-
臭氧具有氧化能力较强、气源丰富易得、制备简单便捷、没有二次污染、脱色除臭能力强等优点,因此,被广泛应用于消毒和废水的处理中[1-2]。气液传质是臭氧氧化效果的主要限制性因素之一。在传统的臭氧氧化过程中,臭氧通常以气泡的形式注入液相,从而实现臭氧在水中的分散、溶解和传质[3-4],但传质受到气泡尺寸的限制,且存在占地面积大、泡沫、液泛等问题[5]。膜接触器是一种可选的替代方案。在膜接触器中,气液两相被膜相隔离,膜相提供了稳定且较大的气液传质界面,气体在浓度差的作用下扩散至液相并溶解,避免了上述问题的同时,可以在较紧凑的结构中达到较高的体积传质系数(
$ {k}_{\mathrm{L}}a $ )[4-7],提高了臭氧的传质效率。因此,膜接触器在臭氧氧化降解污染物方面具有一定的应用前景[8]。由于臭氧具有较强的氧化活性,因此,用于臭氧氧化膜接触器的膜材料必须是耐臭氧的。而PVDF中空纤维膜易制备、成本低、臭氧耐受性较强、具有一定疏水性,因此,常被用作臭氧膜接触器[2-3]。但在长期的运行过程中,传统PVDF中空纤维膜较高的孔隙率会导致部分或完全润湿的现象,增加了膜相气液传质阻力(膜孔内的液相阻力),从而降低了臭氧传质效率[9-12]。而提升膜材料表面疏水性,可减少液体进入膜孔的程度,进而降低膜相传质阻力。PDMS耐臭氧性良好、臭氧渗透性较强,同时具有致密的结构和优秀的疏水性[13-17]。若用PDMS对PVDF膜表面进行改性可有效提升PVDF膜的疏水性,从而改善膜润湿现象,提升其臭氧传质效果。因此,本研究将PDMS涂覆于传统PVDF膜表面,以提高其臭氧传质效率和长期运行稳定性[18-19]。
本研究利用涂覆-热固化法成功制备了PDMS-PVDF改性膜,采用多种方法对改性膜的结构和形貌进行表征,测试接触角、孔径和孔隙率等参数。探究不同实验参数对不同膜臭氧传质的影响,分析其体积传质系数和长期运行效果。同时,对改性膜、原PVDF膜和鼓泡曝气方式降解刚果红的效果进行比较。
-
本研究所用PVDF中空纤维膜购自北京碧水源科技股份有限公司。羟基封端的聚二甲基硅氧烷(PDMS,40 cst)、正庚烷(C7H16,98%)、硅酸四乙酯(TEOS,98%)、二月桂酸二丁基锡(C32H64O4Sn,95%)均购自上海麦克林生化科技有限公司。靛蓝二磺酸钠(C16H8N2Na2O8S2,96%)、磷酸二氢钠(NaH2PO4,AR)、磷酸(H3PO4,AR)购自上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司。刚果红(C32H22N6Na2O6S2,AR)购自天津市天新精细化工开发中心。
-
本研究使用商业PVDF膜自制膜接触器,其中PVDF中空纤维膜外径为1.9 mm、内径为1.0 mm、孔隙率为61.5%、平均孔径为0.224 μm,所制备的膜接触器内径为16 mm,有效长度为100 mm,膜丝数量为39根、比表面积为2 105 m−1、填充率为55%。
以正庚烷为溶剂,并以PDMS质量为基准加入10%的交联剂硅酸四乙酯和2%的催化剂二月桂酸二丁基锡,配制不同质量浓度的PDMS涂覆液,搅拌4 h后备用。将涂覆液通过蠕动泵泵入组装好的膜接触器中1 min,随后在85 ℃下固化12 h,重复3次,制得改性膜[20]。分别用S-0、S-2、S-5和S-10表示涂覆质量分数为0%、2%、5%和10%的样品。
中空纤维膜的孔径由Porolux 1000毛细孔径仪(比利时Porometer NV公司)测定。孔隙率采用干湿重法测定[21-22]。采用SL 200KB型接触角测量仪(美国KINO公司)表征膜外表面的疏水性。利用衰减全反射红外光谱(ATR-FTIR)表征膜的化学结构,所用机型为Nicolet iS20(美国Thermo Scientific公司)。使用Dimension Icon型原子力显微镜(AFM,德国Bruker公司)对膜的形貌和粗糙度进行表征分析。使用配有IXRF Model 550i型能谱仪(EDS)的S-4800型扫描电镜(SEM,日本Hitachi公司)对膜表面、截面的形貌和元素成分进行分析,测试前对膜丝进行液氮淬断及喷金处理。
-
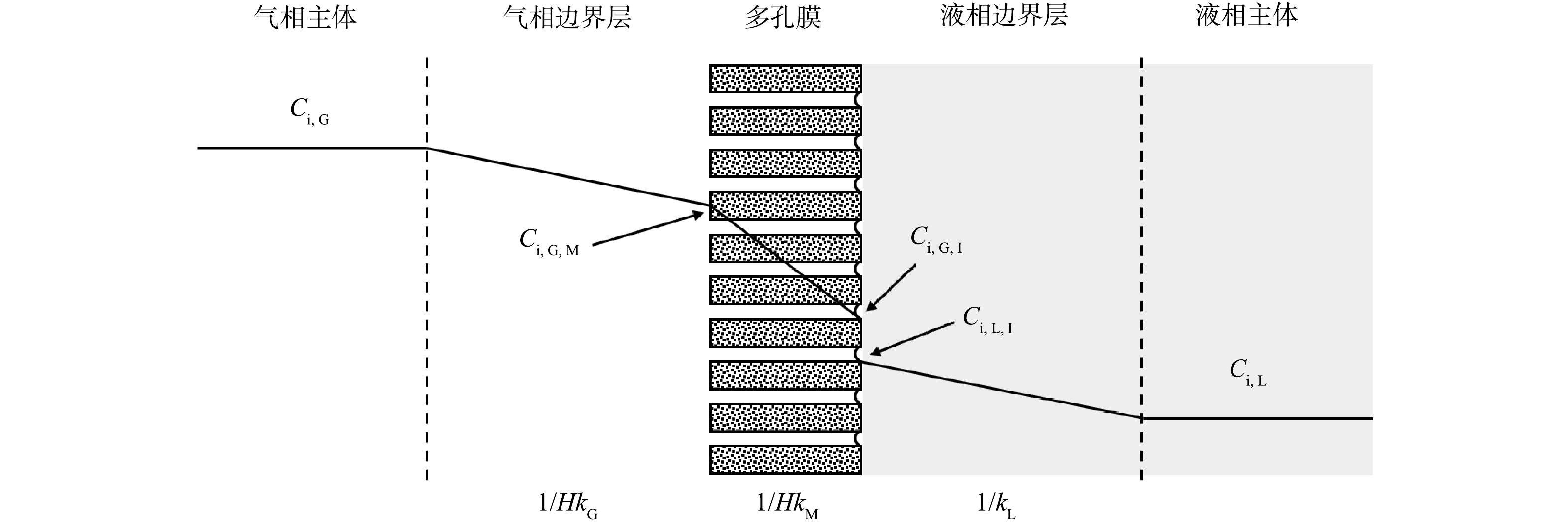
根据双膜理论和亨利定律,气液膜接触器传质模型[2,23]如图1所示。则传质过程中的阻力可描述为式(1)。
式中:
$ H $ 为亨利常数;$ {K}_{\mathrm{T}} $ 、$ {k}_{\mathrm{L}} $ 、$ {k}_{\mathrm{M}} $ 、$ {k}_{\mathrm{G}} $ 分别为总传质系数、液相传质系数、膜相传质系数和气相传质系数,m·s−1。据报道,气相扩散系数和膜相扩散系数远高于液相扩散系数[24],故气相和膜相传质阻力可以忽略,总传质阻力1/
$ {K}_{\mathrm{T}} $ 近似于液相传质阻力1/$ {k}_{\mathrm{L}} $ 。因此,臭氧在水中的传质应符合式(2),对式(2)积分可得式(3)。臭氧降解刚果红的过程遵循伪一级反应动力学,其降解速率常数根据式(4)进行计算。式中:
$ a $ 为膜比表面积,m2·m−3;$ {k}_{\mathrm{L}}a $ 为体积传质系数,min−1;$ C $ 为臭氧的饱和浓度,mg·L−1;$ {C}_{t} $ 为t时刻出水臭氧浓度,mg·L−1。式中:
$ {k}_{\mathrm{c}} $ 为刚果红降解速率常数,min−1;$ {c}_{0} $ 为刚果红初始质量浓度,mg·L−1;$ {c}_{t} $ 为t时刻刚果红质量浓度,mg·L−1。 -
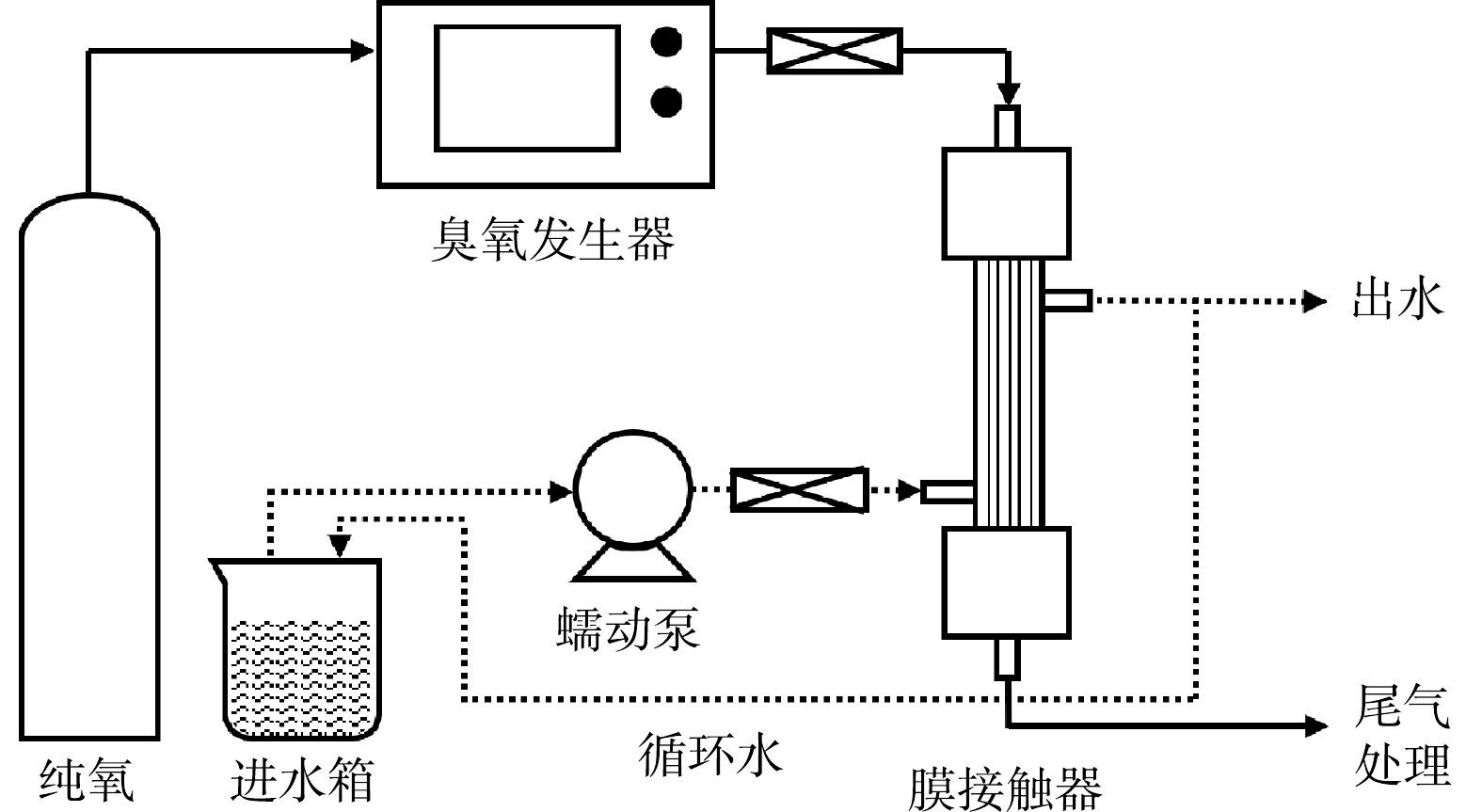
实验装置如图2所示。以纯氧为气源,经臭氧发生器产生一定浓度的臭氧进入膜接触器的管侧,液相则经蠕动泵以一定的流量进入膜接触器的壳侧。气液传质实验中,以超纯水为吸收剂,探究了不同实验参数(包括进水流量、进气流量和进气浓度)对改性膜接触器传质效果的影响,并以出水臭氧浓度和体积传质系数
$ {k}_{\mathrm{L}}a $ (式(3))评价其臭氧传质效果。模拟废水降解实验中,对鼓泡曝气、S-0和S-5用于臭氧氧化降解刚果红的效果进行了比较。其中,液相为初始质量浓度100 mg·L−1的刚果红溶液,在膜接触器中循环流动一定时间后取样并测试刚果红浓度、总有机碳,并根据式(4)计算降解速率常数$ {k}_{\mathrm{c}} $ 。气相臭氧浓度由UVOS-3300V型臭氧分析仪(山东爱迪尔仪器有限公司)测得,以靛蓝二磺酸钠分光光度法测试液相臭氧浓度[25-26]。刚果红的吸光度与浓度之间存在良好的相关性,故采用分光光度法,在刚果红最大吸收波长497 nm下测定其浓度,所用仪器为SP-756P型UV-Vis分光光度计(上海光谱仪器有限公司);总有机碳(TOC)使用N/C 2100s (德国Analytik Jena公司)测定。
-
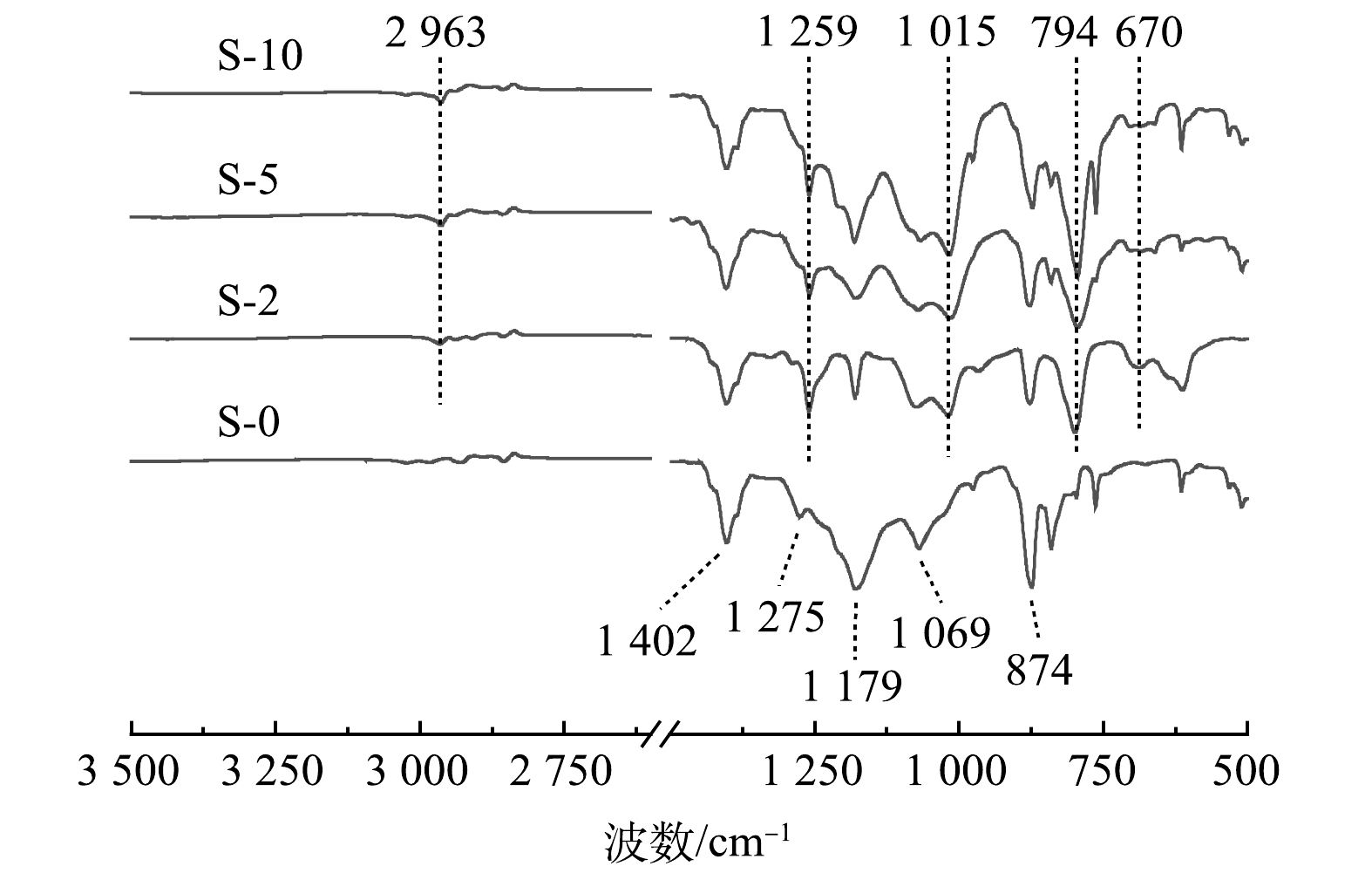
1)化学组成与结构。图3为原PVDF膜和改性膜外表面的ATR-FTIR图谱。在原膜S-0中,874 cm−1是PVDF的无定形峰,1 069 cm−1是其结晶峰,1 402 cm−1是CH2的吸收峰,1 179 cm−1和1 275 cm−1是CF2的伸缩振动峰[24,27]。改性膜中出现了一些新吸收峰,其中794、1 015和1 259 cm−1由Si—O—Si振动引起的,670 cm−1和2 963 cm−1对应于Si—C的伸缩振动[27-28]。这表明PDMS在PVDF膜上成功涂覆。且随着涂覆质量分数的增加,PDMS的相关特征峰强度大致呈现出增加的趋势。
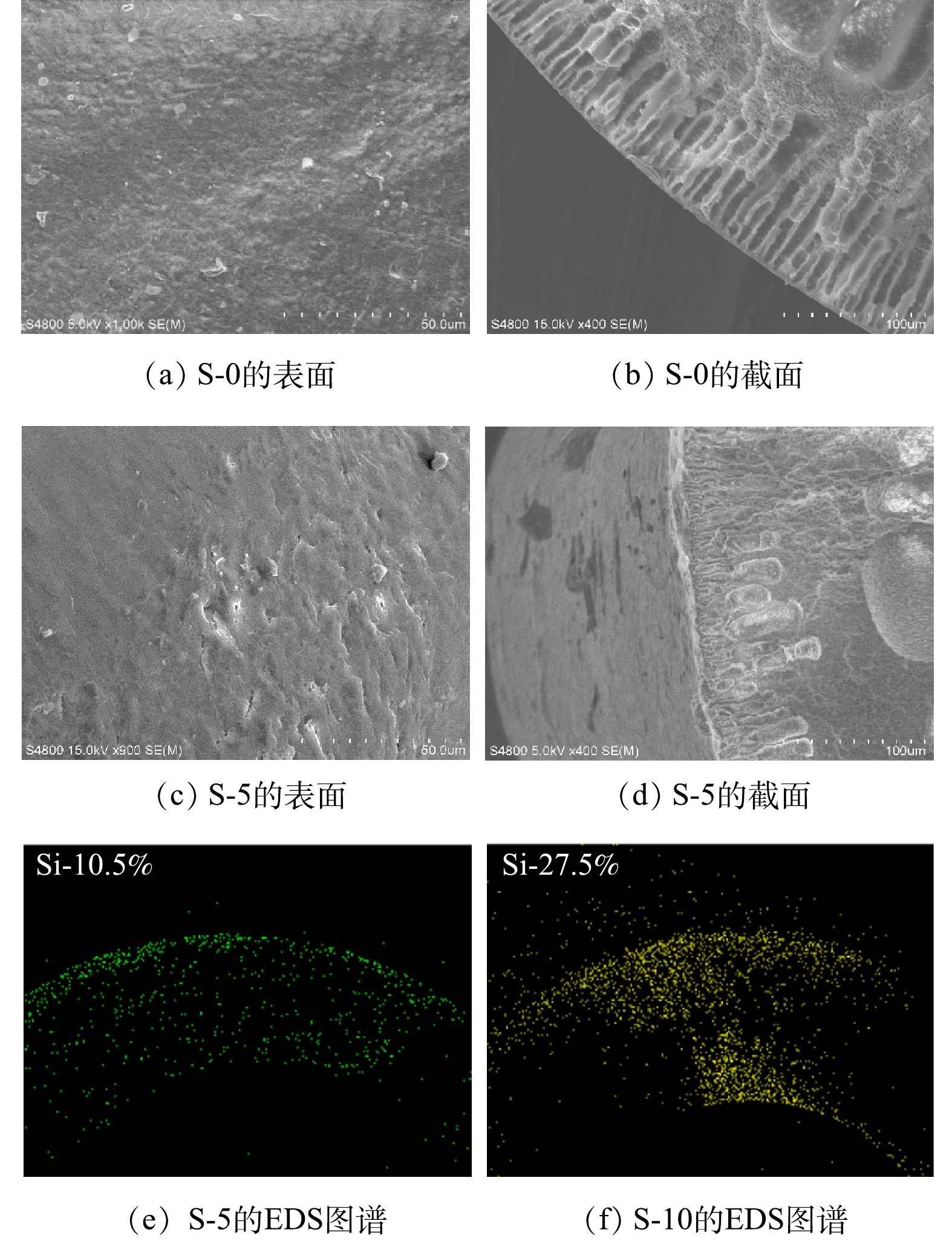
2)对改性膜表面形貌的表征。图4的SEM图像显示 S-0表面较粗糙且有较多孔隙,而涂覆PDMS后的S-5更平滑、致密,横截面SEM表征结果表明PVDF外表面出现了致密薄层。EDS图谱证明了Si元素的存在,表明PDMS成功涂覆在PVDF膜表面上。EDS表征结果还表明随着PDMS涂覆质量分数的提升,Si元素含量由10.5%增加至27.5%,且有向膜内渗透的趋势。这意味着过高的涂覆质量分数可能造成膜孔径和孔隙率下降,不利于臭氧传质[29]。
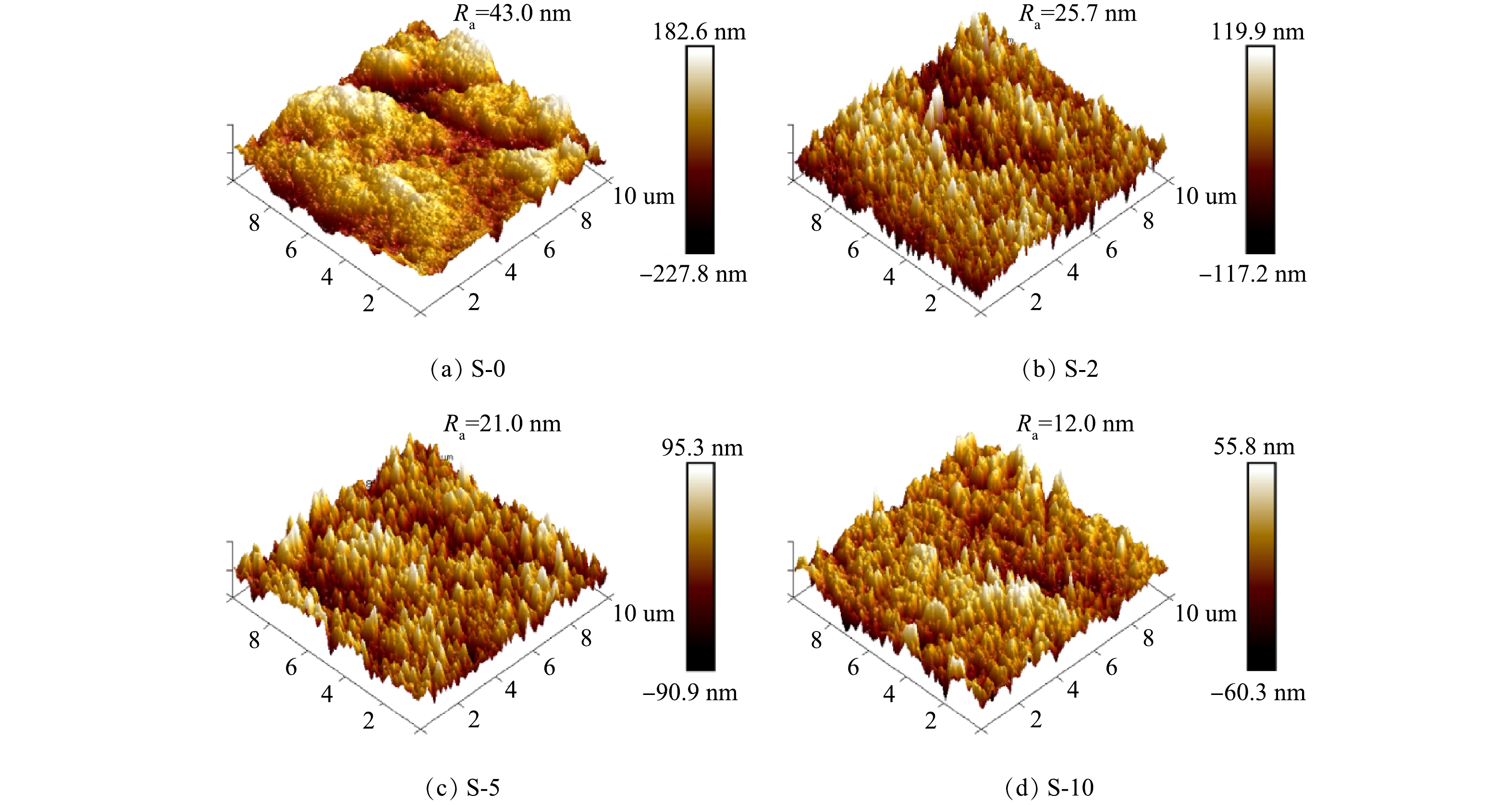
AFM 3D图像如图5所示。S-0的表面呈较大起伏的山峰状,而S-2、S-5、S-10改性膜表面为起伏较小的尖峰状。改性膜的外表面平均粗糙度Ra由原PVDF膜的43.0 nm下降至12.0 nm,说明改性膜外表面形成了更光滑的PDMS层[24]。这与SEM的表征结果基本一致。
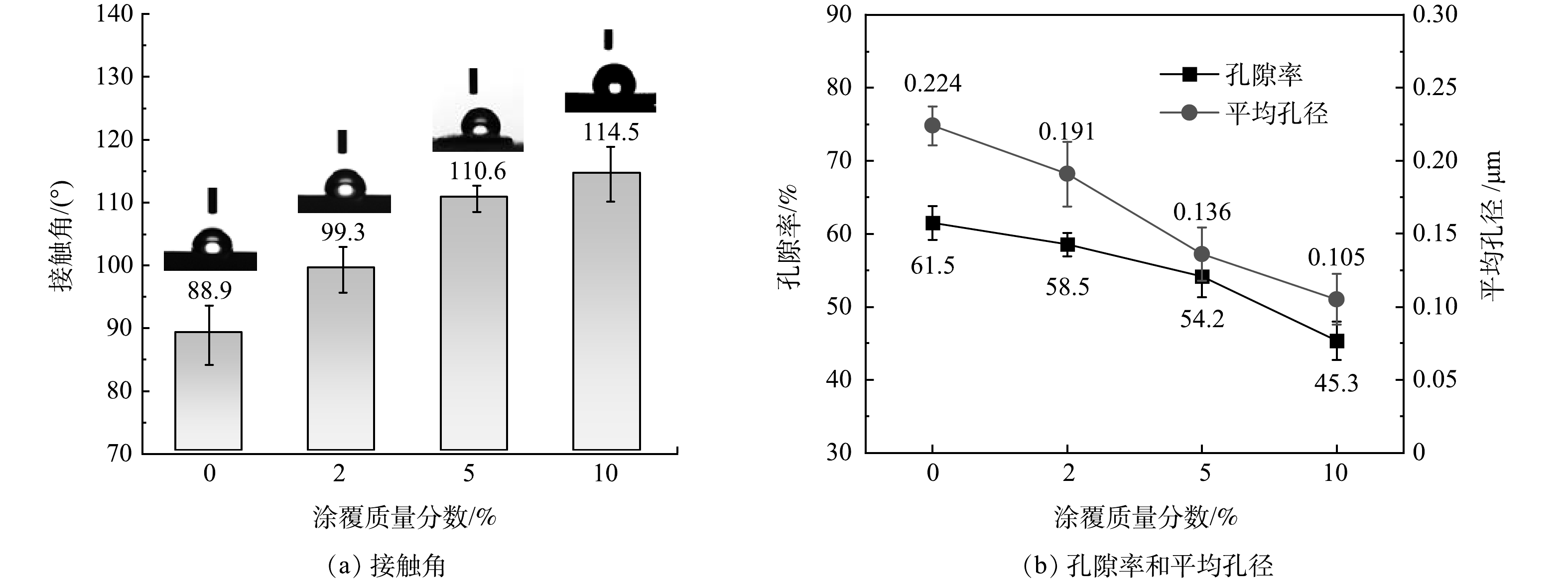
3)接触角、孔径和孔隙率分析。测试原PVDF膜和改性膜的接触角以表征其疏水性,并利用毛细孔径仪及干湿重法测试其平均孔径和孔隙率,结果如图6所示。S-0的接触角仅为88.9°,随着PDMS涂覆质量分数的增加,接触角逐渐提升至114.5°,说明改性膜疏水性逐渐增强。同时其平均孔径由0.224 μm降低至0.105 μm,孔隙率由61.5%下降至45.3%。这表明涂覆过多的PDMS会从膜外表面渗透进入膜孔内部,从而降低孔隙率[29],这与EDS的表征结果一致。
-
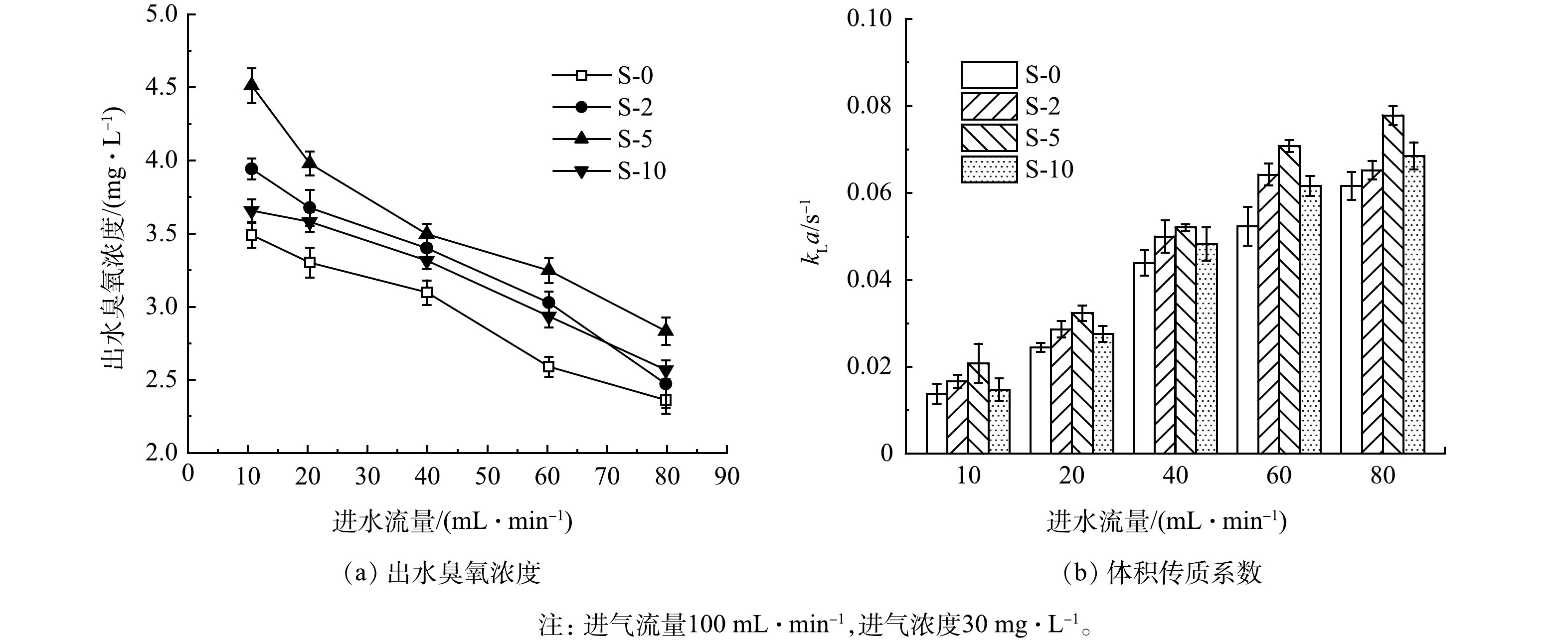
1)进水流量对臭氧传质的影响。如图7所示,改性膜的出水臭氧浓度和体积传质系数
$ {k}_{\mathrm{L}}a $ 均高于原PVDF膜(S-5>S-2>S-10>S-0),说明改性膜具有更好的传质性能,这可能是因为涂覆PDMS后使膜疏水性提升,降低了传质阻力。随着PDMS涂覆质量分数的增加,改性膜接触器的传质效果有所提升,但当PDMS涂覆质量分数超过5%时,传质效果略有下降,这可能是因为膜孔径和孔隙率下降过多会增加传质阻力。而随进水流量的增加,出水臭氧浓度呈下降趋势,这主要是因为液相流速增大,使得气液接触时间缩短。而根据双膜理论,液相流速的增大会减小液相边界层的厚度、加快界面更新从而降低液相传质阻力[11]。因此,随着液相流量的增大,体积传质系数
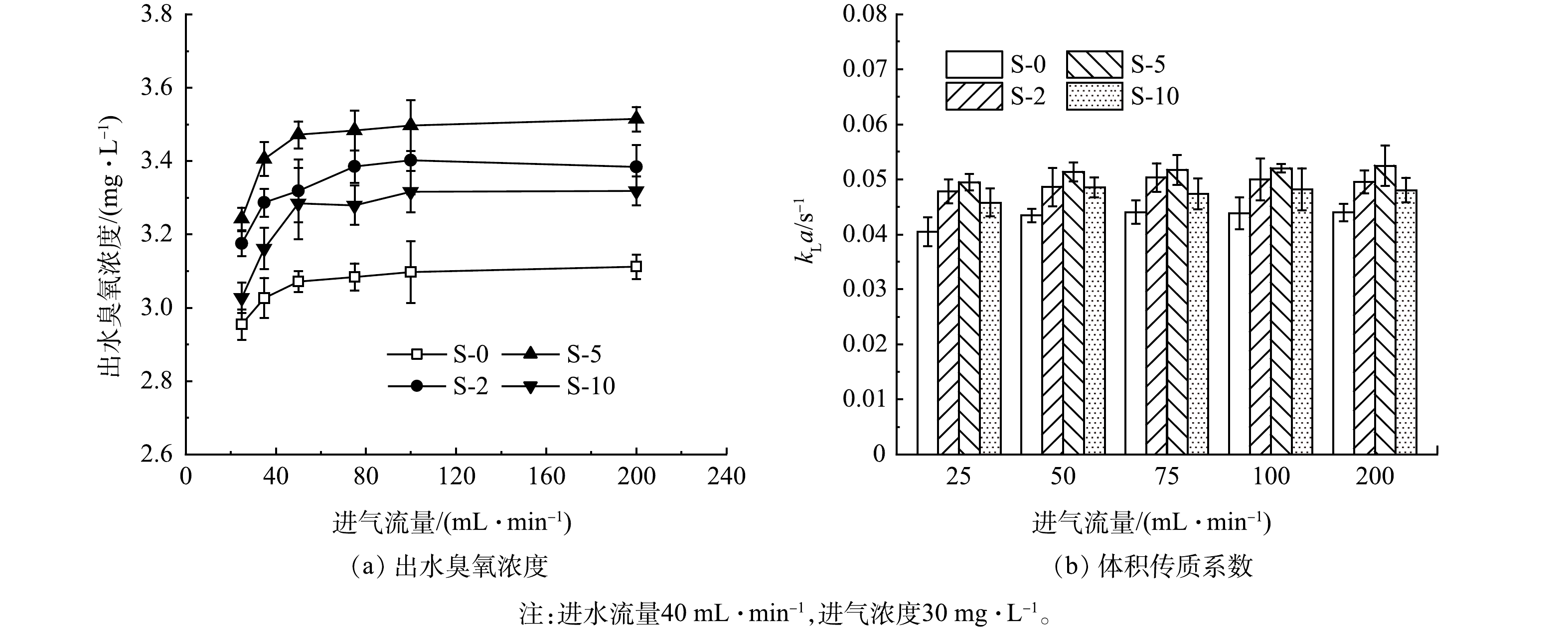
$ {k}_{\mathrm{L}}a $ 出现了明显增加趋势。在进水流量为80 mL·min−1时S-5的体积传质系数$ {k}_{\mathrm{L}}a $ 达到了0.077 8 s−1,比S-0 (0.061 7 s−1)高约26.2%。与文献报道的传统曝气方式及膜接触器(表1)相比,改性膜接触器的传质系数是其1.1~15.6倍。2)进气流量对臭氧传质的影响。进气流量对臭氧传质的影响如图8所示。改性膜的臭氧传质性能仍明显强于S-0。在进气流量从25 mL·min−1增加至50 mL·min−1时,出水臭氧浓度出现小幅上升,这可能是因为在较低气体流量下,气膜的阻力不可忽略[4],此时气体流速的增大有利于降低气相的传质阻力从而提升臭氧传质效果。当进气流量超过50 mL·min−1时出水臭氧浓度变化不大,这主要是因为臭氧气相扩散系数比液相扩散系数高4个数量级[4,33],高气流量时气相边界层的阻力很小,此时进气流量对膜接触器中的臭氧传质影响很小[2]。图8(b)显示进气流量对臭氧的体积传质系数没有显著影响。
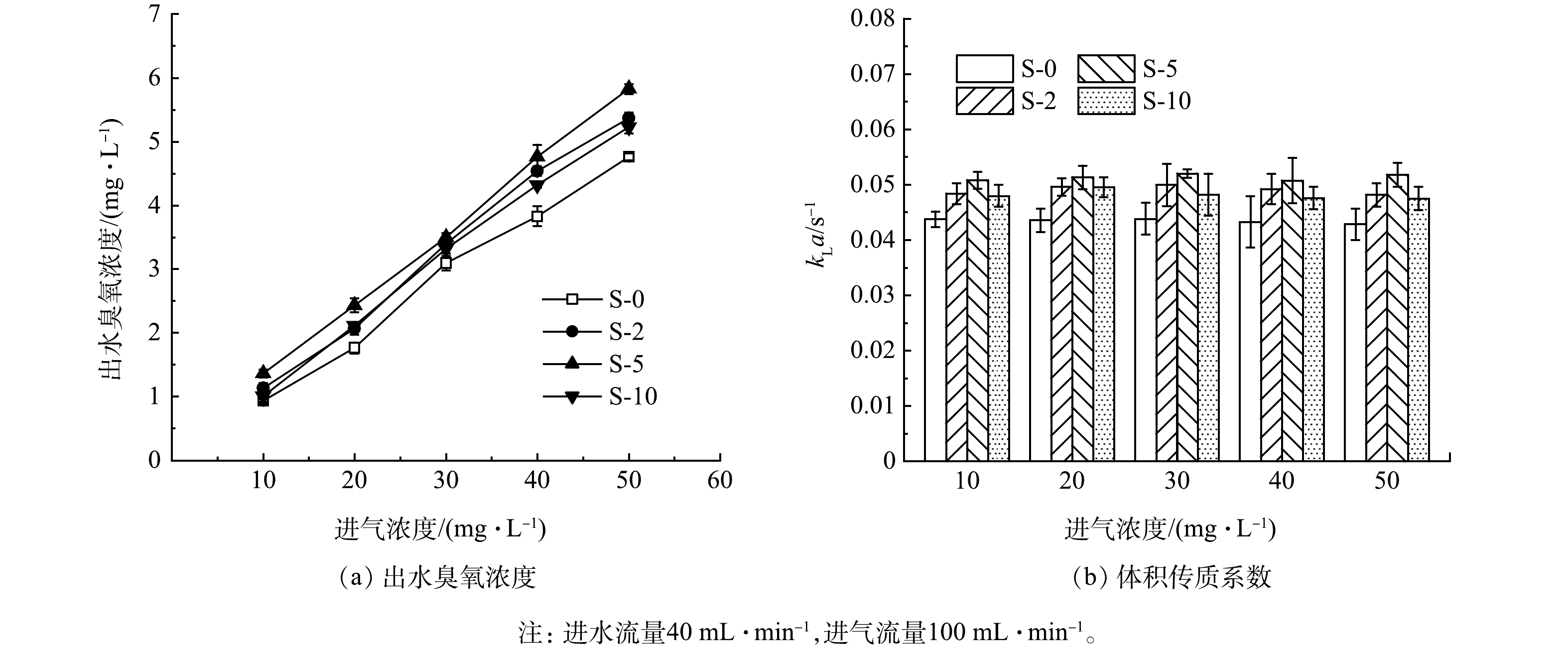
3)进气浓度对臭氧传质的影响。如图9所示,改性膜的出水臭氧浓度和体积传质系数均高于S-0,且随着进气浓度增加,出水臭氧浓度随之增加,其中S-5最高,可达5.4 mg·L−1。这是因为进气臭氧浓度越高,臭氧浓度梯度越大,传质推动力也越大,有利于臭氧扩散传质。而图9(b)表明进气浓度也对体积传质系数无显著影响。
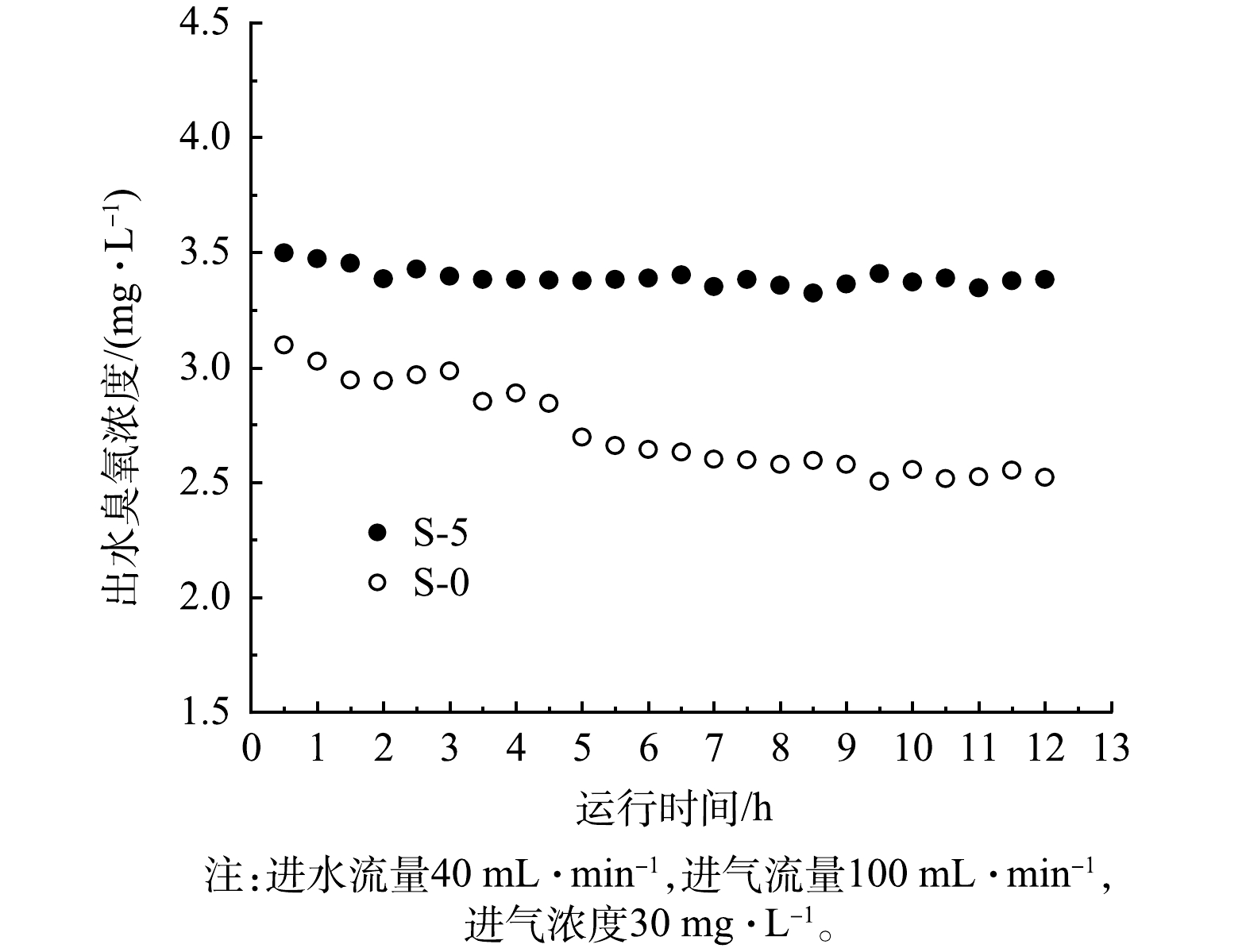
4)长期运行实验。对S-0和S-5开展12 h的长期运行实验,如图10所示。S-0出水臭氧浓度逐渐降低,下降了约18.6%,而S-5仅下降了3.3%。这是因为S-0疏水性不强,在长期运行中容易被润湿,造成传质阻力的增加[10,11,24],从而影响其长期传质性能。而涂覆了PDMS的S-5疏水性较强,不易被润湿,有利于其长期臭氧传质表现。以上结果表明,PDMS-PVDF改性膜接触器的传质效果更好,且在长期运行中具有良好的抗润湿性能,具有一定的实际应用价值。
-
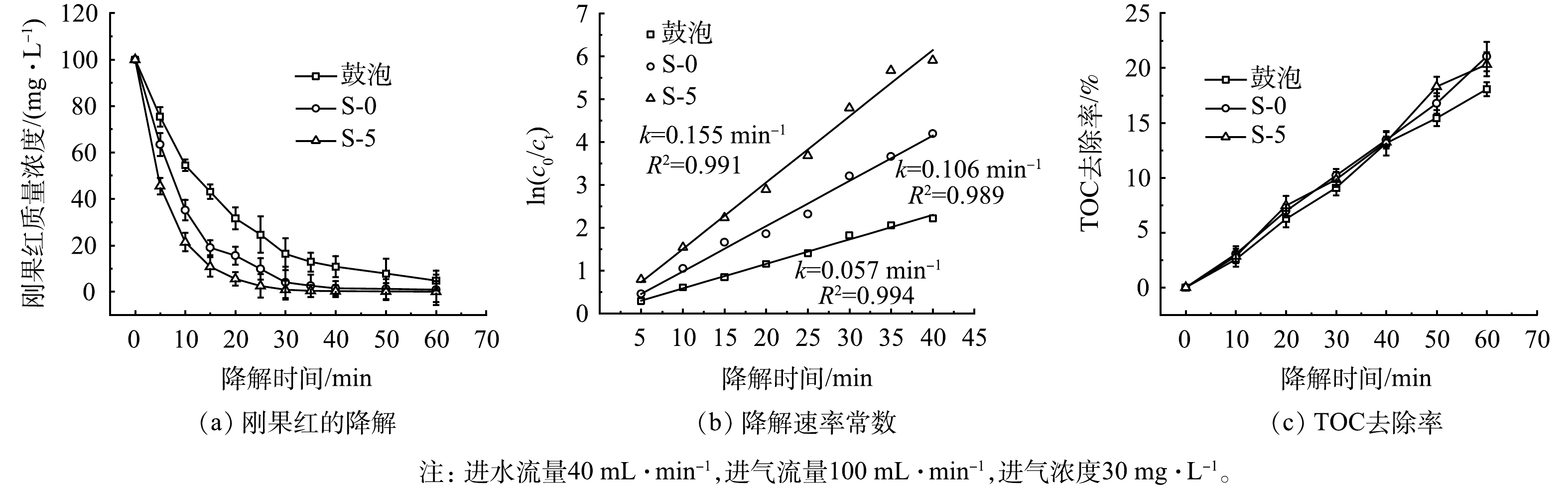
由图11(a)可见,在鼓泡曝气方式下,刚果红在30 min内降解率为83.8%,S-0和S-5的降解率分别为95.9%和99.2%。根据式(4)计算拟合得图11(b)所示的结果,得鼓泡曝气、S-0、S-5的降解速率常数
$ {k}_{\mathrm{c}} $ 分别为0.057、0.106、0.155 min−1。总体而言,S-5相比S-0和鼓泡曝气具有更好的降解效果,这是因为其具有较好的臭氧传质性能,从而可促进对污染物的降解。由图11(c)可见,60 min时改性膜接触器S-5的TOC去除率为20.3%。以上结果表明,改性膜接触器需要结合其他手段(催化臭氧氧化等)提升污染物的矿化效果,但优良的传质性能使其具备高效降解矿化污染物的潜力。 -
1) ATR-FTIR、SEM-EDS结果证明了PDMS在PVDF膜上的成功涂覆,SEM和AFM图谱显示改性膜形成了更致密光滑的表面结构。与原PVDF膜相比,改性膜的接触角从88.9°提升至114.5°,疏水性有所提升。但EDS显示随涂覆质量分数的增加,PDMS渗透入改性膜孔隙内,导致其孔径和孔隙率降低。2) 5% PDMS涂覆质量分数的改性膜接触器S-5臭氧传质效果最优,其体积传质系数可达0.077 8 s−1,比原PVDF膜S-0高26.2%,是传统曝气方式及膜接触器的1.1~15.6倍。3)涂覆质量分数<5%时,疏水性的提升有利于臭氧传质的增强;而过高的涂覆质量分数使孔径和孔隙率降低,增大了膜相传质阻力,不利于臭氧传质。进水流量和进气臭氧浓度的增加有利于降低传质阻力和提高传质推动力,而进气流量对臭氧传质影响较小。具备更优疏水性的改性膜接触器在长期运行实验中传质性能更稳定。4)使用PDMS-PVDF改性膜接触器降解刚果红时的降解速率常数可达0.155 min−1,分别为原PVDF膜和鼓泡曝气方式的1.4和2.7倍。改性膜接触器TOC去除率仅为20.3%,但具备与其他手段结合后高效降解矿化污染物的潜力。
PDMS疏水改性的PVDF膜接触器强化臭氧传质及刚果红的氧化降解效果
Enhanced ozone mass transfer and ozonation degradation of Congo red by PDMS hydrophobically modified PVDF membrane contactor
-
摘要: 中空纤维膜接触器具有界面面积大、传质效率高等特点而被广泛应用于气液传质中。为改善聚偏氟乙烯(PVDF)中空纤维膜接触器的臭氧传质效果,利用聚二甲基硅氧烷(PDMS)对其进行涂覆改性以提高其疏水性,进而提高其臭氧传质和降解污染物的能力。利用ATR-FTIR、SEM-EDS和接触角等方法对膜进行表征,并对其臭氧传质和氧化降解刚果红的效果进行了研究。结果表明,PDMS涂层成功制备,PDMS-PVDF改性膜的疏水性明显提升,接触角由88.9°提升至114.5°。传质实验结果表明,改性膜接触器体积传质系数可达0.077 8 s−1,比原PVDF膜提高了26.2%。改性膜接触器在长期运行实验(12 h)中出水臭氧浓度保持稳定。改性膜接触器30 min内可降解99.2%的刚果红,降解速率常数为0.155 min−1,是原PVDF膜的1.4倍。以上研究结果表明,PDMS-PVDF改性膜接触器具有更高的疏水性和臭氧传质性能,长期运行效果稳定,在污染物处理方面具有一定应用前景。Abstract: Hollow fiber membrane contactors have been widely used in gas-liquid mass transfer process for the advantages of large interface area and high mass transfer efficiency. In this work, the coating modification with polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) was used to increase the hydrophobicity of Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) hollow fiber membranes and improve the ozone mass transfer and ozonation degradation performance for pollutants. The membranes were characterized by ATR-FTIR, SEM-EDS and contact angle test etc. Its effect of ozone mass transfer and ozonation degradation of Congo red were studied. The characterization technologies had confirmed that the PDMS coat had been successfully prepared. The hydrophobicity of original PVDF membrane increased with the modification of PDMS and the contact angle increased from 88.9° to 114.5°. The mass experiment results showed that the ozone mass transfer coefficient of the PDMS-PVDF modified membrane contactor was 0.077 8 s−1, which was 26.2% higher than that of the original PVDF membrane contactor. The modified membrane contactor maintained a stable ozone concentration in effluent and an excellent ozone mass transfer performance during the long-term experiment (12 h). The degradation efficiency for Congo red using the modified membrane contactor achieved 99.2% within 30 min. The degradation kinetic rate was 0.155 min−1, which was 1.4 times of the original PVDF membrane. This work suggested that PDMS-PVDF membrane contactor showed high hydrophobicity, excellent ozone mass transfer performance and long-term stability, which had an application potential for pollutants removal by ozone.
-
Key words:
- membrane contactor /
- hydrophobicity /
- mass transfer /
- ozonation /
- Congo red
-

-
表 1 不同传质方式传质系数对比
Table 1. Mass transfer coefficient for different contactors
-
[1] STYLIANOU S K, SKLARI S D, ZAMBOULIS D, et al. Development of bubble-less ozonation and membrane filtration process for the treatment of contaminated water[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2015, 492: 40-47. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2015.05.036 [2] BAMPERNG S, SUWANNACHART T, ATCHARIYAWUT S, et al. Ozonation of dye wastewater by membrane contactor using PVDF and PTFE membranes[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2010, 72(2): 186-193. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2010.02.006 [3] BEIN E, ZUCKER I, DREWES J E, et al. Ozone membrane contactors for water and wastewater treatment: A critical review on materials selection, mass transfer and process design[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 413: 127393. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.127393 [4] ZHANG Y, LI K L, WANG J, et al. Ozone mass transfer behaviors on physical and chemical absorption for hollow fiber membrane contactors[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2017, 76(6): 1360-1369. doi: 10.2166/wst.2017.254 [5] SCHMITT A, MENDRET J, ROUSTAN M, et al. Ozonation using hollow fiber contactor technology and its perspectives for micropollutants removal in water: A review[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 729: 138664. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138664 [6] 李颖娜, 张玉忠, 陈颖. 气-液膜接触器用膜材料的研究进展[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2014, 30(8): 178-184. doi: 10.16865/j.cnki.1000-7555.2014.08.035 [7] CIARDELLI G, CIABATTI I, RANIERI L, et al. Membrane contactors for textile wastewater ozonation[J]. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 2003, 984(1): 29-38. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb05990.x [8] KAPRARA E, KOSTOGLOU M, KOUTSIANTZI C, et al. Enhancement of ozonation efficiency employing dead-end hollow fiber membranes[J]. Environmental Science Water Research & Technology, 2020, 6(9): 2619-2627. [9] MOSADEGH-SEDGHI S, RODRIGUE D, BRISSON J, et al. Wetting phenomenon in membrane contactors: Causes and prevention[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2014, 452: 332-353. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2013.09.055 [10] BELAISSAOUI B, FAVRE E. Novel dense skin hollow fiber membrane contactor based process for CO2 removal from raw biogas using water as absorbent[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2018, 193: 112-126. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2017.10.060 [11] NGUYEN P T, LASSEUGUETTE E, MEDINA-GONZALEZ Y, et al. A dense membrane contactor for intensified CO2 gas/liquid absorption in post-combustion capture[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2011, 377: 261-272. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2011.05.003 [12] KERBER J, REPKE J U. Mass transfer and selectivity analysis of a dense membrane contactor for upgrading biogas[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2016, 520: 450-464. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2016.08.008 [13] SHANBHAG P V, SIRKAR K K. Ozone and oxygen permeation behavior of silicone capillary membranes employed in membrane ozonators[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 1998, 69(7): 1263-1273. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4628(19980815)69:7<1263::AID-APP1>3.0.CO;2-C [14] ZOUMPOULI G, BAKER R, TAYLOR C, et al. A single tube contactor for testing membrane ozonation[J]. Water, 2018, 10(10): 1416. doi: 10.3390/w10101416 [15] SANTOS F D, BORGES C P, FONSECA F D. Polymeric materials for membrane contactor devices applied to water treatment by ozonation[J]. Materials Research, 2015, 18(5): 1015-1022. doi: 10.1590/1516-1439.016715 [16] BERRY M, TAYLOR C, KING W, et al. Modelling of ozone mass-transfer through non-porous membranes for water treatment[J]. Water, 2017, 9(7): 452. doi: 10.3390/w9070452 [17] HASHEMIFARD S A, ISMAIL A F, MATSUURABC T, et al. Performance of silicon rubber coated polyetherimide hollow fibers for CO2 removal via a membrane contactor[J]. RSC Advances, 2015(5): 48442-48455. [18] BELAISSAOUI B, FAVRE E. Evaluation of a dense skin hollow fiber gas-liquid membrane contactor for high pressure removal of CO2 from syngas using Selexol as the absorbent[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2018, 184: 186-199. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2018.02.028 [19] XU Y L, GOH K, WANG R, et al. A review on polymer-based membranes for gas-liquid membrane contacting processes: Current challenges and future direction[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2019, 229: 115791. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2019.115791 [20] 张静. PDMS渗透汽化膜分离水中有机物的研究进展[J]. 净水技术, 2022, 41(1): 14-22. doi: 10.15890/j.cnki.jsjs.2022.01.003 [21] 袁琪. 交联PDMS/PVDF微孔膜的制备及其膜曝气性能研究[D]. 长春: 长春工业大学, 2021. [22] HANH LE T M, SINGTO S, SAJOMSANG W, et al. Hydrophobic PVDF hollow fiber membrane modified with pulse inductively coupling plasma activation and chloroalkylsilanes for efficient dye wastewater treatment by ozonation membrane contactor[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2021, 635: 119443. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2021.119443 [23] LU J G, ZHENG Y F, CHENG M D. Wetting mechanism in mass transfer process of hydrophobic membrane gas absorption[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2008, 308: 180-190. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2007.09.051 [24] AHMED T, SEMMENS M J. The use of independently sealed microporous hollow fiber membranes for oxygenation of water: model development[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 1992, 69(1): 11-20. [25] 李建渠, 李松田, 唐江宏, 等. 二磺酸靛蓝体系褪色光度法测定水中低浓度臭氧[J]. 理化检验(化学分册), 1998(9): 422-423. [26] 张全忠, 吴潘, 梁斌, 等. 液相中臭氧浓度的检测[J]. 工业水处理, 2001, 21(4): 30-32. [27] SETHUNGA G D, RONGWONG W, WANG R, et al. Optimization of hydrophobic modification parameters of microporous polyvinylidene fluoride hollow-fiber membrane for biogas recovery from anaerobic membrane bioreactor effluent[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 548: 510-518. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2017.11.059 [28] JIN P, HUANG C, LI J X, et al. Surface modification of poly(vinylidene fluoride) hollow fibre membranes for biogas purification in a gas-liquid membrane contactor system[J]. Royal Society Open Science, 2017, 4(11): 171321. doi: 10.1098/rsos.171321 [29] SETHUNGA G D, KARAHAN H E, WANG R, et al. PDMS-coated porous PVDF hollow fiber membranes for efficient recovery of dissolved biomethane from anaerobic effluents[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019, 584: 333-342. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2019.05.016 [30] PINES D S, MIN K N, ERGAS S J, et al. Investigation of an ozone membrane contactor system[J]. Ozone:Science & Engineering, 2005, 27(3): 209-217. [31] MANSOURIZADEH A, REZAEI I, LAU W J, SEAH M Q, et al. A review on recent progress in environmental applications of membrane contactor technology[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2022, 10: 107631. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2022.107631 [32] KUKUZAKI M, FUJIMOTO K, KAI S, et al. Ozone mass transfer in an ozone-water contacting process with Shirasu porous glass(SPG) membranes—A comparative study of hydrophilic and hydrophobic membranes[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2010, 72(3): 347-356. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2010.03.004 [33] 押玉荣, 张娅, 王晓磊, 等. 中空纤维膜无泡曝气氧传质性能实验研究[J]. 中国给水排水, 2020, 36(1): 74-79. -



 下载:
下载: