-
近年来,随着冶金、光伏、锂电池等工业产业的不断发展,产生了大量的含氟废水(检出浓度从几十到上千mg·L−1不等),水体氟污染问题对自然环境以及人体健康都构成了严重威胁[1]。因此,亟须探求一种成本低廉、处理高效、易于操作的除氟技术。目前,去除水体中氟离子的主要方法有沉淀法[2]、离子交换法[3]、膜处理法与吸附法[4]。沉淀法适合高氟水体的预处理过程,并且会改变出水水质;离子交换法、电化学法所需的成本较高、操作复杂;膜处理法因受半透膜的影响效果不稳定、花费较高并且严重浪费水资源,应用范围不广。目前,吸附法因其经济、灵活、操作简单的优点被大量应用于去除氟的研究中[5]。
近年来国内外开发了众多吸附材料并应用于含氟废水处理,主要包含活性氧化铝[6]、粘土材料[7]、活性炭[8]、生物炭[9]、金属有机框架材料[10]等。金属有机框架材料(metal-organic frameworks, MOFs)是一种新型的多孔配位聚合物,由无机金属离子或团簇与有机配体自组装连接而成[11]。MOFs 具有较大的比表面积且制备方法较简单,目前已广泛用于吸附、催化、检测等领域[12-13]。赵瑨云等[14]采用水热合成法制备了一种毛线团状结构的La-MOFs,其对氟的吸附容量可达43.1 mg·g−1。JEYASEELAN等[15]合成了Ce@BDC和Ce@ABDC并用于除氟,结果表明,Ce@BDC和Ce@ABDC对氟的最大吸附容量分别为4.88 mg·g−1和4.91 mg·g−1。HE等[16]以类似的方式合成了Ce(Ⅲ)-BDC,发现Ce(Ⅲ)-BDC对氟的最大吸附容量为128.0 mg·g−1。本团队[17]对比了有机配体(对苯二甲酸(BDC)、邻苯二甲酸、间苯二甲酸)对Ce基MOFs除氟性能影响,发现对苯二甲酸(BDC)为配体形成的Ce-BDC的吸附容量最大(139.5 mg·g−1)。WANG等[18]将NH2-MIL-53(Al)衍生的介孔碳应用于去除水溶液中Cr(Ⅵ)和甲基橙,相比前体,发现衍生碳对污染物的吸附容量有较大提升且材料自身更加稳定。目前,MOFs衍生碳已经被大量研究并应用,但将其应用于除氟领域的研究还较少。
本研究首先以溶剂热法制备得到Ce-BDC,再以此为前驱体,在空气和氮气的气流中热解,得到Ce-BDC-400(A)和Ce-BDC-400(N)。利用多种表征技术分析其结构,结合吸附等温线、吸附动力学和吸附热力学等手段,讨论了这2种衍生碳对氟的吸附性能;此外,考察了共存阴离子、溶液初始 pH 对氟吸附过程的影响;最后将所制得的吸附材料应用于实际含氟废水的处理,分析了Ce-MOFs衍生碳在实际水体中的除氟性能。
-
六水合硝酸铈(Ce(NO3)3•6H2O)、对苯二甲酸(BDC)、N,N-二甲基甲酰胺(C3H7NO,DMF)、氢氧化钠(NaOH)、氟化钠(NaF)、无水乙醇等均为分析纯,以上药品均购于国药集团化学试剂有限公司。实验用水均为去离子水。
-
Ce-BDC的制备。称取2.17 g Ce(NO3)3•6H2O和0.69 g BDC,将2者溶解在60 mL的DMF中,用玻璃棒搅拌至溶解,转入水热反应釜中120 ℃中反应12 h。冷却后,用DMF洗涤3次,取出沉淀物在乙醇中浸泡12 h。倒掉上清液后,产品分别用乙醇和超纯水洗涤3次,得到样品Ce-BDC。
Ce-BDC衍生碳的制备。称取1.00 g Ce-BDC转移至管式炉中,分别通入N2或空气煅烧,以5 ℃·min−1的升温速度升至400 ℃,并在该温度下保持3 h煅烧。之后,所得的产物冷却至室温,再将产物分别用乙醇和超纯水洗涤3次,所得的产物在80 ℃下真空干燥12 h。对在N2、空气中热解形成的衍生碳分别命名为Ce-BDC-400(N),Ce-BDC-400(A)。
-
采用X射线粉末衍射仪(XRD)(Bruker D8Advance,德国)分析样品的物相组成及结构;利用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)(Sigma500,德国)分析样品的表面形态;利用能谱仪(EDS)分析样品表面的元素;采用比表面与孔径分析仪(ASAP 2020PlusHD88,美国)分析样品的比表面积和孔容孔径;采用X射线光电子能谱仪(XPS)(ESCALAB250Xi,美国)用于确定样品表面的元素成分和价态;采用离子色谱(ICS-900,美国)测试溶液中氟离子浓度。
-
通过分批实验验证了MOFs对水中氟化物的吸附性能。通过将一定量的Ce-BDC衍生碳材料(Ce-BDC-400(N),Ce-BDC-400(A))添加到含有100 mL NaF溶液(10~100 mg·L−1)的6个锥形烧瓶中来研究吸附动力学。控制不同的反应温度(293、303、313和323 K)以及反应时间(10~360 min)以探索反应温度及反应时间对不同吸附剂对氟离子吸附能力的影响。吸附结束后,取混合液过0.22 μm聚醚砜滤膜(PES膜),用离子色谱测量滤液中氟离子的浓度,每次实验重复3次。氟的吸附量根据式(1)进行计算。采用准一级动力学模型(式(2))、准二级动力学模型(式(3))、粒内扩散动力学模型(式(4))、Langmuir模型(式(5))、Freundlich模型(式(6))、吸附热力学模型(式(7))等对实验数据进行拟合。
式中:C0为氟的初始质量浓度,mg·L−1;Ce为氟的平衡质量浓度,mg·L−1;V为溶液体积,L;m为吸附剂质量,g;qe为平衡吸附量,mg·g−1。qmax为最大吸附量,mg·g−1;KL为Langmuir模型的平衡常数;
$ \dfrac{1}{n} $ 为异质性因子;C为液膜厚度常数;qt为反应t时间时的吸附量,mg·g−1;k1为准一阶模型的速率常数,min−1;k2为准二阶模型的速率常数,g·(mg·min)−1;ki为粒内扩散动力学模型的速率常数,mg·g−1·min0.5;t为反应时间,min;ΔGº 为吉布斯自由能,kJ·mol−1;R为一般气体常数,8.314 J·(mol· K)−1;T是绝对温度,K;K0是热力学平衡常数。 -
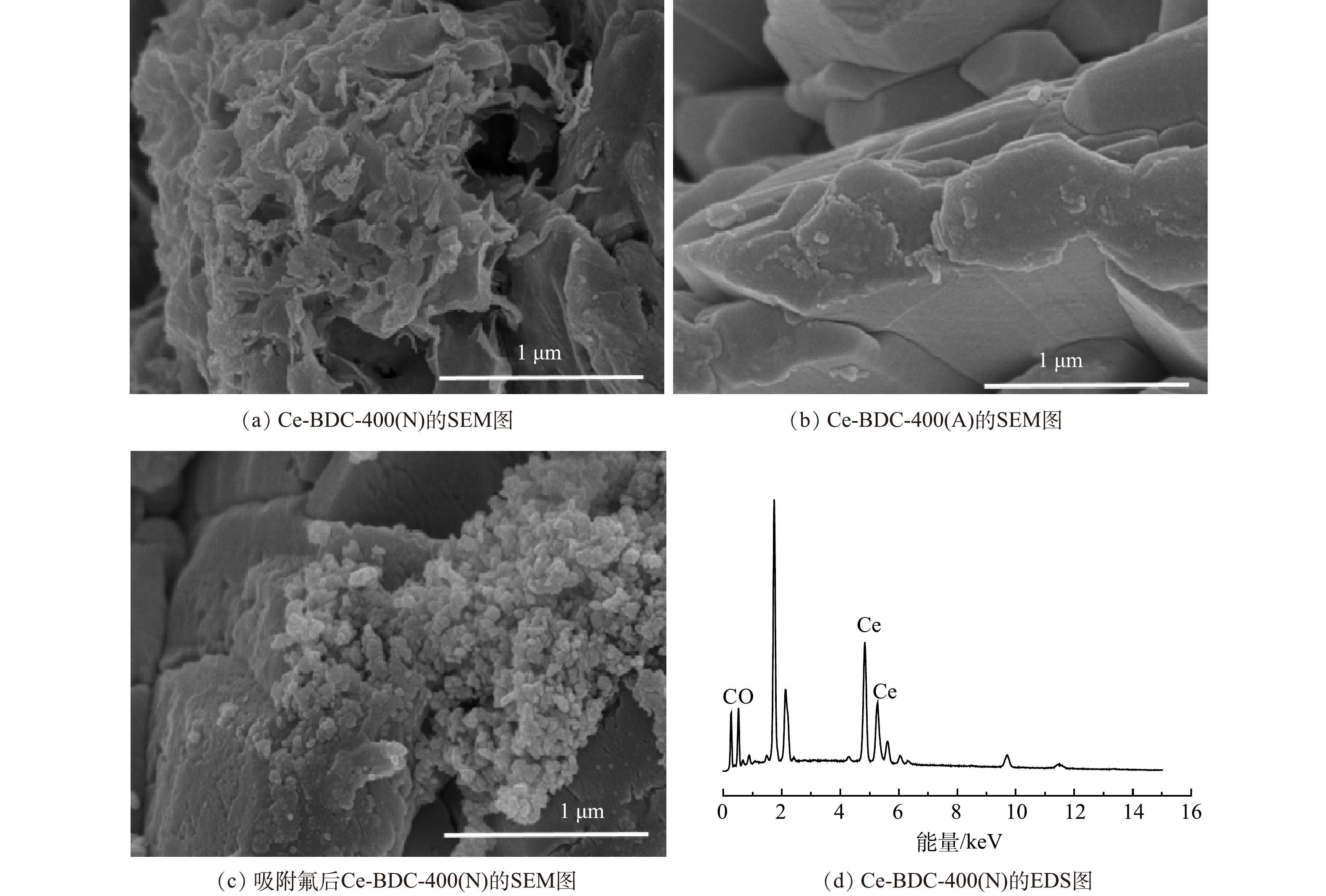
图1为Ce-BDC-400(N)、Ce-BDC-400(A)以及吸附氟后的Ce-BDC衍生碳材料的SEM图像。图1(a)中Ce-BDC-400(N)(图1(a))呈现不规则片柱状结构。图1(b)中Ce-BDC-400(A)显示了鳞片状的薄片结构,这些薄片重叠形成直径在1~4 μm的不规则块状颗粒。图1(c)为Ce-BDC-400(N)吸附氟离子后的SEM图。可以观察到Ce-BDC衍生碳材料的微观形貌发生了显著变化。图1(d)是Ce-BDC-400(N)的EDS谱。结果表明Ce、C、O分布在Ce-BDC-400(N)上。
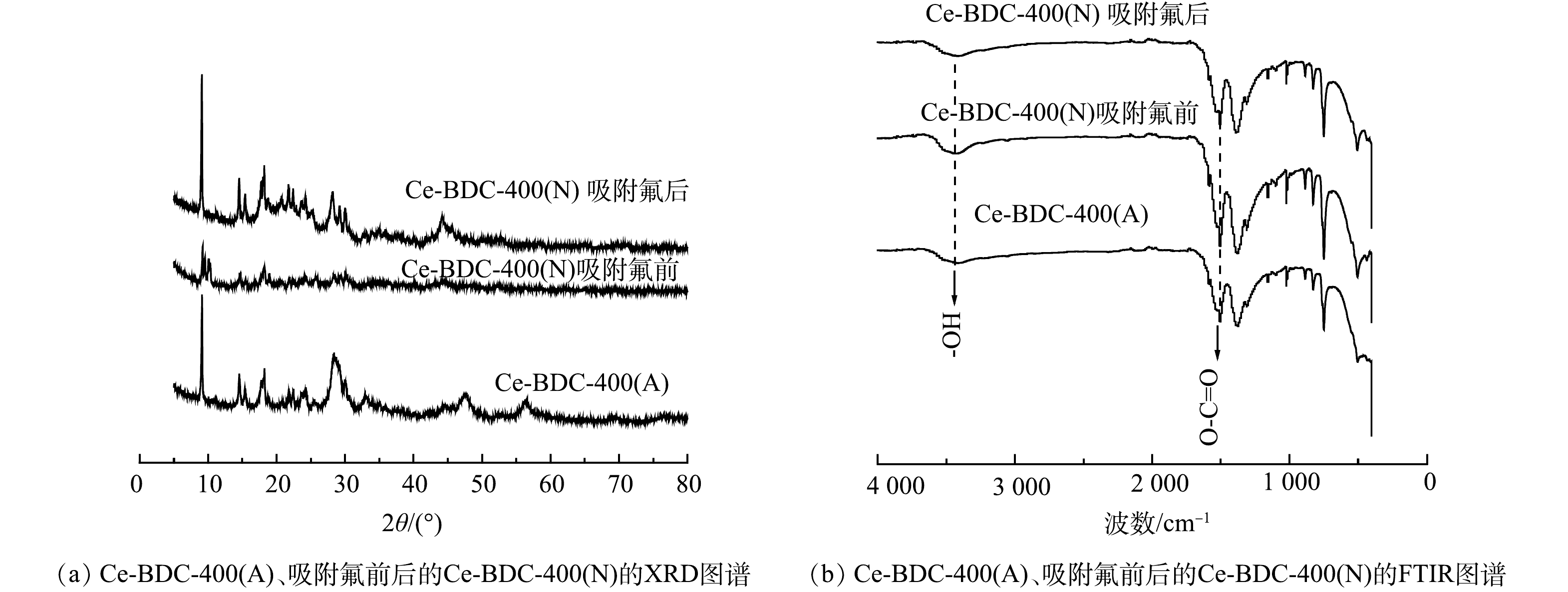
图2(a)为Ce-BDC-400(A)、Ce-BDC-400(N)、吸附氟后的Ce-BDC-400(N)的XRD图谱。Ce-BDC-400(A)在多处出现结晶峰,其衍射峰与其他研究[19]的铈基金属有机框架衍生碳(Ce-MOF-500(S))的特征峰相似。相比Ce-BDC-400(A),Ce-BDC-400(N)的衍射峰强度相对较弱。Ce-BDC-400(N)在吸附氟离子后衍射峰强度增强。图2(b)为Ce-BDC-400(A)、Ce-BDC-400(N)、吸附氟后的Ce-BDC-400(N)的FT-IR光谱图。可见,Ce-BDC-400(A)与Ce-BDC-400(N)的FT-IR光谱图相似。这表明2种材料含有的官能团相似。以Ce-BDC-400(A)为例,其在3 310~3 600 cm−1处的宽峰可归属于O–H拉伸振动。上述2种纳米复合材料中仍存在着有机配体中的O–C=O官能团结构,其对应的不对称和对称拉伸振动出现在1 502 cm−1和1 377 cm−1,这说明不同煅烧氛围所产生的Ce-MOFs衍生碳是部分碳化的[20]。对比吸附氟离子前后的Ce-BDC-400(N)的光谱图可知,所有特征峰均略有移动或出现透光率变化,这可能归因于Ce-BDC-400(N)和氟离子之间的相互作用。
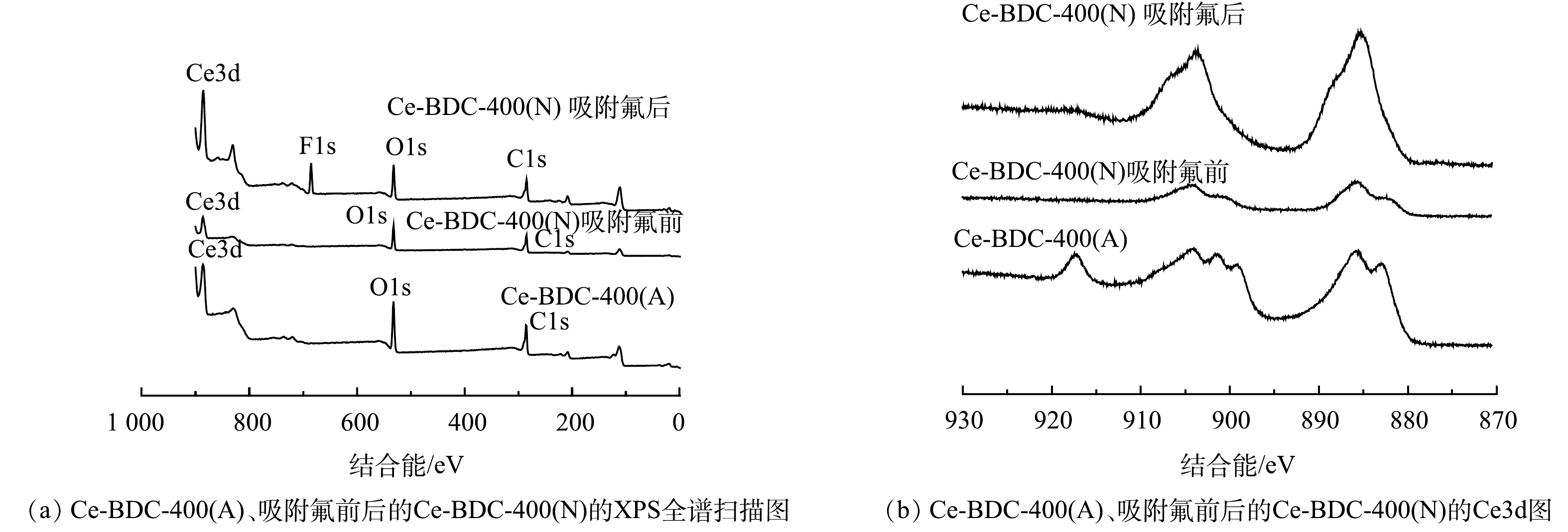
由图3(a)中的XPS全谱扫描图可知,Ce-BDC-400(A)与Ce-BDC-400(N)都存在Ce、O和C。吸附氟后的Ce-BDC-400(N)在684.7 eV处出现一个新峰(F1s峰)。这证明Ce-BDC-400(N)对氟离子有吸附。由图3(b)分析其精细谱结构可知,Ce-BDC-400(N)中Ce3d(885.8 eV和904.1 eV)的峰值对应Ce3d3/2和Ce3d5/2,表明Ce-BDC-400(N)中Ce主要以Ce(Ⅲ)存在[21]。而Ce-BDC-400(A)不仅出现了Ce(Ⅲ)的峰,还出现了Ce(IV)(917.3 eV)[22]。吸附氟后的Ce-BDC-400(N)中氟的含量为16.9%,Ce的峰值相对强度显著增加,这可能与Ce–OH和F−之间的离子交换有关,从而形成Ce–F的结构。
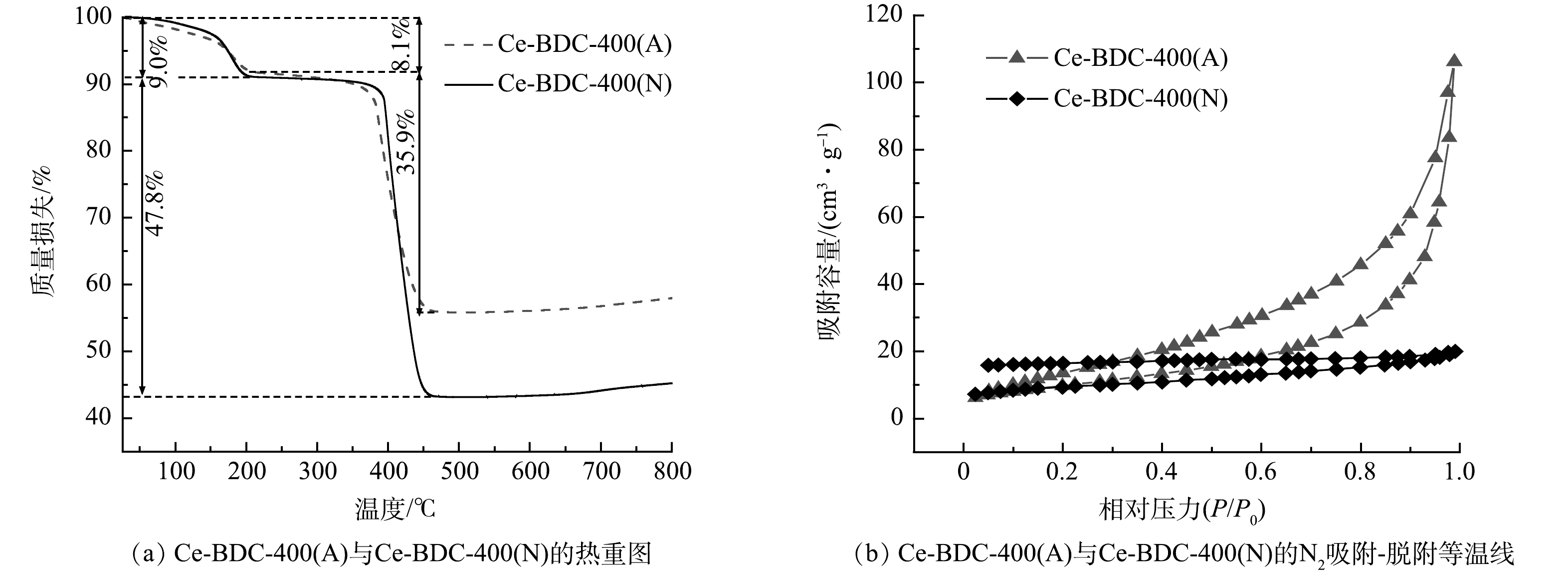
图4(a)反映了Ce-BDC-400(A)与Ce-BDC-400(N)的热稳定性。2种材料的第1阶段的质量下降发生在25~200 ℃,这主要归因于吸附在Ce-MOFs衍生碳上的物理吸附水和晶体配位水的损失。第2阶段的质量迅速下降,当温度高于380 ℃时,出现了Ce-MOFs衍生碳的晶体结构的坍塌和有机配体的热解的情况。具体而言,第2阶段的Ce-BDC-400(A)的质量下降了35.9%,Ce-BDC-400(N)的质量下降了47.8%。上述实验结果表明,第1阶段的残留样品已经转化为第2阶段的CeO2[16]。总的来说,这2种衍生碳均具有良好的热稳定性。图4(b)反映了Ce-BDC-400(A)与Ce-BDC-400(N)的孔结构特征。Ce-BDC-400(A)的N2吸附脱附曲线属于IV型,而Ce-BDC-400(N)的等温曲线在中压下保持稳定,属于典型的I型[23]。如表1所示,Ce-BDC-400(A)和Ce-BDC-400(N)的比表面积分别为36.06 m2·g−1和31.09 m2·g−1。以上结果表明2种Ce-MOFs衍生碳的孔结构存在差异,这是其除氟性能不同的结构基础。
-
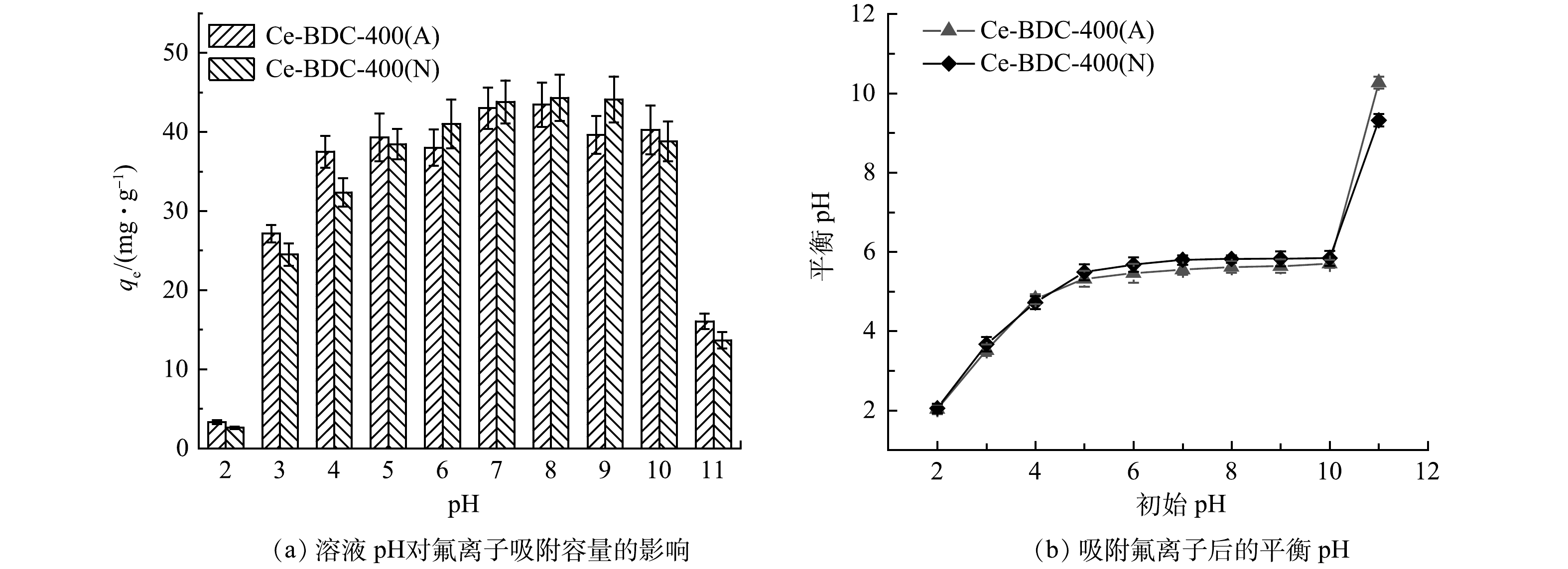
pH对Ce-BDC-400(A)和Ce-BDC-400(N)材料的吸附影响如图5所示,在氟离子初始浓度为10 mg·L−1时,当溶液pH=2时,Ce-BDC-400(A)和Ce-BDC-400(N)的吸附容量分别下降至3.3 mg·g−1和2.6 mg·g−1。在酸性条件下,吸附容量随pH的增加逐渐升高,在pH=8.0时达到最高值。Ce-BDC-400(A)和Ce-BDC-400(N)在pH=3.0~10.0内均能够保持优异的氟离子去除性能。随后,随着pH的增加,对氟的吸附容量有所下降。这可能是由于当pH=2时,溶液中H+的浓度很高(HF的酸度系数pKa为3.18),F−和H+之间会形成氢键(H–F),使F−难以与Ce-BDC-400(A)和Ce-BDC-400(N)上的活性位点结合,导致吸附材料的氟吸附能力有所下降[24]。此外,酸性条件也会在一定程度上影响衍生碳的空间结构的稳定性。而当pH>10的条件下,较高浓度的OH−会与F−竞争Ce-BDC-400(A)和Ce-BDC-400(N)上的活性位点。天然水体的pH一般在6~8,而实验中使用的氟离子溶液的pH约为7。因此,在后续的吸附实验中无需通过加酸或碱来调节含氟溶液的pH。
-
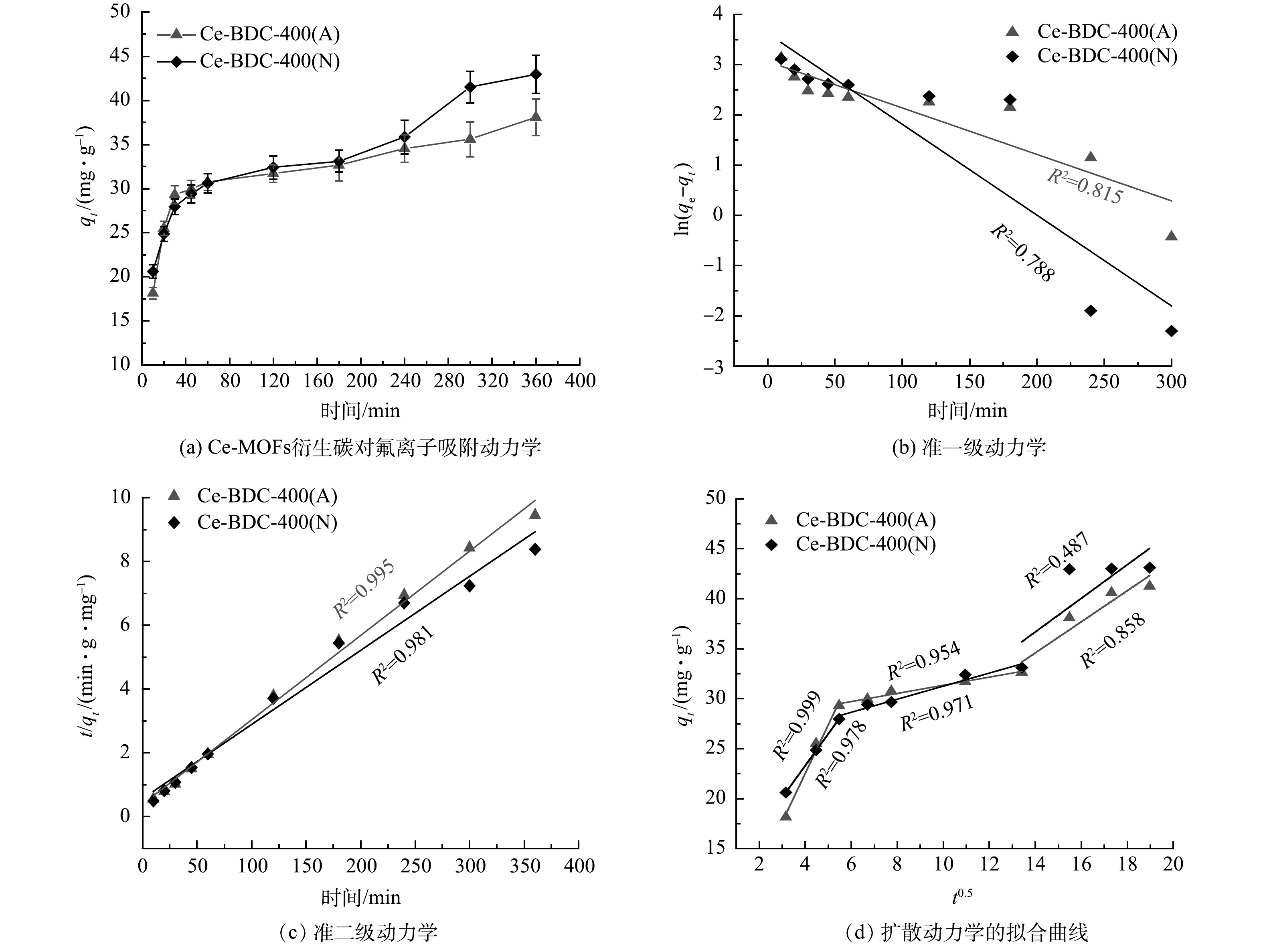
Ce-BDC-400(A)与Ce-BDC-400(N)对氟离子的吸附动力学如图6所示。由图6(a)可以看出,Ce-BDC-400(A)和Ce-BDC-400(N)表现出较快的氟离子吸附速率,前60 min即可达到饱和吸附量的75%。随着吸附时间的延长,Ce-BDC-400(A)和Ce-BDC-400(N)对氟离子的吸附逐渐趋于饱和。总吸附平衡时间在360 min。Ce-BDC-400(A)和Ce-BDC-400(N)的吸附容量分别为38.10 mg·g−1和42.95 mg·g−1。图6(c)~(d)分别是采用准一级动力学和准二级动力学对实验数据进行拟合的结果。可见,Ce-BDC-400(A)和Ce-BDC-400(N)的准二级动力学方程的拟合相关系数R2为0.995和0.981,拟合的吸附容量为37.79 mg·g−1和43.01 mg·g−1,与实验结果接近。这表明Ce-BDC-400(A)和Ce-BDC-400(N)对氟离子的吸附过程更符合准二级动力学过程。
-
在常温的条件下,Ce-BDC-400(A)与Ce-BDC-400(N)的吸附容量随氟离子初始质量浓度变化情况如图7所示。当氟的平衡浓度为0~30 mg·L−1时,2种材料的吸附容量上升,而当平衡浓度为30~80 mg·L−1时,2种材料的吸附容量上升缓慢。这表明上述材料表面的活性位点逐渐被氟占据。分别采用Langmuir和Freundlich等温线模型对实验数据进行拟合,Ce-BDC-400(A)与Ce-BDC-400(N)的Langmuir模型(R2=0.997和R2=0.992)较Freundlich模型拟合程度更好。这表明氟离子在Ce-MOFs衍生碳上的吸附是单层化学吸附[25]。Ce-BDC-400(A)与Ce-BDC-400(N)的Langmuir模型最大吸附容量为145.35 mg·g−1和154.32 mg·g−1,其与实际最大吸附容量(140.6 mg·g−1和155.1 mg·g−1)相近。
-
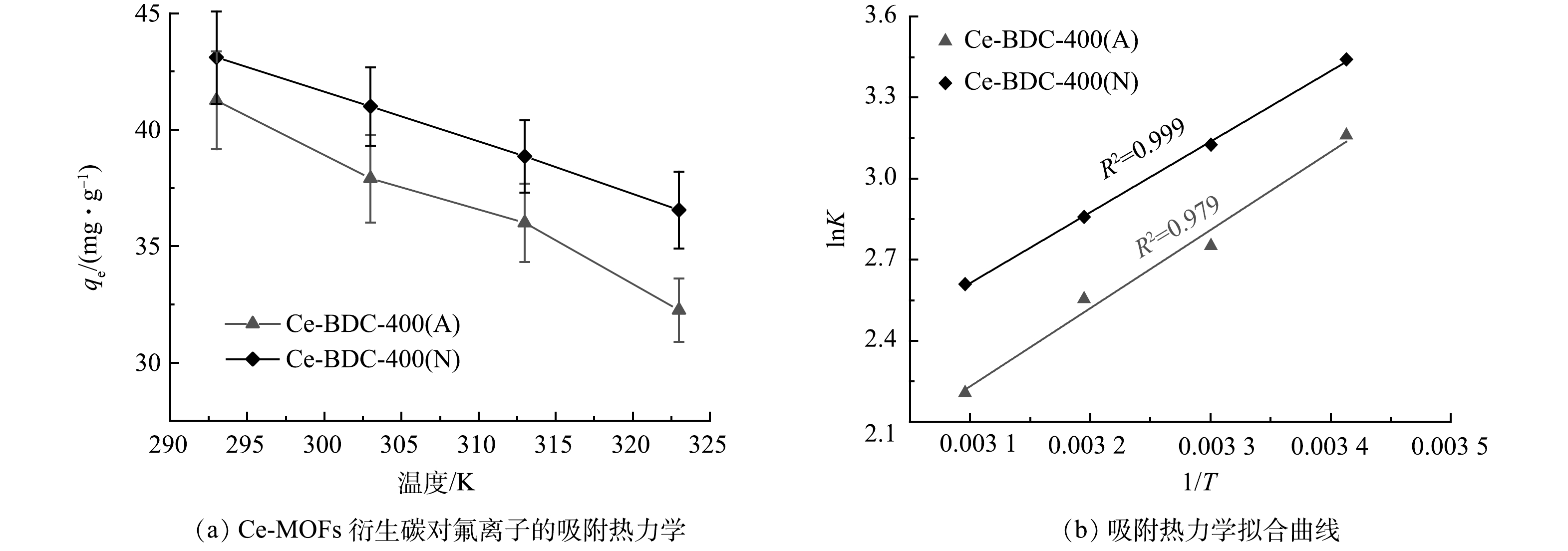
图8所展示的是不同温度(293、303、313和323 K)下Ce-BDC-400(A)和Ce-BDC-400(N)的氟离子吸附性能的影响。如图8(a)所示,Ce-BDC-400(A)与Ce-BDC-400(N)的吸附容量随着温度的升高逐渐下降,但整体性能波动不大。图8(b)展示了吸附热力学拟合曲线,结果表明氟离子在这2种Ce-MOFs衍生碳上的吸附是自发进行的。随着温度的升高,该吸附过程的自发程度出现下降[26]。同时,ΔHº为负值表明这Ce-BDC-400(A)与Ce-BDC-400(N)的氟吸附过程是放热反应。
-
实际水体中,除氟离子外通常还含有其他共存阴离子,这将与氟离子竞争吸附位点导致吸附剂的除氟性能收到较大影响[27]。因此,选择真实水体中常见的Cl−、SO42−、NO3−、CO32−和HCO3−作为竞争离子,对比研究共存阴离子对Ce-BDC-400(A)和Ce-BDC-400(N)的氟吸附过程的影响。如图9(a)所示,共存阴离子对两种材料的除氟性能的影响较小。值得注意的是,CO32−对Ce-BDC-400(A)的氟吸附过程有一定的抑制作用。由于CO32−的存在,Ce-BDC-400(A)的吸附容量出现了一定程度的下降,这主要是因为CO32−水解产生的OH−与F−具有竞争吸附作用。以上结果说明Ce-BDC-400(A)和Ce-BDC-400(N)表现出优异的选择性除氟性能。
为了评估Ce-BDC-400(A)和Ce-BDC-400(N)处理天然地表水中氟化物的可行性,使用不同投加量的Ce-BDC-400(A)和Ce-BDC-400(N)分别吸附水中的氟离子12 h,结果如9(b)所示。通过分别投加1.0 g·L−1的Ce-BDC-400(A)和0.5 g·L−1 Ce-BDC-400(N)进行吸附后,F−的浓度分别降至1.47 mg·L−1和1.45 mg·L−1,表明在较低的投加量处理下水体中氟离子浓度就已经低于世界卫生组织(WHO)建议的饮用水允许阈值(1.5 mg·L−1)[28]。随着投加量的增加,达到吸附平衡时水中的剩余氟离子浓度逐渐降低。经过投加1.5 g·L−1的Ce-BDC-400(A)和Ce-BDC-400(N)进行处理后,吸附平衡时水中的剩余氟离子浓度分别为1.39 mg·L−1和0.92 mg·L−1。因此,这两种优良的氟离子吸附剂Ce-BDC-400(A)和Ce-BDC-400(N)在面对复杂环境下的实际水体中表现出高效且稳定的除氟性能,经其吸附处理后的水体满足人类健康饮用水的要求。
-
1)以Ce-BDC作为前驱体,在空气和N2的气流中热解形成的衍生碳Ce-BDC-400(A)和Ce-BDC-400(N)。衍生碳材料提高了前驱体的比表面积,从而可提升对氟的吸附性能。
2) Ce-BDC-400(A)和Ce-BDC-400(N)对氟的吸附动力学符合准二级动力学模型,吸附等温线符合Langmuir等温线模型。Ce-BDC-400(A)和Ce-BDC-400(N)对氟离子的吸附是自发进行的,且其对氟的吸附过程是放热反应,温度上升会抑制对氟离子的吸附。
3) Ce-BDC-400(A)和Ce-BDC-400(N)对氟的最大吸附容量分别为140.6 mg·g−1和155.1 mg·g−1,在pH=3~10内具有稳定的除氟性能,并在实际水体处理中显示出优异的氟吸附性能。
Ce-BDC衍生碳的除氟性能与机理
Removal performance and mechanism of fluoride by Ce-BDC-derived carbon
-
摘要: 以Ce-BDC为原料,在空气和N2的氛围中煅烧形成的衍生碳Ce-BDC-400(A)和Ce-BDC-400(N)。使用X射线粉末衍射仪、扫描电子显微镜等表征手段 对其微观形貌结构、元素组成、官能团特征、晶型结构分别进行了表征和分析,并通过吸附拟合实验考察了Ce-BDC-400(A)和Ce-BDC-400(N)对水中氟离子的去除性能及可能的机制。结果表明成功制备了2种衍生碳。Ce-BDC-400(A)和Ce-BDC-400(N)对氟离子的吸附动力学符合准二级动力学模型,吸附等温线符合 Langmuir等温线模型。Ce-BDC-400(A)和Ce-BDC-400(N)对氟离子的吸附是自发进行的,且对氟的吸附过程是放热反应。Ce-BDC-400(A)和Ce-BDC-400(N) 对氟离子的最大吸附容量分别为140.6 mg·g−1和155.1 mg·g−1。Ce-BDC-400(A)和Ce-BDC-400(N)在宽 pH (3~10)范围内具有优良而稳定的除氟性能,并在实际水体处理中显示出优异的除氟性能。
-
关键词:
- 铈基金属有机框架材料 /
- 衍生碳 /
- 除氟 /
- 吸附 /
- 水处理
Abstract: The derivatives Ce-BDC-400(A) and Ce-BDC-400(N) were formed by calcination of Ce-BDC in an atmosphere of air and N2. XRD and SEM was used to characterize the microstructure, elemental composition, functional group characteristics, and crystal structure of the two materials. The removal performance and mechanism of fluoride by Ce-BDC derived carbon: Ce-BDC-400(A) and Ce-BDC-400(N), were investigated through absorption fitting experiments. The results showed that the successful synthesis of adsorption materials occurred. The adsorption kinetics of Ce-BDC-400(A) and Ce-BDC-400(N) to fluoride ion conformed to the quasi-second order kinetic model, and the adsorption isotherm conformed to the Langmuir model. The adsorption of fluoride by Ce-BDC-400(A) and Ce-BDC-400(N) was spontaneous and exothermic. The maximum adsorption capacities of Ce-BDC-400(A) and Ce-BDC-400(N) to fluoride were 140.6 and 155.1 mg·g−1, respectively. Ce-BDC-400(A) and Ce-BDC-400(N) presented an excellent and stable fluoride removal performance over a wide pH range (3-10), and an excellent fluoride adsorption performance in actual water treatment.-
Key words:
- cerium based metal–organic framework /
- derived carbon /
- fluoride removal /
- adsorption /
- water treatment
-

-
表 1 Ce-BDC-400(A)和Ce-BDC-400(N)的孔结构参数
Table 1. Textural parameters of Ce-BDC-400(A) and Ce-BDC-400(N)
样品 比表面积/(m2·g−1) 平均孔径/nm 总孔容/(cm3·g−1) Ce- BDC-400 (A) 36.06 18.22 0.164 Ce- BDC-400 (N) 31.09 3.97 0.031 -
[1] JAGTAP S, YENKIE M K, LABHSETWAR N, et al. Fluoride in drinking water and defluoridation of water[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2012, 112(4): 2454-2466. doi: 10.1021/cr2002855 [2] 薛英文, 杨开, 梅健. 混凝沉淀法除氟影响因素试验研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(工学版), 2010, 43(4): 477-480. [3] 宿延涛, 勾阳飞, 王海珍, 等. GW-F90树脂的除氟性能研究[J]. 铀矿冶, 2023, 42(2): 59-63. [4] 朱殿梅, 邵波霖, 钟可意, 等. 镧改性钢渣对水中氟离子的吸附性能[J]. 环境工程学报, 2023, 17(4): 1167-1176. [5] HALDAR D, DUARAH P, PURKAIT M K. MOFs for the treatment of arsenic, fluoride and iron contaminated drinking water: A review[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 251: 126388. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126388 [6] 徐志颖, 李晔, 刘冬雪, 等. 载镧活性氧化铝的除氟及再生性能研究[J]. 化学工程, 2022, 50(2): 1-4. [7] GUIZA S, BROUERS F, BAGANE M. Fluoride removal from aqueous solution by montmorillonite clay: Kinetics and equilibrium modeling using new generalized fractal equation[J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2021, 21: 101187. [8] TOLKOU A K, TRIKALIOTI S, MAKROGIANNI O, et al. Magnesium modified activated carbons derived from coconut shells for the removal of fluoride from water[J]. Sustainable Chemistry and Pharmacy, 2023, 31: 100898. doi: 10.1016/j.scp.2022.100898 [9] 李舒舒, 宋明珊, 童琳, 等. 负载铝铈污泥生物炭对模拟废水的强化除氟作用[J]. 环境工程学报, 2023, 17(3): 750-760. [10] ZHANG H, WAN K, YAN J, et al. The function of doping nitrogen on removing fluoride with decomposing La-MOF-NH2: Density functional theory calculation and experiments[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2024, 135: 118-29. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2023.01.015 [11] TANG X, ZHOU C, XIA W, et al. Recent advances in metal–organic framework-based materials for removal of fluoride in water: Performance, mechanism, and potential practical application[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 446: 137299. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.137299 [12] JEYASEELAN A, VISWANATHAN N. Facile fabrication of zirconium–organic framework–embedded chitosan hybrid spheres for efficient fluoride adsorption[J]. ACS ES& T Water, 2022, 2(1): 52-62. [13] 武鑫霞, 曹占平, 苏婷, 等. Ce改性金属有机骨架材料对氟的吸附[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(10): 2636-2644. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20200225.003 [14] 赵瑨云, 胡家朋, 刘瑞来, 等. La-金属有机骨架化合物的制备及其除氟性能研究[J]. 化学通报, 2021, 84(1): 75-80. [15] JEYASEELAN A, VISWANATHAN N. Facile synthesis of tunable rare earth based metal organic frameworks for enhanced fluoride retentionJ][J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2021, 326: 115163. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2020.115163 [16] HE J, XU Y, XIONG Z, et al. The enhanced removal of phosphate by structural defects and competitive fluoride adsorption on cerium-based adsorbent[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 256: 127056. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127056 [17] TANG X, XIA W, QU X, et al. Structure–performance correlation guided cerium-based metal–organic frameworks: Superior adsorbents for fluoride removal in water[J]. Chemosphere, 2023, 312: 137335. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.137335 [18] WANG B, ZENG Y, XIONG M, et al. Adsorption performance and mechanism of mesoporous carbon-doped Al2O3 adsorbent derived from NH2-MIL-53 (Al) for removing Cr(Ⅵ) and methyl orange from aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2023, 11(3): 110081. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2023.110081 [19] HE J, XU Y, WANG W, et al. Ce(Ⅲ) nanocomposites by partial thermal decomposition of Ce-MOF for effective phosphate adsorption in a wide pH range[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 379: 122431. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122431 [20] CHEN G, GUO Z, ZHAO W, et al. Design of porous/hollow structured ceria by partial thermal decomposition of Ce-MOF and selective etching[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(45): 39594-39601. [21] JEYASEELAN A, NAUSHAD M, AHAMAD T, et al. Fabrication of amino functionalized benzene-1, 4-dicarboxylic acid facilitated cerium based metal organic frameworks for efficient removal of fluoride from water environment[J]. Environmental Science:Water Research & Technology, 2021, 7(2): 384-395. [22] TAO W, ZHONG H, PAN X, et al. Removal of fluoride from wastewater solution using Ce-AlOOH with oxalic acid as modification[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 384: 121373. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121373 [23] GU Y, XIE D, MA Y, et al. Size modulation of zirconium-based metal organic frameworks for highly efficient phosphate remediation[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(37): 32151-32160. [24] ZHANG N, YANG X, YU X, et al. Al-1, 3, 5-benzenetricarboxylic metal–organic frameworks: A promising adsorbent for defluoridation of water with pH insensitivity and low aluminum residual[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 252: 220-229. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.04.090 [25] CAI H, XU L, CHEN G, et al. Removal of fluoride from drinking water using modified ultrafine tea powder processed using a ball-mill[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2016, 375: 74-84. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.03.005 [26] MAZLOOMI S, YOUSEFI M, NOURMORADI H, et al. Evaluation of phosphate removal from aqueous solution using metal organic framework; isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic study[J]. Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering, 2019, 17(1): 209-218. doi: 10.1007/s40201-019-00341-6 [27] 张钰卿, 刘佳, 许兵, 等. 含氟废水处理中的除氟吸附技术研究进展[J]. 净水技术, 2022, 41(5): 23-29. doi: 10.15890/j.cnki.jsjs.2022.05.004 [28] ALIASKARI M, SCHäFER A I. Nitrate, arsenic and fluoride removal by electrodialysis from brackish groundwater[J]. Water Research, 2021, 190: 116683. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116683 -



 下载:
下载: