-
氯酚类污染物(Chlorophenols,CPs)主要来源于农药、医药、纺织印染等工业废水[1-2],具有高毒性、致癌性、生物累积性及难降解性等特点[3-4],一直都是工业水处理领域优先控制污染物。水中CPs常见控制方法包括吸附法、化学还原法、生物法及高级氧化法等[5-6],其中高级氧化法可将其转化为低毒、无毒的小分子有机物,因而备受关注[7-9]。芬顿法以高氧化电位·OH(E0=2.8 eV)作为主要活性氧物种(reactive oxygen species,ROS)[10-11],具有降解能力强、反应速率快等优势,因而应用最为广泛。但传统芬顿法存在pH适用范围窄、Fe(Ⅲ)/Fe(Ⅱ)循环速率慢及H2O2利用率低等不足[12-13]。
非均相芬顿技术虽然能克服均相芬顿pH适用范围窄的弊端,但仍存在Fe(Ⅲ)/Fe(Ⅱ)循环速率慢及H2O2利用率低等不足。非均相光芬顿技术将光照引入催化反应体系,可有效加速Fe(Ⅲ)/Fe(Ⅱ)循环速率、提高H2O2利用率[14-15]。Fe2O3作为一种常见的光芬顿催化剂,具有可见光响应性好、结构可调等优点[16-17]。但Fe2O3光生电子-空穴复合速率高,限制其表面Fe(Ⅲ)/Fe(Ⅱ)循环,导致其光芬顿活性较弱。构建异质结可以提高光生载流子分离效率,是制备高效能催化剂的有效策略[18]。TiO2作为一种廉价稳定且高效的光催化剂,然而TiO2仅能吸收紫外光,难以利用可见光[19]。将Fe2O3纳米簇原位负载于TiO2表面,不仅可以改善单一Fe2O3光生载流子复合速率快的问题,还可解决单一TiO2可见光吸收弱的问题。为此,本研究经过Fe2O3与TiO2的合理搭配,成功构建了异质结,并用于增强光芬顿过程,实现CPs的高效降解。
-
实验试剂:4-氯苯酚(C6H5ClO,4-chlorophenol,4-CP)、2,4-二氯苯酚(C6H4Cl2O,2,4-dichlorophenol,2,4-DCP)、2,4,6-三氯苯酚(C6H3Cl3O,2,4,6-trichlorophenol,2,4,6-TCP)均为分析纯,购于上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;六水合氯化铁(FeCl3·6H2O)、碳酸氢铵(NH4HCO3)、氯化钠(NaCl)、硫酸钠(Na2SO4)、硝酸钠(NaNO3)均为分析纯,购于上海麦克林生化科技股份有限公司;叔丁醇(C4H10O,tert-butylalcohol,TBA)、对苯醌(C6H4O2,1,4-benzoquinone,PBQ)、草酸铵(C2H8N2O4,ammonium oxalate,AO)、苹果酸(C4H6O5,malic acid,MA)、酒石酸(C4H6O6,tartaric acid,TA)、柠檬酸(C6H8O7,citric acid,CA)均为分析纯,腐殖酸(humic acid,HA),购于国药集团化学试剂有限公司;二氧化钛(TiO2)为分析纯,购于天津希恩思生化科技有限公司;5,5-二甲基-1-吡咯啉-N-氧化物(C6H11NO,5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline-N-oxide,DMPO)购于东仁化学科技(上海)有限公司。
实验仪器:液质联用仪(Ultimate 3000,美国赛默飞公司,liquid chromatography-mass spectrometer,LC-MS);电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(Avio500,美国珀金埃尔默公司,inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry,ICP-OES);扫描电子显微镜(Gemini 300,德国蔡司集团,scanning electron microscope,SEM);透射电子显微镜(Talos F200X G2,美国FEI公司,transmission electron microscope,TEM);高效液相色谱仪(LC-2040C,日本岛津公司,high performance liquid chromatography,HPLC);离子色谱(AQUION RFIC,美国赛默飞公司,ion chromatography,IC);稳态/瞬时荧光光谱仪(FLS1000,英国爱丁堡仪器公司,steady-state/lifetime spectrofluorometer,PL);总有机碳分析仪(Multi N/C 3100,德国耶拿分析仪器公司,total organic carbon,TOC);全自动快速比表面积与孔隙度分析仪(ASAP 2460,美国麦克默瑞提克仪器有限公司,automated surface area and porosity analyzer,BET);电子顺磁共振波谱仪(Magnettech ESR5000,德国布鲁克公司,electron paramagnetic resonance,EPR);紫外可见红外分光光度计(UV-3600i Plus,日本岛津公司,UV-Vis diffuse reflection spectroscopy,UV-Vis DRS);X射线衍射仪(Ultima Ⅳ,日本理学株式会社,X-ray diffraction,XRD);电化学工作站(CHI760E,上海辰华仪器有限公司);管式炉(TL 1200,南京博蕴仪器科技有限公司)。
-
首先将不同质量的TiO2(50、100、150、200、250 mg)均匀分散于20 mL乙醇中,超声分散0.5 h得到TiO2悬浮液;向上述悬浮液中加入20 mg FeCl3·6H2O,搅拌0.5 h使FeCl3·6H2O全部溶解,得到前驱体溶液;向前驱体溶液加入30 mg NH4HCO3超声搅拌0.5 h,于60 ℃烘箱中静置6 h至乙醇全部烘干;烘干后的棕红色产物洗涤并干燥后置于管式炉中,使用高纯空气作为保护气(200 mL·min−1),以5 ℃·min−1的速度升温至350 ℃并煅烧2 h,待冷却至室温后制得系列Z型异质结Fe2O3-TiO2-x(x=50、100、150、200、250)。
-
CPs的光芬顿降解实验在光反应器中进行,恒定反应温度为(25±0.5) ℃,使用500 W氙灯作为模拟太阳光,反应于50 mL石英光反应管中进行。实验步骤:称取10 mg催化剂添加至50 mL 10 mg·L−1 CPs水溶液中,超声2 min分散催化剂。将上述悬浮液在黑暗条件下磁力搅拌30 min,以达到吸附平衡。再将5 μL的H2O2滴加至上述悬浮液中。在光反应前打开氙灯预热15 min,预热完成打开灯罩引入光源进行光芬顿反应。按照设定的反应时间间隔间每次取出0.8 mL的样品,加入0.2 mL甲醇溶液进行淬灭,并通过0.22 μm的聚四氟乙烯(PTFE)滤膜过滤置于液相小瓶中,进行后续污染物浓度的测定。进行系列平行实验,减小实验误差和测定误差。
通过HPLC检测CPs浓度,采用C18色谱柱,柱温30 ℃。其中,4-CP的检测方法为:流动相为甲醇/水(v:v=60%:40%),流速为1.0 mL·min−1,检测波长为281 nm,保留时间约为8.0 min;2,4-DCP的检测方法为:流动相为甲醇/水(v:v=70%:30%),流速为1.0 mL·min−1,检测波长为287 nm;保留时间约为7.8 min;2,4,6-TCP的检测方法为:流动相为甲醇/水(v:v=80%:20%),流速为1.0 mL·min−1,检测波长为289 nm,保留时间约为7.6 min。
-
优选的催化剂在每次光芬顿反应后离心收集并用超纯水洗涤3次,去除其表面残留污染物等杂质,在60 ℃下真空干燥6 h以备后续回用实验。收集每次回用实验后的溶液,采用ICP-OES测量溶液中总铁离子浸出浓度。
-
进行活性物种淬灭实验探究光芬顿反应过程中存在的活性物种及其对污染物降解的贡献。选用TBA、PBQ和AO分别作为·OH、·O2−和h+的淬灭剂,淬灭剂浓度为1 mmol·L−1。
-
1)XRD表征。采用XRD表征Fe2O3-TiO2-x的晶体结构和化学组成。如图1(a)所示,Fe2O3-TiO2异质结在25.3°、36.9°、37.8°、38.6°、48.0°、53.9°、55.1°、62.7°、68.8°、70.3°和75.0°处的特征衍射峰分别对应于锐钛矿TiO2的(101)、(103)、(004)、(200)、(105)、(211)、(204)、(116)、(220)和(215)晶面(PDF#21-1272)。表明负载α-Fe2O3后TiO2的晶体结构没有发生变化。同时,Fe2O3-TiO2-50的XRD谱图在24.1°、33.2°、35.6°、43.5°和49.5°处出现新的特征衍射峰,分别来源于α-Fe2O3的(012)、(104)、(110)、(202)和(024)晶面,与α-Fe2O3的PDF标准卡片数据一致(PDF#33-0664),表明α-Fe2O3成功负载于TiO2表面,并且结晶度良好。随着TiO2含量增加,α-Fe2O3的特征衍射峰峰强逐渐降低,TiO2的峰强逐渐增加。综上所述,α-Fe2O3和TiO2两组分成功结合,且两组分晶体结构保持完好。
2)BET表征。通过N2吸附-脱附等温线和BJH孔径分布曲线分析TiO2及Fe2O3-TiO2-200的比表面积和孔径结构。如图1(b)所示,TiO2和Fe2O3-TiO2-200均表现出Ⅳ型可逆吸附等温线,在高压(P/P0=0.7~1.0)范围内有滞回环,表明TiO2和Fe2O3-TiO2-200具有介孔结构。TiO2和Fe2O3-TiO2-200在15 nm附近有明显的尖峰,对应于典型的介孔结构。此外,Fe2O3-TiO2-200在15 nm的尖峰明显高于TiO2,表明引入Fe2O3可以产生更多介孔结构。TiO2的比表面积、总孔容和平均孔径分别为62.39 m2·g−1、0.34 cm3·g−1和21.86 nm;Fe2O3-TiO2-200的比表面积、总孔容和平均孔径分别为66.80 m2·g−1、0.35 cm3·g−1和20.76 nm。这表明Fe2O3的原位负载增加了TiO2的比表面积。
3)SEM及TEM表征。如图1(e)所示,Fe2O3-TiO2-200保持了TiO2原有的纳米颗粒结构。同时,表面变得更粗糙,归因于原位负载的Fe2O3纳米簇。进一步通过X射线能谱分析(EDS)观察催化剂表面元素种类。如图1(f)所示,Ti、O和Fe物种共存,且均匀分布在催化剂表面,表明Fe2O3成功负载于TiO2表面。如图1(g)所示,TiO2呈纳米颗粒状,粒径尺寸约为40.2 nm。在Fe2O3-TiO2-200的高分辨透射电镜(HRTEM)图像中观察到Fe2O3纳米簇锚定于TiO2表面,Fe2O3纳米簇的尺寸约为11.7 nm。此外,在图1(h)中还观察到晶格间距为0.35 nm和0.37 nm的晶格条纹,分别对应于锐钛矿结构TiO2的(101)晶面和α-Fe2O3的(012)晶面。
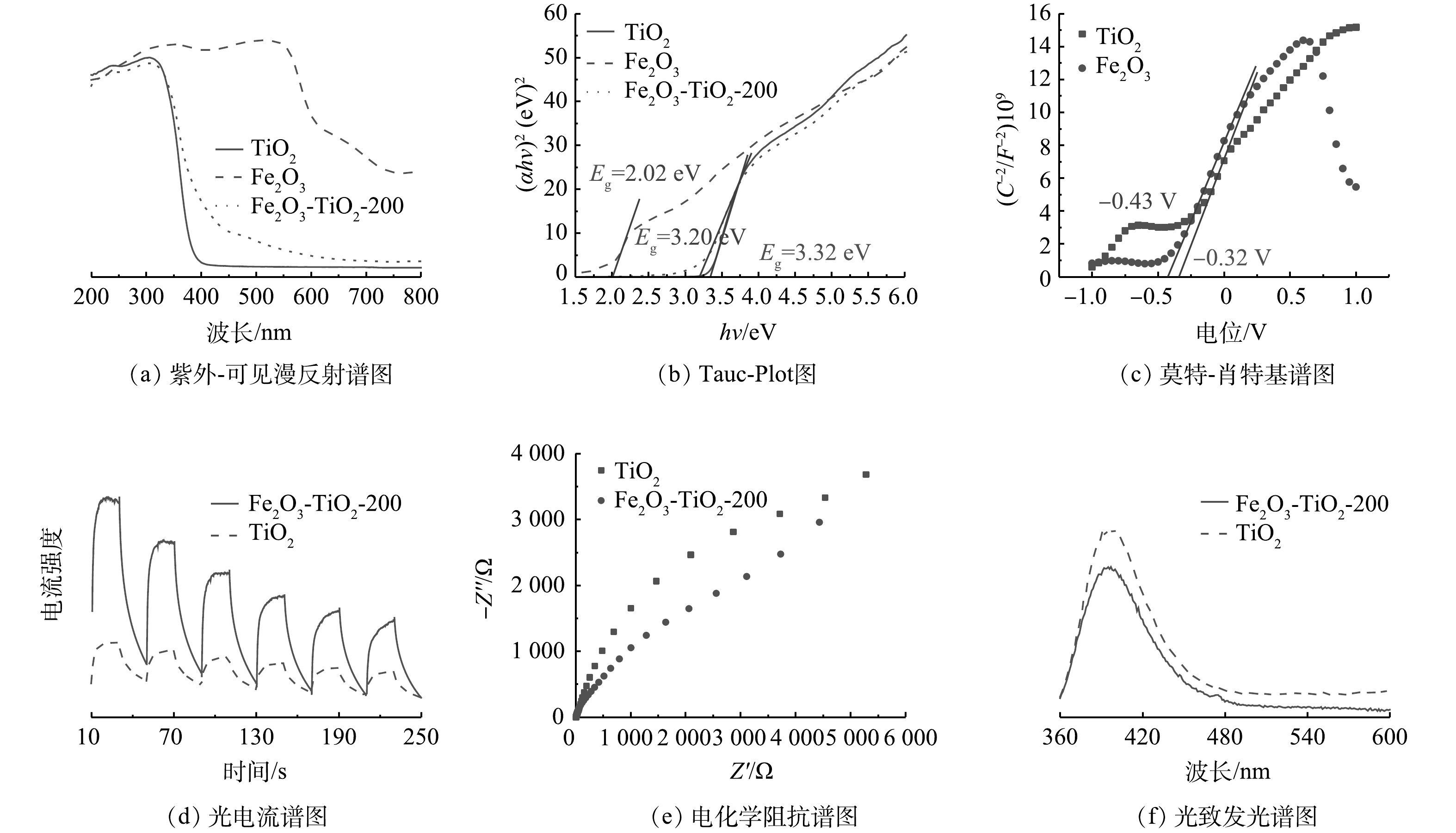
4)光电化学性能分析。通过紫外-可见漫反射表征来分析TiO2和Fe2O3-TiO2-200的光吸收性能。如图2(a)所示,Fe2O3在紫外可见光范围(200~800 nm)表现出较强的光吸收,而TiO2仅能吸收紫外光波段(200~400 nm),对可见光的吸收能力较弱。相比于TiO2,Fe2O3-TiO2-200的吸收峰出现了明显的红移。这主要归因于可见光吸收良好的Fe2O3纳米簇生长于在TiO2表面增强了Fe2O3-TiO2-200对可见光的吸收。如图2(b)所示,根据Tauc-Plot图计算TiO2、Fe2O3和Fe2O3-TiO2-200的带隙分别为3.32、2.02和3.20 eV。
根据TiO2和Fe2O3的莫特-肖特基谱图,计算得到催化剂的导带电位。如图2(c)所示,测定电极为饱和甘汞电极,TiO2和Fe2O3的平带电势分别为−0.32 V和−0.43 V。换算成标准氢电极之后的平带电位分别为−0.08 V和−0.19 V。由于TiO2和Fe2O3的切线斜率为正,故两者皆为n型半导体。结合n型半导体的导带电位低于平带电位0.2 V,因而TiO2和Fe2O3的导带电位分别为−0.28 V和−0.39 V。结合带隙计算得TiO2和Fe2O3的价带电位分别为3.04 V和1.63 V。
光电流曲线可反映光生电子-空穴的分离效率。如图2(d)所示,Fe2O3-TiO2-200显示出更高的光电流强度,表明其具有较快的光生载流子分离速率,与上述光芬顿实验中表现出的优越性能一致。图2(e)为TiO2和Fe2O3-TiO2-200的电化学阻抗谱图。与TiO2相比,Fe2O3-TiO2-200表现出更小的圆弧半径,表明电荷传递阻力更低,光生电子-空穴分离更迅速。图2(f)显示的光致发光光谱中,Fe2O3-TiO2-200的荧光强度明显低于TiO2,表明Fe2O3-TiO2-200产生光生电子-空穴分离速率更快。综上所述,通过TiO2和Fe2O3构建的Z型异质结构有利于促进电子-空穴的分离。
-
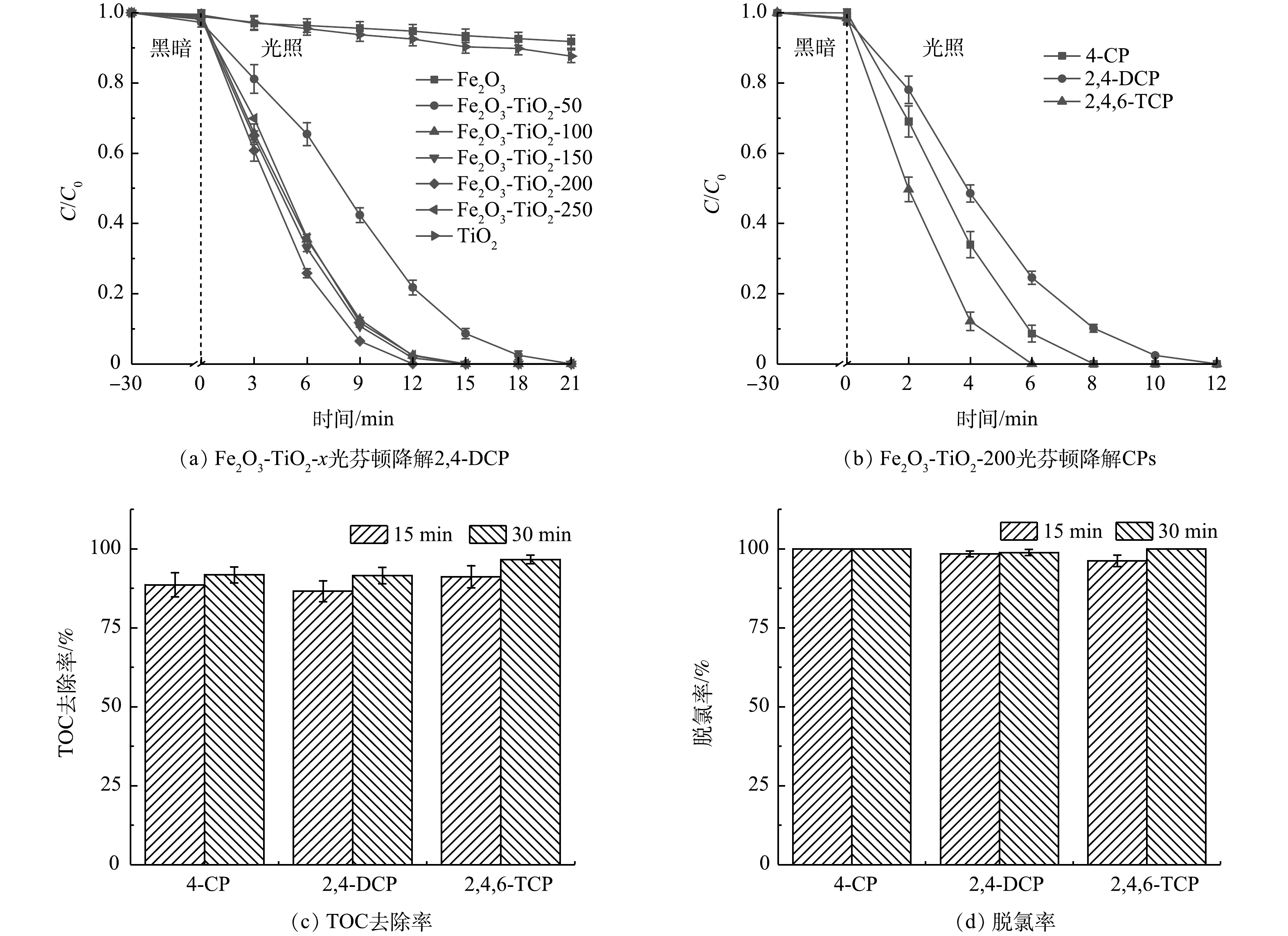
1)光芬顿降解性能。为评估Fe2O3与TiO2间的协同作用,以2,4-DCP为模型污染物系统比较Fe2O3-TiO2-x的光芬顿活性。如图3(a)所示,UV-Vis/H2O2/Fe2O3和UV-Vis/H2O2/TiO2体系对2,4-DCP的降解率分别可达9.20%和13.37%。与之相比,UV-Vis/H2O2/Fe2O3-TiO2-x表现出明显增强的光芬顿活性,且其光芬顿活性与TiO2的含量密切相关。随着Fe2O3比例的增加,2,4-DCP的降解速率先增加后降低。UV-Vis/H2O2/Fe2O3-TiO2-200具有最佳光芬顿活性,2,4-DCP的降解一级动力学常数k值达0.300 9 min−1,分别是UV-Vis/H2O2/Fe2O3和UV-Vis/H2O2/TiO2体系的83.6倍与44.9倍。当Fe2O3占比较低时,催化剂表面Fe(Ⅲ)/Fe(Ⅱ)循环位点较少,光芬顿反应速率受到限制。当Fe2O3占比过高时,过量的Fe2O3在TiO2表面团聚,形成大尺寸颗粒,导致活性位点不均匀。
为验证UV-Vis/H2O2/Fe2O3-TiO2-200体系对CPs去除的普适性,选取3种CPs作为模型污染物全面评估其降解性能、矿化能力和脱氯效率。如图3(b)所示,在光照8、12和6 min后可分别实现对4-CP、2,4-DCP和2,4,6-TCP的完全去除。由图3(c)可见,UV-Vis/H2O2/Fe2O3-TiO2-200体系在光照30 min时对4-CP、2,4-DCP和2,4,6-TCP的TOC去除率分别可达91.8%、91.5%和96.7%。同时,如图3(d)所示,UV-Vis/H2O2/Fe2O3-TiO2-200体系对3种CPs的脱氯效率均达到100%。以上结果表明,UV-Vis/H2O2/Fe2O3-TiO2-200体系对3种CPs均具有良好的去除效果。
表1比较了基于UV-Vis/H2O2/Fe2O3-TiO2-200体系和其他光芬顿体系对2,4-DCP的降解性能。可见,UV-Vis/H2O2/Fe2O3-TiO2-200体系具有降解速率快且H2O2使用量低的优点。
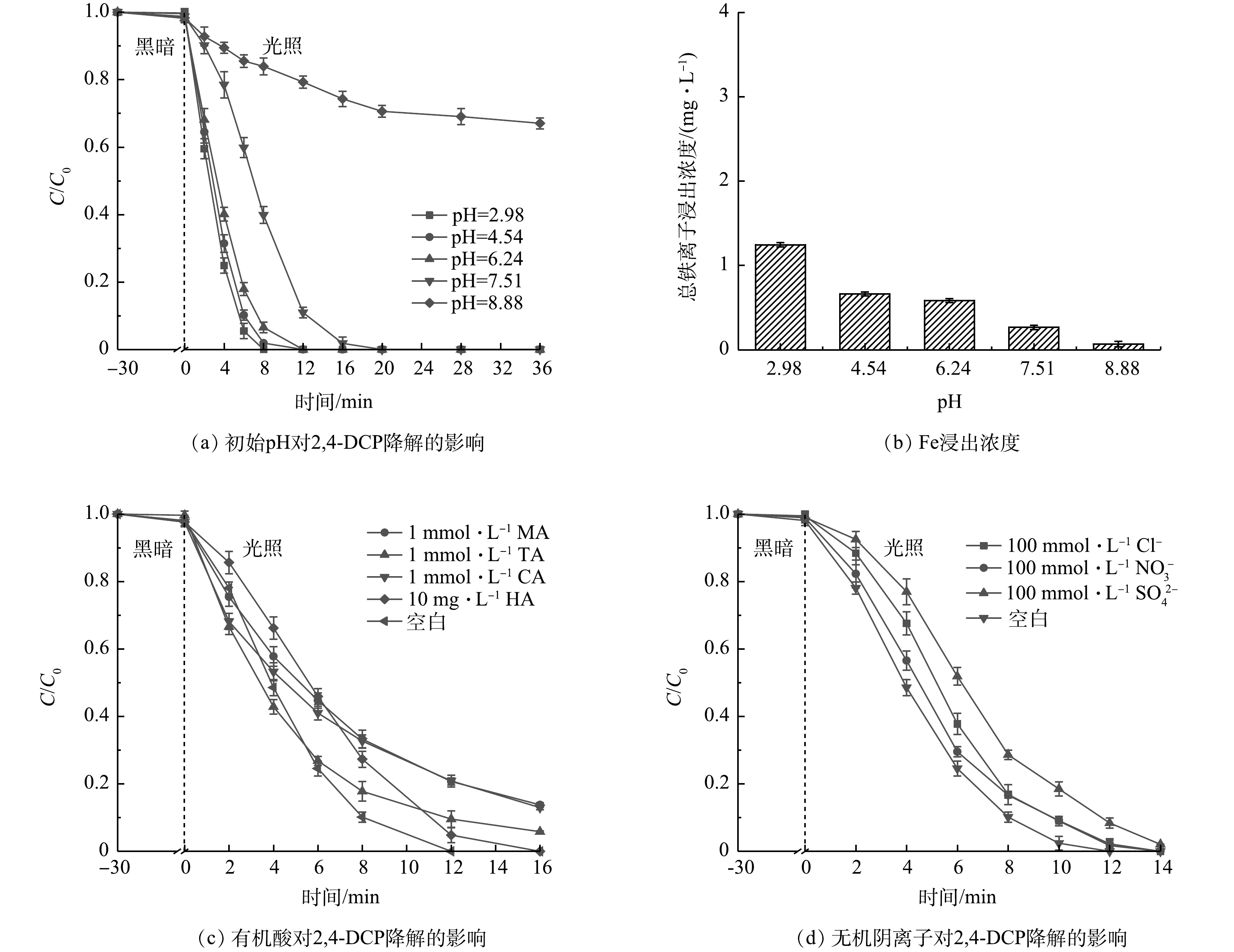
2)环境因子影响。探究pH、共存有机酸和无机阴离子对UV-Vis/H2O2/Fe2O3-TiO2-200体系降解2,4-DCP的影响。如图4(a)所示,在初始pH为2.98~7.51时,2,4-DCP在20 min内均实现完全降解。随着pH增加至8.88,2,4-DCP的降解速率受到显著抑制。这可能一方面归因于弱酸性的H2O2在较高的pH体系中易自分解[20-21],另一方面归因于在高pH体系中·OH氧化能力下降[22-23]。通过ICP-OES测量溶液中Fe浸出浓度。如图4(b)所示,总铁离子浸出质量浓度最高为1.2 mg·L−1。如图4(c)所示,MA、TA、CA或HA共存时2,4-DCP的降解受到一定抑制。这主要归因于有机酸与2,4-DCP竞争消耗·OH等活性物种,从而抑制2,4-DCP降解[24-25]。如图4(d)所示,高浓度Cl−、NO3−和SO42-对2,4-DCP的光芬顿降解仅有轻微的抑制。上述结果表明UV-Vis/H2O2/Fe2O3-TiO2-200体系适用于酸性和中性条件下的有机酸和高浓度阴离子共存的复杂水体。
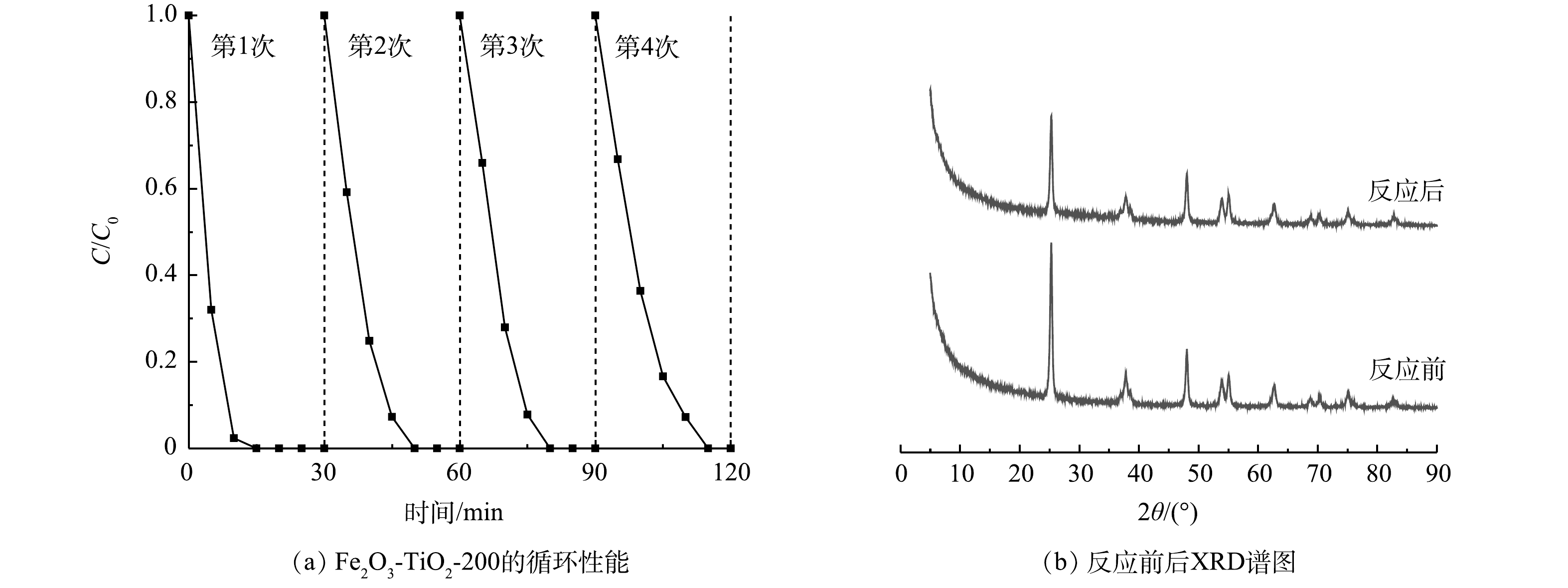
3)稳定性评估。催化剂的循环稳定性是衡量其是否能够实际应用的重要条件。如图5(a)所示,Fe2O3-TiO2-200重复使用后性能稳定,2,4-DCP去除率在4次循环后仍然能够达到100%,总铁离子浸出浓度最大值为0.59 mg·L−1。此外,对比回用后收集的催化剂与初始催化剂的XRD谱图(图5(b)),催化剂在4次运行前后XRD特征峰位置无明显变化。以上结果表明Fe2O3-TiO2-200具有良好的稳定性。
-
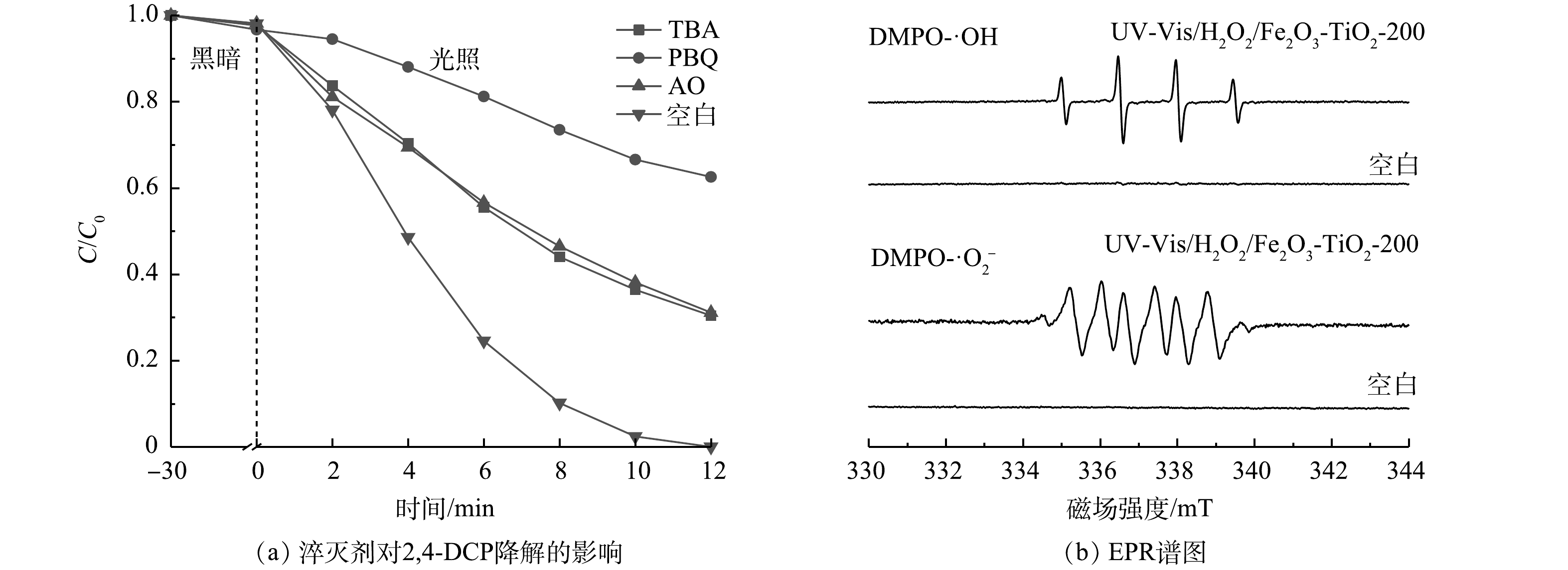
为了探究光芬顿反应过程中H2O2活化和2,4-DCP降解的机制,进行了一系列活性物种淬灭实验以确定UV-Vis/H2O2/Fe2O3-TiO2-200体系中的活性物种。如图6(a)所示,3种淬灭剂均对2,4-DCP的降解起抑制作用,表明·OH、·O2−和h+均参与了2,4-DCP的降解[26-27]。
如图6(b)所示,UV-Vis/H2O2/Fe2O3-TiO2-200体系中能检测到DMPO-·OH和DMPO-·O2−的特征信号,表明光芬顿反应过程中会产生·OH和·O2−,与上述活性物种淬灭实验结果一致。
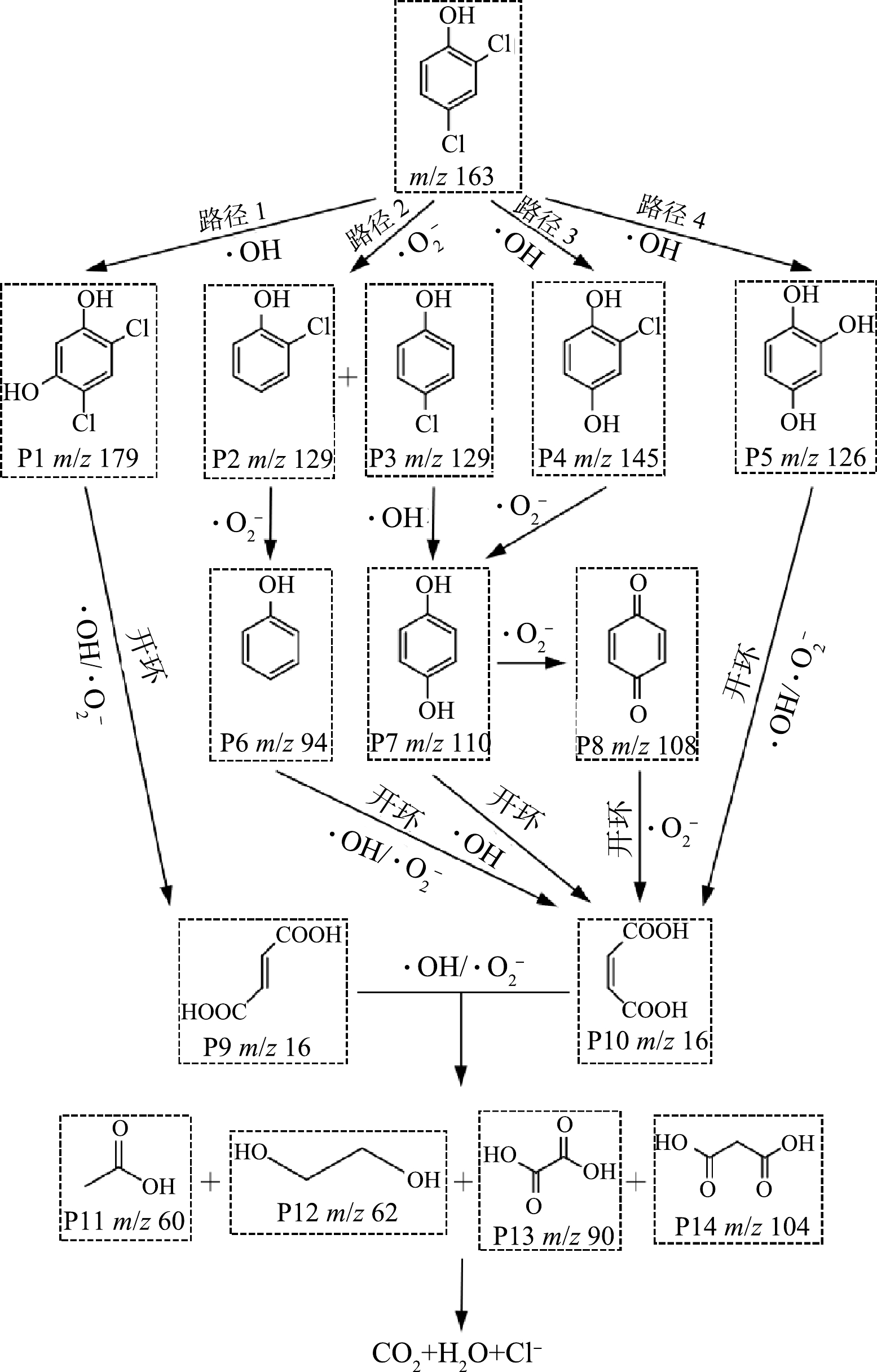
为进一步揭示UV-Vis/H2O2/Fe2O3-TiO2-200降解2,4-DCP的主要机制,通过LC-MS分析2,4-DCP降解可能存在的降解路径。如图7所示,2,4-DCP的邻位、间位和对位均可被·OH和·O2−攻击生成4,6-二氯间苯二酚(P1 m/z=179)、2-氯苯酚(P2 m/z=129)和4-氯苯酚(P3 m/z=129)、2-氯-1,4-苯二酚(P4 m/z=145)和1,2,4-苯三酚(P5 m/z=126)等中间产物。2-氯苯酚和4-氯苯酚被ROS攻击生成苯酚(m/z=94)、对苯酚(m/z=110)、对苯醌(m/z=108)和等环状产物。环状产物进一步被·OH和·O2−攻击发生开环反应生成顺丁烯二酸(m/z=116)和反丁烯二酸(m/z=116)等链式产物。最终在·OH、·O2−和h+共同作用下生成小分子有机物并逐步实现矿化。
采用毒性评估软件对2,4-DCP及其降解中间产物的大鼠口服LD50(半数致死剂量)和生物富集系数进行评估。如表2所示,除2-氯苯酚(P2)外,其余中间产物的大鼠口服LD50均高于2,4-DCP,表明2,4-DCP被降解后毒性降低。2,4-DCP的生物富集系数为57.46,然而中间产物(P1~P14)的生物富集系数均低于30。相较于2,4-DCP,中间产物在生物体内的富集能力明显被削弱。以上毒性评估证实UV-Vis/H2O2/Fe2O3-TiO2-200对2,4-DCP的降解可有效降低其生物毒性。
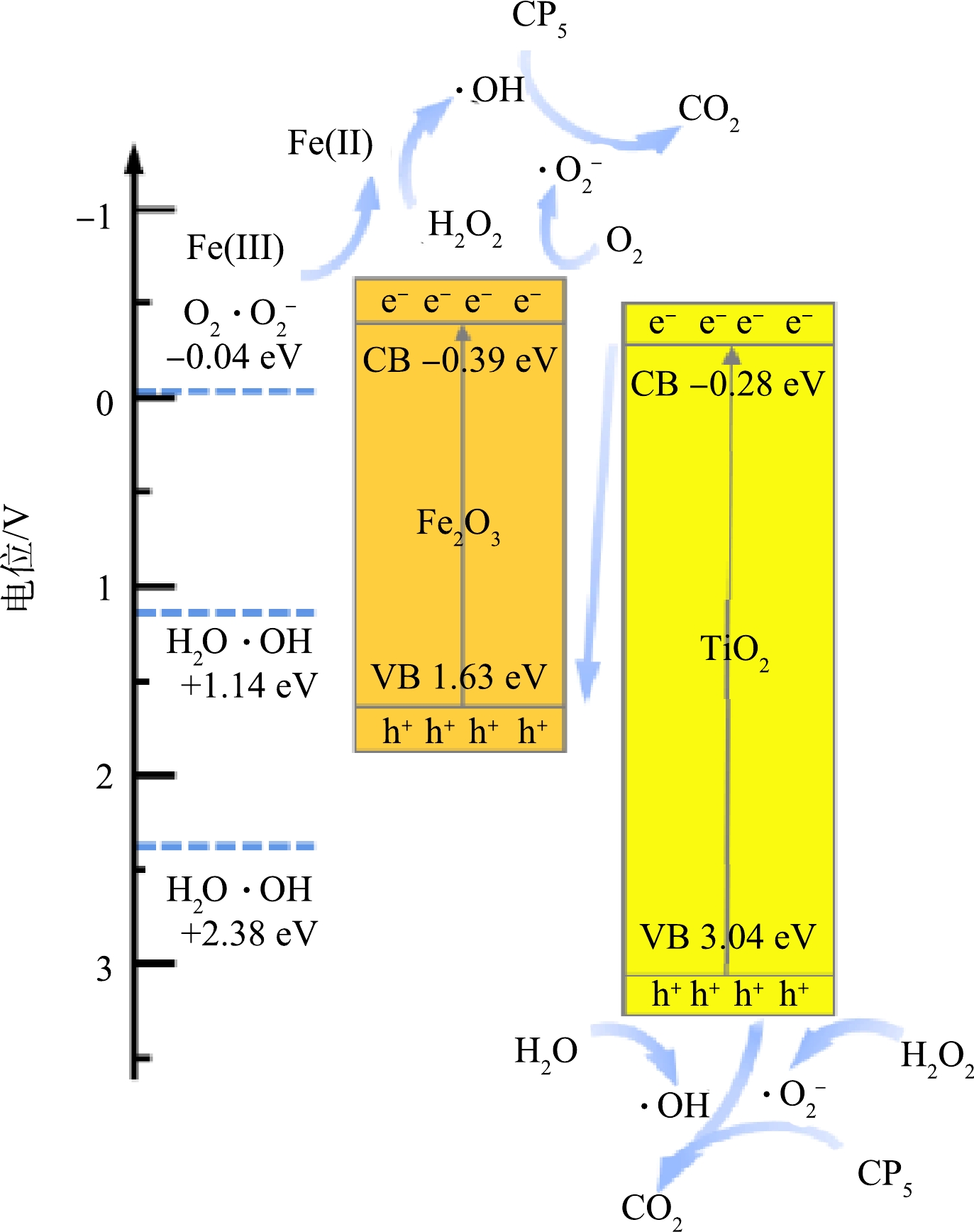
根据上述结果,提出了UV-Vis/H2O2/Fe2O3-TiO2-200体系降解CPs的主导机制(图8和式(1)~(7))。首先,Fe2O3和TiO2之间的费米能级差在Fe2O3-TiO2界面处形成内建电场,驱动光生电子-空穴对快速分离;光生电子主要迁移至Fe2O3表面,而光生空穴主要迁移至TiO2表面(式(1));光生电子可快速将Fe2O3表面Fe(Ⅲ)还原成Fe(Ⅱ)(式(2)),从而活化吸附在Fe2O3表面的H2O2产生·OH(式(3))。此外,光生电子也可活化溶解氧产生·O2−(式(4));光生空穴则氧化吸附在TiO2表面的H2O2生成·O2−(式(5));还可以直接氧化水分子产生·OH(式(6))。以上路径产生的·OH、·O2−和h+经过脱氯和开环等过程,可将CPs矿化成CO2和H2O(式(7))。
-
1)以FeCl3·6H2O为铁源,采用低温煅烧法将Fe2O3纳米簇负载在TiO2表面制备系列Z型异质结Fe2O3-TiO2-x。TiO2用量为200 mg制备的Fe2O3-TiO2-200性能最优。2,4-DCP的降解一级动力学常数为0.300 9 min−1,分别为Fe2O3和TiO2的83.6倍与44.9倍。
2) UV-Vis/H2O2/Fe2O3-TiO2-200在6~12 min内对4-CP、2,4-DCP和2,4,6-TCP的降解率均可达100%;在30 min内实现100%脱氯率,且TOC去除率分别可达91.8%、91.5%和96.7%。
3) 2,4-DCP通过脱氯和开环的路径被有效降解,中间产物生物毒性有效降低。
4)由TiO2和Fe2O3构建的Z型异质结可实现光生电子-空穴的有效分离,促进·OH和·O2−的产生。
新型Z型异质结增强光芬顿降解水中氯酚
Novel Z-type heterojunction enhancing photo-Fenton degradation of aqueous chlorophenols
-
摘要: 增强光生载流子分离和Fe(Ⅲ)/Fe(Ⅱ)循环是增强光芬顿催化剂性能的关键。本研究采用低温煅烧法制备系列新型Z型异质结Fe2O3-TiO2-x,利用X射线衍射、扫描电子显微镜和透射电子显微镜等表征方法证实Fe2O3纳米簇成功结合在TiO2表面。以2,4-二氯苯酚(2,4-DCP)为模型污染物评估系列催化剂的光芬顿性能,发现UV-Vis/H2O2/Fe2O3-TiO2-200体系最佳,可在12 min内实现完全降解。而且光照30 min后,2,4-DCP的矿化率可达91.5%、脱氯率可达100%。采用液质联用仪分析2,4-DCP的降解路径,主要经过脱氯和开环等过程,并发现其降解中间产物的毒性有效降低。深入分析新型Z型异质结增强光芬顿的机制,主要源自于内建电场驱动载流子分离、加速Fe(Ⅲ)/Fe(Ⅱ)循环。此外,UV-Vis/H2O2/Fe2O3-TiO2-200体系适用于酸性和中性、有机酸和高浓度阴离子共存的复杂水体,可高效、深度降解水中氯酚类污染物,具有良好的应用潜力。Abstract: Enhancing photogenerated-carriers separation and Fe(Ⅲ)/Fe(Ⅱ) cycling are the key to improve the performance of photo-Fenton catalyst. In this study, a series of novel Z-type heterojunction Fe2O3-TiO2-x were prepared by low temperature calcination method, the Fe2O3 nanoclusters were successfully anchored on TiO2 surface by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. Taking 2,4-dichlorophenol (2,4-DCP) as the model pollutant, it was found that UV-Vis/H2O2/Fe2O3-TiO2-200 system exhibited the optimal photo-Fenton performance, in which 2,4-DCP was completely degraded within 12 min illumination. The mineralization and dechlorination rates of 2,4-DCP reached 91.5% and 100% after 30 min illumination, respectively. The degradation path of 2,4-DCP was analyzed via Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry instrument, the dechlorination and ring-opening process was identified, and the toxicity of the degradation intermediates was effectively reduced. The enhanced photo-Fenton mechanism of Z-type heterojunction mainly resulted from the internal electric field driven-carrier separation and increased Fe(Ⅲ)/Fe(Ⅱ) cycle. In addition, the UV-Vis/H2O2/Fe2O3-TiO2-200 system could efficiently degrade chlorophenols in the complex water body with the coexistence of organic acids and high concentration of anions under acidic and neutral conditions, which exhibited promising potential for application.
-
Key words:
- photo-Fenton /
- catalysis /
- heterojunction /
- chlorophenol
-

-
表 1 Fe2O3-TiO2-200与已报道光芬顿体系降解2,4-DCP的性能比较
Table 1. Comparison of 2,4-DCP degradation performance by Fe2O3-TiO2-200 with those by previously reported catalysts via photo-Fenton process
表 2 毒性分析
Table 2. Toxicity analysis
化合物 大鼠口服LD50/(mg·L−1) 生物富集系数 化合物 大鼠口服LD50/(mg·L−1) 生物富集系数 2,4-DCP 47.01 57.46 P8 129.96 7.91 P1 N/A 26.33 P9 9 305.88 0.53 P2 40 18.21 P10 707.55 0.53 P3 670.05 24.56 P11 3 308.15 0.6 P4 N/A 21.38 P12 4 698.42 0.74 P5 N/A 3.97 P13 7 506.47 0.17 P6 316.72 7.61 P14 1 310.16 0.2 P7 301.9 13.43 注:N/A表示未检测到。 -
[1] 刘楚琛, 阎秀兰, 刘琼枝, 等. Fenton试剂和活化过硫酸钠氧化降解土壤中的二氯酚和三氯酚[J]. 环境工程学报, 2018, 12(6): 1749-1758. [2] 黄建新, 陈经浩, 陆胜勇, 等. GC-ECD和LC-MS/MS测定垃圾焚烧飞灰中氯苯和氯酚的方法[J]. 环境工程学报, 2017, 11(2): 1293-1299. [3] 吴文慧, 邓亚梅, 施维林, 等. 钒氧化物活化过硫酸钠降解2, 4, 6-三氯酚的机制[J]. 环境工程学报, 2017, 11(5): 3244-3250. [4] 钟少芬, 莫健文, 李阳苹, 等. 粉末活性炭对水中氯酚的吸附[J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(6): 2927-2932. [5] 于荆, 黄力群, 刘承鸿, 等. 微生物燃料电池阴阳两级分步降解对氯酚效果[J]. 环境工程学报, 2017, 11(6): 3507-3510. [6] LIU J, HAN D D, CHEN P J, et al. Positive roles of Br in g-C3N4/PTCDI-Br heterojunction for photocatalytic degrading chlorophenols[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 418:129492. [7] DAVARI N, FARHADIAN M, NAZAR ARS, et al. Degradation of diphenhydramine by the photocatalysts of ZnO/Fe2O3 and TiO2/Fe2O3 based on clinoptilolite: Structural and operational comparison[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2017, 5(6): 5707-5720. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2017.10.052 [8] BABAEI A A, GOLSHAN M, KAKAVANDI B. A heterogeneous photocatalytic sulfate radical-based oxidation process for efficient degradation of 4-chlorophenol using TiO2 anchored on Fe oxides@carbon[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2021, 149: 35-47. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2020.10.028 [9] AHN Y-Y, BAE H, KIM H-I, et al. Surface-loaded metal nanoparticles for peroxymonosulfate activation: Efficiency and mechanism reconnaissance[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2019, 241: 561-569. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.09.056 [10] 谢怡俐, 楚芳, 张敏婷, 等. 芬顿铁泥组分解析及其对造纸废水厌氧处理的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2022, 16(11): 3579-3586. [11] 郑豪, 刘宇涛, 李爱民, 等. 封装型双金属阴极催化剂强化电芬顿技术高效去除磺胺甲恶唑[J]. 环境工程学报, 2022, 16(9): 2862-2873. [12] XIE AT, CUI JY, YANG J, et al. Photo-Fenton self-cleaning membranes with robust flux recovery for an efficient oil/water emulsion separation[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(14): 8491-8502. doi: 10.1039/C9TA00521H [13] VORONTSOV A V. Advancing Fenton and photo-Fenton water treatment through the catalyst design[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 372: 103-112. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.04.033 [14] SU L N, WANG P F, MA X L, et al. Regulating local electron density of iron single sites by introducing nitrogen vacancies for efficient photo-Fenton process[J]. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition, 2021, 60(39): 21261-21266. doi: 10.1002/anie.202108937 [15] JIANG JJ, WANG XY, LIU Y, et al. Photo-Fenton degradation of emerging pollutants over Fe-POM nanoparticle/porous and ultrathin g-C3N4 nanosheet with rich nitrogen defect: Degradation mechanism, pathways, and products toxicity assessment[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 278:119349. [16] XU W, XUE W, HUANG H, et al. Morphology controlled synthesis of alpha-Fe2O3-x with benzimidazole-modified Fe-MOFs for enhanced photo-Fenton-like catalysis[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 291:120129. [17] LIU D, LI C, NI T, et al. 3D interconnected porous g-C3N4 hybridized with Fe2O3 quantum dots for enhanced photo-Fenton performance[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 555:149677. [18] GONG Q J, LIU Y, DANG Z. Core-shell structured Fe3O4@GO@MIL-100(Fe) magnetic nanoparticles as heterogeneous photo-Fenton catalyst for 2, 4-dichlorophenol degradation under visible light[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 371: 677-686. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.03.019 [19] WANG Y X, RAO L, WANG P F, et al. Photocatalytic activity of N-TiO2/O-doped N vacancy g-C3N4 and the intermediates toxicity evaluation under tetracycline hydrochloride and Cr(VI) coexistence environment[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 262:118308. [20] SEN GUPTA S, STADLER M, NOSER C A, et al. Rapid total destruction of chlorophenols by activated hydrogen peroxide[J]. Science, 2002, 296(5566): 326-328. doi: 10.1126/science.1069297 [21] CZAPLICKA M. Photo-degradation of chlorophenols in the aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006, 134(1/2/3): 45-59. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.10.039 [22] YANG G, LIANG Y J, XIONG Z R, et al. Molten salt-assisted synthesis of Ce4O7/Bi4MoO9 heterojunction photocatalysts for Photo-Fenton degradation of tetracycline: Enhanced mechanism, degradation pathway and products toxicity assessment[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 425:130689.. [23] YAN HX, PAN YS, LIAO XB, et al. Enhancement of Fe2+/Fe3+ cycles by the synergistic effect between photocatalytic and co-catalytic of ZnxCd1-xS on photo-Fenton system[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2022, 576:152464. [24] LIN X Q, LI Z L, LIANG B, et al. Accelerated microbial reductive dechlorination of 2, 4, 6-trichlorophenol by weak electrical stimulation[J]. Water Research, 2019, 162: 236-245. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.06.068 [25] LI H, SHAN C, PAN B. Fe(III)-doped g-C3N4 mediated peroxymonosulfate activation for selective degradation of phenolic compounds via high-valent iron-oxo species[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(4): 2197-2205. [26] LOPEZ-VINENT N, CRUZ-ALCALDE A, GUTIERREZ C, et al. Micropollutant removal in real WW by photo-Fenton (circumneutral and acid pH) with BLB and LED lamps[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 379:122416. [27] CHEN X, ZHANG M, QIN H W, et al. Synergy effect between adsorption and heterogeneous photo-Fenton-like catalysis on LaFeO(3/)lignin-biochar composites for high efficiency degradation of ofloxacin under visible light[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 280:119751. [28] CHEN Y, SU R D, WANG F D, et al. In-situ synthesis of CuS@carbon nanocomposites and application in enhanced photo-Fenton degradation of 2, 4-DCP[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 270:129295.. [29] REN L, LU S Y, FANG J Z, et al. Enhanced degradation of organic pollutants using Bi25FeO40 microcrystals as an efficient reusable heterogeneous photo-Fenton like catalyst[J]. Catalysis Today, 2017, 281: 656-661. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2016.06.028 -




 下载:
下载: