-
城市黑臭水体是指散发出刺鼻和恶心气味、呈黑色或灰黑色、生态功能丧失的水体,随着我国城市化的快速发展,其已成为一种普遍的城市病[1-2]。黑臭水体不仅会造成人体感官上的影响,对水体、河流底泥和周围空气均造成污染,同时影响生物健康[3]。因此,城市黑臭水体的治理成为城市生态环境质量改善和生态环境保护修复的重要工作。近年来,国家和各级政府对城市黑臭水体治理极其重视,黑臭水体治理已成为长江保护修复攻坚战行动计划中的一项关键工作,要求各城市逐步消除黑臭水体。因此,黑臭水体已成为城市政府和环保部门的重要工作,也是保障民生和实现城市环境质量改善的关键。
目前,针对黑臭水体的治理主要包括物理法(曝气充氧技术、引水稀释法、底泥疏浚法等)、化学法(混凝法、石灰法等)、生物法(活性污泥法、生物膜法、氧化塘法及水生植物净化技术等)[4-5]。物理法存在工作量大、成效慢等问题;化学法存在成本高、易反弹等缺陷;而生物法也存在成效慢、易受环境条件影响等问题。废水离线处理成为一种广受关注的黑臭河治理手段,其中介质加载混凝由于具有快速高效的处理能力,且易实现小型化及可移动化的装置构建,在黑臭水体的治理中已得到一定的应用。介质加载混凝是指在常规混凝过程中投加重质颗粒物,以实现沉淀时间和沉淀池容积的降低并提升混凝效率的一种混凝升级工艺,其已被广泛应用于水处理中[6-7]。但目前针对黑臭水体的介质加载混凝过程的污染物去除特征及其机理尚未得到关注,限制了其推广和应用。
本研究开展了石英砂和磁种2种介质加载混凝实验,研究了混凝过程中污染物特别是不同形态的磷和溶解性有机物(dissolved organic matter, DOM)的去除特征,考察了絮体粒径、形貌、沉降性能与强度,分析了介质加载混凝机理,以期为介质加载混凝在水处理中的应用提供参考。
全文HTML
-
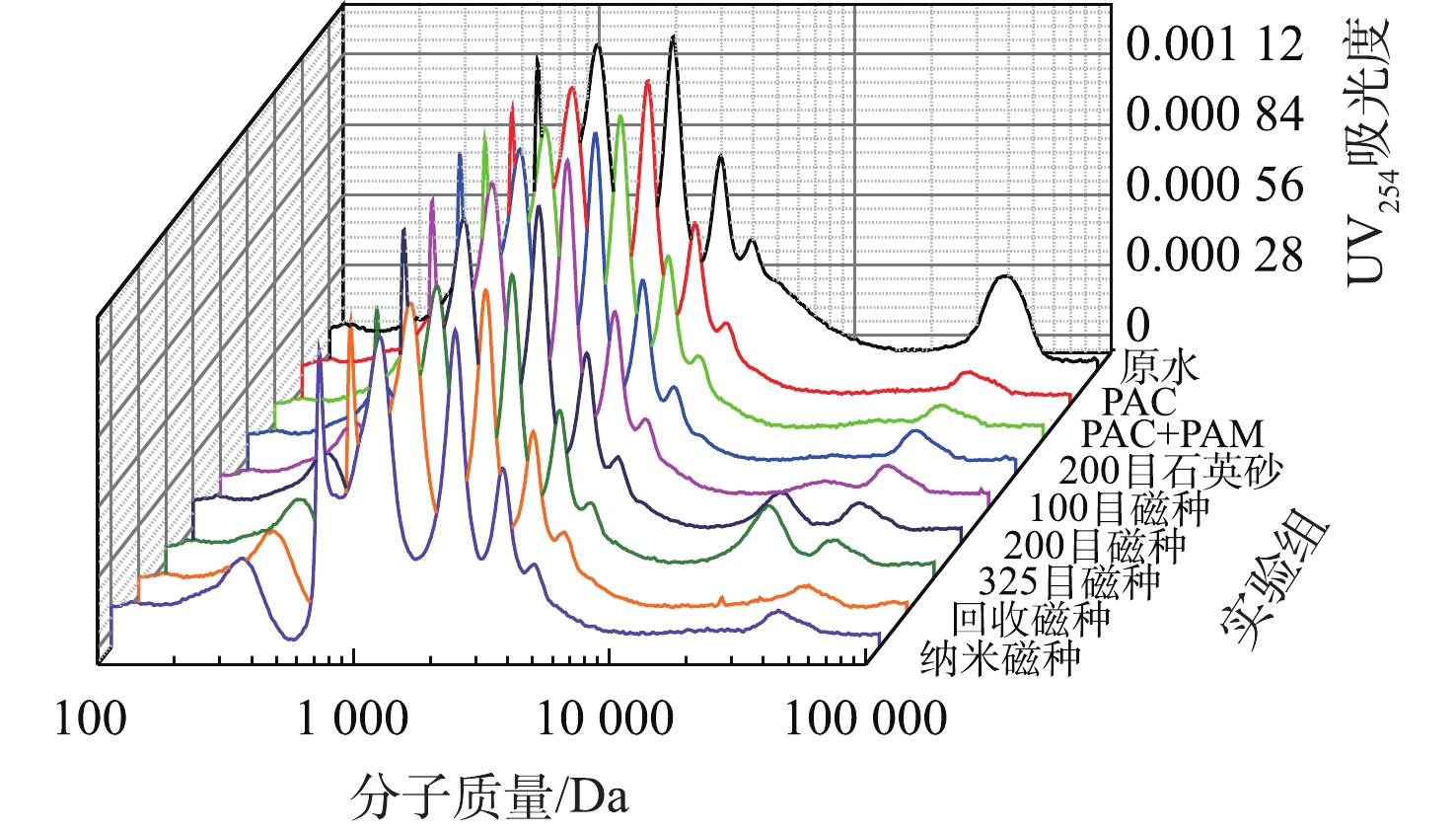
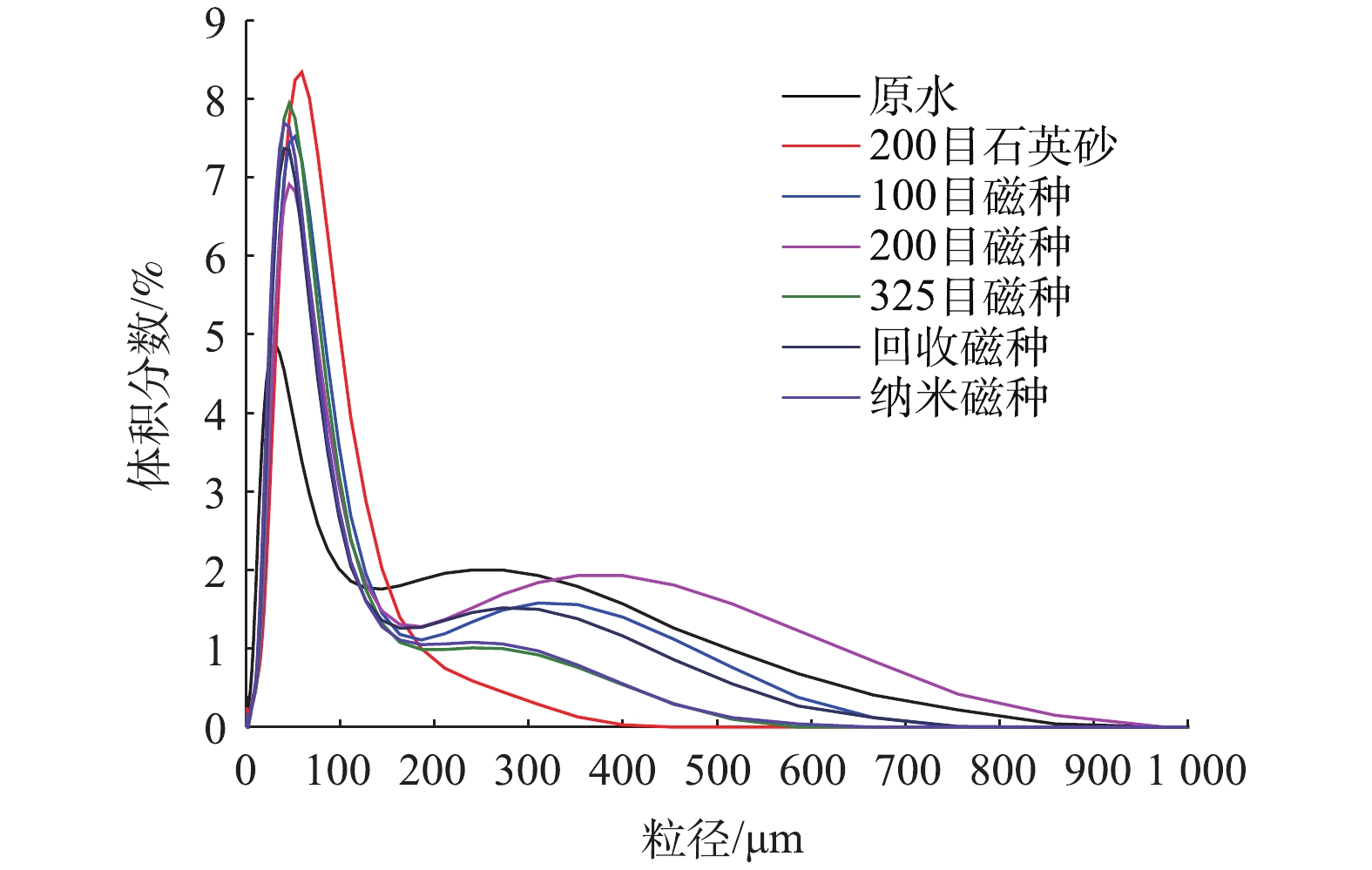
原水取自北京市某黑臭河道,常规水质如下:pH为6.88±0.24,浊度为(31.2±5.3) NTU,电导为(1 620±138) μS·cm−1,总氮为(55.8±3.2) mg·L−1,氨氮为(43.2±2.6) mg·L−1,耗氧有机污染物的浓度(以COD计)为(109±15) mg·L−1,总磷为(2.12±0.36) mg·L−1,磷酸盐为(0.53±0.08) mg·L−1。原水中悬浮物粒径分布较宽,主要在50 μm和300 μm出现分布峰(图1)。
介质加载混凝实验采用六联搅拌器(MY3000-6F,武汉梅宇)进行,以聚合氯化铝(PAC,Al2O3含量≥10%;盐基度≥60%,万水净水器有限公司,中国)为混凝剂,以聚丙烯酰胺(PAM,化学纯,阴离子型,分子质量为3 000 000 Da)为助凝剂,采用石英砂(200目)、磁种 (100、200、325目、纳米级)及325目磁种的混凝过程回收磁种(实际磁混凝工程的回收磁种,采用磁鼓回收,回收率大99%)作为加载介质(粒径分布见图1)。仅投加PAC、PAC+PAM、PAC+PAM+200目石英砂、PAC+PAM+100目磁种、PAC+PAM+200目磁种、PAC+PAM+325目磁种、PAC+PAM+回收磁种、PAC+PAM+纳米磁种的实验组分别标记为A~H。
在混凝过程中,搅拌参数通过预实验确定:先将400 mL的废水倒入500 mL的混凝杯中,加入1.5 g·L−1的介质,以250 r·min−1搅拌60 s;随后加入80 mg·L−1的混凝剂PAC,在250 r·min−1下搅拌60 s,其后加入1.5 mg·L−1的PAM,在250 r·min−1下搅拌20 s,然后在80 r·min−1下搅拌300 s。沉降2 min后,取上清液,沉降5 min倾倒上清液,获得絮体样品。
-
1)常规指标的分析。pH和电导采用便携式电极法现场测定,浊度采用哈希2100AN 型台式浊度仪测定,SCOD采用哈希预制管消解及DR2800分光光度计(HACH, USA)测定,总有机碳(TOC)由TOC-VCPH分析仪(Shimadzu, Japan)测定。
2)不同形态磷的分析。本研究重点关注不同形态的磷在介质加载混凝过程中的去除特征,分析其去除机制,包括总磷(TP)、正磷(
${\rm{PO}}_4^{3 - }$ -P)、溶解性总磷(DTP)、悬浮态总磷(STP)和有机态磷(OTP)。DTP与STP采用0.45 μm滤膜进行分离,OTP为DTP与${\rm{PO}}_4^{3 - } \text{-} {\rm{P}}$ 的差值。TP和DTP采用过硫酸钾消解-钼酸盐分光光度法 (紫外可见分光光度计,Thermo Evolution 300, 美国赛默飞) 测定,${\rm{PO}}_4^{3 - } \text{-} {\rm{P}}$ 采用钼酸盐分光光度法测定。3)溶解性有机物的分析。通过紫外可见分光光谱(UV-vis)、三维荧光光谱(3DEEM)和分子质量分布来表征DOM。UV-vis采用紫外可见分光光度计(Thermo Evolution 300, 美国赛默飞)测试,同时测得UV254、UV260、UV280指标,并计算E254/E365、E300/E400、E280/E472、A226~400、A275~295、A350~400等[8-10]。DOM的分子质量分布采用高效液相色谱-凝胶色谱(HPLC-GPC) (Breeze 1525, 美国沃特世)分析。3D-EEM采用三维荧光光谱仪(F-7000, 日本日立)测定,同时计算荧光指数(f)用于表征腐殖质类物质的来源;生物指数(b)用于表征水中土著微生物的生物活性及DOM的新鲜度;腐殖化指数(h)用于表征DOM的腐熟程度[11-12]。计算方法见式(1)~式(3)。
式中:I(450 nm, 370 nm)为发射光波长450 nm和激发光波长370 nm条件下测得的荧光强度;I(500 nm, 370 nm)为发射光波长500 nm和激发光波长370 nm条件下测得的荧光强度;I(380 nm, 310 nm)为发射光波长为380 nm和激发光波长310 nm条件下测得的荧光强度;ΣI(435~480 nm, 255 nm)、ΣI(300~345 nm, 255 nm)为激发光波长255 nm,发射光波长分别为435~480 nm和300~345 nm条件下测得的荧光强度的和;(I(420~435 nm, 310 nm))max为发射光波长在420~435 nm,激发光波长为310 nm条件下测得的最大荧光强度。
同时,采用区域面积积分法(FRI)计算三维荧光光谱中5大分区(酪氨酸类、色氨酸类、UVA腐殖质类、UVC腐殖质类、微生物代谢产物类有机物)的有机物占比[13],对DOM的组成进行表征。
-
为分析混凝过程中粒径的变化,利用激光粒度仪(Mastersizer 2000,英国马尔文)搭建在线粒度分析装置进行在线分析[14-15],包括便携式混凝实验搅拌器(MY3000-2N,武汉梅宇)、蠕动泵、激光粒度仪,利用蠕动泵实时将形成的絮体泵入激光粒度仪进行分析,测试装置如图2所示。
在线粒度分析过程如下:混凝过程和前面混凝实验相同,为了研究絮体强度及稳定性,沉淀5 min后,进入400 r·min−1破碎快搅阶段(400 r·min−1,60 s),随后开始200 r·min−1破碎阶段(200 r·min−1,60 s),最后进行二次沉淀。在整个过程中,将混凝体系的溶液实时泵入激光粒度仪进行粒径分析。
-
絮体采用冷冻干燥,形貌采用FESEM(HITACHI SU8020, 日本日立)进行观测。为提高样品导电性,观察前对样品进行喷金(HITACHI E-1010 Ion Sputtering device, 日本日立)。
1.1. 介质加载混凝实验
1.2. 水质分析
1.3. 混凝过程中粒径分布的测定
1.4. 絮体形貌分析
-
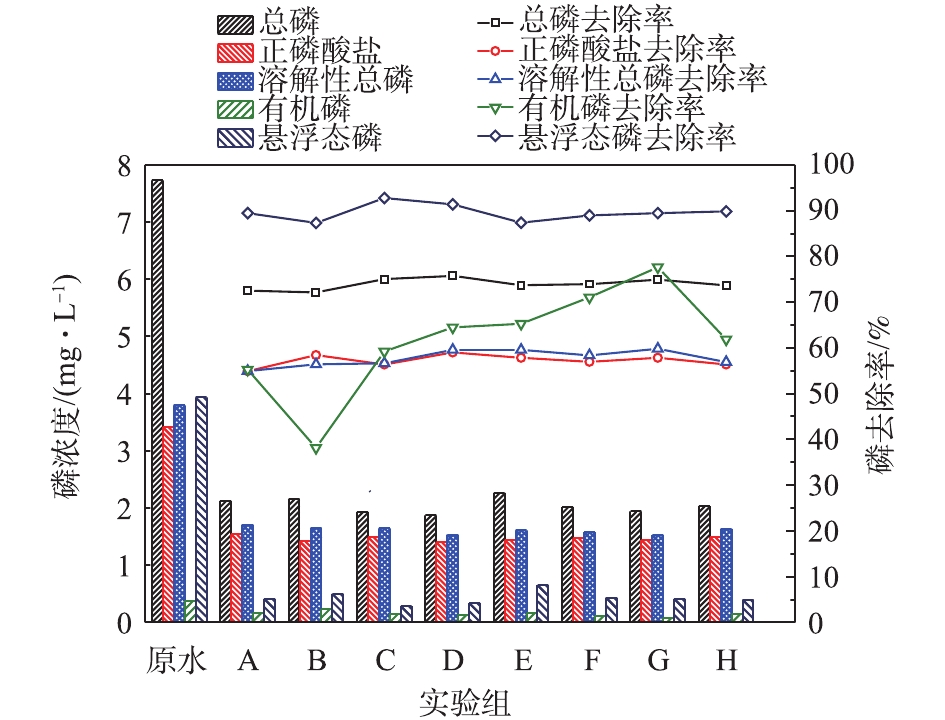
图3为不同介质投加对不同形态磷的去除效果。由图3可以看出,混凝过程对磷有较好的去除效果,TP去除率为72%左右。投加PAM后,对
${\rm{PO}}_4^{3 - } \text{-} {\rm{P}}$ 的去除率基本无影响,而对有机磷的去除率有显著下降,因此DTP去除率略下降,而STP去除率提高。这表明${\rm{PO}}_4^{3 - } \text{-} {\rm{P}}$ 的去除主要是通过无机混凝剂的絮凝作用,而投加PAM后,瞬时形成的大絮体包覆限制了PAC水解产物对有机磷的吸附。由此可以推断,${\rm{PO}}_4^{3 - } \text{-} {\rm{P}}$ 的去除是瞬时过程,在投加PAC后的混凝阶段即可完成。而有机磷的吸附过程较慢,需要在絮凝及慢搅过程进一步实现。投加石英砂与磁种后,TP的去除率提高,对TP去除率的影响顺序为100目磁种>石英砂>回收磁种>325目磁种>200目磁种>纳米磁种。石英砂的投加显著提高DTP去除率,去除率达92.76%;但对有机磷和${\rm{PO}}_4^{3 - } \text{-} {\rm{P}}$ 去除效果较差,导致STP的去除率较低。100目磁种对 STP的去除效率最高,OTP去除效果较差。325目磁种对OTP的去除效果最好,主要是由于其本身的吸附作用[14]。因此,其回收磁种也具有最高的OTP去除率。但回收磁种对各种形态磷的去除率均高于原磁种,主要原因是磁种回收过程中表面仍存在一定的微絮体结构,无机絮体对磷有一定的吸附作用。纳米磁种对磷去除的增强效果最差,相比传统混凝过程,主要增加了OTP的去除。整体而言,投加石英砂主要强化悬浮态磷的去除效果,对溶解态磷的影响较小。投加磁种主要增强有机磷和
${\rm{PO}}_4^{3 - } $ -P的吸附,因此,对DTP的去除效果有明显的增强[16]。磁种对磷的强化作用与磁种粒径无相关性,其可能原因是由于不同批次磁种本身性质差异,因此,磁种吸附能力不随粒径减少而加强。同时,回收磁种因为具有一定的微絮体结构,具有更强的磷强化去除效果。目前,磁混凝工艺可以实现99%以上的磁种回收率,因此,可以认为磁混凝是一种有效的磷去除及污水厂升级改造工艺。 -
DOM是水中的关键污染物,利用混凝技术实现DOM的去除的研究已得到了广泛的报道,但不同介质加载对DOM去除的影响及混凝过程中DOM的深度分析还需要进一步开展。本研究采用UV-vis、3D-EEM和HPSEC方法,分析混凝过程中DOM的去除特征,并比较不同投加介质的主要影响特征。
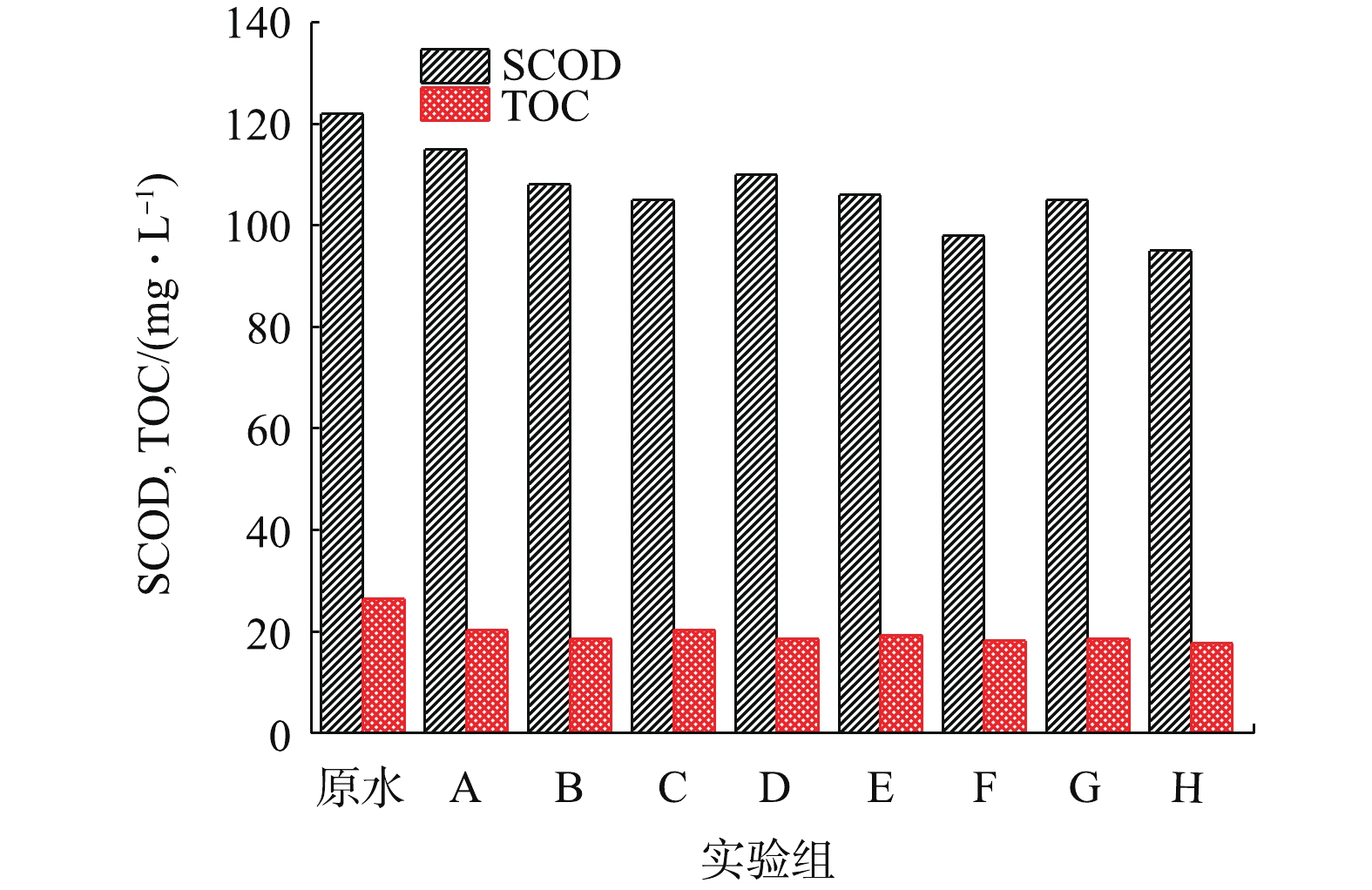
1) DOM整体去除特征。如图4所示,混凝对SCOD和TOC具有一定的去除效果,SCOD和TOC去除率为5%~23%和23%~33%。在投加石英砂后,SCOD和TOC的去除率有所升高,分别为13.93%和23.23%。磁种对SCOD和TOC的去除能力随磁种粒径的降低而升高,这表明DOM去除主要机制为磁种的吸附作用,且粒径越小其吸附比表面积越大。回收磁种对DOM的去除率低于原磁种,原因可能为磁种表面的微絮体的包裹影响了其对有机物的吸附。整体而言,2种加载介质石英砂与磁种对DOM的去除均有一定的强化。
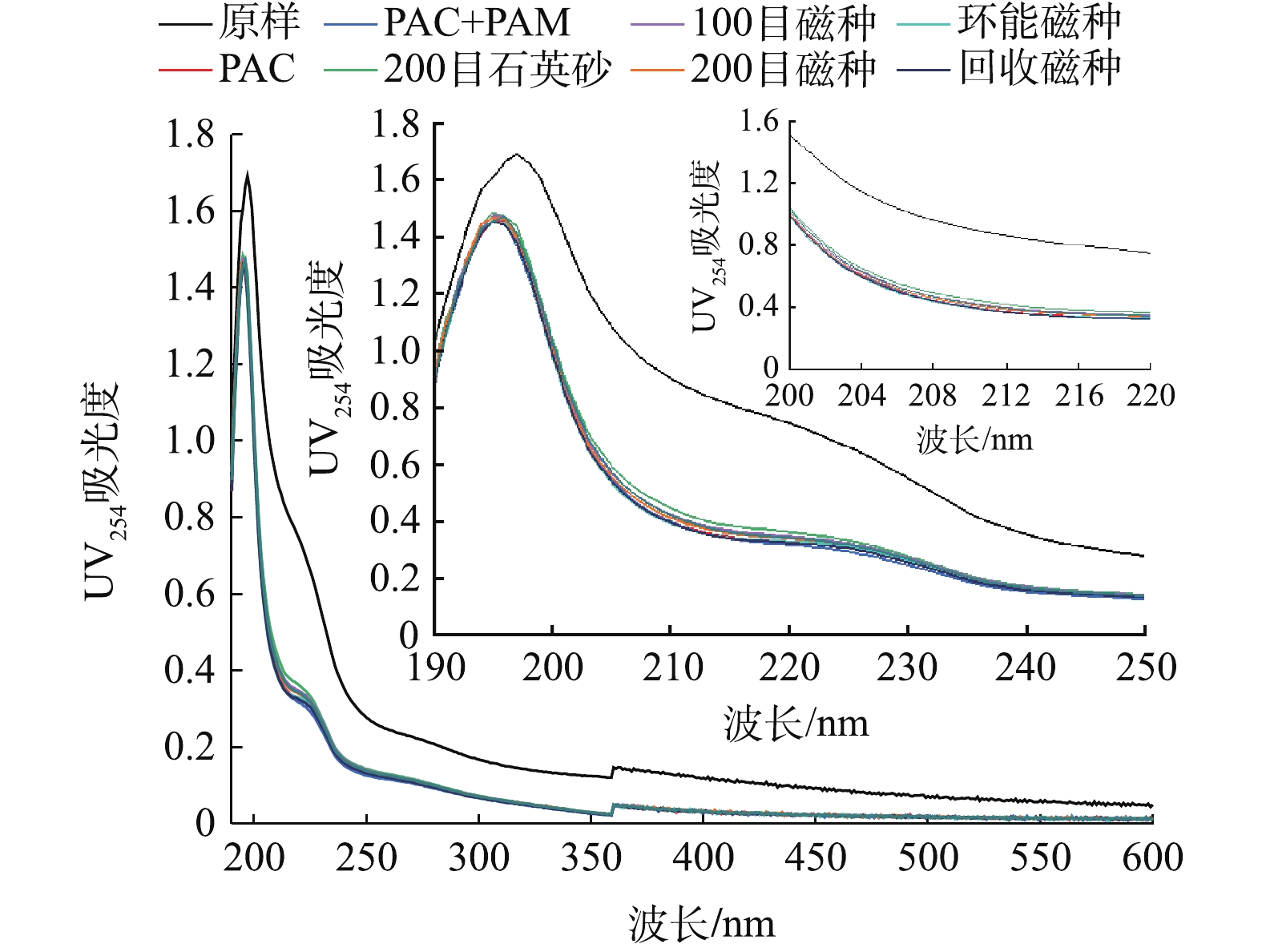
2) 紫外可见光谱。黑臭水体的DOM显著高于其他水体[17],因此,混凝对DOM的去除具有重要意义。本研究采用UV-vis方法,表征DOM的组成及其在混凝过程中的变化,结果如图5所示。相对原水,混凝显著降低了DOM的浓度,在210 nm之后的波段内,吸光度显著降低,这表明混凝对大分子的芳香族类化合物去除效果较好。但投加PAC与PAC+PAM的UV-vis图谱基本重合,且不同加载介质对图谱影响较小。这表明DOM主要去除机制是PAC的作用,主要原因是由于其水解产物对DOM的吸附和螯合作用所致[18]。
进一步分析吸光度指数,发现石英砂组的UV254吸光度最高,这表明石英砂对DOM去除效果较差;磁种可促进DOM的去除,且随着磁种粒径的降低,DOM的去除率上升,投加325目磁种后出水的吸光度最低,其结果与SCOD和TOC相一致;回收磁种的UV-vis图谱与原磁种基本一致,但吸光度相对略高,可能是微絮体影响了DOM的吸附;但投加纳米磁种组中DOM的浓度略高于投加其他磁种组,与SCOD和TOC的结果相反,可能原因是,纳米磁种对在254 nm波段无吸收的DOM有特异性吸附,而对在254 nm波段有吸收特征的DOM的吸附能力相对较差。
如表1所示,混凝后UV254、UV260、UV280、A226~400、A275~295、A350~400显著降低,而E254/E365、E300/E400、E280/E472显著升高,即混凝过程对芳香类、共轭双键、疏水性有机物都具有明显的去除。混凝出水中DOM中小分子有机物比例增加,腐殖酸比例下降,芳香族取代基中脂肪链的比例升高;而羰基、羧基和羟基的比例减少,DOM芳构化程度、分子质量及聚合度下降。投加石英砂后,UV254、UV260、UV280指数略有升高,对DOM的去率除略有降低,但E254/E365、E300/E400显著升高,这表明石英砂显著促进了腐殖酸的去除。相应地,A226~400、A275~295指数相比磁种加载组显著更高,表明其对DOM的去除略差。随磁种粒径的降低,UV254、UV260、UV280、E254/E365、E300/E400、A226~400、A275~295、A350~400指数逐渐下降,而E280/E472指数逐渐升高,表明DOM的去除率升高,废水中有机物腐殖化程度、分子质量、芳香性与聚合度均有所下降。同时,吸光度指数分析进一步表明,回收磁种对DOM的去除率略低于原磁种,主要原因是其表面微絮体的形成所致。
整体而言,不同介质加载的混凝对紫外-可见光图谱影响较小,PAC是DOM去除的关键,即DOM主要的去除机理为无机混凝剂的吸附和螯合作用[19-20]。
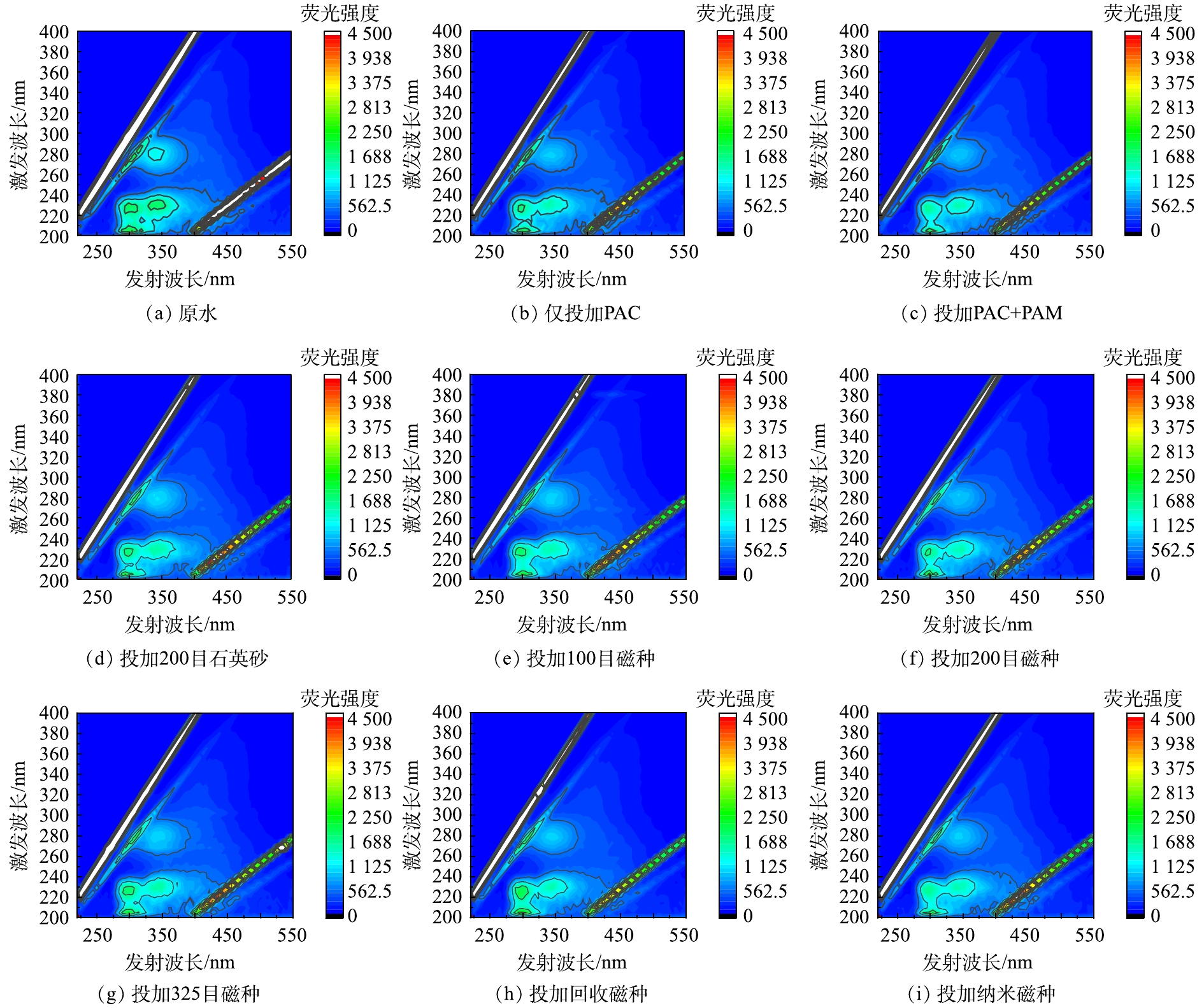
3)三维荧光光谱。采用3D-EEM分析了2种加载介质混凝对污水中主要的5类DOM去除特征的影响。如图6所示,原水中DOM主要为类酪氨酸蛋白、类色氨酸蛋白、UVA腐殖质类、UVC腐殖质类及部分微生物代谢产物[9, 11]。不同介质加载的混凝后DOM的组成基本相同,且与原水保持一致,但产水中各个区域特别是SMP和UVA腐殖质类物质浓度显著降低,与紫外可见光谱的结果相一致.这表明混凝过程同步去除不同类型的DOM,且SMP和UVA腐殖质类中的大分子DOM去除率较高[18, 21]。整体而言,仅投加PAC组与其他组的3D-EEM谱图基本一致,这进一步证实了DOM的去除主要是依靠无机混凝剂的作用。
如表2所示,混凝后水样的f都高于1.9,且b指数都高于1,表明废水及混凝后的水样中的DOM主要为内源性DOM,微生物活性较强;同时,h指数为0.6左右,表明DOM芳香性较高。分析DOM的占比发现,蛋白质类物质和腐殖质类是废水中主要DOM。混凝后,酪氨酸类和色氨酸类蛋白质比例略增加,腐殖质类占比降低,SMP类和UVC腐殖质类比例变化不显著[12],即混凝过程对腐殖质类物质去除较高[19, 21]。介质投加后,f指数升高,h和b指数下降,即加载介质后内源性的DOM占比升高,芳香性DOM占比下降。同时,从DOM组成可以发现,III区占比下降,IV区占比上升,即介质加载可略提升腐殖质类有机物的去除。对比回收磁种与原磁种的结果可发现,f指数有所降低,类酪氨酸蛋白占比下降,腐殖质类有机物占比升高,即回收磁种对腐殖质类有机物去除效果低于原磁种。
4)分子质量的分布。不同介质加载混凝处理后DOM的分子质量分布如图7所示,混凝过后高分子DOM(4 000~50 000 Da)的浓度显著下降。石英砂投加对出水DOM的分子质量分布基本无影响。相比传统混凝出水,在各波长条件下吸光度略高,这说明砂混凝对DOM去除率略低。投加磁种后,出水在20 000~3 000 Da出现一个新的吸收峰,且磁种粒径越小,峰强越高,这可能是磁种本身的杂质所致。但磁种投加后,对5 000 Da的DOM去除效果增强,且随粒径减少,去除率提高,主要原因是磁种的吸附作用。投加回收磁种后,未出现20 000~3 000 Da的吸收峰,且对大分子DOM的去除率高于原磁种,主要原因是微絮体的螯合作用。
-
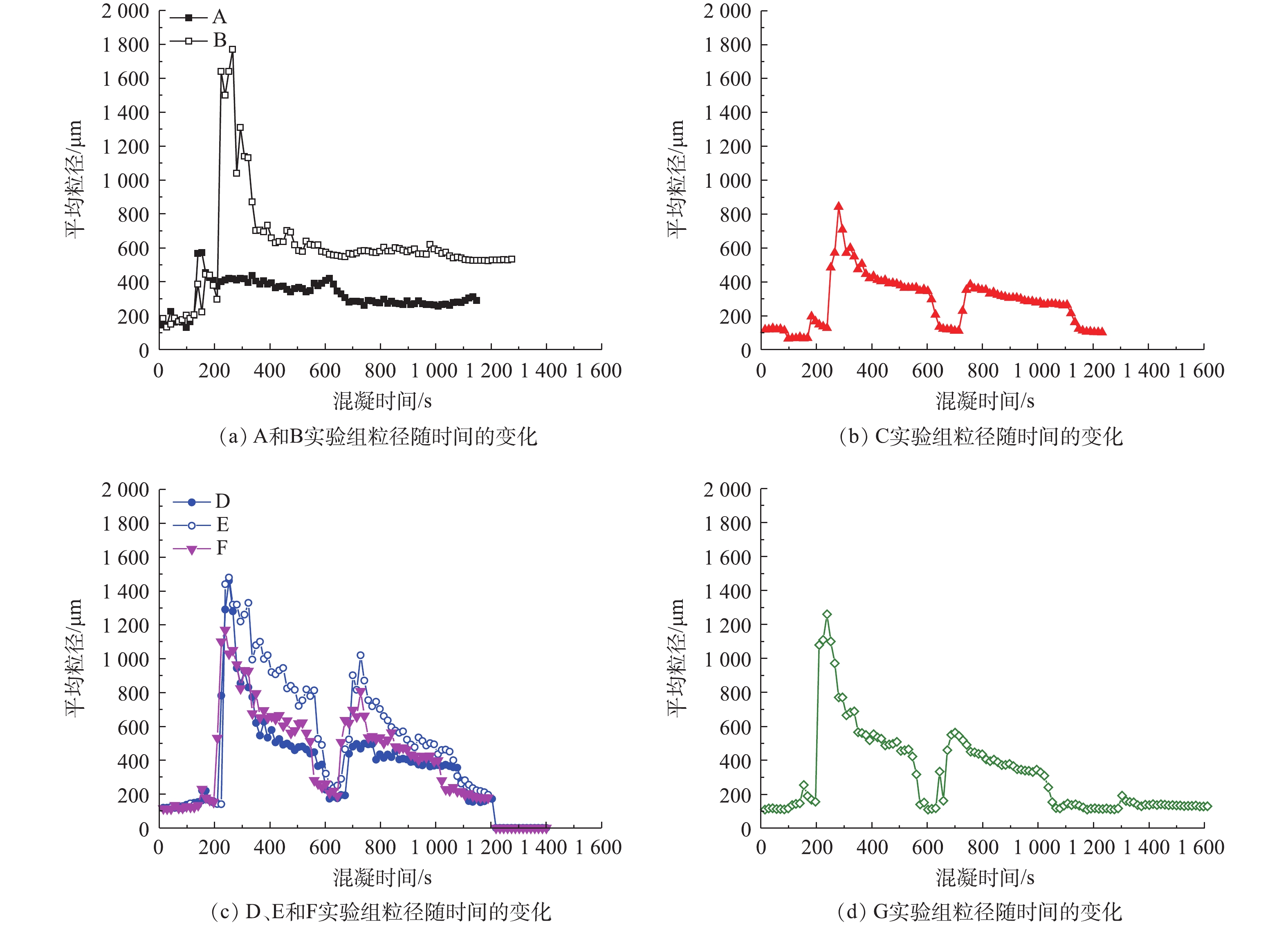
为进一步表征加载的介质对混凝过程的影响,考察了混凝过程中絮体粒径的变化。如图1所示,325目磁种与回收磁种粒径及其分布基本相同,但大粒径的颗粒占比增加,即平均粒径增加。这表明磁种回收后部分絮体仍未完全分离,证实了回收磁种表面微絮体的存在。不同磁种的粒径分布均存在2个明显的粒径峰,表明磁种存在颗粒团聚现象。在混凝过程中絮体的粒径变化见图8,结果表明,在投加PAM后,絮体粒径显著增加,因此,悬浮物的去除率有所增加。但其形成的絮体强度较低,在破碎阶段易破碎,故二次沉淀性能差,导致二次沉淀后污泥量显著高于单独投加PAC组。介质加载后,絮体粒径都低于传统混凝过程,即介质加载混凝可以促进形成高密实度的絮体。也有研究[14, 22]发现,磁种间的磁性力也可促进絮体的压实,因此,介质加载混凝过程可以实现污泥减量。砂加载后混凝过程絮体粒径低于磁种加载组,其在破碎后粒径为混凝过程的一半,即存在絮体破碎,但二次沉降性能远优于传统混凝过程。磁种加载混凝过程的粒径显著高于砂加载混凝,且其絮体沉降性能、强度及再混稳定性也优于砂加载混凝,表明磁加载对于固液分离速率的促进作用高于砂加载,磁种的微磁场作用可能是主要原因[23]。100目磁种投加后形成的絮体强度较低,破碎阶段后粒径为絮凝阶段的1/3,主要原因是其粒径较大,与外层絮体的结合不密实,因此更易破碎。200目和325目磁种形成的磁絮体强度及沉降性能较好,325目磁种形成的絮体粒径略低。回收磁种加载形成的絮体粒径略高于原磁种,沉降性能与强度也较高,主要原因是回收磁种中有一定的微絮体,与絮体具有更高的亲和力。
-
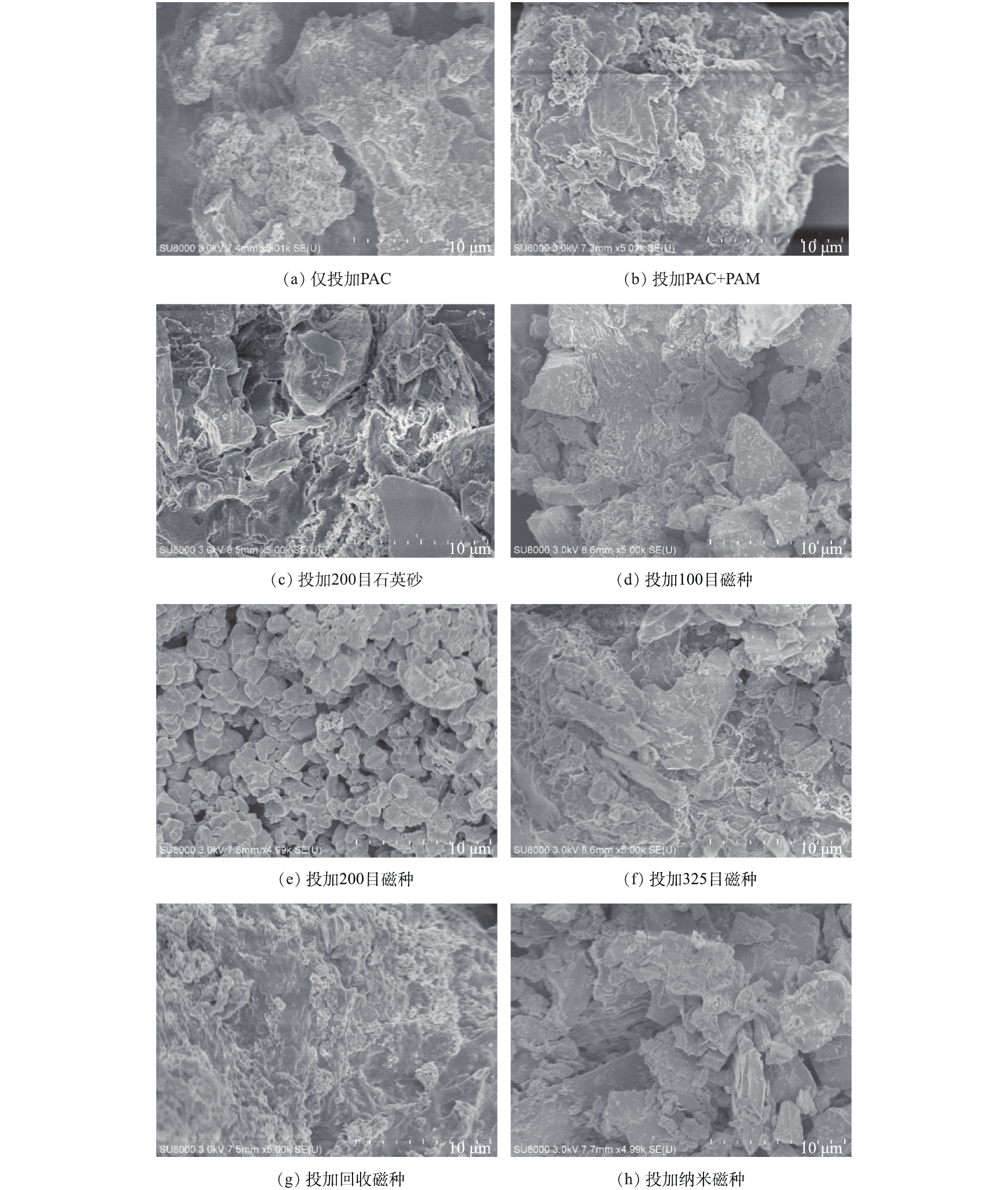
图9不同混凝组SEM的表征结果。由图9可知,投加PAC后形成的絮体较小,而投加PAM后形成的絮体粒径显著增加,在其表面可以看到小颗粒的堆积结构,因此,其在破碎过程中易分离,但强度较低。投加不同介质后,其均可作为絮体核心促进絮体生长[18]。磁种加载后形成的絮体颗粒间贴合度更高,磁种和絮体的亲和力更强,因此,其具有更高的强度,微磁场作用也是其形成密实絮体的一个主要原因[22-23]。同时,磁种粒径越低,越有利于其与絮体的结合,与絮体粒径变化的结果一致。但纳米磁种形成的絮体均质性较差,主要是由于纳米材料易发生团聚造成的。回收磁种投加后完全被絮体包围,因此,形成的絮体均质性较好,其可能原因是,由于回收磁种本身带有微絮体,与絮体有更好的亲和力,因此,其混凝效果最佳。
2.1. 不同介质加载混凝对磷去除的影响
2.2. 不同介质加载混凝对DOM去除的影响
2.3. 多介质加载对混凝过程粒径的影响
2.4. 不同介质加载对絮体形貌的影响
-
1)混凝过程总磷去除率为72%左右,
${\rm{PO}}_4^{3 - } $ -P的主要去除机制是PAC的作用,其吸附是一个瞬时过程。混凝对DOM去除主要机制为PAC水解产物的吸附和螯合作用,高芳香性、腐殖化、分子质量(4 000~50 000 Da)的DOM更易去除。2) 石英砂具有最好的强化磷去除效果,主要是强化悬浮态磷的去除,同时对腐殖酸类物质的去除也有一定的强化作用。磁种主要增强有机磷和
${\rm{PO}}_4^{3 - }$ -P的吸附,对DTP的去除效果有明显强化作用,且可促进DOM特别是5 000 Da左右的DOM的去除。3)介质加载混凝的关键作用在于形成密实性絮体,增强絮体的强度和沉降性能,实现污泥减量。
4)回收磁种表面具有一定的微絮体结构,其对磷及大分子DOM去除效果高于原磁种。因此,本研究认为,介质加载将成为未来常规混凝升级的一种有效策略,基于目前的磁种回收能力及回收磁种的高效去除率,磁混凝将成为一种有效的磷去除及污水厂升级改造工艺。




 下载:
下载: