-
我国城市生活垃圾总量巨大,且人均生活垃圾产量仍以年6%以上的增幅高涨[1]. 渗滤液是垃圾在处理过程中产生的副产物,具有水质复杂、有机污染物浓度高、无机离子存在量大等特点[2]. 垃圾渗滤液中的无机离子主要以高浓度的氯离子(Cl−)以及多种重金属离子存在,其中,Cl−浓度可高达几万mg·L−1;有机污染物主要包括腐殖酸和富里酸等组分[3]. 如果不对垃圾渗滤液中的氯离子和有机污染物进行安全处理,势必会对周围环境和人类健康造成极大的危害.
现阶段废水除氯方法主要有化学沉淀法、膜分离法、蒸发浓缩法、电解法和离子交换法等[4-6],但普遍存在除氯成本高、不能满足实际生产需求等问题. 化学沉淀法是利用化学沉淀剂与渗滤液中的Cl−反应,生成不溶于水的沉淀,再经过固液分离,达到去除Cl−的目的. 化学沉淀法包括超高石灰铝法、亚铜除氯法、Bi2O3除氯法等[7-10],其中,超高石灰铝法中药剂投加量大且会产生许多低附加值除氯产物;亚铜除氯法中亚铜离子不稳定,导致废水中铜离子残留量高;Bi2O3除氯法具有除氯效率高、除氯时间短等特点. 研究发现,封志敏等[11]在Bi2O3与Cl−的物质的量比为1.5∶2、温度为50 ℃、pH值为2和反应时间为2 h的条件下,处理硫酸锌溶液中Cl−的浓度可从2000 mg·L−1降低至280 mg·L−1. Huang等[12]采用含有Bi2O3量子点的铋系除氯剂处理渗滤液,得出在Bi3+和Cl−的物质的量比为1∶1、pH=1、Cl−浓度不低于2500 mg·L−1和搅拌时间为4 h的条件下,除氯效率最佳. 但由于渗滤液水质复杂,Bi2O3除氯法仍然需要较大的药剂投加量,且除氯产物BiOCl再生过程中碱消耗量大,也存在铋的损失[13]. 为解决Bi2O3除氯法遇到的这些难题并消除渗滤液高浓度氯离子和有机污染物的潜在威胁,本文提出利用稀土强化Bi2O3除氯效果,并将除氯产物制备成高附加值的上转换荧光材料,以实现废弃物高效资源化利用.
目前,BiOCl已作为一种新型的稀土掺杂材料而备受关注,因为通过稀土离子掺杂可获得优异的上转换发光性能[14-17]. 宋志国等[18]发明了一种稀土离子掺杂BiOCl的方法,其中,Bi3+、Ho3+、Yb3+、Nd3+按照一定物质的量比进行掺杂,经热处理后制备出发光颜色可调的BiOCl半导体材料,并证实稀土离子掺杂浓度能够影响上转换发光强度. 陈凡丽等[19]采用固相法制备了稀土离子掺杂BiOCl层状半导体,发现Zn2+可诱导Eu3+反常发光,使发光强度出现先减弱后增强的现象. 而垃圾渗滤液中含有一定量的重金属离子,在除氯过程中,它们易混入除氯产物中,可能对改善发光性能具有一定的促进作用. Li等[20]利用稀土离子掺杂铋酸盐微晶玻璃对渗滤液氯离子进行去除,发现部分Er3+和Yb3+离子可转移掺杂进BiOCl,使整个玻璃体系保持了优异的上转换发光强度,并且对抗生素诺氟沙星的光催化降解效率达到98%. 然而,关于稀土离子掺杂除氯产物制备上转换发光材料的研究还鲜有报道. Bi2O3处理渗滤液的产物中包含有未完全反应的Bi2O3、除氯产物BiOCl以及吸附的有机污染物,而引入的稀土氧化物Yb2O3和Er2O3可能有利于增强有机物和Cl-去除效果. 后期高温煅烧下,可使吸附的有机物裂解碳化,利用碳的还原性将Bi2O3中的部分Bi3+转化为单质Bi,并促进Yb3+和Er3+对BiOCl的掺杂,获得上转换荧光增强材料. 另外,吴飞飞等[21]研究了BiOCl的热解行为,发现BiOCl在高温下会形成不同晶相的BixOyClz. 这类BixOyClz通过高温煅烧或固态取代等方法脱除[Bi2O2]2+,被各种形式的O取代而形成,统称为“富氧BiOCl” [22-23]. 富氧BiOCl具有更明显的层状结构,可能较传统BiOCl更具有优势. 因此,利用Bi2O3不仅能初步去除渗滤液中高浓度的Cl-和有机污染物,还能利用Cl-和吸附的腐殖酸有效制备上转换荧光材料,为高浓度含氯有机废水的资源化处理提供新的借鉴.
本文采用化学共沉淀与高温煅烧相结合的方法制备Er3+/Yb3+共掺杂富氧BiOCl荧光材料,即采用Bi2O3、Yb2O3和Er2O3的混合物对渗滤液中的Cl-和有机污染物进行沉淀和吸附,得到上转换荧光材料前驱体,之后进行煅烧处理. 研究了Er3+/Yb3+共掺杂富氧BiOCl (EY-BOC)上转换荧光材料的结构、形貌和发光性能的变化,探讨了温度和不同基质载体对发光强度的影响,揭示了利用渗滤液中的污染物制备上转换荧光增强材料的机理.
-
垃圾渗滤液由常州市生活废弃物处理中心提供. 垃圾渗滤液的特征:pH为8.5、Cl−为25000 mg·L−1、COD为7300 mg·L−1、TOC为2146.5 mg·L−1、NH3-N为2900 mg·L−1. 除氯和制备过程中所涉及到的药剂,如Bi2O3、Yb2O3、Er2O3、BiOCl等皆为购买的分析纯试剂(上海麦克林生化科技有限公司).
-
取适量垃圾渗滤液进行离心以去除其中悬浮固体,用少量浓硫酸将垃圾渗滤液的pH调成1,根据Cl-浓度按照物质的量比Bi3+∶Cl-∶Yb3+∶Er3+=1∶1∶0.2∶0.02[12,20],计算出Bi2O3、Yb2O3和Er2O3的投加质量. 将称量好的药品加入上述离心后的垃圾渗滤液中,室温下搅拌2 h. 将除氯后溶液放置在离心机中以50000 r·min−1速度离心5 min,所得上清液采用离子色谱测试氯离子浓度;所得沉淀物放入烘箱80 ℃烘干12 h,得到前驱体(EY-BOC)样品. 将此烘干后EY-BOC样品在空气中以300 ℃、400 ℃、500 ℃、600 ℃、700 ℃、800 ℃进行煅烧,分别得到样品EY-BOC-300、EY-BOC-400、EY-BOC-500、EY-BOC-600、EY-BOC-700、EY-BOC-800.
-
采用德国Bruker AXS型多晶X射线衍射仪(XRD)测试样品的物相结构,分析条件为:铜靶,工作电压和工作电流分别为40 kV和40 mA,扫描范围为2θ=10—60°. 采用德国Sigma 500场发射扫描电子显微镜(SEM)对样品进行形貌分析,放大倍数为2000—20万倍,加速电压为15—20 kV,同时利用仪器自带的能量分散谱仪(EDS)进行元素种类与含量分析. 采用透射电子显微镜(TEM)对样品的微观结构进行分析,同时利用设备自带的能量分散谱仪(EDS)对特定区域的晶粒进行成分分析. 采用上海般特Bante 320型离子色谱仪测定除氯前后溶液中Cl-浓度. 采用德国元素vario TOC select型总有机碳测试仪测定除氯前后溶液中TOC含量. 采用日本FluoroMax Plus型高级荧光稳态、瞬态测量系统测量样品的上转换发射光谱. 采用江苏盛奥华6B-80型水质速测仪测定反应前后溶液中的吸光度,对照校准曲线得到溶液中的COD值.
-
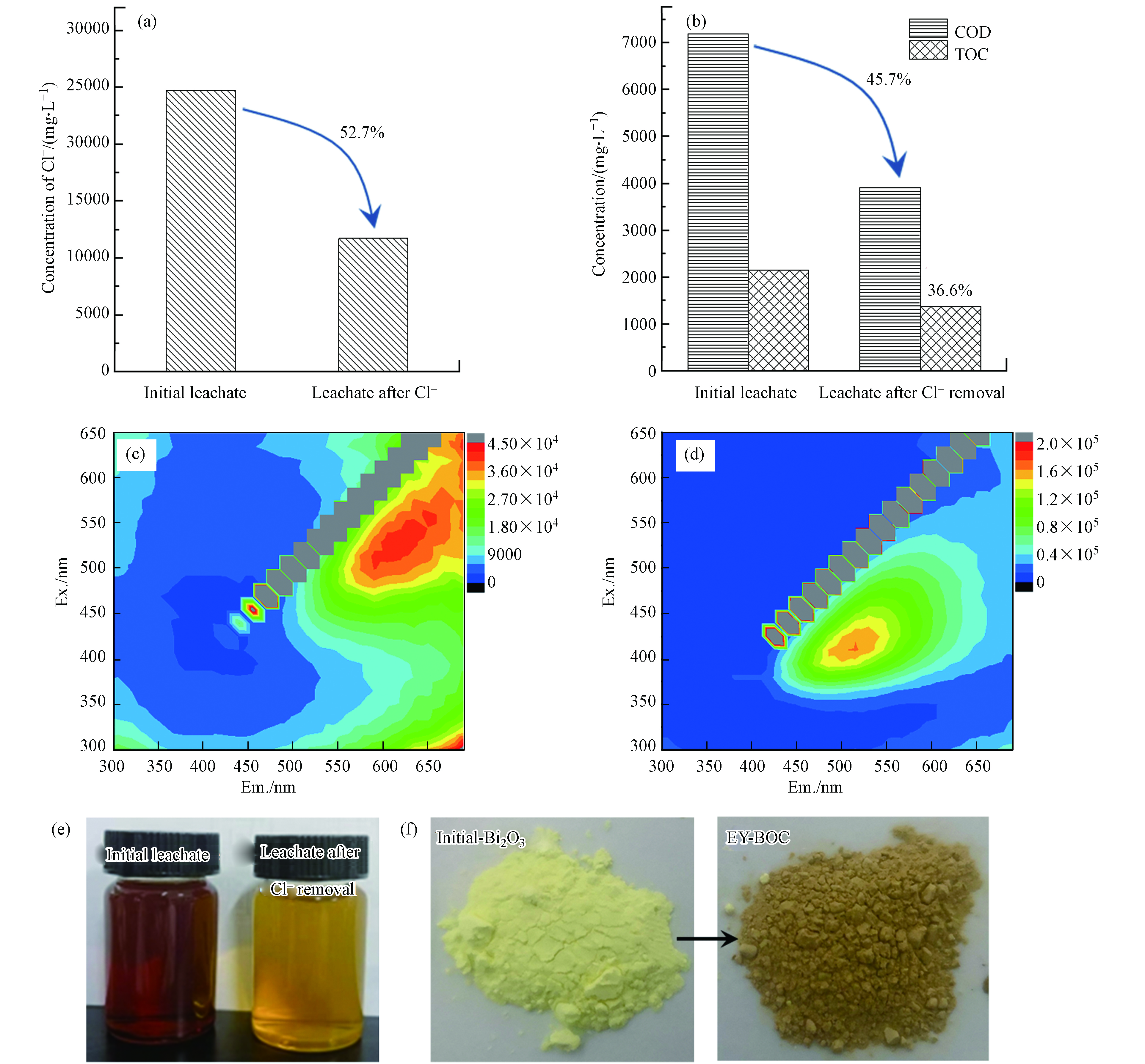
本文所用垃圾渗滤液中Cl−和有机污染物含量均较高,反应前,Cl-、COD和TOC含量分别高达25000 mg·L−1、7300 mg·L−1和2146.5 mg·L−1. 按照Bi3+∶Cl−∶Yb3+∶Er3+=1∶1∶0.2∶0.02的物质的量比投加Bi2O3、Yb2O3和Er2O3并反应2 h后,测定渗滤液中的各组分含量. 由图1(a)和(b)可知,其Cl−、COD和TOC的去除率分别为52.7%、45.7%和36.6%. TOC指水中溶解性和悬浮性有机物含碳的总量,COD表示氧化水中有机物和还原性物质所需的氧量,其测试过程中可能受到渗滤液中氯离子等的影响,所得测试值偏大,而TOC更能直接表示有机物总量[24]. 两者综合分析可知,渗滤液组分复杂,有机污染物只占其中一部分,并且可看出Bi2O3除氯法能协同去除渗滤液中部分有机物.
采用三维荧光光谱对反应前后渗滤液中的腐殖质类物质进行表征和分析. 三维荧光光谱一般可分为5个区域,Ⅰ区为芳香蛋白类Ⅰ(Ex=200—250 nm/Em=280—330 nm);Ⅱ区为芳香蛋白类Ⅱ(Ex=200—250 nm/Em=330—380 nm);Ⅲ区为富里酸类(Ex=200—250 nm/Em>380 nm);Ⅳ区为微生物副产物类(Ex>250nm/Em=280—380 nm);Ⅴ区为腐殖质类有机物(Ex>250 nm/Em>380nm)[25]. 由图1(c)和(b)可知,反应前后的渗滤液在不同位置各有一个特征峰. 反应前渗滤液有一个特征峰(Ex=525 nm/Em=625 nm),判断其为腐殖酸[26-27]. 反应后渗滤液中的部分Cl-和腐殖酸被去除,出现了一个特征峰(Ex=410 nm/Em=520 nm),也为腐殖酸,说明该渗滤液中有机物主要以腐殖酸的形式存在并且反应后荧光峰位置发生了蓝移. 从图1(e)和(f)可分别看出反应前后渗滤液和沉淀的颜色变化,垃圾渗滤液的颜色从原先的深褐色变为浅黄色,除氯产物也由黄色变为棕色,推测是由腐殖酸被大量吸附引起的.
-
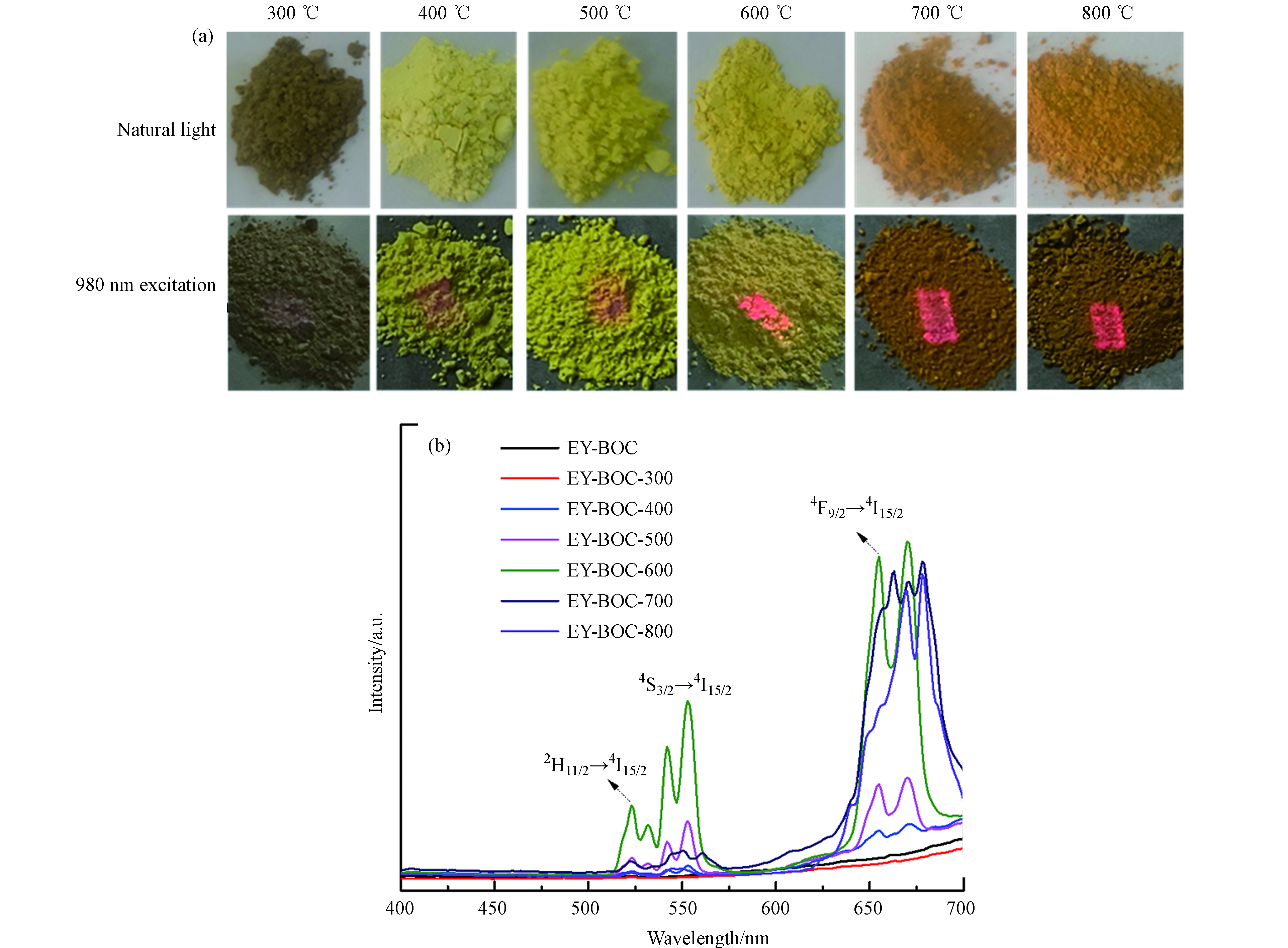
图2(a)所示为除氯产物在不同温度下煅烧后在自然光和980 nm激光器照射下的光学照片,可看出自然光下样品的颜色由棕色变为黄色再变为棕红色,可推测腐殖酸在高温煅烧下已裂解碳化并生成CO2脱去. 在980 nm激光器照射下,可明显看到红光强度随着温度的升高而增强,但在600 ℃下存在明显的黄光,其红光强度并没有700 ℃和800 ℃的样品高. 结合图2(b)不同温度煅烧产物在980 nm近红外光激发下的上转换发射光谱可知:不同温度煅烧所得样品的上转换发射光谱由相似的发射谱带构成,除氯产物及其经300 ℃煅烧样品发光非常微弱,从400 ℃到600 ℃煅烧样品的绿光和红光发射越来越强,绿光主要位于523 nm和553 nm,分别对应Er3+的2
$ {H}_{11/2} $ →4$ {I}_{15/2} $ 和4$ {S}_{3/2} $ →4$ {I}_{15/2} $ 能级跃迁,红光位于655—670 nm,对应Er3+的4$ {F}_{9/2} $ →4$ {I}_{15/2} $ 能级跃迁[28-29]. 由于红光发射强度高于绿光强度,EY-BOC-400和EY-BOC-500的总体荧光颜色表现出红色,而EY-BOC-600的绿光强度相对较高,除了红色荧光外,也存在部分由红光与绿光混合成的黄色荧光. 当煅烧温度达到700 ℃和800 ℃时,绿光发射急剧降低,而红光强度维持在EY-BOC-600的水平,所以EY-BOC-700和EY-BOC-800整体表现出红色荧光. -
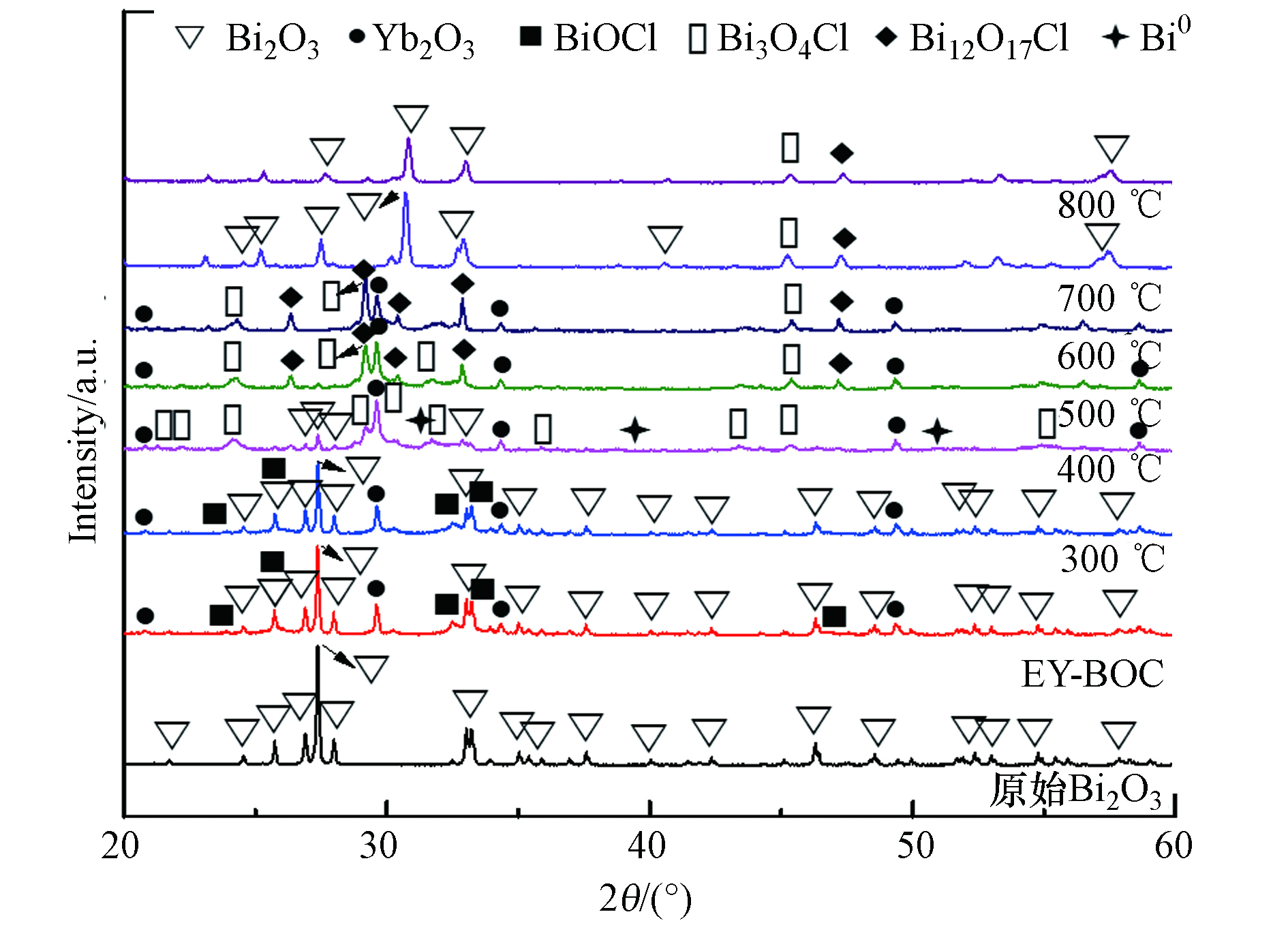
图3为原始Bi2O3、除氯产物及其经过不同温度煅烧2 h后的XRD图谱. 由图3所示,原始Bi2O3所有衍射峰都对应Bi2O3的PDF标准卡片号71-2274,说明纯度高,不存在其它杂相. 除氯产物EY-BOC中主要存在BiOCl (PDF 标准卡片号: 85-0861)、Yb2O3 (PDF 标准卡片号: 43-1037)和Bi2O3,因为渗滤液除氯效率只有52.7%,所以剩下了一部分Bi2O3,而Er2O3未被检测出,因为其含量很低. 除氯产物300 ℃煅烧后,所得EY-BOC-300样品的物相组成差别不大. 煅烧温度升高至400 ℃时,生成了新的物相Bi3O4Cl (PDF 标准卡片号: 36-0760)和Bi0单质(PDF 标准卡片号: 51-0765),并且Bi2O3的衍射峰发生了明显减弱. Bi0单质的形成是由于腐殖酸在高温下裂解碳化,将Bi3+离子还原产生的[30]. Bi3O4Cl是由BiOCl与剩余Bi2O3反应形成[21],见反应式(1),导致Bi2O3的衍射峰发生了大幅降低. 当温度为500 ℃时,不仅存在Bi3O4Cl晶相,还出现新相Bi12O17Cl2 (PDF 标准卡片号: 37-0702),而Bi2O3和Bi0单质衍射峰基本消失,可能是由于过量转化和氧化造成的. 根据文献推测[21,30],Bi12O17Cl2是由于BiOCl发生部分分解形成的BiCl3与剩余BiOCl和Bi2O3反应形成,见反应式(2).
随着煅烧温度提高到600 ℃,存在的物相主要为Bi3O4Cl、Bi12O17Cl2和Yb2O3,并且相对于500 ℃条件下,Bi3O4Cl和Bi12O17Cl2的衍射峰有一定程度的增强. 当煅烧温度为700 ℃和800 ℃时,Bi12O17Cl2和Bi3O4Cl的主强峰消失,并且出现了明显的Bi2O3衍射峰(其晶型与原始Bi2O3存在区别),说明大部分Bi12O17Cl2和Bi3O4Cl发生了分解,形成Bi2O3固相沉淀和BiCl3蒸气[31]. 同时,Yb2O3晶相消失,说明稀土离子Yb3+和Er3+基本上都掺杂进Bi2O3和剩余Bi12O17Cl2和Bi3O4Cl中,这也是新生成Bi2O3的晶型与原始Bi2O3不同的原因. 所得EY-BOC-700和EY-BOC-800样品在980 nm激光激发下主要发出红光,而EY-BOC-600除了发出强烈的红光外,还存在较强的绿光. 根据EY-BOC-600的物相组成,形成了两种富氧BiOCl,即Bi12O17Cl2和Bi3O4Cl,它们具有不同于BiOCl的晶相基质,可能拥有比BiOCl更加优异的掺杂条件.
-
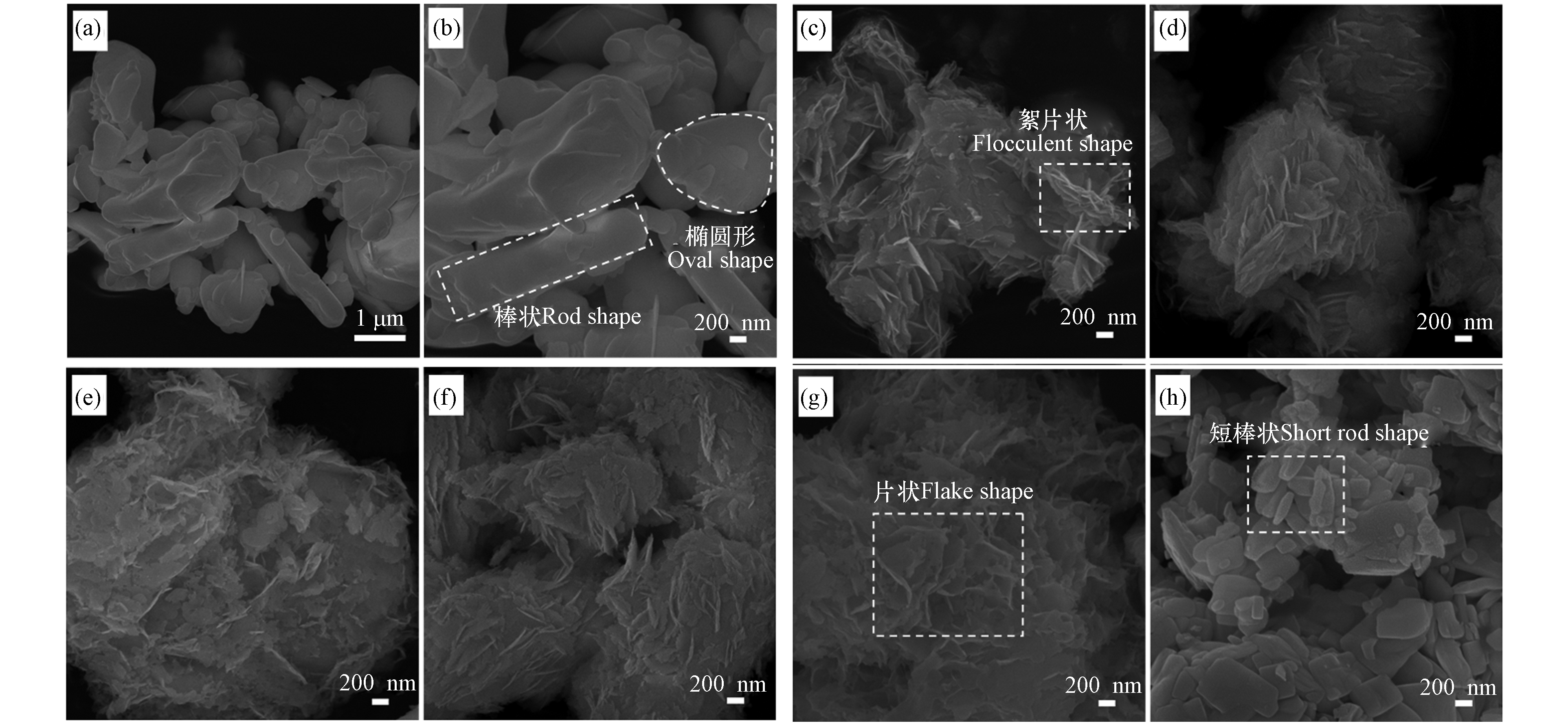
图4为原始Bi2O3、除氯产物及其在不同温度煅烧后的SEM微观形貌. 由图4(a、b)可见:原始Bi2O3形状不规则,呈棒状和椭圆形分布,颗粒较大,表面光滑. 从图4(c)可发现除氯产物EY-BOC在煅烧前,表面存在大量絮片状物质,使整体变得褶皱,判断是因为Bi2O3的表面生成了BiOCl. 在除氯反应过程中,BiOCl包覆性结块阻挡了内层Bi2O3进一步释放铋离子进行除氯反应,导致铋的利用率较低,这也是商用大颗粒Bi2O3的弊端. 但在本文中,剩余的Bi2O3在煅烧过程中可进一步与BiOCl反应形成Bi3O4Cl和Bi12O17Cl2,为稀土离子Yb3+和Er3+提供更好的掺杂环境,以提高上转换发光强度.
图4(d—h)为除氯产物在不同煅烧温度下的形貌变化. 随着温度的提高,Bi2O3和BiOCl逐渐向不同晶相的BixOyClz转变,形貌也逐渐发生变化. 经过300 ℃和400 ℃煅烧后,原本光滑的絮片状形貌变得粗糙,可能与腐殖酸的裂解碳化有关. 500 ℃煅烧后,絮片状形貌继续保留,但此时Bi2O3大部分消失. 当温度达到600 ℃时,表面较为光滑,出现片状分层;800 ℃时,样品呈现和原始Bi2O3相近的形貌,但经过煅烧后,样品的颗粒明显变小,可能是由稀土离子的掺杂效应造成的.
图5(a—f)为除氯产物600 ℃煅烧后的EDS面扫描能谱图,从图中可发现元素Bi、O、Cl、Yb和Er分布均匀,说明Yb3+和Er3+实现了均匀掺杂,而渗滤液可能引入的重金属离子未被明显检测出. 其中,Bi3+∶Cl-的原子百分比为2.8∶1,接近Bi3O4Cl中Bi与Cl元素之比,推测该处结构物相主要为Bi3O4Cl. Yb3+∶Er3+的原子为7.9∶1,接近除氯反应时加入的量,说明Yb3+和Er3+损失小,按比例实现了掺杂.
-
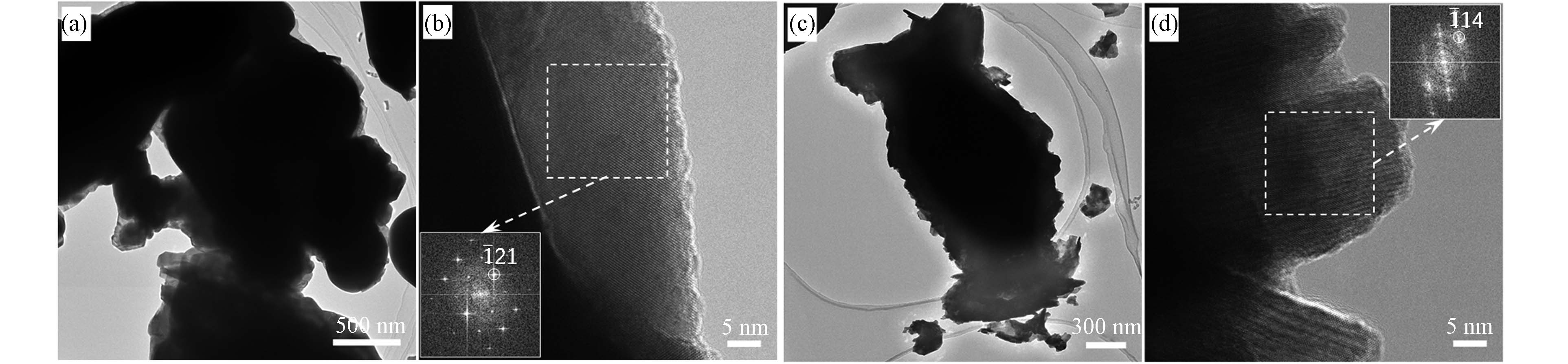
图6为原始Bi2O3和除氯产物600 ℃煅烧下所得EY-BOC-600样品的TEM分析图. 原始Bi2O3的TEM形貌(图6(a))中存在不规则的大尺寸棒状或椭圆形颗粒,边缘局部放大后得到的高分辨TEM (HRTEM)形貌见图6(b),其晶格条纹傅里叶变换(FFT)的电子衍射斑点中存在Bi2O3的(
$ \bar{1} $ 21)晶面,进一步证明了原始Bi2O3纯度高,无其它杂相. 图6(c)为EY-BOC-600样品的TEM形貌,其纳米结构颗粒由大量纳米薄片组成. 这些薄片体的HRTEM形貌见图6 (d),晶格条纹FFT电子衍射斑点中存在($ \stackrel{-}{1} $ 14)晶面,对应晶相Bi3O4Cl,证明EY-BOC-600 样品的薄片体主要以Bi3O4Cl存在. -
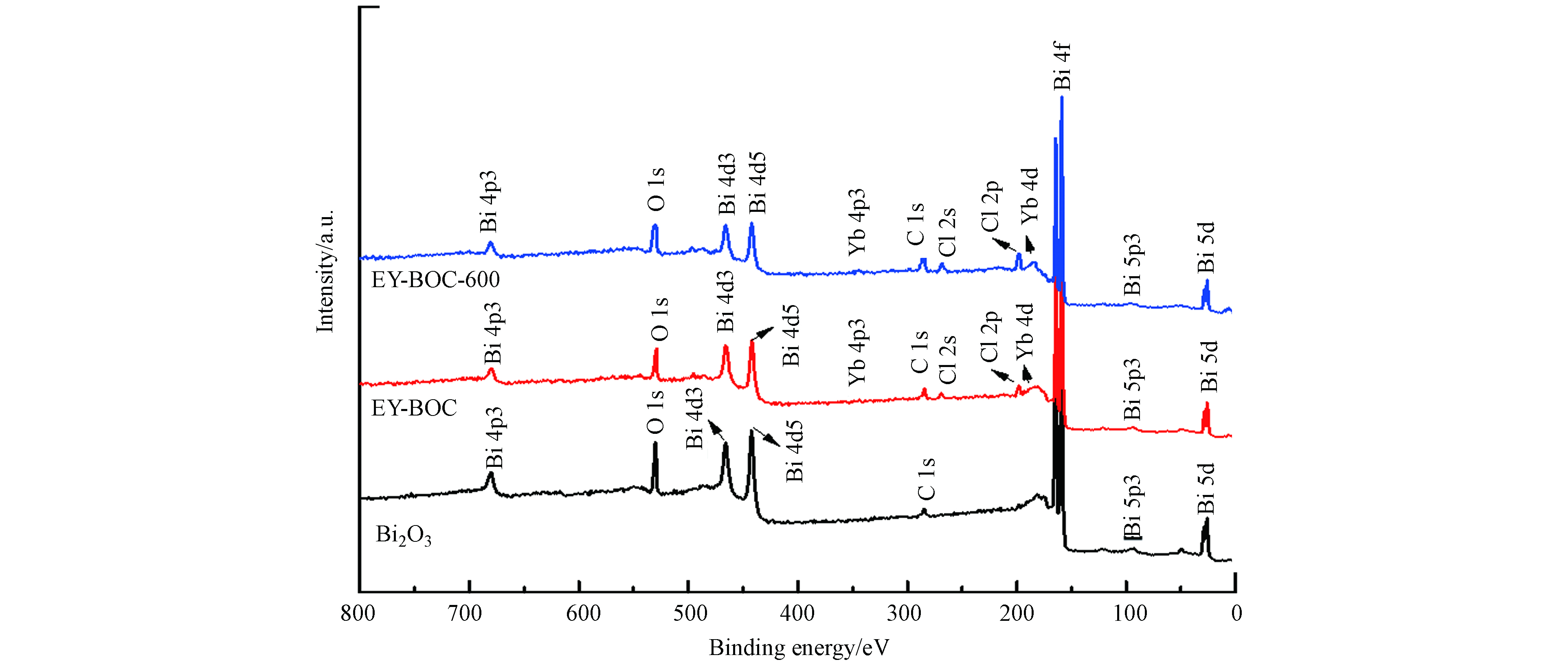
图7为原始Bi2O3、EY-BOC和EY-BOC-600样品的XPS全图谱. 如图所示,原始Bi2O3中除了用于定标的C元素外,只有Bi和O元素存在,说明其纯度高. 经过除氯反应后,所得EY-BOC中还存在Cl和Yb元素,Cl主要来自于渗滤液,Yb来自于引入的Yb2O3. Er元素信号未被检出,这与Er2O3投加量低有关. 另外,渗滤液中可能存在的重金属离子未被明显检出,说明除氯产物中重金属含量很低. 经过600 ℃煅烧后,所得EY-BOC-600样品仍然存在Bi、O、Cl、Yb元素,其它重金属也未被明显检出.
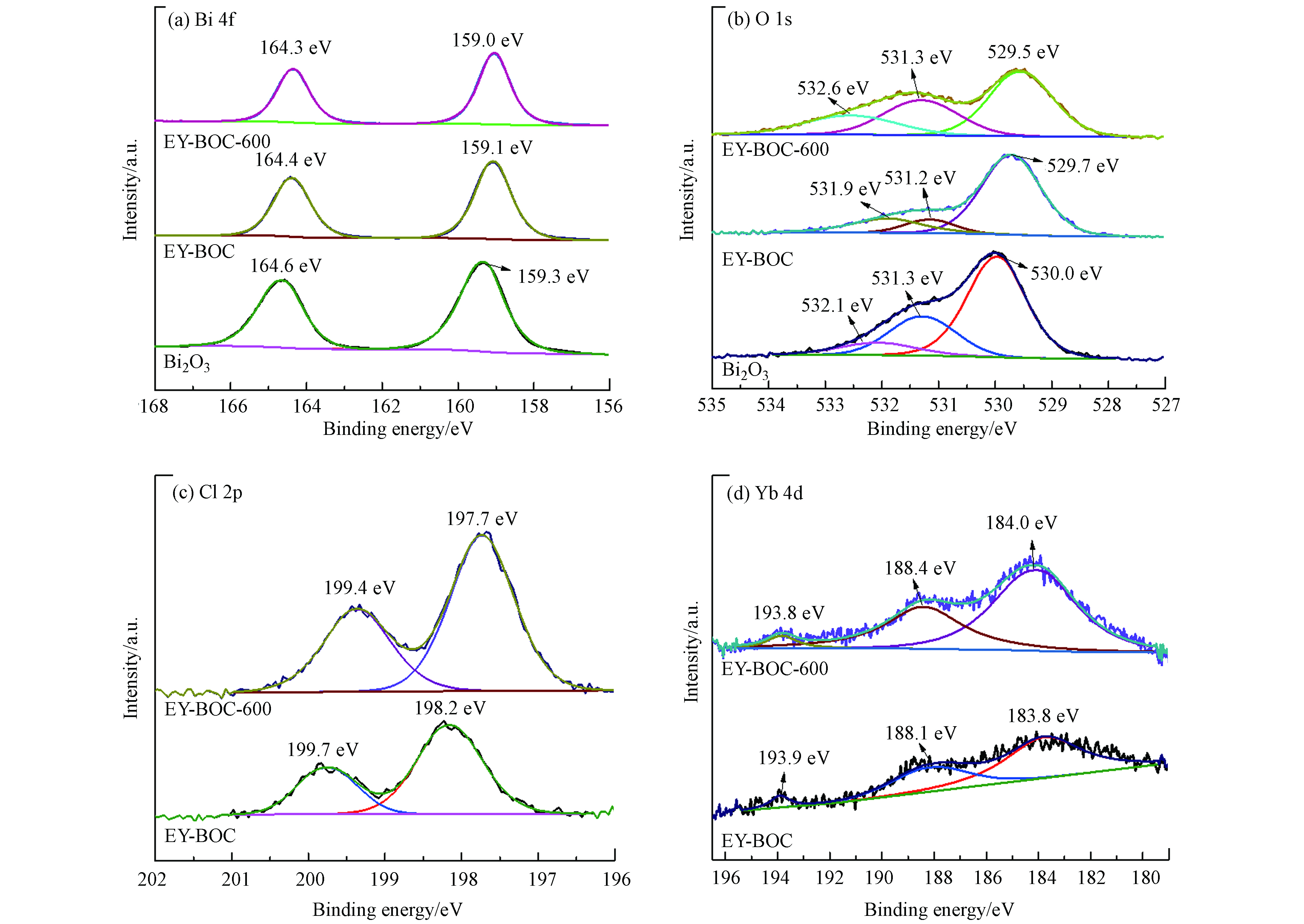
原始Bi2O3、EY-BOC和EY-BOC-600中Bi元素的XPS 高分辨谱图见图8(a),其中两个轨道能级的峰为Bi 4f5/2和Bi 4f7/2,分别位于164.6 、164.4 、164.3 eV和159.3 、159.1、159.0 eV,由此判断Bi元素的化合价为Bi3+. 从原始Bi2O3到EY-BOC,Bi元素峰的少量蓝移是因为产生了BiOCl;煅烧后Bi元素峰的蓝移是因为BiOCl转化为Bi3O4Cl和Bi12O17Cl2,使环境发生了改变[12]. 图8(b)为O 1s的XPS 高分辨谱图,其中元素特征峰明显不对称,说明氧元素价态组分丰富. 通过拟合分析可知,原始Bi2O3在530 eV处主峰属于Bi2O3的晶格氧,EY-BOC和EY-BOC-600样品在529.7 eV和529.5 eV处的主峰主要分别属于Bi2O3/BiOCl和Bi3O4Cl/Bi12O17Cl2的晶格氧[20,32]. 3个样品结合能为(531.2±0.1) eV处的特征峰推测为氧空位的信号[20,33]. 原始Bi2O3、EY-BOC和EY-BOC-600样品的O 1s更高结合能分别在532.1、531.9 、532.8 eV处,可归因于样品表面的化学吸附,如吸附的H2O或O2[32,34].
由图8(c)可知,EY-BOC-600样品在199.4 eV和197.7 eV处的特征峰分别属于Cl 2p1/2和Cl 2p3/2. 与EY-BOC相比,峰值发生了明显的偏移,因为经过600 ℃煅烧后,Bi2O3/BiOCl已全部转变为Bi3O4Cl和Bi12O17Cl2. 从图8(d)可看出EY-BOC在193.9 eV和183.8 eV处的特征峰分别与Yb 4d3/2和Yb 4d5/2一致,而EY-BOC-600特征峰分别移动到了193.8 eV和184 eV. 另外,位于Yb 4d3/2和Yb 4d5/2之间,还出现了一个特征峰,这是因为Yb 4d峰容易受到库仑力作用的影响,可能会出现多个峰值[35],但都属于Yb 4d的特征峰.
-
以上XRD、SEM、TEM和XPS分析了除氯产物EY-BOC样品煅烧前后的物相结构、形貌和成分变化. 所得EY-BOC-600样品中,Er3+和Yb3+按比例掺杂进Bi3O4Cl/ Bi12O17Cl2基质中,而非Bi2O3和BiOCl,并在980 nm激光器激发下能发出明显的绿光(523—553 nm)和红光(655—670 nm). 由于Yb3+对980 nm近红外光的吸收截面远大于Er3+的吸收截面,Yb3+会将吸收的能量传递给Er3+,进而通过Er3+的2
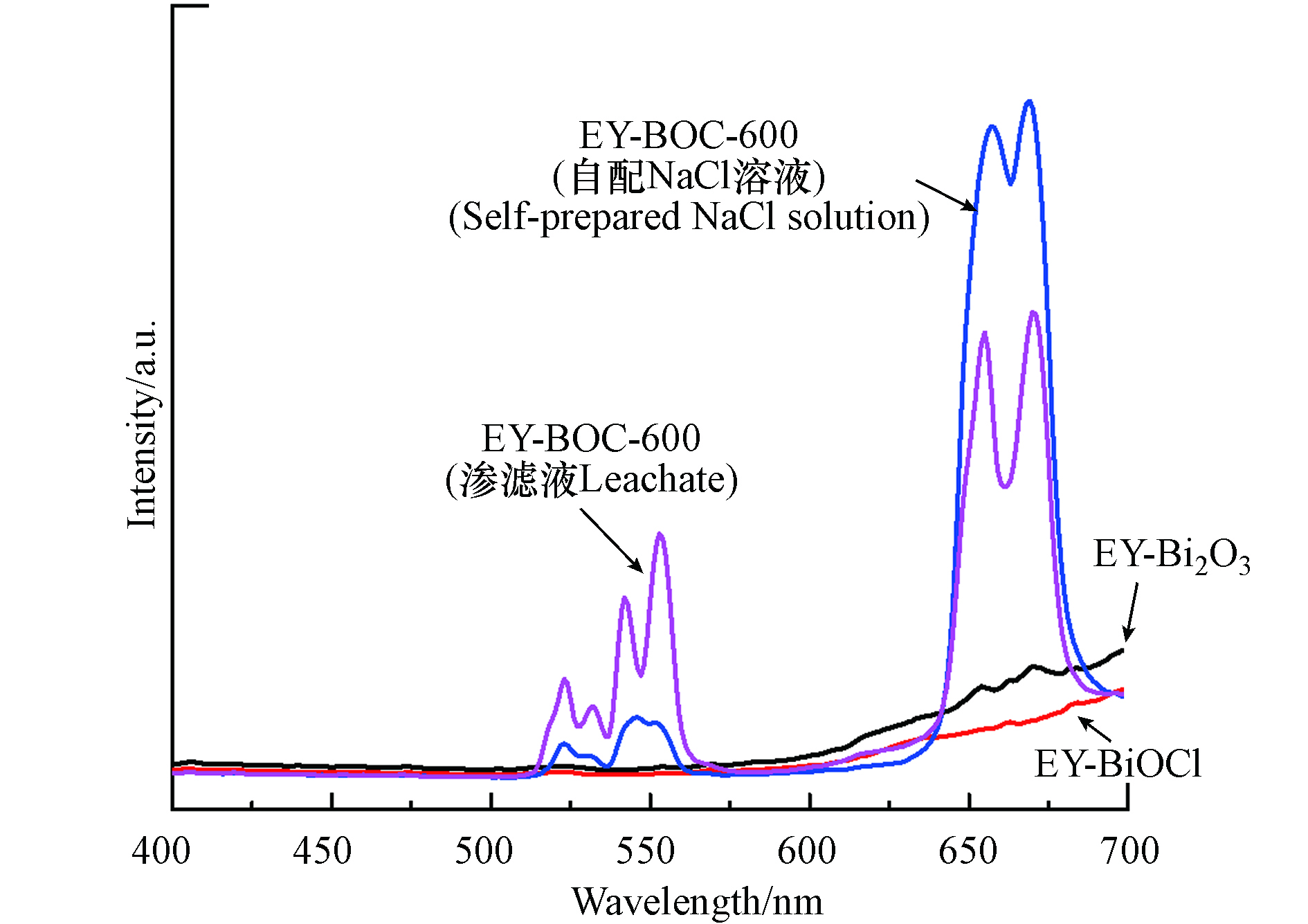
$ {H}_{11/2} $ →4$ {I}_{15/2} $ 和4$ {S}_{3/2} $ →4$ {I}_{15/2} $ 能级跃迁发出绿光和4$ {F}_{9/2} $ →4$ {I}_{15/2} $ 能级跃迁发出红光.为探讨不同基质载体对上转换发光性能的影响,将Bi2O3、Yb2O3和Er2O3按照相同物质的量比加入到去离子水中,室温下搅拌2 h,烘干后将样品在空气中以600 ℃煅烧,得到EY-Bi2O3样品. 将Bi2O3替换为BiOCl,按照相同方法制得EY-BiOCl样品. 同时配制与渗滤液相同Cl-离子浓度的NaCl溶液,按照前文相同的步骤制备EY-BOC-600 (自配NaCl溶液,除氯效率52.4%)样品,它们的上转换发射光谱图如图9所示. 通过比较可知,EY-Bi2O3和EY-BiOCl样品的上转换发射光谱非常弱,说明将稀土离子直接按比例掺杂进Bi2O3和BiOCl基质中的上转换发光性能差. 而EY-BOC-600(渗滤液)和EY-BOC-600(自配NaCl溶液)样品的上转换发射光谱峰明显,存在强烈的绿光和红光发射,表明它们的基质材料Bi3O4Cl和Bi12O17Cl2具有比BiOCl和Bi2O3更好的掺杂环境,这可能与Yb3+掺杂后引起的非对称性和极化性增强有关[36].
通过对比EY-BOC-600(渗滤液)和EY-BOC-600(自配NaCl溶液)样品的上转换发射光谱推测:由于自配NaCl溶液中没有其他杂质的干扰,导致EY-BOC-600(自配NaCl溶液)能发出强烈的红光,而EY-BOC-600(渗滤液)中绿光波段强度明显提升的原因大概率与渗滤液腐殖酸煅烧后引起的形貌结构变化有关;另外,虽然在XRD、SEM-EDS和XPS分析中未明显检测到渗滤液中引入的重金属,但不能完全排除微量重金属对Er3+离子发光的敏化作用,从而说明了可利用渗滤液中的Cl-和污染物来调控上转换荧光材料的发光波段范围.
-
通过化学共沉淀法制备Yb3+和Er3+掺杂型上转换荧光材料前驱体,实现了渗滤液中Cl-和有机污染物的高效去除,并在高温煅烧下得到上转换荧光增强材料. 在Bi3+∶Cl-∶Yb3+∶Er3+物质的量比为1∶1∶0.2∶0.02、pH=1、搅拌时间2 h的条件下,利用Bi2O3实现了对渗滤液中的Cl-、COD和TOC的同步去除,去除率分别达到52.7%、45.7%、36.6%,并且获得了可作为上转换荧光材料前驱体的除氯产物. 除氯产物在600 ℃煅烧下,Er3+和Yb3+成功按比例掺杂进样品,此时样品物相主要为Bi3O4Cl和Bi12O17Cl2,在980 nm近红外光激发下能发出明显的绿光(523—553 nm)和红光(655—670 nm). 通过对比不同基质载体对上转换发光强度的影响,证明了基质材料Bi3O4Cl和Bi12O17Cl2具有比BiOCl和Bi2O3更好的Er3+和Yb3+离子掺杂环境,从而为垃圾渗滤液中Cl-和有机污染物的去除和资源化利用提供了新的途径.
铋法去除垃圾渗滤液氯离子及其产物高值化利用机制
Removal of chloride ions in landfill leachate by bismuth method and the high-value utilization mechanism of its chloride removal product
-
摘要: 高浓度含氯有机废水在处理过程中不仅会消耗过多的化学药剂,还会产生大量的废弃产物. 为实现废弃物氯离子和有机污染物的去除和高值利用,本文以垃圾渗滤液为研究对象,采用化学共沉淀与高温煅烧的方法制备了Er3+和Yb3+掺杂型上转换荧光粉. 实验结果表明,当Bi2O3除氯剂和稀土投加量达到Bi3+∶Cl−∶Yb3+∶Er3+物质的量比为1∶1∶0.2∶0.02时,渗滤液Cl−、COD和TOC的去除效率分别为52.7%、45.7%和36.6%. 除氯产物在温度为600 ℃煅烧后,所得样品在980 nm激光激发下的上转换发光强度最高,发光光谱包括强烈的绿光和红光,绿光区域在523—553 nm和红光区域在655—670 nm. 上转换荧光增强机制分析表明,相对于Bi2O3和BiOCl,基质材料Bi3O4Cl和Bi12O17Cl2为Er3+和Yb3+离子提供了更好的掺杂环境. 因此,虽然除氯产物中还剩余Bi2O3,但其可与BiOCl在高温煅烧下形成Bi3O4Cl和Bi12O17Cl2,为上转换发光强度的提高和光谱调节提供了便利,也为渗滤液中氯离子和有机污染物的去除和高值资源化利用提供了新的方法.Abstract: The treatment of highly concentrated chloride-containing organic wastewater not only consumes too many chemicals, but also produces a large number of wastes. To realize the removal and high-value utilization of the chloride (Cl-) ions and organic pollutants in wastes, in this work, the landfill leachate was used as the research object, and the Er3+/Yb3+ doped upconversion phosphors were prepared by a chemical co-precipitation and high temperature calcination method. The experimental results showed that, when the added dosages of Bi2O3 and lanthanides reached the Bi3+∶Cl−∶ Yb3+∶Er3+ molar ratio of 1∶1∶ 0.2∶0.02, the removal efficiencies of Cl−, chemical oxygen demand (COD) and total organic carbon (TOC) in leachate were 52.7%, 45.7% and 36.6%, respectively. When the terminal chloride removal precipitate was calcinated at the temperature of 600 ℃, the upconversion luminescence intensity of the obtained sample is the highest under 980 nm laser excitation. The luminescence spectrum contained strong green and red light, wherein the green light region was at 523—553 nm and the red light region was at 655—670 nm. The analysis of the enhancement mechanism of upconversion luminescence showed that the matrix agents of Bi3O4Cl and Bi12O17Cl2 provided better doping environments for Er3+ and Yb3+ ions than those of Bi2O3 and BiOCl. Therefore, although Bi2O3 remains in the terminal chloride removal precipitate, it is able to react with BiOCl to form Bi3O4Cl and Bi12O17Cl2 under the high temperature calcination process, which not only facilitates the improvement of upconversion luminescence and spectral adjustment, but also provides a new method for the removal and high-value resource utilization of Cl− ions and organic pollutants in leachate.
-
Key words:
- landfill leachate /
- Bi2O3 /
- chloride ions /
- humic acid /
- upconversion phosphor.
-

-
图 1 (a) 渗滤液Cl−去除效率; (b) 渗滤液Cl−去除前后COD和TOC变化; (c) 渗滤液Cl−去除前的三维荧光图;(d) 渗滤液Cl−去除后的三维荧光图; (e) 渗滤液Cl−去除前后的光学照片; (f) 初始Bi2O3及其除氯产物的光学照片
Figure 1. (a) Cl− removal efficiency of leachate; (b) COD and TOC changes of leachate before and after Cl− removal; (c) Three-dimensional fluorescence spectrum of leachate before Cl− removal; (d) Three-dimensional fluorescence spectrum of leachate after Cl− removal; (e) Optical images of leachate before and after Cl− removal; (f) Optical images of initial Bi2O3 and its terminal chloride removal precipitate
图 2 (a) 除氯产物不同温度煅烧后在自然光和980 nm激光激发下的光照照片; (b) 除氯产物不同温度煅烧后在980 nm激光激发下的上转换发射光谱图
Figure 2. (a) Optical images of the chloride removal precipitates calcined at different temperatures under natural light and 980 nm laser excitation; (b) Upconversion emission spectra of the chloride removal precipitates calcined at different temperatures under 980 nm laser excitation
图 4 (a,b) 原始Bi2O3的SEM形貌; (c) 除氯产物的SEM形貌; 除氯产物经不同温度煅烧后的SEM形貌:(d) 300 ℃, (e) 400 ℃, (f) 500 ℃, (g) 600 ℃, (h) 800 ℃
Figure 4. (a,b) SEM image of pristine Bi2O3; (c) SEM image of the chloride removal precipitate; SEM images of the chloride removal precipitates after calcination at different temperatures: (d) 300 ℃, (e) 400 ℃, (f) 500 ℃, (g) 600 ℃, (h) 800 ℃
-
[1] 王辉. 城市生活垃圾处理设施落地现状与对策研究 [J]. 化工设计通讯, 2022, 48(2): 196-198,210. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6490.2022.02.067 WANG H. Study on the current situation and countermeasures of urban domestic waste treatment facilities [J]. Chemical Engineering Design Communications, 2022, 48(2): 196-198,210(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6490.2022.02.067
[2] TENG C Y, ZHOU K G, PENG C H, et al. Characterization and treatment of landfill leachate: A review [J]. Water Research, 2021, 203: 117525. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.117525 [3] WIJEKOON P, KOLIYABANDARA P A, COORAY A T, et al. Progress and prospects in mitigation of landfill leachate pollution: Risk, pollution potential, treatment and challenges [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 421: 126627. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126627 [4] LI Y M, YANG Z Z, YANG K H, et al. Removal of chloride from water and wastewater: Removal mechanisms and recent trends [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 821: 153174. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153174 [5] CAO K F, CHEN Z, WU Y H, et al. The noteworthy chloride ions in reclaimed water: Harmful effects, concentration levels and control strategies [J]. Water Research, 2022, 215: 118271. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2022.118271 [6] 张阳, 史丙丁, 马保中, 等. 酸性溶液除氯技术研究现状及进展 [J]. 有色金属科学与工程, 2021, 12(5): 10-17. ZHANG Y, SHI B D, MA B Z, et al. Research status and progress of chlorine removal technology in acid solution [J]. Nonferrous Metals Science and Engineering, 2021, 12(5): 10-17(in Chinese).
[7] SUN D Q, ZHOU Z, MING Q, et al. Improving settleability and dewaterability of Friedel's salt for chloride removal from saline wastewater [J]. Desalination, 2021, 509: 115070. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2021.115070 [8] ZHANG L J, LV P, HE Y, et al. Ultrasound-assisted cleaning chloride from wastewater using Friedel's salt precipitation [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 403: 123545. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123545 [9] PENG X J, DOU W Y, KONG L H, et al. Removal of chloride ions from strongly acidic wastewater using Cu(0)/Cu(Ⅱ): Efficiency enhancement by UV irradiation and the mechanism for chloride ions removal [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(1): 383-389. [10] DOU W Y, HU X Y, KONG L H, et al. UV-improved removal of chloride ions from strongly acidic wastewater using Bi2O3: Efficiency enhancement and mechanisms [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(17): 10371-10378. [11] 封志敏, 宁顺明, 王文娟, 等. 氧化铋法从硫酸锌溶液中除氯的研究 [J]. 矿冶工程, 2015, 35(4): 63-66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2015.04.017 FENG Z M, NING S M, WANG W J, et al. Dechlorination of zinc sulfate solution by bismuth oxide [J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2015, 35(4): 63-66(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2015.04.017
[12] HUANG S Q, LI L, ZHU N W, et al. Removal and recovery of chloride ions in concentrated leachate by Bi(Ⅲ) containing oxides quantum dots/two-dimensional flakes [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 382: 121041. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121041 [13] WU Y, CHEN Y W, HUANG S Q, et al. Comparison of bismuth ferrites for chloride removal: Removal efficiency, stability, and structure [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2022, 576: 151804. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.151804 [14] FAN Y Z, WANG T H, ZHANG Y Y, et al. Enhancing the near-infrared photocatalytic activity and upconversion luminescence of BiOCl: Yb3+–Er3+ nanosheets with polypyrrole in situ modification [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2021, 9(42): 15251-15262. doi: 10.1039/D1TC03451K [15] PENG Y H, PENG J C, HAN J J, et al. Intense single-band red upconversion emission in BiOCl: Er3+ layered semiconductor via co-doping Ho3+ [J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2020, 38(6): 577-583. doi: 10.1016/j.jre.2019.11.008 [16] WU W W, CHEN D Q, ZHOU Y, et al. Near-single-band red upconversion luminescence in Yb/Er: BiOX (X = Cl, Br) nanoplatelets [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 682: 275-283. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.04.305 [17] LI Y J, SONG Z G, LI C, et al. Efficient near-infrared to visible and ultraviolet upconversion in polycrystalline BiOCl: Er3+/Yb3+ synthesized at low temperature [J]. Ceramics International, 2013, 39(8): 8911-8916. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.04.085 [18] 宋志国, 王莎莎, 刘桐, 等. 一种稀土离子掺杂氯氧化铋半导体材料及其制备方法: CN109943336B[P]. 2021-09-28. SONG Z G, WANG S S, LIU T, et al. Rare earth ion-doped bismuth oxychloride semiconductor material and preparation method thereof: CN109943336B[P]. 2021-09-28(in Chinese).
[19] 陈凡丽, 李永进, 张相周, 等. Zn2+掺杂诱导Eu3+激活BiOCl层状半导体的反常发光性能研究 [J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(8): 877-883. doi: 10.15541/jim20160597 CHEN F L, LI Y J, ZHANG X Z, et al. Anomalous emission performance of Eu3+-activated BiOCl layered phosphors induced by doping Zn2+ [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(8): 877-883(in Chinese). doi: 10.15541/jim20160597
[20] LI G B, HUANG S Q, ZHU N W, et al. Defect-rich heterojunction photocatalyst originated from the removal of chloride ions and its degradation mechanism of norfloxacin [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 421: 127852. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.127852 [21] 吴飞飞, 马春阳, 焦金龙, 等. 纳米薄片状氯氧化铋的制备及其热解行为 [J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2016, 44(7): 948-952. WU F F, MA C Y, JIAO J L, et al. Preparation and thermal decomposition of nanoflakes bismuth oxychloride crystals [J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2016, 44(7): 948-952(in Chinese).
[22] LI J, YU Y, ZHANG L Z. Bismuth oxyhalide nanomaterials: Layered structures meet photocatalysis [J]. Nanoscale, 2014, 6(15): 8473-8488. doi: 10.1039/C4NR02553A [23] LI H, LI J, AI Z H, et al. Oxygen vacancy-mediated photocatalysis of BiOCl: Reactivity, selectivity, and perspectives [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(1): 122-138. doi: 10.1002/anie.201705628 [24] 张双, 周集体. 高盐有机化工废水中COD与TOC的相关性 [J]. 化工环保, 2018, 38(1): 122-126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2018.01.022 ZHANG S, ZHOU J T. Correlation between COD and TOC in high-salinity organic chemical industrial wastewater [J]. Environmental Protection of Chemical Industry, 2018, 38(1): 122-126(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2018.01.022
[25] CHEN W, WESTERHOFF P, LEENHEER J A, et al. Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2003, 37(24): 5701-5710. [26] 邓阳, 冯传平, 胡伟武, 等. 电化学氧化垃圾渗滤液生化出水过程中溶解性有机物形态及可生化性 [J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(7): 1647-1659. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017100902 DENG Y, FENG C P, HU W W, et al. DOM composition and biodegradability of biologically treated landfill leachate during electrochemical oxidation degradation [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(7): 1647-1659(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017100902
[27] 张正义, 张千, 楼紫阳, 等. 催化臭氧氧化处理渗滤液RO浓液的氧化特性及光谱分析 [J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(10): 5362-5371. doi: 10.11949/0438-1157.20210400 ZHANG Z Y, ZHANG Q, LOU Z Y, et al. Oxidation characteristics and spectral analysis of leachate reverse osmosis concentrate by catalytic ozonation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(10): 5362-5371(in Chinese). doi: 10.11949/0438-1157.20210400
[28] WEI S Q, SHANG X Y, HUANG P, et al. Polarized upconversion luminescence from a single LiLuF4: Yb3+/Er3+ microcrystal for orientation tracking [J]. Science China (Materials), 2022, 65(1): 220-228. doi: 10.1007/s40843-021-1713-x [29] ZHOU X, WANG H, XIA H P, et al. Efficient up-conversion Yb3+, Er3+ co-doped Na5Lu9F32 single crystal for photovoltaic application under solar cell spectrum excitation [J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2019, 17(9): 72-76. [30] WANG M J, HUANG S Q, LV Y Y, et al. Fabrication of monodispersed plasmonic photocatalysts on activated carbon with the carbon source and reduction property of sewage sludge [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 538: 148036. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.148036 [31] 吴岳, 黄寿强, 刘维桥. 废水除氯产物氯氧化铋的干法再生研究 [J]. 江苏理工学院学报, 2021, 27(2): 72-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8522.2021.02.011 WU Y, HUANG S Q, LIU W Q. Study on dry regeneration of bismuth oxychloride obtained from the removal of chloride ions contained in wastewater [J]. Journal of Jiangsu University of Technology, 2021, 27(2): 72-80(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8522.2021.02.011
[32] XU Y X, JIN X L, GE T, et al. Realizing efficient CO2 photoreduction in Bi3O4Cl: Constructing van der Waals heterostructure with g-C3N4 [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 409: 128178. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.128178 [33] XU B R, GAO Y Q, LI Y D, et al. Synthesis of Bi3O4Cl nanosheets with oxygen vacancies: The effect of defect states on photocatalytic performance [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 507: 144806. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144806 [34] FAN C, ZHANG Y H, HUANG S Q, et al. Effect of introducing zinc on the photoluminescence and stability of cesium lead halide perovskite materials [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2022, 584: 152527. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.152527 [35] KAHRAMAN A, KARACALI H, YILMAZ E. Impact and origin of the oxide-interface traps in Al/Yb2O3/n-Si/Al on the electrical characteristics [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 825: 154171. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154171 [36] 李永进, 黄杨彬, 刘群, 等. 近紫外激发具有颜色可调的Er3+/Eu3+共掺BiOCl荧光粉 [J]. 物理学报, 2015, 64(17): 357-362. LI Y J, HUANG Y B, LIU Q, et al. Color-tunableness of Er3+/Eu3+ co-doped BiOCl phosphors for near ultraviolet excitation [J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2015, 64(17): 357-362(in Chinese).
-



 下载:
下载: