-
锰是影响水质的一项金属指标,也是人体的一种必需微量元素,但是过量摄入则会对人体造成损害[1-4], 我国目前规定的饮用水锰含量限值[5]为0.1 mg·L−1,生态环境部门已将锰纳入地表水常规监测项目。松桃河流域地处长江重要支流——沅江的源头地带,流域内锰矿资源丰富,开发利用强度大。2000年以来,松桃河流域聚集了数量可观、规模较大的电解锰企业和锰渣库,特别是靠近松桃县县城的松桃河干流及其支流,分布了规模不等、生产经营情况不同的8家电解锰企业以及13座渣库。过于集中的产业分布,构成了较大的流域水环境风险,特别是电解锰渣不规范填埋处理,使得松桃河锰和氨氮等主要污染物浓度持续维持在较高水平。当前从流域尺度对锰污染的研究还较少[6-8],针对典型锰产业聚集区的流域锰污染的变化特征方面研究更鲜见有报道。摸清锰产业较聚集的松桃河流域的河流锰污染特征,可以为流域锰污染综合防治和水环境管理提供理论依据和决策支持。
本文以贵州省铜仁市松桃县内电解锰行业集聚的松桃河流域为研究区,聚焦流域地表水的锰污染问题,采用Spearman秩相关系数法研究松桃河锰的污染变化趋势,并用系统聚类法分析河流锰浓度的时空分布特征,综合时间和空间聚类结果进一步说明锰污染具体变化趋势。希望通过研究获得松桃河流域锰污染变化趋势、时空分布特征和重要影响因素,为保障松桃河出境断面稳定达标与水环境管理提供科学依据。
-
松桃河发源于贵州省铜仁市松桃苗族自治县冷水溪镇,流经素有中国“锰三角”之称的松桃县、重庆市秀山县和湖南省花垣县,于保靖县注入酉水河。在松桃境内有一级支流14条、二级支流6条,主河道全长191 km,集雨面积1520 km2,多年平均年降雨量1346 mm,水资源总量14.01亿m3,水资源可利用量4.851亿m3。松桃县属中亚热带季风气候,春暖夏凉,四季分明,受特殊的高原山地喀斯特地形地貌的影响,水资源时空分布不均匀,年际变化较大,径流年内分配亦不均匀,年径流量主要集中在汛期,非汛期径流偏小,多年平均流量30.8 m3·s−1,最枯月平均流量为6.97 m3·s−1。松桃县境内分布面积最大的是山地黄壤,次为黄红壤、石灰土、水稻土、紫色土、潮土、黄棕壤及山地灌丛草甸土。
本文研究的流域主要是松桃河流经松桃县城以北工业园区的地表水系,该地表水系为区域的最低侵蚀基准面,地下水主要接受大气降水补给,大气降水及其所形成的地面散流直接地或通过渗透性较高的包气带进入各种岩溶裂隙、岩溶管道“垂直”下渗到地下水面后,再沿岩溶裂隙、水平管道(暗河)、导水断裂带等通道,按最大水力坡降方向排泄区流动,而最终在排泄基准面附近,以岩溶大泉(暗河)、泉点或河底渗流出水的形式排泄。研究区地下水的排泄基准面即是松桃河。
-
松桃河流域位于中国“锰三角”地区,作为流域上游的贵州省松桃县锰矿保有储量居全国第一位,铜仁松桃锰矿整装勘查区锰矿总的资源潜力预测应超过10亿t,资源储量巨大[9]。松桃县现有电解锰行业企业10家,实际生产能力每年20万t金属锰,年产废渣140万t,共有电解锰渣库渣堆20处,现存渣量约1102万m3。目前电解锰生产废水基本上可以做到循环利用,但电解锰渣主要采用渣场堆放的形式进行处理。电解锰渣[10-17]是一种二类工业固体废物,当水体流经锰渣时,会导致锰渣中的大量水溶性锰和氨氮不断析出。据前期调查资料,松桃县因历史原因共有13座未做底部防渗措施的锰渣库,其中位于本文研究区流域内的渣库就有9座,主要渣库的基本情况如表1所示。另外,由于渣库渗漏对地下水的严重影响,在流域内两处较大的地下水水井附近都修建了污水处理站,具体情况见表2。
-
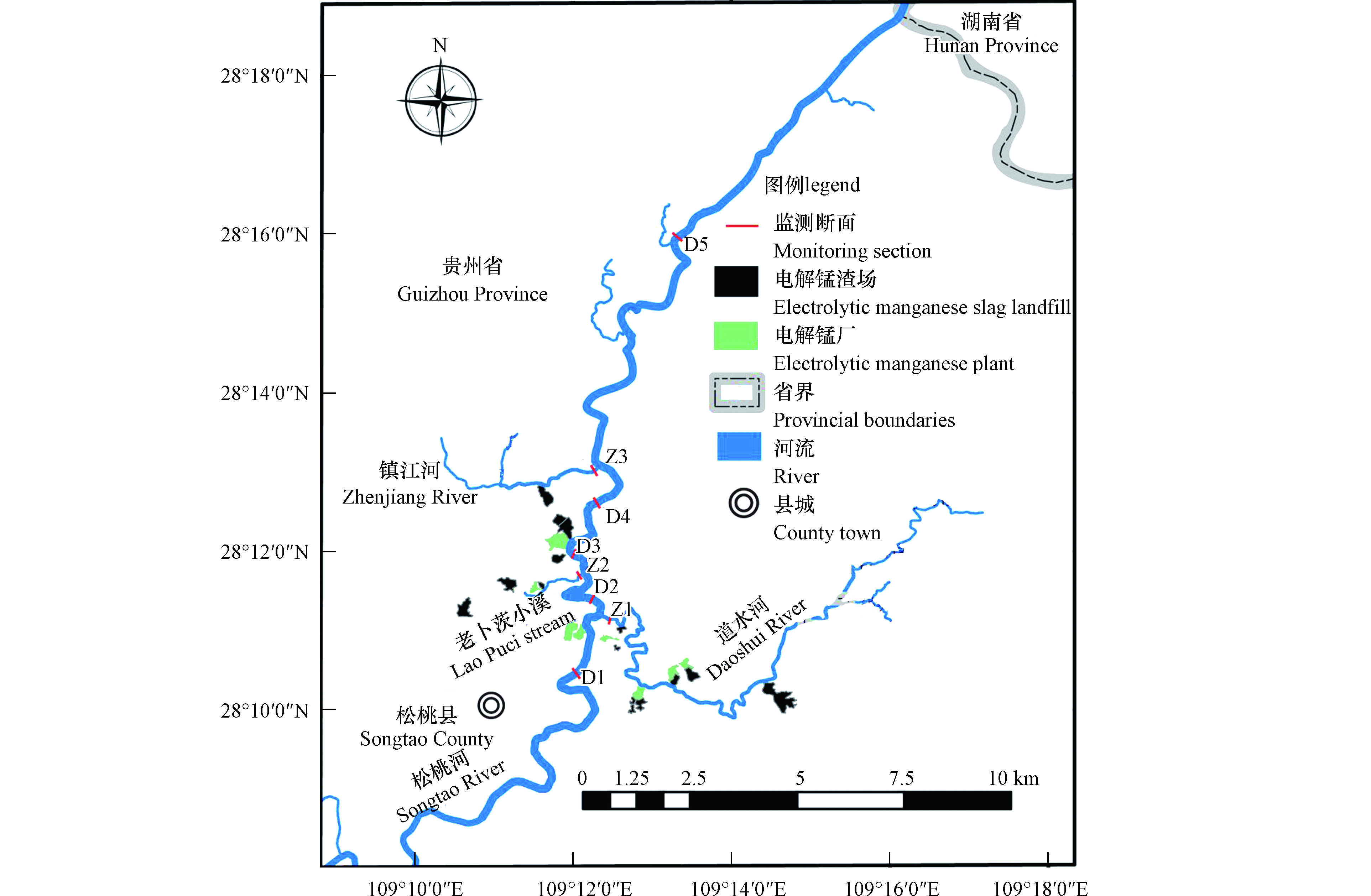
本文选取松桃县城北面锰企与锰渣场分布最为集中的流域作为研究对象,研究的流域面积约35 km2,干流河长约13 km,有3条支流,项目组根据研究区域内松桃河干流和支流的分布情况,设置地表水监测断面8个(图1),监测断面情况介绍详见表3,采样时间为2015年4月到2019年6月每月监测1次,共计51个月的逐月监测。
本次评价指标为总锰,总锰的测定方法为国标《水质 铁、锰的测定 火焰原子吸收分光光度法(GB 11911-89)》,氨氮的测定方法为《水质 氨氮的测定 水杨酸分光光度法(HJ 536-2009)》,其他常规指标为《水和废水监测分析方法》(第四版)中的推荐方法。松桃河流域总体规划为Ⅲ类水质,执行国家《地表水环境质量标准》(GB3838-2002)Ⅲ类水质标准。
-
(1) 秩相关系数法
Spearman秩相关系数法[18-21]和季节性Kendall法[22-26]是常用流域水质变化趋势分析方法。采用 Spearman 秩相关系数法评价污染物随时间变化的规律,对污染物变化趋势进行定量分析。将秩相关系数rs的绝对值同 Spearman秩相关系数统计表中的临界值Wp进行比较。当rs>Wp则表明变化趋势有显著意义;若rs是负值,则表明在评价时段内有关统计量指标变化呈下降或好转趋势;若rs为正值,则表明在评价时段内有关统计量指标变化呈上升或加重趋势;当rs≤Wp则表明变化趋势没有显著意义,说明在评价时段内水质变化稳定或平稳。
(2)聚类分析法
目前,流域水质时空变化研究的主流技术为多元统计分析方法,国内研究者采用系统聚类分析法对我国许多流域[27-31]水质进行时空变化分析,国外学者也采用本法分析了该国流域[32-36]水质时空演变特征。系统聚类分析法(HCA)是一种应用较广泛的聚类分析方法,其实质是根据变量或样品之间的亲疏程度,以逐次聚合的方法将性质最接近的对象结合在一起,直到聚成一类,流域水质评价中常按照监测时间和监测断面的地理位置进行聚类,分析流域水质的时空变化特征。本文数据预处理和多元统计过程采用Microsoft Excel2010,SPSS 21和SigmaPlot14.0等软件。
-
通过水质监测统计结果(表4)可看出,锰和氨氮是流域的特征污染物,锰均值为0.698 mg·L−1,氨氮均值为2.43 mg·L−1,均超过《地表水环境质量标准》(GB3838-2002)Ⅲ类标准限值(锰0.1 mg·L−1,氨氮1.0 mg·L−1)约7倍和2.4倍,其他监测指标均未超标。其中氨氮的标准偏差较高,显示出松桃河流域的氨氮在流域内的变异性较大,说明氨氮受到各种污染源的影响较强烈。另外pH值标准偏差较低,各断面pH值保持在7.6左右,说明流域水体总体呈弱碱性状态。而且相比国内和国外一些有关锰含量研究的河流来说(如表5),松桃河锰浓度均值较高且变幅较大。
-
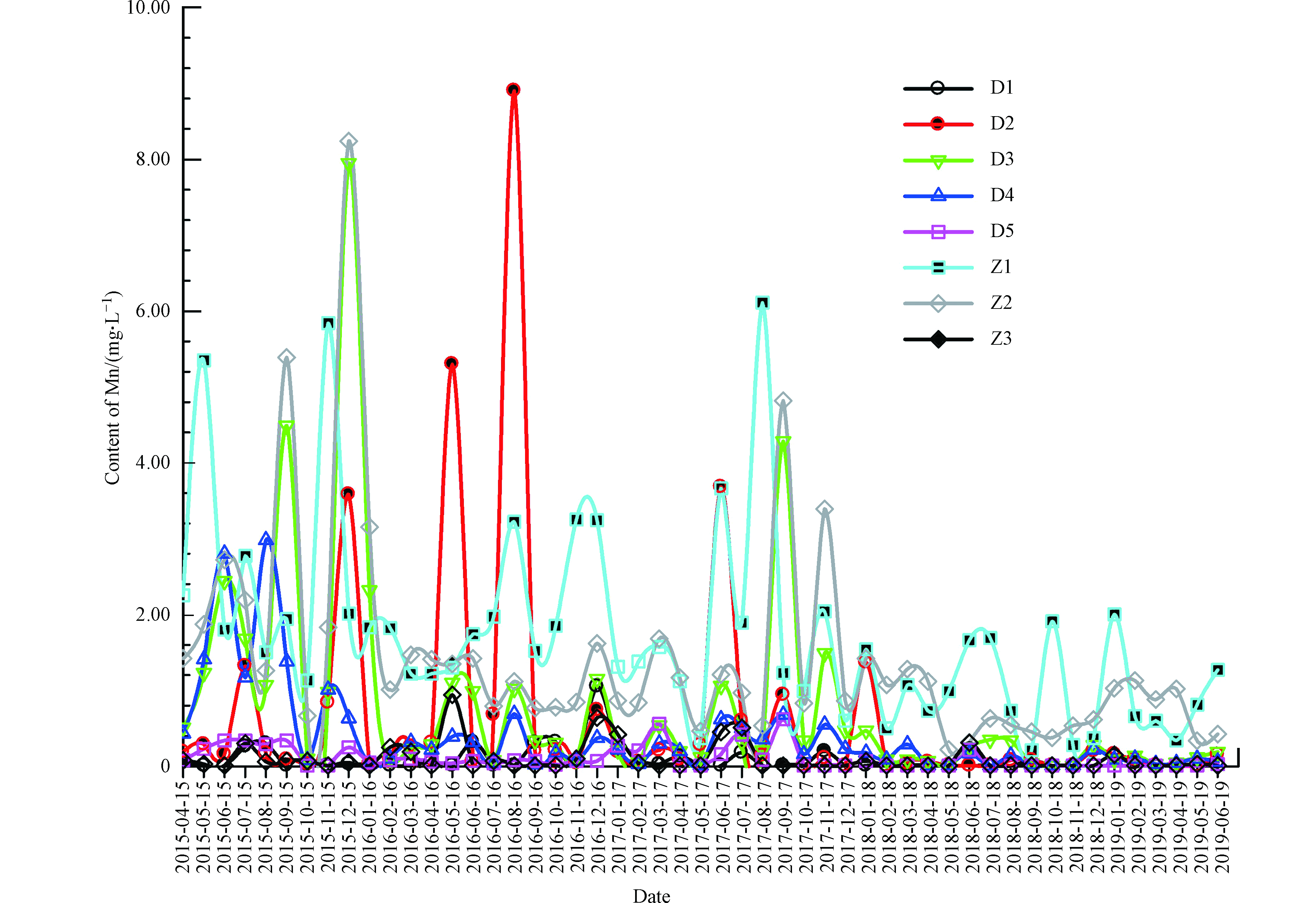
根据上述统计结果分析,由于特征污染物氨氮变异性较大,而且极易受生活源等人为活动影响,故本文选择特征污染物锰进行流域污染趋势分析则更具有代表性,更能反映流域内污染源对河流水质的影响。根据各断面在2015—2019年逐月水质锰监测结果,可得到各断面锰的月变化趋势图,具体见图2,采用Spearman秩相关系数法计算得出各断面锰的秩相关系数rs值,具体数据见表6。
由图2和表6分析可知,D1断面锰的浓度均值(0.0855 mg·L−1)低于地表水环境质量标准(0.1 mg·L−1),且锰的rs< Wp=0.297,说明锰浓度没有显著的上升或下降趋势,因此松桃河锰产业集聚区流域上游断面的水环境质量总体呈平稳的趋势;D2断面锰浓度均值(0.630 mg·L−1)超过标准5倍,超标月份占比52.9%,期间最高值超过标准88倍,rs<0,说明道水河汇入后干流锰浓度有明显的升高,但近年来浓度呈下降趋势;D3断面锰的浓度均值(0.792 mg·L−1)超过标准7倍,超标月份占比70.6%,期间最高值超过标准78倍,rs<0,说明老卜茨小溪汇入后干流锰浓度也有明显的升高,但近年来浓度呈下降趋势;D4断面锰的浓度均值(0.394 mg·L−1)超过标准3倍,超标月份占比58.8%,期间最高值超过标准29倍,rs<0,说明上稿坪渡口断面处锰的浓度也较高,但近年来浓度呈下降趋势;D5断面锰的浓度均值(0.108 mg·L−1)略高于地表水环境质量标准,超标月份占比25.5%,期间最高值超过标准5倍,rs<0,说明松桃河下游木溪出境断面水质已受到一定的影响,但近年来污染物浓度呈下降趋势。支流Z1断面和Z2断面的锰浓度均值超过标准限值16倍和13倍,超标月份占比均为100%,最高值超过标准60倍和81倍,两者rs<0,说明两条支流的锰浓度长期处于高水平但近年来浓度呈下降趋势;Z3断面锰的浓度均值(0.101 mg·L−1)与地表水环境质量标准接近,超标月份占比19.6%,最高值超过标准8倍,rs<0,说明镇江河近年来受到的锰污染影响较小,总体浓度呈下降趋势。
通过上面分析可得出,研究区部分河段超标严重,流域主要断面锰浓度总体呈下降趋势。
-
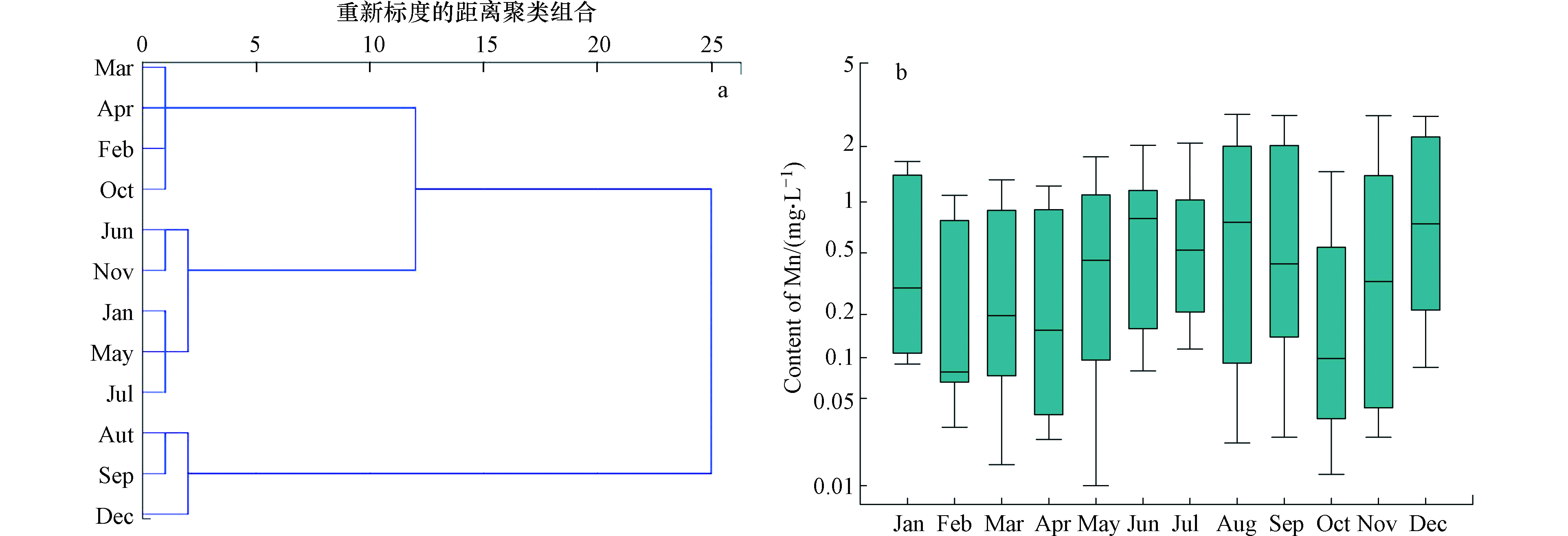
为探讨锰污染年内分布特征,将各断面在近年的逐月水质监测结果进行了均值化,然后采用组间欧氏距离平方计算样本间距离,得到时间聚类分析结果。通过时间聚类结果(图3a)和年内时段尺度差异性及变化趋势(图3b)分析可知,全年可分为3个时段,按浓度从高到低排列分别为:T1时段(8月、9月、12月),分别属于丰水期(雨季后期)和枯水期;T2时段(5—7月、11月、1月),主要属于丰水期(雨季前中期)和枯水期;T3时段(2—4月、10月),主要为枯水期和平水期。从结果可以看出,流域内河流锰污染的年内分布特征主要表现为丰水期(雨季)和枯水期(旱季)浓度较高而平水期相对较低。
分析原因,具体表现为雨季(5—9月)增加的降雨并没有对河流水质起到改善作用,反而增加了对电解锰渣的淋溶作用,部分锰渣淋滤液顺着山势直接排入到河道中,另外由于松桃河流域的渣库大多未做底部防渗,而且大部分渣库所处的地层岩溶发育,根据区域地下水的补径排特征,渣库产生的大量渗滤液能直接进入各种岩溶裂隙、 岩溶管道“垂直”下渗到地下水面,造成地下水污染,地下水再沿岩溶裂隙、水平管道(暗河)、导水断裂带等通道,在地势低洼的溪沟处以泉或点状渗流的形式进入地表溪沟径流,造成地表水污染;另一方面由于电解锰渣中含有的大量的重金属元素会通过长时间的风化和淋滤等作用向土壤和水体中迁移扩散,使土壤和水体中的重金属含量显著增加,参考相关研究如陆凤[41]、蒋宗宏[42]等对贵州铜仁典型锰矿区周边土壤重金属含量及污染评价,结果显示2017年采集的土壤Mn的平均含量超过贵州省土壤背景值(794 mg·kg−1),是背景值的2.56倍,可见铜仁锰矿区周边土壤Mn浓度整体较高,所以雨季不仅会加速锰渣中污染物的迁移扩散,也会增加周边面源的汇入。综合上述原因造成了丰水期水质锰浓度整体较高。而雨季后期(8,9月)相比雨季前中期(5—7月)锰浓度明显升高,也反映了一种水质对降雨的延迟响应现象;雨季过后流域进入相对稳定的平水期(10—11月),随着降雨作用的减弱水质锰浓度有明显减低;但随着进入枯水期后(12—3月),河流径流量明显变小,而渣库的渗滤作用仍在持续,使得水质锰浓度又明显升高;之后又进入平水期(4月),随着河流径流量的增大,水质锰浓度又有所降低。可见研究区流域内未做防渗的渣库较多且渣库对水质有着持续性的影响,另外松桃河流域属于高原山地喀斯特地区,水资源时空分布不均匀且径流年内变化大,加上降雨作用和面源污染等因素,造成了这种独特的变化规律。
-
将各断面监测数据,运用组间欧氏距离平方法得到空间聚类分析结果。通过空间聚类结果(图4a)和空间尺度的差异性比较(图4b)分析可知,松桃河流域水质在空间上可分为3组(A,B,C),A组为D1、D5和Z3,B组为D2、D3和D4,C组为Z1和Z2。锰浓度A组相对较低,B组较高,C组最高,即呈现出中游支流>中游干流>下游和上游的特征。首先从流域监测图(图1)看,上游断面(D1)附近没有电解锰企业和渣库,锰浓度较低,下游木溪站(D5)附近也无锰企和渣库,而且经过沿程降解和河流自净等作用锰浓度已明显降低,支流镇江河出口(Z3)由于支流内只有一个渣库,且受到的锰污染情况较轻,所以三者浓度接近归为A组;B组位于中游,锰污染程度明显高于上游,干流沿途有2个锰企和2个渣库并有2条支流汇入,其中道水河汇入后(D2)和老卜茨小溪汇入后(D3)较高,上稿坪渡口(D4)略低,说明中游水质已受到污染和汇入支流的严重影响;C组为浓度最高的两条支流道水河(Z1)和老卜茨小溪出口(Z2),其中道水河支流有3家锰企和7个渣场,老扑次小溪有1家锰企和3个渣场,而且两条支流都有一个较大的地下水出露点,经调查两个泉点已受到了严重污染。另外从区域水文地质条件分析,由于研究区岩溶发育,松桃河为该区域的最低侵蚀基准面,渣库一旦渗漏后其污染物最终都将排入松桃河中,所以这也是渣库集中的中游河段锰浓度长期超标的重要原因。
为进一步探讨造成流域锰空间分布特征的原因和支流对干流的影响,对河流锰浓度的衰减特征进行分析,采用综合衰减系数法[43-44],选择流量较稳定和面源影响较小的枯水期,根据各断面的浓度变化情况,并结合流速、流量和距离等参数计算各区段的综合衰减系数,结果如表7。从综合衰减系数计算结果分析,D1—D2段和D2—D3段由于都有高浓度的支流汇入,而且距离较短,河流的自净能力不足以使污染物迅速降解,所以综合衰减系数应较低,结果为负数则说明区段内还有其他污染源的汇入,总体使得这两个区段的特征表现为污染物浓度的急剧上升而非衰减;D3—D4段由于无支流汇入,而且距离较长,随着锰在河流弱碱性环境下的沉降以及河流的自净能力,干流锰浓度迅速下降,综合衰减系数较高,该区段的特征为污染物浓度的迅速衰减;D4—D5段虽有支流汇入,但汇入支流浓度较低对干流的影响不大,由于初始浓度不高,加上距离较长和流量变大等因素,D5断面浓度已降到优于地表水Ⅲ类标准水平(<0.1 mg·L−1),综合衰减系数中等,区段特征为污染物浓度的衰减。通过分析可知,两条高浓度支流的距离较近是造成中游锰浓度急剧上升和较难降解的主要原因,而随着沿途污染汇入的降低和河流距离的增大,通过污染物沉降和河流自净等作用,下游锰浓度又逐渐下降到较低水平。同时根据D1—D2和D2—D3两个区段的特征,可基本忽略污染物的降解作用和河流的自净作用,从而估算出两条支流对相应区段的贡献率,即贡献率=支流汇入量/(控制断面的总量-上游断面的量)×100%,由此计算得到道水河和老卜茨小溪对松桃河中游相应区段的贡献率为41.2%和23.5%,其他污染贡献据推测应来源于沿途渣库渗漏后通过其他暗河、泉点或河底渗流等方式汇入松桃河干流。
通过对时间和空间聚类结果的分析,可得出降雨、渣库分布和渗漏、水文地质条件和支流汇入是影响松桃河锰浓度的重要因素。
-
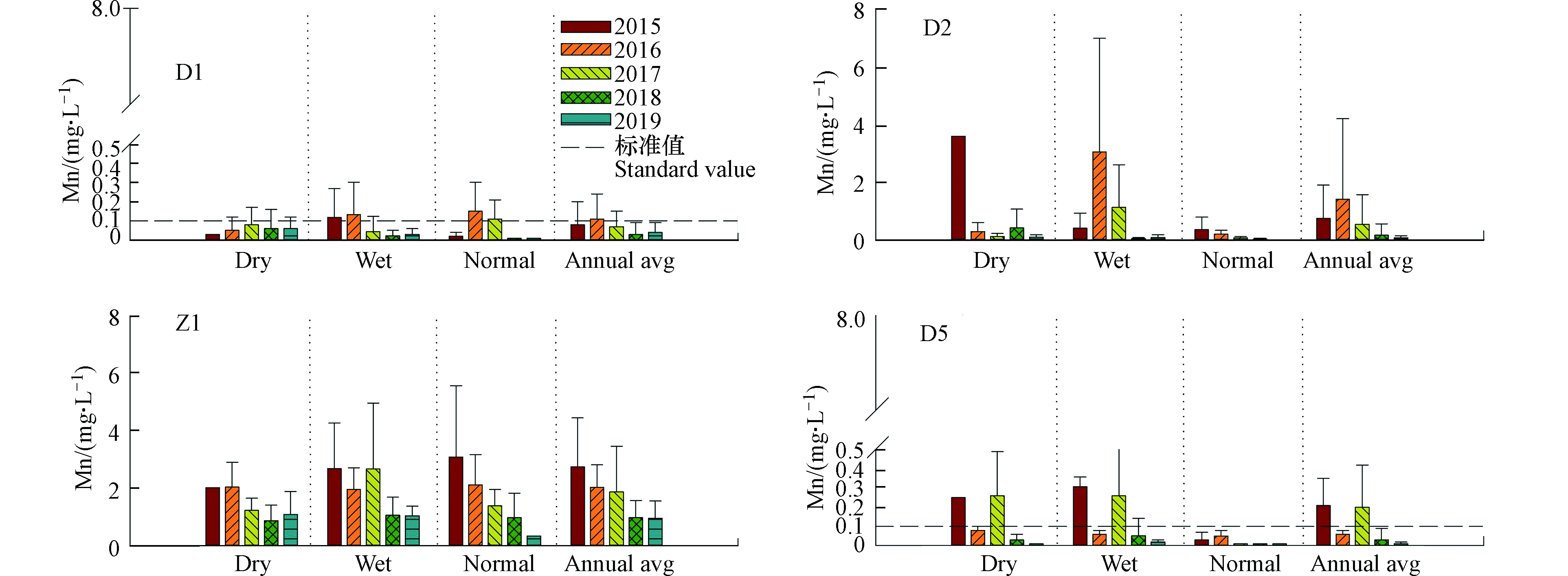
结合聚类结果对做进一步分析,可得到流域内河流锰污染的年度变化趋势。如图5所示,D1代表上游背景断面,近年来河流锰浓度无论在枯丰平水期的年度变化范围都不大,基本都维持在地表水环境质量标准值(0.1 mg·L−1)以下;D2代表典型的干流受污染断面,其锰浓度年度变化剧烈,尤其是枯水期和丰水期的变幅较大,有个别时段出现超高值(如2015年枯水期和2016年丰水期),平水期浓度相对较低而且呈逐年下降趋势,从年均值看2015—2017年间浓度变幅较大,但在2017年以后呈现明显的下降趋势;Z1代表典型的重污染支流断面,近年来锰浓度均远超过标准值,枯水期和丰水期存在明显的年度变化,浓度高值主要出现在2015—2017年,而平水期呈明显的逐年下降趋势,从年均值看近年来总体呈下降趋势,特别是2017年后下降趋势明显;D5代表下游出境断面,在2015—2017年的枯水期和丰水期存在一定的浓度波动情况,其中2015年和2017年的浓度均明显超过标准值,2017年以后呈现明显的下降趋势,平水期近年来都未超过标准值,年均变化趋势与枯丰水期类似。
结果一方面反映了十三五期间政府通过引导企业转型升级、强制企业清洁生产和开展污染综合整治等措施,使松桃河水质特别是2017年以后有了明显的改善,另一方面也说明了流域内的污染源排放存在一定的随机性,特别是在枯水期和丰水期。
-
(1)秩相关系数法分析说明,近年来松桃河锰产业集聚区流域的上游水质较好且稳定,中游污染严重,干流均值超过地表水环境质量标准值(0.1 mg·L−1)3—7倍,下游水质有所恢复,流域内主要断面锰浓度总体呈下降趋势。
(2)时间聚类分析表明,流域内河流锰污染的年内分布主要特征为丰水期(雨季)和枯水期(旱季)浓度较高而平水期相对较低;空间聚类结果表明,流域锰污染总体呈现中游支流>中游干流>下游和上游的分布特征,两条支流道水河和老卜茨小溪对流域中游相应区段的贡献率较大,分别为41.2%和23.5%。
(3) 通过对聚类结果的分析,可得出降雨、渣库分布和渗漏、水文地质条件和支流汇入是影响松桃河锰浓度的重要因素。
(4) 结合聚类结果对流域内河流锰污染的年度变化趋势进一步分析可得出,近年来流域上游河流水质变化不大,中游和下游在枯水期和丰水期的年度变幅较大,但在2017年以后呈现明显的下降趋势。结果反映了十三五期间政府进行综合整治的效果和流域污染源排放的随机性。
电解锰产业集聚区河流锰污染演变趋势和时空分布特征
Variation trend and spatio-temporal distribution of river manganese pollution in the cluster area of electrolytic manganese industry
-
摘要: 松桃河流域是我国锰产业最为集中的区域之一,资源开发和利用形成的污染严重。通过对松桃河电解锰产业集聚区流域2015—2019年的8个典型断面的总锰监测数据的分析,用秩相关系数法探究了河流锰污染总体变化趋势,并用系统聚类分析法分析了河流锰的时空分布特征,结合聚类结果对污染趋势做进一步分析。秩相关系数分析结果表明,近年来松桃河锰产业集聚区流域的上游水质较好且稳定,而中游污染严重,干流均值超过地表水环境质量标准值(0.1 mg·L−1)3—7倍,下游水质有所恢复,流域主要断面锰浓度总体呈下降趋势;时间聚类分析表明,流域内河流锰污染的年内分布主要特征为丰水期(雨季)和枯水期(旱季)浓度较高而平水期相对较低;空间聚类结果显示,流域内河流锰污染呈现出中游支流>中游干流>下游和上游的特征,两条支流道水河和老卜茨小溪对中游相应区段的贡献率较大,分别为41.2%和23.5%;聚类结果分析显示,降雨、渣库分布和渗漏、水文地质条件和支流汇入是影响流域内河流锰浓度的重要因素;结合聚类结果的污染趋势分析得出,中游和下游的水质在枯水期和丰水期的年度变幅较大,但在2017年以后呈现明显的下降趋势,结果反映了期间政府进行综合整治的效果和流域污染源排放的随机性。Abstract: Songtao River basin is one of the most concentrated areas of manganese industry in China, pollution caused by resource exploitation and utilization is serious. According to the total manganese monitoring data of 8 typical sections in Songtao River basin of the cluster area of electrolytic manganese industry from 2015 to 2019, we analyzed the general trend of river manganese pollution in Songtao River basin by rank correlation coefficient method, and the temporal and spatial distributions of manganese in rivers were analyzed by systematic clustering analysis, then combined with the clustering results to make a further analysis of the pollution trend. The rank correlation coefficient analysis results show that, in recent years , the water quality in the upper reaches of the basin was good and stable, but the midstream were seriously polluted, and the average concentration of manganese in the trunk stream was 3 to 7 times higher than the Environmental quality standard value for surface water(0.1 mg·L−1), the water quality had recovered downstream, the manganese concentration in the main section of the basin had showed a decreasing trend. Time clustering analysis showed that, the annual distribution of river manganese pollution in the basin was characterized by high concentration in wet season and dry season while low concentration in normal season. The spatial clustering results showed that, the river manganese pollution in the basin was characterized by the midstream tributary > the middle reaches > downstream and upstream, the two tributaries, Daoshui river and Laobuci stream, contributed more to the corresponding section of the middle reaches, the respective contribution rate was 41.2% and 23.5%. The analysis of the clustering results showed that rainfall, distribution and leakage of slag reservoir, hydrogeological conditions and inflow of tributaries were the important factors affecting the river manganese concentration in the basin. The pollution trend analysis combined with the clustering results showed that, the annual variations of water quality in the midstream and downstream were large in the dry seasons and wet seasons, but showed a significant downward trend after 2017, the results reflected the effect of comprehensive improvements by the government and the randomness of pollutant discharge in the basin.
-

-
表 1 松桃河流域研究区内电解锰渣库基本情况
Table 1. Basic information of electrolytic manganese slag dump in research area of Songtao River basin
渣库名称
Dump name所属流域
Catchment area渣库概况
Dump situation太丰1# 道水河上游 于2009年锰渣库规范化整治行动中封库。进行了表层覆膜、 初期坝加固工程、闭库覆土绿化工程、排水工程、 渗滤液收集池与应急事故池工程等整治工作。渣库底部未做防渗。 群兴1# 金泰2# 宇光1# 道水河下游 宇光2# 金瑞 1# 老卜茨小溪 汇丰 2# 三和 1# 镇江河 于2010年锰渣库规范化整治行动中封库。具体工程同2009年。渣库底部未做防渗。 汇丰 1# 松桃河干流 未进行封库,底部未做防渗。 表 2 流域内地下水处理设施情况
Table 2. Basic conditions of sewage treatment facilities in Songtao River basin
污水处理设施名称
Name of Sewage
treatment facilities所属流域
Catchment area污水处理主要工艺
Main treatment process处理效果
Treatment effect老卜茨水井
污水处理站道水河 主要采用化学絮凝沉淀工艺 处理后废水总锰总体上能达到污水综合排放标准要求,但大多都超过地表水环境质量标准0.1 mg·L−1,且处理效果不稳定,丰水期有井水溢出情况。 文山水井
污水处理站老卜茨小溪 采用“废水收集+絮凝沉降+压缩空气曝气+锰砂过滤”处理工艺 同上。 表 3 松桃河流域监测断面情况介绍
Table 3. Introduction of monitoring section in Songtao River basin
断面编号
Section number断面位置
Position of section周边状况
The surrounding conditions代表区域
Representative regionD1 松桃河上游道水河汇入前 无明显污染源。 上游干流 D2 道水河汇入后下游500 m 主要为支流道水河汇入。 中游干流 D3 老卜茨小溪汇入后下游200 m 主要为支流老卜茨小溪汇入。 中游干流 D4 上稿坪渡口 上游有1家锰企和1个渣场 中游干流 D5 国控出境断面木溪站 无明显污染源。 下游干流 Z1 道水河出口 支流内有3家锰企和7个渣场 中游支流 Z2 老卜茨小溪出口 支流内有1家锰企和3个渣场 中游支流 Z3 镇江河出口 支流内有1个渣场 下游支流 表 4 松桃河流域主要水质指标描述性统计(mg·L−1)
Table 4. Descriptive statistics of surface water quality indicators in Songtao River basin
水质指标
Indicators极小值
Minimum极大值
Maximum均值
Mean标准差
Standard deviationMn 0.01 27.5 0.698 1.57 NH3−N 0.025 153.3 2.43 11.1 pH 7.2 8.4 7.6 0.2 CODMn 1.10 3.50 1.730 0.523 TP 0.0100 0.900 0.068 0.129 F− 0.0700 0.350 0.172 0.053 Cu ND — — — Zn ND — — — As ND — — — Hg ND — — — Cd ND — — — Cr6+ 0.004 0.016 0.001 0.003 Pb ND — — — CN− ND — — — S2- ND — — — 注:“ND”表示未检出,“—”表示不存在,各指标最低检出限为:Cu(0.001 mg·L−1),Zn(0.05 mg·L−1),As(0.007 mg·L−1),Hg
(0.00005 mg·L−1),Cd(0.001 mg·L−1),Pb(0.01 mg·L−1),CN−(0.002 mg·L−1),CN−(0.005 mg·L−1).
Note: “ND” means not Not Detected, “—” means nonexistence, the minimum detection limit of each indicator is: Cu(0.001 mg·L−1), Zn(0.05 mg·L−1), As(0.007 mg·L−1), Hg(0.00005 mg·L−1), Cd(0.001 mg·L−1), Pb(0.01 mg·L−1), CN−(0.002 mg·L−1), CN−(0.005 mg·L−1).表 5 国内外有关研究中河流锰浓度参考值
Table 5. Reference values of river manganese concentration in domestic and foreign studies
编号
Serial number河流
Rivers国家
Countries浓度/(mg·L−1)
Concentration年份
Year参考文献编号
References number1 贵州松桃河 中国 0.698±6.76 2015—2019 — 2 福建九龙江 中国 0.097±0.133 2016—2017 [6] 3 湖南酉水流域 中国 0.295±0.634 2010—2014 [7] 4 恒河支流Ramganga河 印度 0.474±0.680 2018 [32] 5 台湾淡水河 中国 0.56±0.84 2006—2017 [37] 6 布努斯河 马来西亚 0.16±0.09 2016 [38] 7 Kalix河 瑞典 0.0094±0.078 1997 [39] 8 英格兰西北部15条河流 英国 0.017±0.010 1984—1985 [40] 表 6 松桃河流域研究断面近年锰浓度和rs值
Table 6. Manganese concentration and rs values in the main stream section of Songtao River basin in recent years
断面编号
Section number断面名称
Section name浓度/(mg·L−1)
Concentrationrs D1 松桃河上游道水河汇入前 0.0855±0.076 0.139 D2 道水河汇入后下游500m 0.630±8.27 −0.476 D3 老卜茨小溪汇入后下游200m 0.792±7.158 −0.6 D4 上稿坪渡口 0.394±2.586 −0.58 D5 国控出境断面木溪站 0.108±0.512 −0.414 Z1 道水河出口 1.733±4.377 −0.552 Z2 老卜茨小溪出口 1.419±6.821 −0.584 Z3 镇江河出口 0.101±0.839 −0.0149 表 7 各区段综合衰减系数计算
Table 7. The calculation of the comprehensive attenuation coefficient of each section
区段名称
Range name断面名称
Section name浓度/(mg·L−1)
Concentration流量/(m 3 ·s−1)
Flow流速u/(m·s−1)
Flow velocity
Cx/
(mg·L−1)△x/
mK/
h−1D1—D2段 起始断面D1 0.129 5.89 0.55 0.261 500 −2.330 汇入断面Z1 1.792 0.51 — 控制断面D2 0.471 6.32 0.54 D2—D3段 起始断面D2 0.471 6.32 0.54 0.563 200 −5.525 汇入断面Z2 1.778 0.48 — 控制断面D3 0.994 6.65 0.54 D3—D4段 起始断面D3 0.994 6.65 0.54 0.994 1500 1.812 控制断面D4 0.246 6.68 0.53 D4—D5段 起始断面D4 0.246 6.68 0.53 0.235 6300 0.359 汇入断面Z3 0.113 0.59 — 控制断面D5 0.0719 7.38 0.48 注:Cx表示模拟上游断面与支流汇入时的完全混合浓度,Cb为控制断面浓度,△x为支流汇入后到控制断面距离,K为该区段综合衰减系数,K=3600u/△x×ln(Cx/Cb).
Note: Cx represents the fully mixed concentration of the simulated upstream section and the tributary inflow; Cb represents the concentration of the control section; △x represents the distance from the tributary inflow to the control section; K represents the comprehensive attenuation coefficient of this section, K=3600u/△x×ln(Cx/Cb). -
[1] ZONI S, ALBINI E, LUCCHINI R. Neuropsychological testing for the assessment of manganese neurotoxicity: A review and a proposal [J]. American Journal of Industrial Medicine, 2007, 50(11): 812-830. doi: 10.1002/ajim.20518 [2] 丁宏伟, 李岩. 锰的神经毒性机制研究进展 [J]. 实用预防医学, 2016, 23(8): 1022-1025. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3110.2016.08.040 DING H W, LI Y. Advances in the mechanism of manganese-induced neurotoxicity [J]. Pract Prev Med, 2016, 23(8): 1022-1025(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3110.2016.08.040
[3] ROTH JA, LI Z Z, SRIDHAR S, et al. The effect of manganese on dopamine toxicity and dopamine transporter (DAT) in control and dat transfected hek cells [J]. Neurotoxicology, 2013, 35(3): 121-128. [4] 杨心乐, 王桂兰, 张忠诚. 锰与人体健康 [J]. 医学综述, 2006, 12(8): 1134-1136. YANG X L, WANG G L, ZHANG Z C. Manganese and Health of Human Body [J]. Medical Recapitulate, 2006, 12(8): 1134-1136(in Chinese).
[5] GB 3838—2002 地表水环境质量标准[S]. GB 3838—2002 Environmental quality standard value for surface water[S].
[6] 陈能汪, 王德利, 鲁婷, 等. 九龙江流域地表水锰的污染来源和迁移转化机制 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(8): 2955-2964. CHEN N W, WANG D L, LU T, et al. Manganese pollution in the Jiulong River watershed: Sources and transformation [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2018, 38(8): 2955-2964(in Chinese).
[7] 陈燕. “锰三角”对湖南湘西州境内酉水流域锰指标污染状况调查 [J]. 资源节约与环保, 2015, 10: 178-180. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2251.2015.06.146 CHEN Y. Investigation on manganese pollution in Youshui Basin of Xiangxi autonomous Prefecture, Hunan province by "Manganese Triangle" [J]. Resource Conservation and Environmental Protection, 2015, 10: 178-180(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2251.2015.06.146
[8] 黄波, 刘家春. 长江经济带的锰“暴露”—长江干流锰污染状况分析 [J]. 水利水电快报, 2015, 36(10): 33-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0081.2015.10.014 HUANG B, LIU J C. Manganese "exposed" in the Yangtze River Economic Belt—Analysis of manganese pollution in the Yangtze River trunk stream [J]. EWRHI, 2015, 36(10): 33-35(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0081.2015.10.014
[9] 周琦, 杜远生, 袁良军, 等. 贵州铜仁松桃锰矿国家整装勘查区地质找矿主要进展及潜力预测 [J]. 贵州地质, 2016, 33(4): 237-244. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2016.04.001 ZHOU Q, DU Y S, YUAN L J, et al. Main progress and potential prediction of geological prospecting for manganese ore in national integrated exploration area of Songtao, Tongren, Guizhou province [J]. Guizhou Geology, 2016, 33(4): 237-244(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2016.04.001
[10] 陈红亮. 新鲜电解锰渣和长期堆存渣的矿物成分和毒性特征的差异分析 [J]. 贵州师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 34(2): 32-36. CHEN H L. Differences analysis of minerals compositions and toxicity characteristics between the fresh electrolytic manganese residue and the stockpiling residue [J]. Journal of Guizhou Normal University (Natural Sciences), 2016, 34(2): 32-36(in Chinese).
[11] DUAN N, FAN W, CHANGBO Z, et al. Analysis of pollution materials generated from electrolytic manganese industries in China [J]. Resources Conservation and Recycling, 2010, 54(8): 506-511. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2009.10.007 [12] LI Z, PENG X, OUYANG Y. Conditions for leaching manganese from electrolytic manganese waste residue [J]. Jishou University Natural Science, 2006, 27(2): 110-113. [13] 罗乐, 降林华, 段宁. 电解锰废渣的浸出毒性及生石灰固化技术 [J]. 环境工程, 2017, 35(12): 139-143. LUO L, JIANG L H, DUAN N. A EMR solidification technology based on quicklime and leaching toxicity [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2017, 35(12): 139-143(in Chinese).
[14] ZHOU C B, WANG N F. Treating electrolytic manganese residue with alkaline additives for stabilizing manganese and removing ammonia [J]. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2013, 30(11): 2037-2042. doi: 10.1007/s11814-013-0159-8 [15] XIN B, CHEN B, DUAN N, et al. Extraction of manganese from electrolytic manganese residue by bioleaching [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102(2): 1683-1687. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2010.09.107 [16] LI H, ZHANG Z, TANG S, et al. Ultrasonically assisted acid extraction of manganese from slag [J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2008, 15(4): 339-343. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2007.07.010 [17] ZHOU C, DU B, WANG N, et al. Preparation and strength property of autoclaved bricks from electrolytic manganese residue [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2014, 84: 707-714. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.01.052 [18] 杨盼, 卢路, 王继保, 等. 基于主成分分析的spearman秩相关系数法在长江干流水质分析中的应用 [J]. 环境工程, 2019, 37(8): 76-80. YANG P, LU L, WANG J B, et al. Analysis of water quality trend in the main stream of the Yangtze River based on principal component analysis [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2019, 37(8): 76-80(in Chinese).
[19] ZHANG P P, ZHANG X K. Analysis of evolution trend of water resources based on spearman and R/S methods: A case study of agricultural water source in Jinghui Irrigation Area [J]. Journal of Landscape Research, 2020, 12(3): 30-32. [20] 陈雨艳, 杨坪, 向秋实, 等. 岷江流域水质状况评价及变化趋势分析 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2015, 31(6): 53-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2015.06.012 CHEN Y Y, YANG P, XIANG Q S, et al. Evaluation of the water quality in Minjiang River and analysis on its variation trend [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2015, 31(6): 53-57(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2015.06.012
[21] WANG W P, CHEN Y F, BECKER S, et al. Linear trend detection in serially dependent hydrometeorological data based on a variance correction spearman RHO method [J]. Water, 2015, 7(12): 7045-7065. doi: 10.3390/w7126673 [22] 陈欣佛, 柴元冰, 闵敏. 基Kendall检验法的湟水水质变化趋势分析 [J]. 人民黄河, 2019, 41(9): 97-101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2019.09.020 CHEN X F, CHAI Y B, MIN M. Analysis of variation trend of Huangshui water quality based on Kendall method [J]. Yellow River, 2019, 41(9): 97-101(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2019.09.020
[23] KISI O, AY M. Comparison of Mann–Kendall and innovative trend method for water quality parameters of the Kizilirmak River, Turkey [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2014: 362-375. [24] HIRSCH R M, SLACK J R, SMITH R A. Techniques of trend analysis for monthly water quality data [J]. Water Resources Research, 1982, 18(1): 107-121. doi: 10.1029/WR018i001p00107 [25] 胡国华, 唐忠旺, 肖翔群. 季节性Kendall检验及其在三门峡水库水质趋势分析中的应用[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 2004(3): 86-88. HU G H, TANG Z W, XIAO X Q. Trend analysis of water quality of Sanmenxia Reservoir of the Yellow River[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 2004(3): 86-88(in Chinese).
[26] VAN B G, HUGHES J P. Nonparamertic tests for trend in waterquality [J]. Water Resources Research, 1984, 20(1): 127-136. doi: 10.1029/WR020i001p00127 [27] 邱瑀, 卢诚, 徐泽, 等. 湟水河流域水质时空变化特征及其污染源解析 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2017, 37(8): 2829-2837. QIU Y, LU C, XU Z, et al. Spatio-temporal variation characteristics and water pollution sources in the Huangshui River Basin [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2017, 37(8): 2829-2837(in Chinese).
[28] 徐华山, 徐宗学, 唐芳芳, 等. 漳卫南运河流域水质时空变化特征及其污染源识别 [J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(2): 359-369. XU H S, XU Z X, TANG F F, et al. Spatiotemporal variation analysis and identification of water pollution sources in the Zhangweinan River basin [J]. Environmental Science, 2012, 33(2): 359-369(in Chinese).
[29] 王翠榆, 杨永辉, 周丰, 等. 沁河流域水体污染物时空分异特征及潜在污染源识别 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2012, 32(9): 2267-2278. WANG C Y, YANG Y H, ZHOU F, et al. Spatio-temporal characteristics and source identification of water pollutants in River Qinhe Basin [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2012, 32(9): 2267-2278(in Chinese).
[30] 卜红梅, 刘文治, 张全发. 多元统计方法在金水河水质时空变化分析中的应用 [J]. 资源科学, 2009, 31(3): 429-434. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-7588.2009.03.012 PU H M, LIU W Z, ZHANG Q F. The application of multivariate statistical method in the analysis of temporal and spatial variation of water quality in Jinshui River [J]. Resources Science, 2009, 31(3): 429-434(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-7588.2009.03.012
[31] 汤云, 卢毅敏, 吴升. 闽江流域水质时空分布特征及污染源解析 [J]. 长江科学院院报, 2019, 36(8): 30-35,48. doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20171452 TANG Y, LU Y M, WU S. Spatio-temporal distribution and source identification of water pollutants in Minjiang River basin [J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2019, 36(8): 30-35,48(in Chinese). doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20171452
[32] KHAN M Y, GANI K M, CHAKRAPANI G J. Spatial and temporal variations of physicochemical and heavy metal pollution in Ramganga River—a tributary of River Ganges, India [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2017, 76(5): 1-13. [33] SHRESTHA S, KAZAMA. Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of the Fuji river basin, Japan [J]. Environmental Modelling & Software, 2007, 22(4): 464-475. [34] PILLSBURY L A, BYRNE R H. Spatial and temporal chemicalvariability in the Hillsborough River system [J]. Marine Chemistry, 2007, 104: 4-16. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2006.12.005 [35] VAROL M, SEN B. Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of Behrimaz Stream, Turkey [J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2009, 159(1/4): 543-553. [36] VEGA M, PARDO R, BARRADO E. Assessment of seasonal and polluting effects on the quality of river water by exploratory data analysis [J]. Water Research, 1998, 32(12): 3581-3592. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(98)00138-9 [37] LIU W C, KEN P J, LIU H M. Transport and distribution of manganese in tidal estuarine system in Taiwan [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2020, 27: 510-531. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06797-1 [38] RAHIM A, KASMURI N. Assessment of water quality index and heavy metals in Sungai Bunus, Malaysia [J]. Journal of Physics:Conference Series, 2020, 2: 22-28. doi: 10.34306/conferenceseries.v2i11.330 [39] CHRISTER P, JOHAN I, KURT B. Geochemistry of manganese in the Kalix River, northern Sweden [J]. Pergamon, 1992, 56: 1485-1494. [40] DUNCAN L, WILLIAM D, COLIN W. Manganese chemistry in rivers and streams [J]. Pergamon, 1984, 48: 2107-2111. [41] 陆凤. 贵州典型锰矿区锰渣重金属污染特征及环境效应[D]. 贵阳, 贵州大学, 2018, 1 − 91. LU F. Characteristics of heavy metal pollution and environmental effects from manganese residues in typical manganese mining area in Guizhou[D]. Guiyang, Guizhou University, 2018,1 - 91.
[42] 蒋宗宏, 陆凤, 陈淼, 等. 贵州铜仁典型锰矿区土壤及蔬菜重金属污染特征及健康风险评价 [J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2020, 37(2): 293-300. JIANG Z H, LU F, CHEN M, et al. Characteristics and health risk assessments of heavy metals in soils and vegetables in manganese mining areas in Tongren County, Guizhou Province, China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2020, 37(2): 293-300(in Chinese).
[43] 杨育红, 沈万斌. 地表水非点源污染负荷计算方法探讨 [J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2006, 36: 105-107. YANG Y H, SHEN W B. Preliminary study on estimating surface water non-point source pollution loads [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 2006, 36: 105-107(in Chinese).
[44] 朱晓娟, 沈万斌, 高凯, 等. 吉林省松花江干流氨氮综合衰减系数分段研究 [J]. 科学技术与工程, 2013, 13(10): 2758-2761. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2013.10.028 ZHU X J, SHEN W B, GAO K, et al. Sectional study on ammonia nitrogen comprehensive attenuation coefficient of Songhua River trunk stream in Jilin Province [J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2013, 13(10): 2758-2761(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2013.10.028
-



 下载:
下载: