-
近年来,随着化肥过量使用以及工业污染物的排放,导致全球范围内的水源硝酸盐氮(
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ )污染问题严重[1]. 研究表明,水体中的硝酸盐可导致浮游植物富营养化,也可经过还原等反应转化为具有强毒性、致畸性的N-亚硝胺和N-硝酰胺等物质[2],从而对生态环境及人体健康造成危害. 当前,许多国家将硝酸盐氮作为重要的水质指标加以控制,如美国和中国规定饮用水中硝酸盐浓度应不超过10 mg·L−1[3]. 鉴于${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的高溶解度和化学稳定性,水中${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 较难去除,因此去除水中NO3¯是水处理领域一个亟待解决的问题[4].目前,国内外常用的硝酸盐氮去除技术主要有化学还原法[5]、电化学法[6]、生物法[7]、电渗析法[8]、离子交换法[9]和吸附法[10]等. 相比其它水处理技术,吸附法因其操作简单、效率高、投资少等特点,被认为是去除水中硝酸盐方法之一[11]. 对于吸附技术而言,吸附剂的研发是该方法的核心所在. 当前,改性沸石[12]、活性炭[13]、壳聚糖[14]、树脂[15]、金属有机骨架MOF[16]、SnO2纳米球[17]等天然改性及合成材料作为吸附剂广泛应用于水体中硝酸盐的吸附. 刘栋等[18]从天然沸石的改性方法、吸附机理、吸附影响因素、吸附材料的再生等方面系统阐述了改性沸石作为吸附剂去除水体中硝酸盐. 树脂因其具有机械强度高、无毒无害、稳定性好和可再生等特点,被广泛应用于吸附去除水体中无机离子. 鉴于水中硝酸盐溶解度高且化学性质稳定,不易被去除. 因此,选择高效经济环保的吸附剂成为吸附去除
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的热点. 当前,硝酸根去除的研究主要集中在提高${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的去除效率及其吸附选择性方面,阴离子交换树脂合成制备的报道不多. 例如,Kalaruban等[19]采用金属浸渍改性Dowex 21K XLT阴离子交换树脂,其对硝酸盐的最大吸附量由27.6 mg·g−1N增加75.3 mg·g−1N. Li等[20]合成了一系列具有不同三烷基铵基团的阴离子交换树脂,研究表明,在氯离子、硫酸盐和腐殖酸存在下,长链三烷基胺改性的树脂优先吸附硝酸盐,其中性能最优L20树脂对硝酸盐的吸附量可达145.08 mg·g−1. 目前,关于三羟甲基丙烷三甲基丙烯酸酯合成树脂用于去除饮用水中污染物的研究较少,尤其利用盐酸叔胺基树脂对水中${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 尚未见报道.本研究通过自由基聚合的方法制备了盐酸叔胺树脂(tertiary amine hydrochloride macroprous resin,TAHMR)作为吸附剂[21],研究了树脂用量、溶液pH、共存组分和离子强度等因素对水中
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的吸附剂再生性能. 最后,通过傅立叶变换红外光谱(FTIR)和X射线光电子能谱(XPS),对其吸附${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的机理进行探讨,以期开发新型水处理材料提供基础依据. -
所有化学试剂均为分析纯试剂. 硝酸钾(KNO3)、硫酸钠(Na2SO4)、碳酸钠(Na2CO3)、磷酸钠(Na3PO4)、氟化钠(NaF)、氯化钠(NaCl)、氯化镁(MgCl2)和氯化钙(CaCl2)均购自上海国药集团,腐殖酸(HA)购自Sigma-Aldrich化学公司. 实验用水由Millpore纯水仪(Millpore公司,美国)制备的超纯水.
-
参考文献采用悬浮聚合法制备新型盐酸叔胺树脂(TAHMR)[21],具体步骤如下:将一定量的十二烷基苯磺酸钠、膨润土加入溶解有聚乙烯醇去离子水(60 mL)中,加热至100 ℃将其溶解,然后将适量的功能单体甲基丙烯酸二甲氨乙酯溶于甲苯中,依次加入三羟甲基丙烷三甲基丙烯酸酯、致孔剂液体石蜡和引发剂偶氮二异丁腈,室温超声混匀待用;在机械搅拌下将油相缓慢滴加至水相中,70 ℃、搅拌12 h,抽提、水洗、真空干燥制得叔胺树脂(tertiary amine macroprous resin,TAMR). 将TAMR置于1 mmol·L−1的盐酸溶液浸泡24 h,产物经抽滤、水洗、真空干燥得到TAHMR. 采用傅里叶变换红外光谱仪(Nicolet6700,英国),X射线光电子能谱仪(XPS,Thermo Scientific K-Alpha,美国)对吸附剂的官能团和结构进行表征.
对吸附剂的表面形貌结构采用扫描电子显微镜(Carl Zeiss SUPRA-55,德国)进行观察;采用电位仪(Malven Nano-ZS90,英国)测定树脂的Zeta电位[22].
-
将100 mL的0.8 mmol·L−1的
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 置于具塞三角瓶中,加入一定质量的TAHMR,用盐酸或氢氧化钠调节溶液pH,在150 r·min−1、25 ℃条件下恒温振荡吸附24 h. 通过批量实验考察吸附剂投加量、初始溶液pH(2.0—12.0)、离子强度(0—0.1 mmol·L−1)、干扰组分(${\rm{HPO}}_4^{2-} $ 、${\rm{CO}}_3^{2-} $ 、${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 、F−、Cl−、Ca2+和Mg2+,5.0 mmol·L−1)等因素对TAHMR吸附性能的影响. 对于吸附动力学研究,在确定优化的吸附剂用量和pH条件下,不同浓度的${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 溶液(0.4、0.8、1.6 mmol·L−1)加入一定量TAHMR置于25 °C恒温振荡吸附,按上述操作在不同时间内取上清液测定${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 浓度. 在不同温度下(15、25、35 ℃),将0.1 g干树脂加入到100 mL浓度为0.16—8.0 mmol·L−1范围的${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ ,pH为6.0,在150 r·min−1、25 ℃恒温的振荡器中吸附24 h,测定吸附等温线. 在${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 和${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 的共存体系中,将0.05 g TAHMR加入到50 mL含 0—0.5 mmol·L−1${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 和${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 混合浓度溶液中,吸附平衡后,取上清液过滤,分析滤液中的${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 和${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 浓度,测定吸附等温线. 在不同树脂吸附${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 性能实验中,取相同质量的不同树脂,其他实验条件与不同影响因素实验相一致.为了测试TAHMR的实际应用性能,实际水样样品采自广西壮族自治区南丹县地下水、合浦县洪潮水库、南流江地表水和实验室内自来水,并经0.45 μm滤膜处理后,4 ℃保存备用.
根据吸附前后浓度的变化计算
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 或其他吸附对象的吸附量(q)和去除率,${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 在TAHMR上的平衡吸附量(mmol·g−1)与去除率R(%)通过公式(1)和(2)计算:式中,qe为TAHMR树脂对
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的吸附量(mmol·g−1),C0和Ce分别为初始硝酸盐氮浓度和平衡浓度(mmol·L−1);m为TAHMR吸附树脂的质量(g);V为吸附溶液体积(L). -
溶液中
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 和${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 溶液采用离子色谱系统(930 Metrohm, 瑞士)测定,分离柱:Supp-150/4.0 型阴离子交换柱(150 mm × 4.0 mm,瑞士万通公司);淋洗液:3.6 mmol·L−1 Na2CO3溶液;淋洗方式:等浓度淋洗;流速:0.8 mL·min−1;进样体积:250 μL;柱温:30℃;以峰面积进行定量. 所有实验数据重复测量3次取平均值. 水中溶解性有机碳(DOC)采用TOC仪进行测定(Vairo Elementar,德国). -
将处理含
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 水样的TAHMR树脂,分别加入25 mL不同的脱附剂(NaOH、NaHCO3、NaCl、HCl、H2SO4和CH3COOH)在25 ℃下静态脱附平衡后,过滤干燥后得到再生TAHMR树脂,将其用于再吸附,并测定脱附溶液中硝酸盐氮的含量. 将经过脱附再生的TAHMR继续进行多次重复“脱附-再生-吸附”实验,考察TAHMR树脂的重复使用性能. -
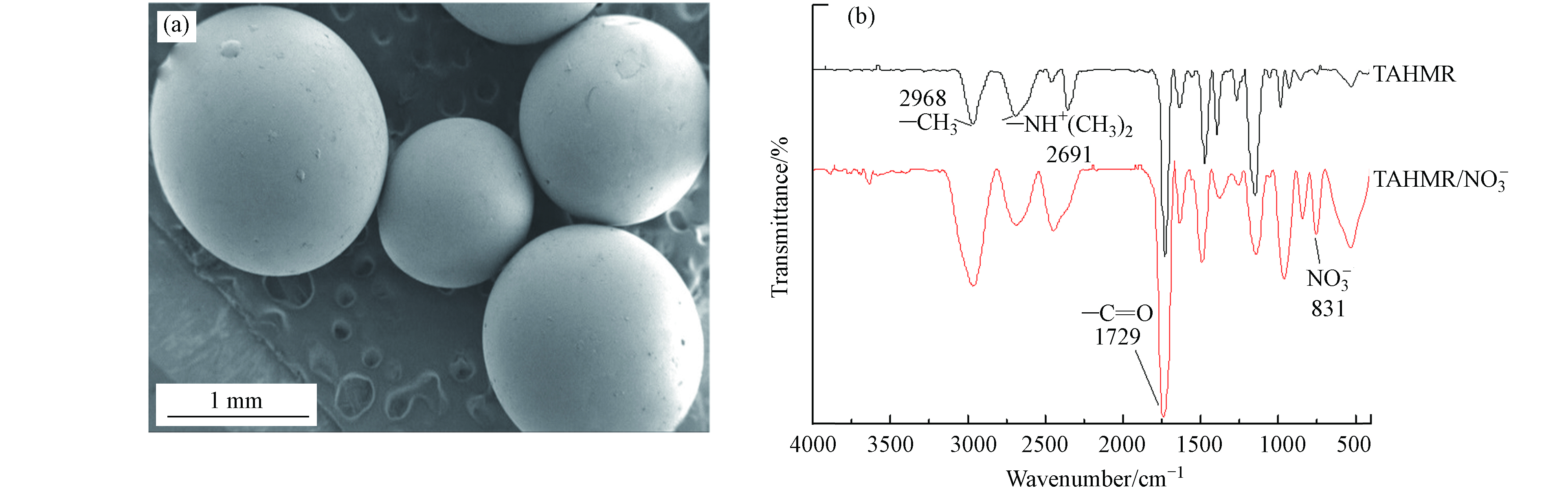
图1a为TAHMR的扫描电镜图. 从图1可看出,TAHMR树脂外观呈球状,表面均一. TAHMR树脂的比表面积为7.9 m2·g−1,平均孔径13.4 nm,总孔体积为0.018 cm3·g−1. TAHMR吸附
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 前后红外光谱图如图1b所示. 吸附前,TAHMR图谱中,在2968 cm−1处出现一个—CH3甲基的伸缩振动、在2691 cm−1(—N(CH3)2H+)、1729 cm−1出现—C=O羰基和1400 cm−1处出现C—N伸缩振动峰. 与TAHMR吸附${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 后的FTIR谱图相比,发现TAHMR吸附${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 后在831 cm−1出现了新的特征峰,该峰为${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的面外弯曲振动吸收峰[23]. 结果表明,在吸附过程中${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 被成功吸附到TAHMR上,其作用位点主要为叔胺基团. -
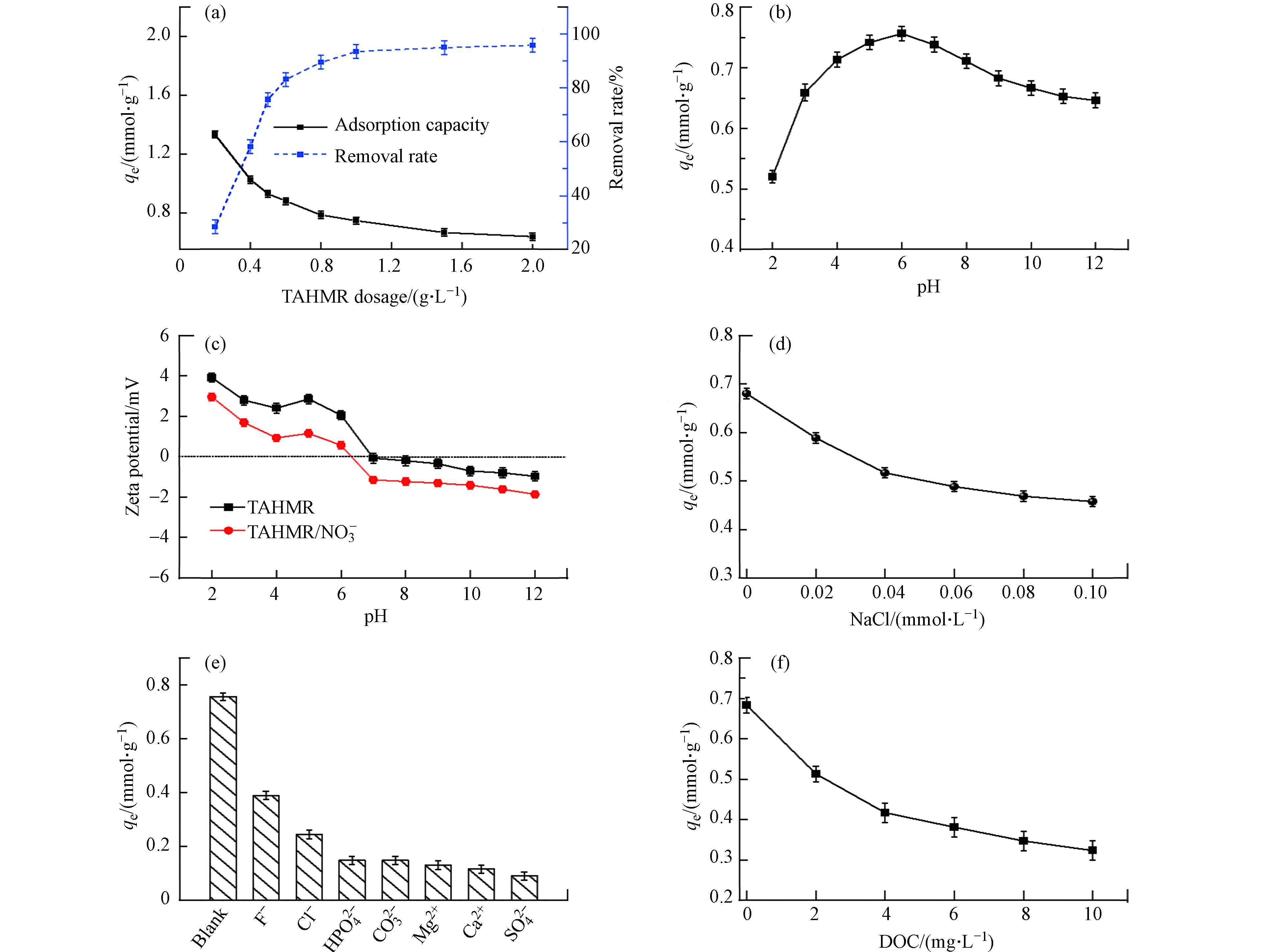
图2a为不同TAHMR投加量对
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 吸附性能的影响. 由图2可知,TAHMR投加量在0.2—1.0 g·L−1范围内,随着投加量的增加,TAHMR对${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的吸附量呈快速下降,去除率呈先快速上升趋势,TAHMR投加量大于1.0 g·L−1时吸附量呈缓慢下降,去除率呈平缓上升. 这是由于吸附剂投加量较少时,TAHMR表面存在大量吸附位点,在浓度差的作用下溶液中的${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 迅速占据TAHMR表面位点;对于单位吸附量而言,TAHMR对水中${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的单位吸附量随着吸附剂投加量的增加而降低,其原因是吸附剂投加量的增加会使吸附剂表面处于不饱和状态的吸附位点增加[22]. 综合考虑吸附量和去除效率,本文的后续研究中选取TAHMR添加量1.0 g·L−1.pH是影响吸附效果的重要因素. 图2b和2c分别为不同pH对TAHMR树脂对
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 吸附量及Zeta电位的影响. 由图2b可知,当溶液pH在2.0—6.0范围内,TAHMR对${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的吸附量随着pH的增加而增加;当pH为6.0时,TAHMR对${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 吸附量为最大值. 这是由于在pH较低时,溶液中的${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 容易质子化为HNO3导致吸附效果不佳;随着pH增加,TAHMR表面的叔胺结构可以与氢离子相结合,使得TAHMR活性位点带正电有利于${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 吸附[24]. pH在6.0—12.0范围内,吸附量随着pH的增加而呈降低趋势. 进一步测定了TAHMR吸附前后的Zeta电位(图2c),结果表明,随着溶液pH的增加TAHMR吸附前后的Zeta电位逐渐降低;pH≤ 6.0时,TAHMR表面正电荷,从而增强TAHMR与${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 吸附作用;当pH>6.0时,TAHMR表面负电荷,其表面负电荷与${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 产生排斥力,不利于TAHMR对${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 吸附. TAHMR吸附${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 前后Zeta电位的变化与pH实验结果一致. 因此,pH为6.0时TAHR吸附${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 效果最佳.图2d为TAHMR随着离子强度(以NaCl为计)变化对
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 吸附的影响. 由图2可知,随着溶液中离子强度的增加,TAHMR对${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 吸附显著降低,溶液中的Cl−与${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 离子存在竞争,从而抑制了TAHMR吸附[25]. 因此,共存离子溶液的存在对TAHMR对${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的去除有一定抑制作用.图2e和2f为不同共存离子(F−、Cl−、Mg2+、
${\rm{HPO}}_4^{2- } $ 、${\rm{CO}}_3^{2-} $ 、Ca2+和${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ )及NOM的存在对TAHMR吸附${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的影响。从图2可见,共存阴离子对TAHMR吸附${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 抑制作用顺序大小为:${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ >${\rm{HPO}}_4^{2- } $ ≈${\rm{CO}}_3^{2-} $ > Cl−>F−,这可能是相同条件下高价态阴离子与吸附剂之间的静电引力更强[26],其与TAHMR吸附${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 产生了竞争作用,导致TAHMR吸附容量下降. 共存阳离子Ca2+对TAHMR吸附${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 抑制作用强于Mg2+,这可能是参与电子给体-受体相互作用的离子配位效应影响TAHMR对${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 吸附. 当水中存在NOM,随着DOC浓度增加,TAHMR对${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 吸附量逐渐降低(图2f), 结果表明水中天然有机物对 TAHMR 吸附 NO-3 均存在显著性影响. -
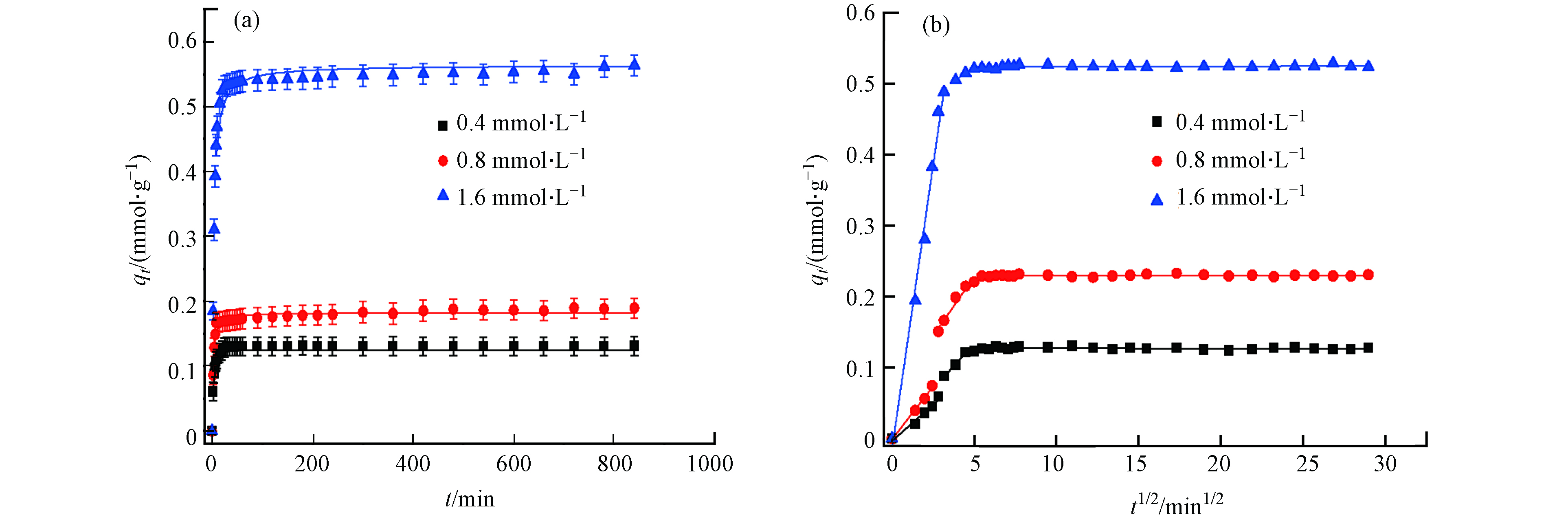
吸附动力学是评价吸附剂吸附速率的重要指标之一. 图3a为不同初始浓度下TAHMR对
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 吸附动力学曲线. 从图3可见,TAHMR对不同浓度的${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 吸附速率均较快,在0−10 min内呈上升趋势,吸附25 min即可达到平衡. 为了进一步研究TAHMR对${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 吸附机制,采用准一级动力学、准二级动力学和粒子内扩散模型拟合动力学数据,其数学表达式分别为式(3)−(5):式中,qe和qt(mmol·g−1)分别为平衡时和t时刻的吸附量,k1(min−1)为准一级动力学方程的吸附速率常数. k2(g·mmol−1·min−1)为准二级动力学的吸附速率常数kid(mmol·g−1·min−0.5)为内扩散速率常数,截距ci为与吸附剂表面特性有关的常数[22].
相关模型的拟合结果见表1所示. 准二级动力学模型相关系数(R2=0.999)优于准一级动力学方程,表明TAHMR树脂对
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 吸附更符合准二级动力学模型. 同时,采用颗粒内扩散模型分析${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 在吸附行为,由图3b可见TAHMR吸附${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 分为外部扩散、内扩撒和吸附平衡的3个阶段. 主要是${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 在TAHMR吸附由外部扩散到内部过程中,扩散阻力逐渐增大. -
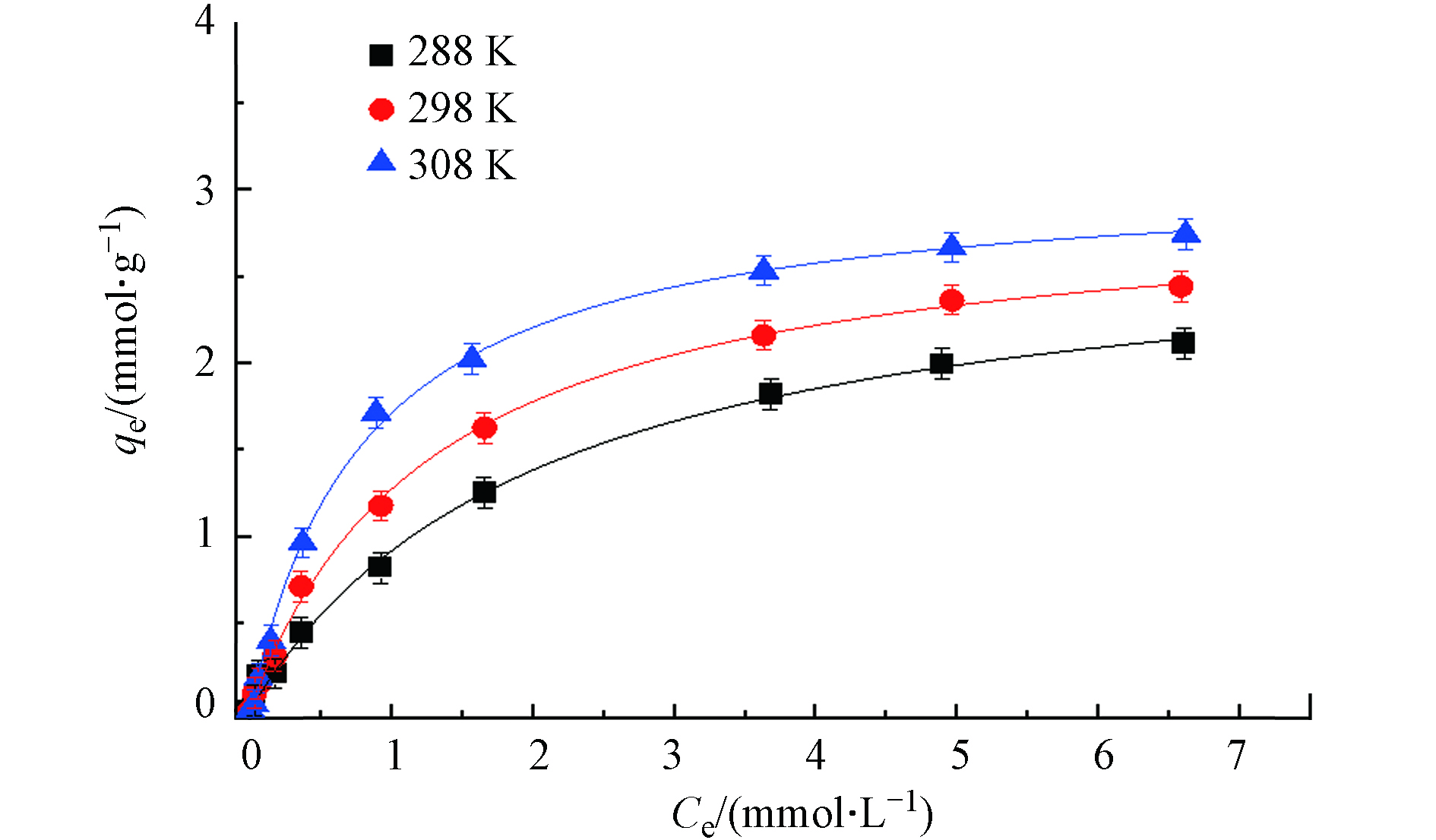
吸附等温线是评价吸附剂吸附能力的重要指标. 图4为不同温度条件下TAHMR树脂对
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的吸附等温线. 由图4可见,溶液中${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的吸附量随溶液中${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的平衡浓度的增大而增大,吸附量随着温度的升高而增加. 进一步采用Langmuir和Freundlich模型来拟合对TAHMR树脂等温吸附数据,得到的拟合参数见表2.Langmuir吸附等温模型式(6):
Freundlich吸附等温式(7):
式中,Ce是
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 吸附达到平衡时的浓度(mmol·L−1);qe为平衡吸附量(mmol·g−1);qmax(mmol·g−1)代表最大吸附量;KL(L·mmol−1)和Kf(mmol·g−1)分别为Langmuir和Freumdlich吸附速率常数[22]. 根据表中相关性系数结果可知,TAHMR对${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 吸附行为符合Langmuir方程,主要以单分子层吸附为主. 根据Langmuir等温拟合结果,${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的最大吸附量为2.94 mmol·g−1(25 ℃). TAHMR对${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 吸附容量远优于文献报道的壳聚糖-乙二醇水凝胶(0.79 mmol·g−1)[14]和β-Fe(Zr)OOH改性的SnO2纳米复合材料(0.38 mmol·g−1)[17]等其他吸附材料,表明TAHMR应用于吸附去除水中${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 具有十分广阔的前景.通过不同温度下(15、25和35 ℃)的吸附实验可以计算吸附过程的标准吉布斯自由能变(ΔGɵ)、焓变(ΔHɵ)和熵变(ΔSɵ)等吸附的相关热力学参数,如公式(8)和(9)所列:
式中,Kd为平衡吸附常数(L·g−1),即平衡时刻吸附剂上吸附质数量与溶液中吸附质数量的比值;T为反应温度(K);R为理想气体常数[8.314 J·(mol·K)−1]. 以lnKd对1/T作图得到Van’t Hoff方程式线性拟合曲线直线方程,由其斜率和截距分别计算相应温度下对应热力学参数,见表3所示. 由表3可知,不同反应温度条件下计算得到的的Δ
$ H^{\rm{e}}_{\rm{ads}} $ 为正值,说明TAHMR吸附${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 过程为吸热过程;Δ$G^{\rm{e}}_{\rm{ads}} $ 均为负值,且随着温度的升高,${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的Δ$ G^{\rm{e}}_{\rm{ads}} $ 逐渐降低,表明升高温度可提高吸附效率;Δ$ S^{\rm{e}}_{\rm{ad}} $ >0,说明吸附过程为熵增加过程,溶液混乱度增大. 通常Δ$G^{\text{ɵ}}_{\rm{ads}} $ <0,并且在物理吸附范围内(−20—0 kJ·mol−1),说明TAHMR树脂对${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的吸附过程是以自发物理吸附为主[27]. -
${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 是水中一种常见的阴离子且对${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的吸附性能影响较大,本文探究其对TAHMR吸附${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 性能的影响. 等温吸附研究表明,单独吸附${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 符合Langmuir等温吸附方程,因此,采用Langmuir竞争模型(LCM)[28]分析了${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 和水中常见的${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 在TAHMR上的平衡数据,用方程式(10)和(11).式中,下标N和S分别代表
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 和${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ . qmax,N和qmax,S分别代表${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 和${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 的最大吸附量. KN和KS是${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 和${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 的Langmuir常数,Ceq,N和Ceq,S是${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 和${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 在混合物中${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 和${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 的平衡浓度(mmol·L−1).结果表明,TAHMR对
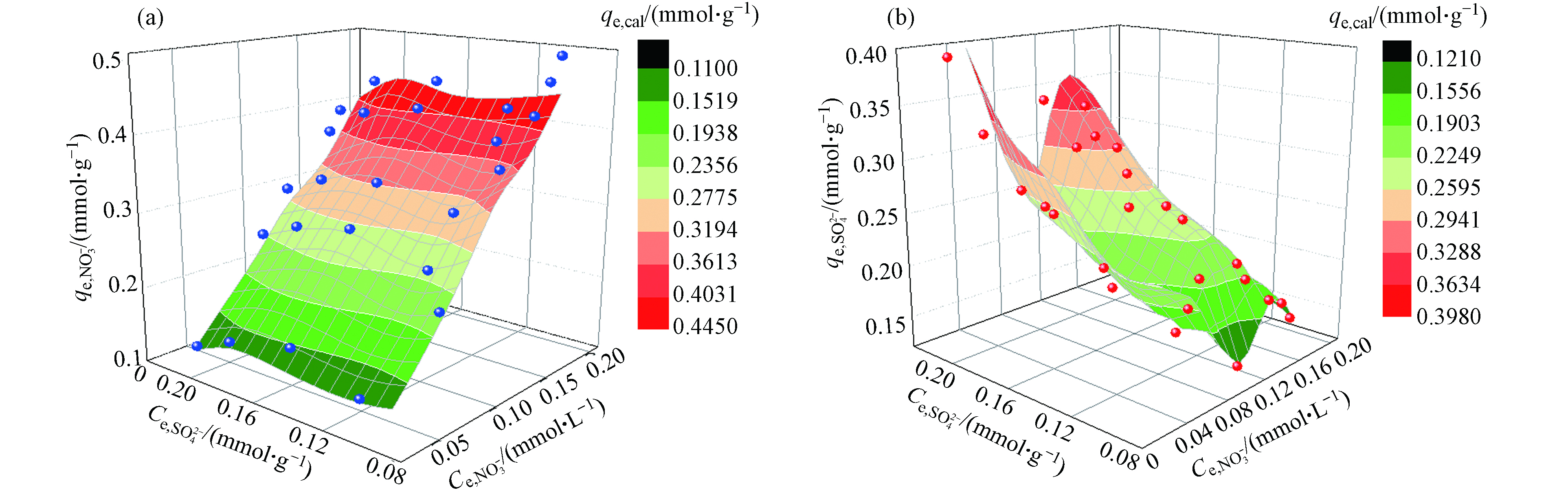
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 吸附量远大于${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ (图5),低浓度的${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 对TAHMR吸附${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 影响不大,但随着${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 浓度增加,其对TAHMR吸附${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的影响逐渐增加. 通过对比TAHMR吸附${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 实验值和理论值.${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 和${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 平衡浓度实验数据与三维吸附等温面相吻合.为了进一步确定图5中的表观预测能否准确地描述TAHMR吸附
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的吸附平衡,对比了吸附的实验值qe,exp和理论值qe,cal,发现TAHMR吸附${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的实验值qe,exp和理论值qe,cal之间的标准差非常小,并得到了${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ >和${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 的方程式分别为qe, cal = 1.38qe, exp+ 7× 10−5(R2 = 0.62)和qe, cal = 0.635qe, exp−3.1× 10−2(R2 = 0.992),结果表明${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 和${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 平衡浓度(Ceq,N和Ceq,S)的实验数据拟合结果符合三维吸附等温面,说明TAHMR对${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 和${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 的竞争吸附过程符合Langmuir竞争模型.采用理想吸附溶液理论(IAST)模型[29]计算TAHMR树脂在等摩尔比条件下,
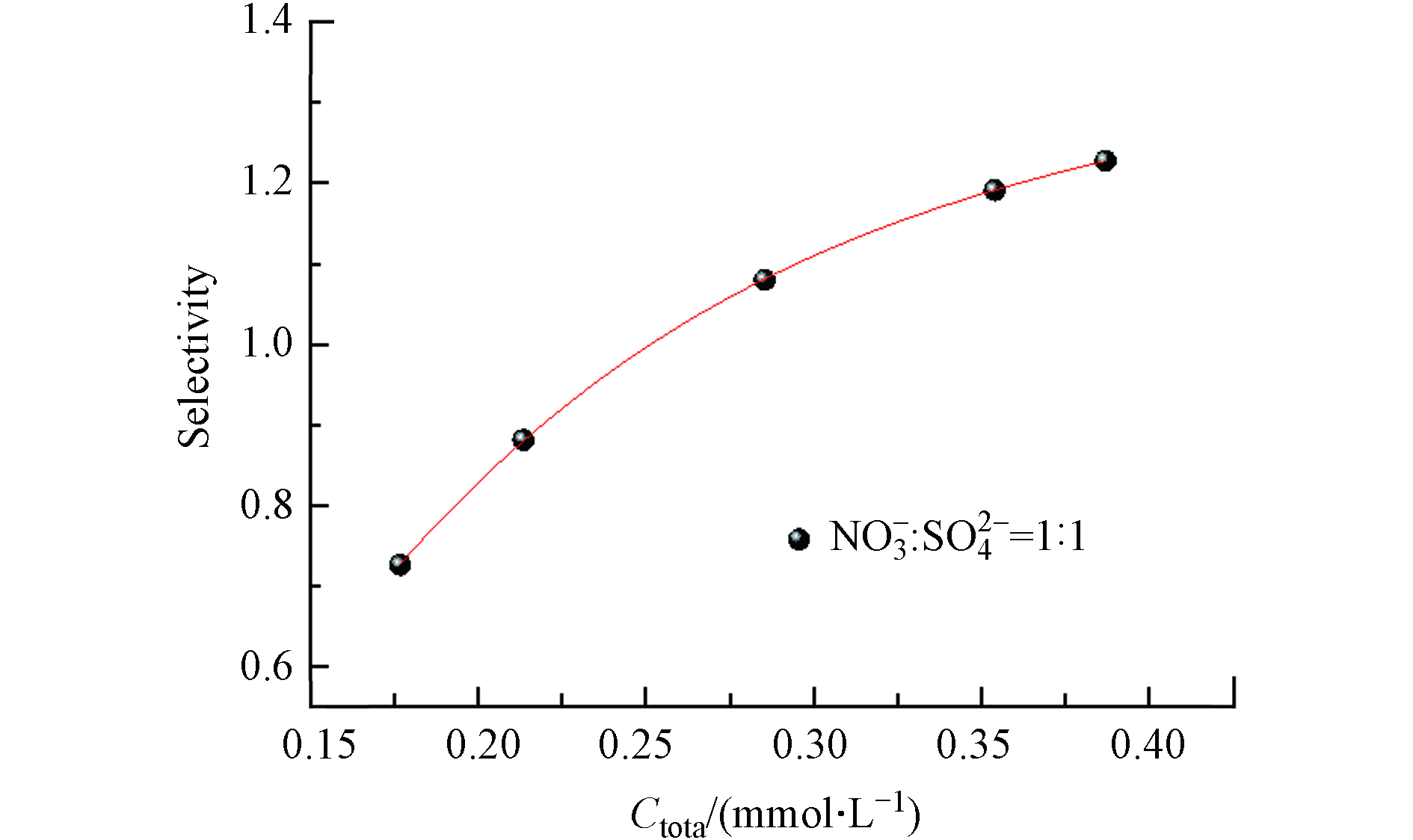
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ /${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 二元体系的吸附选择性,如公式(12)所示. 由图6可知,TAHMR对${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的选择性随着${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 和${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 浓度的增加而增加,在${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 和${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 的二元混合体系中,浓度越大TAHMR对${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 仍具有较高的选择性.式中,ZN和ZS为TAHMR中
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 和${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 的摩尔分数,xN和xS为溶液中${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 和${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 的摩尔分数,Ceq,N和Ceq,S分别为${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 和${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 的平衡浓度,qN和qS为${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 和${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 的吸附量.鉴于大多数实际水体中,
${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ (20—100 mg·L−1)通常高于${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的浓度(<10 mg·L−1),由吸附选择性结果可推断TAHMR可适用于实际水样中高浓度${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 背景下的${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 去除. -
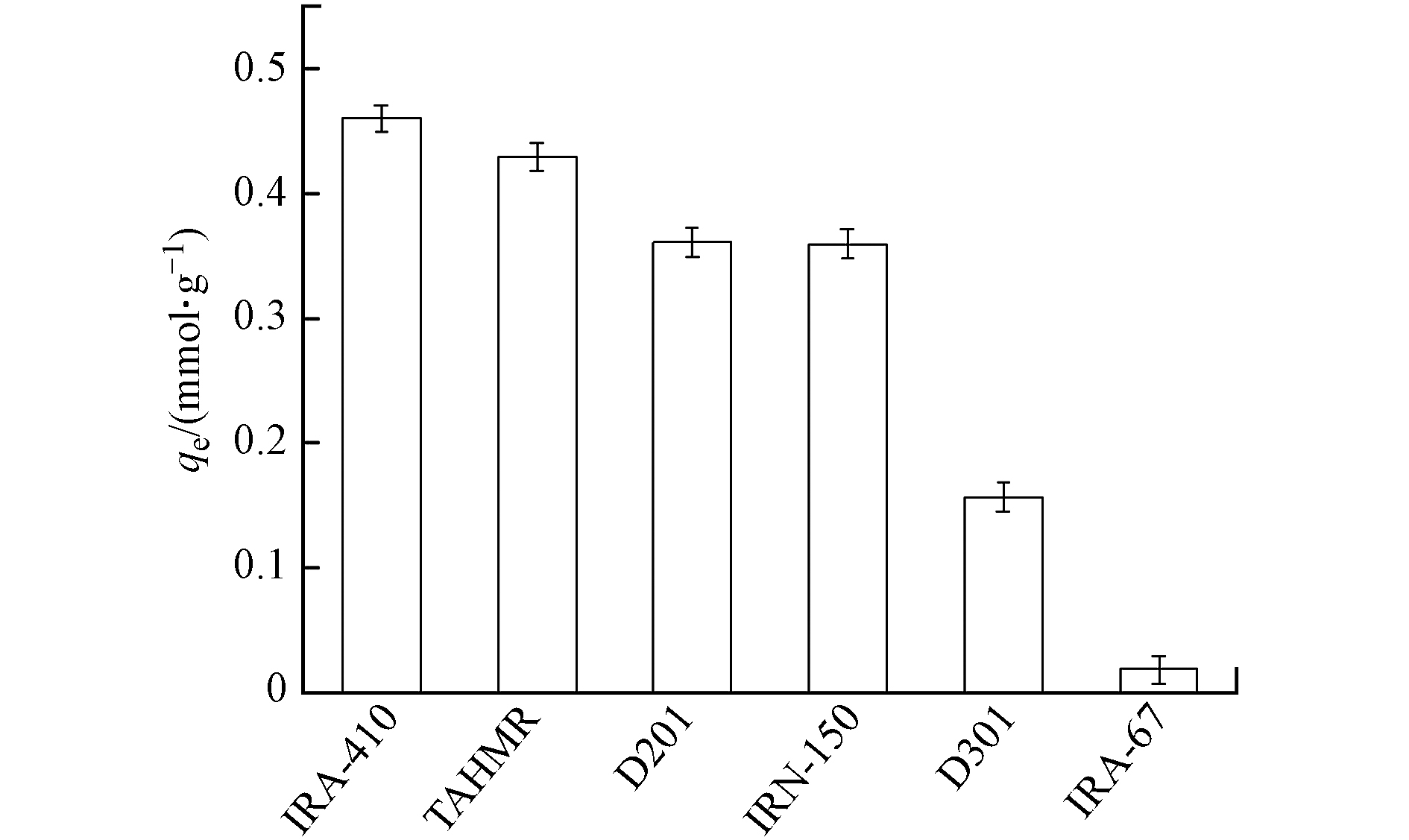
在相同实验条件下([
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ ] = 0.8 mmol·L−1,[树脂投加量] = 1.0 g·L−1,pH = 6.0,T = 25 ℃. )对比考察了不同商品树脂(D201、D301、IRA-167、IRA-410和IRN-150)及TAHMR树脂(理化参数见表4)对${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 吸附情况,结果如图7所示,对${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的吸附量大小顺序为:IRA-410>TAHMR>D201>IRN-150>D301>IRA-167.结果表明,除了IRA-410树脂之外,TAHMR对
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的吸附量仅次于IRA-410且明显大于D201等4种商业树脂,表明TAHMR是去除水体中${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的有效吸附剂. 由此可见,比表面积不是决定吸附容量的唯一参数,吸附剂的吸附容量还与其交换容量和功能基等其它因素有关. -
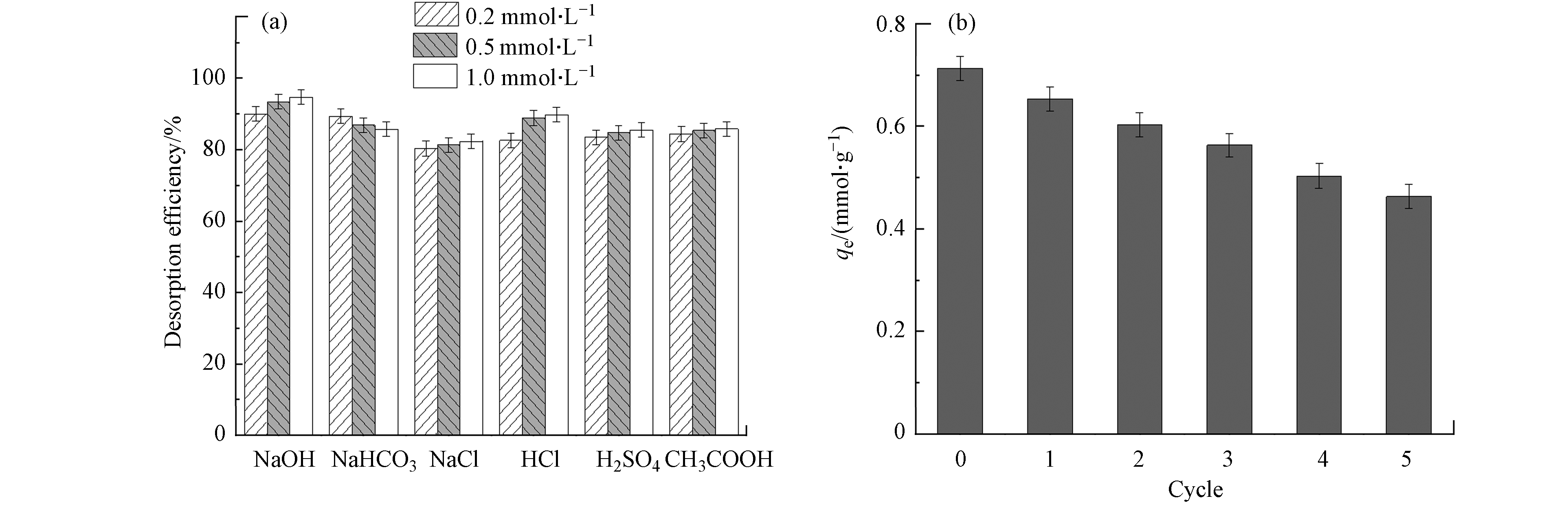
为了评价TAHMR树脂循环的再生性能,分别考察了不同浓度脱附剂(NaOH、NaHCO3、NaCl、HCl、H2SO4和CH3COOH)对其洗脱效率的影响. 结果表明,与其他脱附剂相比,采用1.0 mmol·L−1 NaOH脱附效果最佳(95%)(图8a). 经过多次吸附-脱附-循环再生实验,第5次循环实验TAHMR对
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的吸附量有所下降(图8b). 实验结果说明,TAHMR吸附${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 后的再生性能良好. 通过对吸附后的TAHMR树脂进行解吸的实验结果发现,${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 能够被解吸,可以推断TAHMR树脂对${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的吸附存在物理吸附的作用,进一步证明离子交换作用机制的存在. -
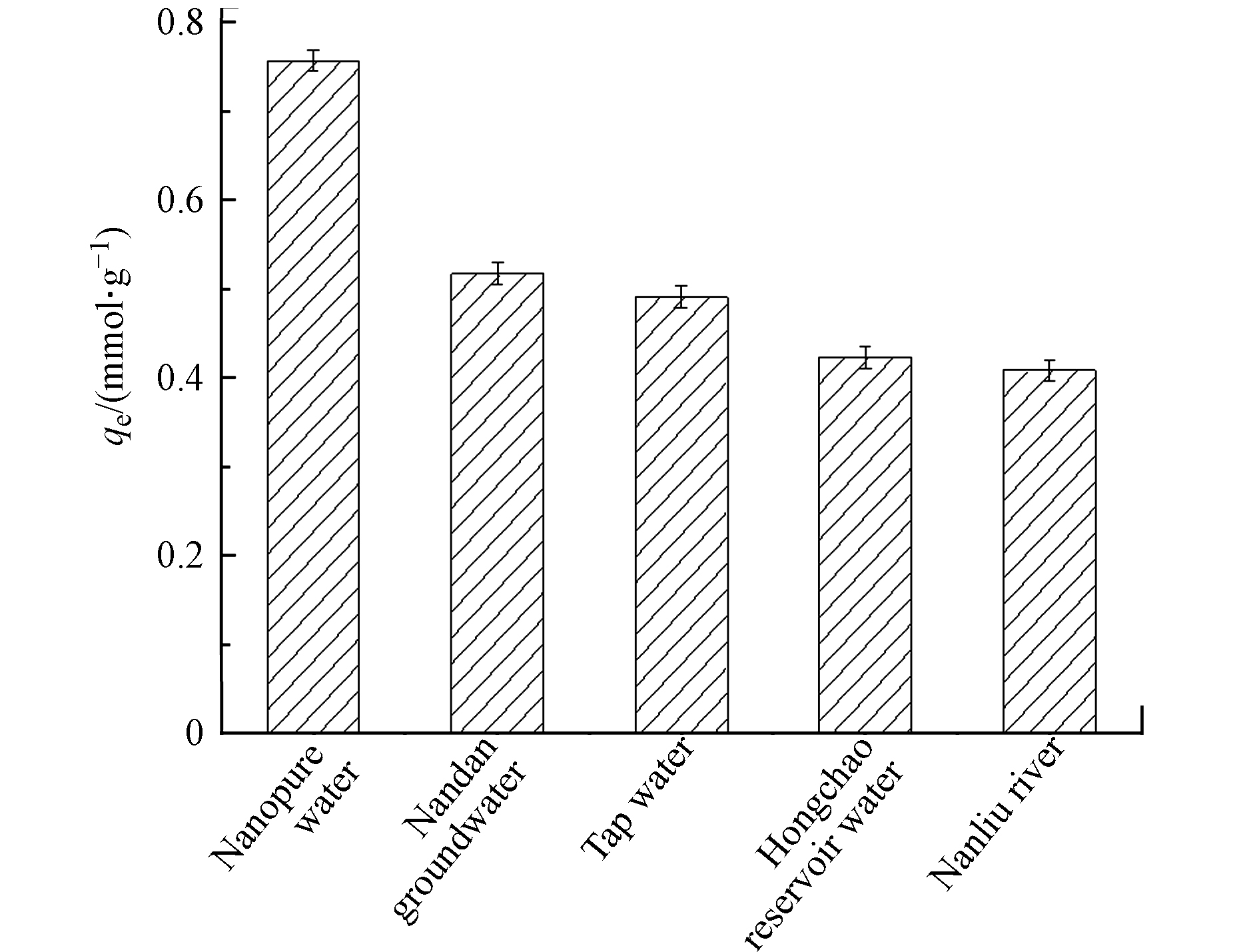
为了进一步检验TAHMR的实际应用性能,考察了龙头水、地表水、地下水和湖库水(水质参数见表5)中
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 浓度,探究不同原水对吸附影响(图9). 由图9可知,天然水体对TAHMR吸附具有显著影响. 其中,以处理地表水和湖库原水情形下,TAHMR吸附${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 能力明显低于其他水样,可能是水中相对高的有机物与TAHMR吸附位点结合,导致TAHMR吸附量降低. TAHMR对${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的吸附仍具有较好应用潜力. -
比较TAHMR吸附
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 前后C1s、O1和N1能谱变化(图10). 从图10可知,吸附前后TAHMR的C—C、C=C、C—N和C=O等结构C1s能谱峰基本保持不变,表明碳原子没有参与吸附. 吸附前,TAHMR的O1s峰值在533.57 eV和532.02 eV分别对应于C—O和C=O的结合能,吸附${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 后的C—O和C=O的结合能变化不大但在532.65 eV处增加了1个N—O峰. 吸附前TAHMR的N1s分峰值为399.40 eV和401.77 eV,分别对应为—N(CH3)2N和—+HN(CH3)2,TAHMR吸附${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 后上述2个能谱特征峰出现不同程度的偏移,且吸附后在405.83 eV处产生了有一个新特征峰,该峰归因于N—O. 从XPS微表征技术表明,TAHMR表面的叔胺基团参与了${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的吸附. -
(1)TAHMR树脂对
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的吸附表现出很好的吸附性能,吸附容量高达2.94 mmol·g−1(pH 6.0和25 ℃). TAHMR投加量1.0 g·L−1,初始溶液pH为6.0时TAHMR对水中${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 吸附去除率最佳,在pH6.0—8.0范围内,吸附能力较好;离子强度及共存组分对TAHMR对${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 去除有抑制作用.(2)TAHMR树脂吸附速率较快在25 min内可达到平衡,吸附过程更符合准二级动力学模型. 温度升高,吸附量增加,树脂吸附
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 符合Langmuir等温吸附模型. TAHMR对${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 吸附量优于多数商品化树脂,TAHMR吸附${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 使用1.0 mmol·L−1 NaOH溶液作为脱附剂,可有效对其脱附再生.(3)由FTIR和XPS证实,在吸附过程中
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 与TAHMR中叔胺基团间存在离子交换作用力. 综上所述,TAHMR树脂作为一种新型环保的树脂在水中微污染物处理领域具有潜在的应用前景.
盐酸叔胺基大孔树脂对水中硝酸盐的吸附性能
Evaluation of performance of Tertiary amine hydrochloride macroporous resin resins for adsorption behavior of nitrate from aqueous solutions
-
摘要: 硝酸盐是水体中重要的污染物之一. 本文以新型盐酸叔胺大孔树脂(TAHMR)为吸附剂,采用扫描电镜、红外光谱(FTIR)、X射线光电子能谱(XPS)和Zeta电位等手段表征了其结构. 系统研究了TAHMR树脂投加量、溶液pH、离子强度和共存组分等因素对水中
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 静态吸附性能的影响. 结果表明,TAHMR在较宽的pH4.0—10.0范围内具有良好的吸附性能,当pH为6.0时吸附量最大. 吸附平衡时间在25 min内,${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 在TAHMR上吸附过程符合拟二级动力学吸附模型,Langmuir等温吸附模型可以很好地描述TAHMR对溶液中${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的吸附过程,最大吸附量为2.94 mmol·g−1(pH=6.0 和25 ℃). 吸附热力学结果表明,在TAHMR上的吸附是一个自发的物理吸附过程,说明吸附过程是自发吸热过程,属于物理吸附. 经FTIR和XPS表征,TAHMR上的叔胺基团参与${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 吸附,并存在离子交换作用力. 脱附再生实验发现,1.0 mmol·L−1 NaOH 溶液脱附效果优于其他脱附液. 具有较强的再生能力,经5次循环后其对${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 的去除率没有明显下降. 因此,TAHMR作为一种经济高效的吸附剂,可为树脂吸附法去除饮用水的${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 提供新的手段.-
关键词:
- 盐酸叔胺离子交换树脂 /
- 硝酸根 /
- 吸附动力学 /
- 竞争吸附 /
- 吸附机制.
Abstract: Nitrate anion (${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ ) is one of the main important pollutants in water. A novel type of Tertiary amine hydrochloride macroporous resin (TAHMR)was used as adsorbent to remove nitrate anion from aqueous solutions. The resins were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy(XPS), and Zeta potential. The adsorptive removal of${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ from aqueous solution was then investigated as a function of TAHMR resin dosage, solution pH, ionic strength, and co-existing components. The results showed that TAHMR resin exhibits the excellent performance in the pH range of 4.0−10.0 and the maximum adsorption capacity of at pH 6.0. The adsorption equilibrium of TAHMR on${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ reached at 25 min, and the adsorption kinetics of${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ on TAHMR was best described by the pseudo second-order kinetic model. The adsorption isotherm data fits well the Langmuir model with the calculated maximum monolayer adsorption capacity was 2.94 mmol·g−1 at pH 6.0 and 25 ℃. Thermodynamic calculations show that the adsorption of${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ was a spontaneous and endothermic process. The combined results of FTIR and XPS further showed that the amine oxide structure on TAHMR resins involved in the adsorption of${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ . Desorption experiments showed that the TAHMR resin could be efficiently regenerated by 1.0 mmol·L−1 NaOH and showed no obvious decrease in adsorption capacity through five regeneration recycles. Therefore, TAHMR, as a cost-effective adsorbent, can provide a new means for the adsorptive removal of${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ in drinking water. -

-
表 1 TAHMR吸附
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ Table 1. Kinetic parameters for adsorption of
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 模型
Model参数
Parameter${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $
$C_{{\rm{NO}}_3^{-}} $ 0.4 mmol·L−1 0.8 mmol·L−1 1.6 mmol·L−1 准一级动力学 qe, cal/(mmol·g−1) 7.26× 10−2 7.26× 10−2 2.74× 10−2 k1/min−1 5.29× 10−3 5.29× 10−3 4.70× 10−3 R2 0.730 0.730 0.620 准二级动力学 Qe,cal/(mmol·g−1) 0.31 0.31 0.11 k2/(g·mmol−1·min−1) 9.44×10−3 9.44×10−3 1.89×10−4 R2 0.999 0.999 0.999 颗粒内扩散 Kid,1/(mmol·g−1·min-0.5) 0.02 0.03 0.16 ci,1 3.22 ×10−3 9.96 ×10−4 1.46 ×10−3 R2 0.958 0.993 0.988 kid,2/(mmol·g−1·min-0.5) 0.03 0.03 0.02 ci,2 6.06 ×10−3 6.20 ×10−3 4.49 ×10−1 R2 0.987 0.949 0.983 表 2 TAHMR对NO3¯等温吸附方程拟合参数
Table 2. Adsorption isotherm parameters for adsorption of NO3¯onto the TAHMR at different temperatures
T/K
Langmuir模型
Langmuir modelFreundlich模型
Freundlich modelqmax/(mmol·g−1) KL/(L·mmol−1) R2 1/n KF/[(mmol·g−1)·(L·mmol−1)1/n] R2 288 2.80 0.49 0.996 0.51 0.87 0.980 298 2.94 0.76 0.998 0.45 1.13 0.970 308 3.09 1.24 0.998 0.40 1.43 0.934 表 3 TAHMR吸附
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ Table 3. Thermodynamic parameters for the adsorption of
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ ΔGɵ/(kJ·mol−1) ΔHɵ/(kJ·mol−1) ΔSɵ/(J·(mol·K)−1) R2 15 ℃ 25 ℃ 35 ℃ −2.13 −2.46 −2.92 9.53 40.39 0.990 表 4 吸附剂的理化参数
Table 4. Physicochemical properties of the adsorbents used in this study
吸附剂
Adsorbent粒径/mm
Particle size比表面积/
(m2·g−1)
Specific surface area平均孔径/nm
Average pore diameter孔容/
(cm3·g−1)
Pore volume基本结构
Basic structure交换容量/
(eq·L−1)
Exchange capacity含水量/%
Moisture content功能基团
Functional groupsTAHMR 0.4—0.6 7.9 16.0 0.1 三甲基丙烯酸
三羟甲基丙酯-
丙烯酸二甲氨基
乙酯共聚物~1.8 45 —N+(CH3)3 IRA-410 0.4—0.6 1.3 2.6 7.6×10−4 苯乙烯-二乙
烯苯共聚物≥ 1.25 45—54 (CH3)2N(CH2)2OH D201 0.4—0.7 47.0 274.0 0.2 苯乙烯-二乙
烯苯共聚物≥ 1.2 50—60 —N+(CH3)3 IRN-150 0.3—1.2 1.1 2.2 6.2×10−4 苯乙烯-二乙
烯苯共聚物≥1.2 49—60 — D301 0.4—0.7 47.0 274.7 0.2 聚苯乙烯 1.7—1.3 49—55 —N+(CH3)3 IRA-67 0.5—0.8 >750.0 0.5 — 聚丙烯酸酯
共聚物≥ 1.6 56—62 —N+(CH3)3 表 5 水质主要指标参数
Table 5. Water quality parameters
水样
Water sampleDOC/(mg·L−1) pH 碱度/(mmol·L−1)
Alkalinity电导率/(μS·cm−1)
Electricity conductivity${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 南丹地下水 3.2 7.23 2.3 323.1 11.7 23.8 龙头水 1.8 7.66 2.1 354.2 5.3 10.6 洪湖水库水 6.7 8.07 3.8 124.3 4.6 29.6 南流江水 6.1 7.95 3.4 206.7 2.7 28.4 -
[1] SINGH S, ANIL A G, KUMAR V, et al. Nitrates in the environment: A critical review of their distribution, sensing techniques, ecological effects and remediation[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 287: 131996. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131996 [2] BISHAYEE B, CHATTERJEE R P, RUJ B, et al. Strategic management of nitrate pollution from contaminated water using viable adsorbents: An economic assessment-based review with possible policy suggestions[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2022, 303: 114081. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.114081 [3] HASEENA P V, MADHU G, SAHOO D K. Removal of nitrate nitrogen and ammonia nitrogen from aqueous media using nano biosorbents[D]. Cochin: Cochin University of Science and Technology, 2020. [4] THANGIAH A S. Spectrophotometric determination of sulphate and nitrate in drinking water at Asia-Pacific international university campus, Muak Lek, Thailand[J]. Rasayan Journal of Chemistry, 2019, 12(3): 1503-1508. doi: 10.31788/RJC.2019.1235201 [5] LOPES D V, SILLANPÄÄ M, WOLKERSDORFER C. Nitrate reduction of the siilinjärvi/finland mine water with zero-valent iron and iron waste as alternative iron sources[J]. Mine Water and the Environment, 2020, 39(2): 280-290. doi: 10.1007/s10230-020-00668-9 [6] GAO W C, GAO L L, LI D, et al. Removal of nitrate from water by the electrocatalytic denitrification on the Cu-Bi electrode[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2018, 817: 202-209. doi: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2018.04.006 [7] ZHAO Y X, FENG C P, WANG Q H, et al. Nitrate removal from groundwater by cooperating heterotrophic with autotrophic denitrification in a biofilm-electrode reactor[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 192(3): 1033-1039. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.06.008 [8] RIVEROS F, GUAJARDO N, VALENZUELA M B, et al. Removal of nitrates from copper-containing aqueous acidic leach solutions by electrodialysis[J]. Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy, 2021, 130(3): 209-217. doi: 10.1080/25726641.2019.1591067 [9] NGUYEN T T, TRAN V A K, TRAN L B, et al. Synthesis of cation exchange resin-supported iron and magnesium oxides/hydroxides composite for nitrate removal in water[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2021, 32: 378-384. doi: 10.1016/j.cjche.2020.11.032 [10] MAZARJI M, AMINZADEH B, BAGHDADI M, et al. Removal of nitrate from aqueous solution using modified granular activated carbon[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2017, 233: 139-148. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2017.03.004 [11] NASSAR H, ZYOUD A, EL-HAMOUZ A, et al. Aqueous nitrate ion adsorption/desorption by olive solid waste-based carbon activated using ZnCl2[J]. Sustainable Chemistry and Pharmacy, 2020, 18: 100335. doi: 10.1016/j.scp.2020.100335 [12] ZHAN Y H, LIN J W, ZHU Z L. Removal of nitrate from aqueous solution using cetylpyridinium bromide (CPB) modified zeolite as adsorbent[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 186(2/3): 1972-1978. [13] ZHANG M, SONG G, GELARDI D L, et al. Evaluating biochar and its modifications for the removal of ammonium, nitrate, and phosphate in water[J]. Water Research, 2020, 186: 116303. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116303 [14] CHEN C H, GUO Y W, LONG L, et al. Biodegradable chitosan-ethylene glycol hydrogel effectively adsorbs nitrate in water[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2020, 27(26): 32762-32769. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09438-0 [15] SAMATYA S, KABAY N, YÜKSEL Ü, et al. Removal of nitrate from aqueous solution by nitrate selective ion exchange resins[J]. Reactive and Functional Polymers, 2006, 66(11): 1206-1214. doi: 10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2006.03.009 [16] ZHUANG S T, LIU Y, WANG J L. Covalent organic frameworks as efficient adsorbent for sulfamerazine removal from aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 383: 121126. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121126 [17] 翁明媚. 功能化SnO2空心纳米球的制备及其去除水中硝酸盐研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 黑龙江大学, 2021. WENG M M. Preparation of functionalized SnO2 hollow nanospheres and study on their removal of nitrate from water[D]. Harbin: Helongjiang University, 2021 (in Chinese).
[18] 刘栋, 李永光, 刘佳豪, 等. 改性沸石材料去除水中硝酸盐研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 2021, 50(11): 3192-3198, 3205. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2021.11.055 LIU D, LI Y G, LIU J H, et al. Research progress of modified zeolite materials for the nitrate removal from aqueous solution[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2021, 50(11): 3192-3198, 3205 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2021.11.055
[19] KALARUBAN M, LOGANATHAN P, SHIM W G, et al. Removing nitrate from water using iron-modified Dowex 21K XLT ion exchange resin: Batch and fluidised-bed adsorption studies[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2016, 158: 62-70. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2015.12.022 [20] LI Q M, LU X Y, SHUANG C D, et al. Preferential adsorption of nitrate with different trialkylamine modified resins and their preliminary investigation for advanced treatment of municipal wastewater[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 223: 39-47. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.02.008 [21] LIU X H, LIU M, DONG H Y, et al. Synthesis of a tertiary amine hydrochloride macroporous resin adsorbent for removal of oxyhalide anions from water: Performance, adsorption mechanism, and toxicity[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2022, 47: 102659. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.102659 [22] 马亚红, 黄婉婷, 刁开盛, 等. 氨化松香基交联聚合树脂对水中诺氟沙星的吸附性能[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(1): 161-169. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201701058 MA Y H, HUANG W T, DIAO K S, et al. Evaluation of performance of an aminated rosin-based resin for adsorption of norfloxacin from aqueous solutions[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(1): 161-169 (in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201701058
[23] 刘露. 羟基硝酸铜Cu2(OH)3NO3的红外和拉曼光谱分析[D]. 天津: 天津工业大学, 2018. LIU L. Infrared and Raman spectra analysis of copper hydroxynitrate CU2(OH)3NO3[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin Polytechnic University, 2018 (in Chinese).
[24] 张涛. 磁性生物质吸附材料的制备及对硝酸盐氮的吸附研究[D]. 保定: 河北大学, 2022. ZHANG T. Preparation of magnetic biomass adsorption material and study its adsorption for nitrate nitrogen[D]. Baoding: Hebei University, 2022 (in Chinese).
[25] 吴志坚, 刘海宁, 张慧芳. 离子强度对吸附影响机理的研究进展[J]. 环境化学, 2010, 29(6): 997-1003. WU Z J, LIU H N, ZHANG H F. Research progress on mechanisms about the effect of ionic strength on adsorption[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2010, 29(6): 997-1003 (in Chinese).
[26] TENG Y, SONG G Q, CHEN R, et al. Carboxymethyl β-cyclodextrin immobilized on hydrated lanthanum oxide for simultaneous adsorption of nitrate and phosphate[J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2022, 132: 104153. doi: 10.1016/j.jtice.2021.11.020 [27] TRAN H N, YOU S J, CHAO H P. Thermodynamic parameters of cadmium adsorption onto orange peel calculated from various methods: A comparison study[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2016, 4(3): 2671-2682. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2016.05.009 [28] WEBER W J, DIGIANO F. A. , Process dynamics in environmental systems(Environmental Science and Technology Series)[M]. New York: Wiley & Sons, 1996. [29] MYERS A L, PRAUSNITZ J M. Thermodynamics of mixed-gas adsorption[J]. AIChE Journal, 1965, 11(1): 121-127. doi: 10.1002/aic.690110125 -

















 下载:
下载: