-
微塑料是粒径小于5 mm的塑料碎片(microplastics, MPs),是环境中一类新兴污染物。已有大量研究证实微塑料广泛存在于海洋、河流、湖泊、海滩、河口等各种水体、农田土壤中,成为全球关注的环境问题[1–4]。已检测到的微塑料主要类型有聚乙烯(PE)、聚丙烯(PP)、聚苯乙烯(PS)、聚氯乙烯(PVC)、聚酰胺(PA)和聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯(PET)[1,5–14]。微塑料粒径小、比表面积大且疏水性强,可吸附有毒有害物质,成为有毒化学物质在环境中迁移的载体,从而改变两者的环境行为和生物效应[15]。已有大量的研究表明微塑料与污染物可长期共存,作为多环芳烃(PAHs)、多氯联苯(PCBs)、六氯环己烷(HCHs)、滴滴涕(DDTs)等有机污染物的载体[1,5–14]。不少文献也研究了微塑料与有机污染物的吸附机理及其影响因素,例如微塑料颗粒大小、微塑料和有机物结构、环境因素都会影响其吸附行为[6–8,16–22]。同时,微塑料与污染物的联合毒性效应也被广泛关注[6,23–29]。例如,微塑料可以作为载体促进生物体对有机污染物吸收,造成生物体内毒性物质增高从而加剧了组织损伤以及机能减弱[23,24]。微塑料也可以减少生物体对污染物的吸附以及富集率并通过竞争吸附降低污染物的生物利用度以及毒性[27-28,30]。
因此,本文就国内外微塑料与有机污染物的相互作用及毒性效应的研究进展进行综述,重点分析不同介质中微塑料与有机污染物的共存水平、吸附机理、影响因素以及联合毒性效应等,并对其今后的相关研究发展趋势进行了展望,以期为微塑料与有机污染物共存及作用机制的环境风险评估及污染控制提供参考[17]。
-
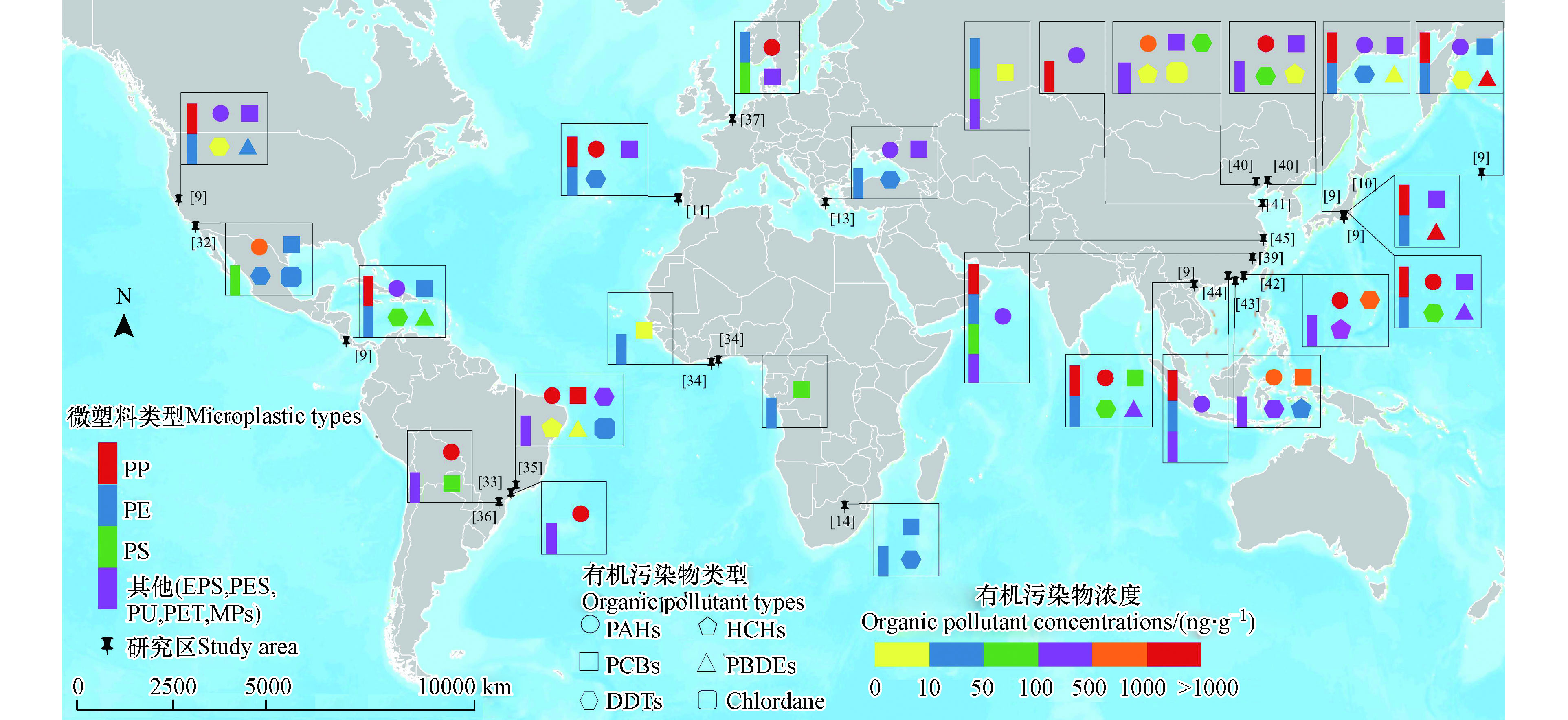
目前在微塑料中检测到的有机物大多数是持久性有机污染物,如多氯联苯(PCBs)、多环芳烃(PAHs)、有机氯农药(OCPs)等,其吸附浓度从μg·g−1到pg·g−1不等,不同区域与微塑料共存的有机污染物浓度相差巨大[6]。本文基于文献调查,总结了国内外相关研究中环境微塑料与有机污染物的共存情况,图1显示了全球水环境与土壤环境中微塑料与有机污染物的共存种类、在全球的分布情况、以及微塑料与有机物的共存水平等特征。
全球环境中微塑料与有机污染物共存的现象主要发生在太平洋沿岸、大西洋西岸、南美洲沿海地区、非洲沿海地区以及欧洲沿海地区[9,12,14,31–34](图1所示)。例如,日本和美国部分沿海地区的海滩微塑料中PCBs的浓度范围为0.28—436 ng·g−1,高于哥斯达黎加和越南偏远海滩微塑料中的PCBs浓度(1—102 ng·g−1),这是因为在六七十年代,日本等发达国家经济高速增长,向沿海环境释放了大量的PCBs[9-10,31]。在日本海滩收集的样品中,由于PE具有高疏水性,其PCBs的浓度高于PP[9-10]。加利福尼亚圣地亚哥的微塑料中PCBs的浓度比较低,这与政府禁止使用此类持久性有机污染物有关[31]。太平洋沿岸的微塑料碎片中也检测到PAHs (0—3028 ng·g−1),城市海滩的微塑料样本中PAHs浓度较高,这是因为城市海滩更靠近工业生产以及人为活动[9,31]。另外,Van等[31]指出,PS泡沫塑料生产过程会产生PAHs,因此污染物在PS泡沫的浓度(240—1700 ng·g−1)远高于PS原始颗粒(12—15 ng·g−1)以及其他微塑料颗粒。DDTs的空间分布与PCBs和PAHs不同,在东京、洛杉矶、圣地亚哥的城市海滩微塑料中的浓度偏低(0.2—52 ng·g−1、2.2—8.4 ng·g−1、n.d.—76 ng·g−1),而越南、哥斯达黎加地区微塑料中DDTs含量偏高(n.d.—124.4 ng·g−1、11—108 ng·g−1)[9,32]。这是因为在大多数国家,DDTs被禁止应用在农业生产中,现存的少量DDTs主要是环境遗留污染物,少数热带国家会使用少量的DDTs来控制疟疾从而导致DDTs含量偏高[9,31]。
在大西洋西岸南美洲沿海地区,巴西沿海作为主要的工业、港口和石油码头所在地,海水系统受到严重的有机污染物污染[34]。在人口聚集、船只交通航道以及用于工业生产的码头区域的海岸线,微塑料中PAHs浓度偏高(192—13708 ng·g−1)[32,34-35]。圣保罗州是世界上PCBs污染最严重的区域之一,其微塑料中PCBs的浓度 (3.41—7554 ng·g−1)远高于在巴拉那州海岸线的微塑料中PCBs的浓度(0.8—104.6 ng·g−1)[34-35]。Taniguchi等[34]的调查结果显示,由于被大量使用于农业生产以及抗击疟疾,圣保罗州海岸线海滩微塑料中DDTs的浓度偏高(<0.11—840 ng·g−1)。
在大西洋东岸的非洲发展中国家,缺乏处理有机污染物的基础设施和资源,导致微塑料中有害物质含量较高[33]。Hosoda等[33]的研究表明,PCBs从加纳阿克拉和特马市区的电子废物现场引入河流,导致城市地区PCBs的浓度(39—69 ng·g−1)高于沿海乡镇(1—15 ng·g−1)。Ryan等[14]检测了1989—2008年间南非沿海水域的PE与POPs的共存情况,研究表明,微塑料主要来源于商业港口以及主要工业区(包括塑料,炭黑,轮胎和车辆制造),PE中POPs共存情况分别为PCBs(25—61 ng·g−1)、HCHs(2—5 ng·g−1)、DDTs(8—31 ng·g−1),近年来由于政府采取相应措施,PCBs、HCHs、DDTs的浓度均呈下降趋势,但用于控制疟疾的DDTs浓度仍然很高。
PAHs、PCBs、DDTs在欧洲沿海地区的微塑料中也广泛存在。PAHs在葡萄牙沿海的微塑料中含量偏高,浓度范围为53—44800 ng·g−1,这可能是由于船舶和工业活动的机油泄漏引起的[11]。其次是比利时沿海地区,浓度范围为1076—3007 ng·g−1,这与该地区高度城市化和工业化有关[36]。希腊海滩微塑料中PAHs的浓度则低得多,为100—500 ng·g−1[13]。另外,PCBs在葡萄牙、比利时以及希腊沿海地区浓度范围相近,分别为2—223 ng·g−1、31—236 ng·g−1、0.09—270 ng·g−1[11,13,36]。DDTs在葡萄牙以及希腊海滩的浓度范围分别为0.42—41 ng·g−1和1.1—42 ng·g−1,DDTs的来源可能是早期农业生产的遗留物[11,13]。
在我国,水体中微塑料与有机污染物共存的现象主要集中在东部、南部沿海地区。工业生产、农业活动以及煤炭的燃烧都可使微塑料中有机污染物浓度增加[37]。Tang等[38]等指出,微塑料污染源包括废物废水排放、海水养殖活动、工业活动以及农业生产,河流径流、人口密度和城市化率均可影响地表水中微塑料的分布。渤海和黄海地区是中国最重要的经济区和重工业基地之一,其微塑料主要为PP、PE、PS,共存的有机污染物主要有PAHs、DDTs、PCBs、HCHs[37,39-40]。秦皇岛东山海滩以及大连正明寺海滩地区检测到PAHs (136.3—2384.2 ng·g−1)、DDTs (1.15—126.95 ng·g−1)、PCBs (21.5—323.2 ng·g−1)[39]。其中,石油产品、煤炭燃烧和港口煤尘是微塑料中PAHs的重要来源,DDTs主要来源于过去农业生产的残留污染物以及船舶上的防污涂料泄漏[39]。黄岛和麦岛沿海地区微塑料中PAHs浓度范围为0.114—0.245 μg·g−1和0.072—0.261 μg·g−1,污水排污口和养殖区是有机污染物的典型污染源[40]。Zhang等[37]等发现,山东半岛沿海地区的地表水微塑料(PE、PP、PS)中有机磷酸酯(OPE)和邻苯二甲酸酯(PAE)的共存现象,OPE的浓度(0—84595.9 ng·g−1)远高于PAE(0–80.4 ng·g−1),微塑料主要来源于树脂颗粒以及风化后的塑料碎片(捕鱼、水产养殖和包装袋中产生的塑料碎片)。
南海是中国船运交通要道,沿海地区微塑料(主要为PP、PE)中主要存在的有机污染物为PAHs、PCBs、DDTs、HCHs。PAHs在汕头湾的浓度偏高(11.2—7714 ng·g−1)[41],其次是中国香港西部和东部水域(70.8—1509 ng·g−1)[42],厦门沿海PAHs 的浓度范围为18.13—247.8 ng·L−1[39],靠近港口、工业区和城市地区的海滩微塑料中PAHs浓度高于偏远海滩。汕头湾的的沉积微塑料中还检测到DDTs (nd —1183 ng·g−1)和HCHs (0.63—782 ng·g−1),研究指出DDTs主要来源于农业水产养殖活动以及渔船上防污涂料的泄漏[41]。在中国香港地区的微塑料中还检测到PCBs、DDX、HCHs,其浓度范围分别为13—1083 ng·g−1、1.96—626 ng·g−1、5.02—63.5 ng·g−1[42]。
受到沿岸的工业以及农业影响,有机污染物进入内陆淡水系统随着水的流动而迁移,并吸附在沉积物中[43]。研究发现,江河沉积物中主要存在的微塑料为PE、PP、PS以及PET[43-44]。例如,北江飞来峡水库地表水中EPS(比表面积较大)对PAHs的吸附能力高于PE和PP,微塑料赋存的PAHs的浓度范围为282.4—427.3 ng·g−1,其主要来源是化石燃料的不完全燃烧并且受到沿岸冶金、采矿和热力发电行业的影响[43]。Fraser等[45]的研究指出,陆上塑料废物可以通过河流输入到海洋环境,PE、PS和PET是钱塘江和杭州湾沉积物样品中主要的微塑料类型,这与它们在农业、水产养殖和工业中的广泛使用有关。其中,赋存在微塑料中的PCBs浓度范围为1.13—1.65 ng·g−1,PCBs浓度会随着深度的增加而增加。
针对土壤,Lu等[45]对福州市郊区农业土壤中微塑料与污染物共存情况进行了研究,检测到的抗生素为四环素(16.16—40.20 μg·kg−1)、土霉素(29.70—107.20 μg·kg−1)、金霉素(24.02—81.02 μg·kg−1)、氧氟沙星(17.08—63.18 μg·kg−1)。研究表明,土壤中微塑料与抗生素的共存水平较高,并且粒径较大或风化度相对较高的微塑料以及蔬菜栽培时间相对较长的土壤中的微塑料可以吸附更多的抗生素。目前关于土壤中的共存研究比较匮乏,从仅有的研究可以得出,在使用农药的农业土壤中,地膜覆盖的微塑料可能作为农药的载体从而加剧污染物的危害[18]。
综上所述,太平洋沿海、大西洋沿岸、非洲沿海以及我国的沿海地区的微塑料主要是PP、PE、PS,微塑料可以作为有机污染物的载体,使污染物进行迁移和累积。微塑料中存在的有机物主要类型为PAHs、PCBs、HCHs、DDTs,其浓度受区域差异影响较大。DDTs主要来源于过去农业生产的污染物残留;少数热带国家使用DDTs控制疟疾疾病也会导致其浓度也偏高。PAHs与PCBs主要来源于石油产品、煤炭燃烧和港口煤尘,其浓度与工业生产、港口运输等有紧密关系,巴西沿海地区以及太平洋西岸是污染比较严重的区域之一。另外,由于非洲发展中国家缺乏处理有机污染物的基础设施和资源,导致微塑料中PAHs与PCBs浓度偏高。因此,在评估海域水体微塑料中有机污染物的浓度和组成差异时,应考虑工业活动、农业活动等人为因素的影响。另外,从已有研究得出,土壤环境微塑料中有机污染物主要来源于农膜大量使用以及灌溉残留物[18],但针对土壤微塑料本身以及土壤微塑料与有机污染物共存的相关系统研究仍有待进一步深入。
-
实际环境的复杂性以及污染物在微塑料上的多样性分布,导致环境检测结果仅能体现微塑料与污染物的共存水平,很难解释其吸附行为和吸附机理,因此大量有关微塑料与有机污染物的吸附行为研究在实验室进行[1]。本节查阅并总结2016年至今收录在ScienceDirect和SpringerLink数据库中关于实验室中微塑料与有机污染物吸附行为的相关文献(图2),发现研究最多的微塑料类型是PE,占文献调研结果的33%,其次是PS(24%)、PP(23%)、PVC(16%)、PA(8%),这也是目前环境中大量存在的微塑料类型。在本文选取的文献中,研究微塑料与抗生素的吸附行为的文献占26%,药品和个人护理产品(PPCP)和PAHs均占总文献的20%,另外,相关的文献还覆盖了农药、全氟烷基酸(PFAAs)、阻燃剂(BFRs)、激素、卤代咔唑(PHC)、双酚类似物、PBDEs、油类、PCBs等有机污染物在微塑料上的吸附行为。
文献调研发现,这些微塑料与有机污染物的吸附行为的研究方法主要采用动力学模型,例如PFOM模型[19,46–48]、PSOM模型[17-18,20,22,49–59]和等温线模型,例如线性等温线模型[7,16–18,20,50,54,56,58,60-61]、Freundlich等温线模型[18,22,46,48,51-53,54–57,62–64]、Langmuir等温线模型[19,22,47–50,53,59,63,65]等对其吸附行为进行模拟,以快速预测环境中的不同微塑料对有机污染物的吸附能力[67]。研究进一步揭示了微塑料与有机污染物的吸附机理,吸附机理主要包括疏水作用[7,16-17,50-52,54–57,58–62,64-65]、静电作用[46,51,54–58,61-62,66]、范德华相互作用[20,56,61,62,65]、表面络合作用[54,55]、极性相互作用[66]、π-π键[16,60,66]、氢键[57,62]、单层覆盖[19,22,48–49]、孔填充机理[48,63]、颗粒内扩散[52]等。
作为新兴污染物,每年都有大量药品和个人护理产品(PPCP)释放到环境中产生不利影响,特别是抗生素,由于其对微生物群落的不利影响而受到越来越多的关注[62]。例如,Xu等[66]通过伪二级动力学模型和线性模型、Freundlich等温线模型研究了磺胺甲恶唑(SMX)在PE上的吸附行为,结果表明,吸附过程涉及疏水相互作用和其他相互作用(例如静电作用)。因此,塑料对不同污染物的吸附能力与污染物本身的疏水作用有关[55,60-61]。Elizalde-Velázquez等[60]指出微塑料(UHMWPE、AMWPE、PS、PP)对抗炎药的吸附能力遵循双氯芬酸钠(DCF)≈布洛芬(IBU)>萘普生(NPX),吸附能力也取决于疏水分配作用。Wu等[61]指出,PE与疏水性药物的结合性更高,因此对3种药物的吸附能力遵循4-甲基亚苄基樟脑(4MBC)>三氯生(TCS)>17α-乙炔雌二醇(EE2)>卡马西平(CBZ)。同样,PE也会降低亲水性药物(SMX)在水生生物组织中的生物蓄积潜力,Razanajatovo 等[54]的研究表明,药物在PE微塑料上的吸附量遵循舍曲林(SER)>普萘洛尔(PRP)>磺胺甲恶唑(SMX)。不少文献进一步比较了不同种类微塑料对抗生素和PPCP的吸附能力的差异,结果表明微塑料的吸附能力与其自身的疏水性、比表面积、官能团特性都有密切关系[55-57,60,63,65]。例如,Guo等[55]的研究指出,泰乐菌素(TYL)在微塑料上的吸附能力遵循PVC>PS>PP>PE,这可能与微塑料的疏水性和比表面积有关。Guo等[56]指出,磺胺二甲嘧啶(SMT)在不同类型的微塑料上的吸附能力遵循PA>PET>PE>PVC>PS>PP,参与吸附的主要机理是静电和范德华相互作用,微塑料极性可以增强微塑料对污染物的吸附能力。Li等[63]的研究指出,相比于PE、PS、PP、PVC,拥有特定官能团的PA对抗生素吸附力更强。Xu等[65]的研究结果表明,四环素在PS上的吸附能力高于PE和PP,这主要是极性相互作用和π-π相互作用增加了PS对四环素的吸附。Elizalde-Velázquez等[61]的研究表明,微塑料对非甾体类抗炎药的吸附能力遵循PE>PS>PP,这与微塑料的比表面积有关。pH值也可能影响微塑料与抗生素、PPCP的吸附能力,例如,在3—6的pH范围内,三氯生(TCS)对PS的吸附比较高,当pH>6时,TCS与带负电的PS产生静电排斥导致吸附降低[58]。Zhang等[58]指出,PS与土霉素的最大吸附发生在pH 5时,是因为微塑料表面与土霉素两性离子之间的静电排斥最小。同时,老化也会影响微塑料和污染物的吸附行为,例如,风化的PP对TCS的吸附能力要高于新的PP,因为老化的微塑料,具有较高的比表、微孔面积和氧化程度,具有更强的吸附能力[46]。
PAHs和农药均是有较强的致突变性和致癌性的有机化合物[16]。有机污染物的疏水性以及极性同样会影响其与微塑料的吸附行为,例如,Wang等[16]指出,相比于非极性菲,疏水分配和π-π相互作用可以显著增强PS对极性硝基苯的吸附作用。与前文结论类似,微塑料的尺寸(比表面积)以及结构特性同样可以影响其对PAHs和农药的吸附能力,例如,Wang等[59]的研究结果表明,3种微塑料对菲的吸附能力依次为PE>PS>PVC。在Wang等[50]的研究中,PE、PS、PVC对芘的吸附能力也遵循PE>PS>PVC。Zhang等[50]研究了9-NAnt与微塑料的吸附行为,吸附能力遵循PE>PS≈PP。3项研究的结果表明,PE对有机污染物的高吸附能力与其较大表面积和类似橡胶的特性有关[49]。除此之外,微塑料表面的官能团也会影响微塑料的吸附能力,Gong等[18]研究指出,可降解微塑料表面含氧官能团(羰基氧)可与氟虫腈的极性部分形成分子间氢键,该键强于氟虫腈与不可降解的微塑料之间的疏水相互作用和π-π相互作用,从而导致聚乳酸(PLA)和聚丁二酸丁二酯(PBS)对氟虫腈的吸附速率远高于PE、PP、PVC、PS。
此外,不少文献针对其它有机污染物与微塑料的吸附能力进行了比较和分析。微塑料的理化性质和分子结构同样影响了其在润滑油、全氟烷基酸(PFAAs)、阻燃剂、激素上的吸附行为[7,48,54,64]。Hu等[54]的研究表明,在pH 5和温度为293 K下,润滑油在纳米PE和PS上的最大吸附容量分别为7.3 g·g−1和6.1 g·g−1,比表面积大的微塑料颗粒拥有更高的吸附能力。Wang等[7]的研究指出,由于官能团的不同,FOSA在PE上的吸附水平高于PFOS,微塑料的分子组成和结构(表面含氧官能团(羰基氧)和橡胶域空间排列)也造成了PFOS和FOSA在PE和PVC上的吸附作用强于PS。Chen等[49]也指出,由于PE和PVC的物理化学性质以及分子结构不同,从而导致PVC对磷酸三(2-氯乙基)酯(TCEP)的亲和力高于PE,但PVC对磷酸三正丁酯(TnBP)低于PE。Liu等[64]的研究指出,海水系统中17β-雌二醇(E2)激素在微塑料上的吸附能力依次为PA>HD/LLD-PE>PP>LD/MD-PE>PS>PC>PMMA>PVC,吸附能力差异主要是由于结晶度不同引起。同样,由于不同的结晶度、比表面积和表面结构,PS对多溴联苯醚(PBDEs)吸附能力高于其他3种微塑料,顺序遵循PS> PA> PP> PE[53]。另外,一些文献通过动力学模型和等温线模型来模拟和预测微塑料对有机污染物的吸附量。例如,Liu等[47]的研究结果表明,在15 ℃和14%盐度,PP对阻燃剂三(2,3-二溴丙基)异氰脲酸酯(TBC)和六溴环十二烷的吸附容量最大,为1954—21489 ng·g−1,TBC的吸附容量远高于HBCD。Zhang等[22]PP与3,6-二溴咔唑(3,6-BCZ)和1,3,6,8-四溴咔唑(1,3,6,8-BCZ)的平衡吸附时间分别约为6 h和8 h,最大吸附容量分别约为6400 ng·g−1和8000 ng·g−1。Zhan等[19]指出,PP在海水、超纯水、正己烷溶液中对3,3',4,4'-四氯联苯(PCB77)的吸附量不同,分别为344.8 μg·g−1、192.3 μg·g−1、93.45 μg·g−1。结果表明,3种类型的有机污染物与微塑料均为化学吸附,并且温度、盐度、反应时间等因素都会对吸附行为产生不同程度的影响。
综上所述,有机污染物在微塑料上的行为主要遵循PFOM、PSOM吸附动力学模型,等温线模型,例如Freundlich、Langmuir模型和线性模型等。有机污染物的疏水性以及微塑料的疏水性、比表面积、官能团特性都会影响其吸附能力。因此,长期存留在环境中的微塑料可以作为污染物在环境中运输的载体。然而,实验室模拟的环境因素较为单一,无法与真实的复杂环境相比,因此得出的仅为理论结论,缺乏特定的物理意义。
-
对影响其吸附行为的因素进行系统的总结,主要包括微塑料的理化性质、污染物的结构以及吸附介质因素对吸附行为的影响。主要包括以下几个方面:
-
研究表明,吸附剂的理化特性会显著影响吸附行为[18,66]。粒径大小是影响污染物的吸附行为的主要因素,这是因为较小尺寸的颗粒具有较大的表面积,可提供的吸附位点多,从而增加液固接触的面积,增大了微塑料的吸附能力[17,19,21,47,51,53,55,58,61]。例如,Zhang等[50]的研究结果表明,当PE和PP的粒径从1.7 mm减小至0.15 mm,其对9-NAnt的吸附容量分别从从0.28%增至1.66%和0.30%增至1.63%。Wang等[17]的研究指出,在相同质量的情况下,尺寸从10 mm减小到1 mm的PE和尼龙对菲吸附作用的提升明显(分别为23.1%、10.4%),随着粒径的减小,可增强微塑料的污染物转移效果。Zhan等[19]的研究显示,当微塑料粒径从2.0—5.0 mm增加到0.18—0.425 mm,其对PCB77的吸附量从>60 μg·g−1增长到>210 μg·g−1,这表明微塑料的吸附能力随着粒径的减小而显着增加。然而仍存在一些特殊情况,菲在50 nm纳米PS的吸附量明显较低,这是由于纳米PS的团聚作用减小了其比表面积[16]。
-
研究表明,微塑料的理化特性可能会显着影响其与有机污染物的吸附过程[18]。微塑料的成分差异可能体现在其聚合物结构单元中含有官能团以及微塑料的橡胶区域特性,这会影响微塑料对污染物的吸附[17-18,46,49,50,55-57,60–63,64-66,67]。例如,Wang等[17]的研究表明,PE(无亲水性官能团)比尼龙(具有亲水性基团)对菲具有更强的吸附能力。Gong等[18]的研究结果显示,氟虫腈在可降解微塑料PLA和PBS上的最大吸附量(228.7 μg·g−1和720.2 μg·g−1)明显高于不可降解的PE、PS、PVC和PP的最大吸附量(38.3—62.7 μg·g−1),这是因为可降解微塑料中存在的羰基氧官能团与氟虫腈之间的氢键强于氟虫腈与不可降解的微塑料之间的疏水相互作用和π-π相互作用。另外,PBS(橡胶状聚合物)对氟虫腈的吸收量比PLA(玻璃状聚合物)更高,这是因为前者具有较高的自由体积,因此对有机污染物的吸附性较高[18]。Li等[63]也表明,由于特定的官能团(即酰胺基)与污染物的羰基之间形成氢键,PA对AMX、TC和CIP具有高吸附性。Zhang等[49]指出,PE、PS、PVC对芘的吸附能力也遵循PE>PS>PVC,PE的类似橡胶的特性可能导致PE对芘的吸附量高于PS或PVC上芘吸收量的重要因素。
另外,在环境中长期存在的微塑料表面会有不同程度的风化以及老化,老化过程可以改变微塑料的表面性质(尺寸、表面积、孔隙率、表面极性),进而改变微塑料的吸附能力[46]。Wu等[46]的研究表明,老化的PP颗粒具有较宽松的物质结构和更大的非晶体结构域从而形成较小尺寸的塑料颗粒,并且老化过程将有助于在颗粒表面产生更多可用的吸附位点,这都可以提高PP对TCS的吸附能力。Zhang等[51]使用人工老化模式研究老化过程对微塑料吸附9-NAnt的影响,结果表明,PS的吸附量最多降低了33.76%,这是因为老化过程会引入含氧的官能团,增强微塑料的表面极性,从而阻碍了疏水性有机污染物的吸附过程。
-
有机污染物的疏水性是影响其吸附强弱的关键因素,疏水性强的有机污染物更容易被吸附在微塑料表面,有机物分子结构中官能团和极性影响分配行为,静电作用也会在一定程度上增强与微塑料的吸附行为[7,60,62-63,66]。例如,Razanajatovo等[69]的研究指出,药物SMX、PRP、SER在PE上的吸附百分比大小遵循SER(28.61%)>PRP(21.61%)>SMX(15.31%),与其疏水性正相关(SMX的lg
KOW <2为低疏水性,PRP的lgKOW <3.5为中等疏水性,SER的lgKOW >3.5为高疏水性)。Li等[62]的研究指出,由于特定官能团的存在,抗生素(SDZ、AMX、CIP、TMP、TC)表现出不同的阳离子、两性离子和阴离子形态,从而造成其在微塑料上的吸附能力不同。Wang等[7]指出,阴离子PFOS分子在PE表面可以产生静电排斥从而减少其在PE颗粒上的分配,而非离子FOSA分子可以容易地在PE颗粒上分配,另外,由于PE是非极性材料,因此对极性更强的PFOS吸附力更高(FOSA是一种高度对称的分子,极性较低)。 -
环境介质不同时,同种微塑料对同种有机污染物的吸附强度差异显著[66]。盐度是环境中差异最大的性质之一,盐度会影响诸如土壤,黏土和沉积物等天然吸附剂对疏水性有机化合物的溶解性,较高浓度的Ca2+和Na+会强烈竞争微塑料表面上的阳离子交换位点从而降低微塑料对有机污染物的吸附能力[19,48,56,62,63,67-67]。例如,Zhan等[19]指出,在模拟海水中,PP对PCB77的吸附量(120 μg·g−1)约为在超纯水中吸附量(约为60 μg·g−1)的两倍。Guo等[56]研究表明,由于阳离子Na+更易于与微塑料的阴离子表面相互作用,当盐度增加,部分静电位点被Na+占据,造成SMT的吸附能力相对降低。此外,离子强度也会影响微塑料的吸附行为[55,57,63]。Guo等[56]的研究表明,随着离子强度增加到一定的浓度,大量的K+与TYL在微塑料的吸附位点上竞争,这会导致吸附相对减少。
另外,pH值也会影响微塑料对有机污染物的吸附,这是因为pH值可以通过改变微塑料和有机污染物的质子化程度使其呈现出不同的带电性从而改变吸附行为[7,46,51,55–58,61,65-67]。例如,Zhang等[50]的研究表明,随着pH值的增加,9-NAnt与PP、PS之间的静电吸引减弱,吸附能力显着下降。另外,对于土霉素而言,在pH值为5时,滩涂样品的表面电荷接近零电荷点,其静电排斥力最低,吸附能力最强;当pH值增高或降低时(pH<5.0或>5.0),由于带电荷的吸附剂和被吸附物电荷相似,静电排斥力更高从而导致吸附能力降低[58]。
最后,介质温度也是影响吸附行为的因素之一。研究表明,随着温度的升高,活性剂的表面张力降低,这削弱了微塑料与表面活性剂的结合,导致吸附能力下降,另外,在高温下,吸附分子的迁移率和溶解度增加,范德华力随着温度的升高而降低,也会导致吸附能力降低[19,21,47-49,52,68]。例如,Zhan等[19]的研究表明,随着温度从19°C升高到27°C,PP对PCB77的吸附量从140 μg·g−1减少到100 μg·g−1,高温会降低溶液的表面张力从而对PP吸附的PCB77产生不利影响。Qiu等[67]的研究指出,高温模拟海水中活性增加的离子可能与多卤咔唑竞争这些塑料颗粒表面上的吸附位点,从而降低了微塑料颗粒的吸附能力。另外,Chen等[49]的研究表明,温度的升高除了会使表面活性剂的表面张力降低,温度的升高也会使TnBP和TECP在高温下的随机分子热运动比在低温下更剧烈,导致污染物和PE之间的范德华力降低,从而价降低其吸附能力。
综上所述,影响微塑料对有机污染物吸附的影响因素主要有:(1)微塑料颗粒大小,通常微塑料粒径越小,比表面积越大,吸附有机物的能力强。(2)微塑料和有机物结构,官能团结构、极性、聚合物状态、微塑料老化程度是影响微塑料与有机物吸附能力的重要因素,通常,老化会增加微塑料比表面积增加吸附能力;官能团极性越强吸附能力越强;疏水性越强吸附能力越强;有机污染物对橡胶状塑料的亲和力比玻璃态塑料高;带电的可解离有机污染物吸附能力高。(3)环境因素,通常,温度越高吸附能力下降;盐度越高吸附能力越弱;pH值可以改变吸附行为。
-
研究发现,微塑料与污染物共存时会产生协同作用,微塑料可作为有机污染物的载体进入生物体的组织和器官内。例如,吸附在PE和PS颗粒上的芘可以被转移到紫贻贝体内的血淋巴、腮、消化系统中[25]。吸附到微塑料颗粒上的卤代污染物也可以被鲈鱼的肠道系统吸收并转移到循环系统中[68]。有文献指出,微塑料有助于改变污染物在生物体内的分布并导致生物利用度以及生物蓄积的增加[26,71]。例如,在NPs的存在下,浮游水蚤(Daphnia Magna)体内菲的蓄积量是无塑料对照组中菲蓄积量的3倍[24]。与单独使用BPA相比,NPs与BPA共同作用下会使斑马鱼头部和内脏的BPA的含量增加2.2—2.6倍[70]。另外,Besseling等[73]的研究表明,较低的PS剂量可将沙蠋体内PCBs的生物蓄积提高到无微塑对照组的1.1—3.6倍。其中,微塑料的尺寸(比表面积)在很大程度上影响有机污染物的生物蓄积[23-24]。例如,相比于MPs,具有较高比表面积的NPs(对疏水性有机污染物的吸附能力较高)可以显著增强水蚤消化道内菲的生物蓄积[24]。500 nm的PS颗粒比30 μm的颗粒有更高的渗透能力,可以更有效地释放其携带苯并(a)芘(BaP)以及雌二醇(E2)进入泥蚶生物体内部[72]。微塑料的浓度也会影响联合作用的生物蓄积与毒性作用,Li等[75]指出,低浓度PS与DBP对小球藻具有拮抗作用,而在较高微塑料浓度下则具有协同作用。因此,在研究微塑料与有机污染物的相互作用时必须综合考虑微塑料和污染物的浓度以及吸附能力。
微塑料与有机污染物的联合作用在增强生物体内污染物蓄积的同时,也会增强急性毒性、神经毒性、发育毒性,对生物的组织器官等系统造成损害[6]。例如,PE和PS与芘的联合作用可以增加紫贻贝对芘的吸收,影响其免疫反应、遗传毒性作用和神经毒性反应,其中PE可导致溶酶体膜的稳定性降低并出现炎症反应[25]。NPs(纳米塑料)和BPA通过循环系统积聚在斑马鱼头部,从而的正常运行[70]。PS与BaP和E2的联合毒性作用会导致泥蚶体内血细胞的吞噬能力降低并限制血细胞对异物的识别、吞噬和降解[74]。Browne等[23]的研究表明,PVC与壬基酚联合作用降低60%以上结肠细胞去除病原细菌的能力,PVC与三氯生的结合会造成55%以上蠕虫的死亡率。联合作用还会降低生物机体机能、免疫功能、摄食能力,并使得生物抵御外源污染物的能力降低[6]。例如,NPs增强了菲对水蚤的慢性毒性并影响其发育和繁殖能力[24]。PE会使芘显着降低虾虎鱼体内乙酰胆碱酯酶、异柠檬酸脱氢酶的活性,影响其生长、繁殖以及生存活动[74]。壬基酚、菲和PVC的联合作用会降低沙蠋的生存率、摄食量和免疫力[23]。氯吡硫磷(CPF)与PE联合使用显示出比单独使用更高的毒性,毒性作用会影响纺锤水蚤的存活率、产卵率、进食以及孵化率[26]。
-
另一方面,微塑料(PE、PP)的存在也会降低环境中溶解的有机污染物的浓度,这是因为微塑料与污染物的吸附行为能够降低环境中有害物质的自由态,从而降低了有机污染物的致命毒性[6,69]。例如,由于TCS与微塑料的竞争吸附降低了有害物质与微藻的接触,使得联合作用毒性小于单一的微塑料和TCS对微藻的毒性[27]。PS的吸附使17α-乙炔雌二醇(EE2)自由溶解浓度降低,减轻了单一EE2对斑马鱼幼虫运动机能的减退作用[28]。关于联合作用减少污染物的致死率,Oliveira等[74]的研究表明,PE颗粒可延缓芘诱发虾虎鱼的死亡,使半数致死时间从29 h延迟至42.1 h。另外,微塑料尺寸也会影响污染物的毒性作用。例如,拥有较小粒径决定了PVC和PVC800与TCS的联合毒性比PE和PS的毒性降低了更多[27]。同样,相比于PE、PS、PA,PE1000和PA1000(具有较大的比表面积)对壬基酚(NP)具有更强的吸收能力,可降低自由态NP的浓度,从而减轻NP对藻类PSII活性的抑制作用以及毒性损害[75]。
另外,微塑料能够调节污染物的生物利用率度[6]。通过分析斑马鱼幼体中生物标志物基因表明,PVC的存在将菲和EE2的生物利用度分别降低了33%和48%,其吸附能力与污染物的类型有关[29]。Zhang等[76]的研究表明,由于大量草甘膦被nPS-NH2吸附(其还原性氨基基团更容易与草甘膦结合),导致藻类吸附草甘膦的量比无微塑料时的吸附量大大降低,从而间接降低了草甘膦的生物利用度。同样,Wang等[30]的研究结果表明,土壤环境中的PS颗粒和有机污染物存在竞争吸附,并且PS颗粒也缺乏对有机污染物的载体作用,这会减少蚯蚓(Eisenia fetida)体内PCBs和PAHs的积累。
综上所述,微塑料可以加剧或减缓有机污染物对生物的毒性作用,目前微塑料与有机污染物的联合毒性的相关研究仍处于比较初级的水平。现有的文献表明(表1),微塑料加剧毒性作用主要来自于两方面,一是微塑料作为载体促进生物体对有机污染物吸收,增加生物利用度蓄积量,造成生物体内有毒有害物质浓度升高;二是微塑料加剧了组织损伤以及机能减弱,并可能影响生物的摄食和抵御能力。微塑料减缓毒性作用主要表现在减少生物体对污染物的吸附以及富集率,另外,微塑料的竞争吸附也可导致污染物生物利用度以及毒性的降低。然而,现实环境中可能出现多种污染物共存的情况,彼此间存在交互作用(拮抗作用和协同作用等),这可能会对现有的研究结果产生影响。总之,影响联合毒性的因素比较复杂,与微塑料尺寸、有机污染物类型以及环境介质关系密切,未来的研究需要进一步综合考虑微塑料对生物联合毒性的影响。
-
通过文献回顾,本文总结了近年来在不同地区的环境介质中微塑料与有机污染物的相互作用与分布特征,并讨论了微塑料与有机污染物的吸附行为、影响因素、联合效应等。研究表明,太平洋沿海、大西洋沿岸、非洲沿海以及我国的沿海地区的微塑料主要是PP、PE、PS,微塑料可以作为有机污染物的载体,使污染物进行迁移和累积。微塑料中存在的有机物主要类型为PAHs、PCBs、HCHs、DDTs,其浓度受区域差异影响较大。DDTs主要来源于过去农业生产的污染物残留以及控制疟疾疾病的使用,PAHs与PCBs主要来源于石油产品、煤炭燃烧和港口煤尘,其浓度与工业生产、港口运输等有紧密关系。因此,在评估海域水体微塑料中有机污染物的浓度和组成差异时,应考虑工业活动、农业活动等人为因素的影响。在实验中中,主要通过吸附动力学(主要遵循PFOM、PSOM吸附动力学)以及等温线模型(包括Freundlich、Langmuir模型和线性模型)对吸附行为进行研究,反应机理主要为物理吸附以及化学吸附(包括氢键,疏水作用,范德华力及静电相互作用)。影响微塑料对有机污染物吸附的影响因素主要有:微塑料尺寸、微塑料结构(理化性质以及老化程度)、有机污染物结构(则包括其疏水性、官能团和空间结构)以及环境因素(pH、温度、盐度、离子强度等)。最后,本文总结了微塑料与污染物的联合作用,包括拮抗和协调作用。环境微塑料可吸附水中和土壤中的污染物,并作为污染物的载体,进入生物体内随食物链传递并对生物体产生影响。
从目前的研究看,大量文献主要集中在水生环境中微塑料与污染物的共存情况,但土壤和大气环境中微塑料的研究仍局限于对微塑料种类与丰度的检测,关于大气和土壤环境中微塑料与污染物共存问题知之甚少。因此今后的研究重点应侧重于对土壤、大气环境中污染物与微塑料的共存情况的研究。此外,目前在实验室模拟的研究中,研究因素较孤立,不能很好地解释自然状态下微塑料与污染物相互作用的关系,因此,未来的研究需要进一步综合考虑生物因素以及非生物因素。最后,本文认为,由于不同介质之间可能存在微塑料和污染物物质交换,因此需要更全面、覆盖面更广的监测系统,以评估全球范围内不同区域的微塑料的分布,并量化各种自然过程和人为因素对土壤、水环境、大气中微塑料污染的贡献。
环境微塑料与有机污染物的相互作用及联合毒性效应研究进展
The interaction and combined toxic effects of microplastics and organic pollutants in the environment:A review
-
摘要: 环境微塑料可吸附有机污染物,并与有机污染物进行相互作用从而改变其毒性效应,增加微塑料的治理难度。本文就全球范围内微塑料与有机污染物的相互作用及毒性效应的研究进展进行综述,分析不同介质中微塑料与有机污染物的共存水平、吸附机理、影响因素以及联合毒性效应等。研究表明,微塑料可作为多环芳烃(PAHs)、多氯联苯(PCBs)、六氯环己烷(HCHs)、滴滴涕(DDTs)等有机污染物的载体,并且吸附的有机污染物浓度在不同区域之间差异较大,在拥有大量工业、港口和农业活动的地区浓度较高。微塑料与有机污染物的共存机制主要为疏水分配以及静电相互作用。吸附过程受微塑料粒径、结构、微塑料老化程度、有机物结构(官能团结构、极性、聚合物状态)以及吸附介质(pH值、温度、盐度等)的影响。微塑料与污染物联合作用可增加生物体内有毒有害物质的浓度,并影响生物生理功能从而增加毒性作用;也可以通过降低环境中污染物的自由态,减少污染物的富集率以及利用度从而使毒性效应减弱。最后,本文提出了现有研究的不足并对今后的相关研究发展趋势进行了展望。Abstract: Microplastics in the environment can absorb and interact with organic pollutants to change their toxic effects and increase the difficulty of microplastics treatment. This article reviews the research progress of the interaction between microplastics and organic pollutants and their toxic effects on a global scale, and analyze the coexistence level, adsorption mechanism, influencing factors and joint toxicity effects of microplastics and organic pollutants in different media. Studies have shown that microplastics can be used as carriers for organic pollutants in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), Hexachlorocyclohexane (HCHs), DDTs, and the concentration of adsorbed organic pollutants varies greatly between different regions, and the concentration is higher in regions with a large number of industries, ports and agricultural activities. The coexistence mechanism of microplastics and organic pollutants is mainly hydrophobic distribution and electrostatic interaction. The adsorption process is affected by the size and structure of microplastics, aging degree of microplastics, the structure of pollutants (functional group structure, polarity, polymer state), and the adsorption medium (pH, temperature, salinity, etc.). In addition, the combined effect of microplastics and pollutants can increase the concentration of toxic substances in organisms and affect biological functions to increase toxicity. It is also possible to reduce the free state of pollutants in the environment and reduce the enrichment rate and utilization of pollutants to reduce the toxic effect. Finally, this article puts forward the shortcomings of the existing research and prospects the development trend of related research in the future.
-
Key words:
- Microplastics /
- organic pollutants /
- mechanism of action /
- influencing factors /
- combined toxicity
-
微塑料是粒径小于5 mm的塑料碎片(microplastics, MPs),是环境中一类新兴污染物。已有大量研究证实微塑料广泛存在于海洋、河流、湖泊、海滩、河口等各种水体、农田土壤中,成为全球关注的环境问题[1–4]。已检测到的微塑料主要类型有聚乙烯(PE)、聚丙烯(PP)、聚苯乙烯(PS)、聚氯乙烯(PVC)、聚酰胺(PA)和聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯(PET)[1,5–14]。微塑料粒径小、比表面积大且疏水性强,可吸附有毒有害物质,成为有毒化学物质在环境中迁移的载体,从而改变两者的环境行为和生物效应[15]。已有大量的研究表明微塑料与污染物可长期共存,作为多环芳烃(PAHs)、多氯联苯(PCBs)、六氯环己烷(HCHs)、滴滴涕(DDTs)等有机污染物的载体[1,5–14]。不少文献也研究了微塑料与有机污染物的吸附机理及其影响因素,例如微塑料颗粒大小、微塑料和有机物结构、环境因素都会影响其吸附行为[6–8,16–22]。同时,微塑料与污染物的联合毒性效应也被广泛关注[6,23–29]。例如,微塑料可以作为载体促进生物体对有机污染物吸收,造成生物体内毒性物质增高从而加剧了组织损伤以及机能减弱[23,24]。微塑料也可以减少生物体对污染物的吸附以及富集率并通过竞争吸附降低污染物的生物利用度以及毒性[27-28,30]。
因此,本文就国内外微塑料与有机污染物的相互作用及毒性效应的研究进展进行综述,重点分析不同介质中微塑料与有机污染物的共存水平、吸附机理、影响因素以及联合毒性效应等,并对其今后的相关研究发展趋势进行了展望,以期为微塑料与有机污染物共存及作用机制的环境风险评估及污染控制提供参考[17]。
1. 环境中微塑料与有机污染物的共存特征(Coexistence characteristics of microplastics and organic pollutants in the environment)
目前在微塑料中检测到的有机物大多数是持久性有机污染物,如多氯联苯(PCBs)、多环芳烃(PAHs)、有机氯农药(OCPs)等,其吸附浓度从μg·g−1到pg·g−1不等,不同区域与微塑料共存的有机污染物浓度相差巨大[6]。本文基于文献调查,总结了国内外相关研究中环境微塑料与有机污染物的共存情况,图1显示了全球水环境与土壤环境中微塑料与有机污染物的共存种类、在全球的分布情况、以及微塑料与有机物的共存水平等特征。
全球环境中微塑料与有机污染物共存的现象主要发生在太平洋沿岸、大西洋西岸、南美洲沿海地区、非洲沿海地区以及欧洲沿海地区[9,12,14,31–34](图1所示)。例如,日本和美国部分沿海地区的海滩微塑料中PCBs的浓度范围为0.28—436 ng·g−1,高于哥斯达黎加和越南偏远海滩微塑料中的PCBs浓度(1—102 ng·g−1),这是因为在六七十年代,日本等发达国家经济高速增长,向沿海环境释放了大量的PCBs[9-10,31]。在日本海滩收集的样品中,由于PE具有高疏水性,其PCBs的浓度高于PP[9-10]。加利福尼亚圣地亚哥的微塑料中PCBs的浓度比较低,这与政府禁止使用此类持久性有机污染物有关[31]。太平洋沿岸的微塑料碎片中也检测到PAHs (0—3028 ng·g−1),城市海滩的微塑料样本中PAHs浓度较高,这是因为城市海滩更靠近工业生产以及人为活动[9,31]。另外,Van等[31]指出,PS泡沫塑料生产过程会产生PAHs,因此污染物在PS泡沫的浓度(240—1700 ng·g−1)远高于PS原始颗粒(12—15 ng·g−1)以及其他微塑料颗粒。DDTs的空间分布与PCBs和PAHs不同,在东京、洛杉矶、圣地亚哥的城市海滩微塑料中的浓度偏低(0.2—52 ng·g−1、2.2—8.4 ng·g−1、n.d.—76 ng·g−1),而越南、哥斯达黎加地区微塑料中DDTs含量偏高(n.d.—124.4 ng·g−1、11—108 ng·g−1)[9,32]。这是因为在大多数国家,DDTs被禁止应用在农业生产中,现存的少量DDTs主要是环境遗留污染物,少数热带国家会使用少量的DDTs来控制疟疾从而导致DDTs含量偏高[9,31]。
在大西洋西岸南美洲沿海地区,巴西沿海作为主要的工业、港口和石油码头所在地,海水系统受到严重的有机污染物污染[34]。在人口聚集、船只交通航道以及用于工业生产的码头区域的海岸线,微塑料中PAHs浓度偏高(192—13708 ng·g−1)[32,34-35]。圣保罗州是世界上PCBs污染最严重的区域之一,其微塑料中PCBs的浓度 (3.41—7554 ng·g−1)远高于在巴拉那州海岸线的微塑料中PCBs的浓度(0.8—104.6 ng·g−1)[34-35]。Taniguchi等[34]的调查结果显示,由于被大量使用于农业生产以及抗击疟疾,圣保罗州海岸线海滩微塑料中DDTs的浓度偏高(<0.11—840 ng·g−1)。
在大西洋东岸的非洲发展中国家,缺乏处理有机污染物的基础设施和资源,导致微塑料中有害物质含量较高[33]。Hosoda等[33]的研究表明,PCBs从加纳阿克拉和特马市区的电子废物现场引入河流,导致城市地区PCBs的浓度(39—69 ng·g−1)高于沿海乡镇(1—15 ng·g−1)。Ryan等[14]检测了1989—2008年间南非沿海水域的PE与POPs的共存情况,研究表明,微塑料主要来源于商业港口以及主要工业区(包括塑料,炭黑,轮胎和车辆制造),PE中POPs共存情况分别为PCBs(25—61 ng·g−1)、HCHs(2—5 ng·g−1)、DDTs(8—31 ng·g−1),近年来由于政府采取相应措施,PCBs、HCHs、DDTs的浓度均呈下降趋势,但用于控制疟疾的DDTs浓度仍然很高。
PAHs、PCBs、DDTs在欧洲沿海地区的微塑料中也广泛存在。PAHs在葡萄牙沿海的微塑料中含量偏高,浓度范围为53—44800 ng·g−1,这可能是由于船舶和工业活动的机油泄漏引起的[11]。其次是比利时沿海地区,浓度范围为1076—3007 ng·g−1,这与该地区高度城市化和工业化有关[36]。希腊海滩微塑料中PAHs的浓度则低得多,为100—500 ng·g−1[13]。另外,PCBs在葡萄牙、比利时以及希腊沿海地区浓度范围相近,分别为2—223 ng·g−1、31—236 ng·g−1、0.09—270 ng·g−1[11,13,36]。DDTs在葡萄牙以及希腊海滩的浓度范围分别为0.42—41 ng·g−1和1.1—42 ng·g−1,DDTs的来源可能是早期农业生产的遗留物[11,13]。
在我国,水体中微塑料与有机污染物共存的现象主要集中在东部、南部沿海地区。工业生产、农业活动以及煤炭的燃烧都可使微塑料中有机污染物浓度增加[37]。Tang等[38]等指出,微塑料污染源包括废物废水排放、海水养殖活动、工业活动以及农业生产,河流径流、人口密度和城市化率均可影响地表水中微塑料的分布。渤海和黄海地区是中国最重要的经济区和重工业基地之一,其微塑料主要为PP、PE、PS,共存的有机污染物主要有PAHs、DDTs、PCBs、HCHs[37,39-40]。秦皇岛东山海滩以及大连正明寺海滩地区检测到PAHs (136.3—2384.2 ng·g−1)、DDTs (1.15—126.95 ng·g−1)、PCBs (21.5—323.2 ng·g−1)[39]。其中,石油产品、煤炭燃烧和港口煤尘是微塑料中PAHs的重要来源,DDTs主要来源于过去农业生产的残留污染物以及船舶上的防污涂料泄漏[39]。黄岛和麦岛沿海地区微塑料中PAHs浓度范围为0.114—0.245 μg·g−1和0.072—0.261 μg·g−1,污水排污口和养殖区是有机污染物的典型污染源[40]。Zhang等[37]等发现,山东半岛沿海地区的地表水微塑料(PE、PP、PS)中有机磷酸酯(OPE)和邻苯二甲酸酯(PAE)的共存现象,OPE的浓度(0—84595.9 ng·g−1)远高于PAE(0–80.4 ng·g−1),微塑料主要来源于树脂颗粒以及风化后的塑料碎片(捕鱼、水产养殖和包装袋中产生的塑料碎片)。
南海是中国船运交通要道,沿海地区微塑料(主要为PP、PE)中主要存在的有机污染物为PAHs、PCBs、DDTs、HCHs。PAHs在汕头湾的浓度偏高(11.2—7714 ng·g−1)[41],其次是中国香港西部和东部水域(70.8—1509 ng·g−1)[42],厦门沿海PAHs 的浓度范围为18.13—247.8 ng·L−1[39],靠近港口、工业区和城市地区的海滩微塑料中PAHs浓度高于偏远海滩。汕头湾的的沉积微塑料中还检测到DDTs (nd —1183 ng·g−1)和HCHs (0.63—782 ng·g−1),研究指出DDTs主要来源于农业水产养殖活动以及渔船上防污涂料的泄漏[41]。在中国香港地区的微塑料中还检测到PCBs、DDX、HCHs,其浓度范围分别为13—1083 ng·g−1、1.96—626 ng·g−1、5.02—63.5 ng·g−1[42]。
受到沿岸的工业以及农业影响,有机污染物进入内陆淡水系统随着水的流动而迁移,并吸附在沉积物中[43]。研究发现,江河沉积物中主要存在的微塑料为PE、PP、PS以及PET[43-44]。例如,北江飞来峡水库地表水中EPS(比表面积较大)对PAHs的吸附能力高于PE和PP,微塑料赋存的PAHs的浓度范围为282.4—427.3 ng·g−1,其主要来源是化石燃料的不完全燃烧并且受到沿岸冶金、采矿和热力发电行业的影响[43]。Fraser等[45]的研究指出,陆上塑料废物可以通过河流输入到海洋环境,PE、PS和PET是钱塘江和杭州湾沉积物样品中主要的微塑料类型,这与它们在农业、水产养殖和工业中的广泛使用有关。其中,赋存在微塑料中的PCBs浓度范围为1.13—1.65 ng·g−1,PCBs浓度会随着深度的增加而增加。
针对土壤,Lu等[45]对福州市郊区农业土壤中微塑料与污染物共存情况进行了研究,检测到的抗生素为四环素(16.16—40.20 μg·kg−1)、土霉素(29.70—107.20 μg·kg−1)、金霉素(24.02—81.02 μg·kg−1)、氧氟沙星(17.08—63.18 μg·kg−1)。研究表明,土壤中微塑料与抗生素的共存水平较高,并且粒径较大或风化度相对较高的微塑料以及蔬菜栽培时间相对较长的土壤中的微塑料可以吸附更多的抗生素。目前关于土壤中的共存研究比较匮乏,从仅有的研究可以得出,在使用农药的农业土壤中,地膜覆盖的微塑料可能作为农药的载体从而加剧污染物的危害[18]。
综上所述,太平洋沿海、大西洋沿岸、非洲沿海以及我国的沿海地区的微塑料主要是PP、PE、PS,微塑料可以作为有机污染物的载体,使污染物进行迁移和累积。微塑料中存在的有机物主要类型为PAHs、PCBs、HCHs、DDTs,其浓度受区域差异影响较大。DDTs主要来源于过去农业生产的污染物残留;少数热带国家使用DDTs控制疟疾疾病也会导致其浓度也偏高。PAHs与PCBs主要来源于石油产品、煤炭燃烧和港口煤尘,其浓度与工业生产、港口运输等有紧密关系,巴西沿海地区以及太平洋西岸是污染比较严重的区域之一。另外,由于非洲发展中国家缺乏处理有机污染物的基础设施和资源,导致微塑料中PAHs与PCBs浓度偏高。因此,在评估海域水体微塑料中有机污染物的浓度和组成差异时,应考虑工业活动、农业活动等人为因素的影响。另外,从已有研究得出,土壤环境微塑料中有机污染物主要来源于农膜大量使用以及灌溉残留物[18],但针对土壤微塑料本身以及土壤微塑料与有机污染物共存的相关系统研究仍有待进一步深入。
2. 微塑料对有机污染物的吸附行为(adsorption of organic pollutants by microplastics)
实际环境的复杂性以及污染物在微塑料上的多样性分布,导致环境检测结果仅能体现微塑料与污染物的共存水平,很难解释其吸附行为和吸附机理,因此大量有关微塑料与有机污染物的吸附行为研究在实验室进行[1]。本节查阅并总结2016年至今收录在ScienceDirect和SpringerLink数据库中关于实验室中微塑料与有机污染物吸附行为的相关文献(图2),发现研究最多的微塑料类型是PE,占文献调研结果的33%,其次是PS(24%)、PP(23%)、PVC(16%)、PA(8%),这也是目前环境中大量存在的微塑料类型。在本文选取的文献中,研究微塑料与抗生素的吸附行为的文献占26%,药品和个人护理产品(PPCP)和PAHs均占总文献的20%,另外,相关的文献还覆盖了农药、全氟烷基酸(PFAAs)、阻燃剂(BFRs)、激素、卤代咔唑(PHC)、双酚类似物、PBDEs、油类、PCBs等有机污染物在微塑料上的吸附行为。
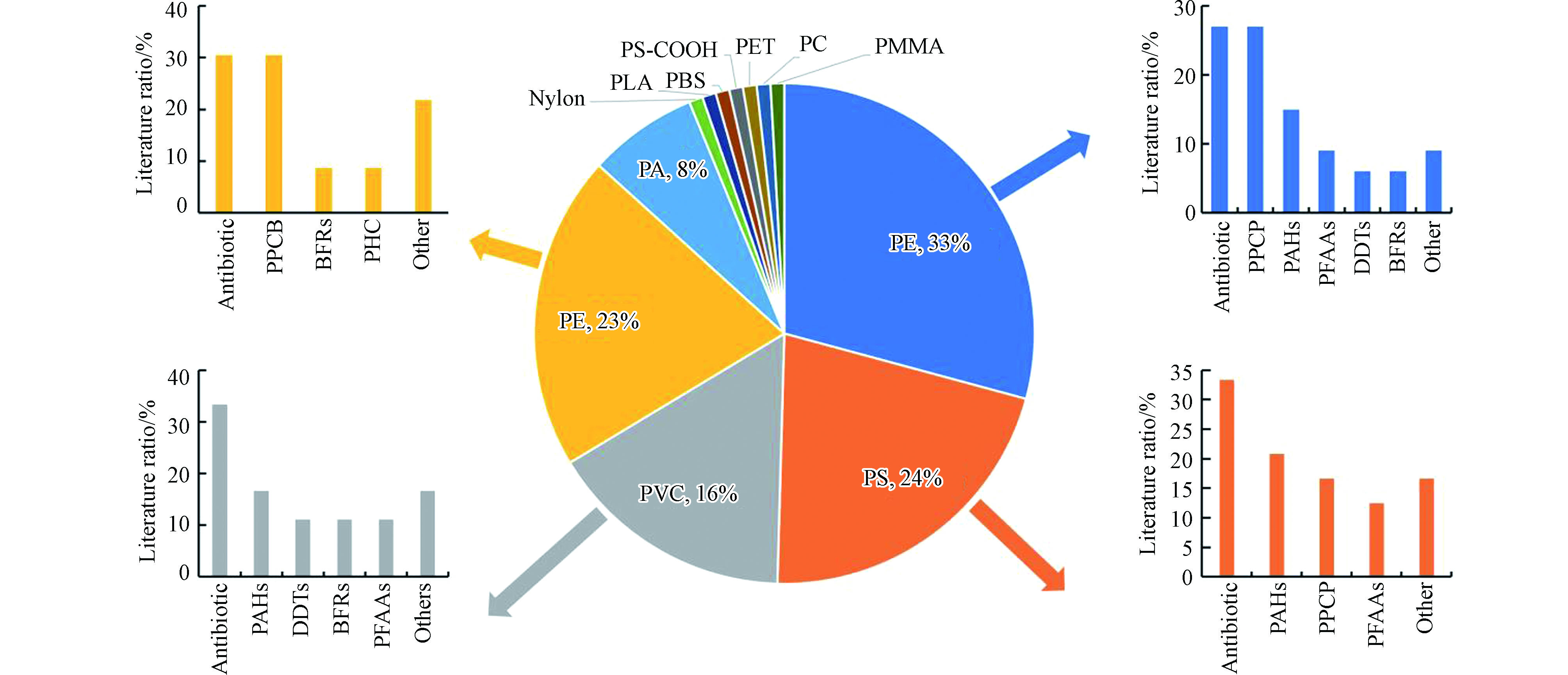 图 2 在实验室研究中微塑料类型和微塑料上的有机物种类分布Figure 2. Microplastics types and pollutants on microplastics (the size of each pie area represents the ratio of literature on the sorption behaviors of different types of microplastics and the size of the bar graph represents the ratio of literature on the sorption behaviors of different types of organic pollutants).(饼状图表示不同种类微塑料吸附行为的文献比例,柱状图表示不同种类有机物吸附行为的文献比例)
图 2 在实验室研究中微塑料类型和微塑料上的有机物种类分布Figure 2. Microplastics types and pollutants on microplastics (the size of each pie area represents the ratio of literature on the sorption behaviors of different types of microplastics and the size of the bar graph represents the ratio of literature on the sorption behaviors of different types of organic pollutants).(饼状图表示不同种类微塑料吸附行为的文献比例,柱状图表示不同种类有机物吸附行为的文献比例)文献调研发现,这些微塑料与有机污染物的吸附行为的研究方法主要采用动力学模型,例如PFOM模型[19,46–48]、PSOM模型[17-18,20,22,49–59]和等温线模型,例如线性等温线模型[7,16–18,20,50,54,56,58,60-61]、Freundlich等温线模型[18,22,46,48,51-53,54–57,62–64]、Langmuir等温线模型[19,22,47–50,53,59,63,65]等对其吸附行为进行模拟,以快速预测环境中的不同微塑料对有机污染物的吸附能力[67]。研究进一步揭示了微塑料与有机污染物的吸附机理,吸附机理主要包括疏水作用[7,16-17,50-52,54–57,58–62,64-65]、静电作用[46,51,54–58,61-62,66]、范德华相互作用[20,56,61,62,65]、表面络合作用[54,55]、极性相互作用[66]、π-π键[16,60,66]、氢键[57,62]、单层覆盖[19,22,48–49]、孔填充机理[48,63]、颗粒内扩散[52]等。
作为新兴污染物,每年都有大量药品和个人护理产品(PPCP)释放到环境中产生不利影响,特别是抗生素,由于其对微生物群落的不利影响而受到越来越多的关注[62]。例如,Xu等[66]通过伪二级动力学模型和线性模型、Freundlich等温线模型研究了磺胺甲恶唑(SMX)在PE上的吸附行为,结果表明,吸附过程涉及疏水相互作用和其他相互作用(例如静电作用)。因此,塑料对不同污染物的吸附能力与污染物本身的疏水作用有关[55,60-61]。Elizalde-Velázquez等[60]指出微塑料(UHMWPE、AMWPE、PS、PP)对抗炎药的吸附能力遵循双氯芬酸钠(DCF)≈布洛芬(IBU)>萘普生(NPX),吸附能力也取决于疏水分配作用。Wu等[61]指出,PE与疏水性药物的结合性更高,因此对3种药物的吸附能力遵循4-甲基亚苄基樟脑(4MBC)>三氯生(TCS)>17α-乙炔雌二醇(EE2)>卡马西平(CBZ)。同样,PE也会降低亲水性药物(SMX)在水生生物组织中的生物蓄积潜力,Razanajatovo 等[54]的研究表明,药物在PE微塑料上的吸附量遵循舍曲林(SER)>普萘洛尔(PRP)>磺胺甲恶唑(SMX)。不少文献进一步比较了不同种类微塑料对抗生素和PPCP的吸附能力的差异,结果表明微塑料的吸附能力与其自身的疏水性、比表面积、官能团特性都有密切关系[55-57,60,63,65]。例如,Guo等[55]的研究指出,泰乐菌素(TYL)在微塑料上的吸附能力遵循PVC>PS>PP>PE,这可能与微塑料的疏水性和比表面积有关。Guo等[56]指出,磺胺二甲嘧啶(SMT)在不同类型的微塑料上的吸附能力遵循PA>PET>PE>PVC>PS>PP,参与吸附的主要机理是静电和范德华相互作用,微塑料极性可以增强微塑料对污染物的吸附能力。Li等[63]的研究指出,相比于PE、PS、PP、PVC,拥有特定官能团的PA对抗生素吸附力更强。Xu等[65]的研究结果表明,四环素在PS上的吸附能力高于PE和PP,这主要是极性相互作用和π-π相互作用增加了PS对四环素的吸附。Elizalde-Velázquez等[61]的研究表明,微塑料对非甾体类抗炎药的吸附能力遵循PE>PS>PP,这与微塑料的比表面积有关。pH值也可能影响微塑料与抗生素、PPCP的吸附能力,例如,在3—6的pH范围内,三氯生(TCS)对PS的吸附比较高,当pH>6时,TCS与带负电的PS产生静电排斥导致吸附降低[58]。Zhang等[58]指出,PS与土霉素的最大吸附发生在pH 5时,是因为微塑料表面与土霉素两性离子之间的静电排斥最小。同时,老化也会影响微塑料和污染物的吸附行为,例如,风化的PP对TCS的吸附能力要高于新的PP,因为老化的微塑料,具有较高的比表、微孔面积和氧化程度,具有更强的吸附能力[46]。
PAHs和农药均是有较强的致突变性和致癌性的有机化合物[16]。有机污染物的疏水性以及极性同样会影响其与微塑料的吸附行为,例如,Wang等[16]指出,相比于非极性菲,疏水分配和π-π相互作用可以显著增强PS对极性硝基苯的吸附作用。与前文结论类似,微塑料的尺寸(比表面积)以及结构特性同样可以影响其对PAHs和农药的吸附能力,例如,Wang等[59]的研究结果表明,3种微塑料对菲的吸附能力依次为PE>PS>PVC。在Wang等[50]的研究中,PE、PS、PVC对芘的吸附能力也遵循PE>PS>PVC。Zhang等[50]研究了9-NAnt与微塑料的吸附行为,吸附能力遵循PE>PS≈PP。3项研究的结果表明,PE对有机污染物的高吸附能力与其较大表面积和类似橡胶的特性有关[49]。除此之外,微塑料表面的官能团也会影响微塑料的吸附能力,Gong等[18]研究指出,可降解微塑料表面含氧官能团(羰基氧)可与氟虫腈的极性部分形成分子间氢键,该键强于氟虫腈与不可降解的微塑料之间的疏水相互作用和π-π相互作用,从而导致聚乳酸(PLA)和聚丁二酸丁二酯(PBS)对氟虫腈的吸附速率远高于PE、PP、PVC、PS。
此外,不少文献针对其它有机污染物与微塑料的吸附能力进行了比较和分析。微塑料的理化性质和分子结构同样影响了其在润滑油、全氟烷基酸(PFAAs)、阻燃剂、激素上的吸附行为[7,48,54,64]。Hu等[54]的研究表明,在pH 5和温度为293 K下,润滑油在纳米PE和PS上的最大吸附容量分别为7.3 g·g−1和6.1 g·g−1,比表面积大的微塑料颗粒拥有更高的吸附能力。Wang等[7]的研究指出,由于官能团的不同,FOSA在PE上的吸附水平高于PFOS,微塑料的分子组成和结构(表面含氧官能团(羰基氧)和橡胶域空间排列)也造成了PFOS和FOSA在PE和PVC上的吸附作用强于PS。Chen等[49]也指出,由于PE和PVC的物理化学性质以及分子结构不同,从而导致PVC对磷酸三(2-氯乙基)酯(TCEP)的亲和力高于PE,但PVC对磷酸三正丁酯(TnBP)低于PE。Liu等[64]的研究指出,海水系统中17β-雌二醇(E2)激素在微塑料上的吸附能力依次为PA>HD/LLD-PE>PP>LD/MD-PE>PS>PC>PMMA>PVC,吸附能力差异主要是由于结晶度不同引起。同样,由于不同的结晶度、比表面积和表面结构,PS对多溴联苯醚(PBDEs)吸附能力高于其他3种微塑料,顺序遵循PS> PA> PP> PE[53]。另外,一些文献通过动力学模型和等温线模型来模拟和预测微塑料对有机污染物的吸附量。例如,Liu等[47]的研究结果表明,在15 ℃和14%盐度,PP对阻燃剂三(2,3-二溴丙基)异氰脲酸酯(TBC)和六溴环十二烷的吸附容量最大,为1954—21489 ng·g−1,TBC的吸附容量远高于HBCD。Zhang等[22]PP与3,6-二溴咔唑(3,6-BCZ)和1,3,6,8-四溴咔唑(1,3,6,8-BCZ)的平衡吸附时间分别约为6 h和8 h,最大吸附容量分别约为6400 ng·g−1和8000 ng·g−1。Zhan等[19]指出,PP在海水、超纯水、正己烷溶液中对3,3',4,4'-四氯联苯(PCB77)的吸附量不同,分别为344.8 μg·g−1、192.3 μg·g−1、93.45 μg·g−1。结果表明,3种类型的有机污染物与微塑料均为化学吸附,并且温度、盐度、反应时间等因素都会对吸附行为产生不同程度的影响。
综上所述,有机污染物在微塑料上的行为主要遵循PFOM、PSOM吸附动力学模型,等温线模型,例如Freundlich、Langmuir模型和线性模型等。有机污染物的疏水性以及微塑料的疏水性、比表面积、官能团特性都会影响其吸附能力。因此,长期存留在环境中的微塑料可以作为污染物在环境中运输的载体。然而,实验室模拟的环境因素较为单一,无法与真实的复杂环境相比,因此得出的仅为理论结论,缺乏特定的物理意义。
3. 影响微塑料吸附有机污染物的因素(Influencing factors on the sorption of organic pollutants by microplastics)
对影响其吸附行为的因素进行系统的总结,主要包括微塑料的理化性质、污染物的结构以及吸附介质因素对吸附行为的影响。主要包括以下几个方面:
3.1 微塑料颗粒大小
研究表明,吸附剂的理化特性会显著影响吸附行为[18,66]。粒径大小是影响污染物的吸附行为的主要因素,这是因为较小尺寸的颗粒具有较大的表面积,可提供的吸附位点多,从而增加液固接触的面积,增大了微塑料的吸附能力[17,19,21,47,51,53,55,58,61]。例如,Zhang等[50]的研究结果表明,当PE和PP的粒径从1.7 mm减小至0.15 mm,其对9-NAnt的吸附容量分别从从0.28%增至1.66%和0.30%增至1.63%。Wang等[17]的研究指出,在相同质量的情况下,尺寸从10 mm减小到1 mm的PE和尼龙对菲吸附作用的提升明显(分别为23.1%、10.4%),随着粒径的减小,可增强微塑料的污染物转移效果。Zhan等[19]的研究显示,当微塑料粒径从2.0—5.0 mm增加到0.18—0.425 mm,其对PCB77的吸附量从>60 μg·g−1增长到>210 μg·g−1,这表明微塑料的吸附能力随着粒径的减小而显着增加。然而仍存在一些特殊情况,菲在50 nm纳米PS的吸附量明显较低,这是由于纳米PS的团聚作用减小了其比表面积[16]。
3.2 微塑料结构
研究表明,微塑料的理化特性可能会显着影响其与有机污染物的吸附过程[18]。微塑料的成分差异可能体现在其聚合物结构单元中含有官能团以及微塑料的橡胶区域特性,这会影响微塑料对污染物的吸附[17-18,46,49,50,55-57,60–63,64-66,67]。例如,Wang等[17]的研究表明,PE(无亲水性官能团)比尼龙(具有亲水性基团)对菲具有更强的吸附能力。Gong等[18]的研究结果显示,氟虫腈在可降解微塑料PLA和PBS上的最大吸附量(228.7 μg·g−1和720.2 μg·g−1)明显高于不可降解的PE、PS、PVC和PP的最大吸附量(38.3—62.7 μg·g−1),这是因为可降解微塑料中存在的羰基氧官能团与氟虫腈之间的氢键强于氟虫腈与不可降解的微塑料之间的疏水相互作用和π-π相互作用。另外,PBS(橡胶状聚合物)对氟虫腈的吸收量比PLA(玻璃状聚合物)更高,这是因为前者具有较高的自由体积,因此对有机污染物的吸附性较高[18]。Li等[63]也表明,由于特定的官能团(即酰胺基)与污染物的羰基之间形成氢键,PA对AMX、TC和CIP具有高吸附性。Zhang等[49]指出,PE、PS、PVC对芘的吸附能力也遵循PE>PS>PVC,PE的类似橡胶的特性可能导致PE对芘的吸附量高于PS或PVC上芘吸收量的重要因素。
另外,在环境中长期存在的微塑料表面会有不同程度的风化以及老化,老化过程可以改变微塑料的表面性质(尺寸、表面积、孔隙率、表面极性),进而改变微塑料的吸附能力[46]。Wu等[46]的研究表明,老化的PP颗粒具有较宽松的物质结构和更大的非晶体结构域从而形成较小尺寸的塑料颗粒,并且老化过程将有助于在颗粒表面产生更多可用的吸附位点,这都可以提高PP对TCS的吸附能力。Zhang等[51]使用人工老化模式研究老化过程对微塑料吸附9-NAnt的影响,结果表明,PS的吸附量最多降低了33.76%,这是因为老化过程会引入含氧的官能团,增强微塑料的表面极性,从而阻碍了疏水性有机污染物的吸附过程。
3.3 有机污染物结构
有机污染物的疏水性是影响其吸附强弱的关键因素,疏水性强的有机污染物更容易被吸附在微塑料表面,有机物分子结构中官能团和极性影响分配行为,静电作用也会在一定程度上增强与微塑料的吸附行为[7,60,62-63,66]。例如,Razanajatovo等[69]的研究指出,药物SMX、PRP、SER在PE上的吸附百分比大小遵循SER(28.61%)>PRP(21.61%)>SMX(15.31%),与其疏水性正相关(SMX的lg
KOW KOW KOW 3.4 吸附介质的影响
环境介质不同时,同种微塑料对同种有机污染物的吸附强度差异显著[66]。盐度是环境中差异最大的性质之一,盐度会影响诸如土壤,黏土和沉积物等天然吸附剂对疏水性有机化合物的溶解性,较高浓度的Ca2+和Na+会强烈竞争微塑料表面上的阳离子交换位点从而降低微塑料对有机污染物的吸附能力[19,48,56,62,63,67-67]。例如,Zhan等[19]指出,在模拟海水中,PP对PCB77的吸附量(120 μg·g−1)约为在超纯水中吸附量(约为60 μg·g−1)的两倍。Guo等[56]研究表明,由于阳离子Na+更易于与微塑料的阴离子表面相互作用,当盐度增加,部分静电位点被Na+占据,造成SMT的吸附能力相对降低。此外,离子强度也会影响微塑料的吸附行为[55,57,63]。Guo等[56]的研究表明,随着离子强度增加到一定的浓度,大量的K+与TYL在微塑料的吸附位点上竞争,这会导致吸附相对减少。
另外,pH值也会影响微塑料对有机污染物的吸附,这是因为pH值可以通过改变微塑料和有机污染物的质子化程度使其呈现出不同的带电性从而改变吸附行为[7,46,51,55–58,61,65-67]。例如,Zhang等[50]的研究表明,随着pH值的增加,9-NAnt与PP、PS之间的静电吸引减弱,吸附能力显着下降。另外,对于土霉素而言,在pH值为5时,滩涂样品的表面电荷接近零电荷点,其静电排斥力最低,吸附能力最强;当pH值增高或降低时(pH<5.0或>5.0),由于带电荷的吸附剂和被吸附物电荷相似,静电排斥力更高从而导致吸附能力降低[58]。
最后,介质温度也是影响吸附行为的因素之一。研究表明,随着温度的升高,活性剂的表面张力降低,这削弱了微塑料与表面活性剂的结合,导致吸附能力下降,另外,在高温下,吸附分子的迁移率和溶解度增加,范德华力随着温度的升高而降低,也会导致吸附能力降低[19,21,47-49,52,68]。例如,Zhan等[19]的研究表明,随着温度从19°C升高到27°C,PP对PCB77的吸附量从140 μg·g−1减少到100 μg·g−1,高温会降低溶液的表面张力从而对PP吸附的PCB77产生不利影响。Qiu等[67]的研究指出,高温模拟海水中活性增加的离子可能与多卤咔唑竞争这些塑料颗粒表面上的吸附位点,从而降低了微塑料颗粒的吸附能力。另外,Chen等[49]的研究表明,温度的升高除了会使表面活性剂的表面张力降低,温度的升高也会使TnBP和TECP在高温下的随机分子热运动比在低温下更剧烈,导致污染物和PE之间的范德华力降低,从而价降低其吸附能力。
综上所述,影响微塑料对有机污染物吸附的影响因素主要有:(1)微塑料颗粒大小,通常微塑料粒径越小,比表面积越大,吸附有机物的能力强。(2)微塑料和有机物结构,官能团结构、极性、聚合物状态、微塑料老化程度是影响微塑料与有机物吸附能力的重要因素,通常,老化会增加微塑料比表面积增加吸附能力;官能团极性越强吸附能力越强;疏水性越强吸附能力越强;有机污染物对橡胶状塑料的亲和力比玻璃态塑料高;带电的可解离有机污染物吸附能力高。(3)环境因素,通常,温度越高吸附能力下降;盐度越高吸附能力越弱;pH值可以改变吸附行为。
4. 微塑料与有机污染物的联合毒性作用(Combined toxicity of microplastics and organic pollutants)
4.1 微塑料与有机污染物的协同作用
研究发现,微塑料与污染物共存时会产生协同作用,微塑料可作为有机污染物的载体进入生物体的组织和器官内。例如,吸附在PE和PS颗粒上的芘可以被转移到紫贻贝体内的血淋巴、腮、消化系统中[25]。吸附到微塑料颗粒上的卤代污染物也可以被鲈鱼的肠道系统吸收并转移到循环系统中[68]。有文献指出,微塑料有助于改变污染物在生物体内的分布并导致生物利用度以及生物蓄积的增加[26,71]。例如,在NPs的存在下,浮游水蚤(Daphnia Magna)体内菲的蓄积量是无塑料对照组中菲蓄积量的3倍[24]。与单独使用BPA相比,NPs与BPA共同作用下会使斑马鱼头部和内脏的BPA的含量增加2.2—2.6倍[70]。另外,Besseling等[73]的研究表明,较低的PS剂量可将沙蠋体内PCBs的生物蓄积提高到无微塑对照组的1.1—3.6倍。其中,微塑料的尺寸(比表面积)在很大程度上影响有机污染物的生物蓄积[23-24]。例如,相比于MPs,具有较高比表面积的NPs(对疏水性有机污染物的吸附能力较高)可以显著增强水蚤消化道内菲的生物蓄积[24]。500 nm的PS颗粒比30 μm的颗粒有更高的渗透能力,可以更有效地释放其携带苯并(a)芘(BaP)以及雌二醇(E2)进入泥蚶生物体内部[72]。微塑料的浓度也会影响联合作用的生物蓄积与毒性作用,Li等[75]指出,低浓度PS与DBP对小球藻具有拮抗作用,而在较高微塑料浓度下则具有协同作用。因此,在研究微塑料与有机污染物的相互作用时必须综合考虑微塑料和污染物的浓度以及吸附能力。
微塑料与有机污染物的联合作用在增强生物体内污染物蓄积的同时,也会增强急性毒性、神经毒性、发育毒性,对生物的组织器官等系统造成损害[6]。例如,PE和PS与芘的联合作用可以增加紫贻贝对芘的吸收,影响其免疫反应、遗传毒性作用和神经毒性反应,其中PE可导致溶酶体膜的稳定性降低并出现炎症反应[25]。NPs(纳米塑料)和BPA通过循环系统积聚在斑马鱼头部,从而的正常运行[70]。PS与BaP和E2的联合毒性作用会导致泥蚶体内血细胞的吞噬能力降低并限制血细胞对异物的识别、吞噬和降解[74]。Browne等[23]的研究表明,PVC与壬基酚联合作用降低60%以上结肠细胞去除病原细菌的能力,PVC与三氯生的结合会造成55%以上蠕虫的死亡率。联合作用还会降低生物机体机能、免疫功能、摄食能力,并使得生物抵御外源污染物的能力降低[6]。例如,NPs增强了菲对水蚤的慢性毒性并影响其发育和繁殖能力[24]。PE会使芘显着降低虾虎鱼体内乙酰胆碱酯酶、异柠檬酸脱氢酶的活性,影响其生长、繁殖以及生存活动[74]。壬基酚、菲和PVC的联合作用会降低沙蠋的生存率、摄食量和免疫力[23]。氯吡硫磷(CPF)与PE联合使用显示出比单独使用更高的毒性,毒性作用会影响纺锤水蚤的存活率、产卵率、进食以及孵化率[26]。
4.2 微塑料与有机污染物的拮抗作用
另一方面,微塑料(PE、PP)的存在也会降低环境中溶解的有机污染物的浓度,这是因为微塑料与污染物的吸附行为能够降低环境中有害物质的自由态,从而降低了有机污染物的致命毒性[6,69]。例如,由于TCS与微塑料的竞争吸附降低了有害物质与微藻的接触,使得联合作用毒性小于单一的微塑料和TCS对微藻的毒性[27]。PS的吸附使17α-乙炔雌二醇(EE2)自由溶解浓度降低,减轻了单一EE2对斑马鱼幼虫运动机能的减退作用[28]。关于联合作用减少污染物的致死率,Oliveira等[74]的研究表明,PE颗粒可延缓芘诱发虾虎鱼的死亡,使半数致死时间从29 h延迟至42.1 h。另外,微塑料尺寸也会影响污染物的毒性作用。例如,拥有较小粒径决定了PVC和PVC800与TCS的联合毒性比PE和PS的毒性降低了更多[27]。同样,相比于PE、PS、PA,PE1000和PA1000(具有较大的比表面积)对壬基酚(NP)具有更强的吸收能力,可降低自由态NP的浓度,从而减轻NP对藻类PSII活性的抑制作用以及毒性损害[75]。
另外,微塑料能够调节污染物的生物利用率度[6]。通过分析斑马鱼幼体中生物标志物基因表明,PVC的存在将菲和EE2的生物利用度分别降低了33%和48%,其吸附能力与污染物的类型有关[29]。Zhang等[76]的研究表明,由于大量草甘膦被nPS-NH2吸附(其还原性氨基基团更容易与草甘膦结合),导致藻类吸附草甘膦的量比无微塑料时的吸附量大大降低,从而间接降低了草甘膦的生物利用度。同样,Wang等[30]的研究结果表明,土壤环境中的PS颗粒和有机污染物存在竞争吸附,并且PS颗粒也缺乏对有机污染物的载体作用,这会减少蚯蚓(Eisenia fetida)体内PCBs和PAHs的积累。
综上所述,微塑料可以加剧或减缓有机污染物对生物的毒性作用,目前微塑料与有机污染物的联合毒性的相关研究仍处于比较初级的水平。现有的文献表明(表1),微塑料加剧毒性作用主要来自于两方面,一是微塑料作为载体促进生物体对有机污染物吸收,增加生物利用度蓄积量,造成生物体内有毒有害物质浓度升高;二是微塑料加剧了组织损伤以及机能减弱,并可能影响生物的摄食和抵御能力。微塑料减缓毒性作用主要表现在减少生物体对污染物的吸附以及富集率,另外,微塑料的竞争吸附也可导致污染物生物利用度以及毒性的降低。然而,现实环境中可能出现多种污染物共存的情况,彼此间存在交互作用(拮抗作用和协同作用等),这可能会对现有的研究结果产生影响。总之,影响联合毒性的因素比较复杂,与微塑料尺寸、有机污染物类型以及环境介质关系密切,未来的研究需要进一步综合考虑微塑料对生物联合毒性的影响。
表 1 微塑料与有机污染物的复合污染及联合毒性作用Table 1. Compound pollution and joint toxicity of microplastics and pollutants联合作用Joint interaction 介质Medium 微塑料类型Microplastics 生物种类Biological species 有机污染物Organic Pollutants 联合作用影响Combined effect 参考文献References 协同作用 海水 PE、PS 紫贻贝 芘 增加芘的吸收,影响免疫反应、遗传毒性作用和神经毒性反应 [25] 海水 低密度PE 欧洲鲈鱼 卤代污染物 增加生物蓄积以及毒性作用(肝脏代谢,免疫系统,氧化应激) [68] M4培养基 纳米级塑料(NPs) 大型蚤(Daphnia magna) 菲 增强生物蓄积和毒性作用,影响其发育和繁殖能力 [24] 人工淡水 纳米级塑料(NPs) 斑马鱼(Danio rerio) 双酚A(BPA) 增强内脏和头部的BPA积累,引起神经毒性 [70] 海洋沉淀物 PS 沙蠋(Arenicola marina) PCBs 增加生物蓄积 [71] 海水 PS 泥蚶(Tegillarca granosa) 苯并(a)芘(BaP)、雌二醇(E2) 增加生物蓄积,降低血细胞的吞噬能力以及对异物的识别、吞噬和降解能力 [72] 海洋沉淀物 PVC 沙蠋(Arenicola marina) 壬基酚、菲、三氯生、PBDE-47 降低生存率和进食,损害免疫系统和抗氧化酶系统 [23] 海水 PE 汤氏纺锤水蚤(Acartia tonsa) CPF(氯吡硫磷) 增加毒性,影响存活率、产卵率、进食以及孵化率 [26] 人造海水 PE 斑马鱼(Danio rerio) 芘 降低乙酰胆碱酯酶、异柠檬酸脱氢酶的活性,影响生理活动 [74] 拮抗作用 人造海水 PE、PS、PVC、PVC800 骨条藻(Skeletonema costatum) 三氯生(TCS) 降低毒性 [27] 超纯水 PS 斑马鱼幼体(Danio rerio) 17α-乙炔雌二醇(EE2) 缓解运动机能的减退 [28] 人造海水 PE 虾虎鱼吸虫幼体 芘 延缓芘诱导的死亡率 [76] 无菌BG-11培养基 PE, PA, PS 小球藻 壬基酚(NP) 减轻NP对藻类生长、PSII活性、酶活性的抑制作用 [75] 人造水 PVC 斑马鱼幼体(Danio rerio) 菲、EE2 降低污染物的生物利用度 [29] 去离子水和BG11培养基 NPS-NH2 铜绿微囊藻(Microcystis aeruginosa) 草甘膦 减轻草甘膦对铜绿假单胞菌的抑制作用,降低毒性作用 [76] 农业土壤 PE, PS 蚯蚓(Eisenia fetida) PAHs、PCBs 降低生物利用度降和毒性 [30] 5. 结论与展望(Conclusion and prospects)
通过文献回顾,本文总结了近年来在不同地区的环境介质中微塑料与有机污染物的相互作用与分布特征,并讨论了微塑料与有机污染物的吸附行为、影响因素、联合效应等。研究表明,太平洋沿海、大西洋沿岸、非洲沿海以及我国的沿海地区的微塑料主要是PP、PE、PS,微塑料可以作为有机污染物的载体,使污染物进行迁移和累积。微塑料中存在的有机物主要类型为PAHs、PCBs、HCHs、DDTs,其浓度受区域差异影响较大。DDTs主要来源于过去农业生产的污染物残留以及控制疟疾疾病的使用,PAHs与PCBs主要来源于石油产品、煤炭燃烧和港口煤尘,其浓度与工业生产、港口运输等有紧密关系。因此,在评估海域水体微塑料中有机污染物的浓度和组成差异时,应考虑工业活动、农业活动等人为因素的影响。在实验中中,主要通过吸附动力学(主要遵循PFOM、PSOM吸附动力学)以及等温线模型(包括Freundlich、Langmuir模型和线性模型)对吸附行为进行研究,反应机理主要为物理吸附以及化学吸附(包括氢键,疏水作用,范德华力及静电相互作用)。影响微塑料对有机污染物吸附的影响因素主要有:微塑料尺寸、微塑料结构(理化性质以及老化程度)、有机污染物结构(则包括其疏水性、官能团和空间结构)以及环境因素(pH、温度、盐度、离子强度等)。最后,本文总结了微塑料与污染物的联合作用,包括拮抗和协调作用。环境微塑料可吸附水中和土壤中的污染物,并作为污染物的载体,进入生物体内随食物链传递并对生物体产生影响。
从目前的研究看,大量文献主要集中在水生环境中微塑料与污染物的共存情况,但土壤和大气环境中微塑料的研究仍局限于对微塑料种类与丰度的检测,关于大气和土壤环境中微塑料与污染物共存问题知之甚少。因此今后的研究重点应侧重于对土壤、大气环境中污染物与微塑料的共存情况的研究。此外,目前在实验室模拟的研究中,研究因素较孤立,不能很好地解释自然状态下微塑料与污染物相互作用的关系,因此,未来的研究需要进一步综合考虑生物因素以及非生物因素。最后,本文认为,由于不同介质之间可能存在微塑料和污染物物质交换,因此需要更全面、覆盖面更广的监测系统,以评估全球范围内不同区域的微塑料的分布,并量化各种自然过程和人为因素对土壤、水环境、大气中微塑料污染的贡献。
-
图 2 在实验室研究中微塑料类型和微塑料上的有机物种类分布
Figure 2. Microplastics types and pollutants on microplastics (the size of each pie area represents the ratio of literature on the sorption behaviors of different types of microplastics and the size of the bar graph represents the ratio of literature on the sorption behaviors of different types of organic pollutants).
表 1 微塑料与有机污染物的复合污染及联合毒性作用
Table 1. Compound pollution and joint toxicity of microplastics and pollutants
联合作用Joint interaction 介质Medium 微塑料类型Microplastics 生物种类Biological species 有机污染物Organic Pollutants 联合作用影响Combined effect 参考文献References 协同作用 海水 PE、PS 紫贻贝 芘 增加芘的吸收,影响免疫反应、遗传毒性作用和神经毒性反应 [25] 海水 低密度PE 欧洲鲈鱼 卤代污染物 增加生物蓄积以及毒性作用(肝脏代谢,免疫系统,氧化应激) [68] M4培养基 纳米级塑料(NPs) 大型蚤(Daphnia magna) 菲 增强生物蓄积和毒性作用,影响其发育和繁殖能力 [24] 人工淡水 纳米级塑料(NPs) 斑马鱼(Danio rerio) 双酚A(BPA) 增强内脏和头部的BPA积累,引起神经毒性 [70] 海洋沉淀物 PS 沙蠋(Arenicola marina) PCBs 增加生物蓄积 [71] 海水 PS 泥蚶(Tegillarca granosa) 苯并(a)芘(BaP)、雌二醇(E2) 增加生物蓄积,降低血细胞的吞噬能力以及对异物的识别、吞噬和降解能力 [72] 海洋沉淀物 PVC 沙蠋(Arenicola marina) 壬基酚、菲、三氯生、PBDE-47 降低生存率和进食,损害免疫系统和抗氧化酶系统 [23] 海水 PE 汤氏纺锤水蚤(Acartia tonsa) CPF(氯吡硫磷) 增加毒性,影响存活率、产卵率、进食以及孵化率 [26] 人造海水 PE 斑马鱼(Danio rerio) 芘 降低乙酰胆碱酯酶、异柠檬酸脱氢酶的活性,影响生理活动 [74] 拮抗作用 人造海水 PE、PS、PVC、PVC800 骨条藻(Skeletonema costatum) 三氯生(TCS) 降低毒性 [27] 超纯水 PS 斑马鱼幼体(Danio rerio) 17α-乙炔雌二醇(EE2) 缓解运动机能的减退 [28] 人造海水 PE 虾虎鱼吸虫幼体 芘 延缓芘诱导的死亡率 [76] 无菌BG-11培养基 PE, PA, PS 小球藻 壬基酚(NP) 减轻NP对藻类生长、PSII活性、酶活性的抑制作用 [75] 人造水 PVC 斑马鱼幼体(Danio rerio) 菲、EE2 降低污染物的生物利用度 [29] 去离子水和BG11培养基 NPS-NH2 铜绿微囊藻(Microcystis aeruginosa) 草甘膦 减轻草甘膦对铜绿假单胞菌的抑制作用,降低毒性作用 [76] 农业土壤 PE, PS 蚯蚓(Eisenia fetida) PAHs、PCBs 降低生物利用度降和毒性 [30] -
[1] GUO X, WANG J L. The chemical behaviors of microplastics in marine environment : A review [J]. Marine pollution bulletin, 2019, 142: 1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.03.019 [2] LIU M T, LU S B, SONG Y, et al. Microplastic and mesoplastic pollution in farmland soils in suburbs of Shanghai, China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 242: 855-862. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.07.051 [3] BAI Y C, ZANG C Y, GU M J, et al. Sewage sludge as an initial fertility driver for rapid improvement of mudflat salt-soils [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 578: 47-55. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.083 [4] URBANIAK M, WYRWICKA A, TOLOCZKO W, et al. The effect of sewage sludge application on soil properties and willow ( Salix sp. ) cultivation [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 586: 66-75. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.012 [5] ROCHMAN C M, HOH E, HENTSCHEL B T, et al. Long-term field measurement of sorption of organic contaminants to five types of plastic pellets: Implications for plastic marine debris [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(3): 1646-1654. [6] 张哿, 邹亚丹, 徐擎擎, 等. 微塑料与水中污染物的联合作用研究进展 [J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2019(2): 59-69. ZHANG G, ZOU Y D, XU Q Q, et al. Proceedings of joint effect of microplastics and pollutants in water [J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2019(2): 59-69(in Chinese).
[7] WANG F, SHIH K M, LI X Y. Chemosphere The partition behavior of perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanesulfonamide ( FOSA ) on microplastics [J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 119: 841-847. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.08.047 [8] WANG J, LIU X H, LI Y, et al. Microplastics as contaminants in the soil environment: A mini-review [J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2019, 691: 848-857. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.209 [9] HIRAI H, TAKADA H, OGATA Y, et al. Organic micropollutants in marine plastics debris from the open ocean and remote and urban beaches [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2011, 62(8): 1683-1692. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.06.004 [10] YEO B G, TAKADA H, YAMASHITA R, et al. PCBs and PBDEs in microplastic particles and zooplankton in open water in the Pacific Ocean and around the coast of Japan [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2020, 151: 110806. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110806 [11] ANTUNES J C, FRIAS J G L, MICAELO A C, et al. Resin pellets from beaches of the Portuguese coast and adsorbed persistent organic pollutants [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2013, 130: 62-69. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2013.06.016 [12] CAMACHO M, HERRERA A, GÓMEZ M, et al. Organic pollutants in marine plastic debris from Canary Islands beaches [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 662: 22-31. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.422 [13] KARAPANAGIOTI H K, ENDO S, OGATA Y, et al. Diffuse pollution by persistent organic pollutants as measured in plastic pellets sampled from various beaches in Greece [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2011, 62(2): 312-317. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2010.10.009 [14] RYAN P G, BOUWMAN H, MOLONEY C L, et al. Long-term decreases in persistent organic pollutants in South African coastal waters detected from beached polyethylene pellets [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2012, 64(12): 2756-2760. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.09.013 [15] VERLA A W, ENYOH C E, VERLA E N, et al. Microplastic–toxic chemical interaction: A review study on quantified levels, mechanism and implication [J]. SN Applied Sciences, 2019, 1(11): 1-30. doi: 10.1007/s42452-019-1352-0 [16] WANG J, LIU X H, LIU G N, et al. Size effect of polystyrene microplastics on sorption of phenanthrene and nitrobenzene [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 173: 331-338. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.02.037 [17] WANG Z, CHEN M L, ZHANG L W, et al. Sorption behaviors of phenanthrene on the microplastics identified in a mariculture farm in Xiangshan Bay, southeastern China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 628/629: 1617-1626. [18] GONG W W, JIANG M Y, HAN P, et al. Comparative analysis on the sorption kinetics and isotherms of fipronil on nondegradable and biodegradable microplastics [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 254: 112927. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.07.095 [19] ZHAN Z W, WANG J D, PENG J P, et al. Sorption of 3, 3′, 4, 4′-tetrachlorobiphenyl by microplastics: A case study of polypropylene [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2016, 110(1): 559-563. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.05.036 [20] XU B L, LIU F, BROOKES P C, et al. The sorption kinetics and isotherms of sulfamethoxazole with polyethylene microplastics [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2018, 131: 191-196. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.04.027 [21] ZHANG X J, ZHENG M G, WANG L, et al. Sorption of three synthetic musks by microplastics [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2018, 126: 606-609. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.09.025 [22] ZHANG X J, ZHENG M G, YIN X C, et al. Sorption of 3, 6-dibromocarbazole and 1, 3, 6, 8-tetrabromocarbazole by microplastics [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 138: 458-463. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.11.055 [23] BROWNE M A, NIVEN S J, GALLOWAY T S, et al. Microplastic moves pollutants and additives to worms, reducing functions linked to health and biodiversity [J]. Current Biology, 2013, 23(23): 2388-2392. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2013.10.012 [24] MA Y N, HUANG A N, CAO S Q, et al. Effects of nanoplastics and microplastics on toxicity, bioaccumulation, and environmental fate of phenanthrene in fresh water [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 219: 166-173. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.10.061 [25] AVIO C G, GORBI S, MILAN M, et al. Pollutants bioavailability and toxicological risk from microplastics to marine mussels [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2015, 198: 211-222. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2014.12.021 [26] BELLAS J, GIL I. Polyethylene microplastics increase the toxicity of chlorpyrifos to the marine copepod Acartia tonsa [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 260: 114059. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114059 [27] ZHU Z L, WANG S C, ZHAO F F, et al. Joint toxicity of microplastics with triclosan to marine microalgae Skeletonema costatum [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 246: 509-517. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.12.044 [28] CHEN Q Q, GUNDLACH M, YANG S Y, et al. Quantitative investigation of the mechanisms of microplastics and nanoplastics toward zebrafish larvae locomotor activity [J]. Science of the total environment, 2017, 584: 1022-1031. [29] SLEIGHT V A, BAKIR A, THOMPSON R C, et al. Assessment of microplastic-sorbed contaminant bioavailability through analysis of biomarker gene expression in larval zebrafish [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2017, 116(1/2): 291-297. [30] WANG J, COFFIN S, SUN C L, et al. Negligible effects of microplastics on animal fitness and HOC bioaccumulation in earthworm Eisenia fetida in soil [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 249: 776-784. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.03.102 [31] van A, ROCHMAN C M, FLORES E M, et al. Persistent organic pollutants in plastic marine debris found on beaches in San Diego, California [J]. Chemosphere, 2012, 86(3): 258-263. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.09.039 [32] FISNER M, TANIGUCHI S, MOREIRA F, et al. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in plastic pellets: Variability in the concentration and composition at different sediment depths in a sandy beach [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2013, 70(1/2): 219-226. [33] HOSODA J, OFOSU-ANIM J, SABI E B, et al. Monitoring of organic micropollutants in Ghana by combination of pellet watch with sediment analysis: E-waste as a source of PCBs [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2014, 86(1/2): 575-581. [34] TANIGUCHI S, COLABUONO F I, DIAS P S, et al. Spatial variability in persistent organic pollutants and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons found in beach-stranded pellets along the coast of the state of São Paulo, southeastern Brazil [J]. Marine pollution bulletin, 2016, 106(1/2): 87-94. [35] GORMAN D, MOREIRA F T, TURRA A, et al. Organic contamination of beached plastic pellets in the South Atlantic: Risk assessments can benefit by considering spatial gradients [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 223: 608-615. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.02.094 [36] GAUQUIE J, DEVRIESE L, ROBBENS J, et al. A qualitative screening and quantitative measurement of organic contaminants on different types of marine plastic debris [J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 138: 348-356. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.06.029 [37] ZHANG H B, ZHOU Q, XIE Z Y, et al. Occurrences of organophosphorus esters and phthalates in the microplastics from the coastal beaches in North China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 616/617: 1505-1512. [38] TANG G W, LIU M Y, ZHOU Q, et al. Microplastics and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Xiamen coastal areas: Implications for anthropogenic impacts [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 634: 811-820. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.336 [39] ZHANG W W, MA X D, ZHANG Z F, et al. Persistent organic pollutants carried on plastic resin pellets from two beaches in China [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2015, 99(1/2): 28-34. [40] GAO F L, LI J X, SUN C J, et al. Study on the capability and characteristics of heavy metals enriched on microplastics in marine environment [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 144: 61-67. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.04.039 [41] SHI J C, SANGANYADO E, WANG L S, et al. Organic pollutants in sedimentary microplastics from eastern Guangdong: Spatial distribution and source identification [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2020, 193: 110356. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110356 [42] LO H S, WONG C Y, TAM N F Y, et al. Spatial distribution and source identification of hydrophobic organic compounds (HOCs) on sedimentary microplastic in Hong Kong [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 219: 418-426. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.12.032 [43] TAN X L, YU X B, CAI L Q, et al. Microplastics and associated PAHs in surface water from the Feilaixia Reservoir in the Beijiang River, China [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 221: 834-840. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.01.022 [44] FRASER M A, CHEN L, ASHAR M, et al. Occurrence and distribution of microplastics and polychlorinated biphenyls in sediments from the Qiantang River and Hangzhou Bay, China [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2020, 196: 110536. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110536 [45] LU X M, LU P Z, LIU X P. Fate and abundance of antibiotic resistance genes on microplastics in facility vegetable soil [J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2020, 709: 136276. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136276 [46] WU X W, LIU P, HUANG H, et al. Adsorption of triclosan onto different aged polypropylene microplastics: Critical effect of cations [J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2020, 717: 137033. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137033 [47] LIU X W, ZHENG M G, WANG L, et al. Sorption behaviors of tris-(2, 3-dibromopropyl) isocyanurate and hexabromocyclododecanes on polypropylene microplastics [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2018, 135: 581-586. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.07.061 [48] CHEN S P, TAN Z R, QI Y S, et al. Sorption of tri-n-butyl phosphate and tris (2-chloroethyl) phosphate on polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride microplastics in seawater [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 149: 110490. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110490 [49] WANG W F, WANG J. Comparative evaluation of sorption kinetics and isotherms of Pyrene onto microplastics [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 193: 567-573. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.11.078 [50] ZHANG J H, CHEN H B, HE H, et al. Adsorption behavior and mechanism of 9-Nitroanthracene on typical microplastics in aqueous solutions [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 245: 125628. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125628 [51] WU P F, CAI Z W, JIN H B, et al. Adsorption mechanisms of five bisphenol analogues on PVC microplastics [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 650: 671-678. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.049 [52] XU P C, GE W, CHAI C, et al. Sorption of polybrominated diphenyl ethers by microplastics [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 145: 260-269. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.05.050 [53] HU J Q, YANG S Z, GUO L, et al. Microscopic investigation on the adsorption of lubrication oil on microplastics [J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2017, 227: 351-355. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2016.12.043 [54] GUO X T, PANG J W, CHEN S Y,et al. Sorption properties of tylosin on four different microplastics [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 136: 240-245. [55] GUO X T, PANG J W, CHEN S Y, et al. Sorption properties of tylosin on four different microplastics [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 209: 240-245. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.06.100 [56] GUO X, LIU Y, WANG J L. Sorption of sulfamethazine onto different types of microplastics: A combined experimental and molecular dynamics simulation study [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 145: 547-554. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.06.063 [57] ZHANG H B, WANG J Q, ZHOU B Y, et al. Enhanced adsorption of oxytetracycline to weathered microplastic polystyrene: Kinetics, isotherms and influencing factors [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 243: 1550-1557. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.09.122 [58] LI Y D, LI M, LI Z, et al. Effects of particle size and solution chemistry on triclosan sorption on polystyrene microplastic [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 231: 308-314. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.116 [59] WANG W F, WANG J. Different partition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon on environmental particulates in freshwater: Microplastics in comparison to natural sediment [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 147: 648-655. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.09.029 [60] ELIZALDE-VELÁZQUEZ A, SUBBIAH S, ANDERSON T A, et al. Sorption of three common nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to microplastics [J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2020, 715: 136974. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136974 [61] WU C X, ZHANG K, HUANG X L, et al. Sorption of pharmaceuticals and personal care products to polyethylene debris [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2016, 23(9): 8819-8826. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-6121-7 [62] LI J, ZHANG K N, ZHANG H. Adsorption of antibiotics on microplastics [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 237: 460-467. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.02.050 [63] BAKIR A, ROWLAND S J, THOMPSON R C. Transport of persistent organic pollutants by microplastics in estuarine conditions [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2014, 140: 14-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2014.01.004 [64] LIU X M, XU J, ZHAO Y P, et al. Hydrophobic sorption behaviors of 17β-estradiol on environmental microplastics [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 226: 726-735. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.03.162 [65] XU B L, LIU F, BROOKES P C, et al. Microplastics play a minor role in tetracycline sorption in the presence of dissolved organic matter [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 240: 87-94. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.04.113 [66] 王一飞, 李淼, 于海瀛, 等. 微塑料对环境中有机污染物吸附解吸的研究进展 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2019, 14(4): 23-30. WANG Y F, LI M, YU H Y, et al. Research progress on the adsorption and desorption between microplastics and environmental organic pollutants [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2019, 14(4): 23-30(in Chinese).
[67] QIU Y, ZHENG M G, WANG L, et al. Sorption of polyhalogenated carbazoles (PHCs) to microplastics [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 146: 718-728. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.07.034 [68] GRANBY K, RAINIERI S, RASMUSSEN R R, et al. The influence of microplastics and halogenated contaminants in feed on toxicokinetics and gene expression in European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) [J]. Environmental Research, 2018, 164: 430-443. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2018.02.035 [69] WANG T, WANG L, CHEN Q Q, et al. Interactions between microplastics and organic pollutants: Effects on toxicity, bioaccumulation, degradation, and transport [J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2020, 748: 142427. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142427 [70] CHEN Q Q, YIN D Q, JIA Y L, et al. Enhanced uptake of BPA in the presence of nanoplastics can lead to neurotoxic effects in adult zebrafish [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 609: 1312-1321. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.144 [71] BESSELING E, WEGNER A, FOEKEMA E M, et al. Effects of microplastic on fitness and PCB bioaccumulation by the lugworm Arenicola marina (L. ) [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(1): 593-600. [72] TANG Y, RONG J H, GUAN X F, et al. Immunotoxicity of microplastics and two persistent organic pollutants alone or in combination to a bivalve species [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 258: 113845. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113845 [73] LI Z C, YI X L, ZHOU H, CHI T, et al. Combined effect of polystyrene microplastics and dibutyl phthalate on the microalgae Chlorella pyrenoidosa [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 261: 113604. [74] CHEN Q, GUNDLACH M, YANG S, et al. Quantitative investigation of the mechanisms of microplastics and nanoplastics toward zebrafish larvae locomotor activity [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 584/585: 1022-1031. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.01.156 [75] YANG W F, GAO X X, WU Y X, et al. The combined toxicity influence of microplastics and nonylphenol on microalgae Chlorella pyrenoidosa [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2020, 195: 110484. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110484 [76] ZHANG Q, QU Q, LU T, et al. The combined toxicity effect of nanoplastics and glyphosate on Microcystis aeruginosa growth [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 243: 1106-1112. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.09.073 -






 下载:
下载:







