-
随着化工、印染、纺织、造纸等行业的迅速发展,人类所面临的水污染环境问题愈发突出,亟待得到妥善处理。其中染料废水含有难以生物降解的有机大分子,使用常规水处理技术无法彻底将其从水中去除,因此需要找到处理效率高且经济成本合理的处理方式[1-3]。采用基于硫酸根自由基的高级氧化水处理技术可以有效去除难生物降解污染物,过硫酸盐过氧键可以断裂产生硫酸根自由基(
SO⋅−4 ),其氧化还原电位与羟基自由基近似,且具有选择性更强、在溶液中存在时间更长、pH范围宽广的优点[4-6]。在非均相硫酸根自由基体系中引入可见光,通过光生电子与空穴的迁移作用,能够加速产生一系列活性自由基,从而提高氧化效率,更快的将有机污染物矿化为CO2和H2O。刘杨等[7]研究了可见光下TiO2催化过硫酸盐降解罗丹明B,在30 min中内降解率达到100%。张塞等[8]研究了g-C3N4在可见光下活化过二硫酸盐(PS)对双酚A的光降解活性,RGO/g-C3N4催化剂在40 min内能够完全去除溶液中的BPA。目前,协同可见光催化过硫酸盐体系增强光催化材料的效能,以及研究复合体系协同降解机理的研究仍然较为缺乏,需要继续开展深入的理论研究。在半导体光催化材料中,BiVO4以其独特的价带结构,展现出良好的光催化性能以及光生电子与空穴迁移性能。但是,单独的BiVO4材料的光催化效率较低,电子和空穴无法有效分离[9-11]。因此,需要对BiVO4进行修饰,以增强光降解效率。通过在BiVO4结构中引入铜元素,可影响BiVO4的能带结构,提高电荷载流子的分离效率,完成对光生电子空穴的转移、分离及复合的控制,从而增强光催化效率[12-14]。
本研究针对可见光助过硫酸盐体系存在的问题,以LED灯为可见光光源,进行了光催化降解实验。LED灯具有使用寿命长,高效节能且绿色环保的优点。依据BiVO4分子结构特点,将Cu掺杂到BiVO4中,制备Cu元素掺杂BiVO4光催化剂,研究了Cu-BiVO4光催化剂应用于可见光助过硫酸盐体系的强化与协同作用,以及催化剂投加量、PMS浓度、pH等影响因素的作用,并探讨了可见光助Cu-BiVO4活化PMS技术对橙黄Ⅱ的协同降解作用机制。
全文HTML
-
实验材料:20 mg·L−1橙黄Ⅱ水溶液(北京源叶生物集团有限公司),五水硝酸铋(Bi(NO3)3·5H2O,AR,天津市科密欧化学试剂有限公司),过一硫酸钾(KHSO5,AR,天津市大茂化学试剂厂)、硝酸铜(Cu(NO3)3·9H2O,AR,天津市大茂化学试剂厂)、十二烷基苯磺酸钠(SDBS)、草酸铵((NH4)2C2O4)、对苯醌(BQ)、叔丁醇(TBA)、甲醇(MeOH)等均为分析纯,购于天津市大茂化学试剂厂,实验用水为超纯水(上海和泰仪器有限公司)。
-
以摩尔比例1∶1混合五水硝酸铋和偏钒酸铵溶液。溶液A:1.0 mmol (Bi(NO3)3·5H2O + Cu(NO3)2·3H2O) 与0.1 g SDBS溶解于3 mol·L−1硝酸溶液中[15]。溶液B:1.0 mmol NH4VO3溶解于去离子水中。然后将B溶液缓慢与A溶液相溶,持续搅拌2 h后转入100 mL聚四氟乙烯内衬的反应釜中,随后反应釜加热至160 oC保持18 h,反应结束后自然冷却至室温,交替使用乙醇和去离子水洗涤,离心后在70 oC下真空干燥12 h,研磨得到淡灰色粉末产物。将掺杂比例为0、1%、3%和5%的催化剂记为BiVO4、1Cu-BiVO4、3Cu-BiVO4和5Cu-BiVO4。
-
以30 W LED灯为光源,在可见光照条件下对Cu-BiVO4催化PMS降解橙黄Ⅱ的催化活性进行了研究。分别用BiVO4和Cu-BiVO4对含有20 mg·L−1的橙黄Ⅱ溶液进行催化降解。在光照之前,将催化剂投加入橙黄Ⅱ溶液中在暗环境下搅拌吸附1 h,建立吸附-解吸平衡。在光照开始后,加入一定浓度的PMS,每隔10 min取样,用紫外-可见分光光度计(上海仪电分析仪器有限公司)分析橙黄Ⅱ的浓度,并且运用液相色谱(Agilent 1100 LC/MSD)在有干扰的情况下测定橙黄Ⅱ浓度,液相色谱为C18 柱(1.7 μm, 50 mm×2.1 mm),检测器波长设定为485 nm,柱温为30 °C,每次进样量20 μL,流动相为乙腈与乙酸铵(30∶70)的混合物,流速是0.4 mL·min−1。使用Elementar vario检测在降解过程中总有机碳(TOC)的变化。在波长为485 nm处测定反应前后对橙黄Ⅱ的吸光度,根据式(1)计算橙黄Ⅱ的降解率。
式中:D为橙黄Ⅱ降解率;C为t时刻橙黄Ⅱ的浓度,mg·L−1;C0为橙黄Ⅱ的初始浓度,mg·L−1。
-
用X射线衍射仪(D8 ADVANCE,Bruker)测试样品的XRD谱;用场发射扫描电子显微镜(SU8220,Hitach,日本)和场发射透射电子显微镜(Talos F200S,FEI,捷克)测试样品的形貌;用紫外-可见漫反射分光光度计(Solid Spec-3700型,日本岛津公司)测试样品的UV-Vis DRS光谱;用X-射线光电子能谱(Escalab 250Xi,Thermo,Fisher)测试样品的XPS图谱。
1.1. 催化剂Cu-BiVO4的制备
1.2. 光催化反应
1.3. 样品的表征
-
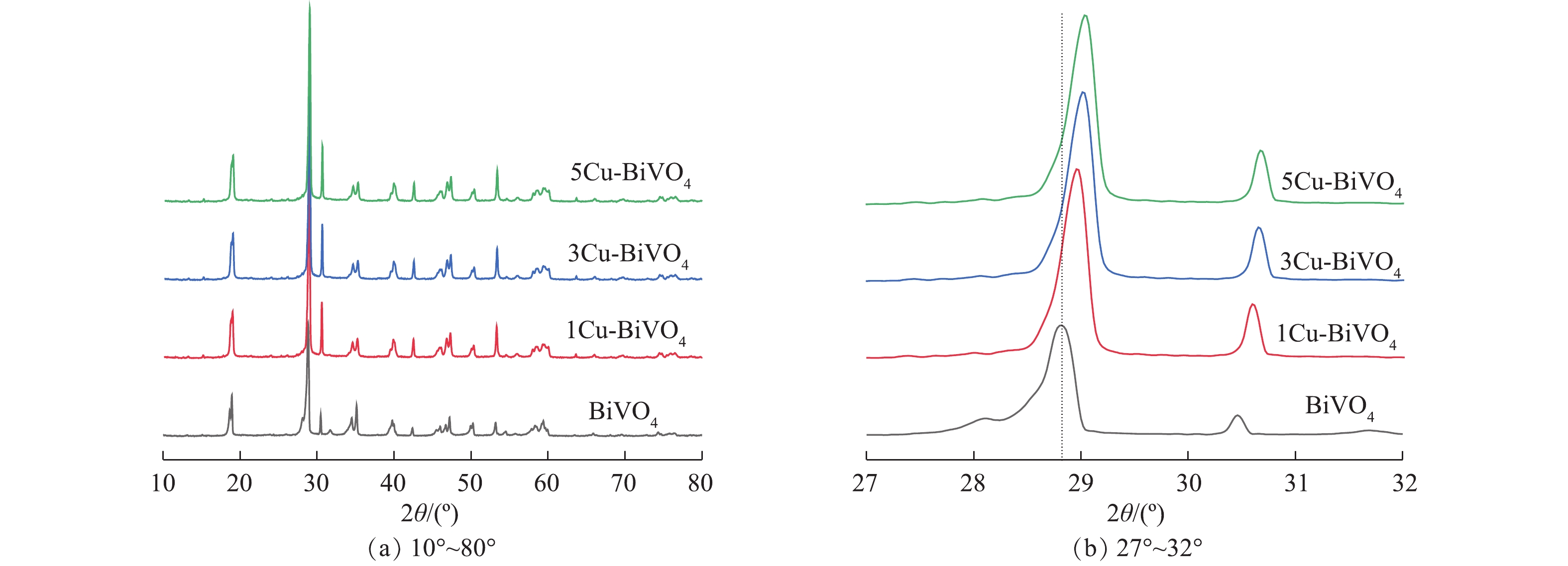
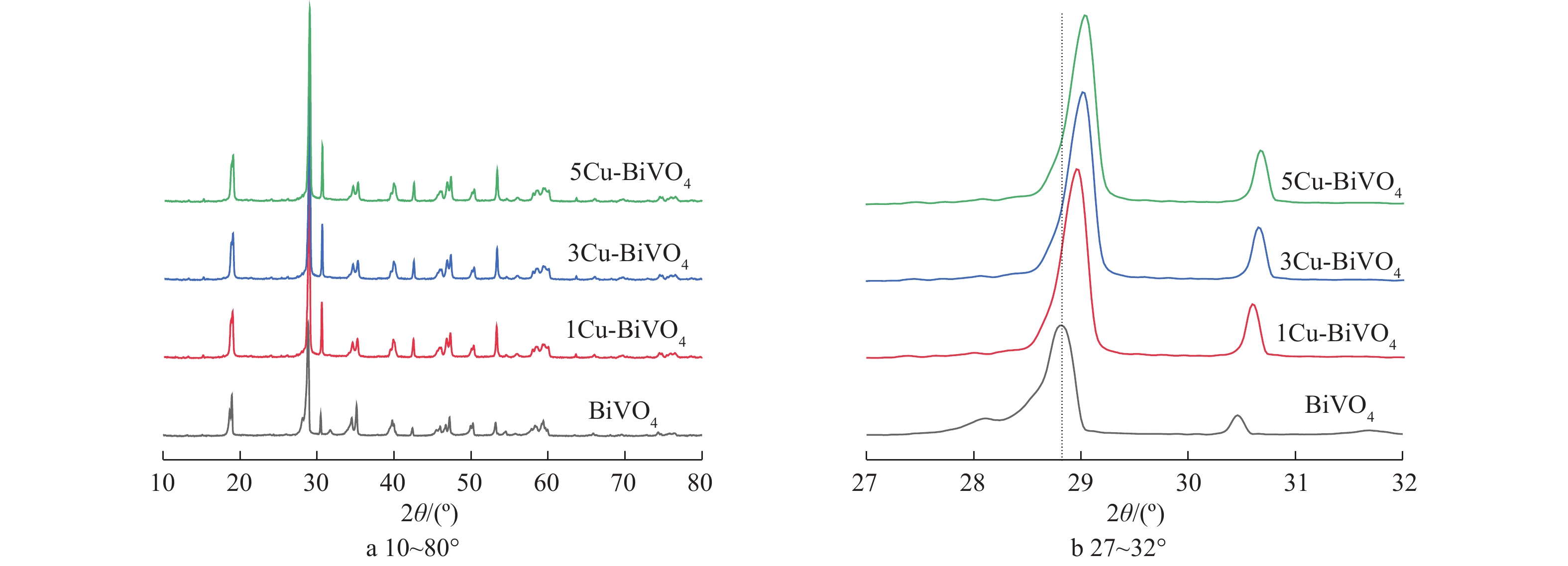
图1为BiVO4,1Cu-BiVO4,3Cu-BiVO4和5Cu-BiVO4的XRD图谱。由图1可以看出,制备的BiVO4样品的衍射峰位置与标准图谱JCPDS卡片14-0688一致,在2θ为18.7°和28.6°处出现的强衍射峰与(011)和(112)晶面位置相对应,这说明制备未掺杂的BiVO4样品为单斜相[16-18]。在引入Cu元素后,衍射峰位置18.7°、28.6°、30.5°、34.81°、47.1°分别归属于四方相,对应于(101)、(200)、(211)、(220)、(312)晶面。在Cu掺杂样品的衍射峰中未观察到CuO的衍射峰,表明Cu掺杂在BiVO4晶体中呈现出高度分散,不以晶体存在。这说明Cu的掺杂对于其晶体结构和物相均无明显影响,表明有Cu成功掺杂入BiVO4晶体结构中。此外,样品特征峰向高角度移动,这是由于铜离子半径(0.075 nm)小于Bi3+离子半径(0.103 nm),容易取代BiVO4晶格中Bi3+离子,从而引起衍射峰向高角度偏移。
采用Debye-Scherrer方程计算BiVO4和5Cu-BiVO4样品的晶粒尺寸,分别为97.6 nm和70.7 nm,掺杂后的晶粒尺寸减小,这表明掺杂对与BiVO4晶粒生长有抑制作用。同时晶粒尺寸的减少有利于提高Cu-BiVO4光催化剂的催化活性,有利于光生电子和光生空穴的迁移,降低电子与空穴的复合。
-
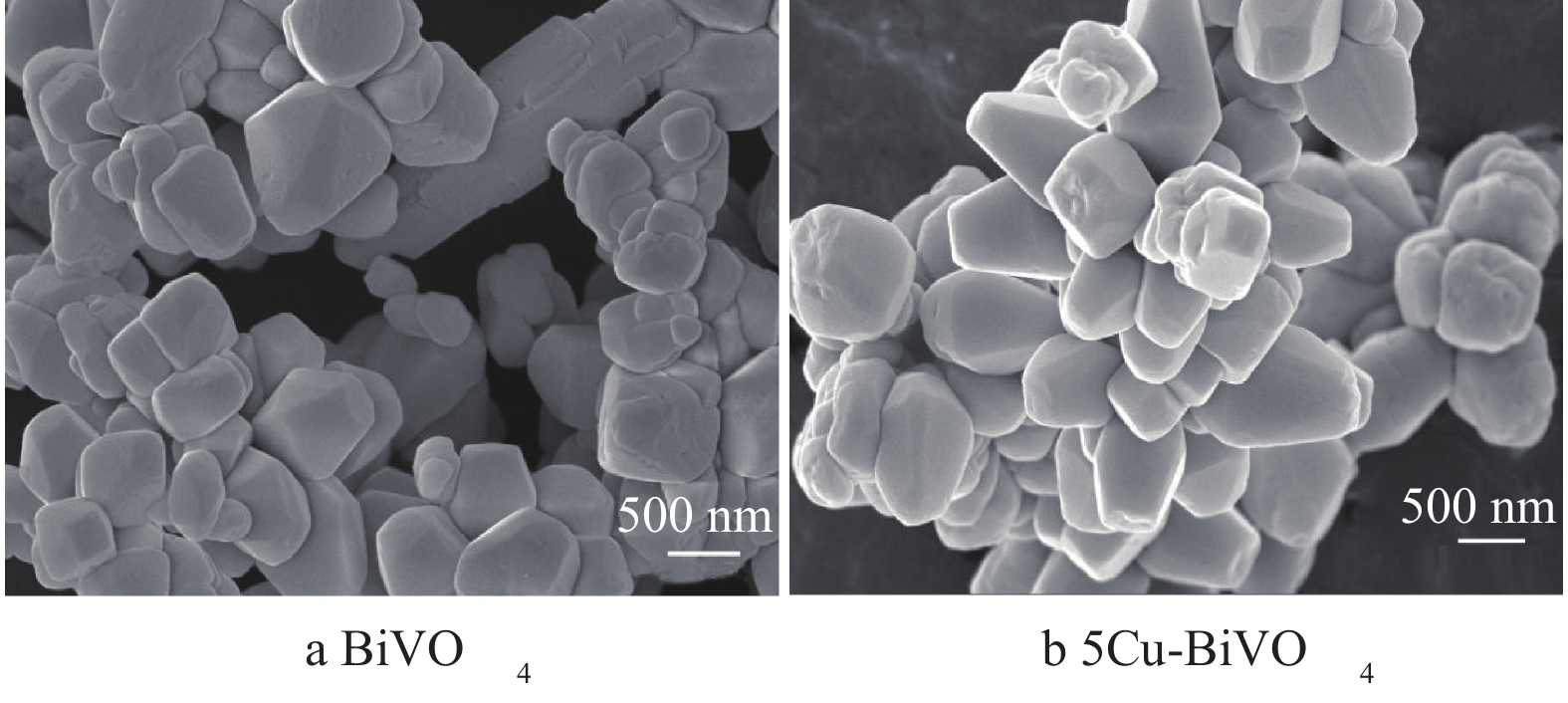
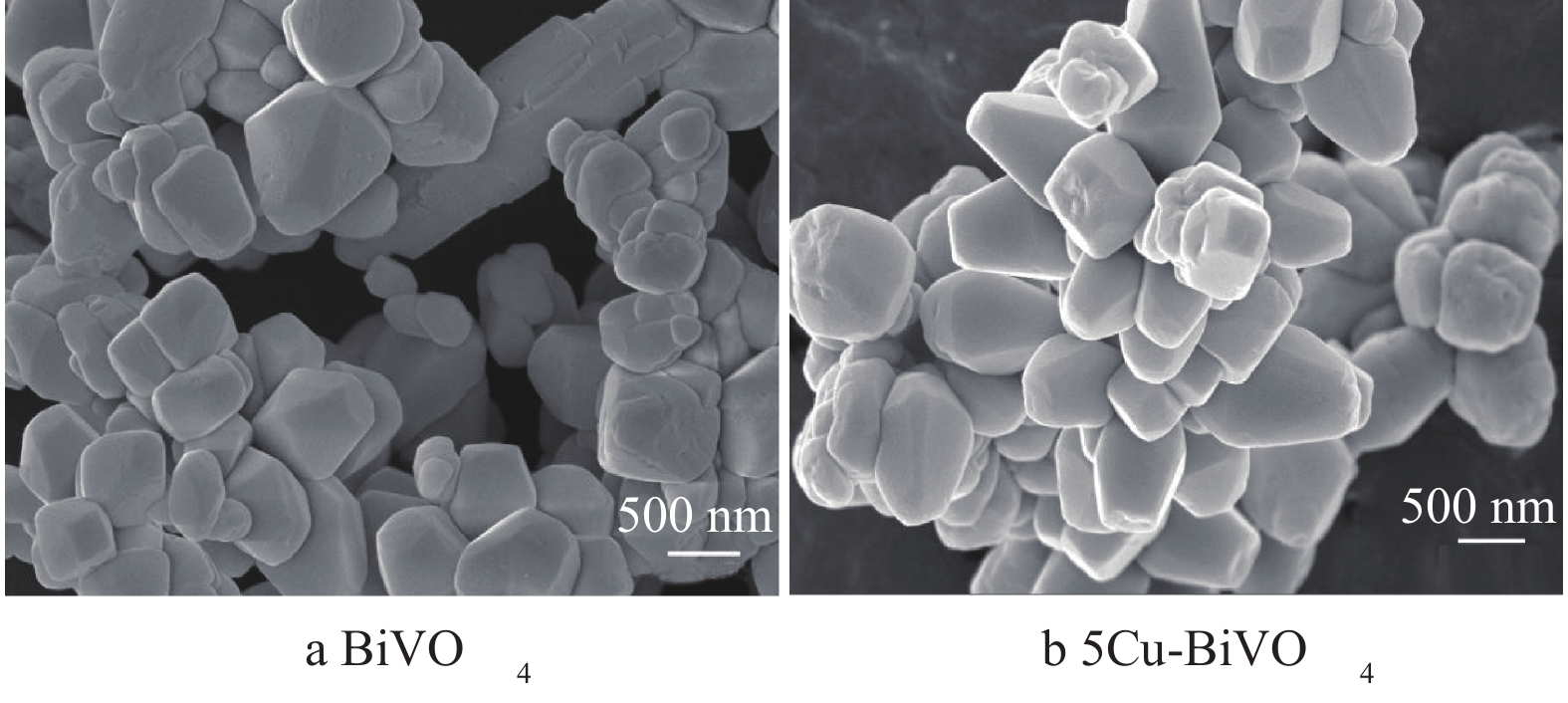
图2为BiVO4和5Cu-BiVO4纳米材料的SEM图片。由图2可以看出,单个颗粒呈现哑铃状,掺杂Cu离子后BiVO4的形貌没有发生明显变化,这说明Cu的掺杂对BiVO4形貌的影响不大。纳米粒子轮廓清晰,形貌规整,表明纳米粒子的结晶性能良好。纳米粒子大小约为60~65 nm,大小分布均匀,与XRD表征结果相吻合。
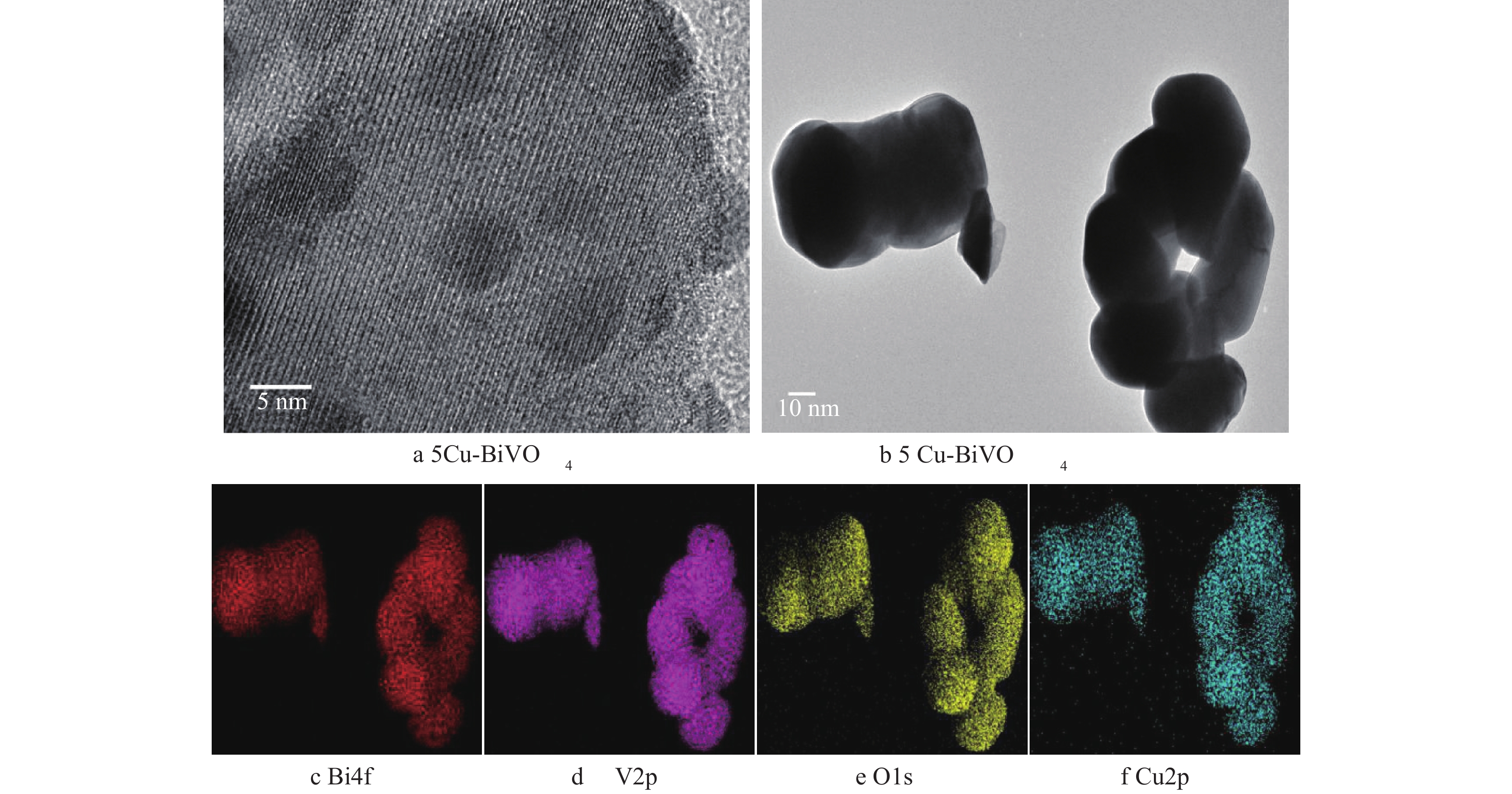
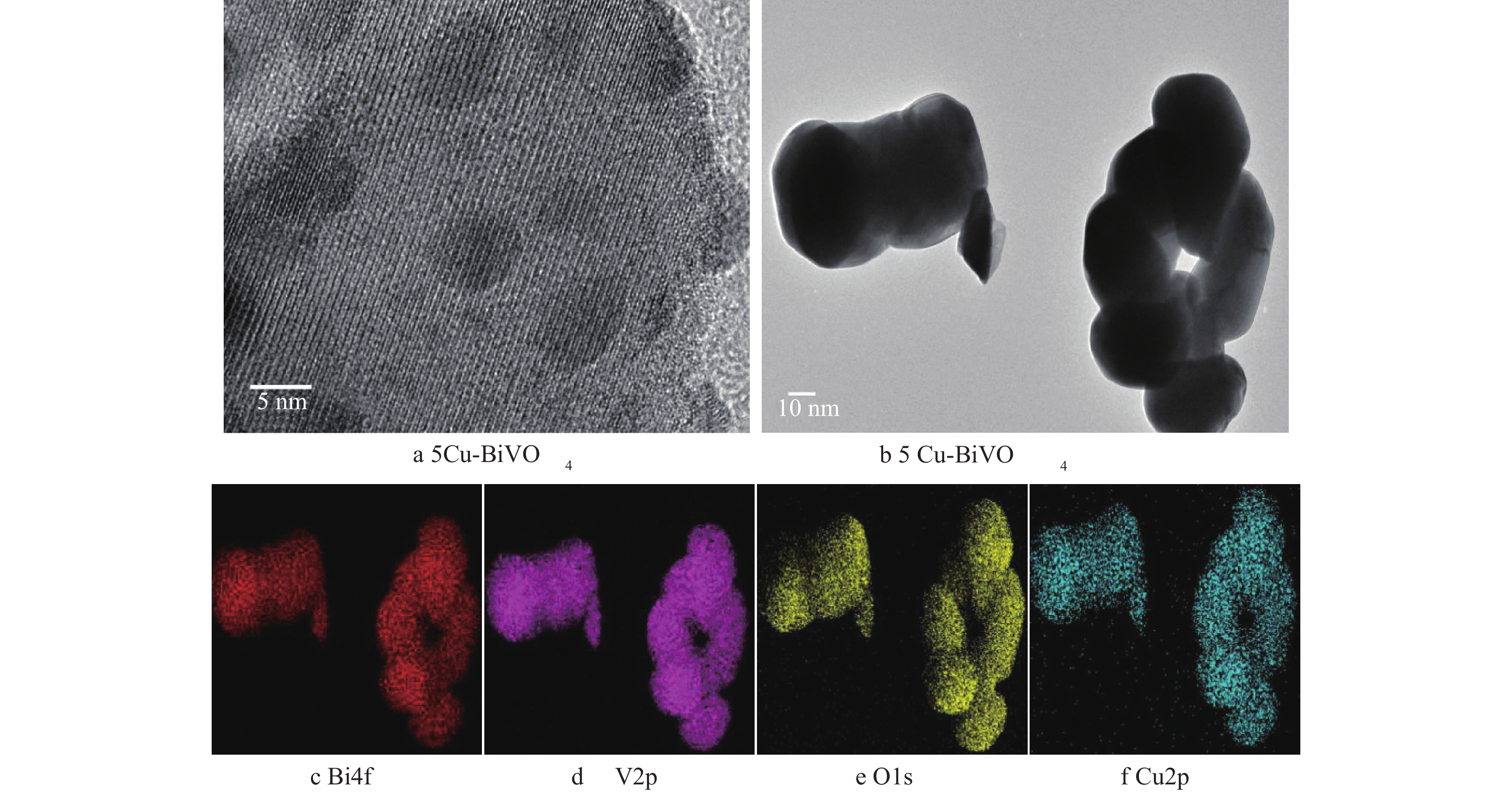
图3为5Cu-BiVO4纳米材料的TEM图片。由图3可以看出,铜掺杂后样品为球形纳米颗粒。从图3(f)中可以看出有高度分散的Cu均匀分布在纳米颗粒上,证实Cu成功掺杂到主体结构中,Cu-BiVO4的尺寸大小约为57 nm。
-
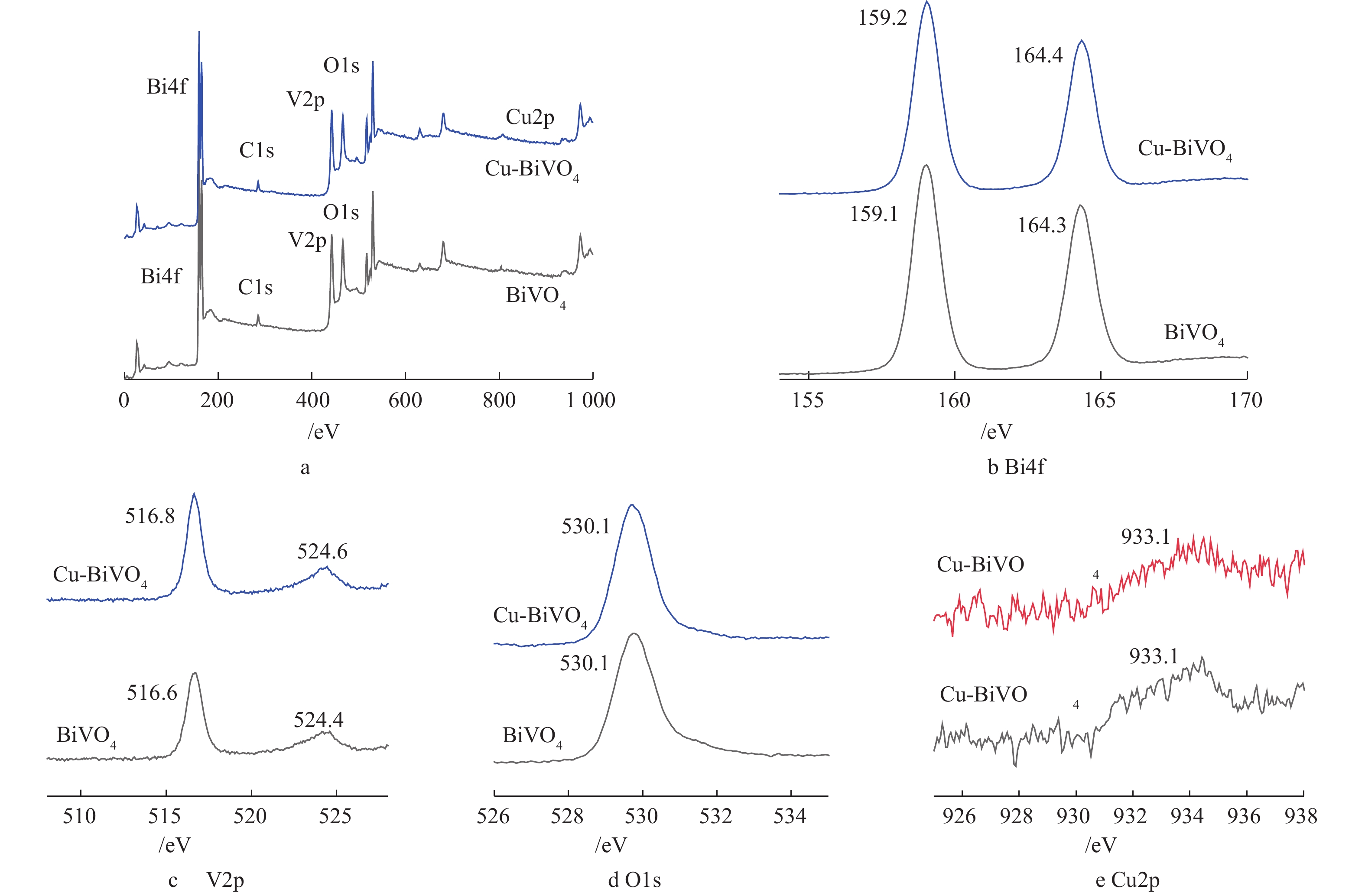
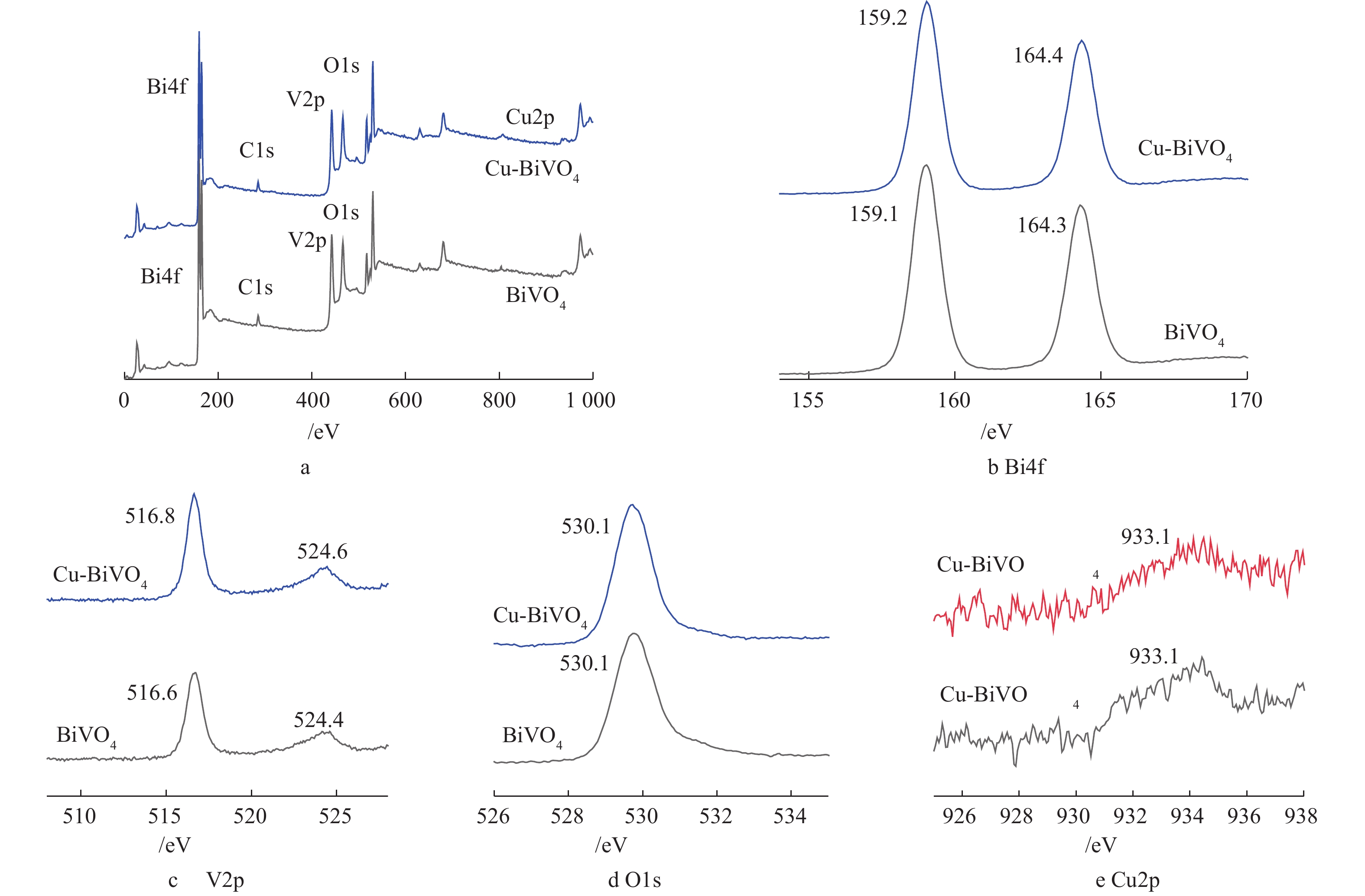
为研究纳米材料的化学组成和价态变化,对Cu掺杂BiVO4光催化剂进行XPS表征。图4为BiVO4和5Cu-BiVO4纳米材料的XPS图谱。由图4(a)可见,样品中含有Cu、Bi、V和O 元素,Bi4f7/2和Bi4f5/2的结合能分别为159.2 eV和164.4 eV,与纯BiVO4相比,其结合能向高能态方向移动0.1 eV。V2p1/2和V2p3/2的结合能分别是516.8 eV和524.6 eV,与纯BiVO4相比,其结合能向高能态方向移动0.2 eV,这是由于铜离子掺杂到BiVO4结构中,产生一定的晶格畸变,导致结合能发生移动[19-21]。O1s的特征峰分别为530.1 eV和531.2 eV,分别对应样品中的晶格氧和表面吸附态氧。结合能位于933.1 eV处的特征峰对应Cu2p3/2,归属于Cu-BiVO4中的Cu离子。XPS的表征结果进一步证实了铜离子掺杂入BiVO4的主体结构。
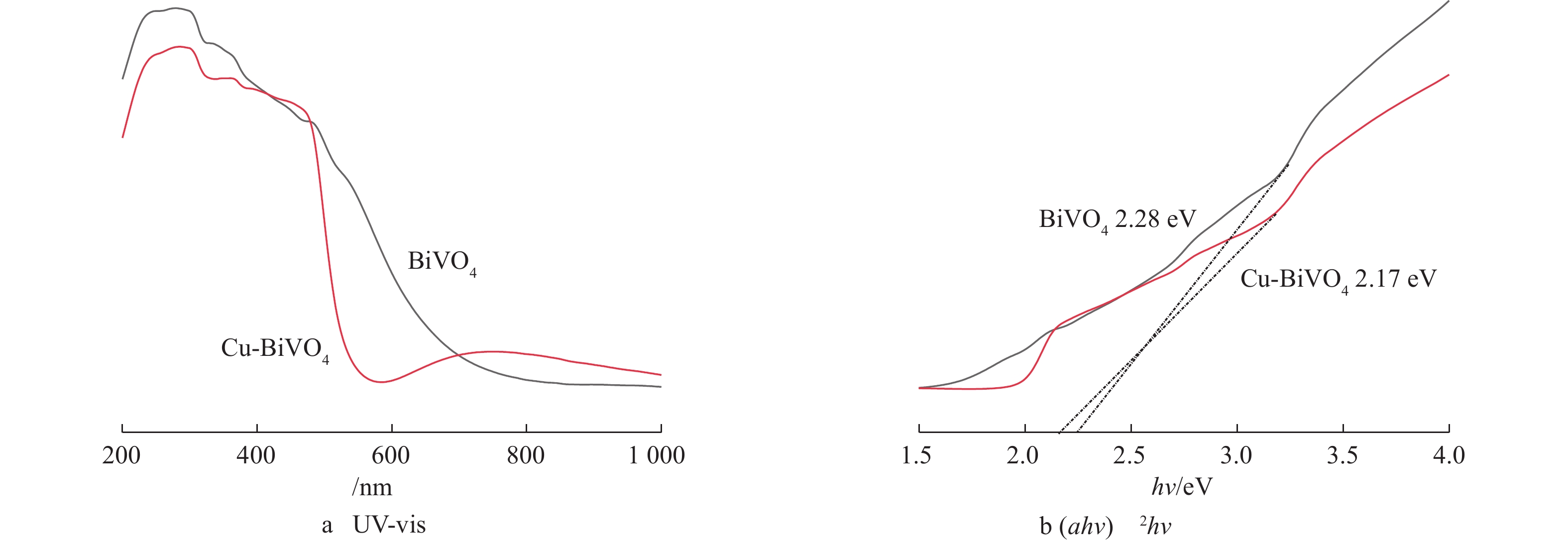
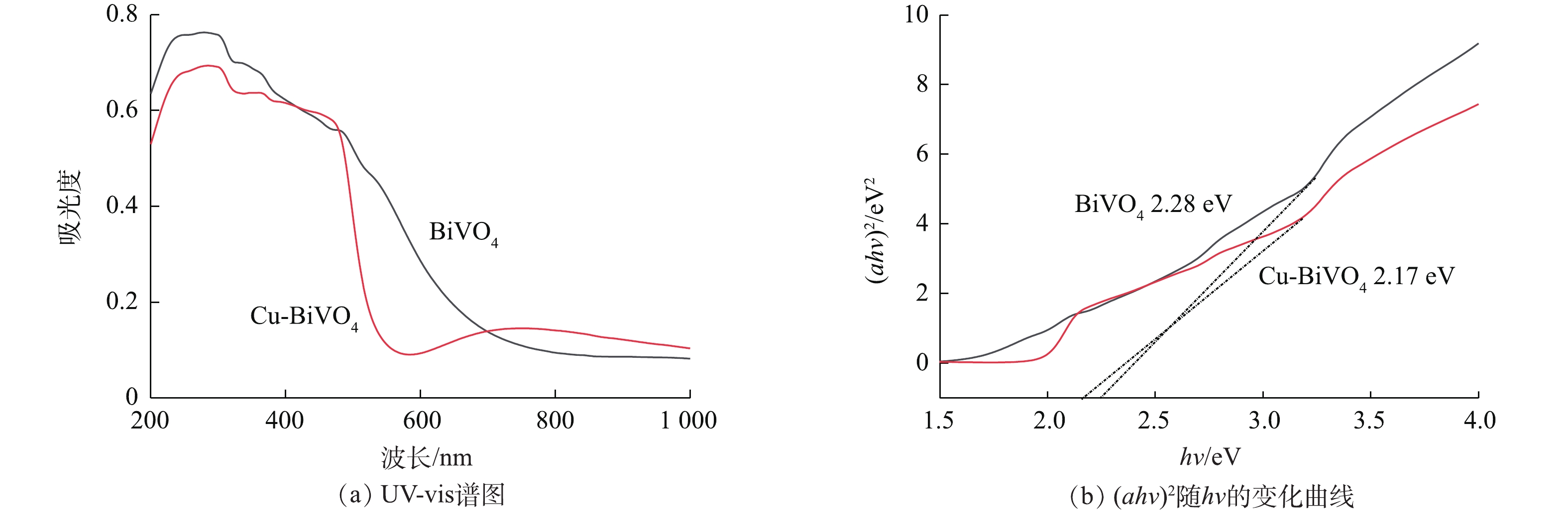
图5为纯BiVO4和Cu-BiVO4样品的UV-vis光谱图。由图5可知,单独BiVO4吸收在540 nm,而Cu掺杂BiVO4在可见光区有较强的吸收。在530~800 nm的可见光区,Cu掺杂BiVO4的光吸收能力较单独BiVO4有明显增强,这有利于光催化反应的进行。计算得出BiVO4和Cu-BiVO4的禁带宽度Eg分别计算为2.28 eV和2.17 eV。
-
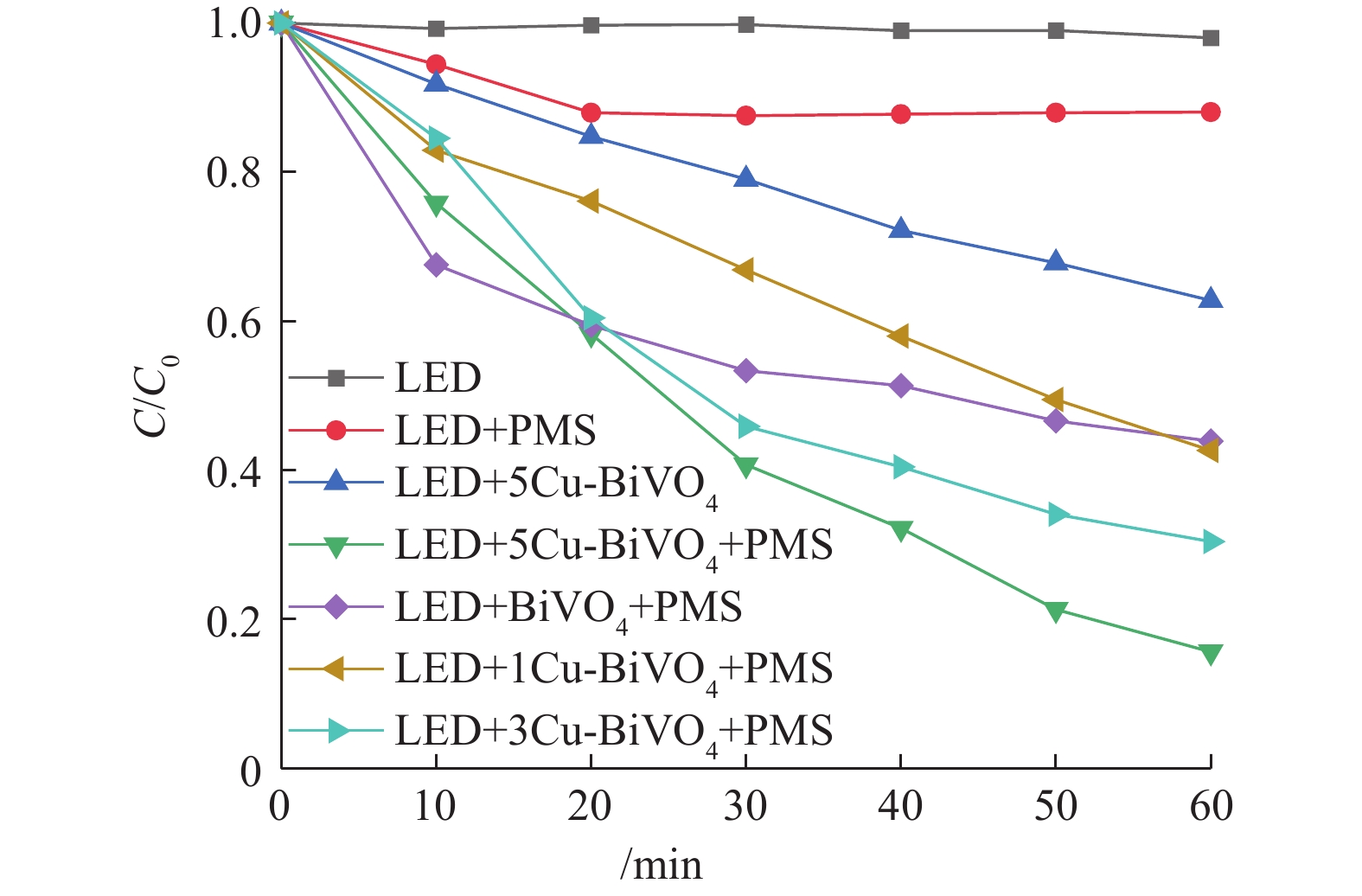
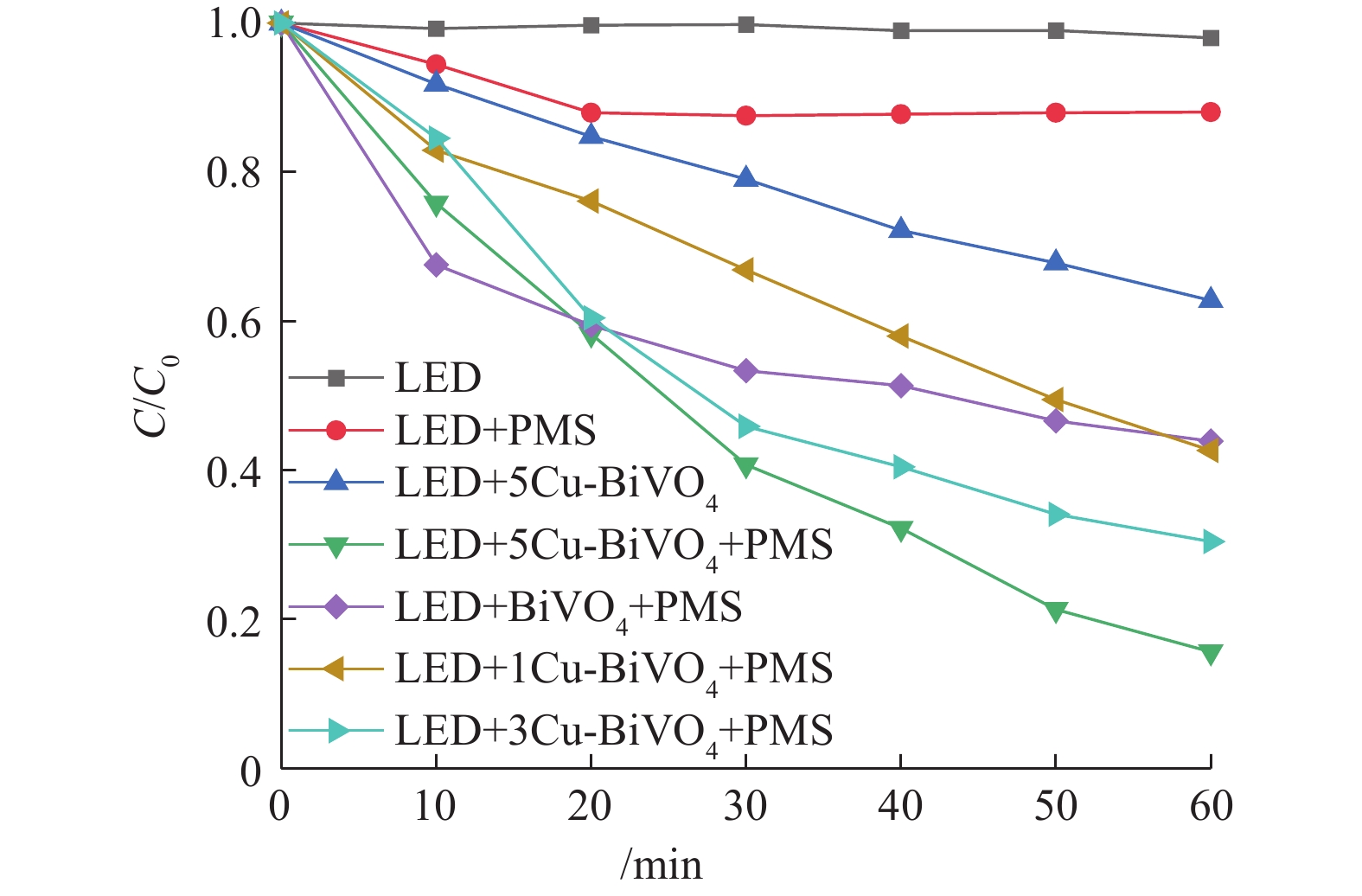
前期的预实验结果表明,单独光照体系、单独PMS体系和催化剂吸附体系对于橙黄Ⅱ几乎没有降解作用。如图6所示,在催化剂投加量为0.5 g·L−1、PMS投加量为0.6 mmol·L−1时,在可见光与PMS体系中,橙黄Ⅱ的降解率为11.9%。这是由于光照条件下PMS可以被催化裂解产生高活性硫酸根自由基从而降解橙黄Ⅱ。在可见光与催化剂体系中,橙黄Ⅱ降解率接近37.2%。这证明催化剂对橙黄Ⅱ的降解作用是在光照条件下进行,产生一系列活性自由基从而降解橙黄Ⅱ,单独催化剂的吸附作用有限。在有可见光照射的条件下,非均相5Cu-BiVO4/PMS体系中橙黄Ⅱ的降解率为84.38%。这证明可见光的引入对非均相过硫酸盐体系有良好的促进协同作用。
将不同质量分数的Cu掺杂的一系列Cu-BiVO4催化剂中,经比较发现,单独BiVO4降解橙黄Ⅱ的效率最低。随着Cu掺杂量的增加,对橙黄Ⅱ的降解率逐步增加,这是由于Cu元素掺杂入BiVO4结构中构成活性位点,掺杂Cu元素增加,活性位点增加,能够产生的活性自由基数量增加,橙黄Ⅱ的降解率随之上升[22-24]。在各个催化剂中催化活性对比中,单独BiVO4对橙黄Ⅱ的降解率最低。
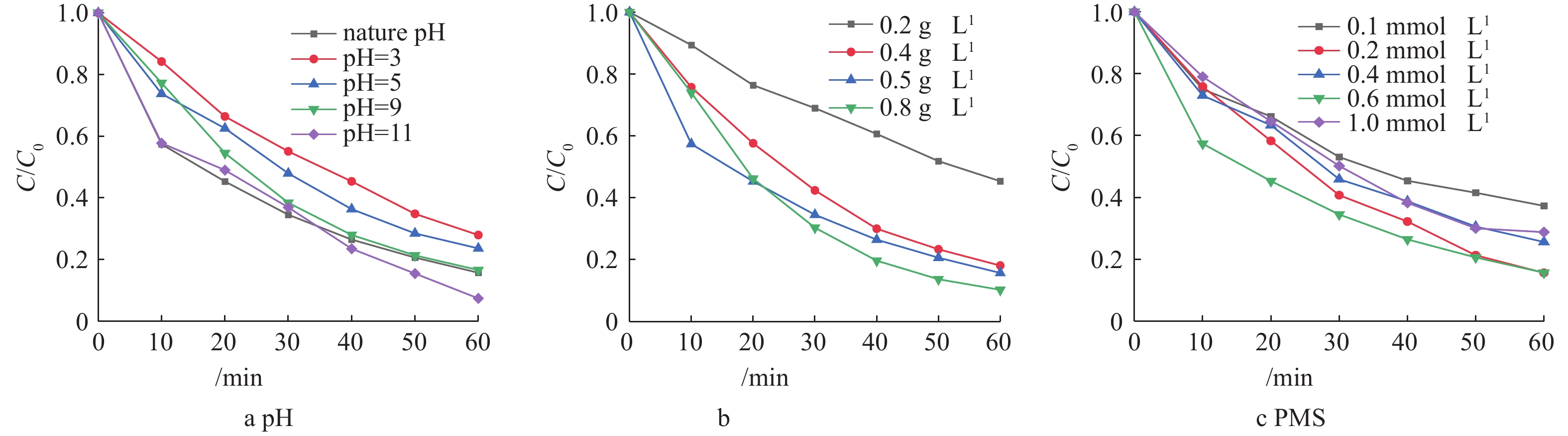
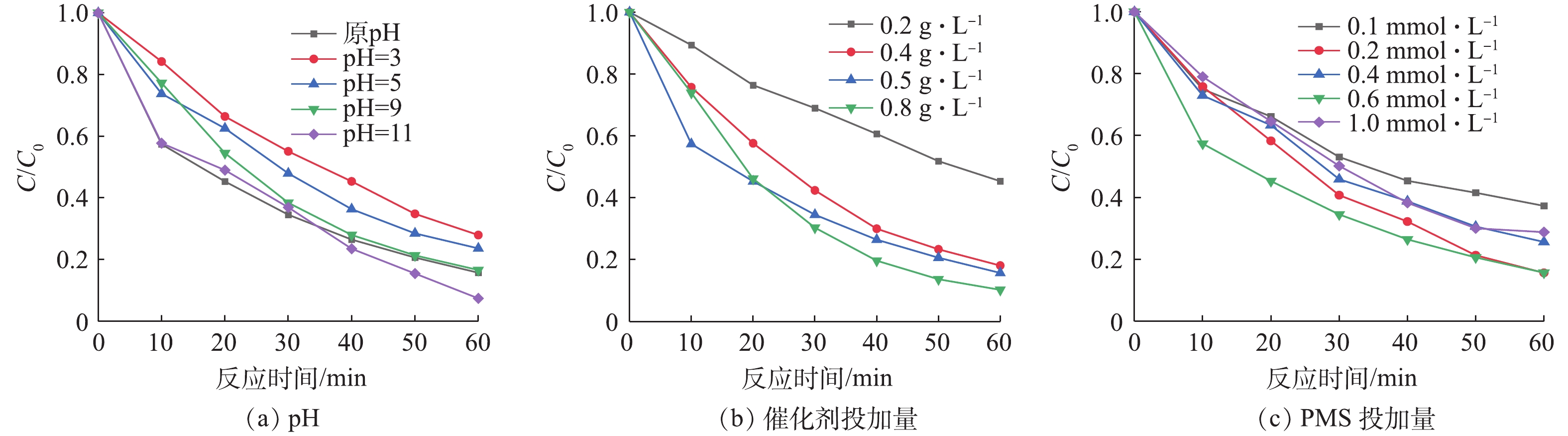
将20 mg·L−1的橙黄Ⅱ溶液调节pH分别为3、5、7、9、11,测定pH变化对橙黄Ⅱ的影响如图7(a)所示。由图7(a)可以看出,在酸性条件下,橙黄Ⅱ的降解率偏低,随着pH的升高,橙黄Ⅱ的降解率逐步升高。这是由于在酸性条件下,橙黄Ⅱ和H+在催化剂表面存在竞争吸附,H+浓度过高,使得催化剂表面活性位点被H+占据,橙黄Ⅱ的降解率偏低;而在碱性条件下,PMS能够水解反应生成羟基自由基,参与到降解过程中[25-27]。由此可见,在后续实验过程中,出于经济的考虑橙黄Ⅱ溶液未调节pH进行反应。
在橙黄Ⅱ的初始浓度为20 mg·L−1,Cu-BiVO4的投加量分别为0.1、0.3、0.5和0.8 g·L−1, PMS投加量为0.6 mM时,考察Cu-BiVO4投加量对橙黄Ⅱ降解率的影响,结果如图7(b)所示。由图7(b)可知,当Cu-BiVO4投加量为0.8 g·L−1时,橙黄Ⅱ的降解率最大为89.7%。随着Cu-BiVO4投加量的增加,橙黄Ⅱ的降解率先增大后逐渐减小。这是由于投加量较小时,催化剂的活性反应位点不足,产生的活性自由基有限。而当催化剂投加量增大至一定程度后,过多的催化剂会产生聚集,导致反应体系中催化剂的活性反应位点减少,造成光能利用率下降,降解效率随之下降。
在橙黄Ⅱ的初始浓度为20 mg·L−1、5Cu-BiVO4的投加量为0.5 g·L−1时,PMS的投加量分别为0.2、0.4、0.6和1.0 mmol·L−1时,考察PMS投加量对橙黄Ⅱ降解率的影响,结果如图7(c)所示。由图7(c)可知,当PMS投加量为0.6 mmol·L−1时,橙黄Ⅱ的降解率最佳。随着PMS投加量的增加,橙黄Ⅱ的降解率先增大后逐渐减小。在PMS浓度较低时能产生的硫酸根自由基有限,导致橙黄Ⅱ降解率不高;当PMS浓度过高时,由于PMS与硫酸根自由基存在竞争反应,导致自由基数量减少,导致其降解率降低。
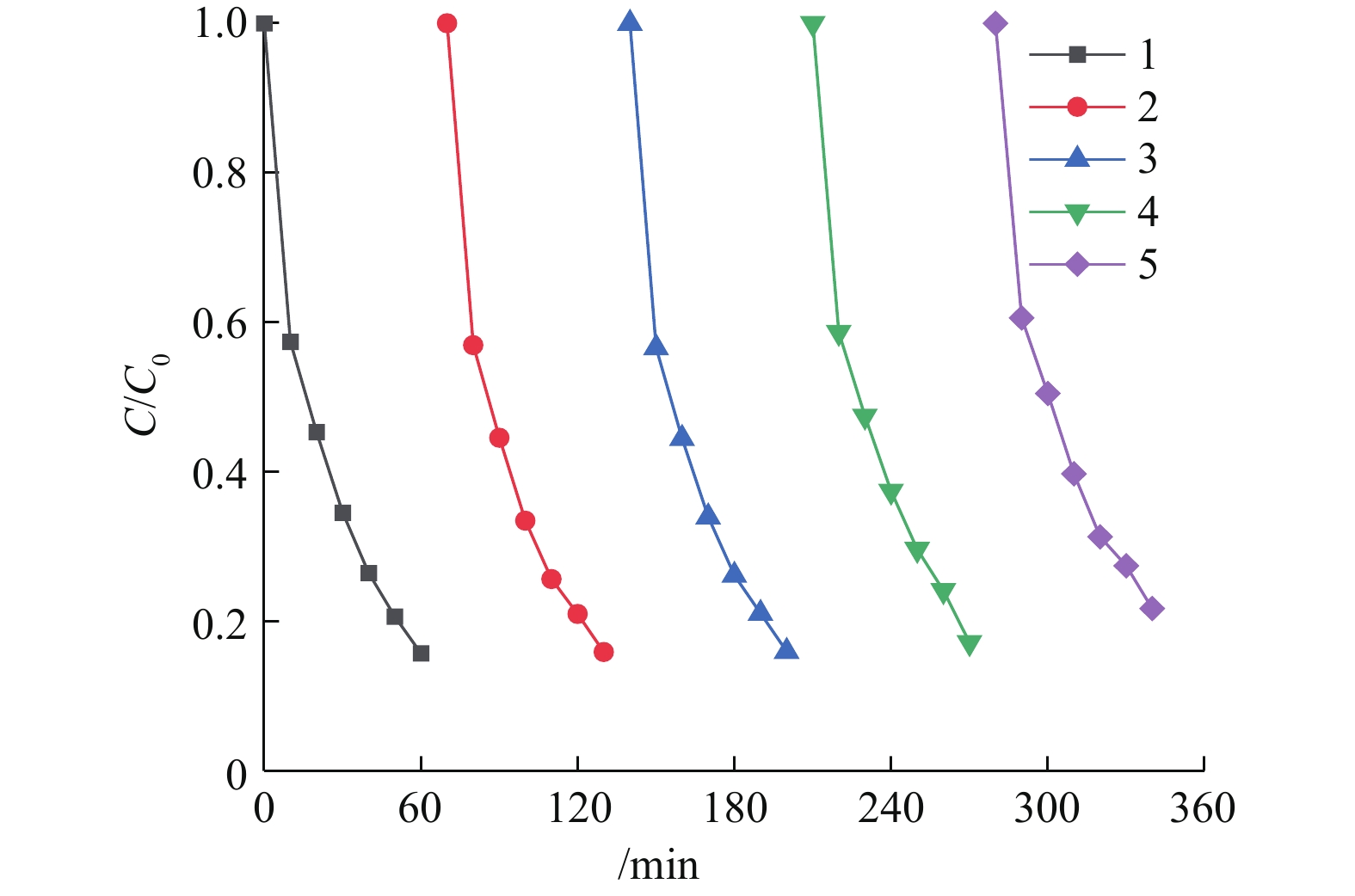
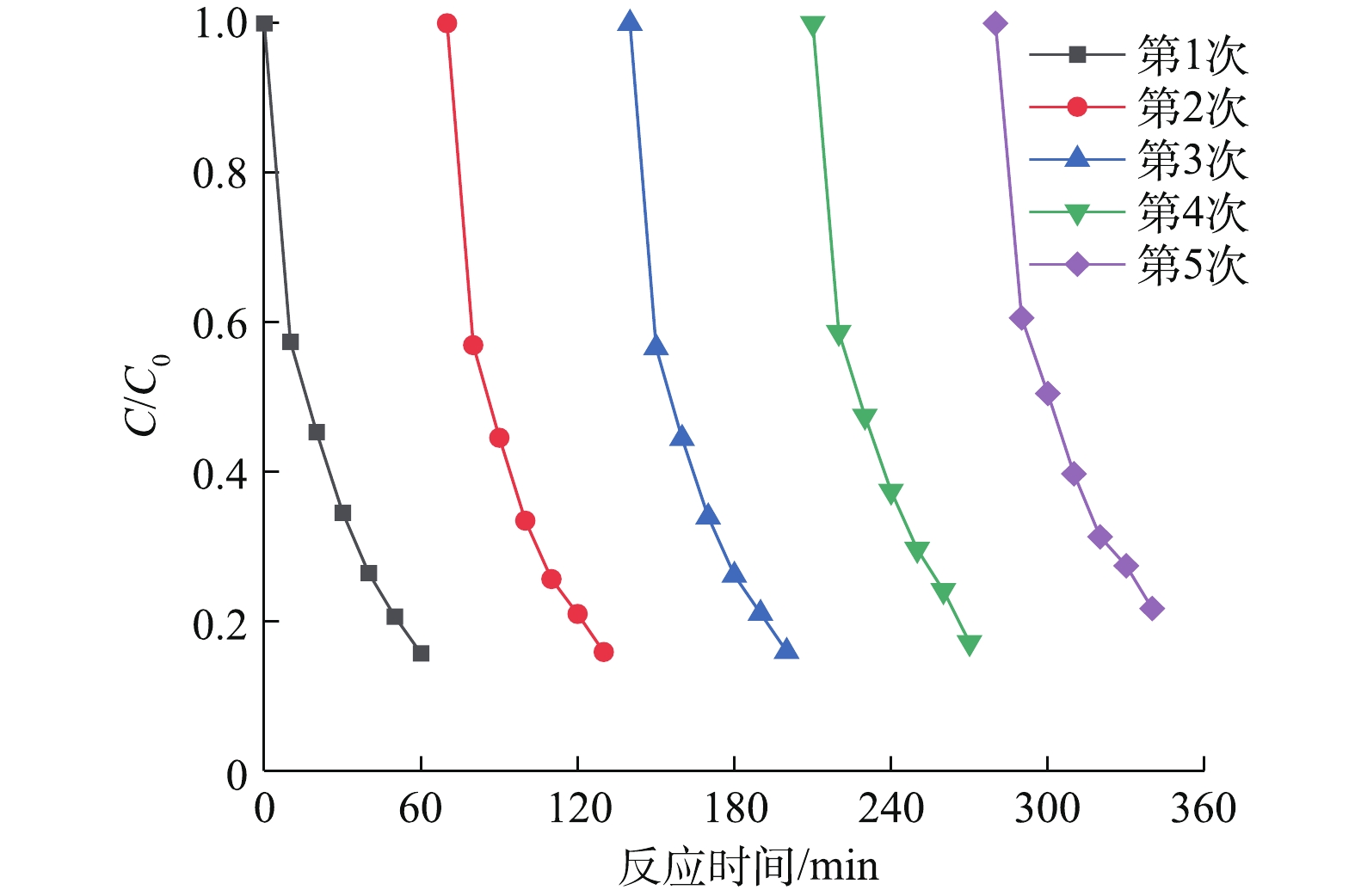
同时,可见光助Cu/BiVO4/PMS降解橙黄Ⅱ的过程中,30 min和60 min后降解橙黄Ⅱ的总有机碳TOC降解率分别为15.43%和42.79%,对应的橙黄Ⅱ降解率为59.24%和84.38%。这是由于投加的PMS(0.6 mmol·L−1)的剂量低于理论PMS投加量(2.56 mmol·L−1),橙黄Ⅱ能够被部分矿化降解。光催化剂的稳定性和重复使用性能也是值得考量的重要参数之一。通过进行催化剂平行实验,在数次催化反应结束之后,对使用的5Cu-BiVO4催化剂进行回收、洗涤、干燥之后,混合均匀进行下一次循环实验,排除因无法完全回收材料带来的影响,以评价催化剂的重复利用特性,结果如图8所示。由图8可知,催化剂对橙黄Ⅱ的降解率随着重复使用次数的增加有所降低。这是由于催化剂无法做到完全回收,催化剂上的活性位点被部分覆盖无法继续反应。但是,5Cu-BiVO4在重复使用5次之后降解率依然高达78.3%,铜离子沥出小于0.2 mg·L−1。这说明Cu掺杂BiVO4是一种催化性能和稳定性能良好的光催化剂。
-
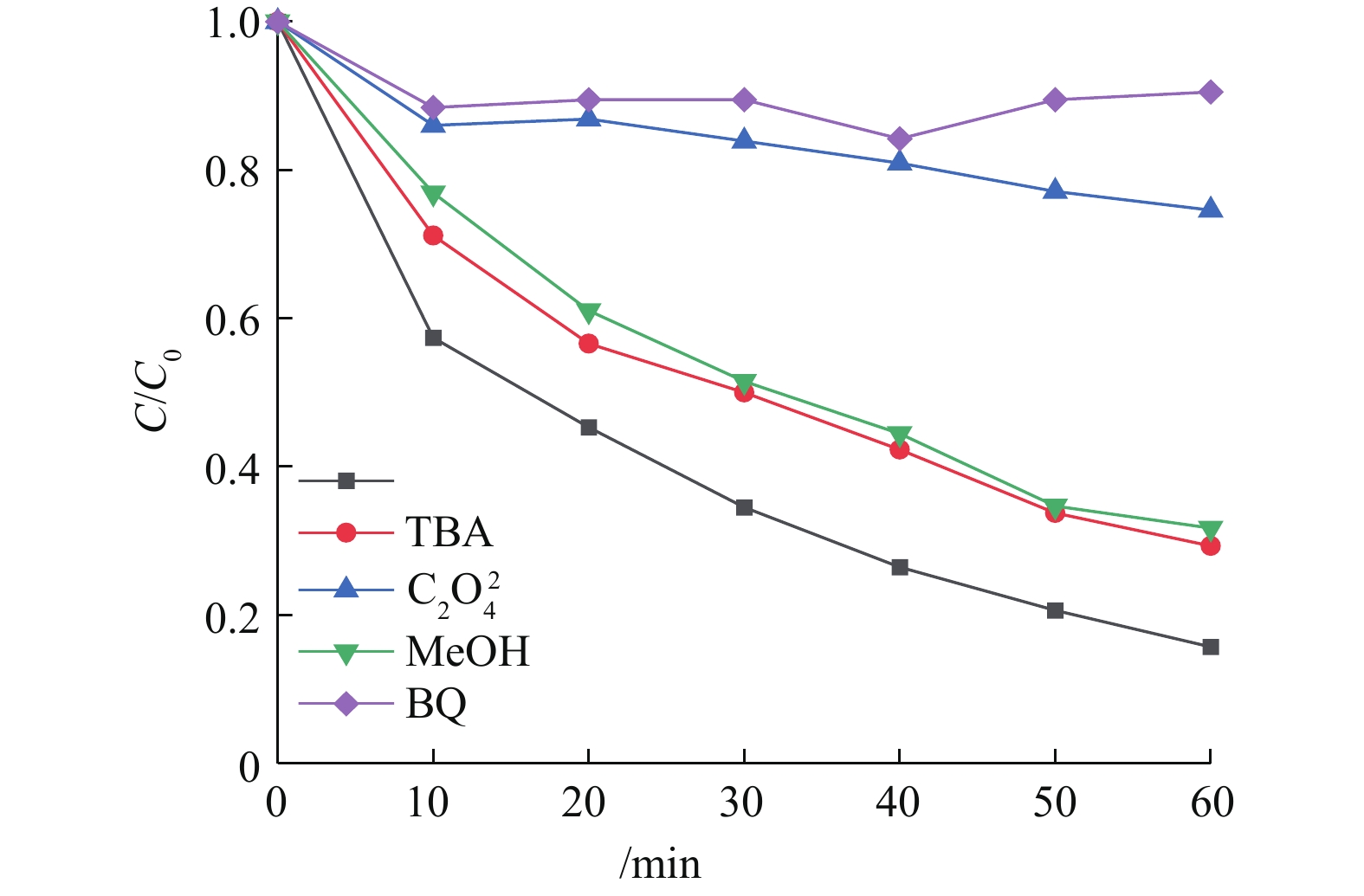
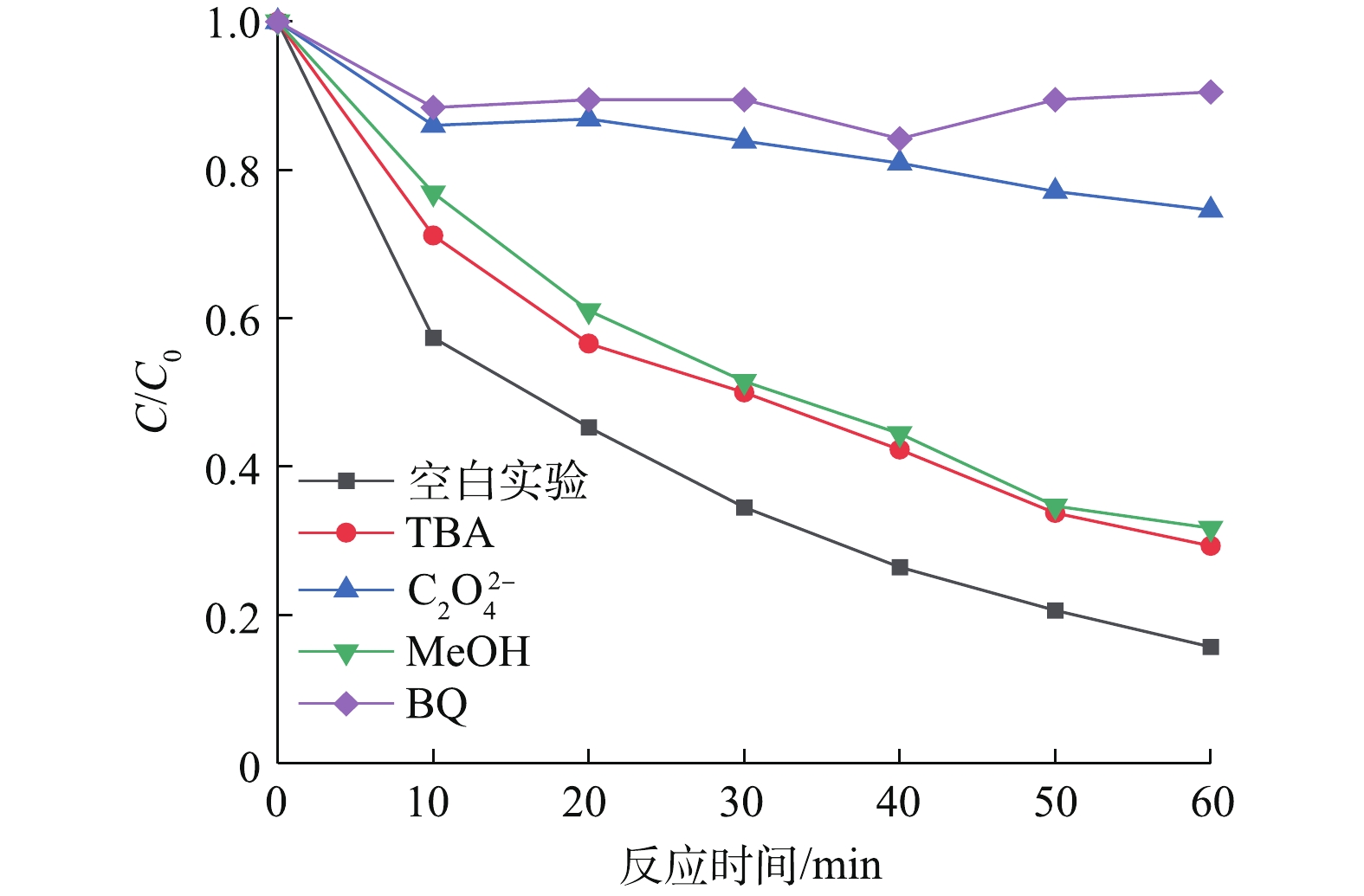
在可见光助Cu-BiVO4/PMS反应体系中分别加入叔丁醇、甲醇、对苯醌和草酸铵,以捕获反应体系中产生的羟基自由基,羟基自由基和硫酸根自由基,超氧自由基和光生空穴,以确认橙黄Ⅱ降解过程中可能存在的自由基,结果如图9所示。由图9可知,加入自由基捕获剂后,橙黄Ⅱ的光催化降解率降低,在光照60 min后,橙黄Ⅱ的降解率分别9.5%(对苯醌)、25.4%(草酸铵)、68.3%(甲醇)和70.7%(叔丁醇)。以上结果表明,在整个橙黄Ⅱ光催化降解体系中,4种活性自由基均有产生并参与到橙黄Ⅱ的氧化降解反应过程。羟基自由基和硫酸根自由基在降解橙黄Ⅱ的过程的贡献远远低于光生空穴和超氧自由基[28-33]。
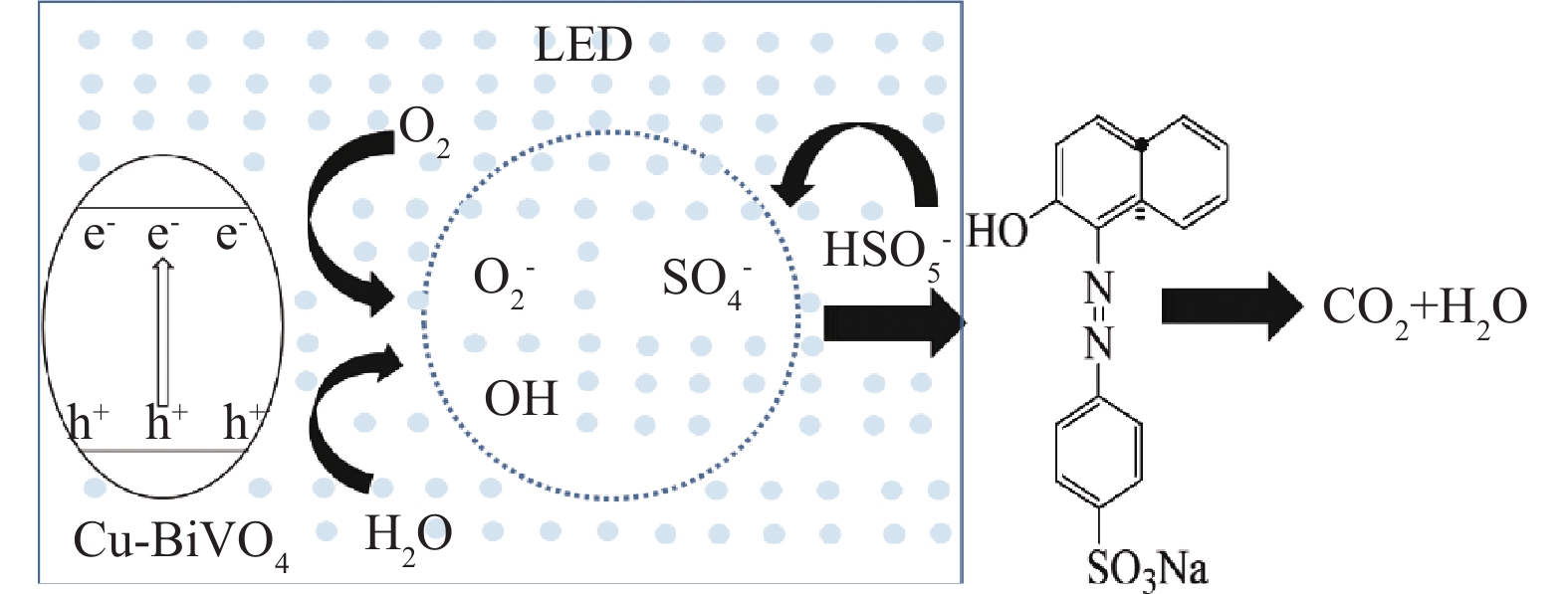
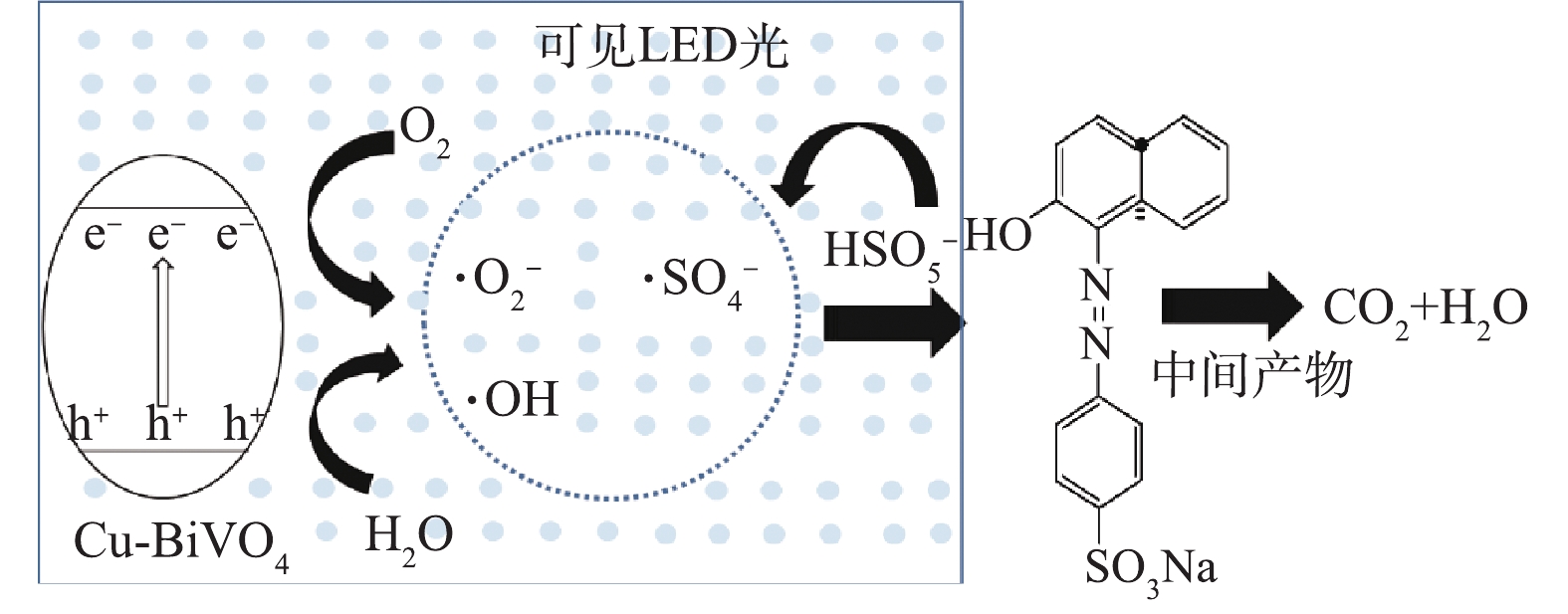
根据Cu-BiVO4的结构特性和实验结构,可以得出光助Cu-BiVO4/PMS体系的催化机理,如图10所示。在可见LED光照射下,催化剂价带上的电子可以被激发从而转移到导带上,在Cu-BiVO4催化剂表面产生光生电子和光生空穴。其次,掺杂Cu离子增强了BiVO4对可见光的响应范围,从而提高了其光催化活性,同时也能够提供Cu2+/Cu+转换的活性反应位点[34-36]。
光生电子和空穴能够与催化剂表面的溶解氧和水发生反应,从而生成一系列活性自由基,其可参与后续的光催化反应。此外,由于Cu+的存在能够活化PMS,在催化剂表面与PMS反应产生硫酸根自由基和羟基自由基,最终,橙黄Ⅱ被大量产生的自由基降解,最终矿化成CO2和H2O。
2.1. XRD分析
2.2. SEM分析和TEM分析
2.3. XPS分析与UV-vis吸收光谱
2.4. PMS协同Cu-BiVO4的可见光性能测试
2.5. Cu-BiVO4光催化反应机理
-
1)通过一步水热合成法成功制备了催化剂Cu-BiVO4,并将其应用至可见光助Cu-BiVO4/PMS体系中降解橙黄Ⅱ。在可见光照射条件下,非均相Cu-BiVO4/PMS体系的光催化降解效果显著优于暗反应条件下,反应60 min后橙黄Ⅱ的光催化降解率约为84.38%。
2) Cu-BiVO4在铜掺杂量为5%、投加量为0.5 g·L−1、PMS浓度为0.6 mmol·L−1时,对20 mg·L−1橙黄Ⅱ的催化降解率达到最高;其被重复利用5次后,对橙黄Ⅱ催化降解率依然高达78.3%,且铜离子的沥出小于0.2 mg·L−1,这说明催化剂稳定性能良好。
3)将铜离子掺杂入BiVO4结构中,能够有效的去除目标污染物。这说明Cu-BiVO4是一种催化性能和重复利用性能良好的光催化材料。
4)在Cu掺杂BiVO4体系中,体系中
SO⋅−4 、·OH和⋅O−2 和光生空穴实现橙黄Ⅱ的氧化降解。





 下载:
下载: