-
随着经济和社会快速发展,中国已成为全球最大的汽车市场,汽车销量连续8年位居全球第一,汽车报废量也在逐年递增[1]。报废汽车作为城市矿产,其处理过程主要包括去除污染物、拆解和破碎三个阶段,除铁、有色金属等可回收利用外,剩余的残留物被称为汽车拆解破碎残渣(automotive shredder residue, ASR)[2]。预计2022年我国汽车报废量将超过2 450×104 辆,产生的ASR (平均每辆车重按1 000 kg计算,ASR约占报废汽车总重量的25 %) 将超过612×104 t。
ASR成分复杂、热值较高且多为难降解物质,通过热处理方式进行资源化利用是更为绿色经济的处理方式[3-4]。将ASR与城市固废掺混焚烧可实现能量回收,但ASR氯含量较高,容易造成热处理设备的腐蚀,ASR含有的矿物质在剧烈焚烧条件下容易产生飞灰或结渣。气化可在较温和条件下实现有机固废能源化处理,清洁合成气可用于再生铝等其他循环经济工艺[5-8]。
本研究在自制的小型固定床气化实验装置上,以ASR为原料、采用空气作为气化剂,开展ASR空气气化特性研究,考察了空气当量比、反应温度对合成气品质、气化效率和碳转化率的影响。最后,根据气化实验结果对ASR气化过程进行质量和能量平衡分析,为ASR固定床空气气化系统设计和运行提供理论依据与指导。
-
实验所用ASR取自江苏某再生资源公司,利用粉碎机粉碎后备用。其工业、元素分析和低位热值结果如表1所示。由表格数据及研究团队以往研究数据[9]可知,ASR相比城市生活垃圾(municipal solid waste, MSW),具有低水分和灰分、高挥发分和固定碳的特点,挥发分是MSW的5.15倍、固定碳是MSW的2.16倍,而灰分仅为MSW的1/4。根据研究团队另一项研究[10],与典型的水稻秸秆对比,ASR的固定碳相对较高、灰分相对较低。
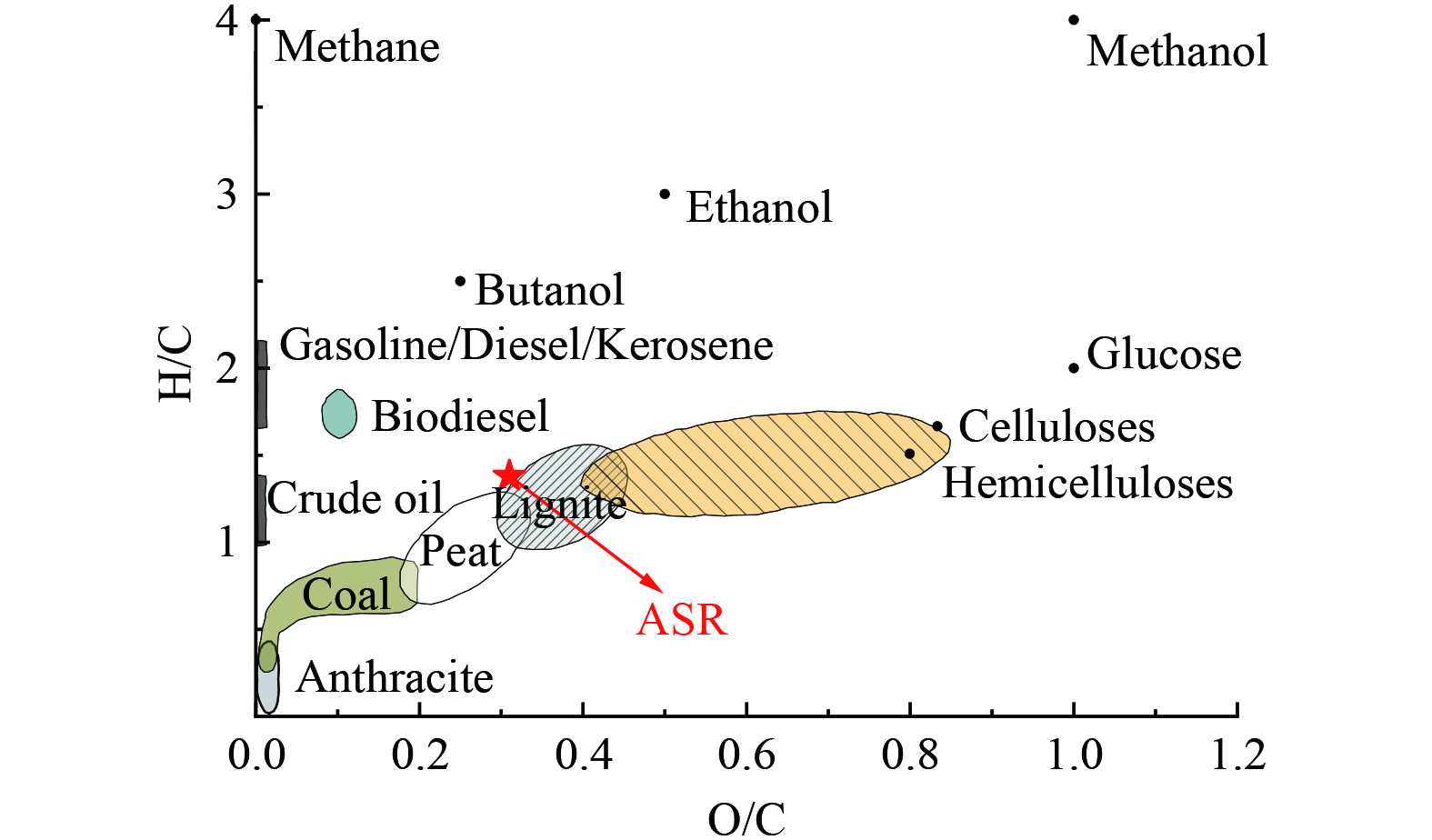
如图1所示为各种典型物料的元素范式图,ASR的O/C和H/C比分别为0.31、1.38,由图可知,与典型褐煤极为相似。我国的能源结构决定未来一定时间内煤炭仍然会是我国的主体能源,单从元素分布而言,ASR有着与褐煤相似能源开发潜力[11-12]。
-
ASR 固定床空气气化实验装置如图2所示,主要由配气系统、固定床气化炉、冷凝系统、气相色谱分析系统4部分组成。ASR固定床空气气化实验主要步骤如下。
1) 备料:称取0.5 g ASR,利用石英棉将物料均匀固定于石英管中一端,将石英管插入管式炉。
2) 氮气吹扫及升温:利用泡沫水检查装置气密性,并使用大气量氮气吹扫反应系统,排出反应器内部的空气,将管式炉均匀升温至设定温度。
3) 热解/气化反应:以空气作为气化剂,氮气作为载气 (热解实验时仅打开氮气阀门,气化实验时的空气流量通过空气当量比和反应时间的值确定) ,混合气体总流量设置为100 mL·min−1,待气路流量稳定后,将石英管一端的ASR推入固定床炉膛内,开始反应,需确保ASR装填区位于管式炉有效常温区内。
4) 产物收集及分析:产生的气体从石英管右端排出,进入由冰盐浴装置和冷凝管组成的冷凝系统。合成气中的焦油和水蒸气凝结在冷阱瓶中,冷凝塔对合成气中的水蒸气进行二次收集。气体由气袋收集,使用气相色谱仪进行分析。
5) 反应结束后将石英管推出,停止通入空气,关闭温控装置;氮气持续吹扫以确保完全收集管路中残余的合成气,固体残渣冷却至室温后收集。
-
碳转化率是合成气中的碳占单位质量燃料中碳的百分率,碳转化率
$ {\eta _{\text{C}}} $ 的计算如式(1)所示[13]。式中:M为碳元素的摩尔质量,12 kg·kmol−1;CO%、CO2%、CH4%、CnHm%分别为气袋中各气体组分的体积百分含量,由气相色谱仪测得,%;
$ \phi $ 为单位质量ASR反应后总气体量,m3·kg−1;Vm为气体摩尔体积,22.4 m3·kmol−1;C为1 kg ASR中碳的含量,%。气化效率是指ASR合成气总热量与气化反应投入原料的总热量之比,是衡量气化质量的主要指标之一,冷煤气
$ {\eta _{{\text{cold}}}} $ 的计算如公式(2)所示[13]。式中:
$ {Q_{{\text{gas}}}} $ 为单位质量原料产生的合成气的总热量,kJ·(kg ASR)−1;$ {Q_{{\text{ASR}}}} $ 为单位质量原料的低位热值,kJ·(kg ASR)−1。 -
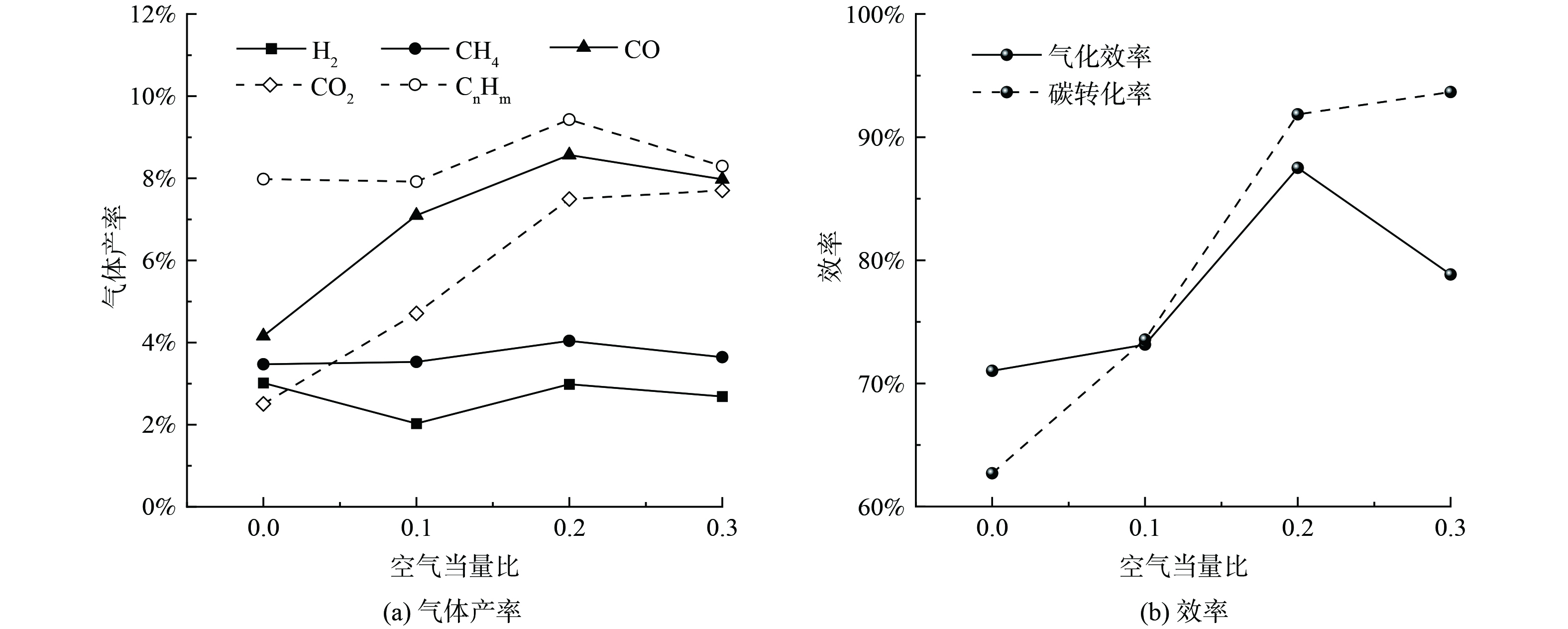
根据现有研究,有机固废气化空气当量比范围为0~0.3。如图3所示为气化温度为900 ℃时,空气当量比从0增大到0.3,气化产生的合成气各组分产率、气化效率及碳转化率的变化情况。由图3(a)可知,ASR合成气中CH4、CO和CnHm的产率随空气当量比的增大呈现先增大后减小的规律,均在空气当量比为0.2时达到最大值;CO2的产率随空气当量比的增大而增大;空气当量比对H2产率的影响不明显。陈雨佳等[14]的实验研究也发现了类似的现象。
空气当量比增大带来2方面影响:第一方面是燃烧产生的热量导致系统温度升高,进而增强ASR热解强度和均相重整反应过程,生成更多CH4、CO和CnHm等可燃气体;第二方面是过量O2导致可燃组分燃烧,产生更多CO2。由图3可见,空气当量比由0增至0.2的过程中,CH4、CO和CnHm等组分含量的上升更多是第一方面占主导作用,而空气当量比由0.2增至0.3的过程更多是第二方面占主导作用。随着当量比的增加,产生和消耗H2的速度可大致抵消,导致H2产量变化不明显。
由图3(b)可知气化效率在当量比为0.2时达到最大值87.5%,随着当量比增加,燃烧反应加剧,碳转化率增加。因此,本实验工况下的最优当量比为0.2。
-
图4为空气当量比为0.2时,ASR在700、800、900 ℃温度下的气化特性。随着温度的升高,气化反应速率加快,产气中H2、CH4、CO和CnHm的产率增加,CO2的产率降低。随着温度升高,难降解物质发生了热解,且促进了焦油裂解、水煤气反应和甲烷水蒸气重整反应等吸热反应的发生,从而使得CH4、CO和CnHm等小分子可燃组分的产率上升。高温下的Boudouard反应使得CO2含量下降,CO进一步增加。CH4的产率受2方面因素影响:一是温度升高后,CH4的分解反应、CH4与水蒸气的重整反应等均会消耗CH4,使得CH4浓度有降低趋势;二是随着温度升高焦油裂解反应速率增大,生成更多的CH4,使得CH4浓度有上升趋势。由图4中CH4变化曲线可知,温度升高时,第二种作用占据主导地位,导致CH4含量呈升高趋势。随着气化温度升高,气体可燃组分产率增加,气化效率、碳转化率也不断增加,此趋势与张伟等[15]的研究结果类似。
需要解释说明的是:升高炉内温度,通常需要增加物料或可燃气的燃烧份额,进而可能导致合成气热值和气化过程效率下降。因本研究中气化实验在固定床实验系统中展开,通过管式炉以外加供热的方式实现温度控制,因此随温度的升高,气化效率并未下降,而呈增加的趋势。
-
任意选取气化温度为900 ℃、空气当量比为0.1工况下的气化过程,进行质量平衡分析。以气化系统为研究对象,输入系统物质流包括ASR、空气和氮气,系统输出的物质流有:气化残渣、合成气和焦油。就每一种元素而言,一定时间内系统的元素质量也符合守恒定律[16]。考虑到氮气不参与气化反应,本次计算不考虑氮气对系统输入输出的影响。
收入项中ASR每次实验进样量均为0.5 g,氧气量可由所用当量比计算得到。支出项中气化残渣质量在实验后收集残渣称量得到;合成气质量近似于产生的合成气中H2、CH4、CO、CO2和CnHm (仅考虑C2、C3) 各气体组分质量之和,其中气袋收集气体后通过气相色谱分析得到各气体组分的百分含量,以氮气平衡和流速可以求得各气体质量,并加和得到合成气总质量。本研究由于受实验装置限制,单次实验进样量较小,导致产生的焦油量较少,难以准确收集称量,通过选定工况进行多次重复实验,累积得到足够焦油后,进行元素分析和热值测定,得到选定工况下气化产生的焦油特性。
收入项中碳含量可由ASR进样量和其元素分析结果计算得到,支出项中气化残渣碳含量可由残渣产量和其元素分析结果计算得到,合成气碳含量由各气体组分的量计算得到,根据碳元素守恒,即可得到焦油中的碳含量,由于焦油元素分析结果已知,进而可计算得到单次实验产生的焦油质量。
此工况下ASR气化过程的系统物料平衡如表2所示,质量平衡误差为 (1−0.57/0.59)×100%=5%,基本满足化学反应质量守恒[17]。5%的误差原因可能是ASR气化反应产生的水不能准确收集定量,未能考虑进衡算中,且所用的气相色谱仪检测气体含量时亦存在误差。
-
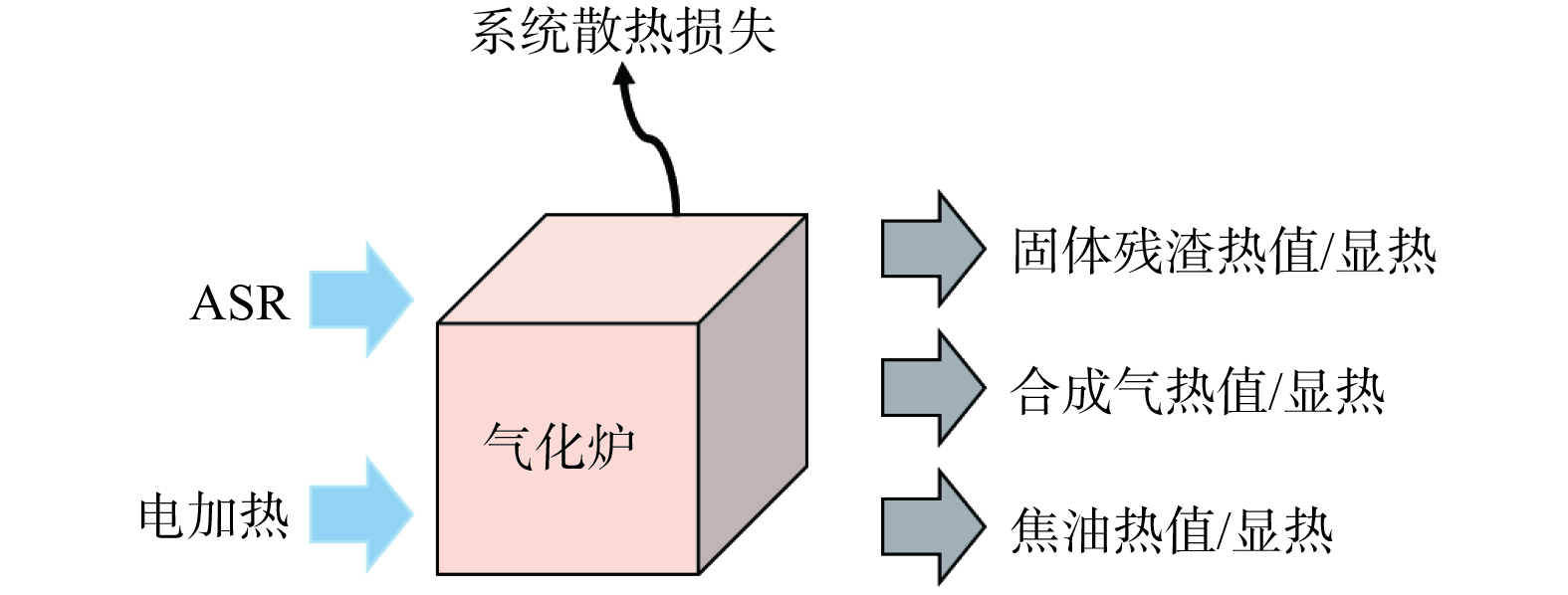
以气化系统为研究对象,其能量平衡示意图如图5所示。
输入系统的能量包括ASR的热值QASR和管式炉热电偶提供的能量Qele。系统输出的能量包括固体残渣、焦油和合成气各自的化学热Qchar、Qtar、Qgas和各自的显热Qcx、Qtx和Qgx,以及系统热量损失Q0。整个气化系统的能量平衡方程式如式(3)所示。
表3为ASR气化系统能量平衡计算时用到的已知各项参数,为方便计算,进样量按1 kg计算,其他各项产物产量亦换算为1 kg ASR反应的产生量。
1) 气化系统输出的能量
①固体残渣化学热
对ASR气化残渣进行元素分析后,采用门捷列夫公式估算其热值,如式(4)所示。
固体残渣化学热计算如式(5)所示。
计算得到,固体残渣化学热为547.64 kJ。
②固体残渣显热
固体残渣显热计算如式(6)所示。
气化结束后残余的底渣,可认为初始形成温度与气化温度一样为900 ℃,反应结束后冷却至室温25 ℃。因此固体残渣的显热为173.25 kJ。
③焦油化学热
ASR气化产生的焦油化学热计算如式(7)所示。
计算得到焦油的化学热为6 365.25 kJ。
④焦油显热
焦油显热计算如式(8)所示。
同样假设焦油初始温度为900 ℃,气态的焦油随合成气经过冷阱时被收集后冷却至室温25 ℃。计算得到产物焦油的显热为365.34 kJ。
⑤合成气化学热
根据各组分的产量及其低位热值,计算得到ASR气合成气的化学热Qgas为17 691.26 kJ。
⑥合成气显热
炉膛出口处温度为900 ℃,可认为合成气初始温度也是900 ℃,最终冷却至室温25 ℃,根据气体组分的产量及其定压比热容计算气体显热,如式(9)所示。
式中:Cp, i, 900 ℃、Cp, i, 25 ℃为各气体组分在900和25 ℃时的定压比热容,kJ·(m3· ℃)−1,如表4所示;Vi为各气体组分的产率,m3。根据气体各组分的产量及其物性参数可以计算出,含1 kg ASR气化中合成气带出的显热为6 797.59 kJ。
2) 输入气化系统的能量
热电偶外加热量Qele提供的能量去向一共有2部分:一部分能量Qg用于气化反应的发生,被气化过程中相关吸热反应所消耗;另一部分Qs用来提供气化反应时的高温氛围,最终散入周围环境中。
根据上述分析,在不考虑Qele最终散入周围环境中的那部分热量的情况下,ASR气化系统应满足能量平衡方程,如式(10)所示。
本气化工艺是在炉膛温度达到900 ℃后将ASR推进炉膛进行气化反应,可近似认为ASR瞬间从室温升高到900 ℃的高温。ASR成分复杂,实际气化过程中的反应过程也极其复杂。为方便计算,假设ASR进入高温环境后分3阶段进行反应,且互不影响:首先为干燥阶段,即ASR中的水分快速蒸发,吸收热量Q1;干燥后的ASR被极快地加热到900 ℃,吸收热量Q2;最后发生复杂的气化反应,此过程可能吸收热量,也可能放出热量,为Q3。综上,可认为Qg是由这3个阶段的热量共同组成,如式(11)所示。
Q1和Q2的计算如式(12)和式(13)所示。
式中:W为ASR中的水分含量,wt%;
$ \Delta {T_1} $ 为脱水阶段的温度差,室温以25 ℃计算,该温差为75 ℃;$ \Delta {T_{\text{2}}} $ 为ASR快速升温阶段的温度差,该温差为800 ℃;$ {C}_{\text{p},900 \text{°C}} $ 、$ {C}_{\text{p},100 \text{°C}} $ 为水在900和100 ℃时的定压比热容,查阅相关标准JC488-92得知,其数值分别为1.696、1.506 kJ·(m3· ℃)−1;CpA为ASR的比热容,估算为1.55 kJ·(kg· ℃)−1。计算可得Q1=154.54 kJ,Q2=1 242.12 kJ。由于ASR实际气化过程极其复杂,受实验条件限制,无法直接算出Q3的准确值,此处通过式10和11对其进行了粗略估算。
1 kg ASR进料的化学热QASR=1 kg×24 180 kJ·kg−1=24 180 kJ,固体残渣的化学热Qchar=0.18 kg×3 042.46 kJ·kg−1=547.64 kJ,焦油的化学热Qtar=0.225 kg×28 290 kJ·kg−1=6 365.25 kJ,合成气的化学热Qgas=17 691.26 kJ。根据式(10)计算可得Qg=424.15 kJ,可知整个ASR反应为吸热反应。根据式(11)进一步计算得到Q3=−972.52 kJ,说明ASR气化过程存在放热过程。
对质量为1 kg的ASR进行空气气化,以管式炉加热为例,各产物化学热及其显热减去ASR本身的热值得到的差值即为最小理论外加热量Qmin,当外加热量大于最小理论外加热量Qmin时,额外的热量视为通过炉体散去,即无效热量。在900 ℃,空气当量比为0.1的条件下,ASR气化系统的能量平衡计算如表5所示。
该工况下的能量回收率
$ \varepsilon $ 计算如式(14)所示。气化产物能耗比
$ \delta $ 计算如式(15)所示。该研究目的为制备高品位合成气,因此在计算能量回收率和产物能耗比时,产物指标只考虑了合成气的化学热。在选定的实验条件下,气化实验装置气化能量回收率和能耗比计算结果分别为55.39 %和2.28。由于实验规模小,且偏机理性研究,并未回用合成气的化学能,实际工程应用中可充分回用该部分能量用于补充气化系统能量。由上述计算可知,ASR合成气化学能是17 691.26 kJ·(kg ASR)−1,假设设备回收热效率为80%,得到可回收热量即为14 153.01 kJ·(kg ASR)−1,远大于最小理论外加热量,可实现气化热自持的同时,为其他工艺过程提供能量。
-
1) 气化温度为900 ℃,随着空气当量比增大,CO、CH4和CnHm产率先增大后减小,CO2产率随空气当量比的增大而增大,空气当量比对H2产率的影响不明显;气化效率先升高后降低,空气过量系数为0.2时气化效率最高;碳转化率始终升高。
2) 空气过量系数为0.2,随着气化温度升高,气化反应速率加快,产气中H2、CH4、CO和CnHm的产率增加,CO2产率降低;气化效率和碳转化率均随着气化温度的升高而提高,这主要是因为电外加热对气化系统进行了热量补充。
3) 选取温度为900 ℃、空气过量系数0.1的工况进行了质量和能量平衡计算,结果表明质量平衡误差为5%,能量回收率和能耗比分别为55.39%和2.28,合成气不仅可以为气化过程本身提供热自持所需热量,还可为后续其他工艺过程提供能量。
汽车拆解废弃物固定床空气气化特性
Study on gasification characteristics of automotive shredder residue
-
摘要: 中国作为全球最大的汽车市场,报废汽车拆解破碎残渣已成为备受关注的“城市矿山”。在自制的固定床气化实验装置上,以汽车拆解废弃物为原料,考察了空气当量比、反应温度对合成气品质及气化指标的影响。结果表明:在0~0.3范围内,随着空气当量比的增大,合成气中可燃气组分产率先增大后减小、气化效率先升高后降低、碳转化率逐渐增大;在700-900 ℃温度范围内,随着温度的提高,合成气中可燃气体组分产率增大、气化效率和碳转化率均逐渐增大;当空气当量比为0.2、气化温度为900 ℃时,气化效率最高。对900 ℃气化实验结果进行质量和能量平衡分析,结果表明:该系统质量平衡误差仅为5%,满足质量平衡要求;能量回收率和能耗比分别为55.39%和2.28,汽车拆解废弃物气化具有系统热自持和为其他用能工艺过程提供能源的潜力。Abstract: On a self-made fixed bed gasifier, the effects of air equivalence ratio and reaction temperature on the quality of synthetic gas and gasification indicators were investigated using automotive shredder residue (ASR) as feedstock. The results showed that within a range of 0-0.3, with the increase of air equivalence ratio, the production of combustible gas components in synthesis gas increased first and then decreases, the gasification efficiency first increased and then decreased, and the carbon conversion rate gradually increased. Within the temperature range of 700-900 ℃, as the temperature increased, the yield of combustible gas components in the synthesis gas increased, and the gasification efficiency and carbon conversion rate gradually increased. When the air equivalence ratio was 0.2 and the gasification temperature was 900 ℃, the cold gas efficiency was the highest. The mass and energy balance analysis of the gasification test at 900 ℃ showed that the mass balance error of the system was only 5%, which met the mass balance requirements. The energy recovery rate and energy consumption ratio were 55.39% and 2.28, respectively, indicating that gasification of ASR had the potential for systematic thermal self-sufficiency and providing energy for other energy-consuming processes.
-
Key words:
- automotive shredder residue /
- gasification /
- air equivalent ratio /
- temperature /
- mass balance /
- energy balance
-

-
表 1 ASR的工业分析、元素分析和热值
Table 1. Proximate, ultimate and heating value analyses of ASR
工业分析/%, ad 热值QLHV/MJ·kg−1 水分 灰分 挥发分 固定碳 1.56 13.00 71.68 13.76 24.18 元素分析/%, ad 碳 氢 氧 氮 硫 55.22 6.33 23.17 2.12 0.16 表 2 选定工况下的系统物料平衡表
Table 2. Mass balance under selected operating condition
g 收入项 支出项 ASR 氧气 总计 气化残渣 合成气 焦油 总计 0.50 0.087 0.59 0.09 0.37 0.11 0.57 表 3 ASR气化能量平衡计算参数
Table 3. Parameters for ASR gasification balance calculation
参数及单位 符号 数值 原料进口温度/ ℃ T0 25.00 出口温度/ ℃ T1 900.00 进样量/kg MA 1.00 焦油产量/kg Mt 0.23 残渣产量/kg Mc 0.18 水的比热容/kJ·(kg· ℃)−1 Cw 4.18 焦油的比热容/ kJ·(kg· ℃)−1 Cpt 1.45 焦油的汽化潜热/ kJ·kg−1 △Ht 355.00 固体残渣比热容/ kJ·(kg· ℃)−1 Cpc 1.10 气体热值/kJ Qg 17 691.26 焦油热值/ kJ·kg−1 qt 28 290.00 残渣热值/ kJ·kg−1 qc 3 042.46 水的汽化潜热/ kJ·kg−1 $ \Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{vap}}}} $ 2 257.20 表 4 各气体组分的物性参数
Table 4. Physical parameters of gaseous components
参数 Cp,i,T ℃/kJ (m3 ℃)−1 25 ℃ 900 ℃ H2 1.277 1.323 N2 1.293 1.380 CO 1.302 1.403 CO2 1.593 2.179 CH4 1.566 2.596 C2H4 1.716 3.450 C2H6 2.266 4.546 C3H6 2.744 5.442 C3H8 3.155 6.568 表 5 选定工况下的气化系统能量平衡表
Table 5. Energy balance under selected operating condition
收入项 热量/kJ ASR的化学能 24 180 最小理论外加热量 7 760.33 总计 31 940.33 支出项 热量/kJ 固体残渣化学热 547.64 合成气化学热 17 691.26 焦油化学热 6 365.25 固体残渣显热 173.25 合成气显热 6 797.59 焦油显热 365.34 总计 31 940.33 -
[1] 王博翰, 杨斌 陈铭. 报废汽车破碎残余物及其塑料组分的催化热解研究[J]. 机械设计与制造, 2020(3): 9-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2020.03.003 [2] NOTARNICOLA M, CORNACCHIA G, DE GISI S, et al. Pyrolysis of automotive shredder residue in a bench scale rotary kiln[J]. Waste Management, 2017, 65: 92-103. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2017.04.002 [3] MANCINI G, VIOTTI P, LUCIANO A, et al. On the ASR and ASR thermal residues characterization of full scale treatment plant[J]. Waste Management, 2014, 34(2): 448-457. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2013.11.002 [4] LOMBARDI L, CARNEVALE E, CORTI A. A review of technologies and performances of thermal treatment systems for energy recovery from waste[J]. Waste Management, 2015, 37: 26-44. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2014.11.010 [5] ANZANO M, COLLINA E, PICCINELLI E, et al. Lab-scale pyrolysis of the automotive shredder residue light fraction and characterization of tar and solid products[J]. Waste Management, 2017, 64: 263-271. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2017.03.013 [6] DONAJ P, YANG W H, BŁASIAK W, et al. Recycling of automobile shredder residue with a microwave pyrolysis combined with high temperature steam gasification[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 182: 80-89. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.05.140 [7] DE MARCO I, CABALLERO B M, CABRERO M A, et al. Recycling of automobile shredder residues by means of pyrolysis[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2007, 79: 403-408. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2006.12.002 [8] ZOLEZZI M, NICOLELLA C , FERRARA S, et al. Conventional and fast pyrolysis of automobile shredder residues (ASR)[J]. Waste Management, 2004, 24(7): 691-699. [9] DONG W G, CHEN Z W, CHEN J C, et al. A novel method for the estimation of higher heating value of municipal solid wastes[J]. Energies, 2022, 15(7): 2593-2607. doi: 10.3390/en15072593 [10] QI R Y, CHEN Z W, WANG M F, et al. Prediction method for torrefied rice gusk based on gray-scale analysis[J]. Acs Omega, 2019, 4(18): 17837-17842. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.9b02478 [11] LIU S M, SUN H T, ZHANG D M, et al. Experimental study of effect of liquid nitrogen cold soaking on coal pore structure and fractal characteristics[J]. Energy, 2023, 275: 127470. [12] 刘晓锋, 杨攀博, 王健, 等. 麦秆与褐煤共热解特性及动力学分析[J]. 太阳能学报, 2021, 42(9): 410-415. doi: 10.19912/j.0254-0096.tynxb.2020-0666 [13] 郑志行, 张家元, 李谦, 等. 下吸式固定床的生物质H2O/CO2气化数值模拟研究[J]. 太阳能学报, 2022, 43(5): 377-382. [14] 陈雨佳, 王勤辉, 王中霞, 等. 秸秆循环流化床空气气化特性的实验研究[J]. 动力工程学报, 2019, 39(10): 847-852. [15] 张伟, 陈晓平, 王清, 等. 城市污泥流化床中低温空气气化及重金属迁移特性[J]. 化工进展, 2019, 38(4): 2011-2021. doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2018-1231 [16] 于旷世. 循环流化床双床煤气化工艺试验研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院研究生院, 2012. [17] 杨益. 烟草废弃物热解和气化的实验及机理研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2012. -



 下载:
下载: