detected moderate near river entrances, and other sample heavy metals are mild. The comprehensive potential ecological risk is a minor. Above all, comprehensive potential ecological risk of three areas in the wetland from large to small: the central wetland > wetland east > wetland west.
-
Key words:
- wetland heavy metals /
- ecological risk assessment /
- Dongda River /
- Dianchi Lake
-

-
表 1 地质累积指数(Igeo)与重金属污染水平分级
Table 1. Geoaccumulation index (Igeo) and corresponding pollution degree
Igeo <0 0—1 1—2 2—3 3—4 4—5 >5 污染级别 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 污染程度 无污染 轻度污染 偏中度污染 中度污染 偏重污染 重度污染 严重污染 表 2 重金属潜在生态风险分级
Table 2. Classification of potential ecological risk of heavy metals
$ {E}_{r}^{i} $ RI $ {E}_{r}^{i} < $ 轻微生态危害 RI<150 轻微生态危害 40 $ \le {E}_{r}^{i} < $ 中等生态危害 150 $ \le $ 中等生态危害 80 $ \le {E}_{r}^{i} < $ 强生态危害 300 $ \le $ 强生态危害 160 $ \le {E}_{r}^{i} < $ 很强生态危害 RI $ \ge $ 很强生态危害 $ {E}_{r}^{i}\ge 320 $ 极强生态危害 表 3 重金属环境背景值(
$ {C}_{n}^{i} $ $ {T}_{r}^{i} $ Table 3. Heavy metals background values (
$ {C}_{n}^{i} $ $ {T}_{r}^{i} $ 元素
ElementZn Cu Ni Pb Cr $ {C}_{n}^{i} $ 81 25 29 32.5 67 $ {T}_{r}^{i} $ 1 5 5 5 2 表 4 东大河湿地沉积物重金属含量统计特征(mg·kg−1)
Table 4. Statistical characteristics of heavy metals in sediments of Dongda River Wetland(mg·kg−1)
指标
IndexZn Cu Ni Pb Cr 最大值 70.07 11.09 12.91 33.23 90.36 最小值 348.56 50.72 51.81 265.87 241.87 平均值 221.38 30.4 29.19 79.73 154 标准差 86.8 9.05 8.44 41.41 35.32 变异系数% 39.21% 29.78% 28.91% 51.93% 22.94% 云南省土壤背景值 80.5 33.6 33.4 36.0 57.6 中国南方水系沉积物背景值 81.0 25.0 29.0 32.3 67.0 表 5 典型湿地表层沉积物重金属含量(mg·kg−1)
Table 5. Content of heavy metals in surface sediments of typical wetland
研究区
Study areaZn Cu Ni Pb Cr 东大河湿地(本研究) 70.07—348.56 11.09—50.72 12.91—51.81 33.23—265.87 90.36—241.87 滇池[39] 128.00 86.60 — 78.20 113.00 草海湖滨带[40] 313.02 174.36 61.34 84.17 61.28 外海湖滨带[40] 165.09 148.24 52.31 70.24 51.10 滇池宝丰湿地[41] 225.75 91.00 47.00 69.75 101.00 阳宗海[42] 149.20 97.60 55.10 40.30 145.80 太湖竺山湾湿地[43] 269.61 176.78 183.09 30.12 160.24 巢湖[44] 142.04 27.67 35.53 56.00 168.24 云南省土壤背景值[31] 80.5 33.6 33.4 36.0 57.6 江苏省下蜀黄土背景值[43] 59.2 18.9 15.7 19.5 79.3 安徽省江淮流域土壤背景值[44] 53.2 24.9 25.0 25.9 69.4 “-”表示相关文献没有提供数据. No data are available in the literature. 表 6 东大河湿地沉积物重金属地质累积指数和污染等级
Table 6. Geoaccumulation index and pollution grade of heavy metals in sediments of Dongda River Wetland
采样点
Sampling siteIgeo值
Igeo valueIgeo等级
Igeo levelZn Cu Ni Pb Cr Zn Cu Ni Pb Cr 东大河湿地 0.87 −0.30 −0.58 0.72 0.62 1 0 0 1 1 湿地中部 1.23 −0.03 −0.38 1.05 0.76 2 0 0 2 1 湿地东部 0.60 −0.50 −0.65 0.28 0.50 1 0 0 1 1 湿地西部 0.04 −0.85 −0.96 0.17 0.38 1 0 0 1 1 表 7 东大河湿地沉积物重金属潜在生态危害系数(
$ {E}_{r}^{i} $ Table 7. Potential ecological risk (
$ {E}_{r}^{i} $ 采样点
Sampling site$ {E}_{r}^{i} $ RI Zn Cu Ni Pb Cr 东大河湿地 2.73 6.08 5.03 12.34 4.60 30.79 湿地中部 3.52 7.37 5.74 15.50 5.08 37.21 湿地东部 2.28 5.29 4.77 9.10 4.25 25.68 湿地西部 1.54 4.16 3.87 8.46 3.91 21.94 -
[1] 刘惠良, 刘红峰. 洞庭湖湿地生物多样性保护的价值评估 [J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2021, 41(10): 140-147. doi: 10.14067/j.cnki.1673-923x.2021.10.016 LIU H L, LIU H F. Value evaluation of biodiversity conservation in Dongting Lake wetland [J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2021, 41(10): 140-147(in Chinese). doi: 10.14067/j.cnki.1673-923x.2021.10.016
[2] PAN L B, WANG Y, MA J, et al. A review of heavy metal pollution levels and health risk assessment of urban soils in Chinese cities [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2018, 25(2): 1055-1069. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-0513-1 [3] LI G, SUN G X, REN Y, et al. Urban soil and human health: A review [J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 2018, 69(1): 196-215. doi: 10.1111/ejss.12518 [4] 储金宇, 张金萍, 周晓红, 等. 镇江市古运河河岸沉积物重金属分布特征及潜在生态风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2015, 34(4): 763-771. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.04.2014091805 CHU J Y, ZHANG J P, ZHOU X H, et al. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk evaluation of heavy metals in riverside sediments of Zhenjiang Canal [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 34(4): 763-771(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.04.2014091805
[5] ARGUDÍN M A, HOEFER A, BUTAYE P. Heavy metal resistance in bacteria from animals [J]. Research in Veterinary Science, 2019, 122: 132-147. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2018.11.007 [6] YIN K, WANG Q N, LV M, et al. Microorganism remediation strategies towards heavy metals [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 360: 1553-1563. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.10.226 [7] 朱源, 胡灿实, 张明明, 等. 贵州草海湿地水鸟重金属暴露风险评估与应用 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(10): 4770-4781. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.10.034 ZHU Y, HU C S, ZHANG M M, et al. Risk assessment and application of heavy metal exposure of waterbirds in Caohai Wetland, Guizhou Province, China [J]. China Environmental Science, 2021, 41(10): 4770-4781(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.10.034
[8] 马康, 史璇, 尤晓光, 等. 河流岸带湿地沉积物重金属分布对植被物种多样性和底栖动物群落特征的影响 [J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(5): 2001-2010. MA K, SHI X, YOU X G, et al. Relationship of the heavy metals distribution in sediments to vegetation diversity and macroinvertebrate communities in riparian wetlands [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(5): 2001-2010(in Chinese).
[9] 李贝, 道金荣, 朱润云, 等. 滇池重金属污染的分布、积累和风险评估 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(6): 1808-1818. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020020202 LI B, DAO J R, ZHU R Y, et al. Distribution, accumulation and risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in Dianchi Lake [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(6): 1808-1818(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020020202
[10] 李仁英, 杨浩, 陈捷, 等. 盘龙江口滇池沉积物重金属的分布及污染评价 [J]. 土壤, 2006, 38(2): 186-191. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9829.2006.02.013 LI R Y, YANG H, CHEN J, et al. Distribution and pollution evaluation of heavy metals in sediments of lake Dianchi in the estuary of the panlongjiang river [J]. Soils, 2006, 38(2): 186-191(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9829.2006.02.013
[11] 刘勇, 朱元荣, 吴丰昌, 等. 滇池沉积物中重金属污染特征及其生态风险评估 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2014, 23(7): 1181-1186. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2014.07.014 LIU Y, ZHU Y R, WU F C, et al. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Dianchi Lake [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2014, 23(7): 1181-1186(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2014.07.014
[12] 肖冬冬, 史正涛, 苏斌, 等. 滇池宝象河表层沉积物重金属含量空间分布特征及污染评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(12): 2719-2728. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017041102 XIAO D D, SHI Z T, SU B, et al. Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in surface sediment of Baoxiang River, Dianchi Lake [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(12): 2719-2728(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017041102
[13] 昆明市统计局. 昆明统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2021: 36-42. Statistic bureau of Kunming. Kunming Statistical Yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2021: 36-42 (in Chinese).
[14] 散剑娣, 蔡德所, 靖志浩, 等. 龙江河沉积物重金属污染特征及生态风险评价 [J]. 人民长江, 2021, 52(11): 34-41. doi: 10.16232/j.cnki.1001-4179.2021.11.006 SAN J D, CAI D S, JING Z H, et al. Pollution characteristics of heavy metals in Longjiang River sediments and ecological risk assessment [J]. Yangtze River, 2021, 52(11): 34-41(in Chinese). doi: 10.16232/j.cnki.1001-4179.2021.11.006
[15] 夏南, 薛桂澄, 傅杨荣, 等. 海南岛主要河流水体中重金属元素迁移富集特征 [J]. 地下水, 2012, 34(6): 208-210. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2012.06.077 XIA N, XUE G C, FU Y R, et al. Migration and enrichment characteristics of heavy metal element in the main river water of Hainan Island [J]. Ground Water, 2012, 34(6): 208-210(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2012.06.077
[16] 杨红, 潘曲波. 南滇池国家湿地公园水生植物多样性研究 [J]. 西南林业大学学报(社会科学), 2021, 5(1): 41-47. YANG H, PAN Q B. Study on the diversity of aquatic plants in south Dianchi national wetland park [J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University (Social Sciences), 2021, 5(1): 41-47(in Chinese).
[17] 张仁锋, 宁平, 李彬, 等. 东大河口湖滨湿地净化入滇池河水研究 [J]. 水处理技术, 2009, 35(5): 95-97. doi: 10.16796/j.cnki.1000-3770.2009.05.029 ZHANG R F, NING P, LI B, et al. Study on purification of river water flowing into Dianchi Lake by estuarine wetland in dongdahe river lakeshore [J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 2009, 35(5): 95-97(in Chinese). doi: 10.16796/j.cnki.1000-3770.2009.05.029
[18] 陈冬妮. 滇中湖泊不同生态修复型湿地净化效能及其影响因素研究[D]. 昆明: 云南大学, 2017.CHEN D N. The purification efficiency and influencing factors in different ecological remediation wetlands within lakes of central Yunnan[D]. Kunming: Yunnan University, 2017(in Chinese). [19] 包立, 张乃明, 农明英. 滇池东大河流域土壤磷素累积规律及空间分布特征研究 [J]. 土壤, 2014, 46(3): 470-474. doi: 10.13758/j.cnki.tr.2014.03.014 BAO L, ZHANG N M, NONG M Y. Soil phosphorus variation, accumulation and spatial distribution in dongda river basin, Dianchi lake [J]. Soils, 2014, 46(3): 470-474(in Chinese). doi: 10.13758/j.cnki.tr.2014.03.014
[20] 周翠云. 环滇池湿地公园公共体育服务供给现状调查及对策研究[D]. 昆明: 云南师范大学, 2018.ZHOU C Y. Investigation and countermeasure research on the present situation of public sports service supply in Dianchi wetland park[D]. Kunming: Yunnan Normal University, 2018(in Chinese). [21] 生态环境部. 土壤和沉积物 铜、锌、铅、镍、铬的测定 火焰原子吸收分光光度法: HJ 491—2019[S]. 北京: 中国环境出版社, 2019. Soil and sediment—Determination of copper, zinc, lead, nickel and chromium—Flame atomic absorption spectrophotometry: HJ 491—2019[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2019 (in Chinese).
[22] 徐双贵, 杨莎, 秦西伟, 等. 湟水河流域西宁段河流表层沉积物重金属空间分布及生态风险评估 [J]. 地球与环境, 2021, 49(5): 561-569. doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2021.49.074 XU S G, YANG S, QIN X W, et al. Spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments from Xining section of the Huangshui River Basin [J]. Earth and Environment, 2021, 49(5): 561-569(in Chinese). doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2021.49.074
[23] MÜLLER G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River [J]. Geology Journal, 1969, 2: 108-118. [24] 匡晓亮, 彭渤, 张坤, 等. 湘江下游沉积物重金属污染模糊评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(4): 800-809. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.04.2015090905 KUANG X L, PENG B, ZHANG K, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution using the fuzzy function normalization method for sediments of the lowermost Xiangjiang River [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(4): 800-809(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.04.2015090905
[25] 历军, 赵伟强, 俞龙生, 等. 珠江三角洲某河流型饮用水源地的土壤重金属污染源解析和风险评价 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2020, 42(12): 1511-1514,1522. doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2020.12.014 LI J, ZHAO W Q, YU L S, et al. Pollution source analysis and risk evaluation of heavy metals in soil of a river drinking water source in Pearl River Delta [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2020, 42(12): 1511-1514,1522(in Chinese). doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2020.12.014
[26] 陈霞, 彭子凌, 周显, 等. 咸宁市水库淤积物品质特性及资源化利用 [J]. 长江科学院院报, 2021, 38(12): 33-38,45. doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20200825 CHEN X, PENG Z L, ZHOU X, et al. Quality characteristics and resource utilization of reservoir sediments in Xianning City [J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2021, 38(12): 33-38,45(in Chinese). doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20200825
[27] HAKANSON L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. a sedimentological approach [J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8 [28] 郭志娟, 周亚龙, 王乔林, 等. 雄安新区土壤重金属污染特征及健康风险 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(1): 431-441. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.01.049 GUO Z J, ZHOU Y L, WANG Q L, et al. Characteristics of soil heavy metal pollution and health risk in Xiongan New District [J]. China Environmental Science, 2021, 41(1): 431-441(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.01.049
[29] 张義, 于一雷, 李胜男, 等. 潮河沉积物重金属污染特征及生态风险评价 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2020, 43(7): 169-179. doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2020.07.023 ZHANG Y, YU Y L, LI S N, et al. Characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metal in sediments of Chao River, North China [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 43(7): 169-179(in Chinese). doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2020.07.023
[30] 闫晓露, 孙才志, 胡远满, 等. 围垦对辽东湾北部滨海湿地土壤重金属含量的影响及生态风险评价 [J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(3): 1055-1067. YAN X L, SUN C Z, HU Y M, et al. Effect of reclamation on soil heavy metal content of coastal wetland and ecological risk assessment in Northern Liaodong Bay, China [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(3): 1055-1067(in Chinese).
[31] 国家环境保护局主持, 中国环境监测总站主编. 中国土壤元素背景值[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1990: 330-381. The National Environmental Protection Agency, Chief of China's Environmental Monitoring Centre Background Values of Soil Elements in China [M]. Beijing: China Environment Science Press, 1990: 330-381(in Chinese).
[32] 程志中, 谢学锦, 潘含江, 等. 中国南方地区水系沉积物中元素丰度 [J]. 地学前缘, 2011, 18(5): 289-295. CHENG Z Z, XIE X J, PAN H J, et al. Abundance of elements in stream sediment in South China [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2011, 18(5): 289-295(in Chinese).
[33] 刘玮晶, 黄顺生, 金洋, 等. 江苏省中部城镇河流底泥重金属污染评价及来源分析 [J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2021, 32(2): 97-102. LIU W J, HUANG S S, JIN Y, et al. Assessment and source analysis of heavy metal pollution in river sediment of a town in central Jiangsu Province [J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 2021, 32(2): 97-102(in Chinese).
[34] 孙芹芹, 姬厚德, 赵东波, 等. 闽江下游土地利用格局对河流沉积物中重金属含量的影响 [J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2020(3): 113-119. doi: 10.13984/j.cnki.cn37-1141.2020.03.015 SUN Q Q, JI H D, ZHAO D B, et al. Sediments of the Minjiang lower reaches [J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2020(3): 113-119(in Chinese). doi: 10.13984/j.cnki.cn37-1141.2020.03.015
[35] 林绍霞, 柳小兰, 张转铃, 等. 贵州草海表层沉积物重金属污染特征与源解析 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2021, 40(2): 390-399. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-1078 LIN S X, LIU X L, ZHANG Z L, et al. Heavy metal pollution characteristics and source apportionment in overlying deposits of Caohai Lake, Guizhou Province [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2021, 40(2): 390-399(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-1078
[36] 张杰, 郭西亚, 曾野, 等. 太湖流域河流沉积物重金属分布及污染评估 [J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(5): 2202-2210. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201809168 ZHANG J, GUO X Y, ZENG Y, et al. Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in river sediments from lake Taihu Basin [J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(5): 2202-2210(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201809168
[37] WANG L F, YANG L Y, KONG L H, et al. Spatial distribution, source identification and pollution assessment of metal content in the surface sediments of Nansi Lake, China [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 140: 87-95. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.02.008 [38] LIU Y Z, ENGEL B A, COLLINGSWORTH P D, et al. Optimal implementation of green infrastructure practices to minimize influences of land use change and climate change on hydrology and water quality: Case study in Spy Run Creek watershed, Indiana [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 601/602: 1400-1411. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.015 [39] 字润祥, 李振宇, 王向宇. 滇池表层底泥中重金属分布特征及污染评价层次分析法 [J]. 昆明理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 45(3): 93-97,99. doi: 10.16112/j.cnki.53-1223/n.2020.03.012 ZI R X, LI Z Y, WANG X Y. Distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Dianchi Lake [J]. Journal of Kunming University of Science and Technology (Natural Science), 2020, 45(3): 93-97,99(in Chinese). doi: 10.16112/j.cnki.53-1223/n.2020.03.012
[40] 焦伟, 卢少勇, 李光德, 等. 滇池内湖滨带重金属污染及其生态风险评价 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2010, 29(4): 740-745. JIAO W, LU S Y, LI G D, et al. Heavy metals pollution and potential ecological risk assessment of inner lakeside belt of lake Dianchi [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2010, 29(4): 740-745(in Chinese).
[41] 肖冬冬. 滇池宝象河表层沉积物重金属特征及潜在生态风险评价[D]. 昆明: 云南师范大学, 2018.XIAO D D. Characteristics and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Baoxiang River, Dianchi[D]. Kunming: Yunnan Normal University, 2018(in Chinese). [42] 张玉玺, 孙继朝, 向小平, 等. 阳宗海表层沉积物中的重金属生态风险评估 [J]. 水资源保护, 2012, 28(5): 19-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6933.2012.05.004 ZHANG Y X, SUN J C, XIANG X P, et al. Evaluation of ecological risk of heavy metals in surface sediments from Yangzonghai Lake [J]. Water Resources Protection, 2012, 28(5): 19-24(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6933.2012.05.004
[43] 黄玉洁, 张银龙, 李文朝, 等. 太湖竺山湾湿地表层沉积物重金属的分布特征及其污染评价 [J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2011, 33(3): 608-615. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2286.2011.03.036 HUANG Y J, ZHANG Y L, LI W C, et al. Distribution characteristics and pollution assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediments in Zhushan Bay [J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2011, 33(3): 608-615(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2286.2011.03.036
[44] 夏建东, 龙锦云, 高亚萍, 等. 巢湖沉积物重金属污染生态风险评价及来源解析 [J]. 地球与环境, 2020, 48(2): 220-227. doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2020.01.020 XIA J D, LONG J Y, GAO Y P, et al. Ecological risk assessment and source analysis of heavy metal pollutions in sediments of the Chaohu Lake [J]. Earth and Environment, 2020, 48(2): 220-227(in Chinese). doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2020.01.020
[45] 苏海民, 孙朋, 张勇. 宿州市沱河城市景观河流重金属富集及污染评价 [J]. 河南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 49(2): 118-124. doi: 10.16366/j.cnki.1000-2367.2021.02.016 SU H M, SUN P, ZHANG Y. Enrichment and contamination evaluation of heavy metal of urban landscape river of Tuo River in Suzhou City [J]. Journal of Henan Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(2): 118-124(in Chinese). doi: 10.16366/j.cnki.1000-2367.2021.02.016
[46] 陈斌, 尹晓娜, 姜广甲, 等. 珠江口外陆架海域表层沉积物重金属潜在生态风险评价及来源分析 [J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2021, 40(3): 520-528. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2021.03.017 CHEN B, YIN X N, JIANG G J, et al. Assessment of the potential ecological risk of heavy metals in the sediments of continental shelf and their sources off the Pearl River Estuary [J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2021, 40(3): 520-528(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2021.03.017
[47] 于孝坤, 熊欣怡, 范廷玉, 等. 芜湖河道沉积物重金属污染及生态风险评估 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2021, 44(6): 153-162. doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2021.06.020 YU X K, XIONG X Y, FAN T Y, et al. Pollution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in river sediments from Wuhu [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 44(6): 153-162(in Chinese). doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2021.06.020
[48] 王栋, 张伯镇, 陈伯俭, 等. 河流沉积物与悬浮颗粒物的重金属来源及风险差异 [J]. 水电能源科学, 2021, 39(6): 50-54. WANG D, ZHANG B Z, CHEN B J, et al. Differences in sources and risks of heavy metals in river sediments and suspended particulate matter [J]. Water Resources and Power, 2021, 39(6): 50-54(in Chinese).
[49] 张杨, 许梦雅, 张超, 等. 白洋淀村落水域沉积物中营养元素和重金属分布特征及风险评价 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(10): 4074-4085. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2021.0126 ZHANG Y, XU M Y, ZHANG C, et al. Distribution characteristics of nutrient elements and heavy metals and its risk assessment in sediments around villages in Baiyangdian Lake [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2021, 41(10): 4074-4085(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2021.0126
[50] 陈文轩, 李茜, 王珍, 等. 中国农田土壤重金属空间分布特征及污染评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(6): 2822-2833. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201910075 CHEN W X, LI Q, WANG Z, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics and pollution evaluation of heavy metals in arable land soil of China [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(6): 2822-2833(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201910075
[51] 王洋洋, 李方方, 王笑阳, 等. 铅锌冶炼厂周边农田土壤重金属污染空间分布特征及风险评估 [J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(1): 437-444. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201803031 WANG Y Y, LI F F, WANG X Y, et al. Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in surface farmland soil around a lead and zinc smelter [J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(1): 437-444(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201803031
[52] 王峰, 冯聪, 杜雪明. 共伴生矿产的概念辨析及其矿业权管理 [J]. 中国国土资源经济, 2020, 33(2): 30-33,38. doi: 10.19676/j.cnki.1672-6995.000353 WANG F, FENG C, DU X M. Concept discrimination of symbiotic-associated minerals and its management of mining rights [J]. Natural Resource Economics of China, 2020, 33(2): 30-33,38(in Chinese). doi: 10.19676/j.cnki.1672-6995.000353
[53] 舒玲, 李悟庆. 铅锌矿区不同类型用地土壤铅、锌、铜、镉元素累积特征及机理分析 [J]. 国土资源导刊, 2021, 18(3): 66-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5603.2021.03.014 SHU L, LI W Q. Accumulation characteristics and mechanism analysis of lead, zinc, copper and cadmium in different types of land in lead-zinc mine area [J]. Land & Resources Herald, 2021, 18(3): 66-71(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5603.2021.03.014
-



 下载:
下载: