-
随着经济的快速发展以及人们工农业生产活动的增多,大量含磷废水排入环境中,导致河道和湖泊的水质急剧恶化,众多流域爆发藻类事件[1],出现水体黑臭现象[2],使得水体的生态功能部分或全部丧失[3]。有研究[4]表明,过量磷含量是导致淡水体系中藻类大量繁殖较为关键的因素。因此,经济高效的除磷技术的开发成为研究的重点。目前污水除磷技术主要包括化学沉淀法、离子交换法、生物法和吸附法等[5]。其中,吸附法因具有材料来源广、去除率高、经济效益好、可重复利用等优势,在污水除磷中得到广泛应用[6]。因此,高效吸附材料的开发至关重要。
膨润土是一种以蒙脱石为有效成分的黏土矿物,因其储量丰富、价格低廉且具有较大的阳离子交换容量和优良的吸附性能等特点[7],常被当作优良吸附剂用于水体中重金属、有机物等污染物的去除,但在实际生产应用中未改性膨润土往往难以达到处理要求,一般需要通过改性来提高其处理效果[8]。常用的膨润土改性方法[9]有钠化改性法、酸改性法、焙烧改性法、盐改性法、有机改性法和无机柱撑改性法、无机-有机复合改性法等。有研究[10]表明,两性-阳离子表面活性剂复合改性膨润土可提高其对水中重金属和有机物的去除能力,阳离子表面活性剂能提高其对磷酸盐的去除能力[11],以上改性研究均较为广泛,但两性-阳离子表面活性剂复合改性膨润土吸附磷酸盐则鲜有研究报道。
本研究采用两性表面活性剂——十二烷基二甲基磺丙基甜菜碱(DSB)和阳离子表面活性剂溴代十六烷基吡啶(CPB)复合改性膨润土,并对其表面形貌和结构进行了相关表征,考察了改性比例、温度、pH等因素对其吸附磷酸盐的影响效果,为两性-阳离子表面活性剂复合改性膨润土吸附除磷提供参考。
全文HTML
-
主要仪器:SHA-B恒温振荡器(上海力辰邦西仪器科技有限公司),TG16-WS数显台式高速离心机(湖南湘仪离心机仪器有限公司),FE20实验室pH计(梅特勒-托利多仪器有限公司),紫外-可见分光光度计(上海仪电分析仪器有限公司)。
主要试剂:十二烷基二甲基磺丙基甜菜碱(DSB),购于南京旋光科技有限公司;溴代十六烷基吡啶(CPB)、磷酸二氢钾(KH2PO4)、AgNO3,购于国药集团化学试剂有限公司。以上试剂均为分析纯。实验用水为去离子水。
材料:钠基膨润土,购于浙江安吉,其阳离子交换量(CEC)为0.825 mmol·g−1,蒙脱石含量为82%。
-
称取一定质量膨润土,配制成膨润土浆液(水土比10∶1),按CEC的不同比例[12]计算并称取一定质量DSB(CPB)加入其中,60 ℃恒温搅拌4 h,静置冷却后抽滤分离,并洗涤至无Br−(AgNO3检测),于60 ℃烘干后,研磨过100目筛,即得改性膨润土,其名称使用数字前缀加相应的表面活性剂英文缩写表示。
本研究中DSB改性比例以CEC为基准,设置50%和100% 2个比例(0.5DSB、1.0DSB),复合改性加入CPB比例以膨润土CEC为基准,在DSB改性基础上,设置25%、50%、100%和150% 4个比例(0.5DSB+0.25CPB、0.5DSB+0.5CPB、0.5DSB+1.0CPB、0.5DSB+1.5CPB、1.0DSB+0.25CPB、1.0DSB+0.5CPB、1.0DSB+1.0CPB、1.0DSB+1.5CPB)。
-
采用X射线衍射仪(PANalytical X`Pert PRO型,PANalytical公司,荷兰)对改性膨润土的晶体结构进行分析;采用红外光谱仪器(Nicolet iS10型,Thermo Scientifc公司,美国)进行傅里叶红外光谱分析;采用热场式发射扫描电镜(SU5000型,日立,日本)对改性膨润土表面形貌进行观察;采用静态接触角仪(XG-CAMA型,上海轩准仪器有限公司,中国)对改性膨润土的亲疏水性进行分析;采用热重分析仪(SDT-Q600型,沃特士公司,美国)对改性膨润土的热稳定性进行分析。
-
按照钼酸铵分光光度法(GB 11893-1989)中的要求配置50 mg·L−1的模拟含磷废水标准储备溶液。称取0.25 g土样于250 mL具塞锥形瓶中,加入50 mL模拟含磷废水,以150 r·min−1恒温振荡5 h,静置离心,采用钼酸铵分光光度法(GB 11893-1989)测定上清液中磷酸盐的质量浓度,根据式(1)计算平衡吸附量Qe。
式中:Qe为土样对磷酸盐的平衡吸附量,mg·g−1;C0和Ce分别为溶液磷酸盐初始浓度和平衡浓度,mg·L−1;m为土样质量,g;V为加入模拟含磷废水体积,mL。每个实验处理均设置3个重复,实验结果取平均值。
在进行吸附动力学实验时,分别称取0.25 g原土、两性改性膨润土(0.5DSB)、复合改性膨润土(0.5DSB+1.5CPB),加入至初始浓度为50 mg·L−1的50 mL模拟含磷废水中,在pH=7、30 ℃的条件下,控制反应时间为0~5 h,测定膨润土吸附量随时间的变化。
在进行吸附等温线实验时,分别量取50 mL浓度梯度为1、2、4、6、8、12、20、30、40、50 mg·L−1 模拟含磷废水于250 mL锥形瓶中,称取0.25 g各土样加入锥形瓶中,在pH=7、30 ℃、反应时间为5 h条件下反应,测定膨润土吸附量随初始浓度的变化。
-
分别称取0.25 g复合改性膨润土0.5DSB+1.5CPB和1.0DSB+1.5CPB,将其加入到初始浓度为50 mg·L−1的50 mL模拟含磷废水中,在30 ℃、反应时间为5 h条件下,控制溶液pH为3、5、7、9,测定膨润土吸附量随pH的变化。
分别称取0.25 g复合改性膨润土0.5DSB+1.5CPB和1.0DSB+1.5CPB,将其加入到初始浓度为50 mg·L−1的50 mL模拟含磷废水中,在pH=7、反应时间为5 h的条件下,分别控制反应温度为20、30、40 ℃,再测定膨润土吸附量随温度的变化。
1.1. 主要仪器与试剂
1.2. 改性膨润土制备
1.3. 改性膨润土的表征
1.4. 实验方法
1.5. 反应条件对吸附的影响
-
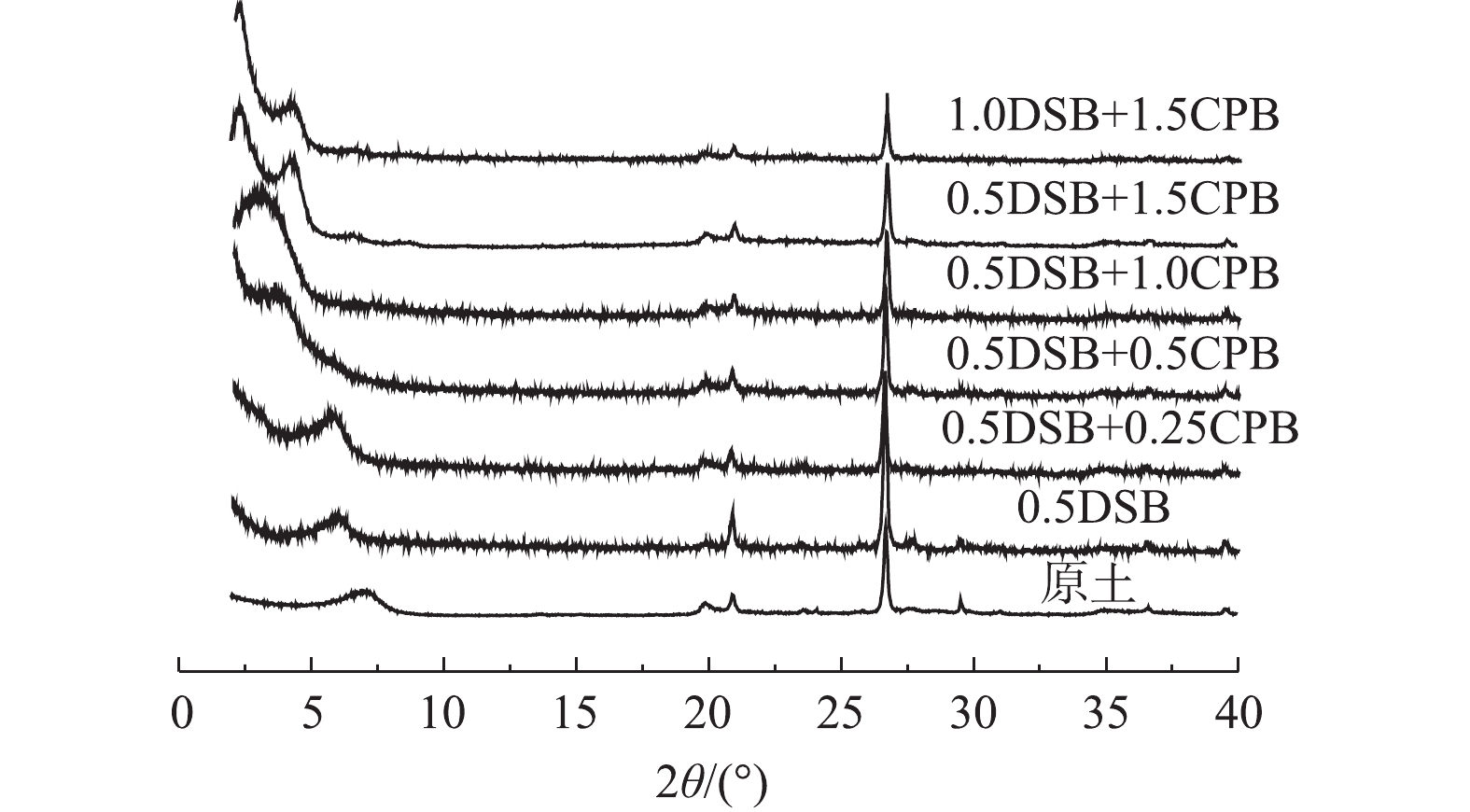
图1为改性前后各膨润土XRD图谱。由图1可见,0.5DSB两性改性膨润土衍射峰相较于原土向小角度偏移,其衍射角2θ分别为6.080°和6.911°;对于复合改性膨润土,随着CPB改性比例的增加,进入膨润土层间的改性剂量增多,衍射峰继续向小角度偏移,衍射角2θ分别为5.798°、3.572°、3.041°、2.344°;当CPB改性比例相同时(1.5CEC),1.0DSB+1.5CPB改性膨润土衍射角小于0.5DSB+1.5CPB为2.243°。采用文献中的方法[13]计算其层间距,膨润土层间距d(001)由原土的1.278 nm分别变为1.452、1.523、2.471、2.903、3.766、3.935 nm,其大小的变化趋势与衍射角的变化一致。可见随改性比例增加,各膨润土层间距逐渐增大,这表明改性剂插层成功。
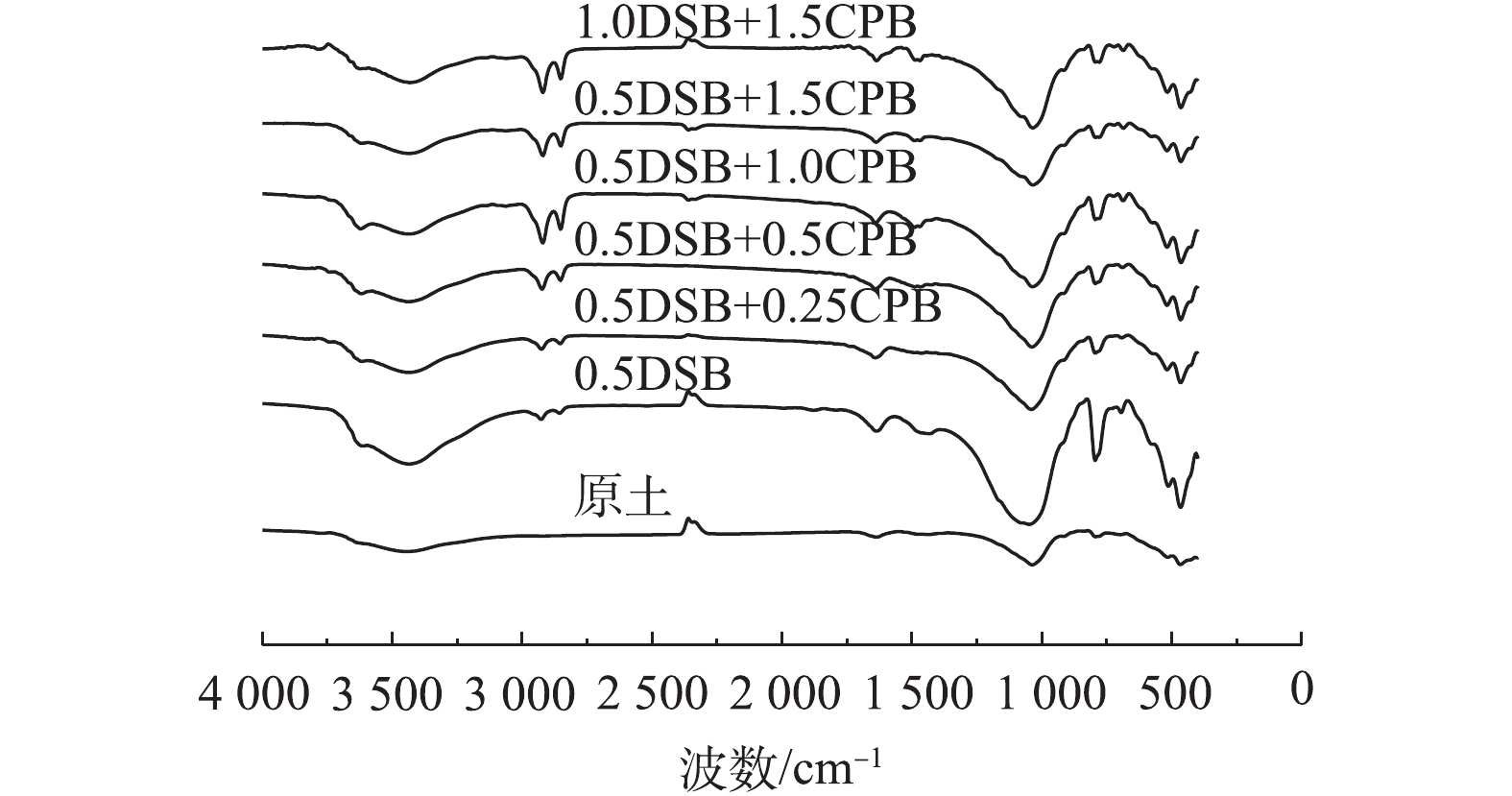
图2为改性前后各膨润土FT-IR图谱。由图2可知,所有土样均在1 037~1 041 cm−1处有Si—O—Si的伸缩振动峰,在518 cm−1附近出现Si—O—Al的伸缩振动峰,这说明改性并没有改变膨润土的层状硅酸盐结构,基本骨架未被破坏[14-15]。与原土相比,改性膨润土在2 852~2 927 cm−1处出现C—H的伸缩振动峰,这说明膨润土改性成功[16]。
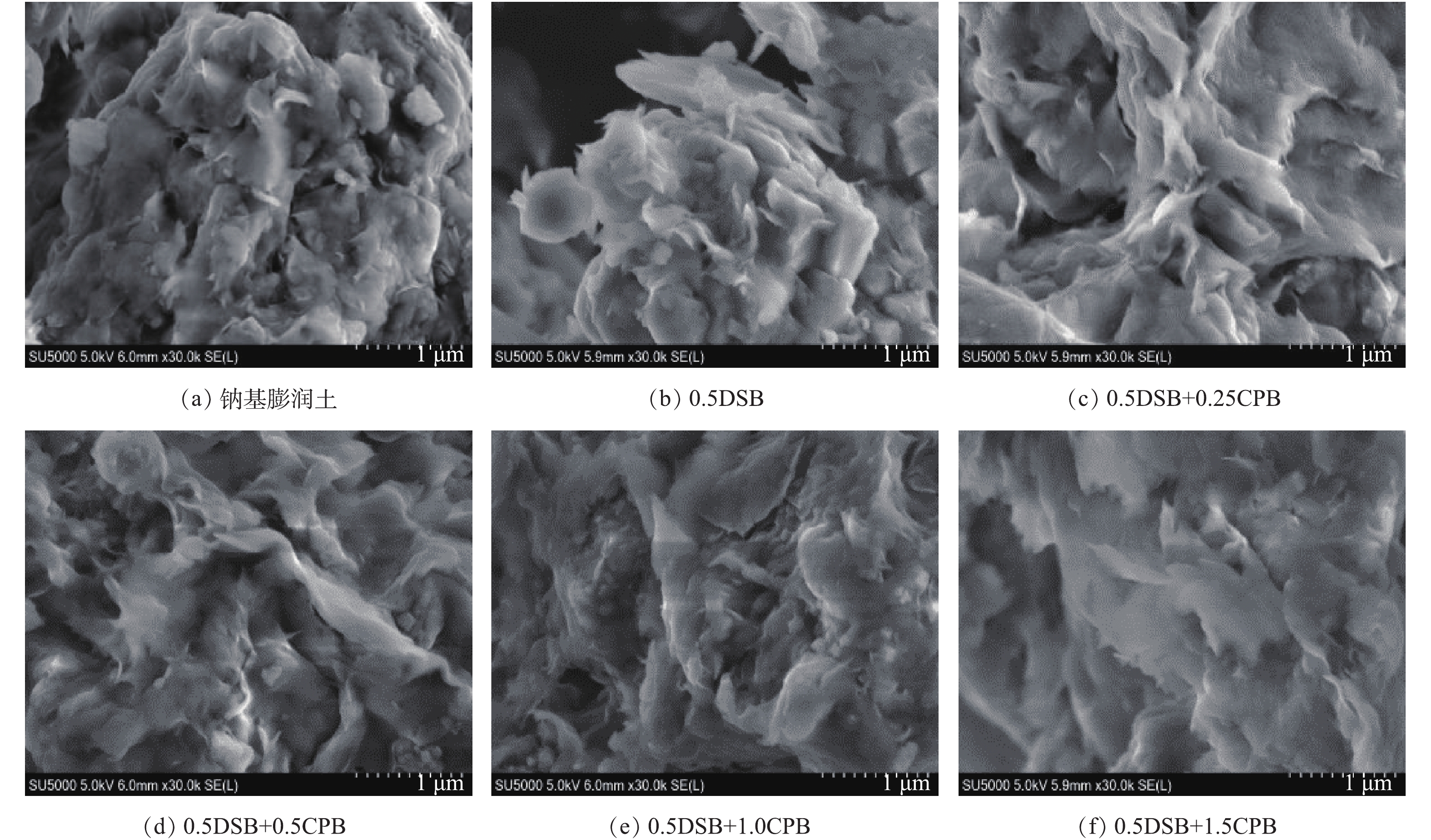
图3为改性前后膨润土SEM图。由图3可知,钠基膨润土原土颗粒尺寸较大,表面结构紧密,晶片层较厚且孔隙相对较少。随着改性剂的插入,钠基膨润土层状结构开始剥落,出现明显不规则的松散片状结构,片层边缘棱角锋利,且层间空隙变大[17],这表明改性剂进入膨润土层间,撑开片层的同时,部分附着在膨润土表面,改变了膨润土形貌特征。当改性比例不断增加,片状结构变得更为松散蓬松,层间空隙也越来越大,同时片层间存在的一些细小颗粒,进一步撑开膨润土片层,使层间距增大,这与XRD分析结果相吻合。
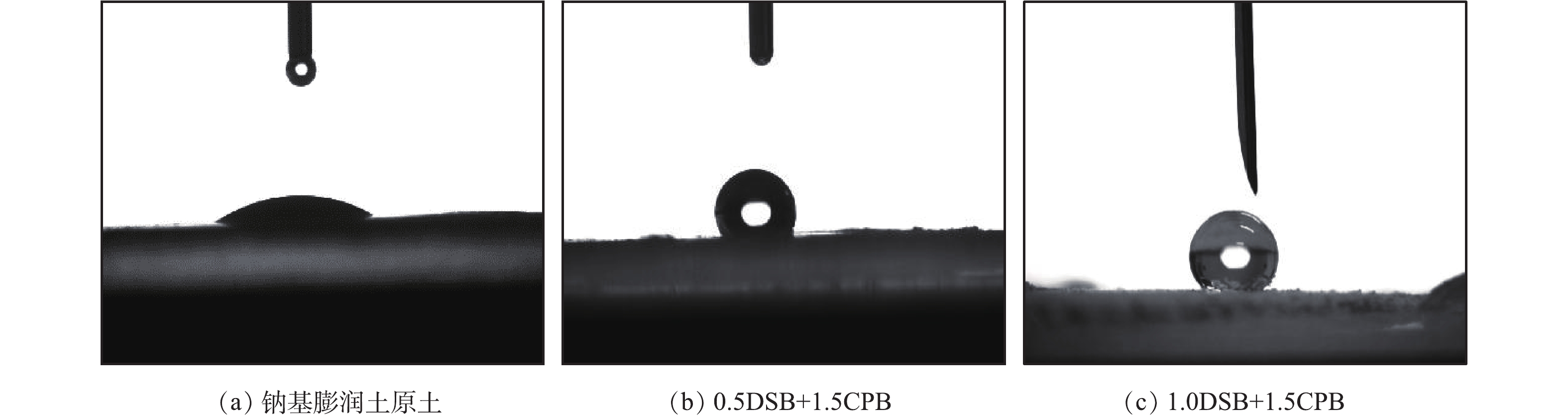
图4(a)为钠基膨润土原土接触角测定图,经测定其接触角为33.04°<90°,这说明钠基膨润土表面呈亲水性;图4(b)和图4(c)分别为0.5DSB+1.5CPB和1.0DSB+1.5CPB复合改性膨润土的接触角测定图,其接触角分别为121.96°和132.28°,均大于90°,呈现疏水性[18]。这说明改性剂的添加能够显著降低钠基膨润土的表面极性,从而改变了其表面性质。
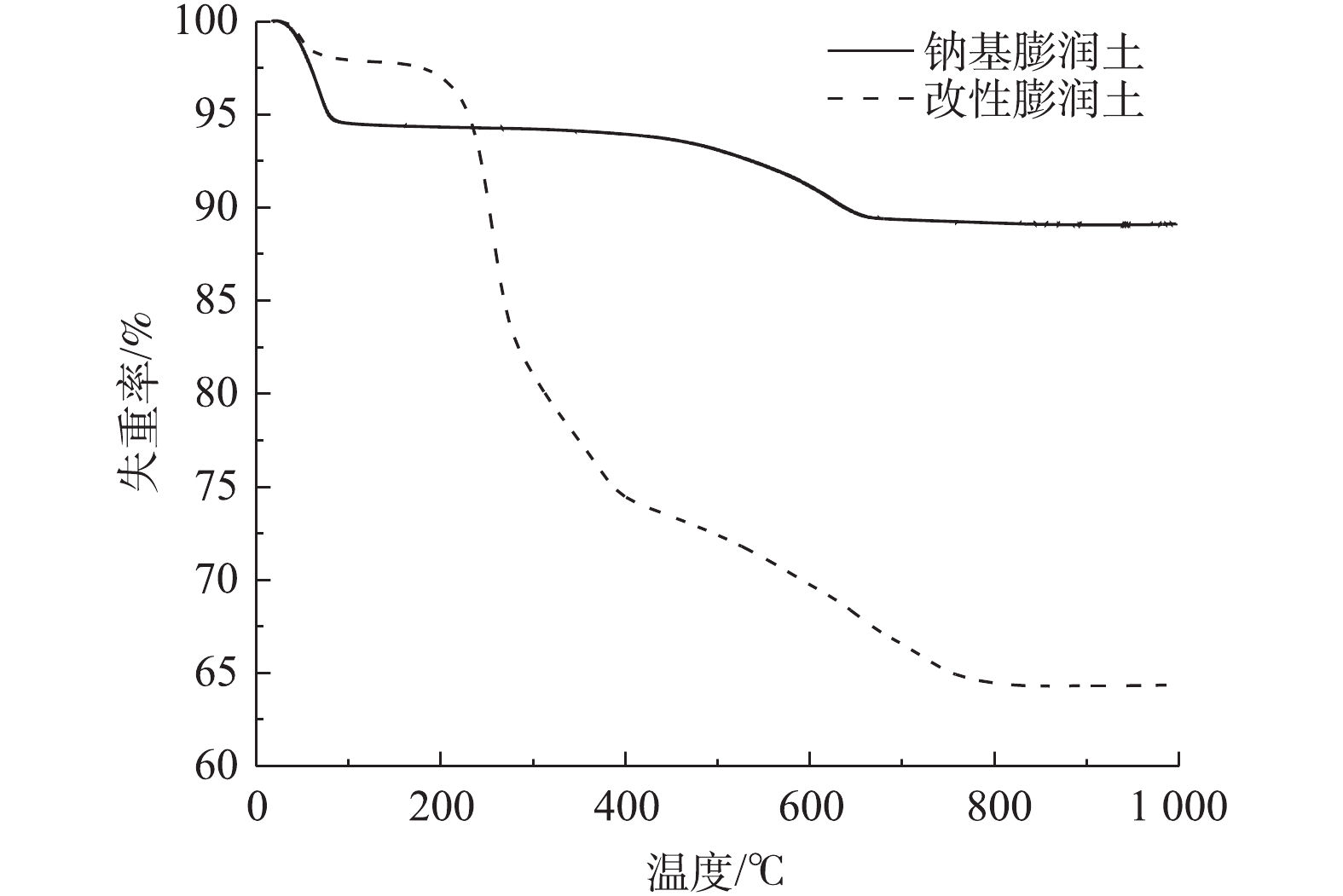
图5为钠基膨润土原土和0.5DSB+1.5CPB复合改性膨润土的TG曲线。可以看出,随着温度升高,0.5DSB+1.5CPB复合改性土样质量变化分为3个阶段。第1阶段的温度低于200 ℃,质量损失(烧失量)约2.98%,此阶段主要表现为自由水和层间水的散失[19];第2阶段的温度为200~400 ℃,此阶段质量损失约22.56%,而钠基膨润土原土基本没有质量损失,主要原因可能是高温使膨润土层及表面附着的有机改性剂分解[20],此阶段失重结果与MONTEIRO等[19]研究结果相似;第3阶段的温度为400~800 ℃,此阶段质量损失约9.98%,这主要是由膨润土晶格层间坍塌引起的[21]。TG曲线的阶段性变化进一步表明改性成功。
-
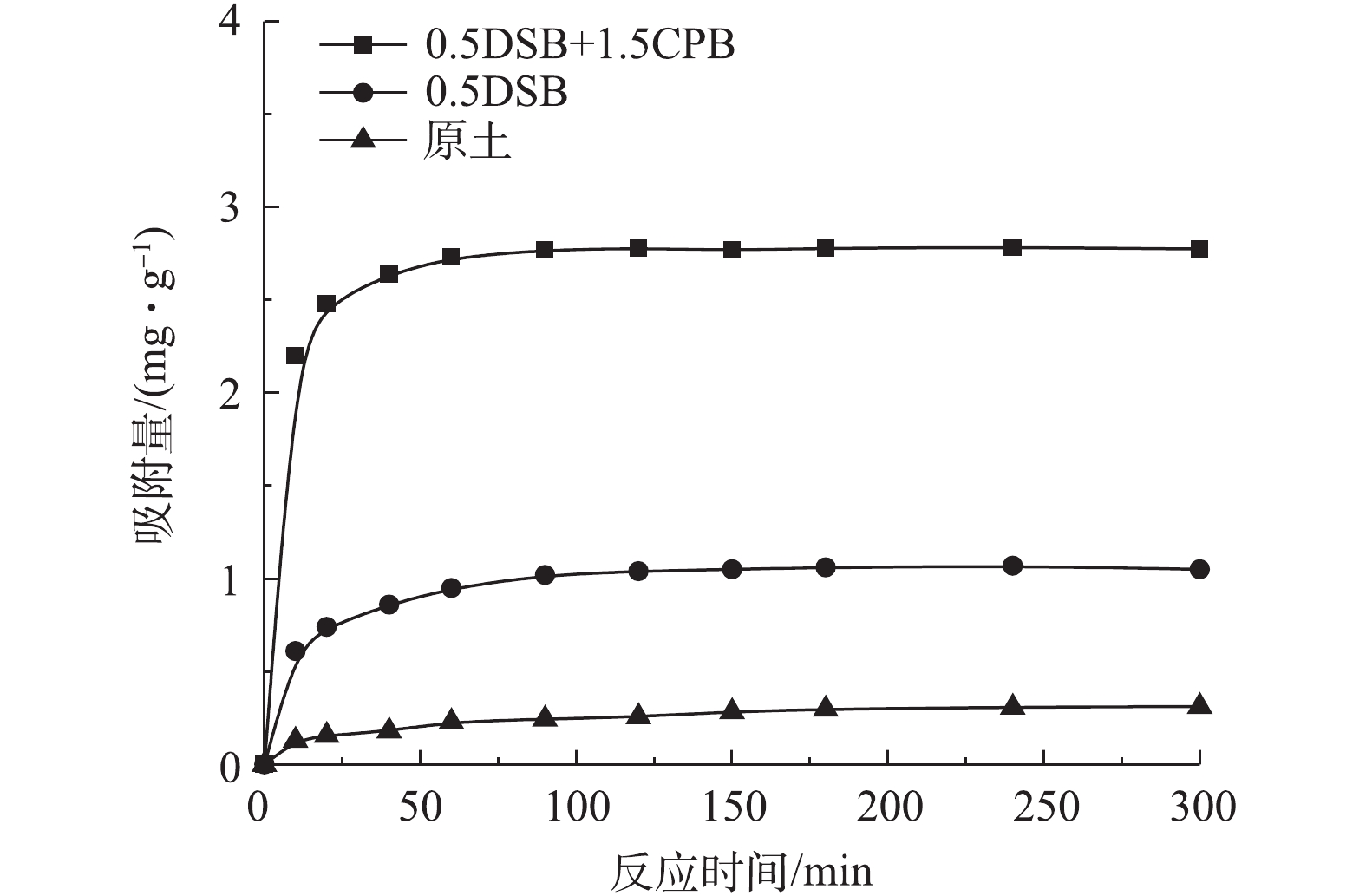
图6为各土样对磷酸盐的吸附动力学曲线。由图6可知,0.5DSB+1.5CPB复合改性膨润土在60 min时吸附量可达到平衡吸附量的97.92%,而0.5DSB改性膨润土和原土的吸附量仅为平衡吸附量的87.64%和70.99%,且其对应的平衡吸附量分别为2.78、1.04、0.32 mg·g−1。这表明0.5DSB+CPB复合改性膨润土的吸附速率和平衡吸附量均大于0.5DSB改性膨润土和原土。各土样对磷酸盐的吸附随时间变化分为3个阶段:快速吸附,速率变缓和吸附平衡。这是因为吸附开始阶段,膨润土表面具有的大量吸附位点被磷酸盐快速占据,表现为较高的吸附速率。随着吸附反应的进行,表面吸附位点逐渐减少,膨润土对磷酸盐的吸附变得困难,表现为吸附速率减缓。
为进一步探究复合改性膨润土对磷酸盐的吸附扩散情况,分别用伪一级动力学方程(式(2))、伪二级动力学方程(式(3))对图6中的数据进行了拟合分析,拟合参数见表1。
式中:Qt为t时刻的吸附量,mg·g−1;k1为伪一级动力学常数,min−1;t为反应时间,min,k2为伪二级动力学常数,g·(mg·min)−1。
由表1可知,各膨润土土样伪二级动力学模型拟合效果均优于伪一级动力学模型(R2>0.990),且拟合平衡吸附量与实际平衡吸附量也较为接近,这说明伪二级吸附动力学模型能较好的描述改性膨润土对磷酸盐的吸附过程,化学吸附为其限速步骤[22]。
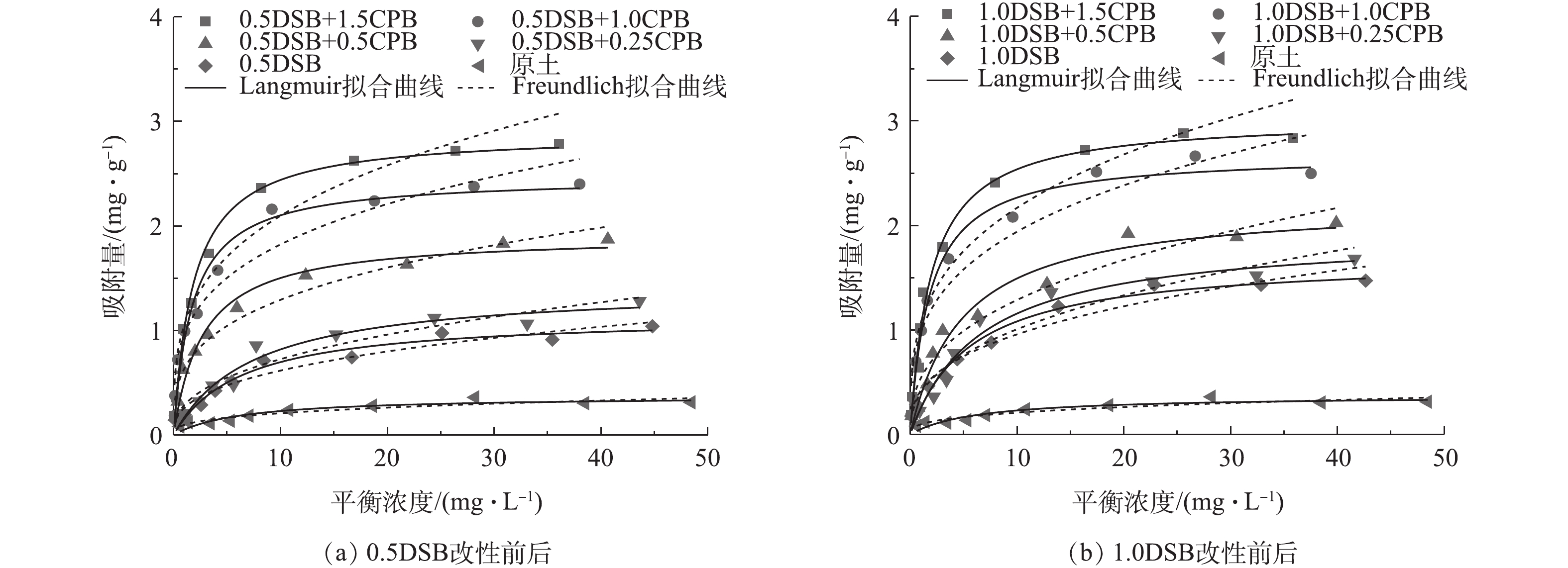
图7为各土样对磷酸盐的吸附等温曲线。由图7可知,各土样对磷酸盐的吸附量随着磷酸盐平衡浓度增大而增加,逐渐趋于平衡,且等温线均为非线性,这说明吸附模式以表面吸附为主[23],与吸附动力学的描述相符。为进一步探究其吸附机制和最大吸附容量,本研究采用Langmuir和Freundlich吸附等温方程对实验数据进行拟合,拟合参数结果列于表2。Langmuir和Freundlich等温模型的数学表达式[24]分别如式(4)和式(5)所示。
式中:Qm为改性膨润土对磷酸盐的最大吸附量,mg·g−1;KL为Langmuir常数,L·mg−1;KF和1/n均为Freundlich参数。
由表2可知,2种吸附等温方程都能较好的对实验数据进行拟合,但Langmuir方程的可决系数相较Freundlich方程更优,所以本研究中膨润土对磷酸盐的吸附更符合Langmuir吸附模型。
本研究考察了改性比例对吸附的影响。由表2可知,对于DSB两性改性膨润土,1.0DSB对应的最大吸附量高于0.5DSB。对于复合改性膨润土,当DSB的改性比例相同时,随CPB的改性比例增加,其最大吸附量依次增大,即DSB+0.25CPB<DSB+0.5CPB<DSB+1.0CPB<DSB+1.5CPB;当CPB的改性比例相同时,其最大吸附量均呈现出随DSB改性比例增加而增大的趋势,即0.5DSB+CPB<1.0DSB+CPB。以上各土样最大吸附量的大小变化趋势与表征分析中XRD图谱层间距变化情况一致。
改性膨润土的吸附量与原土相比提高明显。0.5DSB和1.0DSB两性改性膨润土对磷酸盐的最大吸附量分别为原土的3.08倍和4.57倍;0.5DSB+0.25CPB、0.5DSB+0.5CPB、0.5DSB+1.0CPB、0.5DSB+1.5CPB复合改性膨润土对磷酸盐的最大吸附量分别是0.5DSB两性改性膨润土的1.25、1.68、2.17和2.54倍;1.0DSB+0.25CPB、1.0DSB+0.5CPB、1.0DSB+1.0CPB、1.0DSB+1.5CPB复合改性膨润土对磷酸盐的最大吸附量分别是1.0DSB两性改性膨润土的1.14、1.31、1.59和1.79倍。这说明DSB改性能提高膨润土对磷酸盐的吸附能力,且CPB的复合可显著促进DSB两性改性膨润土对磷酸盐的吸附。
由图7和表2可以看出,膨润土原土对磷酸盐的吸附效果并不理想,主要是因为膨润土表面带的大量负电荷,会因电性斥力影响其对磷酸盐的吸附。当加入两性表面活性剂DSB对其进行改性后,DSB分子结构中带正电荷的季胺基亲水基团N+端可与膨润土表面的负电荷位点结合[10],同时DSB分子结构中的十二烷基疏水长碳链在膨润土表面形成有机相,导致疏水性变强,且外表面正电荷基团可与磷酸盐形成电性吸引,故其吸附效果优于原土[25-26]。
当加入阳离子表面活性剂CPB进行复合改性后,CPB分子结构中带正电的季胺基可以与DSB分子结构中的负电荷磺丙基基团和未被DSB结合的膨润土表面负电荷点位相结合。与此同时,CPB与DSB分子结构中的疏水长碳链通过疏水作用,在膨润土表面形成有机相,增强膨润土表面疏水性,且有机相向外的正电荷端会进一步提升复合改性膨润土对磷酸盐的吸附能力[12]。因此,DSB+CPB复合改性膨润土吸附磷酸盐的能力优于DSB两性改性膨润土,且随CPB改性比例的增大,这种吸附优势也越明显。
-
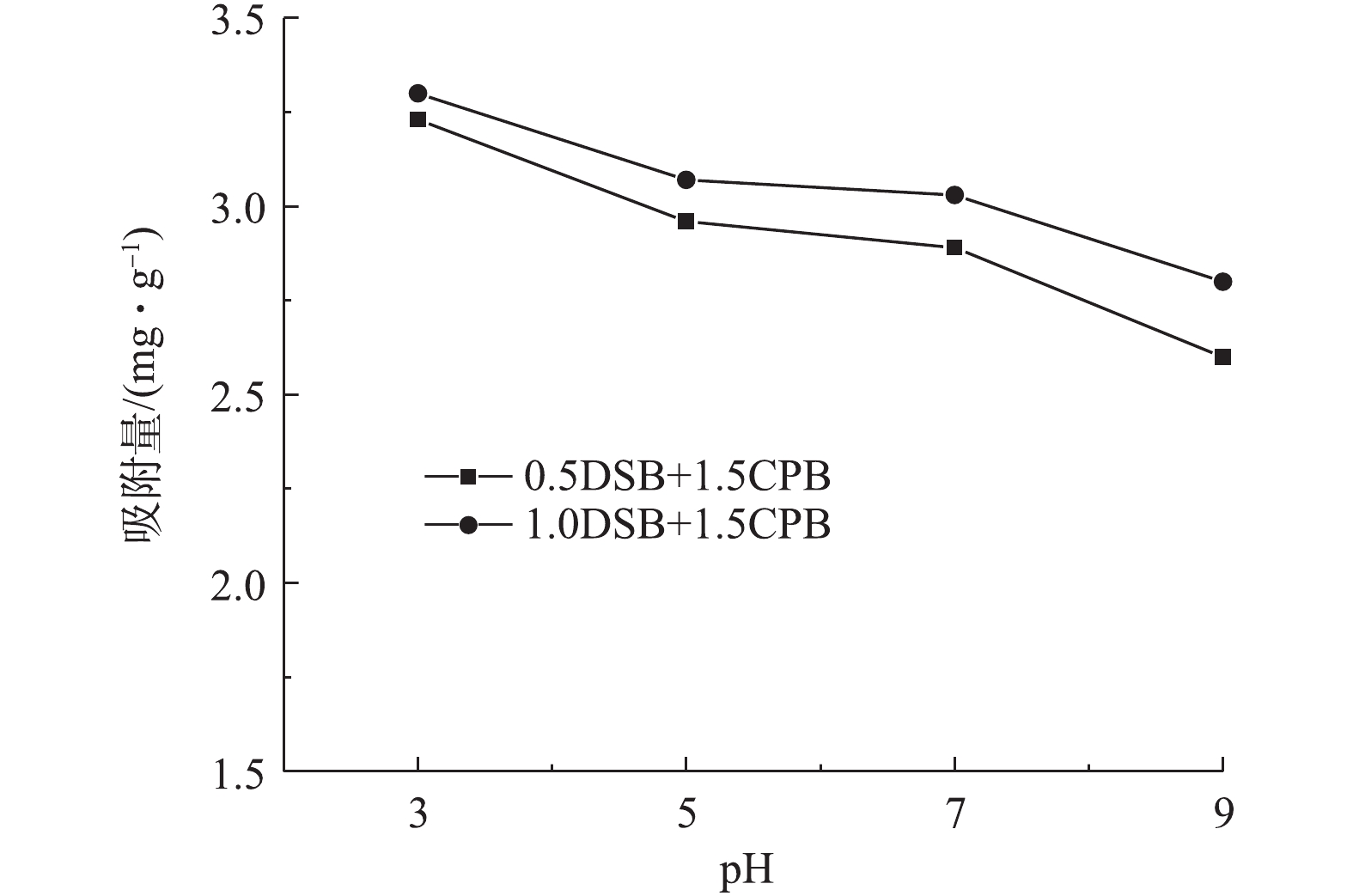
图8反映了pH对0.5DSB和1.0DSB最佳复合改性土样(0.5DSB+1.5CPB、1.0DSB+1.5CPB)吸附磷酸盐的影响。由图8可知:当溶液pH由3增加到5时,改性膨润土对磷酸盐的吸附量显著下降;当pH在5~7时,改性膨润土对磷酸盐的吸附量变化较小;当pH升高到9时,改性膨润土对磷酸盐的吸附量继续下降,随溶液pH的升高,改性膨润土对磷酸盐的吸附量均呈下降趋势。这主要是因为pH的变化会影响膨润土表面的电荷特征及磷酸盐在水中的存在形态,进而影响膨润土对磷酸盐的吸附能力[27]。
在酸性条件下,溶液中H+浓度较高,部分H+附着在膨润土表面,增多了改性膨润土表面的正电荷,通过静电引力作用,提高了膨润土对磷酸盐的吸附能力。酸性溶液中磷酸盐的主要存在形式是
${{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{PO}}_{\rm{4}}^{\rm{ - }}$ 和${\rm{HPO}}_{\rm{4}}^{{\rm{2 - }}}$ 。当溶液的pH由3增加到7时,溶液中正电荷减少,${{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{PO}}_{\rm{4}}^{\rm{ - }}$ 含量降低,${\rm{HPO}}_{\rm{4}}^{{\rm{2 - }}}$ 含量增加,因${{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{PO}}_{\rm{4}}^{\rm{ - }}$ 的吸附自由能小于${\rm{HPO}}_{\rm{4}}^{{\rm{2 - }}}$ ,从而导致改性膨润土对磷酸盐的吸附能力随pH的升高而下降[28-29]。在碱性条件下,随pH的升高,溶液中OH−浓度增加,从而使其竞争膨润土表面吸附活性位点的能力增强,并且pH的升高会使两性表面活性剂DSB上的部分基团呈负电荷[30],增强了磷酸盐和改性膨润土表面之间的静电斥力,从而导致碱性条件下改性膨润土对磷酸盐的吸附能力显著低于酸性条件。
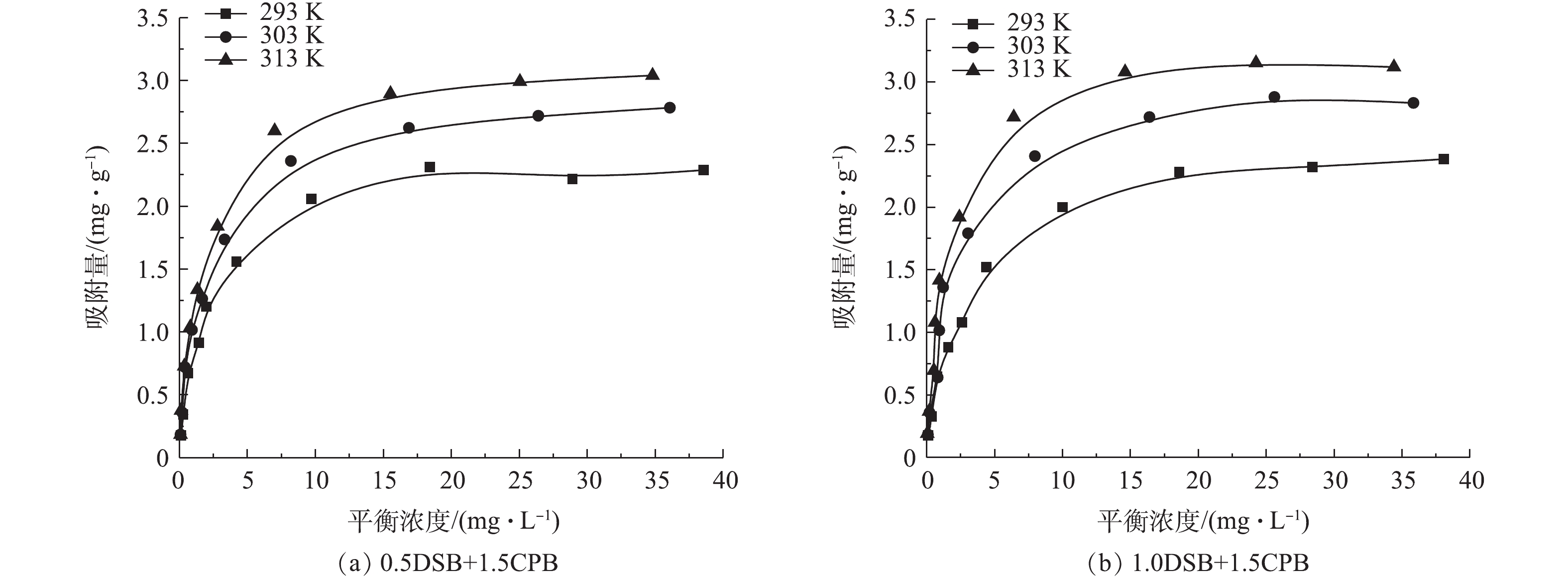
温度对吸附的影响如图9所示。可以看出,随温度的升高,0.5DSB+1.5CPB和1.0DSB+1.5CPB复合改性土样对磷酸盐的吸附量均有所增大,呈现增温正效应,这可能是由于吸附过程受到非极性相互作用的影响,一定程度上增强了对亲水性磷酸盐的吸附阻力,因而需要吸收能量来克服[31]。
吸附热力学参数相关公式[32]如式(6)~式(8)所示。
式中:Kd为平衡吸附分配系数;ΔS为标准吸附熵变,J·(mol·K)−1;ΔH为标准吸附焓变,kJ·mol−1;ΔG为标准吸附自由能变,kJ·mol−1,T为绝对温度,K;R为摩尔气体常数,取值8.314 J·(mol·K)−1,ΔS和ΔH由lnKd对−1/T作图得出,拟合结果见表3。由表3可知,改性膨润土对磷酸盐吸附的标准焓变ΔH均大于0,为吸热反应,与前文所提到的增温正效应一致;而标准熵变ΔS也均大于0,这是由于改性使膨润土表面吸附点位增加,故在膨润土吸附反应过程中会使磷酸盐排列具有多向性,导致混乱度增加,即熵变增大[12]。
不同温度下改性膨润土对磷酸盐吸附的标准自由能变ΔG均小于0,说明吸附过程为自发反应,且随着温度增加,ΔG的绝对值均呈增大的趋势,这说明自发程度逐渐增强,即升温有利于反应的进行,又因所有ΔG均为−20~0 kJ·mol−1,这说明在吸附过程中没有新的化学物质生成,因此,此过程以物理吸附为主,其相互作用力主要包括静电作用力、氢键和范德华力等作用[33]。
2.1. 改性膨润土表征分析
2.2. 吸附性能分析
2.3. 反应条件对吸附的影响
-
1) DSB改性可提高膨润土对磷酸盐的吸附能力,CPB改性可进一步促进DSB改性膨润土对磷酸盐的吸附,且随CPB改性比例的增加,其对磷酸盐的吸附量增大。
2)改性膨润土对磷酸盐的吸附过程可用伪二级动力学方程(R2>0.990)和Langmuir吸附等温模型描述,最佳改性比例(1.0DSB+1.5CPB)的最大吸附量分别为原土和1.0 DSB两性改性膨润土的8.19倍和1.79倍,复合改性可显著提高膨润土对磷酸盐的吸附能力。
3)溶液pH的变化会影响膨润土表面的电荷特征及磷酸盐在水中的存在形态,进而影响膨润土对磷酸盐的吸附能力。随着溶液pH的增大,改性膨润土对磷酸盐的吸附呈下降趋势。
4)改性膨润土对磷酸盐的吸附为物理吸附和化学吸附同时存在的自发、吸热、熵增过程。



 下载:
下载: