-
人类社会快速发展的同时,生态环境遭到了破坏,阻碍全球的可持续发展. 其中,工业活动中产生的大量氮氧化物(NOx)等有害气体,不仅会引起酸雨、臭氧层空洞、光化学烟雾等环境问题[1–2],还会危害人类健康[3–5]. 与多数发达国家类似,中国的大气污染正从以二氧化硫(SO2)为主转向以NOx和臭氧(O3)为主[6]. 随着我国空气污染的大力治理,至2019年NOx排放量下降至1233.9万吨,其中工业源的排放量下降到548.1万吨[7],但是,其他非电行业(如:焦化、钢铁、玻璃、陶瓷、水泥、燃气锅炉、垃圾焚烧等)NOx排放量仍旧处于高位[8–10]. 因此,有效降低非电行业NOx排放是目前我国环境污染治理的重要目标之一.
通常非电行业采用氨选择性催化还原(NH3-SCR)技术进一步降低NOx的排放,在催化剂的作用下,以氨(NH3)作为还原剂,将烟气中 NOx 选择还原为氮气(N2). 目前,非电行业烟气排放温度普遍低于300 °C,特别是湿法脱硫工艺后烟气温度甚至更低;此外,烟气成分复杂,含有SO2、水、碱金属、重金属和飞灰等[9],上述杂质会对SCR催化剂产生毒化作用,削弱反应活性,最终导致催化剂性能下降[11]. 因此,开发高性能抗中毒的中低温催化剂对于净化烟气尤为重要.
催化消除NOx的材料主要包括贵金属、氧化物、分子筛和碳基催化剂等. 通常,贵金属催化剂多用于机动车尾气净化,贵金属催化剂大多数以金、铂、银、钯、铑等作为活性组分,氧化铝(Al2O3)、二氧化锆(ZrO2)、二氧化硅(SiO2)、二氧化铈(CeO2)、二氧化钛(TiO2)等为载体,两者协同作用后呈现出良好的低温脱硝活性[12–18]. 氧化物催化剂通常是锰基(MnOx)、铈基(CeO2)、钒基(VOx)、铜基(CuO)、铁基(FeOx)等复合催化剂[19 – 23],该类催化剂相比贵金属价格低廉,适用于工业化生产,表1归纳总结了不同工况下的NH3-SCR催化剂. 分子筛催化剂具有水热稳定性好、温度窗口宽、净化效率高、无毒无害等优点,广泛应用于柴油车尾气处理[24],主要有ZSM-5、SAPO-34、SSZ-13及BEA等种类[25–29]. 碳基催化剂是以碳作为载体的一类催化剂[30],该类催化剂比表面积大、官能团丰富,且廉价易得,可作为潜在的SCR催化剂载体. 针对中低温SCR催化剂在不同工况下可能的中毒机制,结合目前的研究进展和本课题的工作,总结了抗中毒与再生技术,为提升中低温SCR催化剂的性能和稳定性提供研究思路.
-
中低温NH3-SCR反应工况下通常含有硫、碱(土)金属、水、砷、铅和粉尘等杂质,容易造成催化剂中毒失活. 因此,本部分分别讨论了不同杂质对催化剂的毒化机制,以及抗中毒策略,为中低温NH3-SCR催化剂的设计研发提供指导.
-
工业中含硫矿物的燃烧是烟气SO2的主要来源,如:钢铁冶炼过程中焦化、烧结工序,玻璃熔制工序等[37–38]. 低温下SO2对SCR催化剂的毒化主要表现为在催化剂上生成含硫物质,研究表明形成的含硫物质主要包括硫酸氢氨(NH4HSO4,ABS)、金属硫酸盐等. 硫中毒过程主要如下:(1)SO2在催化剂作用下被氧化为三氧化硫(SO3),当烟气中存在H2O时,SO3与NH3生成的ABS黏度极高,易覆盖在催化活性位点上和堵塞孔道、降低催化性能和稳定性,引起催化剂中毒;(2)SO2与氧化物活性组分反应生成金属硫酸盐,破坏活性位点,降低催化剂的氧化能力[39–44].
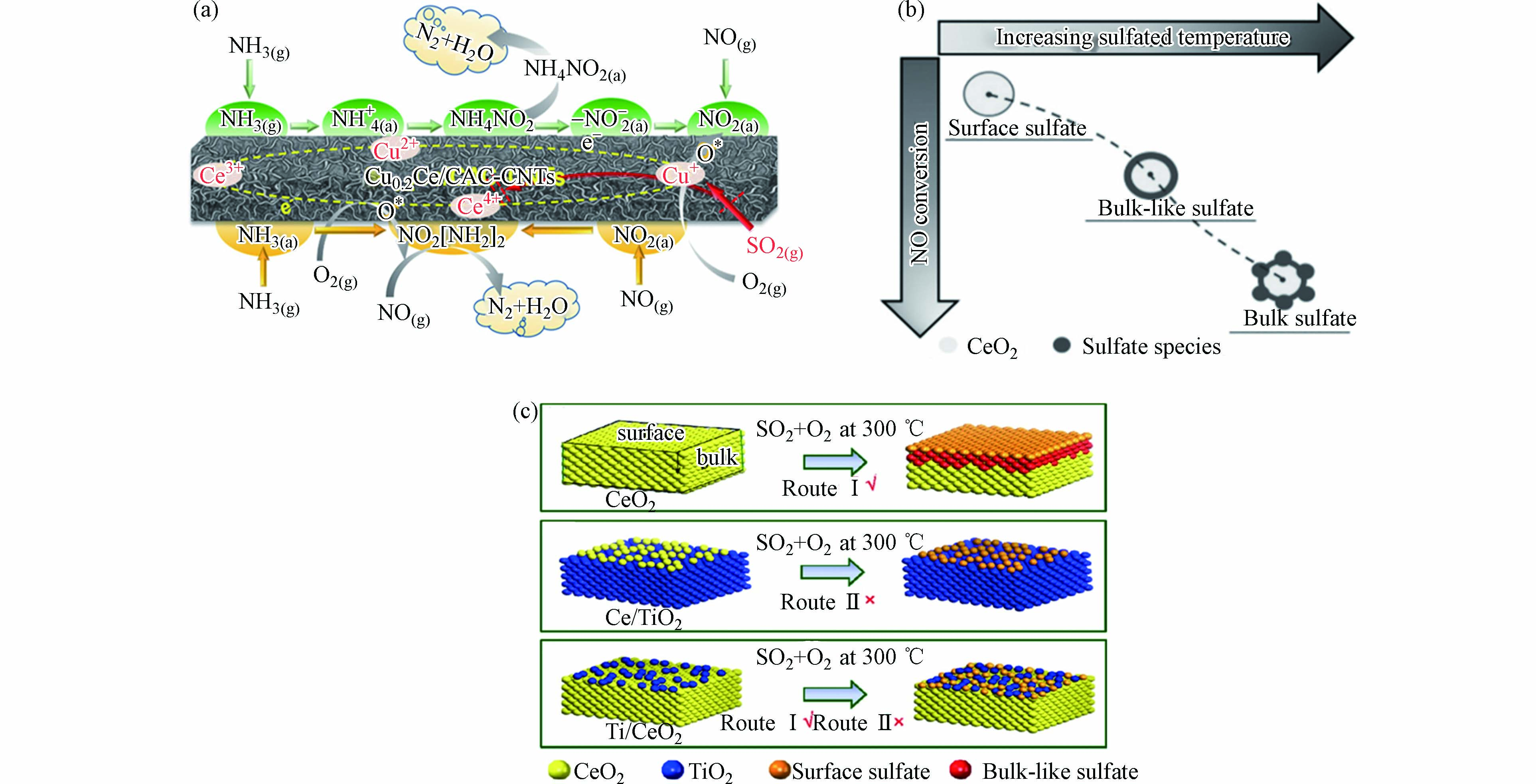
针对上述硫中毒机制,国内外研究者们开展了大量的研究工作以提升催化剂的抗硫中毒性能. 通过引入助剂或者改变催化剂形貌等方法,提升催化剂在中低温下的抗硫性能. Li等[45]将锰氧化物(MnOx)和氧化铁(Fe2O3)限域在二氧化钛纳米管(TNTs)中,合成出低温抗硫性能高的核壳结构催化剂. 热重结果表明Fe2O3壳层限制了硫酸锰的形成,从而提高了抗硫性能. 此外,利用900 ℃ 煅烧勃姆石得到的Al2O3(记为900cal Al)可以显著提高V2O5/WO3-TiO2催化剂(5VWTi)的抗硫性能[46]. 在220 ℃,0.003% SO2,10% H2O,GHSV = 10000 h−1条件下反应22 h后,NOx转化率相比于5VWTi提升了10%;其他条件不变,引入0.01% SO2时,NOx转化率更是提升了约22%. 抗硫性能提升的关键机制是Al2O3与V的密切接触促进ABS从V活性位点迁移至Al2O3位点,Al2O3位点捕获了硫酸盐使得钒活性位点上没有生成ABS,从而保护活性中心钒物种. Yang等[47]使用原位生长法制备活性炭与碳纳米管复合材料(CAC-CNT)载体,负载CuCe后得到CuxCe/CAC-CNT催化剂. 发现当Cu/Ce物质的量比为0.2时,其低温NH3-SCR性能最好. 这主要由于Cu的引入提高Cu0.2Ce/CAC-CNTs催化剂Lewis酸、晶格氧和Ce3+含量,图1a是Cu0.2Ce/CAC-CNTs表面NH3−SCR反应机制示意图,酸位点增加提高NH3吸附能力,促进Ce4+ + Cu+ ↔ Ce3+ + Cu2+的电对循环,Cu的引入抑制了催化剂对SO2的吸附和氧化,使催化剂具有优异抗硫性能.
本课题组在提高SCR催化剂抗硫性能方面也做了不少研究工作. 通过调控催化剂孔道尺寸,降低沉积的ABS的分解温度,提升抗硫中毒性能. 将一定量ABS分别沉积在不同孔径的SBA-15载体上,发现随着载体孔径增大,负载ABS的分解温度明显降低,主要归因于载体孔内ABS平衡蒸气压的差异,表明ABS热分解过程存在独特的催化剂孔径促进效应[48–49]. 此外,工况温度会影响生成的硫酸盐物种的状态,改变催化的性能[50]. 通过合适温度下SO2的预处理可以在CeO2催化剂中引入大量的酸性位,促进反应物氨的吸附、活化,提高NH3-SCR反应性能;但是,随着温度的升高,CeO2催化剂中产生的硫酸盐由表面转变为体相物种,阻碍了CeO2与表面硫酸盐的协同催化作用,导致反应活性下降(图1b). 同时,在CeO2/TiO2和TiO2/CeO2催化剂上观测到不同的抗硫性能,CeO2/TiO2催化剂容易硫中毒的原因是生成的硫酸盐吸附在活性位Ce-O-Ti上,而TiO2/CeO2催化剂利用TiO2的修饰抑制了CeO2中体相硫酸盐的形成,使得TiO2/CeO2催化剂的抗硫性能比CeO2/TiO2显著优异(图1c)[51].
因此,通过调变催化剂的电子和空间结构(如:组分、形貌、价态等),可以减少ABS在活性位点的沉积、降低其分解温度、或者抑制催化剂中体相硫酸盐的生成和深度硫酸化过程等,最终提升催化剂的抗硫中毒性能.
-
玻璃、钢铁、工业铝和水泥等行业烟气飞灰中含有大量碱(土)金属[31, 52–53],工况中的碱金属(钠、钾等)和碱土金属(钙等)会降低SCR催化剂的酸性、氧化还原性、织构性质(比表面积、孔隙率等),进而影响催化性能[54]. 但是,碱金属如何与SCR催化剂活性位点作用并使其中毒的机制还不是很明晰,因此不少研究者围绕碱金属中毒机制开展研究. Wang等[55]发现,Na+引入使得Cu/SAPO-34催化剂中Cu+形成CuAl2O4,减少孤立态Cu+数量,NH3吸附量减少,从而导致低温段催化剂活性降低. Liu等[56]通过密度泛函理论探究了K+对CeO2/TiO2催化剂吸附性能的影响规律,发现在最佳吸附位点K+的吸附热高达347.17 kJ·mol−1,因此K+很容易吸附在CeO2/TiO2催化剂表面,降低了NH3的吸附热,从而与Lewis酸性位点的Ce竞争吸附 NH3,削弱了NH3在Ce表面的吸附能力;同时NO和O2的吸附热增加,使得更多的NO和O2结合生成不参与反应的非活性NOx中间物,占据了活性位点,最终导致SCR催化剂失活. 此外,何德良等[57]提出了TiO2-V2O5-WO3催化剂上不同的钙中毒机理. 他们分别使用氯化钙(CaCl2)、硝酸钙(Ca(NO3)2)和硫酸钙(CaSO4)等3种钙盐溶液浸渍处理催化剂,并研究这3种溶液浸渍后的催化剂活性,证实CaCl2和Ca(NO3)2对催化剂的毒化作用主要表现为降低表面酸量,减弱反应物分子NH3与氢离子的结合,不利于NH3的吸附;而CaSO4中和表面酸性能力弱于CaCl2和Ca(NO3)2,其毒化催化剂主要来源于催化剂内部孔道堵塞.
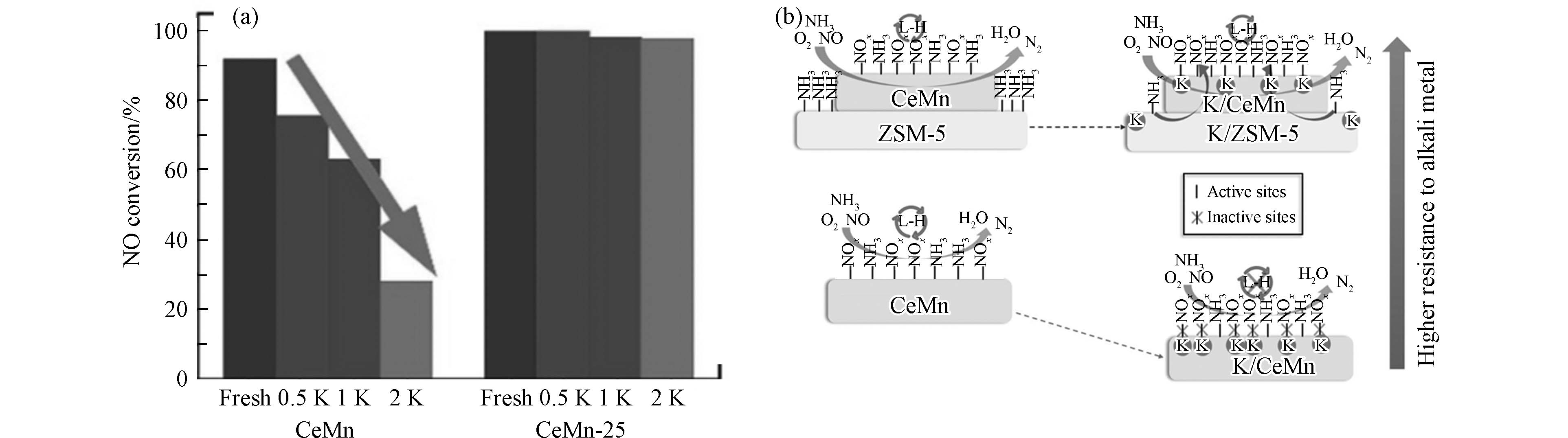
本课题组也围绕SCR催化剂的碱金属中毒机制开展了系列工作. 通过机械研磨法将铈锰氧化物与ZSM-5物理混合制备出新型的SCR催化剂CeMn-Z5,研究发现,该催化剂相比其他的抗K中毒的催化剂(CuNbTi、Cu-SAPO-34等)表现出更优异的抗K中毒能力[58]. 相比于CeMn催化剂,CeMn-Z5具有更宽的活性窗口(100—250 ℃)和对K更强的抗毒性(图2a). CeMn碱金属中毒的主要原因是不参与SCR反应的“惰性”硝酸盐抑制了SCR反应中L-H循环. 而在CeMn-Z5催化剂中,ZSM-5沸石捕获部分K+物种,并充当牺牲位点,缓解了CeMn中毒;同时ZSM-5引入的氨物种可以重新激活CeMn上形成的“惰性”硝酸盐,从而将NOx吸附位点由惰性转化为活性,使得CeMn-Z5催化剂具有优异的抗K中毒性能(图2b).
-
水蒸气引入到SCR反应中,催化剂的脱硝性能明显下降[59–60]. 这主要由于水的引入减少氧空位的数量,降低NO的吸附,关键亚硝基中间物种难以产生;此外,氧空位数量的减少会降低NH3的解离吸附性能[61] ,抑制低温SCR反应. 通常,水的抑制作用分为以下两种:一是可逆失活,主要来自于H2O与NH3、NO在催化剂表面Lewis酸性位点上的物理竞争吸附,当温度高于200 ℃时,催化剂活性恢复,水蒸气的毒化影响基本可以忽略,其抑制作用消失. 二是不可逆失活的化学吸附,水解离后在催化剂形成表面羟基,它在250 ℃以下时具有热稳定性,同时此类羟基类会促进硝基类中间物的产生,使得低温下催化剂中毒失活,即使切断水也难以恢复性能[61-63].
改变催化剂结构或引入组分可显著提升催化剂低温抗水性能. Zhu等[64]通过溶剂热法制备出均匀的分层花状结构锰钴二元氧化物催化剂(记为Mn-Co-F),抗水实验表明,Mn/Co物质的量比为1:1的花状锰钴催化剂(记为Mn-Co-F(1:1))在140 ℃、15% vol. H2O、GHSV = 76000 h−1条件下达到99% NOx转化率,表现出高抗水性能. 通过表征发现,Mn-Co-F(1:1)催化剂中具有最高的Mn4+/(Mn3+ + Mn4+)(60.3%)以及Co3+/(Co2+ + Co3+)(49.8%),Mn4+提供大量的表面活性氧物种,Co3+提高氧化还原性能和促进NH3化学吸附能力,加速NH3-SCR过程. 此外,均匀的分层花状结构具有高比表面积,为NH3和NO物种提供较短的扩散通道和更多的吸附位点,在Mn和Co氧化物间的协同作用下催化剂具有增强丰富的Lewis酸位点和优异的NO氧化能力,使催化剂优先吸附NH3而不是H2O,避免了催化剂低温通水失活. 此外,孔径大小与催化剂的低温抗水性能密切相关. 通过引入痕量SiO2于Mn-Ti氧化物上,可以增大Mn0.2Ti0.8SO2催化剂的孔径,削弱催化剂对水的毛细凝聚作用,提高催化剂的抗水性能[62]. 构建催化剂的孔内限域作用可以在通水条件下促进催化性能. 在SBA-15中限域薄层TiO2并负载Fe2O3(Fe/Ti@Si-3)不仅可以有效地抗水中毒,而且在水存在下催化性能有一定提升[63]. 构建的SBA-15空间限域的薄层TiO2(Ti@Si)具有较大的比表面积,以及其非晶态结构促进缺陷和相关氧物种的生成,相比于颗粒TiO2具有更多的Brønsted酸位点. 与常规Fe/TiO2催化剂相比,制备的催化剂的脱硝性能和抗H2O/SO2中毒能力均有较大提高.
-
除了常见的硫、碱金属和水中毒外,重金属(如:砷、铅)和粉尘[65]等也会使得SCR催化剂失活. 砷(As)对SCR催化剂的毒害作用主要有如下方面[66]:一是砷氧化物堵塞催化剂的孔道和覆盖其表面,阻碍反应物分子的吸附和扩散;二是砷与催化剂的活性组分反应,降低催化剂酸性位点和氧化还原能力,不利于NH3吸附/活化、NO氧化和快速SCR反应. Li等[67]探究了CeO2-WO3/TiO2 催化剂的砷中毒机理,发现在低温条件下,砷的引入使得配位NH3的数量远低于NH4+,NOx吸附能力减弱,导致硝酸盐和NO2减少,限制了快速SCR过程. Jiang等[68] 探究CeO2-WO3-Al2O3抗砷中毒机理,提出增强其抗砷性能关键在于恢复、补充Lewis酸位点以及提高Lewis酸位点的稳定性. 铝掺杂可以增强CeO2和WO3之间的相互作用,促进Ce—O—W键的形成,进而阻止催化剂上砷表面羟基(As—OH)形成,减少对表面活性氧的干扰,且恢复的Ce3+物种为SCR反应提供Lewis酸位和氧空位,促进催化剂活性提升. 铅(Pb)的引入同样破坏了催化剂的表面酸性和氧化还原性能,抑制了NH3的活化和NO氧化[69-70]. Ali等[71]研究Pb对V2O5-MoO3/TiO2催化剂的毒化作用,催化活性测试表明中毒催化剂在200—250 ℃下的NO转化率不到65%. 这主要由于Pb与V作用促进V5+还原为V4+/V3+,同时催化剂表面的Pb2+氧化为Pb4+,导致SCR活性下降. 此外,Pb会减少化学吸附氧物种,同时与催化剂反应生成的颗粒物覆盖酸位点和堵塞孔道,进一步导致催化剂失活. 高含量粉尘会导致SCR催化剂物理失活,比如,水泥生产过程中排放的烟气粉尘含量高,造成处理烟气的SCR催化剂塔运行阻力增加、堵塞孔道、冲刷活性组分,严重磨损催化剂,降低催化剂使用寿命,增加SCR系统成本[72].
硫、碱(土)金属、 水、砷、铅和粉尘等杂质对中低温NH3-SCR催化剂的毒化作用主要由于杂质堵塞催化剂的孔道和覆盖其表面,削弱了反应物分子的吸附、活化过程,同时杂质与催化剂发生化学反应,影响了酸碱、氧化还原性能、和快速SCR反应等过程,最终导致催化剂失活. 通过调变催化剂的电子和空间结构(如:组分、形貌、价态等),可以在一定程度上减少杂质对活性位点的毒化作用,抑制杂质与催化剂发生反应等,进而提高中低温NH3-SCR催化剂的抗中毒性能. 但是在实际工况下,常常两种或多种杂质共存,协同毒化作用会加快催化剂的失活,因此,协同中毒机制还需要进一步深入研究.
-
催化剂再生是指去除导致催化剂失活的有毒物质,恢复催化剂活性的方法,主要是去除催化剂的外表或孔隙内部的粉尘、沉积物、中间副产物等. 常见再生方法有水洗、热(还原)和酸碱处理等[73]. 再生技术的开发可以促进催化剂的重复使用,降低SCR脱硝系统的运行成本,因此受到研究者的关注.
-
水洗是较为简便的再生方法. 水洗技术可以去除中毒催化剂的亚硫酸盐和硫酸盐物种,再生催化剂性能. 比如:通过水洗再生活性焦炭负载Mn-Cu催化剂,恢复中毒催化剂的比表面积和总孔体积,去除中毒催化剂表面的亚硫酸盐和硫酸盐,进而使得活性重新恢复到新鲜催化剂水平[74];通过水洗去除硫中毒MnOx / PG(坡缕石)催化剂表面的硫酸铵盐和SO42−聚合体,恢复表面暴露的锰氧化物活性组分,催化剂吸附反应气体能力提升,性能恢复且不会造成活性组分的损失[75–76]. 此外,水洗技术也可以再生其他酸类中毒的脱硝催化剂. 采用热水洗涤法对磷中毒的Cu-SSZ-13催化剂进行再生,发现磷中毒的Cu-SSZ-13催化剂经热水洗涤后,催化剂表面部分磷物种溶解于溶剂,五氧化二磷(P2O5)、偏磷酸盐(PO3−)和磷酸盐(PO43−)含量减少;在水分子的作用下,缩合和长链的磷物种分裂为短链磷物种. 在去除沸石颗粒上堵塞孔道的磷物种聚合物后,催化剂表面积和微孔体积也恢复到原有水平. 同时热水洗涤后,Brønsted酸位点(Al-OH-Si基团)和部分Lewis酸位点(Cu2+)得到恢复. 且磷负载量越低,洗涤时间越长,低温活性恢复越好[77]. 经过多次中毒-再生循环后,催化剂的中低温段活性完全恢复,甚至相比新鲜催化剂略微提高,表明了该方法具有一定的重复性.
-
热处理再生技术主要在惰性气体气氛下,将失活催化剂进行焙烧,恢复催化活性位点,从而再生催化剂的方法,因铵盐受热易分解,该法适用于铵盐中毒的催化剂再生. 热还原处理是在热再生的基础上,在惰性气体中通入还原性气体(NH3、H2等)将硫化铵物种还原为SO2或 H2S,实现催化剂的再生. 再生效果取决于热处理是否能消除催化剂表面沉积的NH4HSO4和金属硫酸盐.
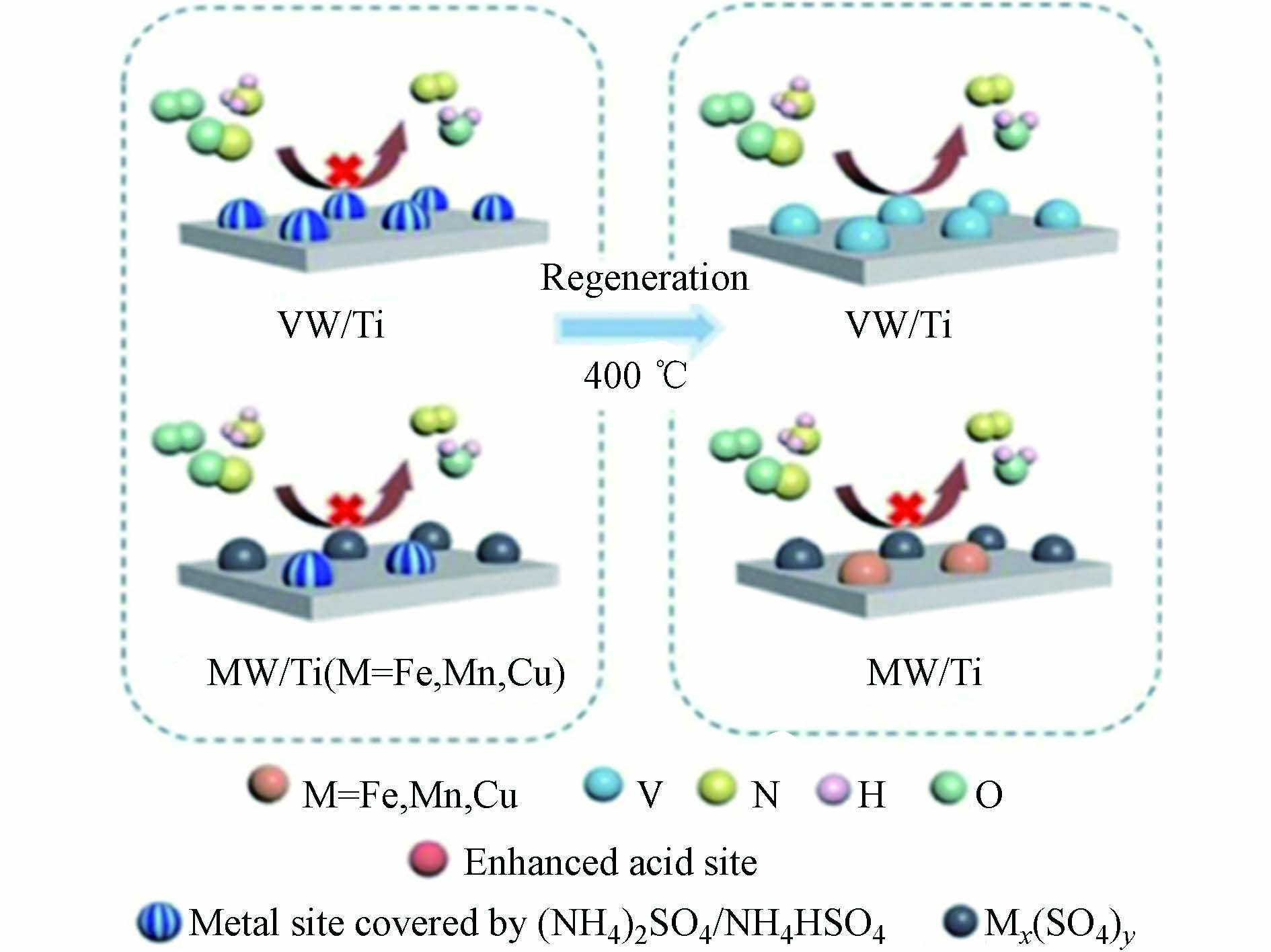
研究发现低温下H2O引起的Cu-SAPO-34的失活是部分可逆的,通过热再生使得Cu(OH)2与Brønsted酸位点相互作用转化为活性Cu(Ⅱ)离子[78]. 热再生技术可以使得部分硫中毒的催化剂恢复性能[79]. 通过浸渍法制备了5%wt. Fe2O3–WO3/TiO2(FeW/Ti)、5%wt. MnO2–WO3/TiO2(MnW/Ti)、5%wt. CuO–WO3/TiO2(CuW/Ti)和1%wt. V2O5–WO3/TiO2(VW/Ti)催化剂,将硫中毒催化剂放入N2气氛下,400 ℃下加热30 min后,只有VW/Ti催化剂恢复了活性(图3). 这主要由于硫中毒的VW/Ti催化剂表面只生成了NH4HSO4,而NH4HSO4在280 ℃开始分解[80],这就解释了失活VW/Ti催化剂的最佳的热再生条件. 然而MW/Ti(M = Fe, Mn, Cu)催化剂表面除了NH4HSO4,还有硫酸盐Mx(SO4)y物种,而硫酸盐在400 ℃无法被消除,覆盖在金属位上严重影响了催化剂的氧化还原性能. 因此,硫中毒催化剂热再生的可能性还取决于金属硫酸盐的热稳定性.
-
酸洗通常用于处理碱金属中毒的催化剂. Wang等[81]利用不同类型和强度的酸再生被氧化钾毒化的催化剂(K-CuNbTi),发现硫酸、草酸和钨硅酸再生效率较高. 与水处理相比,酸再生催化剂可以去除K-CuNbTi表面的大部分沉积的钾,促进了催化剂上-NH2活性物种的形成,具有较好的催化活性. 因此,草酸和钨硅酸可作为酸再生碱中毒SCR催化剂的潜在材料. 此外,酸、碱溶液均可处理砷中毒的工业V2O5-WO3/TiO2催化剂. 利用超声方法清洗砷中毒后的V2O5-WO3/TiO2催化剂,通过氯化铁溶液和重金属捕获剂,可分别去除催化剂表面83.67%和94.57%的砷[82]. 经上述两种溶液超声清洗再生的催化剂,在400 ℃下,氮氧化物的转化率从69.83%分别恢复至90.57%和96.5%,两种溶液洗涤后的催化剂活性组分损失小. 其再生原因主要由于氯化铁和重金属捕获剂可以增大催化剂比表面积和孔体积,显著增强表面Lewis和Brønsted酸位点,氧化还原性能等,进而恢复了SCR性能.
-
有研究表明直接退火方法可以再生ABS中毒的SCR催化剂[83]. 另外,一些表面活性剂也可以有效地再生碱金属中毒催化剂. 采用环境友好的表面活性剂烷基酚聚氧乙烯醚(OP-10)对钙中毒的V2O5-WO3/TiO2催化剂再生,发现相比传统的稀硫酸溶液法,OP-10具有较高的Ca2+去除率和较低的活性组分V2O5的损耗,改善了催化剂表面的酸位点和活性氧物种[84]. 虽然酸碱联合可以处理砷中毒的催化剂,但是再生产品中仍然残留一定量的砷,超过再生行业标准. 最近发现生物浸出法可以深度脱除中毒催化剂中的砷. Niu等[85]首次利用嗜酸性氧化硫硫杆菌制备出高活性的生物浸出液,通过浸出液再生催化剂,其内部砷沉积物被去除,孔体积增加. 此外,氧化硫硫杆菌可以促进大量活性物质半胱氨酸的形成,半胱氨酸巯基(—S—H)中带负电的—S−攻击O—As键中的带正电的As3+和As5+,释放出更多的As3+和As5+. 此生物浸出法促进了As的释放和再生产物的活化,相比与传统酸碱法更加绿色环保和高效. 总之,再生技术不仅要考虑催化剂性能的恢复,而且还需要注意酸、碱、表面活性剂、热(还原)处 理过程中所带的环境、运行成本、安全等问题.
-
中低温NH3-SCR是目前非电行业烟气脱硝的主流技术,由于工况成分复杂,该技术面临催化剂易中毒的问题. 本文重点总结了非电行业工况中硫、碱(土)金属、水、砷、铅和粉尘等杂质对NH3-SCR催化剂的毒化机制,和抗中毒SCR催化剂的设计策略,以期在一定程度上减少杂质对活性位点的毒化作用,抑制杂质与催化剂发生反应等,进而提高抗中毒性能. 此外,对于失活的脱硝催化剂,介绍了已有的再生技术. 但是,催化活性、抗硫耐水、抗碱(土)金属中毒仍是目前需要解决的难题. 未来仍然需发展出更简单的催化剂合成技术以及适应多种工况的高性能中低温催化剂,推进非电行业气态污染物控制的可持续发展.
中低温NH3-SCR催化剂抗中毒与再生研究进展
Research progress on anti-poisoning and regeneration of catalysts at medium-low temperature NH3-SCR
-
摘要: 中低温氨选择性催化还原(NH3-SCR)氮氧化物(NOx)催化剂广泛应用于钢铁、焦化、陶瓷、玻璃、水泥、垃圾焚烧、燃气锅炉等非电行业. 不同工况下,硫、酸、碱金属、飞灰等会导致SCR催化剂中毒. 因此,如何制备抗中毒性能好的脱硝催化剂,并且有效再生失活SCR催化剂一直是研究热点. 本综述针对不同中低温SCR的工况,对比总结脱硝催化剂的应用、抗中毒机制与再生方法,最后对中低温SCR脱硝催化技术进行展望.
-
关键词:
- 中低温氨选择性催化还原 /
- 脱硝 /
- 催化剂 /
- 抗中毒 /
- 再生.
Abstract: The selective catalytic reduction (SCR) technology of NOx with NH3 at medium-low temperature are widely used in steel, coking, ceramics, glass, cement, waste incineration, gas boilers and other non-electric industries. Different working conditions, e.g., sulfur, acid, alkali metals, fly ash, etc. lead to the poisoning of SCR catalysts. Therefore, SCR catalysts with the excellent anti-poisoning ability and regeneration performance are big challenges and attract more attention. This review compares and summarizes the antipoisoning mechanisms and regeneration methods under various industrial SCR conditions of medium-low temperature. Finally, the prospect of SCR technology at medium-low temperature is discussed.-
Key words:
- medium-low temperature NH3-SCR /
- deNOx /
- catalyst /
- antipoisoning mechanisms /
- regeneration.
-

-
图 1 (a)Cu0.2Ce/CAC-CNTs表面NH3−SCR反应机制示意图[47];(b)氧化铈上硫酸盐存在状态与NO转化的示意图[50];(c)SO2分别在CeO2、CeO2/TiO2和TiO2/CeO2上的反应机制[51]
Figure 1. (a) Schematic diagram of NH3−SCR of Cu0.2Ce/CAC-CNTs[47]; (b) Schematic diagram of relationships between the sulfate species and NO conversion on the sulfated CeO2[50]; (c) Reaction routes of SO2 proposed on CeO2, CeO2/TiO2 and TiO2/CeO2[51]
图 2 (a)在100 ℃下,CeMn和CeMn-Z5催化剂的NO转化率与K2O负载量的关系. 反应条件:0.05% NO,0.05% NH3,5% O2,5% H2O,用Ar作为平衡气体,WHSV = 60000 mL·h−1·g−1;(b)CeMn/ZSM-5催化剂抗K中毒机理示意图[58]
Figure 2. (a) NO conversion versus loading K2O amounts at 100 ℃ over CeMn and CeMn-Z5. Reaction conditions: 0.05% NO, 0.05% NH3, 5% O2, 5% H2O, and balanced with Ar, WHSV = 60000 mL·h−1·g−1; (b) Schematic illustration of the anti-K poisoning mechanism over CeMn catalyst coupled with ZSM-5[58]
表 1 不同工况下的NH3-SCR催化剂
Table 1. NH3-SCR catalysts applied in different industrial conditions
行业
Industry工况
Working condition催化剂种类
Catalyst type钢铁 80—200 ℃,NOx:200—310 mg·m−3,SO2:400—1500 mg·m−3,粉尘约100 mg·m−3,含二氧化碳、氟化氢和二噁英等[10] V2O5/TiO2 焦化 180—300 ℃,NOx:100—1200 mg·m−3,SO2:30—190 mg·m−3,粉尘:5—100 mg·m−3,含一氧化碳、二氧化碳、硫化氢和苯并芘等[10] V2O5/TiO2 陶瓷 80—150 ℃,NOx:200—1100 mg·m−3,SO2:500—5000 mg·m−3,含氟化物、氯化物、重金属等[10] V2O5/TiO2 玻璃 180—220 ℃,NOx:1200—3000 mg·m−3,SO2:300—3300 mg·m−3,粉尘:200—280 mg·m−3,含氯化氢、氟化氢、碱性氧化物、少量重金属[10, 31] V2O5/TiO2 [32] 水泥 120—180 ℃,NOx:800—1200 mg·m−3,SO2:50—200 mg·m−3,颗粒物30000—80000 mg·m−3,含二氧化碳、氢氟酸[10] Ce掺杂的TiO2-V2O5-WO3[33] 垃圾焚烧 含有氯化氢、硫氧化物、NOx(主要为燃料型NOx)、粉尘、二噁英和重金属等污染物,含水率20%以上[34] V2O5-WO3/TiO2或V2O5-WO3/TiO2
为配方的蜂窝催化剂[34]燃气锅炉 120—160 ℃,NOx:1000—1200 mg·m−3,含CO2、H2O [35] Cu/Al2O3[35],Mn-V-Ce/TiO2(烟气中SO2含量极少时)[36] -
[1] SILAS K, WAN AZLINA WAN AB KARIM GHANI, CHOONG T S Y, et al. Carbonaceous materials modified catalysts for simultaneous SO2/NOx removal from flue gas: A review [J]. Catalysis Reviews, 2019, 61(1): 134-161. doi: 10.1080/01614940.2018.1482641 [2] ROLLINS A W, BROWNE E C, MIN K E, et al. Evidence for NOx control over nighttime SOA formation [J]. Science, 2012, 337(6099): 1210-1212. doi: 10.1126/science.1221520 [3] KAMPA M, CASTANAS E. Human health effects of air pollution [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2008, 151(2): 362-367. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2007.06.012 [4] LELIEVELD J, EVANS J S, FNAIS M, et al. The contribution of outdoor air pollution sources to premature mortality on a global scale [J]. Nature, 2015, 525(7569): 367-371. doi: 10.1038/nature15371 [5] MOSTAFAVI N, VLAANDEREN J, CHADEAU-HYAM M, et al. Inflammatory markers in relation to long-term air pollution [J]. Environment International, 2015, 81: 1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2015.04.003 [6] ZENG Y Y, CAO Y F, QIAO X, et al. Air pollution reduction in China: Recent success but great challenge for the future [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 663: 329-337. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.262 [7] 中华人民共和国生态环境部. 2016-2019年全国生态环境统计公报[R]. 2020. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China. National Ecological and Environmental Statistics Bulletin: 2016-2019 [R]. 2020 (in Chinese).
[8] 汤铃, 贾敏, 伯鑫, 等. 中国钢铁行业排放清单及大气环境影响研究 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(4): 1493-1506. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.04.014 TANG L, JIA M, BO X, et al. High resolution emission inventory and atmospheric environmental impact research in Chinese iron and steel industry [J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(4): 1493-1506(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.04.014
[9] 张道军, 马子然, 王宝冬, 等. SCR脱硝技术在非电行业烟气治理中的应用进展 [J]. 现代化工, 2019, 39(10): 24-28. ZHANG D J, MA Z R, WANG B D, et al. Progress in application of SCR denitrification technology in treating flue gas of non-electric industries [J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2019, 39(10): 24-28(in Chinese).
[10] 王修文, 李露露, 孙敬方, 等. 我国氮氧化物排放控制及脱硝催化剂研究进展 [J]. 工业催化, 2019, 27(2): 1-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1143.2019.02.001 WANG X W, LI L L, SUN J F, et al. Analysis of NOx emission and control in China and research progress in denitration catalysts [J]. Industrial Catalysis, 2019, 27(2): 1-23(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1143.2019.02.001
[11] 汤常金, 孙敬方, 董林. 超低温(<150℃)SCR脱硝技术研究进展 [J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(11): 4873-4884,5362. TANG C J, SUN J F, DONG L. Recent progress on elimination of NOx from flue gas via SCR technology under ultra-low temperatures(<150℃) [J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(11): 4873-4884,5362(in Chinese).
[12] 周涛, 刘少光, 唐名早, 等. 选择性催化还原脱硝催化剂研究进展 [J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2009, 37(2): 317-324. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0454-5648.2009.02.029 ZHOU T, LIU S G, TANG M Z, et al. Research progress on selective catalytic reduction de-NOx catalysts [J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2009, 37(2): 317-324(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0454-5648.2009.02.029
[13] CHAIEB T, DELANNOY L, CASALE S, et al. Evidence for an H2 promoting effect in the selective catalytic reduction of NOx by propene on Au/Al2O3 [J]. Chemical Communications (Cambridge, England), 2015, 51(4): 796-799. doi: 10.1039/C4CC07349E [14] NGUYEN L Q, SALIM C, HINODE H. Roles of nano-sized Au in the reduction of NOx by propene over Au/TiO2: An in situ DRIFTS study [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2010, 96(3/4): 299-306. [15] MORE P M, NGUYEN D L, GRANGER P, et al. Activation by pretreatment of Ag-Au/Al2O3 bimetallic catalyst to improve low temperature HC-SCR of NOx for lean burn engine exhaust [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2015, 174/175: 145-156. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.02.035 [16] KANG M, KIM D J, PARK E D, et al. Two-stage catalyst system for selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3 at low temperatures [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2006, 68(1/2): 21-27. [17] LAN T W, ZHAO Y F, DENG J, et al. Selective catalytic oxidation of NH3 over noble metal-based catalysts: State of the art and future prospects [J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2020, 10(17): 5792-5810. [18] CAMPA M C, DOYLE A M, FIERRO G, et al. Simultaneous abatement of NO and N2O with CH4 over modified Al2O3 supported Pt, Pd, Rh [J]. Catalysis Today, 2022, 384/385/386: 76-87. [19] LI J H, CHANG H Z, MA L, et al. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over metal oxide and zeolite catalysts—A review [J]. Catalysis Today, 2011, 175(1): 147-156. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2011.03.034 [20] SHAN Y, LIU Y X, LI Y, et al. A review on application of cerium-based oxides in gaseous pollutant purification [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 250: 117181. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117181 [21] JABŁOŃSKA M, PALKOVITS R. Copper based catalysts for the selective ammonia oxidation into nitrogen and water vapour—Recent trends and open challenges [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2016, 181: 332-351. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.07.017 [22] HUSNAIN N, WANG E L, LI K, et al. Iron oxide-based catalysts for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 [J]. Reviews in Chemical Engineering, 2019, 35(2): 239-264. doi: 10.1515/revce-2017-0064 [23] XU J Q, CHEN G R, GUO F, et al. Development of wide-temperature vanadium-based catalysts for selective catalytic reducing of NOx with ammonia: Review [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 353: 507-518. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.05.047 [24] TIAN H Y, PING Y, ZHANG Y B, et al. Atomic layer deposition of silica to improve the high-temperature hydrothermal stability of Cu-SSZ-13 for NH3 SCR of NOx [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 416: 126194. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126194 [25] MOHAN S, DINESHA P, KUMAR S. NOx reduction behaviour in copper zeolite catalysts for ammonia SCR systems: A review [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 384: 123253. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123253 [26] SJÖVALL H, BLINT R J, OLSSON L. Detailed kinetic modeling of NH3 SCR over Cu-ZSM-5 [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2009, 92(1/2): 138-153. [27] NIU C, SHI X Y, LIU F D, et al. High hydrothermal stability of Cu-SAPO-34 catalysts for the NH3-SCR of NOx [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 294: 254-263. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.02.086 [28] GAO F, WASHTON N M, WANG Y L, et al. Effects of Si/Al ratio on Cu/SSZ-13 NH3-SCR catalysts: Implications for the active Cu species and the roles of Brønsted acidity [J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2015, 331: 25-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2015.08.004 [29] MIHAI O, WIDYASTUTI C R, ANDONOVA S, et al. The effect of Cu-loading on different reactions involved in NH3-SCR over Cu-BEA catalysts [J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2014, 311: 170-181. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2013.11.016 [30] 王艳莉, 何自国, 李晓晓, 等. 碳基催化剂上低温NH3选择性催化还原NO的研究进展 [J]. 化学工业与工程, 2015, 32(3): 46-52. WANG Y L, HE Z G, LI X X, et al. Research progress on carbon supported catalysts for low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 [J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering, 2015, 32(3): 46-52(in Chinese).
[31] 苏云, 邵萍, 眭国荣, 等. 玻璃熔窑烟气脱硝技术探讨 [J]. 环境工程, 2012, 30(4): 73-75,52. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.2012.04.004 SU Y, SHAO P, SUI G R, et al. Study on technologies of flue gas denitration in glass furnaces [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2012, 30(4): 73-75,52(in Chinese). doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.2012.04.004
[32] 唐志雄, 岑超平, 陈雄波, 等. 平板玻璃工业窑炉烟气中低温SCR脱硝中试研究 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2015, 9(2): 817-822. TANG Z X, CEN C P, CHEN X B, et al. Pilot-scale study on SCR technology applied in flue gas deNOx of flat glass furnaces at low & middle temperatures [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2015, 9(2): 817-822(in Chinese).
[33] 刘海兵, 顾军, 李威, 等. Ce掺杂TiO2-V2O5-WO3催化剂在水泥窑脱硝中的应用 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2019, 41(6): 668-671. LIU H B, GU J, LI W, et al. Denitration application of Ce additive TiO2-V2O5-WO3 catalyst in cement kiln [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2019, 41(6): 668-671(in Chinese).
[34] 能士峰, 刘庆岭, 张旺, 等. 垃圾焚烧SCR脱硝催化剂的研究进展 [J]. 现代化工, 2022, 42(2): 31-34. NAI S F, LIU Q L, ZHANG W, et al. Research progress on application of SCR denitrification catalyst in waste incineration [J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2022, 42(2): 31-34(in Chinese).
[35] WU Y J, LUO C H, WU W, et al. Denitration of the gas-fired boiler flue gas based on chemical-looping combustion [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 361: 41-49. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.12.013 [36] 郑足红, 童华, 童志权, 等. Mn-V-Ce/TiO2低温催化还原NO性能研究 [J]. 燃料化学学报, 2010, 38(3): 343-351. ZHENG Z H, TONG H, TONG Z Q, et al. Catalytic reduction of NO over Mn-V-Ce/TiO2 catalysts at low reaction temperature [J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2010, 38(3): 343-351(in Chinese).
[37] SUN W Q, ZHOU Y, LV J X, et al. Assessment of multi-air emissions: Case of particulate matter (dust), SO2, NOx and CO2 from iron and steel industry of China [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 232: 350-358. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.05.400 [38] 钟悦之, 宋晓晖, 王彦超, 等. 中国平板玻璃行业大气污染物排放特征研究 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2018, 38(12): 4451-4459. doi: 10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000-6923.2018.0499 ZHONG Y Z, SONG X H, WANG Y C, et al. Emission characteristics from flat-glass industry in China [J]. China Environmental Science, 2018, 38(12): 4451-4459(in Chinese). doi: 10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000-6923.2018.0499
[39] CHEN Y X, LI C, CHEN J X, et al. Self-prevention of well-defined-facet Fe2O3/MoO3 against deposition of ammonium bisulfate in low-temperature NH3-SCR [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(20): 11796-11802. [40] ZHANG L, WANG D, LIU Y, et al. SO2 poisoning impact on the NH3-SCR reaction over a commercial Cu-SAPO-34 SCR catalyst [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2014, 156/157: 371-377. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.03.030 [41] WANG H J, HUANG B C, YU C L, et al. Research progress, challenges and perspectives on the sulfur and water resistance of catalysts for low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3 [J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2019, 588: 117207. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2019.117207 [42] XU G Y, GUO X L, CHENG X X, et al. A review of Mn-based catalysts for low-temperature NH3-SCR: NOx removal and H2O/SO2 resistance [J]. Nanoscale, 2021, 13(15): 7052-7080. doi: 10.1039/D1NR00248A [43] GAO C, SHI J W, FAN Z Y, et al. Sulfur and water resistance of Mn-based catalysts for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx: A review [J]. Catalysts, 2018, 8(1): 11. doi: 10.3390/catal8010011 [44] HAN L P, CAI S X, GAO M, et al. Selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 by using novel catalysts: State of the art and future prospects [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2019, 119(19): 10916-10976. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00202 [45] LI Y F, HOU Y Q, ZHANG Y Z, et al. Confinement of MnOx@Fe2O3 core-shell catalyst with titania nanotubes: Enhanced N2 selectivity and SO2 tolerance in NH3- SCR process [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2022, 608: 2224-2234. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2021.10.078 [46] JEON S W, SONG I, LEE H, et al. Enhanced SO2 resistance of V2O5/WO3−TiO2 catalyst physically mixed with alumina for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 433: 133836. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.133836 [47] YANG L, WANG P C, YAO L, et al. Copper doping promotion on Ce/CAC-CNT catalysts with high sulfur dioxide tolerance for low-temperature NH3–SCR [J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2021, 9(2): 987-997. [48] GUO K, JI J W, SONG W, et al. Conquering ammonium bisulfate poison over low-temperature NH3-SCR catalysts: A critical review [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2021, 297: 120388. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.120388 [49] GUO K, FAN G F, GU D, et al. Pore size expansion accelerates ammonium bisulfate decomposition for improved sulfur resistance in low-temperature NH3-SCR [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(5): 4900-4907. [50] ZHANG L, ZOU W X, MA K L, et al. Sulfated temperature effects on the catalytic activity of CeO2 in NH3-selective catalytic reduction conditions [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2015, 119(2): 1155-1163. doi: 10.1021/jp511282c [51] ZHANG L, LI L L, CAO Y, et al. Getting insight into the influence of SO2 on TiO2/CeO2 for the selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3 [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2015, 165: 589-598. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.10.029 [52] LI S C, HUANG W J, XU H M, et al. Alkali-induced deactivation mechanism of V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst during selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3 in aluminum hydrate calcining flue gas [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2020, 270: 118872. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.118872 [53] 杜勇乐, 刘鹤欣, 谭厚章, 等. 燃煤水泥窑尾颗粒物粒径分布及污染特征 [J]. 环境工程, 2019, 37(9): 113-118,148. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201909021 DU Y L, LIU H X, TAN H Z, et al. Characteristics of distribution and emission for fine particulates from a cement kiln tail [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2019, 37(9): 113-118,148(in Chinese). doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201909021
[54] CHEN L, LI J H, GE M F. The poisoning effect of alkali metals doping over nano V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalysts on selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3 [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011, 170(2/3): 531-537. [55] WANG C, WANG C, WANG J, et al. Effects of Na+ on Cu/SAPO-34 for ammonia selective catalytic reduction [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2018, 70: 20-28. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2017.11.002 [56] LIU T Y, JIANG Y, YANG Z D, et al. Insight into the influence of K on the adsorption performance and reaction pathways of CeO2/TiO2 catalyst [J]. Fuel, 2022, 312: 122813. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.122813 [57] 何德良, 任慧莺, 朱天时, 等. V2O5-WO3/TiO2 SCR催化剂的钙中毒机理研究 [J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报, 2018, 26(1): 1-11. HE D L, REN H Y, ZHU T S, et al. Study on the calcium-poisoning mechanism of the V2O5-WO3/TiO2 SCR catalyst [J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 2018, 26(1): 1-11(in Chinese).
[58] JI J W, TANG Y, HAN L, et al. Cerium manganese oxides coupled with ZSM-5: A novel SCR catalyst with superior K resistance [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 445: 136530. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.136530 [59] KIJLSTRA W S, BRANDS D S, POELS E K, et al. Mechanism of the selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3 over MnOx/Al2O3. 1. Adsorption and desorption of the single reaction components [J]. Journal of Catalysis, 1997, 171(1): 208-218. doi: 10.1006/jcat.1997.1788 [60] KIJLSTRA W S, BRANDS D S, POELS E K, et al. Mechanism of the selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3 over MnOx/Al2O3. 2. Reactivity of adsorbed NH3 and NO complexes [J]. Journal of Catalysis, 1997, 171(1): 219-230. doi: 10.1006/jcat.1997.1789 [61] 李云涛, 钟秦. 低温NH3-SCR反应机理及动力学研究进展 [J]. 化学进展, 2009, 21(6): 1094-1100. LI Y T, ZHONG Q. Recent advances in mechanisms and kinetics of low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 [J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2009, 21(6): 1094-1100(in Chinese).
[62] YU S H, JIANG N X, ZOU W X, et al. A general and inherent strategy to improve the water tolerance of low temperature NH3-SCR catalysts via trace SiO2 deposition [J]. Catalysis Communications, 2016, 84: 75-79. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2016.06.001 [63] GUO K, JI J W, OSUGA R, et al. Construction of Fe2O3 loaded and mesopore confined thin-layer titania catalyst for efficient NH3-SCR of NOx with enhanced H2O/SO2 tolerance [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2021, 287: 119982. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.119982 [64] ZHU Y J, XIAO X X, WANG J T, et al. Enhanced activity and water resistance of hierarchical flower-like Mn-Co binary oxides for ammonia-SCR reaction at low temperature [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 569: 150989. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.150989 [65] 房晶瑞, 马忠诚, 汪澜. 水泥窑炉烟气催化还原脱硝技术研究进展 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2013, 35(2): 85-92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2013.02.018 FANG J R, MA Z C, WANG L. Research progress on catalytic reduction technique for denitration of cement flue gas [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2013, 35(2): 85-92(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2013.02.018
[66] 陆强, 裴鑫琦, 徐明新, 等. SCR脱硝催化剂抗砷中毒改性优化与再生研究进展 [J]. 化工进展, 2021, 40(5): 2365-2374. doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2020-1072 LU Q, PEI X Q, XU M X, et al. Progress in the development and regeneration of SCR catalysts for anti-arsenic poisoning [J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2021, 40(5): 2365-2374(in Chinese). doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2020-1072
[67] LI X, LI J H, PENG Y, et al. Mechanism of arsenic poisoning on SCR catalyst of CeW/Ti and its novel efficient regeneration method with hydrogen [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2016, 184: 246-257. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.11.042 [68] JIANG S, LI T, ZHENG J K, et al. Unveiling the remarkable arsenic resistance origin of alumina promoted cerium-tungsten catalysts for NH3-SCR [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(22): 14740-14749. [69] JIANG Y, GAO X, ZHANG Y X, et al. Effects of PbCl2 on selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over vanadia-based catalysts [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 274: 270-278. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.04.026 [70] JIANG Y, LIANG G T, BAO C Z, et al. The poisoning effect of PbO and PbCl2 on CeO2-TiO2 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2018, 528: 82-91. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2018.05.061 [71] ALI Z, WU Y W, WU Y, et al. Inhibition effects of Pb species on the V2O5-MoO3/TiO2 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3: A DFT supported experimental study [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 525: 146582. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.146582 [72] CAI J, WU H X, REN Q Q, et al. Innovative NOx reduction from cement kiln and pilot-scale experimental verification [J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2020, 199: 106306. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2019.106306 [73] 刘兴誉, 贾媛媛, 唐中华, 等. 废旧SCR脱硝催化剂再生研究进展 [J]. 应用化工, 2020, 49(7): 1839-1844. doi: 10.16581/j.cnki.issn1671-3206.20200416.016 LIU X Y, JIA Y Y, TANG Z H, et al. Research progress on regeneration of waste SCR denitration catalyst [J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2020, 49(7): 1839-1844(in Chinese). doi: 10.16581/j.cnki.issn1671-3206.20200416.016
[74] REN X S, OU Z L, WU B. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction DeNOx and regeneration of Mn-Cu catalyst supported by activated coke [J]. Materials (Basel, Switzerland), 2021, 14(20): 5958. doi: 10.3390/ma14205958 [75] 张先龙, 马康, 蔡程, 等. MnOx/PG低温SCR催化剂二氧化硫中毒及再生特性 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(6): 1403-1412. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018090503 ZHANG X L, MA K, CAI C, et al. Sulfur dioxide poisoning and regeneration characteristics of MnOx/PG low temperature SCR catalysts [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(6): 1403-1412(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018090503
[76] ZHANG X L, LIU S W, MA K, et al. Study on the mechanism of SO2 poisoning of MnOx/PG for lower temperature SCR by simple washing regeneration [J]. Catalysts, 2021, 11(11): 1360. doi: 10.3390/catal11111360 [77] CHEN Z, BIAN C, GUO Y B, et al. Efficient strategy to regenerate phosphorus-poisoned Cu-SSZ-13 catalysts for the NH3-SCR of NOx: The deactivation and promotion mechanism of phosphorus [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2021, 11(21): 12963-12976. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.1c03752 [78] MA Y, WU X D, LIU L P, et al. Critical roles of Cu(OH)2 in low-temperature moisture-induced degradation of Cu-SAPO-34 SCR catalyst: Correlating reversible and irreversible deactivation [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2020, 278: 119306. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119306 [79] WANG Y Z, YI W, YU J, et al. Novel methods for assessing the SO2 poisoning effect and thermal regeneration possibility of MOx-WO3/TiO2 (M = Fe, Mn, Cu, and V) catalysts for NH3-SCR [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(19): 12612-12620. [80] KIM J, HO KIM D, HA H P. Investigating multi-functional traits of metal-substituted vanadate catalysts in expediting NOX reduction and poison degradation at low temperatures [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 397: 122671. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122671 [81] WANG X X, MA H Y, SHI Y, et al. Regeneration of alkali poisoned TiO2-based catalyst by various acids in NO selective catalytic reduction with NH3 [J]. Fuel, 2021, 285: 119069. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119069 [82] 赵重阳, 李国波, 眭华军, 等. 砷中毒商业V2O5-WO3/TiO2催化剂再生研究 [J]. 分子催化, 2020, 34(5): 407-414. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.7103291361 ZHAO C Y, LI G B, SUI H J, et al. Study on regeneration of commercial V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst for arsenic poisoning [J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis (China), 2020, 34(5): 407-414(in Chinese). doi: 10.3724/SP.J.7103291361
[83] SONG L Y, CHAO J D, FANG Y J, et al. Promotion of ceria for decomposition of ammonia bisulfate over V2O5-MoO3/TiO2 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 303: 275-281. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.05.124 [84] LI X S, LIU C D, LI X, et al. A neutral and coordination regeneration method of Ca-poisoned V2O5-WO3/TiO2 SCR catalyst [J]. Catalysis Communications, 2017, 100: 112-116. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2017.06.034 [85] NIU T Q, WANG J, CHU H C, et al. Deep removal of arsenic from regenerated products of spent V2O5-WO3/TiO2 SCR catalysts and its concurrent activation by bioleaching through a novel mechanism [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 420: 127722. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.127722 -



 下载:
下载: