-
甲基橙(methyl orange, MO)是一种水溶性偶氮染料,染料释放到天然水体中将严重影响水生生物生长,危害人类健康,具有致畸、致癌和致突变的作用[1]。MO在水中可电离为Na+与有机阴离子,并在微生物的作用下,产生芳香胺类中间体产物,随着食物链传播,在生物体内富集,加剧了人体健康的危害[2]。众所周知,塑料是一种可塑性强、化学稳定性高的高分子材料, 广泛应用于服装、包装、电子等各类产品中[3-6]。但是塑料的危害并没有引起人们的足够重视,80%的塑料产品没有经过有效处理就流入垃圾填埋场和自然环境中,并在重力作用、生物作用、水力作用、天气作用以及人类活动等外界驱动力的作用下,形成粒径<5 mm 的微塑料[7]。微塑料具有不规则的表面结构、较大的比表面积以及对疏水性污染物较强的亲和力,使其能够作为环境污染物的载体,影响污染物在环境中的迁移转化[8-10]。
环境中的微塑料容易受到光照作用而发生老化,老化后的微塑料会产生新的含氧基团(如羟基、羰基等),增加对有机污染物或重金属的吸附能力[11]。BHAGAT等[12]通过研究发现紫外(ultraviolet light, UV)老化增加了微塑料对有机污染物的亲和力;LI等[13]研究发现PE/PS/PA三种微塑料在UV老化后对Cr(VI)的吸附增强。但由于UV条件下微塑料老化速率较低,限制了人们研究微塑料在环境中与污染物的迁移转化。因此,关于微塑料的实验室加速老化技术逐渐被研究和开展。光催化技术是实验室加速微塑料老化的一种有效手段,常见的光催化剂有 TiO2、ZnO、Cds、H3BO3等,不同的光催化剂对PVC老化的影响如表1所示,其中 TiO2因具有活性高、热稳定性好、成本低等特点,使用最为广泛[14],但TiO2光催化降解过程中光激发产生的电子-空穴对的复合会导致催化活性的降低。由于O3本身及其在水中分解产生的自由基具有一定的氧化能力,可以达到加速老化的目的[15-16],因此将光催化和O3结合可以有效增强单一光催化技术的氧化能力,利用TiO2/UV协同老化过程中产生的 e−可与O3反应生成氧化性更强的·OH,抑制了电子-空穴对的复合,使光催化性能得到进一步提高[17]。综上所述,本文以PVC微塑料为研究对象,采用TiO2/UV/O3协同老化的方法对PVC进行加速老化实验,研究微塑料表面形貌及微观结构的变化,以及PVC对MO的吸附行为,为研究环境中的微塑料在污染物迁移转化过程中所起到的作用提供参考。
-
实验材料微塑料聚氯乙烯(polyvinyl chloride, PVC, 300 μm)购自科信达建材有限公司,使用前将PVC置于1 L大烧杯中,加入无水乙醇漫过塑料超过1/4,磁力搅拌30 min,过滤后加入相同量的纯水搅拌均匀,重复上述操作3次滤干,在35 ℃下烘干备用。实验试剂包括二氧化钛、甲基橙(纯度>96%)、无水乙醇(AR)。
主要实验仪器:电子分析天平(JJ124B型,常熟市双杰测试仪器厂);优普超纯水仪(UPHW-I-90T型,上海四科仪器设备有限公司);磁力搅拌器(Feb-78-2型,江苏荣华仪器制造有限公司);电热鼓风干燥箱(101-3A型,上海喆钛机械制造有限公司);紫外灯(GGZ175-1型,上海季光特种照明电器厂);恒温水浴搅拌器(SHA-C型,常州市金坛区指前镇旭日实验仪器厂);循环水式多用真空泵(SHZ-D(Ⅲ)型,郑州科丰仪器设备有限公司);低速台式离心机(TDL-4型,上海安亭科学仪器);数控超声波冲洗器(KQ-50DB型,昆山市超声仪器有限公司);臭氧机(CF-YG5型,北京山美水美环保高科技有限公司)。
-
1) UV老化PVC 在UV光照下进行,将1 g微塑料样品加入1 L烧杯中搅拌均匀,加入一定量的纯水,用磁力搅拌器不间断搅拌保证微塑料和光催化剂在水体中充分接触。在室温下,于1×175 W紫外灯 (λ=365 nm) 下照射,期间每隔一定时间补充纯水。分别老化0.5、1、1.5和2 h后,超声离心30 min,将老化后的PVC进行抽滤,收集在9 mm的培养皿中,放入50 ℃烘箱中烘干备用,将样品分别编号为UV0.5-PVC,UV1-PVC,UV1.5-PVC,UV2-PVC。
2) UV/TiO2协同老化PVC 在UV光照下进行,将1 g微塑料样品和0.01 g TiO2光催化剂加入1 L烧杯中搅拌均匀,其余实验步骤与(1)UV老化相同,最后将样品分别编号为UV/T0.5-PVC,UV/T1-PVC,UV/T1.5-PVC,UV/T2-PVC。
3) TiO2/ UV /O3协同老化PVC 在UV光照下进行,将1 g微塑料样品和0.01 g TiO2光催化剂加入1 L烧杯中搅拌均匀,加入一定量的纯水,用磁力搅拌器不间断搅拌保证微塑料和光催化剂在水体中充分接触。在室温下,于1×175 W紫外灯 (λ=365 nm) 下照射,并在同一时刻通入5 L·min−1 的O3气体,其余实验步骤与(1)UV老化相同,最后将样品分别编号为O3-PVC-T0.5,O3-PVC-T1,O3-PVC-T1.5,O3-PVC-T2。
-
采用扫描电子显微镜(scanning electron microscope, SEM,FlexSEM 1 000,株式会社日立制作所)分析老化前后微塑料表面形貌特征变化;傅里叶变换红外光谱(Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, FTIR ,Nicolet is50,美国赛默飞)鉴别不同体系老化前后官能团的变化;X射线衍射(X-ray diffractometer, XRD ,Smartlab SE,日本理学)在扫描范围2θ=10.0 °~60.0 °,扫描速度5.0 °·min−1,管电流 50 mA,管电压 40 kV下测定光催化老化微塑料PVC的晶型结构;纳米激光粒度Zeta电位仪(Zeta potential,Zetasizer Pro,马尔文帕纳科)在高稳定性He-Ne激光器,4 mW,632.8 nm条件下测定体系中微塑料的固-液界面电性,并对PVC在与不同光催化剂共存下老化0.5、1、1.5、2 h后的失重率进行分析。
-
1)吸附动力学实验: 称取0.1 g不同老化程度的PVC于50 mL锥形瓶中,加入30 mg·L−1 MO溶液30 mL,用玻璃盖密封瓶口进行吸附动力学实验。将样品置于(25±1) ℃,150 r·min−1恒温水浴振荡器中避光振荡(1、2、4、6、8、10、24、48、96 h),静止5 min后,离心后进行抽滤,并用分光光度法测量滤液,每个实验组设置3个平行样,1个空白样。
2)吸附等温线实验: 准确称取0.1 g不同老化程度的PVC于50 mL锥形瓶中,分别加入质量浓度为10、20、30、50 mg·L−1 MO溶液30 mL并用玻璃盖密封。在恒温水浴振荡器中设置(25±1) ℃、150 r·min−1、避光条件下进行振荡48 h,离心后进行抽滤,并用分光光度法测量滤液,每个实验组设置3个平行样,1个空白样。
-
分别称取0.1 g PVC和TiO2/ UV /O3协同老化2 h的PVC于50 mL锥形瓶中,加入30 mg·L−1 MO溶液30 mL,在恒温水浴振荡器中设置(25±1) ℃、150 r·min−1、避光条件下进行振荡48 h,在离心机中离心10 min(3 000 r·min−1),去除上清液,把吸附平衡后的微塑料干燥24 h。用玛瑙研钵充分研磨,采用Nicolet is50 傅里叶变换红外光谱仪测定,分辨率为4 cm−1,扫描范围为4 000~500 cm−1。
-
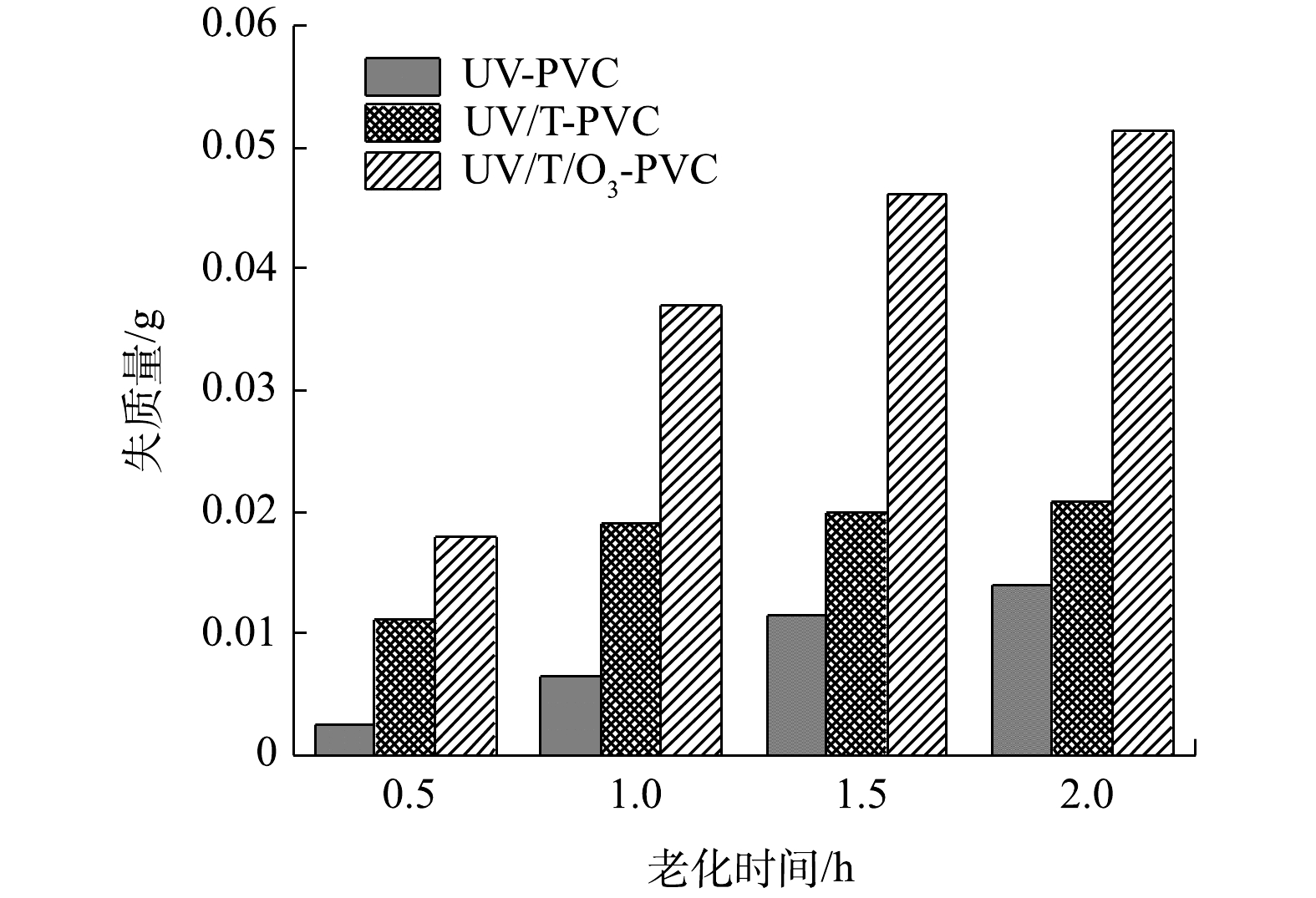
微塑料在老化过程中的重量变化可以直观的反映微塑料的老化程度。图1反映了UV老化PVC,TiO2/UV协同老化PVC,TiO2/ O3/UV协同老化PVC的质量损失情况。结果表明, TiO2/ O3/UV协同老化对PVC的老化效果最好,失质量均随着老化时间的增加而增加,不难推测,在阳光下使用较低数量的光催化剂亦可以有效地加速PVC的降解老化。在THOMAS[21]的研究中也证实了这一点,他通过将微塑料PE和TiO2制备成复合膜在高时效性的自然光照下老化,结果表明复合膜在老化后失重率为18.1%,相比于纯样微塑料0.5%是一个质的提升。
-
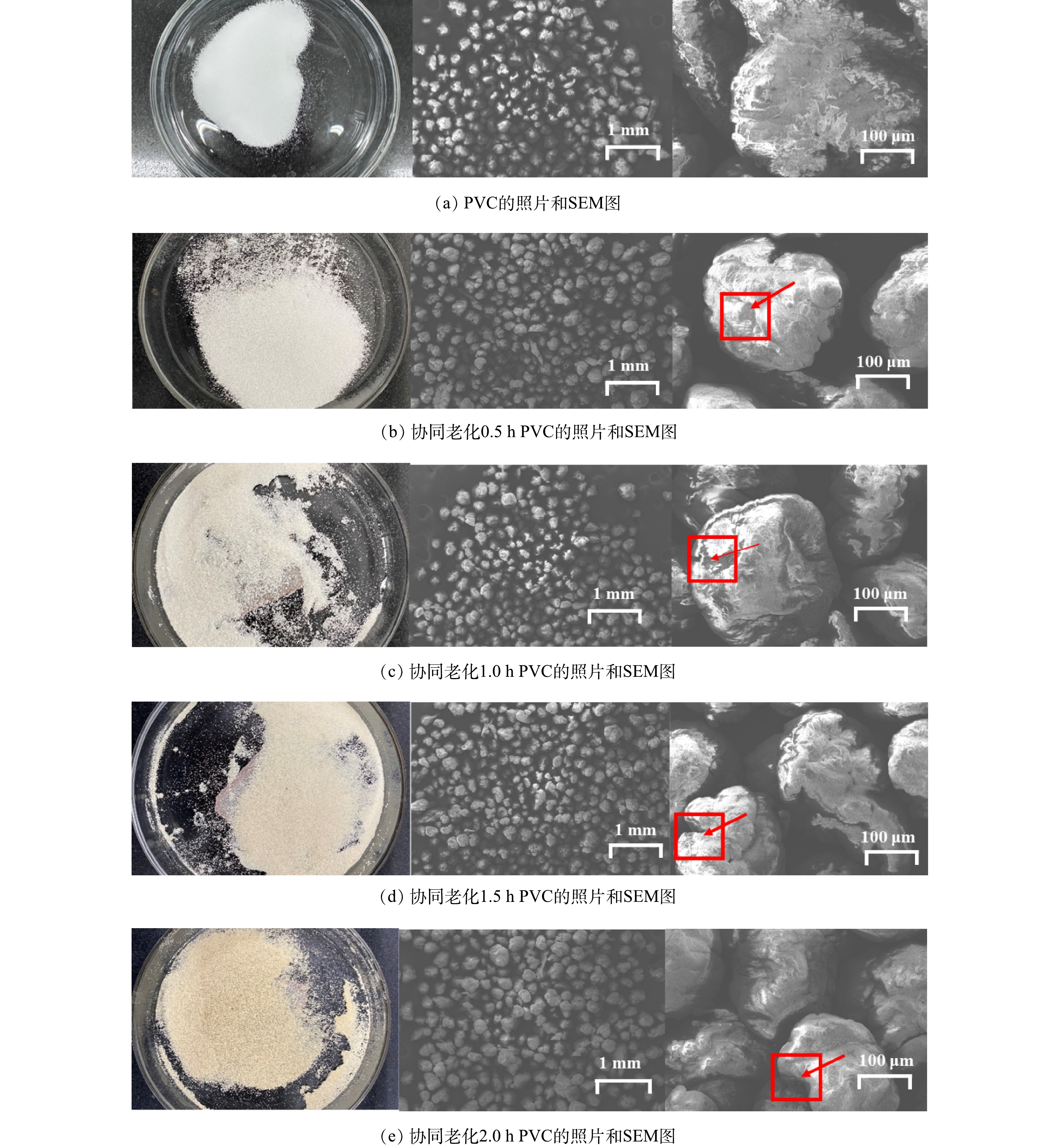
图2为PVC在介导二氧化钛下的协同老化不同时间的扫描电镜图。从图中可以看出未进行老化的原始PVC表面相对光滑,老化0.5 h的微塑料表面已经出现了明显的裂纹和凸起。伴随着老化时间的增加,老化程度逐渐加深,微塑料表面的褶皱相比单一光催化老化更加密集,颗粒的粒径也随着老化时间的增大而减小,老化后的PVC直径约为160~230 μm。同时,在图2中可以清晰的观察到老化后的PVC微塑料颜色由白色转变为黄色,这是由于多烯序列的形成(脱氢氯化反应)和随后的氧化(光漂白)之间的竞争引起的,式 (1)~(5) 表示了PVC在TiO2/UV/O3协同老化作用下产生自由基的过程[22]。
-
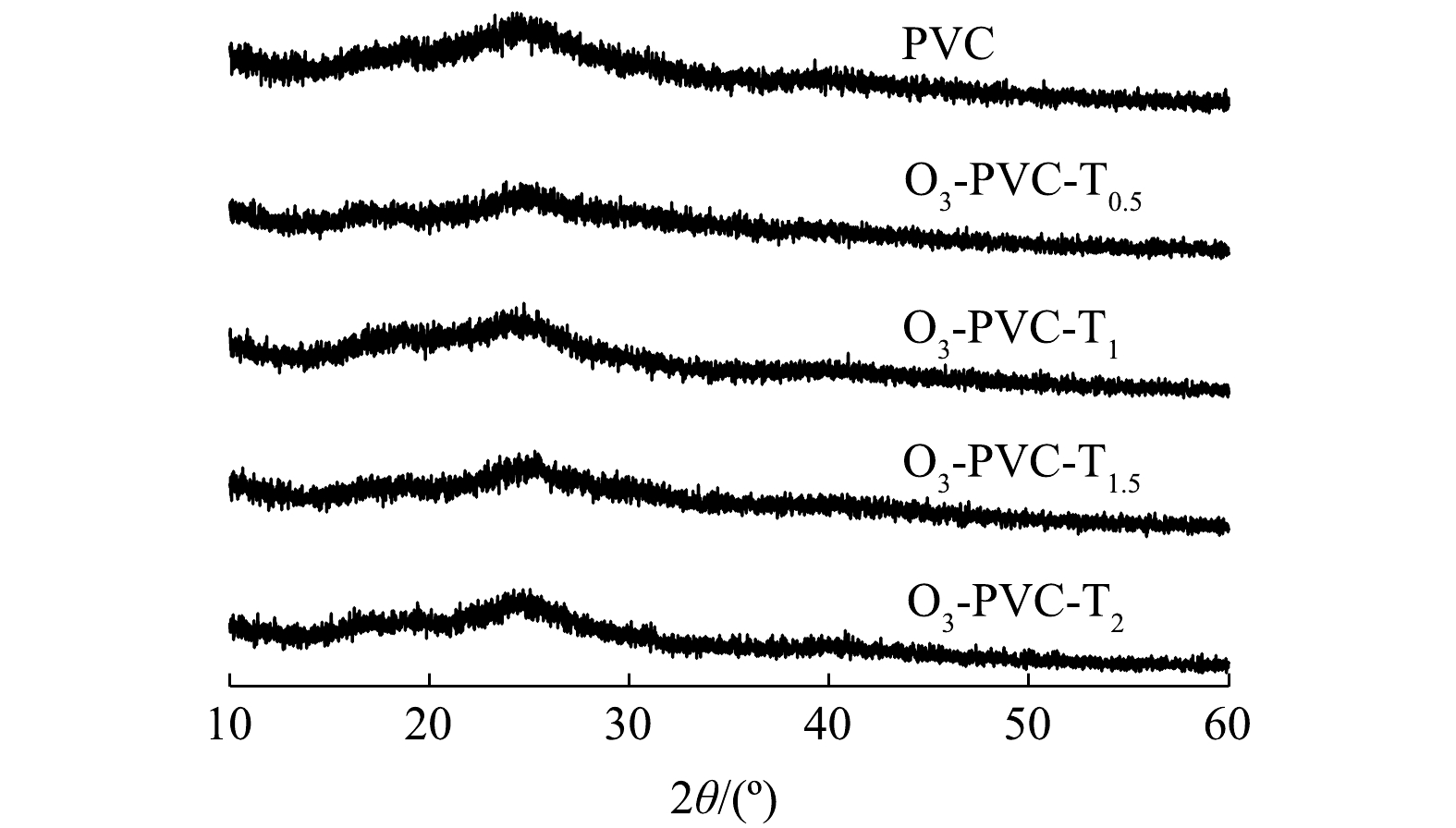
XRD可以反映聚合物表面晶相结构的比例,进一步分析光老化前后PVC的微观结构和结晶度,结果如图3所示。从图中可以看出,PVC 的 XRD 谱图呈弥散状态并未出现明显的结晶峰,表明 PVC 为非结晶性聚合物[23]。但与原始PVC相比,介导TiO2的光老化PVC在老化了不同时间后的吸收峰都有不同程度的降低,说明混合了TiO2的光老化实验会使PVC结晶度略有降低,这种现象可能是因为PVC表面部分官能团受到破坏以及新的官能团的产生。
-
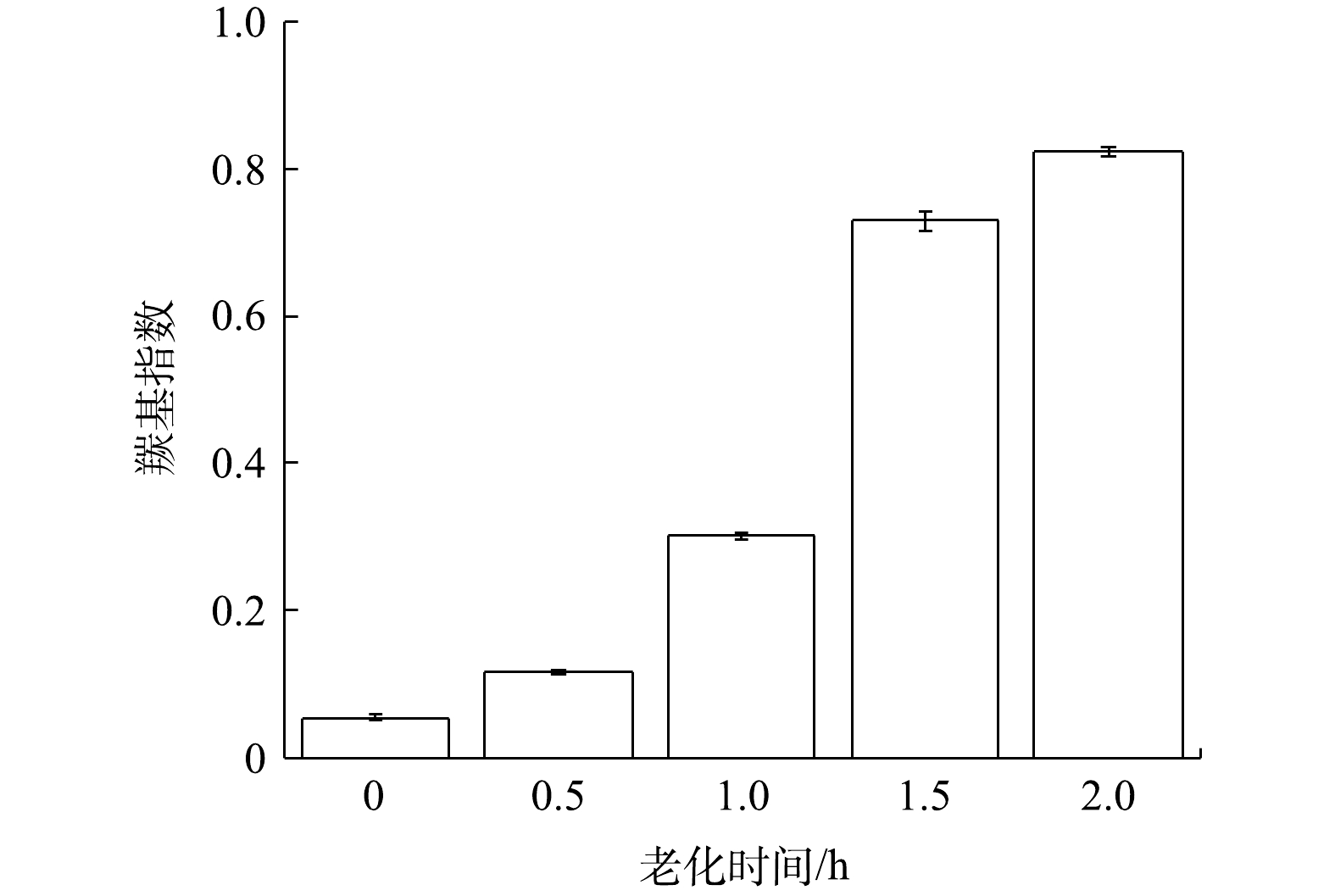
为了揭示TiO2和O3联合UV光照处理后PVC微塑料化学性质的变化,采用红外光谱法测定了微塑料官能团的变化。如图4所示,在1 736 cm−1(C=O)和3 445 cm−1(O-H)出现了两个额外的吸收带,对应于COOH基团的拉伸振动。这些变化反映了PVC微塑料在光老化作用下表面结构的变化。2 909 cm−1的吸收带强度属于CH2的不对称拉伸,此外1 250 cm−1~1 400 cm−1处的吸收带和605 cm−1处的峰值强度增大,这些分别是因为CH-Cl的拉伸振动和C-Cl的拉伸振动。这些变化均与PVC的氧化反应和脱氯反应相对应。推测可能是聚合物的骨架受到·OH的攻击而断裂,因此带有C=O和O-H基团的有机分子脱落,在PVC表面形成了含氧官能团[24]。通过羰基(1 736 cm−1)和碳氢键(2 909 cm−1)的吸收带来确定和量化PVC的联合光催化老化作用。微塑料PVC在TiO2/O3/UV联合作用下老化的羰基指数如图5所示,可以看出羰基指数同老化时间的变化呈现逐渐上升的趋势,这表明,在这段时间内,PVC的光氧化主要是由羟基而不是羰基副产物形成[25]。
-
老化前后的PVC均带负电荷,由图6可见,PVC、O-PVC-T0.5、O-PVC-T1、O-PVC-T1.5和O-PVC-T2电位分别为−31.68、−19.73、−16.73、−4.62和−3.80 mV。与原始PVC相比,老化PVC的负电荷更低,这可以解释为光氧化过程后PVC表面形成的羰基[26]。Zeta电位也可用于预测粒子的稳定性或分散性,基于表面电荷,老化PVC比原始PVC显示出更低的稳定性,并且似乎更容易团聚[27]。随后,C=O的增加和C-H基团的减少以及负电荷的减少可能会改变老化PVC在溶液中的芳香性和稳定性。
-
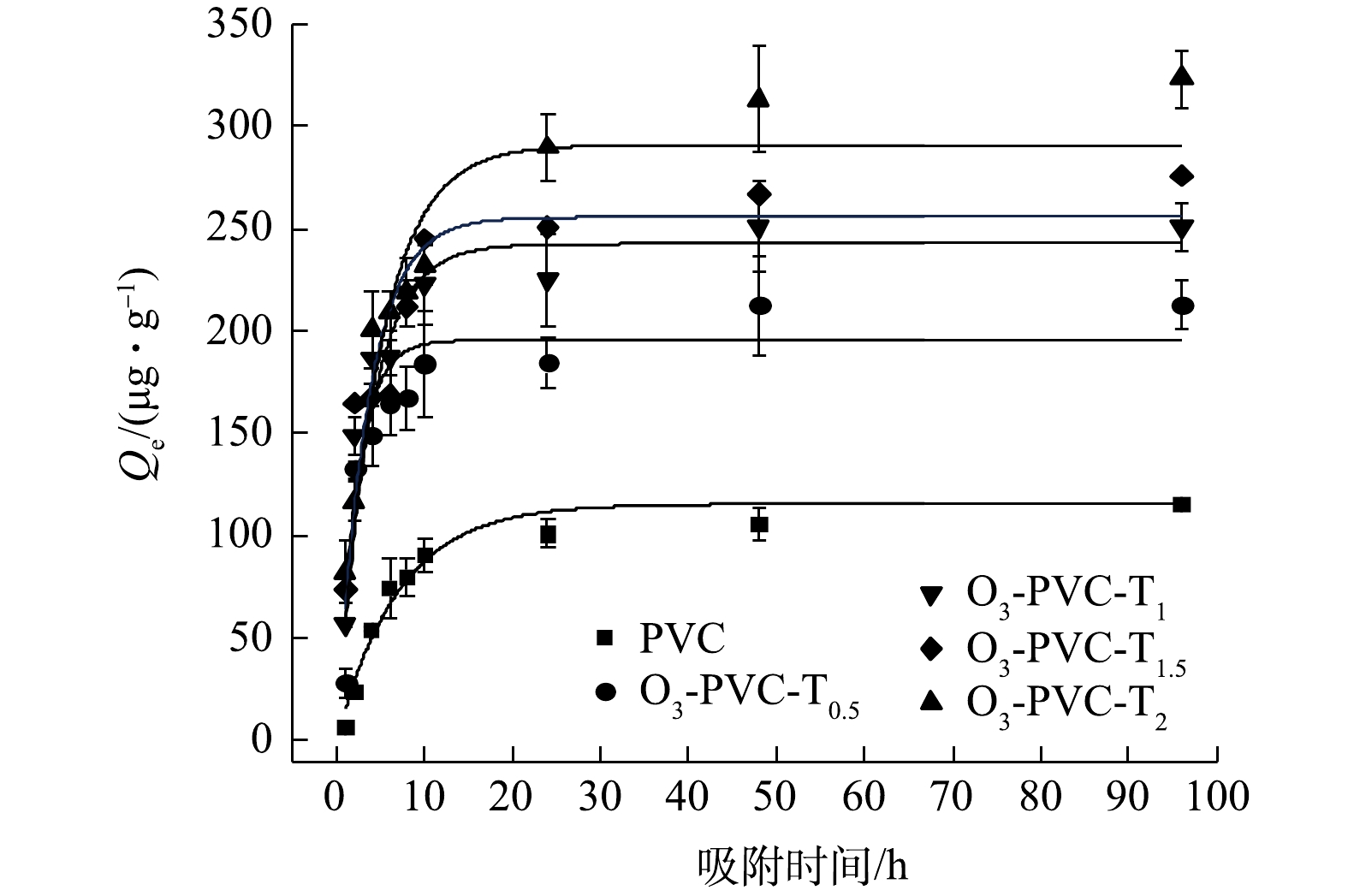
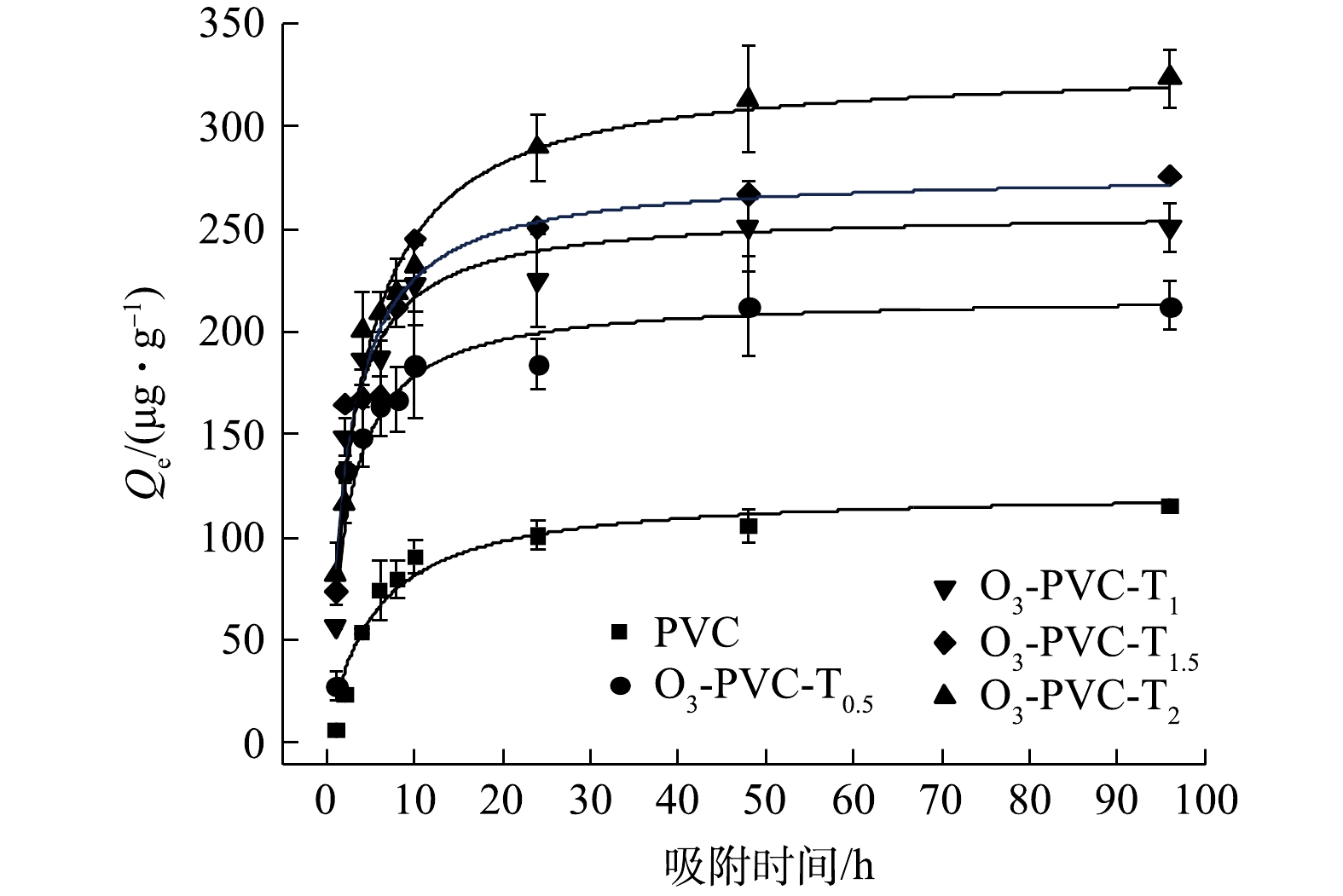
为进一步探讨联合老化PVC对MO吸附过程的影响,选取了老化程度较高的TiO2/O3/UV协同老化的PVC进行吸附MO的动力学实验。图7和图8为MO在老化前后PVC上的吸附动力学数据拟合结果。由图9可以看出,TiO2/O3/UV协同老化PVC颗粒对MO的吸附过程可以分为3个阶段,分别是快速吸附阶段、慢速吸附阶段和平衡阶段。在开始实验的6 h内,PVC对MO的吸附速度较快,吸附量可以达到各自平衡吸附量的75%左右,表明吸附初期的吸附速率较快,这可能与MPs水的初始浓度差带来的传质驱动力以及MPs表面存在大量的吸附位点有关;在之后的18 h内,老化前后的PVC对MO的吸附速率逐渐降低,吸附量略微增加步入缓慢吸附阶段;最终在48 h左右达到吸附平衡,这是因为两相的浓度差减小,MPs表面的吸附位点可能达到饱和[28-30]。此外,原始PVC和老化时间0.5、1、1.5、2 h的PVC的吸附量分别为115.522、212.314、250.798、275.791、323.091 ug·g−1,表明随着老化的持续进行,老化PVC的吸附能力呈现出递增的趋势。
为深入了解联合老化PVC对MO的吸附过程,分别采用拉格朗日准一级动力学模型、准二级动力学模型对吸附动力学数据进行拟合。表2总结了MO在老化前后PVC上吸附的2种动力学模型得出的参数。与准一级动力学模型相比(R2 > 0.775),准二级动力学模型较好的描述了吸附过程,其拟合的相关系数值 R2 > 0.871,其得出的吸附量 qe值能够更好的与实验测量的qe值相吻合,表明化学吸附很可能是吸附过程中的限制步骤。
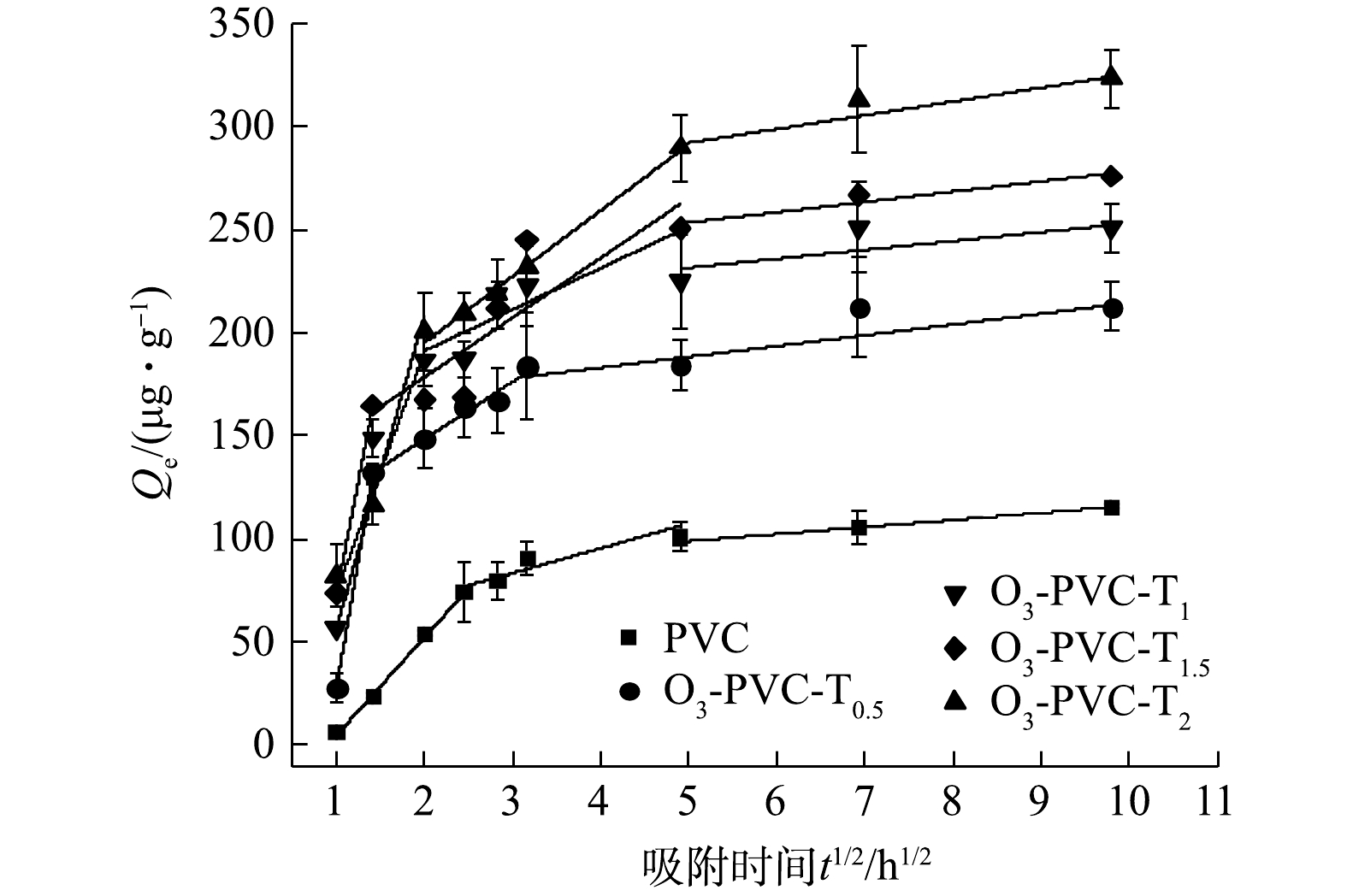
采用颗粒内扩散模型,深入分析了吸附行为及控制过程的关键阶段,如传质、内部扩散和动态平衡。由图9可以看出,整个吸附过程并不呈线性变化,根据现有的研究方法可以将其分为0~6、6~24和24~96 h 3个阶段进行拟合,拟合参数如表3所示。可以看出,一开始的颗粒内扩散模型拟合表现出较好的线性关系(R12 > 0.870),这一阶段主要为液膜扩散控制,反应速度快,发生外表面吸附,而第2阶段以颗粒内扩散为主,相互作用明显减弱,速率较慢( kw1>kw2),第3阶段可能达到动态平衡过程[31]。由qe与t1/2的曲线不通过原点,可以推测吸附控制步骤同时受到外表面扩散和粒子内扩散的控制。从以上分析结果可以看出,MO在PVC上的吸附过程是一个非均匀扩散过程。在吸附过程的早期阶段,吸附过程主要由外表面的液膜扩散控制,而在后期阶段,颗粒内扩散过程发挥了重要作用[32]。然而,粒子内扩散步骤所需的时间取决于许多因素(如吸附剂粒径、温度、溶质浓度等),并且难以控制或预测[33]。因此,通过人为划分吸附过程区间来确定kwi值可能存在一些偏差和不合理性。
-
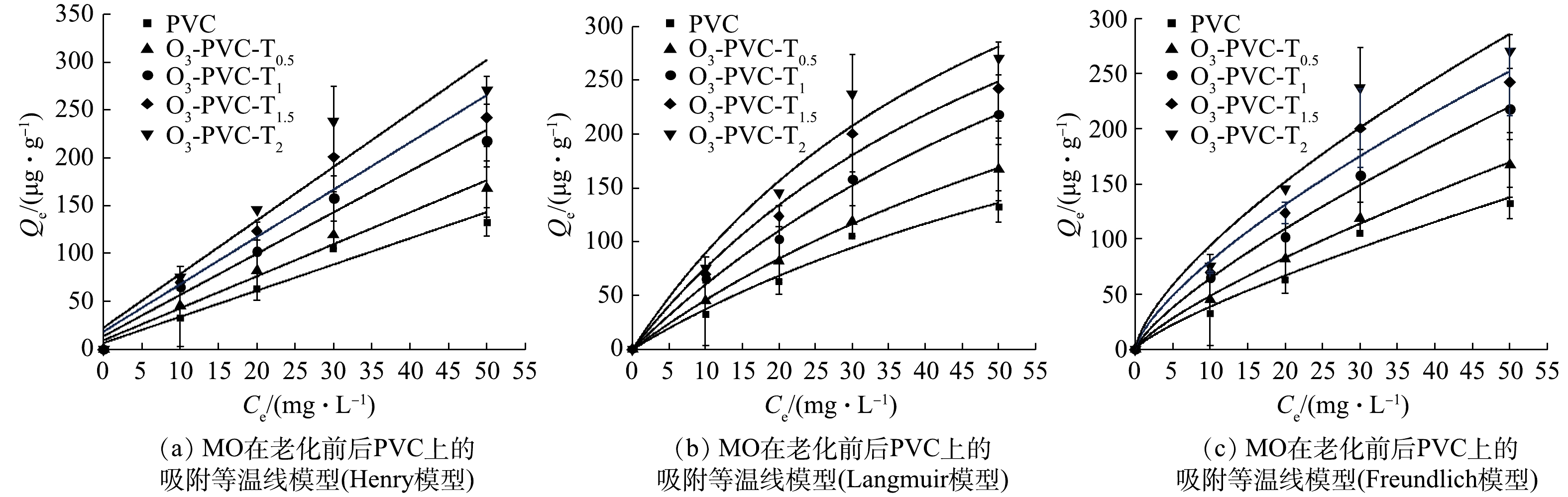
吸附等温线反映了吸附过程达到平衡时,吸附物分子在液相和固相之间的分布情况。本文采用Langmuir等温线、Freundlich等温线、Henry等温线来描述平衡吸附,结果如图10所示。Langmuir模型是一个非线性等温线,基于吸附和解吸与吸附剂表面积相关的模型,该模型认为吸附与吸附剂开放的表面积成正比,解吸与吸附剂覆盖的表面成正比。在这种情况下,吸附质分子的吸附发生在吸附剂的一个特定位点,而没有进一步的吸附发生在同一位点,适用于单分子层吸附。Freundlich模型,该模型建立在吸附过程发生在吸附剂的异质表面这一假说之上,适用于单分子层和多分子层[34]。Henry模型,在液相溶质平衡时,吸附剂中有机物的浓度和溶液中有机物的浓度成正比[35]。
表4列出了MO在TiO2/O3/UV联合老化不同处理时间下PVC上吸附得到的吸附等温线常数。由表4中可以看出,3种模型拟合的线性相关系数都较高,R2均大于0.90。其中,Langmuir等温线模型的线性回归系数R2大于0.914,低于Freundlich等温线模型 (R2>0.947~0.996)值最高。因此,Freundlich等温线能较好地拟合MO在PVC上的吸附,这表明MO和PVC之间的相互作用是在非均匀表面上的多层吸附,同时受到化学和物理吸附过程的影响,吸附机制主要以分配作用为主[36]。WU等[37]在研究中发现,5种双酚类物质在PVC上的吸附可以用Freundlich模型更好地描述。Freundlich模型的n值可以用来评估吸附效果和吸附过程,1/n表示浓度对吸附量影响的强弱。由表4中还可以看出,n在0.7~0.79,表明随着浓度的增加不同老化程度的PVC对MO的吸附量逐渐减小。这可能是由于在吸附过程中老化PVC的高能量吸附位点首先被占据,然后随着吸附的进行,低能吸附点位继续吸附MO。同时,随着老化时间的增加,KF逐渐增大,说明老化可以增强PVC对MO的亲和力。这可能是因为老化过程减少了PVC表面的负电荷,削弱了PVC和MO的静电斥力作用[36]。此外,结晶度对微塑料吸附的影响也是不可忽视的。GUO等[38] 在研究中发现不同PE颗粒对菲(phenanthrene)、林丹(lindane)、萘(naphthalene)的吸附随结晶度降低而增加。
-
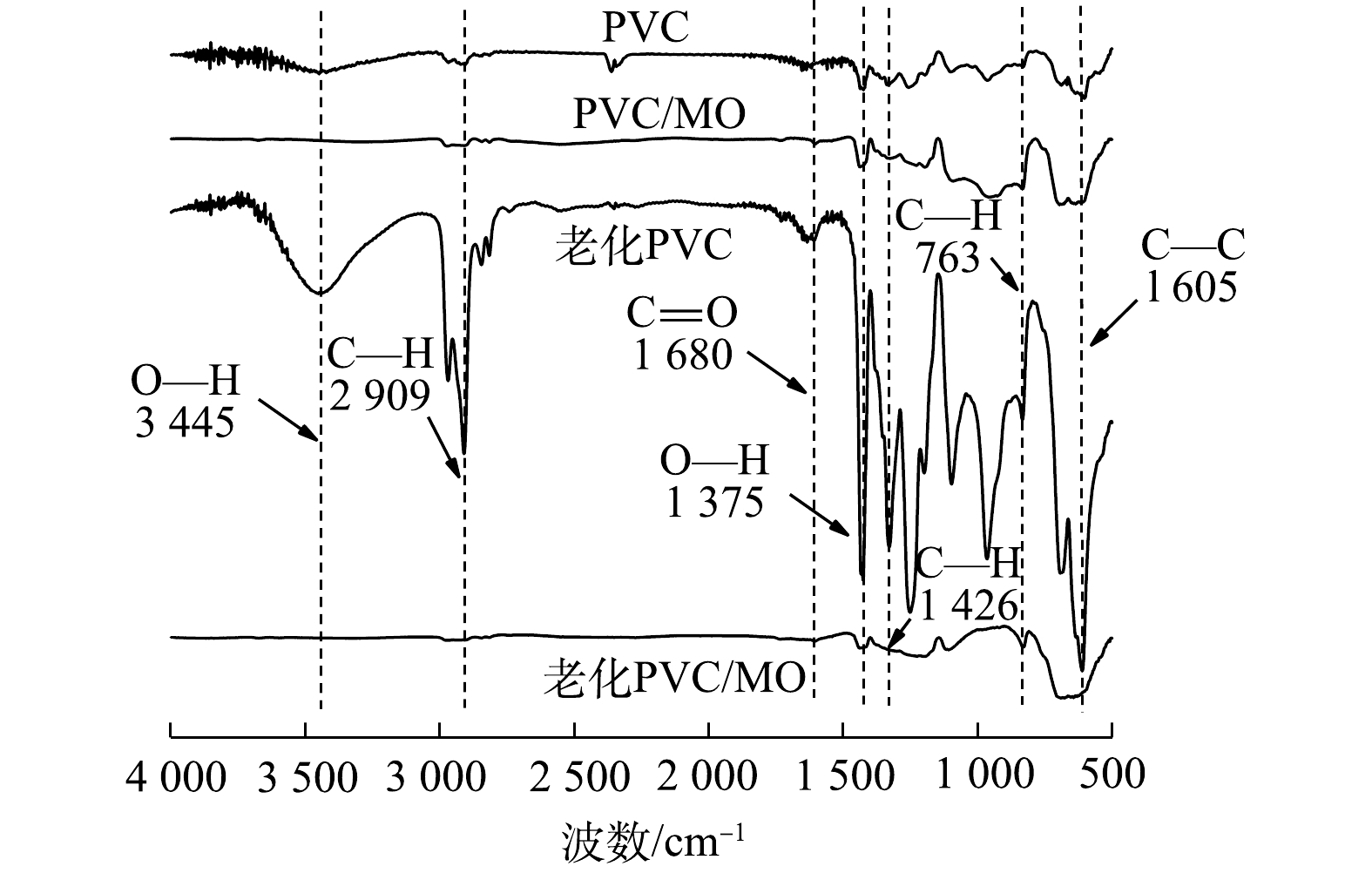
从微塑料吸附MO前后的红外光谱图(图11)上可以明显看出,老化PVC吸附MO后表面发生了明显的结构的变化。老化PVC吸附MO后在 3 445cm–1和3 775 cm–1的O-H伸缩振动消失,在2 909、1 426、763 cm–1的C-H伸缩振动消失,在1 680 cm–1的C=O伸缩振动消失,在605 cm–1处的C—Cl伸缩振动消失。进一步证实了,老化PVC对MO的吸附机理主要归因于羰基和羟基等含氧官能团增加,氢键作用及静电作用。
-
1)经过TiO2/O3/UV联合老化后的PVC表面出现裂纹,羰基和羟基等含氧官能团有所增加,CI升高,Zeta电位值降低。
2)一级动力学模型可以较好地拟合PVC对MO的吸附过程,而老化过后PVC更适合二级动力学模型,吸附模式为液膜扩散和颗粒内扩散,老化前的PVC对MO的吸附以物理吸附为主,而老化后的PVC对MO的吸附以化学吸附为主。
3)老化前后的PVC均能与Freundlich等温线较好地拟合,MO与PVC之间的相互作用是在非均匀表面上的多层吸附,吸附机制主要以分配作用为主。
4)含氧官能团、氢键及静电作用对老化PVC的吸附性能有重要影响。相比原始 PVC,老化后的PVC对MO的吸附量增加了2~3倍,老化处理可增强PVC对共存污染物的运载能力。
TiO2/UV/O3协同老化对微塑料吸附甲基橙的影响
Effect of TiO2/UV/O3 collaborative aging on adsorption of methyl orange by microplastics
-
摘要: 为了探究协同老化后的微塑料与有机污染物的相互作用机制,以PVC作为研究对象,采用TiO2/UV/O3协同老化方式,对比考察了老化前后PVC对甲基橙(MO)的吸附性能。结果表明,随着老化的进行,PVC颗粒表面碎片化加深,粒径明显减小,Zeta电位值降低,并出现了新的含氧官能团。原始PVC对MO的吸附符合准一级动力学模型,而老化后的PVC对MO的吸附符合准二级动力学模型,且主要的吸附模式均为液膜扩散和颗粒内扩散。动力学拟合结果表明老化前的PVC对MO的吸附以物理吸附为主,而老化后的PVC对MO的吸附以化学吸附为主。老化前后的PVC对MO的吸附均符合Freundlich等温吸附模型,表明MO与微塑料之间的相互作用是在非均匀表面上的多层吸附。以上研究结果可为微塑料携带有机污染物在环境中的迁移转化的行为提供参考。Abstract: To explore the interaction mechanism between microplastics and organic pollutants after collaborative aging, PVC was taken as the research object and TiO2/UV/O3 collaborative aging method was adopted to compare the adsorption characteristics of MO on PVC before and after aging. The results showed that with the aging process, the surface fragmentation of PVC particles was deepened, their particle size decreased obviously, their Zeta potential decreased, and new oxygen-containing functional groups appeared. The adsorption of MO on the original PVC conformed to the quasi-first-order kinetic model, while the adsorption of MO on the aging PVC conformed to the quasi-second-order kinetic model, and the main adsorption modes were liquid film diffusion and intra-particle diffusion. The difference of kinetics indicated that the adsorption of MO on PVC before aging was mainly physical adsorption, while the adsorption of MO on PVC after aging was mainly chemical adsorption. The adsorption of MO on PVC before and after aging conformed to Freundlich isothermal adsorption model, indicating that the interaction between MO and microplastics was the multi-layer adsorption on the non-uniform surface. Therefore, this can provide a reference for studying the migration and transformation behavior of organic pollutants carried by microplastics in the environment.
-
Key words:
- microplastics /
- collaborative aging /
- adsorption /
- methyl orange
-
甲基橙(methyl orange, MO)是一种水溶性偶氮染料,染料释放到天然水体中将严重影响水生生物生长,危害人类健康,具有致畸、致癌和致突变的作用[1]。MO在水中可电离为Na+与有机阴离子,并在微生物的作用下,产生芳香胺类中间体产物,随着食物链传播,在生物体内富集,加剧了人体健康的危害[2]。众所周知,塑料是一种可塑性强、化学稳定性高的高分子材料, 广泛应用于服装、包装、电子等各类产品中[3-6]。但是塑料的危害并没有引起人们的足够重视,80%的塑料产品没有经过有效处理就流入垃圾填埋场和自然环境中,并在重力作用、生物作用、水力作用、天气作用以及人类活动等外界驱动力的作用下,形成粒径<5 mm 的微塑料[7]。微塑料具有不规则的表面结构、较大的比表面积以及对疏水性污染物较强的亲和力,使其能够作为环境污染物的载体,影响污染物在环境中的迁移转化[8-10]。
环境中的微塑料容易受到光照作用而发生老化,老化后的微塑料会产生新的含氧基团(如羟基、羰基等),增加对有机污染物或重金属的吸附能力[11]。BHAGAT等[12]通过研究发现紫外(ultraviolet light, UV)老化增加了微塑料对有机污染物的亲和力;LI等[13]研究发现PE/PS/PA三种微塑料在UV老化后对Cr(VI)的吸附增强。但由于UV条件下微塑料老化速率较低,限制了人们研究微塑料在环境中与污染物的迁移转化。因此,关于微塑料的实验室加速老化技术逐渐被研究和开展。光催化技术是实验室加速微塑料老化的一种有效手段,常见的光催化剂有 TiO2、ZnO、Cds、H3BO3等,不同的光催化剂对PVC老化的影响如表1所示,其中 TiO2因具有活性高、热稳定性好、成本低等特点,使用最为广泛[14],但TiO2光催化降解过程中光激发产生的电子-空穴对的复合会导致催化活性的降低。由于O3本身及其在水中分解产生的自由基具有一定的氧化能力,可以达到加速老化的目的[15-16],因此将光催化和O3结合可以有效增强单一光催化技术的氧化能力,利用TiO2/UV协同老化过程中产生的 e−可与O3反应生成氧化性更强的·OH,抑制了电子-空穴对的复合,使光催化性能得到进一步提高[17]。综上所述,本文以PVC微塑料为研究对象,采用TiO2/UV/O3协同老化的方法对PVC进行加速老化实验,研究微塑料表面形貌及微观结构的变化,以及PVC对MO的吸附行为,为研究环境中的微塑料在污染物迁移转化过程中所起到的作用提供参考。
表 1 不同光催化剂对PVC的降解实例Table 1. Examples of degradation of microplastics by different photocatalysts1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
实验材料微塑料聚氯乙烯(polyvinyl chloride, PVC, 300 μm)购自科信达建材有限公司,使用前将PVC置于1 L大烧杯中,加入无水乙醇漫过塑料超过1/4,磁力搅拌30 min,过滤后加入相同量的纯水搅拌均匀,重复上述操作3次滤干,在35 ℃下烘干备用。实验试剂包括二氧化钛、甲基橙(纯度>96%)、无水乙醇(AR)。
主要实验仪器:电子分析天平(JJ124B型,常熟市双杰测试仪器厂);优普超纯水仪(UPHW-I-90T型,上海四科仪器设备有限公司);磁力搅拌器(Feb-78-2型,江苏荣华仪器制造有限公司);电热鼓风干燥箱(101-3A型,上海喆钛机械制造有限公司);紫外灯(GGZ175-1型,上海季光特种照明电器厂);恒温水浴搅拌器(SHA-C型,常州市金坛区指前镇旭日实验仪器厂);循环水式多用真空泵(SHZ-D(Ⅲ)型,郑州科丰仪器设备有限公司);低速台式离心机(TDL-4型,上海安亭科学仪器);数控超声波冲洗器(KQ-50DB型,昆山市超声仪器有限公司);臭氧机(CF-YG5型,北京山美水美环保高科技有限公司)。
1.2 老化塑料的制备
1) UV老化PVC 在UV光照下进行,将1 g微塑料样品加入1 L烧杯中搅拌均匀,加入一定量的纯水,用磁力搅拌器不间断搅拌保证微塑料和光催化剂在水体中充分接触。在室温下,于1×175 W紫外灯 (λ=365 nm) 下照射,期间每隔一定时间补充纯水。分别老化0.5、1、1.5和2 h后,超声离心30 min,将老化后的PVC进行抽滤,收集在9 mm的培养皿中,放入50 ℃烘箱中烘干备用,将样品分别编号为UV0.5-PVC,UV1-PVC,UV1.5-PVC,UV2-PVC。
2) UV/TiO2协同老化PVC 在UV光照下进行,将1 g微塑料样品和0.01 g TiO2光催化剂加入1 L烧杯中搅拌均匀,其余实验步骤与(1)UV老化相同,最后将样品分别编号为UV/T0.5-PVC,UV/T1-PVC,UV/T1.5-PVC,UV/T2-PVC。
3) TiO2/ UV /O3协同老化PVC 在UV光照下进行,将1 g微塑料样品和0.01 g TiO2光催化剂加入1 L烧杯中搅拌均匀,加入一定量的纯水,用磁力搅拌器不间断搅拌保证微塑料和光催化剂在水体中充分接触。在室温下,于1×175 W紫外灯 (λ=365 nm) 下照射,并在同一时刻通入5 L·min−1 的O3气体,其余实验步骤与(1)UV老化相同,最后将样品分别编号为O3-PVC-T0.5,O3-PVC-T1,O3-PVC-T1.5,O3-PVC-T2。
1.3 老化PVC的表征与分析
采用扫描电子显微镜(scanning electron microscope, SEM,FlexSEM 1 000,株式会社日立制作所)分析老化前后微塑料表面形貌特征变化;傅里叶变换红外光谱(Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, FTIR ,Nicolet is50,美国赛默飞)鉴别不同体系老化前后官能团的变化;X射线衍射(X-ray diffractometer, XRD ,Smartlab SE,日本理学)在扫描范围2θ=10.0 °~60.0 °,扫描速度5.0 °·min−1,管电流 50 mA,管电压 40 kV下测定光催化老化微塑料PVC的晶型结构;纳米激光粒度Zeta电位仪(Zeta potential,Zetasizer Pro,马尔文帕纳科)在高稳定性He-Ne激光器,4 mW,632.8 nm条件下测定体系中微塑料的固-液界面电性,并对PVC在与不同光催化剂共存下老化0.5、1、1.5、2 h后的失重率进行分析。
1.4 老化微塑料吸附MO实验
1)吸附动力学实验: 称取0.1 g不同老化程度的PVC于50 mL锥形瓶中,加入30 mg·L−1 MO溶液30 mL,用玻璃盖密封瓶口进行吸附动力学实验。将样品置于(25±1) ℃,150 r·min−1恒温水浴振荡器中避光振荡(1、2、4、6、8、10、24、48、96 h),静止5 min后,离心后进行抽滤,并用分光光度法测量滤液,每个实验组设置3个平行样,1个空白样。
2)吸附等温线实验: 准确称取0.1 g不同老化程度的PVC于50 mL锥形瓶中,分别加入质量浓度为10、20、30、50 mg·L−1 MO溶液30 mL并用玻璃盖密封。在恒温水浴振荡器中设置(25±1) ℃、150 r·min−1、避光条件下进行振荡48 h,离心后进行抽滤,并用分光光度法测量滤液,每个实验组设置3个平行样,1个空白样。
1.5 吸附机理实验及表征
分别称取0.1 g PVC和TiO2/ UV /O3协同老化2 h的PVC于50 mL锥形瓶中,加入30 mg·L−1 MO溶液30 mL,在恒温水浴振荡器中设置(25±1) ℃、150 r·min−1、避光条件下进行振荡48 h,在离心机中离心10 min(3 000 r·min−1),去除上清液,把吸附平衡后的微塑料干燥24 h。用玛瑙研钵充分研磨,采用Nicolet is50 傅里叶变换红外光谱仪测定,分辨率为4 cm−1,扫描范围为4 000~500 cm−1。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 老化微塑料的质量分析
微塑料在老化过程中的重量变化可以直观的反映微塑料的老化程度。图1反映了UV老化PVC,TiO2/UV协同老化PVC,TiO2/ O3/UV协同老化PVC的质量损失情况。结果表明, TiO2/ O3/UV协同老化对PVC的老化效果最好,失质量均随着老化时间的增加而增加,不难推测,在阳光下使用较低数量的光催化剂亦可以有效地加速PVC的降解老化。在THOMAS[21]的研究中也证实了这一点,他通过将微塑料PE和TiO2制备成复合膜在高时效性的自然光照下老化,结果表明复合膜在老化后失重率为18.1%,相比于纯样微塑料0.5%是一个质的提升。
2.2 微塑料的形态特征
图2为PVC在介导二氧化钛下的协同老化不同时间的扫描电镜图。从图中可以看出未进行老化的原始PVC表面相对光滑,老化0.5 h的微塑料表面已经出现了明显的裂纹和凸起。伴随着老化时间的增加,老化程度逐渐加深,微塑料表面的褶皱相比单一光催化老化更加密集,颗粒的粒径也随着老化时间的增大而减小,老化后的PVC直径约为160~230 μm。同时,在图2中可以清晰的观察到老化后的PVC微塑料颜色由白色转变为黄色,这是由于多烯序列的形成(脱氢氯化反应)和随后的氧化(光漂白)之间的竞争引起的,式 (1)~(5) 表示了PVC在TiO2/UV/O3协同老化作用下产生自由基的过程[22]。
O3→TiO2(吸附) (1) TiO2+hv→TiO2+h++e−(2)e−+O3→O−3 (3) O−3+H+→HO3⋅ (4) HO3⋅→O2+⋅OH (5) 2.3 微塑料的晶体结构特征
XRD可以反映聚合物表面晶相结构的比例,进一步分析光老化前后PVC的微观结构和结晶度,结果如图3所示。从图中可以看出,PVC 的 XRD 谱图呈弥散状态并未出现明显的结晶峰,表明 PVC 为非结晶性聚合物[23]。但与原始PVC相比,介导TiO2的光老化PVC在老化了不同时间后的吸收峰都有不同程度的降低,说明混合了TiO2的光老化实验会使PVC结晶度略有降低,这种现象可能是因为PVC表面部分官能团受到破坏以及新的官能团的产生。
2.4 微塑料红外图谱
为了揭示TiO2和O3联合UV光照处理后PVC微塑料化学性质的变化,采用红外光谱法测定了微塑料官能团的变化。如图4所示,在1 736 cm−1(C=O)和3 445 cm−1(O-H)出现了两个额外的吸收带,对应于COOH基团的拉伸振动。这些变化反映了PVC微塑料在光老化作用下表面结构的变化。2 909 cm−1的吸收带强度属于CH2的不对称拉伸,此外1 250 cm−1~1 400 cm−1处的吸收带和605 cm−1处的峰值强度增大,这些分别是因为CH-Cl的拉伸振动和C-Cl的拉伸振动。这些变化均与PVC的氧化反应和脱氯反应相对应。推测可能是聚合物的骨架受到·OH的攻击而断裂,因此带有C=O和O-H基团的有机分子脱落,在PVC表面形成了含氧官能团[24]。通过羰基(1 736 cm−1)和碳氢键(2 909 cm−1)的吸收带来确定和量化PVC的联合光催化老化作用。微塑料PVC在TiO2/O3/UV联合作用下老化的羰基指数如图5所示,可以看出羰基指数同老化时间的变化呈现逐渐上升的趋势,这表明,在这段时间内,PVC的光氧化主要是由羟基而不是羰基副产物形成[25]。
2.5 微塑料的 Zeta电位表征
老化前后的PVC均带负电荷,由图6可见,PVC、O-PVC-T0.5、O-PVC-T1、O-PVC-T1.5和O-PVC-T2电位分别为−31.68、−19.73、−16.73、−4.62和−3.80 mV。与原始PVC相比,老化PVC的负电荷更低,这可以解释为光氧化过程后PVC表面形成的羰基[26]。Zeta电位也可用于预测粒子的稳定性或分散性,基于表面电荷,老化PVC比原始PVC显示出更低的稳定性,并且似乎更容易团聚[27]。随后,C=O的增加和C-H基团的减少以及负电荷的减少可能会改变老化PVC在溶液中的芳香性和稳定性。
2.6 吸附动力学
为进一步探讨联合老化PVC对MO吸附过程的影响,选取了老化程度较高的TiO2/O3/UV协同老化的PVC进行吸附MO的动力学实验。图7和图8为MO在老化前后PVC上的吸附动力学数据拟合结果。由图9可以看出,TiO2/O3/UV协同老化PVC颗粒对MO的吸附过程可以分为3个阶段,分别是快速吸附阶段、慢速吸附阶段和平衡阶段。在开始实验的6 h内,PVC对MO的吸附速度较快,吸附量可以达到各自平衡吸附量的75%左右,表明吸附初期的吸附速率较快,这可能与MPs水的初始浓度差带来的传质驱动力以及MPs表面存在大量的吸附位点有关;在之后的18 h内,老化前后的PVC对MO的吸附速率逐渐降低,吸附量略微增加步入缓慢吸附阶段;最终在48 h左右达到吸附平衡,这是因为两相的浓度差减小,MPs表面的吸附位点可能达到饱和[28-30]。此外,原始PVC和老化时间0.5、1、1.5、2 h的PVC的吸附量分别为115.522、212.314、250.798、275.791、323.091 ug·g−1,表明随着老化的持续进行,老化PVC的吸附能力呈现出递增的趋势。
为深入了解联合老化PVC对MO的吸附过程,分别采用拉格朗日准一级动力学模型、准二级动力学模型对吸附动力学数据进行拟合。表2总结了MO在老化前后PVC上吸附的2种动力学模型得出的参数。与准一级动力学模型相比(R2 > 0.775),准二级动力学模型较好的描述了吸附过程,其拟合的相关系数值 R2 > 0.871,其得出的吸附量 qe值能够更好的与实验测量的qe值相吻合,表明化学吸附很可能是吸附过程中的限制步骤。
表 2 MO在老化前后PVC上的吸附动力学参数Table 2. Adsorption kinetics parameters of MO on PVC before and after aging样品 qe/(μg·g−1) 准一级动力学 准二级动力学 qe/(μg·g−1) K1 R2 qe/(μg·g−1) K2(×10−5) R2 PVC 115.522 115.455 0.143 0.989 122.886 161 0.948 O3-PVC-T0.5 212.314 195.531 0.454 0.775 217.416 211 0.871 O3-PVC-T1 250.798 242.483 0.275 0.972 258.5 200 0.927 O3-PVC-T1.5 275.791 255.491 0.289 0.813 277.505 158 0.902 O3-PVC-T2 323.091 290.845 0.217 0.907 329.7 89.726 0.979 采用颗粒内扩散模型,深入分析了吸附行为及控制过程的关键阶段,如传质、内部扩散和动态平衡。由图9可以看出,整个吸附过程并不呈线性变化,根据现有的研究方法可以将其分为0~6、6~24和24~96 h 3个阶段进行拟合,拟合参数如表3所示。可以看出,一开始的颗粒内扩散模型拟合表现出较好的线性关系(R12 > 0.870),这一阶段主要为液膜扩散控制,反应速度快,发生外表面吸附,而第2阶段以颗粒内扩散为主,相互作用明显减弱,速率较慢( kw1>kw2),第3阶段可能达到动态平衡过程[31]。由qe与t1/2的曲线不通过原点,可以推测吸附控制步骤同时受到外表面扩散和粒子内扩散的控制。从以上分析结果可以看出,MO在PVC上的吸附过程是一个非均匀扩散过程。在吸附过程的早期阶段,吸附过程主要由外表面的液膜扩散控制,而在后期阶段,颗粒内扩散过程发挥了重要作用[32]。然而,粒子内扩散步骤所需的时间取决于许多因素(如吸附剂粒径、温度、溶质浓度等),并且难以控制或预测[33]。因此,通过人为划分吸附过程区间来确定kwi值可能存在一些偏差和不合理性。
表 3 MO在老化前后PVC上的内扩散模型参数Table 3. Internal diffusion model parameters of MO on PVC before and after aging样品 第1阶段 第2阶段 第3阶段 C1 Kw1 R12 C2 Kw2 R22 C3 Kw3 R32 PVC −45.69 49.65 0.99 56.48 9.20 0.82 84.85 3.13 0.98 O3−PVC-T0.5 −224.87 252.53 0.99 93.32 27.58 0.98 162.16 5.23 0.79 O3−PVC-T1 −146.8 220.33 0.99 120.69 28.91 0.69 228.49 4.99 0.87 O3−PVC-T1.5 −94.84 151.89 0.87 151.17 20.04 0.46 210 4.3 0.70 O3−PVC-T2 −42.77 116.78 0.92 131.35 32 0.99 258.75 6.68 0.91 2.7 吸附等温线
吸附等温线反映了吸附过程达到平衡时,吸附物分子在液相和固相之间的分布情况。本文采用Langmuir等温线、Freundlich等温线、Henry等温线来描述平衡吸附,结果如图10所示。Langmuir模型是一个非线性等温线,基于吸附和解吸与吸附剂表面积相关的模型,该模型认为吸附与吸附剂开放的表面积成正比,解吸与吸附剂覆盖的表面成正比。在这种情况下,吸附质分子的吸附发生在吸附剂的一个特定位点,而没有进一步的吸附发生在同一位点,适用于单分子层吸附。Freundlich模型,该模型建立在吸附过程发生在吸附剂的异质表面这一假说之上,适用于单分子层和多分子层[34]。Henry模型,在液相溶质平衡时,吸附剂中有机物的浓度和溶液中有机物的浓度成正比[35]。
表4列出了MO在TiO2/O3/UV联合老化不同处理时间下PVC上吸附得到的吸附等温线常数。由表4中可以看出,3种模型拟合的线性相关系数都较高,R2均大于0.90。其中,Langmuir等温线模型的线性回归系数R2大于0.914,低于Freundlich等温线模型 (R2>0.947~0.996)值最高。因此,Freundlich等温线能较好地拟合MO在PVC上的吸附,这表明MO和PVC之间的相互作用是在非均匀表面上的多层吸附,同时受到化学和物理吸附过程的影响,吸附机制主要以分配作用为主[36]。WU等[37]在研究中发现,5种双酚类物质在PVC上的吸附可以用Freundlich模型更好地描述。Freundlich模型的n值可以用来评估吸附效果和吸附过程,1/n表示浓度对吸附量影响的强弱。由表4中还可以看出,n在0.7~0.79,表明随着浓度的增加不同老化程度的PVC对MO的吸附量逐渐减小。这可能是由于在吸附过程中老化PVC的高能量吸附位点首先被占据,然后随着吸附的进行,低能吸附点位继续吸附MO。同时,随着老化时间的增加,KF逐渐增大,说明老化可以增强PVC对MO的亲和力。这可能是因为老化过程减少了PVC表面的负电荷,削弱了PVC和MO的静电斥力作用[36]。此外,结晶度对微塑料吸附的影响也是不可忽视的。GUO等[38] 在研究中发现不同PE颗粒对菲(phenanthrene)、林丹(lindane)、萘(naphthalene)的吸附随结晶度降低而增加。
表 4 老化前后的PVC对 MO的吸附等温线拟合参数表Table 4. The fitting parameters of PVC adsorption isotherm towards MO before and after aging样品 Henry Langmuir Freundlich Kd×10−3/(L·g−1) R2 Qm/(μg·g−1) KL R2 KF/(μg·g−1) n R2 PVC 6.601 0.948 401.811 0.010 0.952 6.268 0.790 0.969 O3-PVC-T0.5 3.338 0.976 506.753 0.010 0.989 8.031 0.780 0.996 O3-PVC-T1 4.306 0.971 579.578 0.015 0.949 11.069 0.764 0.993 O3-PVC-T1.5 4.934 0.928 604.564 0.017 0.914 15.421 0.715 0.968 O3-PVC-T2 5.587 0.900 633.214 0.011 0.947 19.181 0.691 0.987 2.8 吸附机理
从微塑料吸附MO前后的红外光谱图(图11)上可以明显看出,老化PVC吸附MO后表面发生了明显的结构的变化。老化PVC吸附MO后在 3 445cm–1和3 775 cm–1的O-H伸缩振动消失,在2 909、1 426、763 cm–1的C-H伸缩振动消失,在1 680 cm–1的C=O伸缩振动消失,在605 cm–1处的C—Cl伸缩振动消失。进一步证实了,老化PVC对MO的吸附机理主要归因于羰基和羟基等含氧官能团增加,氢键作用及静电作用。
3. 结论
1)经过TiO2/O3/UV联合老化后的PVC表面出现裂纹,羰基和羟基等含氧官能团有所增加,CI升高,Zeta电位值降低。
2)一级动力学模型可以较好地拟合PVC对MO的吸附过程,而老化过后PVC更适合二级动力学模型,吸附模式为液膜扩散和颗粒内扩散,老化前的PVC对MO的吸附以物理吸附为主,而老化后的PVC对MO的吸附以化学吸附为主。
3)老化前后的PVC均能与Freundlich等温线较好地拟合,MO与PVC之间的相互作用是在非均匀表面上的多层吸附,吸附机制主要以分配作用为主。
4)含氧官能团、氢键及静电作用对老化PVC的吸附性能有重要影响。相比原始 PVC,老化后的PVC对MO的吸附量增加了2~3倍,老化处理可增强PVC对共存污染物的运载能力。
-
表 1 不同光催化剂对PVC的降解实例
Table 1. Examples of degradation of microplastics by different photocatalysts
表 2 MO在老化前后PVC上的吸附动力学参数
Table 2. Adsorption kinetics parameters of MO on PVC before and after aging
样品 qe/(μg·g−1) 准一级动力学 准二级动力学 qe/(μg·g−1) K1 R2 qe/(μg·g−1) K2(×10−5) R2 PVC 115.522 115.455 0.143 0.989 122.886 161 0.948 O3-PVC-T0.5 212.314 195.531 0.454 0.775 217.416 211 0.871 O3-PVC-T1 250.798 242.483 0.275 0.972 258.5 200 0.927 O3-PVC-T1.5 275.791 255.491 0.289 0.813 277.505 158 0.902 O3-PVC-T2 323.091 290.845 0.217 0.907 329.7 89.726 0.979 表 3 MO在老化前后PVC上的内扩散模型参数
Table 3. Internal diffusion model parameters of MO on PVC before and after aging
样品 第1阶段 第2阶段 第3阶段 C1 Kw1 R12 C2 Kw2 R22 C3 Kw3 R32 PVC −45.69 49.65 0.99 56.48 9.20 0.82 84.85 3.13 0.98 O3−PVC-T0.5 −224.87 252.53 0.99 93.32 27.58 0.98 162.16 5.23 0.79 O3−PVC-T1 −146.8 220.33 0.99 120.69 28.91 0.69 228.49 4.99 0.87 O3−PVC-T1.5 −94.84 151.89 0.87 151.17 20.04 0.46 210 4.3 0.70 O3−PVC-T2 −42.77 116.78 0.92 131.35 32 0.99 258.75 6.68 0.91 表 4 老化前后的PVC对 MO的吸附等温线拟合参数表
Table 4. The fitting parameters of PVC adsorption isotherm towards MO before and after aging
样品 Henry Langmuir Freundlich Kd×10−3/(L·g−1) R2 Qm/(μg·g−1) KL R2 KF/(μg·g−1) n R2 PVC 6.601 0.948 401.811 0.010 0.952 6.268 0.790 0.969 O3-PVC-T0.5 3.338 0.976 506.753 0.010 0.989 8.031 0.780 0.996 O3-PVC-T1 4.306 0.971 579.578 0.015 0.949 11.069 0.764 0.993 O3-PVC-T1.5 4.934 0.928 604.564 0.017 0.914 15.421 0.715 0.968 O3-PVC-T2 5.587 0.900 633.214 0.011 0.947 19.181 0.691 0.987 -
[1] DAMAYANTI D, SAPUTRI D R, MARPAUNG D S S, et al. Current prospects for plastic waste treatment[J]. Polymers, 2022, 14: 3133. doi: 10.3390/polym14153133 [2] XANTHOS D, WALKER T R. International policies to reduce plastic marine pollution from single-use plastics (plastic bags and microbeads): A review[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2017, 118(1/2): 17-26. [3] YU L, BI J, SONG Y, et al. Isotherm, Thermodynamics, and kinetics of methyl orange adsorption onto magnetic resin of chitosan microspheres[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(22): 13839. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213839 [4] 宋欢, 罗锡明, 张莉, 等. 微塑料对水中甲基橙的吸附特征分析[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(6): 19-27. doi: 10.13745/j.esf.sf.2019.7.1 [5] LI J, SONG Y, CAI Y. Focus topics on microplastics in soil: Analytical methods, occurrence, transport, and ecological risks[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 257: 113570. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113570 [6] C. T R, J. M C, S. V S F, et al. Plastics, the environment and human health: Current consensus and future trends[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B, 2009, 364(1526): 2153-2166. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2009.0053 [7] THOMPSON R C, OLSEN Y, MITCHELL R P, et al. Lost at sea: Where is all the plastic?[J]. Science (New York, NY), 2004, 304(5672): 838. doi: 10.1126/science.1094559 [8] WANG Q, XIAOXUE W, ZHANG Y, et al. The toxicity of virgin and UV-aged PVC microplastics on the growth of freshwater algae chlamydomonas reinhardtii[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 749: 141603. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141603 [9] HOLMES L A, TURNER A, THOMPSON R C. Adsorption of trace metals to plastic resin pellets in the marine environment[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2012, 160(1): 42-48. [10] REN Z F, GUI X Y, XU X Y, et al. Microplastics in the soil-groundwater environment: Aging, migration, and co-transport of contaminants-a critical review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 419: 216455. [11] 吴小伟, 黄何欣悦, 石妍琦, 等. 水环境中微塑料的光老化过程及影响因素研究进展[J]. 科学通报, 2021, 66(36): 4619-4632. [12] BHAGAT K, BARRIOS A C, RAJWADE K, et al. Aging of microplastics increases their adsorption affinity towards organic contaminants[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 298: 134238. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134238 [13] LI Y, ZHANG Y, SU F, et al. Adsorption behaviour of microplastics on the heavy metal Cr(VI) before and after ageing[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 302: 134865. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134865 [14] ZHAO X, LI Z W, CHEN Y, et al. Enhancement of photocatalytic degradation of polyethylene plastic with CuPc modified TiO2 photocatalyst under solar light irradiation[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2008, 254(6): 1825-1829. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2007.07.154 [15] ENCINAS A, RIVAS F J, BELTRAN F J, et al. Combination of black-Light photocatalysis and ozonation for emerging contaminants degradation in secondary effluents[J]. Chemical Engineering & Technology, 2013, 36(3): 492-499. [16] 薛彬, 蓝文陆, 林海英, 等. 老化微塑料对Hg(Ⅱ)的吸附解吸行为及机理研究环境科学与技术[J]. 2022, 45(8): 31-37. [17] WANG Q, ZHANG Y, WANGJIN X, et al. The adsorption behavior of metals in aqueous solution by microplastics effected by UV radiation[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2020, 87: 272-280. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2019.07.006 [18] ZHANG K, CAO W, ZHANG J. Solid-phase photocatalytic degradation of PVC by Tungstophosphoric acid: A novel method for PVC plastic degradation[J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2004, 276(1-2): 67-73. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2004.07.056 [19] YANG C, GONG C, PENG T, et al. High photocatalytic degradation activity of the polyvinyl chloride (PVC)-vitamin C(VC)-TiO2 nano-composite film[J]. Jourunal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 178(1-3): 152-156. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.01.056 [20] CHAKRABARTI S, CHAUDHURI B, BHATTACHARJEE S, et al. Degradation mechanism and kinetic model for photocatalytic oxidation of PVC-ZnO composite film in presence of a sensitizing dye and UV radiation[J]. Jourunal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 154(1-3): 230-236. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.10.015 [21] THOMAS R T, NAIR V, SANDHYARANI N. TiO2 nanoparticle assisted solid phase photocatalytic degradation of polythene film: A mechanistic investigation[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2013, 422: 1-9. [22] 孙若阳, 赵显一. 二氧化钛光催化剂的制备及应用进展[J]. 当代化工, 2023, 52(1): 202-208. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2023.01.043 [23] 程新峰, 留芳芳, 潘玲, 等. 微塑料老化对其理化性质和盐酸四环素吸附行为的影响研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2023, 43(3): 150-161. [24] MIAO F, LIU Y, GAO M, et al. Degradation of polyvinyl chloride microplastics via an electro-Fenton-like system with a TiO2/graphite cathode[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 399: 123023. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123023 [25] UHEIDA A, MEJIA H G, ABDEL-REHIM M, et al. Visible light photocatalytic degradation of polypropylene microplastics in a continuous water flow system[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 406: 124299. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124299 [26] ZHANG Z, FLAHERTY D W. Modified potentiometric titration method to distinguish and quantify oxygenated functional groups on carbon materials by pKa and chemical reactivity - ScienceDirect[J]. Carbon, 2020, 166: 436-445. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.05.040 [27] ZHU X, ZHAO W, CHEN X, et al. Growth inhibition of the microalgae Skeletonema costatum under copper nanoparticles with microplastic exposure[J]. Marine Environmental Research, 2020, 158: 105005. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2020.105005 [28] MA J, ZHAO J, ZHU Z, et al. Effect of microplastic size on the adsorption behavior and mechanism of triclosan on polyvinyl chloride[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 254: 113104. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113104 [29] HUFFER T, HOFMANN T. Sorption of non-polar organic compounds by micro-sized plastic particles in aqueous solution[J]. Environmental pollution, 2016, 214: 194-201. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.04.018 [30] WANG W, WANG J. Comparative evaluation of sorption kinetics and isotherms of pyrene onto microplastics[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 193: 567-573. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.11.078 [31] ZHOU X, WEI J, LIU K, et al. Adsorption of bisphenol A based on synergy between hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interaction[J]. Langmuir, 2014, 30(46): 13861-13868. doi: 10.1021/la502816m [32] EL'TEKOVA N A, EL'TEKOV Y A. Kinetics of the adsorption of polystyrene macromolecules from dilute solutions in methyl ethyl ketone on carbon black[J]. Russion Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2007, 81(4): 602-606. doi: 10.1134/S0036024407040176 [33] WU F C, TSENG R L, JUANG R S. Initial behavior of intraparticle diffusion model used in the description of adsorption kinetics[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2009, 153(1/2/3): 1-8. [34] HAMEED B H, TAN I A W, AHMAD A L. Adsorption isotherm, kinetic modeling and mechanism of 2, 4, 6-trichlorophenol on coconut husk-based activated carbon[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2008, 144(2): 235-244. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2008.01.028 [35] LIU F F, LIU G Z, ZHU Z L, et al. Interactions between microplastics and phthalate esters as affected by microplastics characteristics and solution chemistry[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 214: 688-694. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.09.174 [36] ANDERSSON K I, ERIKSSON M, NORGREN M. Removal of lignin from wastewater generated by mechanical pulping using activated charcoal and fly ash: Adsorption kinetics[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2011, 50(13): 7733-7739. [37] WU P, CAI Z, JIN H, et al. Adsorption mechanisms of five bisphenol analogues on PVC microplastics[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 650: 671-678. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.049 [38] GUO X, WANG X, ZHOU X, et al. Sorption of four hydrophobic organic compounds by three chemically distinct polymers: Role of chemical and physical composition[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2012, 46(13): 7252-7259. doi: 10.1021/es301386z 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 葛建华,辛侠彬,卫洲,刘丹,张世文. O_3对PET微塑料吸附有机污染物的影响机制. 安徽理工大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(06): 53-62 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)
-






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: